Some good practices in Open Science
Text-content license: CC-BY 4.0
Related slides: Open Science. Good practices in Bioinformatics
Open Science

Open Science

Document
Write it down or ...
it didn't happen!
Document: Why?
- Organise ideas
- Understanding code and steps in the future for you and others
- Fixing errors
- Help in future publication
Document: Where?
- File System (e.g. README or TODO files)
-
Control Version System
- Git, SVN, etc.
-
Content Management System
- Wiki CMS, Drupal, etc.
Document: How?
- Plain text
- Format
- Unstructured
- Free
- Markdown
- Wikitext
- Unstructured
Markdown

Tag and track
I never said so!
Tag and track: Why?
- Convenient backup
- Error tracking and reversion
- Checking history
- Allowing collaboration on different time points
- Publication of specific snapshots
Tag and track: Where?
-
Code, documentation:
- Control Version System (Git, SVN, etc.)
- Wiki CMS (e.g. [Semantic] MediaWiki)
-
Data, files
- Document Management Systems
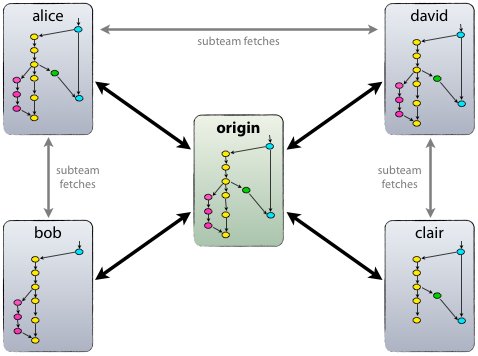
Git: collaboration
Tag and track: Publish
-
Working and executable code
- Docker & Singularity hubs
-
Identify Content & Code (DOI)
- Figshare
- Zenodo (with Github)
Reproduce
Run it again, Sam!
Reproduce: Why?
- Nowadays not only textual statements but also code and data
-
Peers and collaborators should be able to reproduce by themselves
- Check errors
- Improve code, data
- Test in different conditions
Reproduce: How?
- Code requirements, recipes
-
Virtualisation
- Hypervisor: VirtualBox, VMWare, etc.
- Containers: Docker, Singularity
Reproduce: Jupyter
- Former IPython Notebook
- Combines in a single notebook documentation (Markdown), comments and executable code with its output
- Can be exported into PDF, HTML, etc.
Reproduce: Jupyter

Reproduce: DevOps

Reproduce: Containers

Reproduce: Docker & Singularity


Pipelines & Workflows
Guilty by association
Pipelines & Workflows: Why?
- Write programs that do one thing and do it well.
- Write programs to work together.
- Write programs to handle text streams, because that is a universal interface.
Unix Philosophy
D. McIlroy, P.H.Salus
Pipelines & Workflows: How?
- Traditionally from Shell script files
-
Frameworks or applications
- Web-based
- GUI and command-line
- Command-line
- Common Workflow Language
- Fast prototyping
- Polyglot (any programming language can be included)
- Highly scalable and portable (many HPC and cloud environments)
- Reproducible (native support containers)
- Continuous checkpoints / resuming. Expanding pipelines

Questions?
Comments?
Some good practices in Open Science
By Similis.cc
Some good practices in Open Science
A short tutorial about good practices and tools focused on Open Science
- 3,192



