Public Key Infrastructure
PKI

Agenda
-
What ?
-
How ?
-
Why ?
-
When ?
-
Where ?
What is it all about?
-
Public Key
-
Private Key
-
Certificates
-
Certification Authority
-
Registration Authority
-
Revocation
Public Key
-
Encrypts data
-
Usually associated with certificate
-
Used by sender
-
Can be used by anyone
-
Cannot decrypt data

Private Key
-
Decrypts data
-
Has to be kept secret
-
Used by receiver

Certificates
-
Checks identity
-
Associated with public key
-
Encrypted asymmetrically itself
-
Issued by CA
Certificate Authority
-
Issues, revokes, distributes certificates
-
Can be 3rd party or in-house
-
Enables to verify public key
Registration Authority
-
Entry point to issue certificate
-
Verifies entities
-
Do not sign certificate
Revocation
-
Certificate expiration
-
Entity name change
-
Entity request
-
Private key leak
How it works?
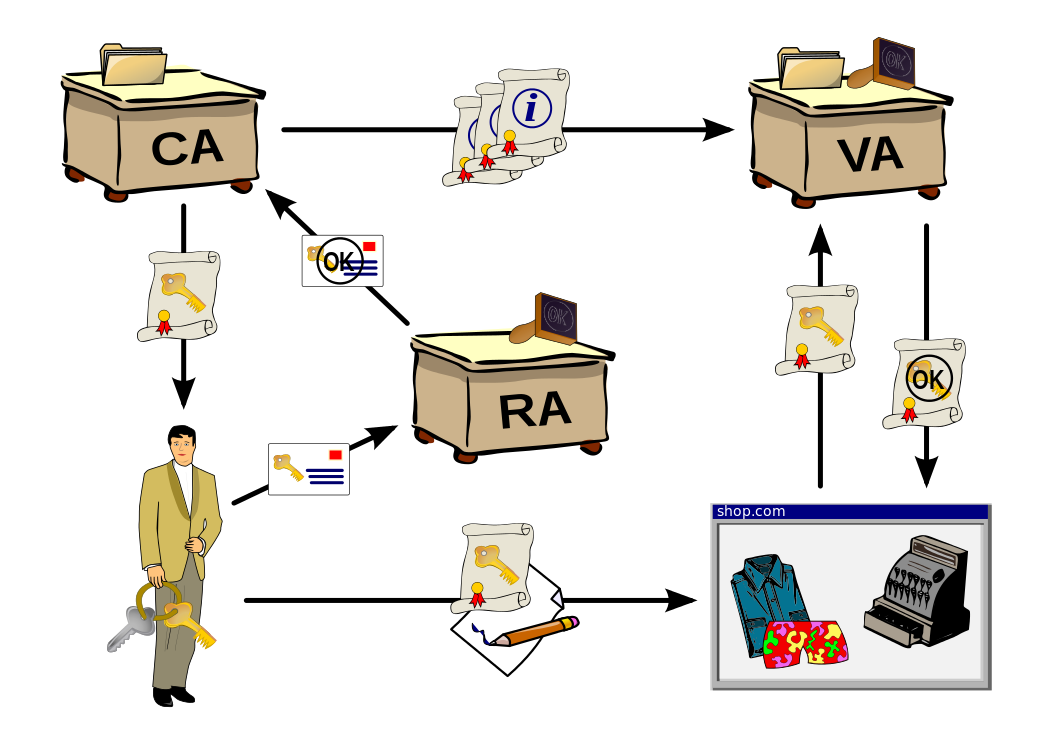
Why?
-
Confidentiality
-
Integrity
-
Authentication
Confidentiality
"is the property, that information is not made available or disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities, or processes"
Integrity
"maintaining and assuring the accuracy and completeness of data over its entire life-cycle"
Authentication
"verifying a claim of identity"
When:
-
Server identification
-
Web apps authorization & authentication
-
Electronic documents signing
-
Message encryption
-
Wireless access
Where?
PKI Infrastructure
By Szymon Łyszkowski
PKI Infrastructure
- 941


