Data structures in JS
What they are for
Map relations between scalar values/other data structures
Make data access fast and convenient
What does fast mean?
How to measure speed?
We don't
We can prove mathematically how an operation scales when more items are involved
Big OH notation
O(n)
O(n log n)
...
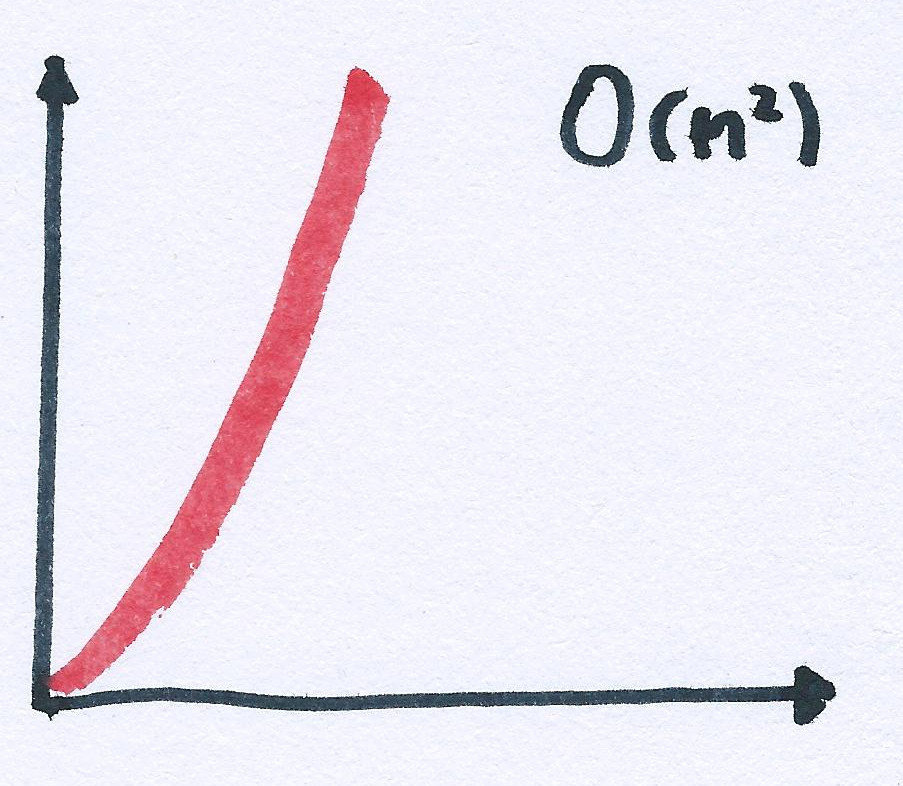
O(n²)
Big OH notation
Makes sense only if:
Big numbers
Worst possible scenario
Big OH notation
4+5n²
n²
This one doesn't make sense
This one does
Big OH notation
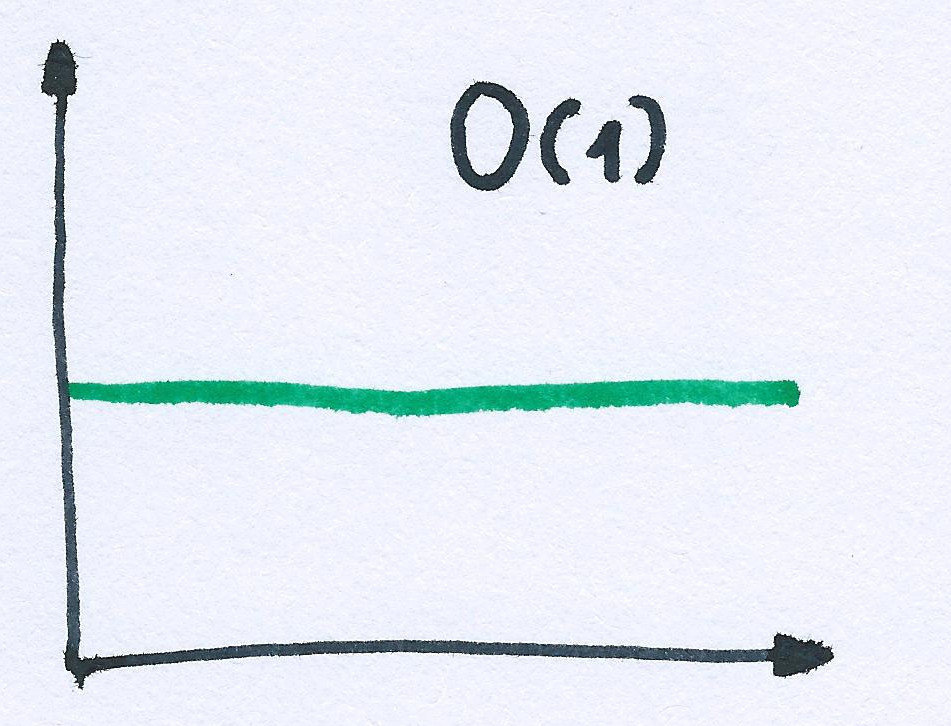
obj.foo = 'bar';Big OH notation
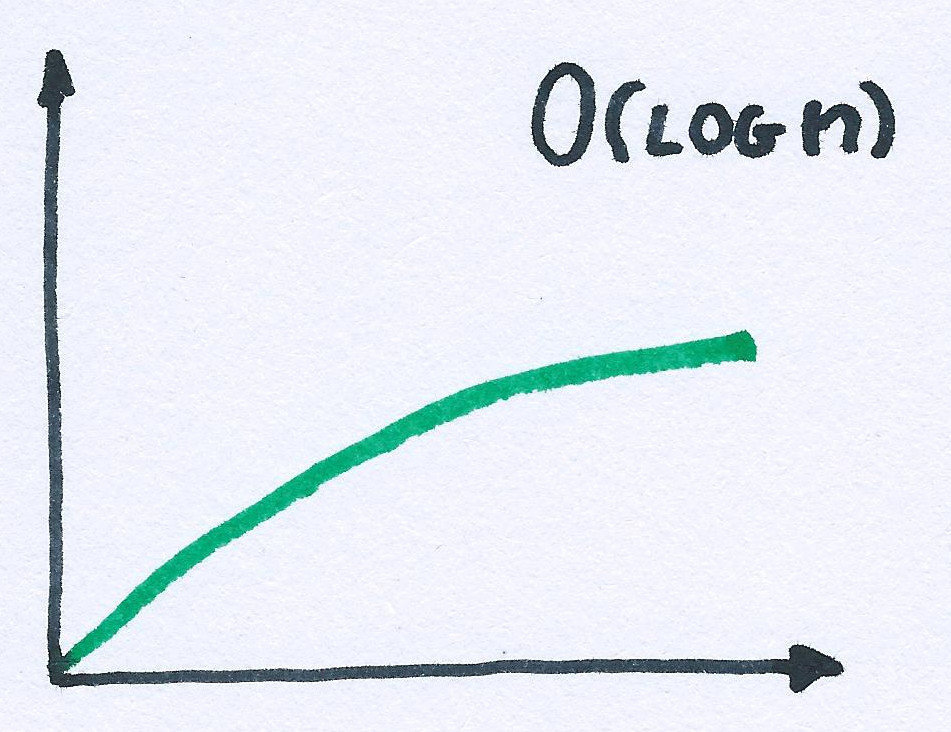
_.sortedIndexOf(sortedArray, value)Big OH notation
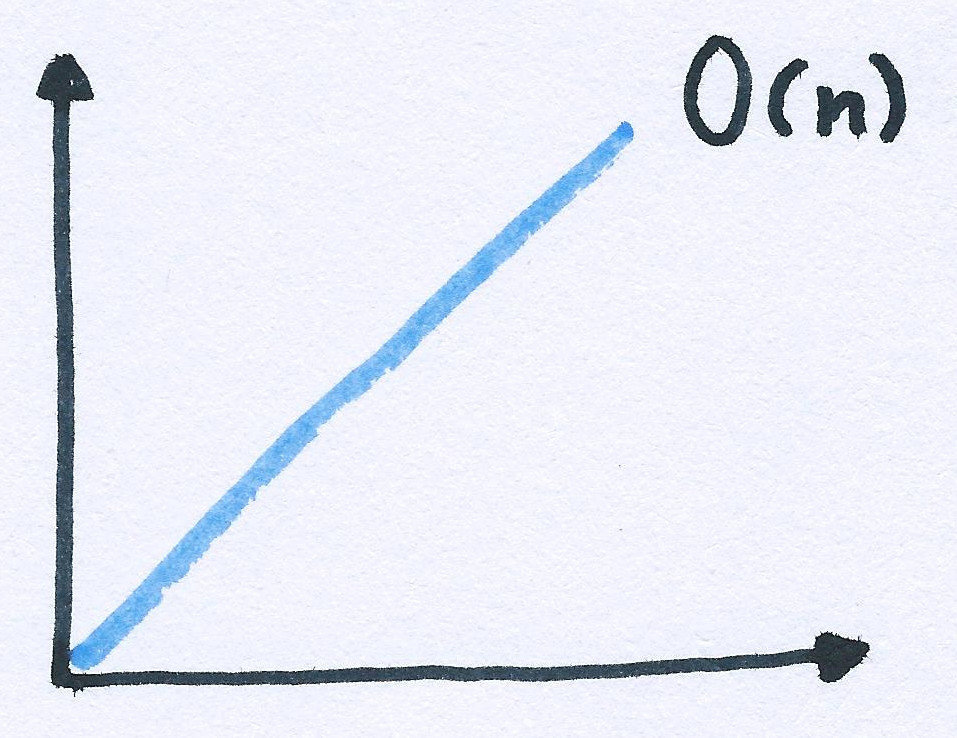
unsortedArray.indexOf(value);Big OH notation
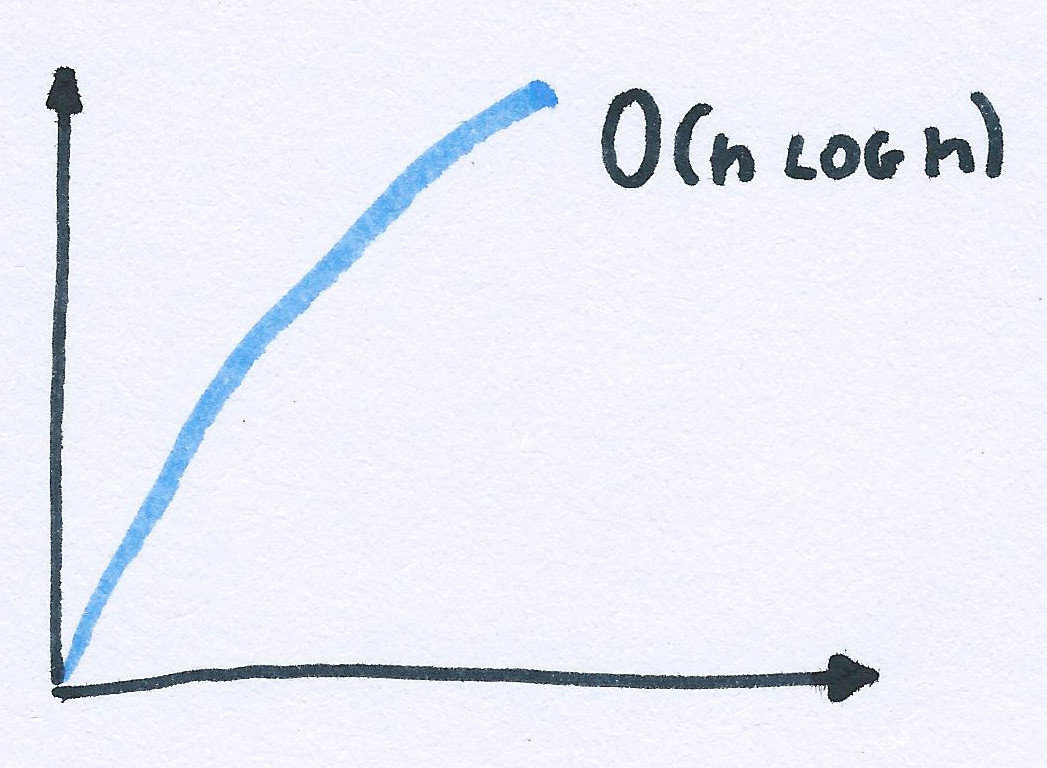
array.sort();Big OH notation
JS data structures: arrays
- access with known index O(1)
- indexOf O(n)
- sort O(n log n)
- splice/slice O(n)
- push/pop O(1) *
- shift/unshift O(n) ?
JS data structures: objects
- access with known key O(1)
- adding a new item O(1)
- unsorted*
and ES6 Maps and Sets
Are they enough?
No
They are building blocks
Example:
Caching temperatures
We can use a key-value store (js object)
But it will grow indefinitely
we need an algorithm of cache invalidation
LRUCache
Removes the
Least
Recently
Used
items
Fixed maximum size cache!
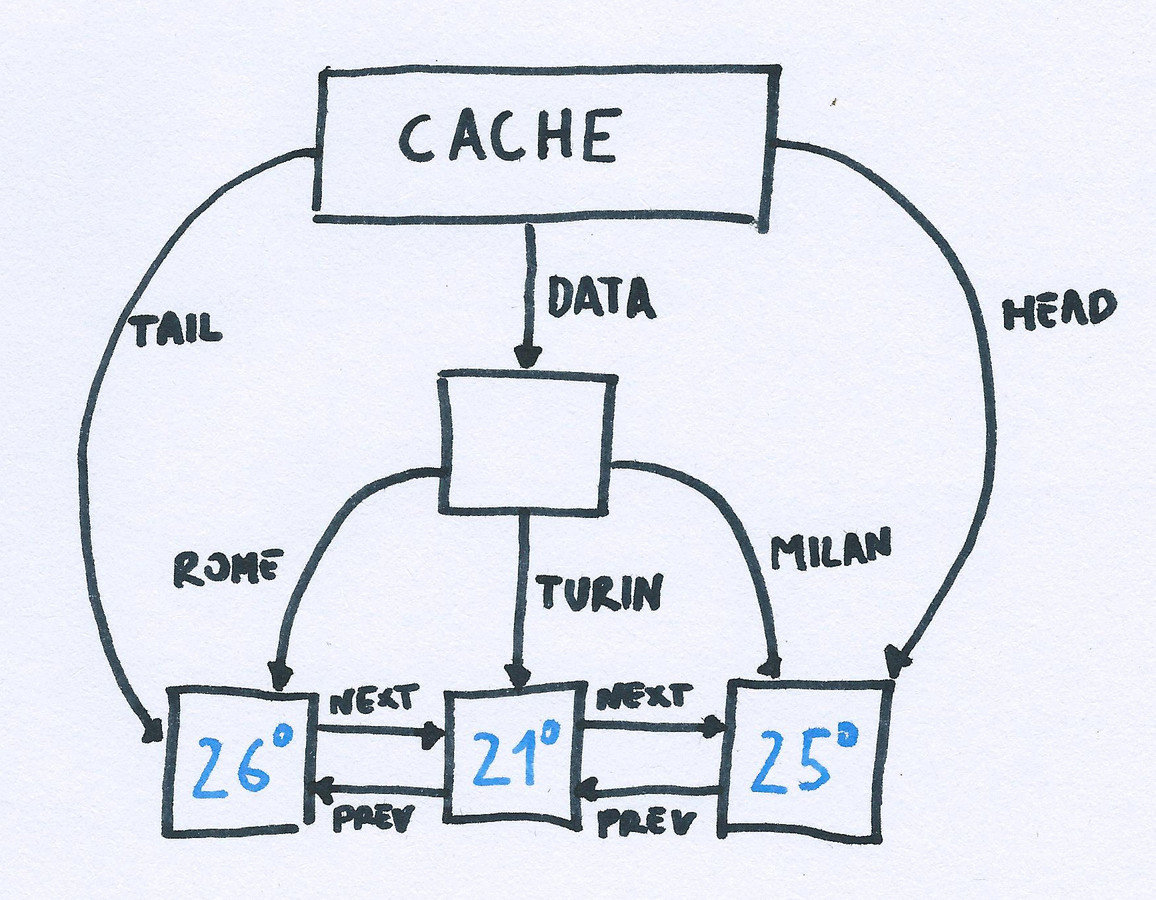
Using an object and a double linked list (max size 3)
LRUCache
LRUCache
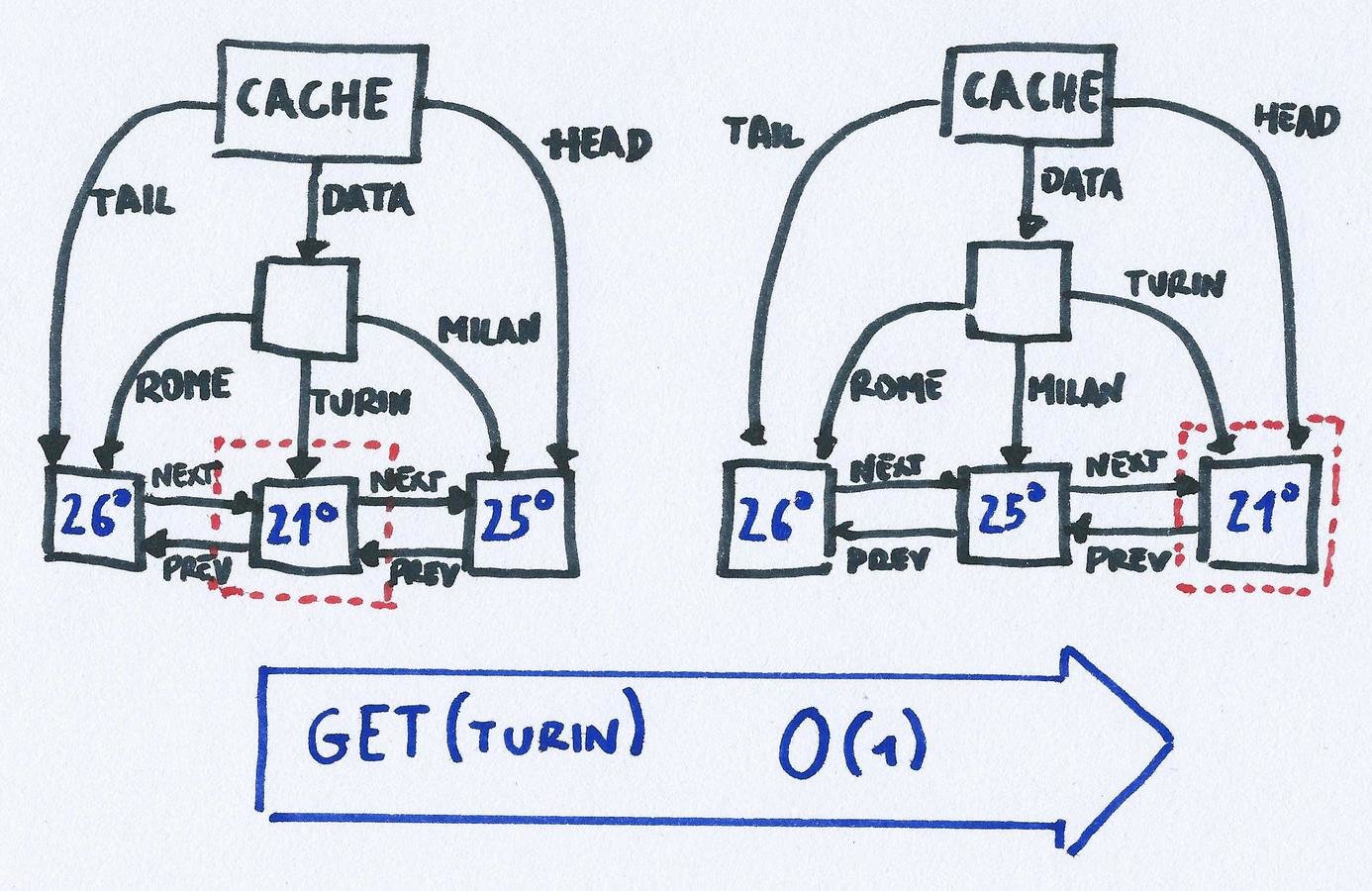
LRUCache
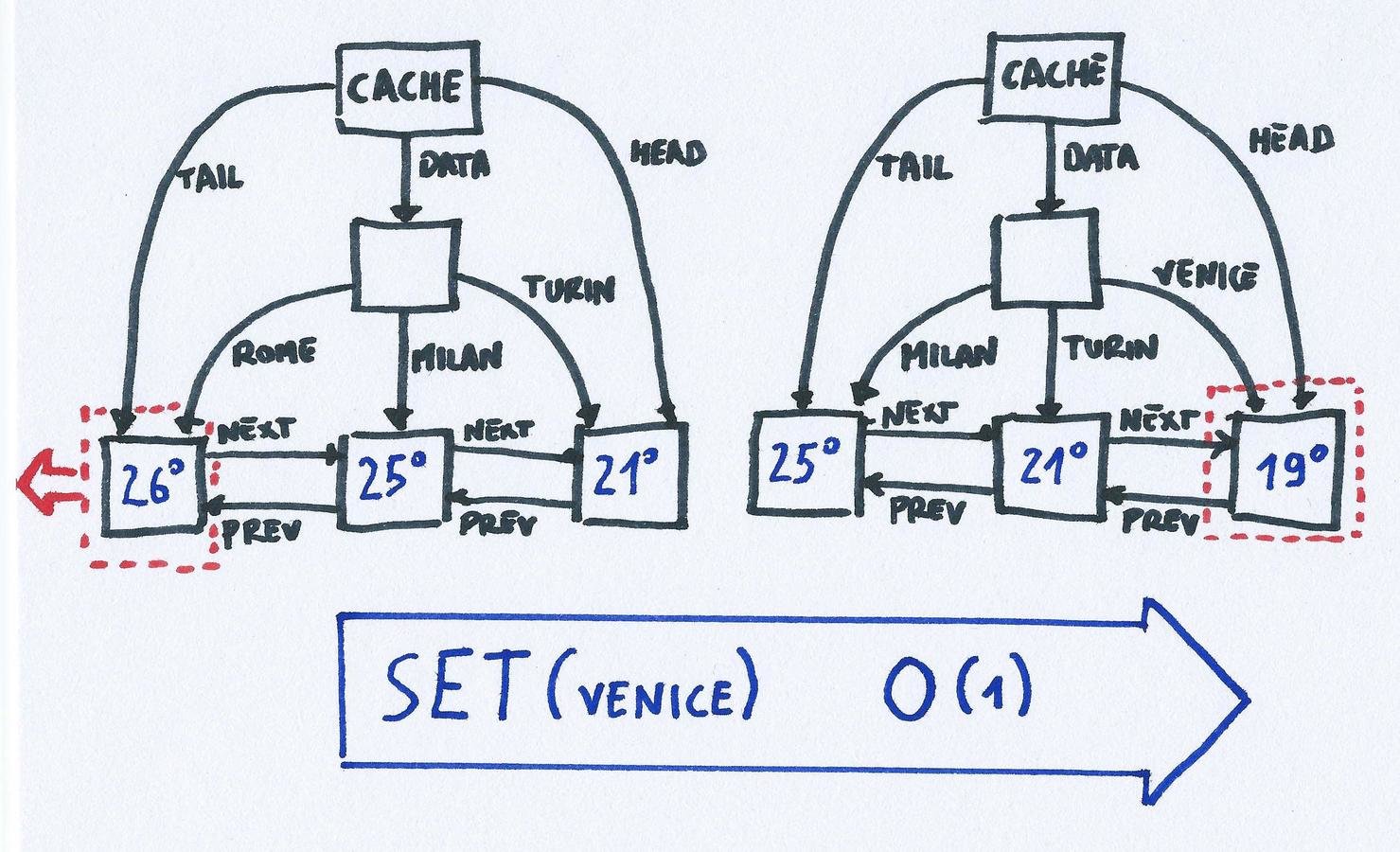
Example:
Priority queue
Can we use an array?
Heap
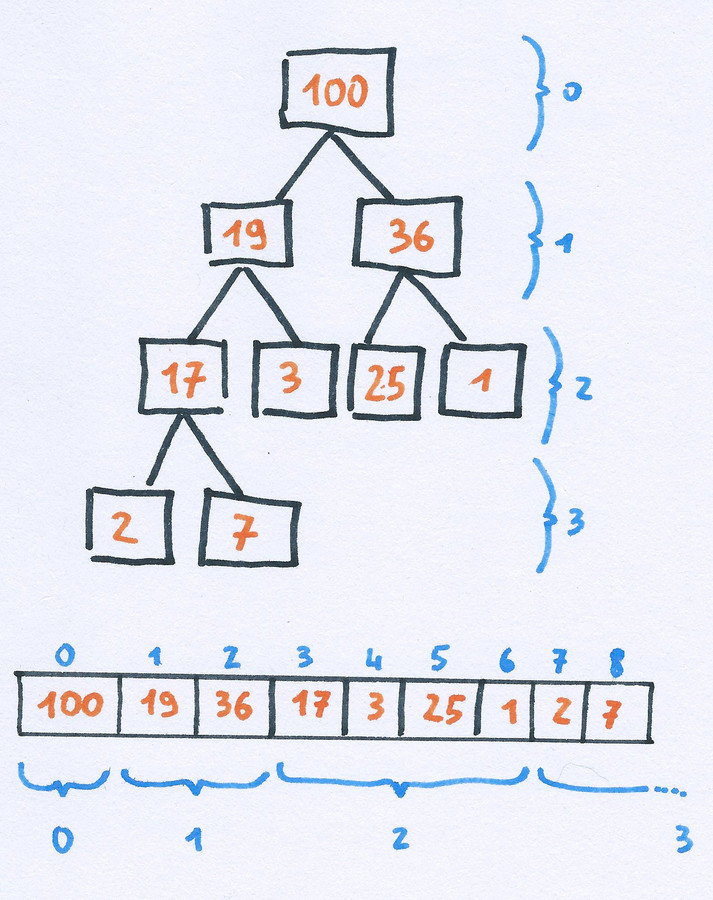
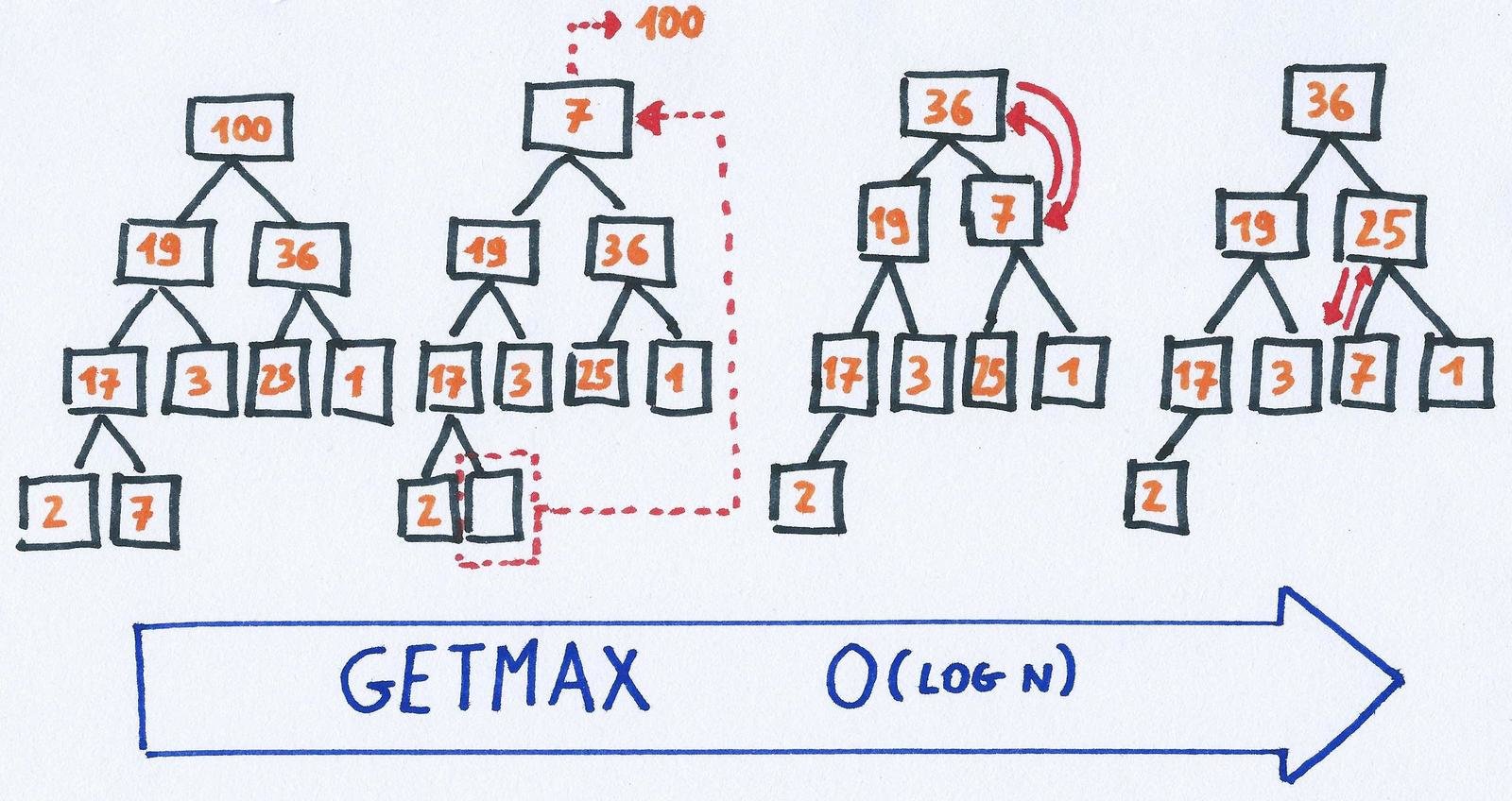
Heap
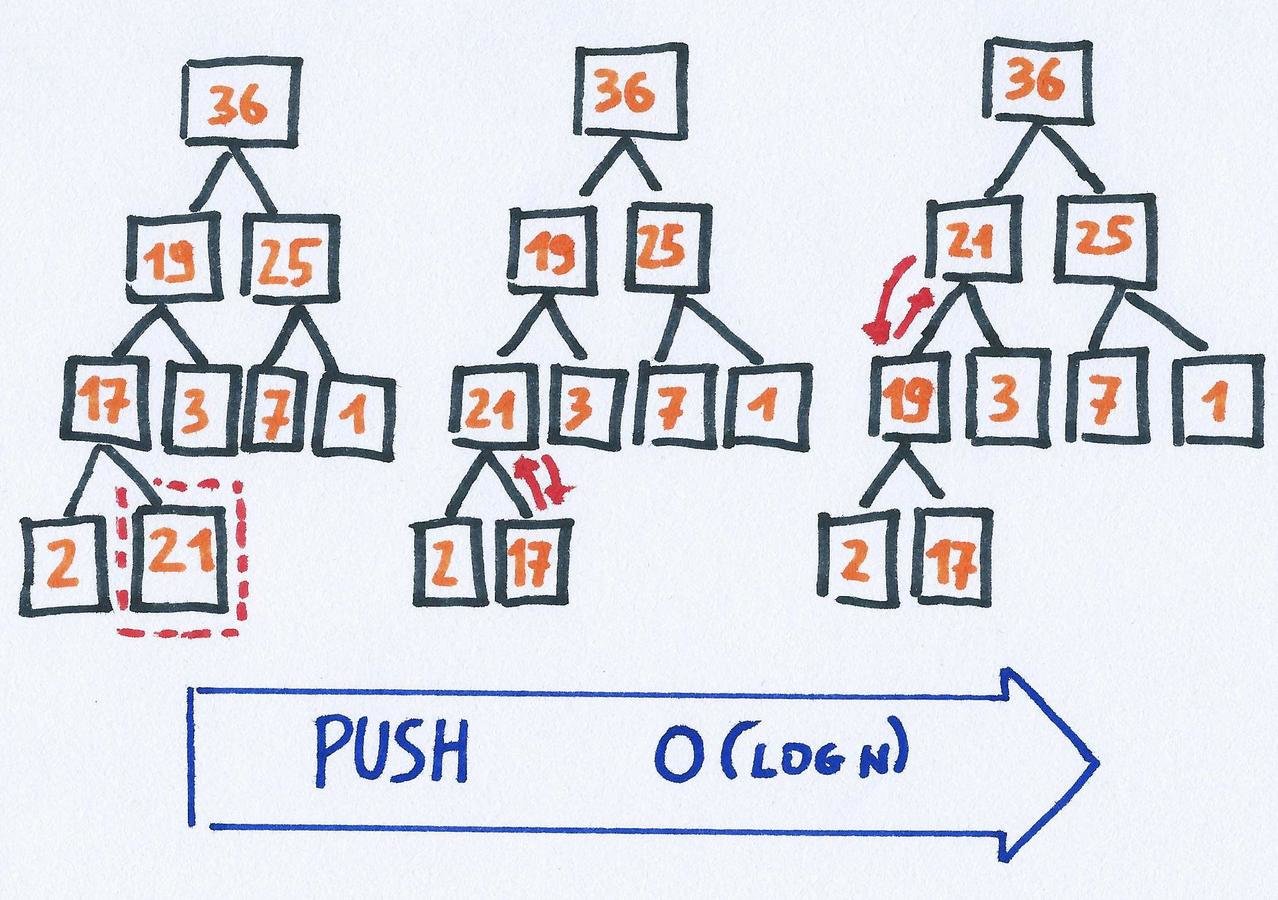
Heap
Other applications
Heapsort O(n log n)
Shortest path algorithm
Order statistic (kth smallest/largest item)
Thanks for listening
You can find some example in my js data structures library: "little-ds-toolkit"
Data structures in js
By Maurizio Lupo
Data structures in js
- 559



