Operators & Control Statements in Java


Agenda



-
Arithmetic Operators
-
Relational Operators
-
Assignment vs Equality
-
Compound Assignment
-
Postfix & Prefix Operators
-
Branching - if else
-
Branching - Switch case
-
Logical Operators

Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on variables and data.

Arithmetic Operators
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 5;
int b = 3;
int c = a + b;
System.out.println("Sum = " + c);
}
}

Relational Operators are used to check some relationship between two operands.

Relational Operators
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 5;
int b = 3;
System.out.println(a < b); // false
}
}


Relational Operators
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| == | Is equal to | 10 == 5 return false |
| > | Greater than | 10 > 5 returns true |
| < | Less than | 10 < 5 returns false |
| >= | Greater than or Equal to | 10 >= 5 returns true |
| <= | Less than or Equal to | 10 <= 5 returns false |
| != | Not Equal to | 10 != 5 returns true |


class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10, b = 5;
// == operator
System.out.println(a == b); // false
// != operator
System.out.println(a != b); // true
// > operator
System.out.println(a > b); // true
// < operator
System.out.println(a < b); // false
// >= operator
System.out.println(a >= b); // true
// <= operator
System.out.println(a <= b); // false
}
}Relational Operators

The = is an assignment operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left.
The == is the equality operator which is used to check whether two items are equal in value.

Assignment vs Equality Operator
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x = 5;
// x is assigned value 5
float y = 2.3;
// y is assigned value 2.3
System.out.println(x == 5); // true
System.out.println(y == 2); // false
}
}
Compound assignment operators are a short-hand way of applying an operation and to assign the value to the variable on the left hand side.

Compound Assignment
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
a *= 5; // equivalant to a = a * 5;
b -= 2; // equivalant to b = b - 2;
System.out.println(a); // 25
System.out.println(b); // 8
}
}
Prefix operator – The pre-increment or pre-decrement initially increases or decrements the value before performing the specified operation.
Postfix operator – The post-increment or post-decrement performs the specified action first before increasing or decreasing the value.

Prefix & Postfix Operators
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 5;
int b = a++;
System.out.println(a); // 6
System.out.println(b); // 5
}
}class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 5;
int b = ++a;
System.out.println(a); // 6
System.out.println(b); // 6
}
}Example - Prefix Increment
Example - Postfix Increment


Branching - if else
- The if statement is used to test a condition. It checks boolean condition: true or false.
- It can optionally have an else if and an else statement attached with it as well.
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String weather = "rainy";
if (weather == "rainy") {
System.out.println("Take an umbrella");
}
else if (weather == "sunny") {
System.out.println("Wear sunglasses");
}
else {
System.out.println("Check weather forecast");
}
}
}


Check Odd or Even
Given an integer N, check whether it is odd or even.
Sample Input
N = 5
Sample Output
Odd


In Java, a switch statement is used to transfer control to a particular block of code, based on the value of the variable being tested.

Switch Case
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String weather = "rainy";
if (weather == "rainy") {
System.out.println("Take an umbrella");
}
else if (weather == "sunny") {
System.out.println("Wear sunglasses");
}
else {
System.out.println("Check weather forecast");
}
}
}

In Java, a switch statement is used to transfer control to a particular block of code, based on the value of the variable being tested.

Switch Case
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String weather = "rainy";
switch (weather) {
case "rainy":
System.out.println("Take an umbrella");
break;
case "sunny":
System.out.println("Wear sunglasses");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Check weather forecast");
}
}
}


Days in a month
Given the number of the month, print its name and no. of days as output.
(Assume non-leap year)
Sample Input
N = 3
Sample Output
March
31 days



Vowel or Consonant
Given a lowercase character, state whether it is a vowel or a consonant.
Sample Input
e
Sample Output
Vowel


Ternary operator is a condensed form of if-else statement which evaluates a condition and executes the code based on the evaluated condition.

Ternary Operator
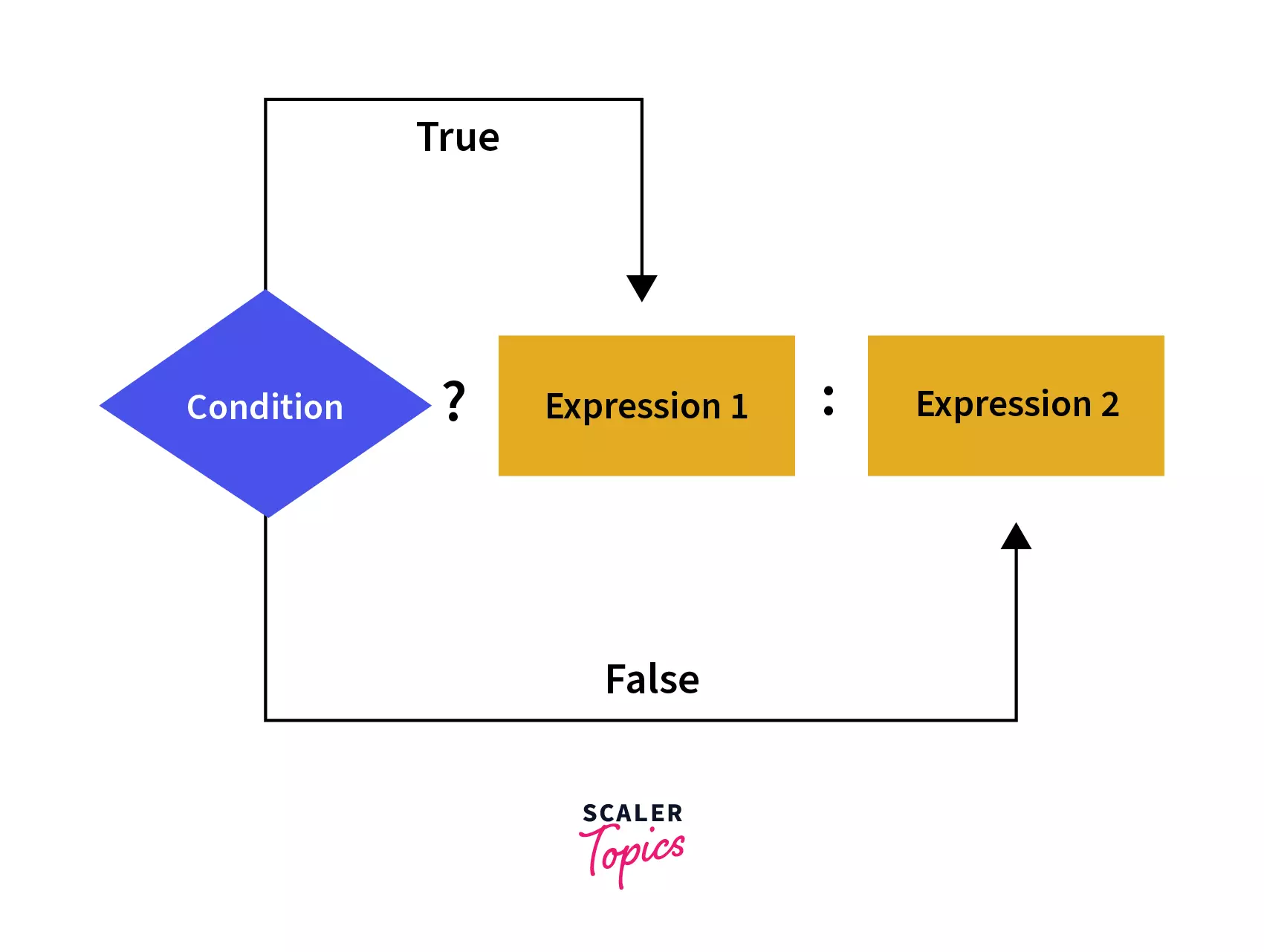
result = (condition) ? expression1: expression2 ;
result: The final variable which gets the value.
condition: This is the test condition statement that gets evaluated to true or false.
expression1: If condition gets evaluated to true then expression1 is assigned to result.
expression2 : If condition gets evaluated to false then expression 2 is assigned to result.


Ternary Operator
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
String ans;
if (num % 2 == 0) {
ans = "Even";
} else {
ans = "Odd";
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}Given an integer number, check whether its odd or even.



Ternary Operator
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
String ans = num % 2 == 0 ? "Even" : "Odd";
System.out.println(ans);
}
}Given an integer number, check whether its odd or even.


Logical Operators are used making decisions in programming based on some other conditions.
There are three types of Logical Operators in Java
- AND
- OR
- NOT

Logical Operators

The AND operator takes two expressions and returns True if both the expressions are True, else it returns False.
It is denoted by &

Logical AND - &
| Expression1 | Expression2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |

Short Circuit AND behaves just like Logical AND however, it only evaluates the second expression if the first expression yields true.
It is denoted by &&

Logical Short Circuit AND - &&
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 15;
String citizenship = "Indian";
if (age >= 18 && citizenship == "Indian") {
System.out.println("Person may vote");
} else {
System.out.println("Person cannot vote");
}
}
}
The OR operator takes two expressions and returns true if either one of the two expressions is true, else false.
It is denoted by |

Logical OR
| Expression1 | Expression2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| False | True | True |
| False | False | False |


Logical Short Circuit OR
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String org = "Interviewbit";
if (org == "Scaler" || org == "Interviewbit") {
System.out.println("User permitted");
} else {
System.out.println("User not permitted");
}
}
}Short Circuit OR behaves just like Logical OR however, it only evaluates the second expression if the first expression yields false.
It is denoted by ||

The logical NOT operator the return the negation of a boolean value.
That is, it returns true for false and vice-versa.

Logical NOT
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
boolean flag = false;
if (!flag) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
}

Homework
- Write a program to check if the given no. is positive and even.
- Write a program to check if the given no. is divisible by either 2 or 5, but not both.

Operators & Control Statements
By Tarun Luthra
Operators & Control Statements
- 33


