Memory management
Heap vs Stack
What is Heap?
-
an area of memory used for dynamic allocation.
-
memory that is not manage automatically
-
if fail to dealocate memory, you will end up with memory leak
-
does not have size restrictions on variable size
What is Stack?
-
the stack is where memory is allocated for automatic variables within functions
-
"LIFO" (last in first out) data structure
-
memory is managed automatically
-
there is a limit on the size of variables
-
stack overflow occurs if call stack pointer exceeds stack boundary
When is heap and stack used?
-
Memory space for objects is always allocated in heap.
-
Built-in datatypes like int, double, float and parameters to methods are allocated on the stack.
-
Even though objects are held on heap, references to them are also variables and they are placed on stack.
How to store object in heap?
-
When you create an object using the new operator,
myobj = new Object();
-
it allocates memory for the myobj object on the heap.
-
When you do a string initialization,
String myString;
-
it is a reference to an object so it will be created using new and hence it will be placed on the heap.
- keyword "static" create variable in heap memory
Can an object store in stack?
-
If you create an object inside a function without using the “new” operator then this will create and store the object on the stack, and not on the heap.
-
The stack memory space is used when you declare automatic variables.
Example:

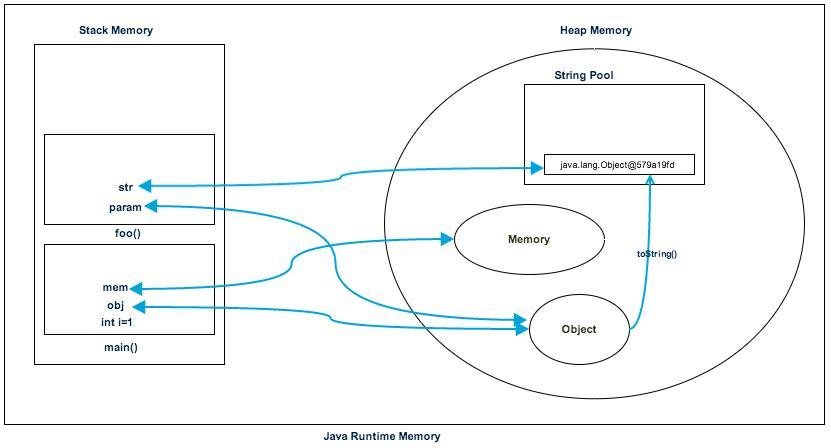
When to use?
Heap
-
if you need to allocate a large block of memory
-
if you need to keep the variable around a long time
-
if you need variables like arrays and structs that can change size dynamically
Stack
-
if you are dealing with realtively small variables that only need to persist as long as the function using them is alive
Summary
| No. | Heap | Stack |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | manually deleted by programmer | automatically deallocate |
| 2. | no limit on memory size | limit on stack size |
| 3. | slower access | fast access |
| 4. | global variable | local variable only |
| 5. | memory leak | stack overflow |
| 6. | initialized at runtime | initialized before runtime |
| 7. | live from start to the end of application | short-lived |
Thank you.
See you again next week
Heap vs Stack
By shirlin1028
Heap vs Stack
- 396



