JavaScript
Asynchronous Programming
Lecturer: 土豆
Date: 2019/12/1
大綱
- Synchronous vs. Asynchronous
- Callback
- Promise
- Async / Await
- 實作Time
測試環境
- Windows 10
- Chrome
- Node.js (10.15.3)
Synchronous
Asynchronous
vs.
Synchronous
等餐點
點餐
取餐
客人A
客人B
客人C
客人A
等餐點
點餐
取餐
走人!
客人B
走人!
客人C
走人!

菜好囉!
Asynchronous
AJAX
Request A
waiting
send request
data processing
Done!
Request B
Request C
Done!
Done!
基底HTML
待會都會用這個HTML來測試
<!-- index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Asyncccccccc</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="change_this.js"></script> <!-- 改這裡!! -->
</body>
</html>Callback
在那古早的時代...
// callback.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post) {
setTimeout(() => {
posts.push(post);
}, 3000);
}
createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'});
getPost();先跑跑看,跟你預期的有沒有一樣
Post Three去哪了?
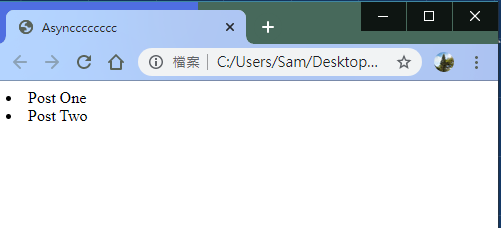
因為沒有同步好
getPost
createPost
3s
1s
Render!
Create!
這時候就需要Callback了
getPost
createPost
3s
1s
Render!
Create!
Callback
Callback Function
當createPost完成後,再呼叫getPost
修改成callback版本
// callback.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
posts.push(post);
callback();
}, 3000);
}
createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'}, getPost);如果createPost的時間是亂數
需Reload兩次,且順序可能亂掉
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
posts.push(post);
console.log(posts);
callback();
}, Math.random()*1000);
}
createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'}, getPost);
createPost({title: 'Post Four', body: 'This is post four'}, getPost);可以這樣寫
// callback_hell.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
posts.push(post);
console.log(posts);
callback();
}, Math.random()*1000);
}
createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Four', body: 'This is post four'}, () => {
getPost();
})
});如果你想要create Three ~ Ten
讓我們有請!!!
Callback Hell!!!!
// callback_hell.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
posts.push(post);
console.log(posts);
callback();
}, Math.random()*1000);
}
createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Four', body: 'This is post four'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Five', body: 'This is post five'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Six', body: 'This is post six'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Seven', body: 'This is post seven'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Eight', body: 'This is post eight'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Nine', body: 'This is post nine'}, () => {
createPost({title: 'Post Ten', body: 'This is post ten'}, () => {
getPost();
})
})
})
})
})
})
})
});波動拳!!!

同場加映
by 一年前的我
所以promise就誕生了
Promise
ES6時代
function promise_func(){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const error = false;
if (!error) {
resolve('done!');
} else {
reject('Error!');
}
});
}
promise_func().then(value => {console.log(value)});
/*
promise_func()
.then(value => {console.log(value)})
.catch(err => {console.log(err)});
*/基本架構
function return Promise物件
resolve: 成功時回傳
reject: 失敗時回傳
then: 成功時接收到resolve的值並執行
catch: 失敗時接收到reject的值執行
使用Promise物件
// promise.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof(post) !== "object") {
reject("Wrong data type!");
} else {
posts.push(post);
resolve("done");
}
}, 3000);
});
}
createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'})
.then(getPost)
.catch(err => {console.log(err)});改成promise版本
// promise_chain.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof(post) !== "object") {
reject("Wrong data type!");
} else {
posts.push(post);
resolve("done");
}
}, Math.random()*1000);
});
}
createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'})
.then(() => createPost({title: 'Post Four', body: 'This is post four'}))
.then(() => createPost({title: 'Post Five', body: 'This is post five'}))
.then(() => createPost({title: 'Post Six', body: 'This is post six'}))
.then(() => createPost({title: 'Post Seven', body: 'This is post seven'}))
.then(() => createPost({title: 'Post Eight', body: 'This is post eight'}))
.then(() => createPost({title: 'Post Nine', body: 'This is post nine'}))
.then(() => createPost({title: 'Post Ten', body: 'This is post ten'}))
.then(getPost).catch(err => {console.log(err)});promise chain
callback hell的promise版本
如果用node.js跑,請先
npm install node-fetch --global然後在程式碼加上
const fetch = require('node-fetch');// fecth_something.js
let data = fetch("http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users").then(res =>
res.json()
).then(value =>
console.log(value)
);看一點生活上的例子
fetch是瀏覽器提供的api,所以請在瀏覽器上跑
fetch會幫我們跟伺服器要資料
Async / Await
ES7時代
基本架構
// async_await_basic.js
// 前面一樣要有一個回傳promise物件的函數
function promise_func(){
return new Promise((resove, reject) => {
const error = true;
if (!error) {
resove("Done!");
} else {
reject("Error!");
}
});
}
// 但是在處理這個promise物件時,可以不用then來處理,改成async/await
(async () => {
let value = await promise_func();
console.log(value);
})();
// errer handler版本
/*
(async () => {
try {
let value = await promise_func();
} catch(e) {
console.log(e);
}
console.log(value);
})();
*/async加在function前面
await只能在async的function內使用
async內部的await會依序執行,外部則不受影響
處理promise的另一種方式
others
async
wait
execute
IIFE(Immediately Invoked Function Expression)
宣告一個函式之後就馬上執行
// iife_demo.js
(function iife_func(){
console.log("Yo ho!");
})();
// 加上參數
(function hello(name){
console.log(`Hello ${name}`);
})('Sam');
// arrow function version
// 箭頭函數版本,當你硬是要有個function又不想幫它取名時
(() => {
console.log('Yo hoooooo!');
})();IIFE(Immediately Invoked Function Expression
- 當你硬是需要一個函數,但是用完即丟時就可用IIFE
- async一定要加在function之前,所以我們需要IIFE
- IIFE內的變數不會汙染外部
// async_await.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof(post) !== "object") {
reject("Wrong data type!");
} else {
posts.push(post);
resolve("done");
}
}, 3000);
});
}
(async () => {
try {
await createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'});
} catch(e) {
console.log(e);
}
getPost();
})();改改我們的post程式
看起來又更簡單了
// async_await_not_hell.js
const posts = [
{title: 'Post One', body: 'This is post one'},
{title: 'Post Two', body: 'This is post two'}
];
function getPost() {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = '';
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
}
function createPost(post) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof(post) !== "object") {
reject("Wrong data type!");
} else {
posts.push(post);
resolve("done");
}
}, Math.random()*1000);
});
}
(async () => {
try {
await createPost({title: 'Post Three', body: 'This is post three'});
await createPost({title: 'Post Four', body: 'This is post four'});
await createPost({title: 'Post Five', body: 'This is post five'});
await createPost({title: 'Post Six', body: 'This is post six'});
await createPost({title: 'Post Seven', body: 'This is post seven'});
await createPost({title: 'Post Eight', body: 'This is post eight'});
await createPost({title: 'Post Nine', body: 'This is post nine'});
await createPost({title: 'Post Ten', body: 'This is post ten'});
} catch(e) {
console.log(e);
}
getPost();
})();再來改改callback hell
看起來一點都不hell了呢
// async_await_fetch_something.js
(async () => {
let res = await fetch("http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users");
res = await res.json();
console.log(res);
})();來改改fetch程式
// ...
if (event.text.includes("喵喵講話")){
(async () => {
const result = await web.chat.postMessage({
text: '話。',
channel: event.channel,
});
})();
// ...這邊使用了async / await處理傳送訊息的函式
實作Time
一周天氣
- 取得台北市公開資料的一周氣象資訊
- 將未來一周台北市的天氣以列表呈現在網頁上
- hint1: 在網址後加上 &limit=10 可以限制結果數量
- hint2: 要用regular expression才能處理的像我這麼漂亮

參考步驟
- 先看看資料長怎樣 (用瀏覽器送request)
- 嘗試fetch看看,拿到的資料格式是甚麼,想辦法拿到你要用的那個部分
- 想辦法把日期以及天氣抓出來
- 把資料拼起來,寫到網頁上
hint: 一天有兩次預報(0點到6點、6點到18點),任選一個即可
解答
(async () => {
let res = await fetch('https://data.taipei/opendata/datalist/apiAccess?scope=resourceAquire&rid=e6831708-02b4-4ef8-98fa-4b4ce53459d9&limit=14');
let data = await res.json();
data = data.result.results;
let weathers = '';
for (let [i, d] of data.entries()) {
if (i % 2 !== 0){
weathers += `<li>${d.startTime.match(/\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}/)}: ${d.parameterName1}</li>`;
}
}
document.body.innerHTML = weathers;
})();參考資料
- 2019/11/30檢自: Async JS Crash Course - Callbacks, Promises, Async Await
- 2019/11/30檢自: 來點 JavaScript 的 Promise
- 2019/11/30檢自: [筆記] 談談JavaScript中的IIFEs(Immediately Invoked Functions Expressions)
謝謝聆聽
JavaScript Asynchronous Programming
By Sam Yang
JavaScript Asynchronous Programming
- 688



