Game Theory and Managerial Decision Making
A case study on Taurus Packaging Pvt Ltd
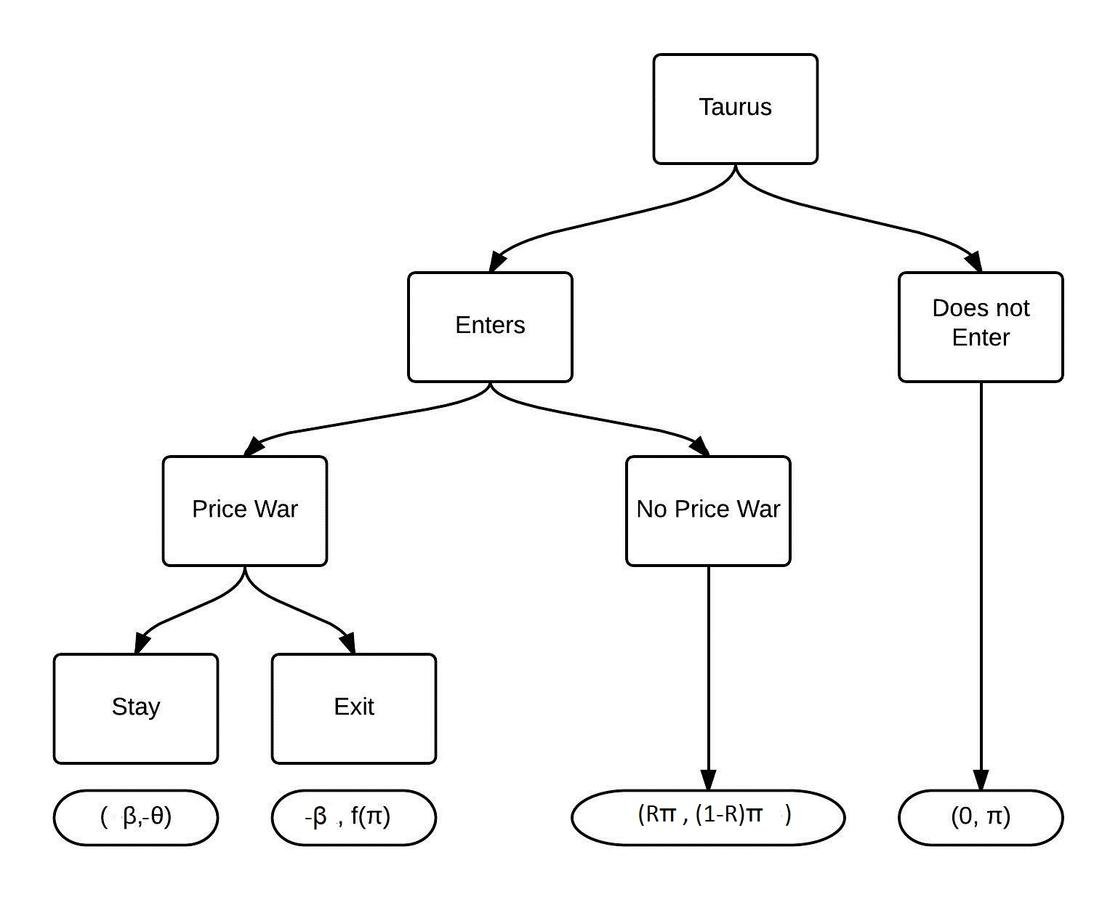
Taurus Packaging
Text





What do they want?
Expansion
-
Geographically
- Product Lines

How can we help them?
Maybe...

Yes! Why not apply game theory?
What is game theory?
Study of Strategy
Study of Decisions
Study of Games
Output
Optimal Strategy
Players
Actions
Payoffs
Game
Game Tree
-
Sequential games
-
Nodes = Actions
- Same player at alternate levels
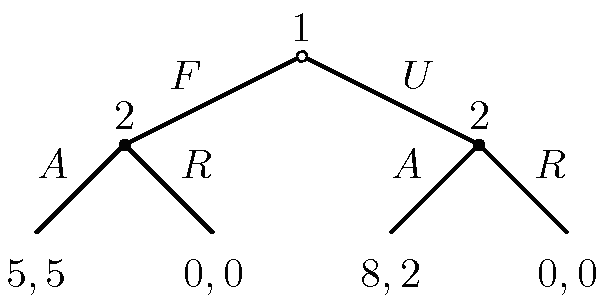
Backward Induction
Used to solve the game tree and come up with the optimal solution of the game



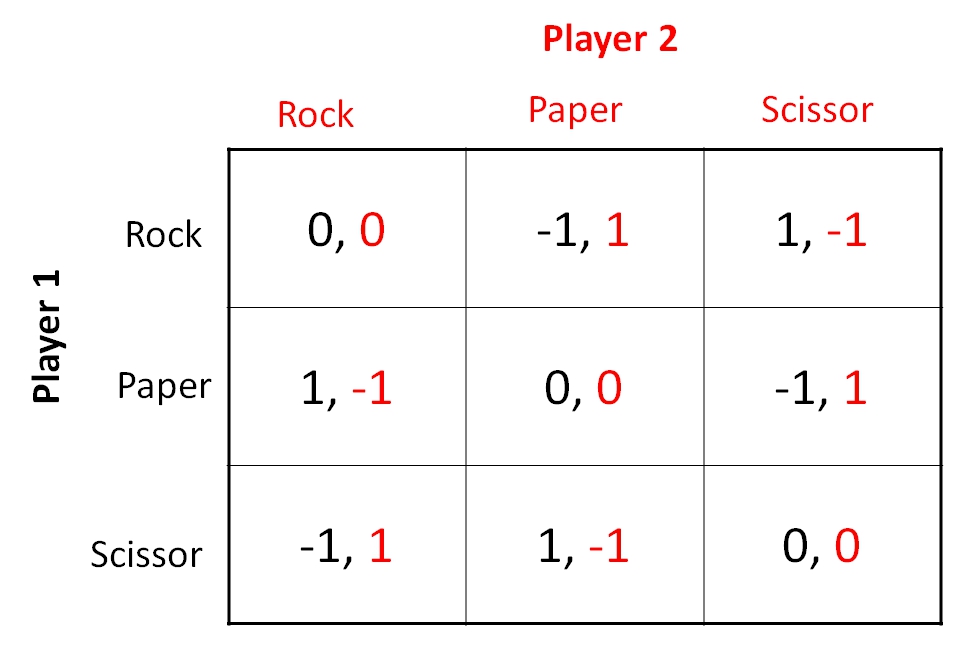
Payoff Matrix
Simultaneous Games
Matrix structure
Rows & Columns = Actions of the players
Elements = Payoffs
Model
Entry in Market
Advertising
Compensation of employees
Entry in Market
Porter's Five Forces
- Competition within the industry
- Suppliers
- Buyers
- Substitutes
- Potential new entrants
Entry in Market
Tanzania
Kenya
South Africa
Entry in Market
Assumptions
- Manufacturing firm
- Well defined and rigid supply chain
- Quality of products very important
- Competitive pricing
- Perfect Information
- Rational firms
Entry in Market
Parameters
Market Structure
Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
Marginal Cost
High
Low
Technology
Normal
Advanced
Products
Homogeneous
Heterogeneous
Entry in Market
Parameters
Price War Threat
Non-credible
Credible
Information
Complete
Incomplete
Sensitiveness of customers
To quality
To price
Price of product
High
Low
Heterogeneity of products
Firms want to set their product apart
Go for differentiation strategy
Based on location, quality, customer service, durability
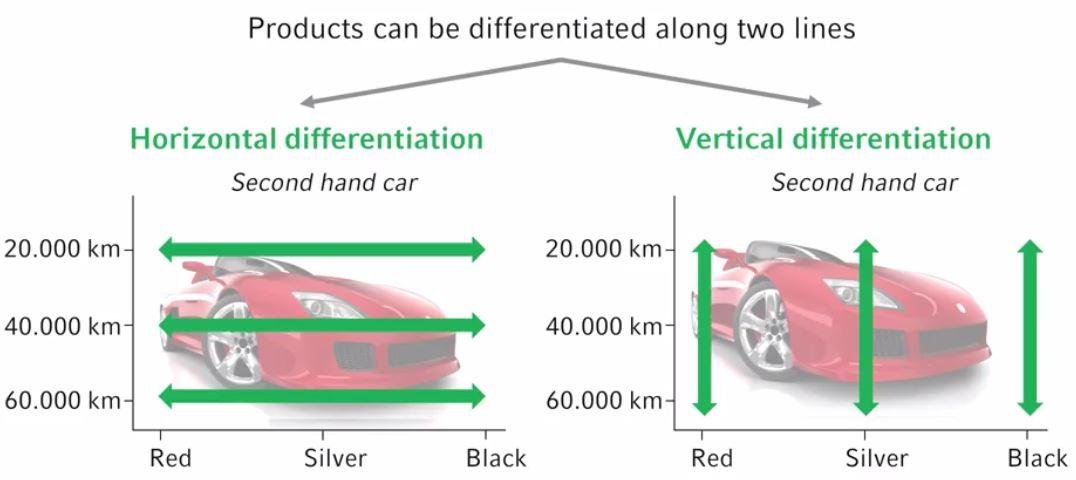
Generic Strategies

Entry in Market

Symmetric costs of both firms
Same technology used by both firms
Homogeneous products
If price set by both firms is same, the demand gets equally divided. Hence the profit of each firm is half the total profits in the market
Entry in Market
New Technology
Higher Marginal Cost
Quality-sensitive customers
Entry in Market

New Technology
Lower Marginal Cost
Price-sensitive customers
Price war credible threat by other seller
Entry in Market
From the incumbent's side

Marketing
Advertising
Trade Expo/Fair
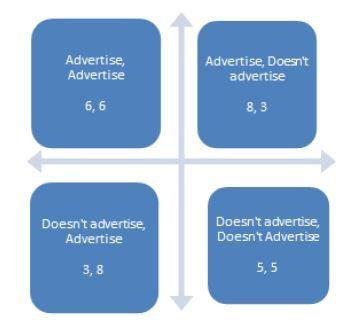
Compensation of employees
Principal-Agent problem
- Adverse selection
- Signalling
- Moral hazard

Moral Hazard
How to ensure that employee works hard when he is given a fixed salary?
Agent takes action
Principal observes outcome
Favourable for principal
Unfavourable for principal
Solving Moral Hazard
Fixed wage contract based on reservation utility of agent
Wage rates based on effort level = wH, wL
Wage rates based on outcome achieved by agent
Outcome-based contract
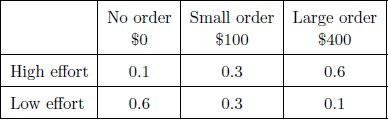
Wages corresponding to no order, small order and large order
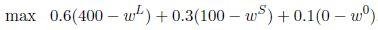
Principal wants to maximize =
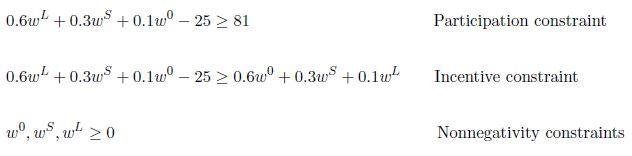
Constraints =
Solution
= 118
= 117
= 1
Solved using linear programming
Thank You!
Shreya Khurana
Shubham Goel
deck
By Shreya Khurana
deck
- 1,073



