webutvikling og api-design
03: Tooling: npm, Babel, Webpack, ES2015
higher-order components
- I was wrong
- f(component) —> component
function loadable(TheComponent) {
return class extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { loading: true };
}
componentDidMount() {
doSomethingAsync()
.then(() => this.setState({loading: false});
}
render() {
if (this.state.loading) {
return <p>Loading…</p>;
}
return <TheComponent someNewProp={…}/>;
}const ExampleComponent =
loadable(<SomeComponent/>);
ReactDOM.render(<ExampleComponent/>);- View library for web apps (browser)
- Declarative
- React: Put this value here
- JQuery:
- 1. Retrieve this value like this
- 2. Display it here like this
-
3. Update the value like this
- Static webapp!

Data binding with props
// ES2015 class syntax
class Greeting extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
// JSX
<p>Hello, {this.props.name}</p>
);
}
}
// NB: JSX
var greeting = <Greeting name="Martin" />;
// Add the element to the DOM
ReactDOM.render(
greeting,
document.getElementById('container')
);Composition
- Components "own" other components
- No inheritance (only React.Component)
- No field variables, only props
- Functional components:
- No state
- component = f(props) => jsx
Working with children
ReactDOM.render((
<A>
<B /> {/* "Child" node: passed to A as props.children */}
</A>
), document.getElementById('container'));
class B extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Heading</h1>
<p>Body text</p>
</div>
);
}
}
class A extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div style={{padding: '1em', border: 'solid black 1px'}}>
{this.props.children} {/* Render B */}
</div>
);
}
}
General, reusable wrappers!

- JS on the server (not the browser)
- Built on the V8 JS Engine (Chrome)
- Runs on all platforms (Win/OSX/Linux)
- Still not compiled
- Pretty darn fast
- Package (3rd party lib) manager for JS
- Used a lot for Node (but also the browser)
- Comes with Node installation
- Comes with Node installation
- Easy to publish packages!


First node app
'use strict';
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
const liam = new Person('Liam');
console.log(liam);
index.js
➜ node index.js
Person { name: 'Liam' }Run the code with node <filename>
('use strict'; to allow classes for now)
- Metadata for NPM
- In project root
- Similar to pom.xml
package.json
{
"name": "timetracker-client-react",
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --config webpack.config.prod.js",
"dev": "node -r babel/register dev-server.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"bootstrap": "^3.3.5",
"react": "^0.14.3",
"react-dom": "^0.14.3",
"react-redux": "^4.0.0",
"redux": "^3.0.4",
"style-loader": "^0.13.0",
"superagent": "^1.4.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"babel": "^5.8.34",
"babel-core": "^5.8.25",
"babel-loader": "^5.3.2",
"babel-plugin-react-transform": "^1.1.1",
"express": "^4.13.3",
"react-transform-catch-errors": "^1.0.0",
"react-transform-hmr": "^1.0.1",
"redbox-react": "^1.2.0",
"redux-devtools": "^2.1.5",
"webpack": "^1.12.6",
"webpack-dev-middleware": "^1.2.0",
"webpack-hot-middleware": "^2.5.0"
}
}
$ npm install
$ npm install --save react
$ npm install --save-dev babelLibs (modules)
@
./node_modules/
npm scripts
- Give names to shell commands
- Has installed modules on path
{
"name": "f03-npm-scripts",
"scripts": {
"build": "concat src/**/*.js > output/script.js"
}
}
➜ npm run build(.npmrc)
- npm config (not metadata)
- Where are modules installed?
- Which browser to open?
- Coloured output
- Loglevel
- …
- Typically in project root (with package.json)
- Global .npmrc @ /path/to/npm/.npmrc
- https://docs.npmjs.com/misc/config
Webapp deps with npm
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>f03!</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css"/>
<script src="node_modules/babel-core/browser.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/react/dist/react.js"></script>
<script src="node_modules/react-dom/dist/react-dom.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
const text = 'blah';
ReactDOM.render((
<p>Hello </p>
), document.getElementById('container'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
{
"name": "f03-demo",
"dependencies": {
"babel": "^5.8.35",
"bootstrap": "^3.3.6",
"react": "^0.14.7",
"react-dom": "^0.14.7"
}
}
package.json
index.html
- Originally called 6to5
- Translates new JS (ES2015) to JavaScript (ES5)
- Also supports JSX
- Also supports JSX
- We've been using it already: browser.js
- Can output files (but doesn't have to)
- Works with Node and browser

Babel Basics
- Takes one or more files as input
- Runs the content through transforms
- Outputs the transformed content (concatenated)
➜ babel script.jsx
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
toString() {
return `This person is called ${ this.name }!`;
}
}
const martin = new Person("Martin");
console.log(martin);
No transforms
A Transform
- Takes one or more files as input
-
Runs the content through transforms
- Outputs the transformed content
➜ babel script.jsx
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
toString() {
return `This person is called ${ this.name }!`;
}
}
const martin = new Person("Martin");
console.log(martin);
No transforms
➜ babel script.jsx --plugins transform-es2015-block-scoping
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
toString() {
return `This person is called ${ this.name }!`;
}
}
var martin = new Person("Martin");
console.log(martin);
block scoping transform
Presets
- Babel is plugin-based since v6.0.0
- Needs a transform
to do anything
-
Preset
=
set of transforms
- es2015 = full spec
➜ babel script.jsx --presets es2015
"use strict";
var _createClass = function () { function defineProperties(target, props) { for (var i = 0; i < props.length; i++) { var descriptor = props[i]; descriptor.enumerable = descriptor.enumerable || false; descriptor.configurable = true; if ("value" in descriptor) descriptor.writable = true; Object.defineProperty(target, descriptor.key, descriptor); } } return function (Constructor, protoProps, staticProps) { if (protoProps) defineProperties(Constructor.prototype, protoProps); if (staticProps) defineProperties(Constructor, staticProps); return Constructor; }; }();
function _classCallCheck(instance, Constructor) { if (!(instance instanceof Constructor)) { throw new TypeError("Cannot call a class as a function"); } }
var Person = function () {
function Person(name) {
_classCallCheck(this, Person);
this.name = name;
}
_createClass(Person, [{
key: "toString",
value: function toString() {
return "This person is called " + this.name + "!";
}
}]);
return Person;
}();
var martin = new Person("Martin");
console.log(martin);Ouptut to file with preset
➜ babel script.jsx --presets es2015 > output/script.js- > writes stdout to file
- >> concatenates (irrelevant here)
.babelrc
- Config for Babel
- JSON file called .babelrc
- Usually in project root
- Presets & the like
Babel Require hook
- Most useful for the Node environment
- We'll get back to this next lecture!
- … but it exists.
Webpack
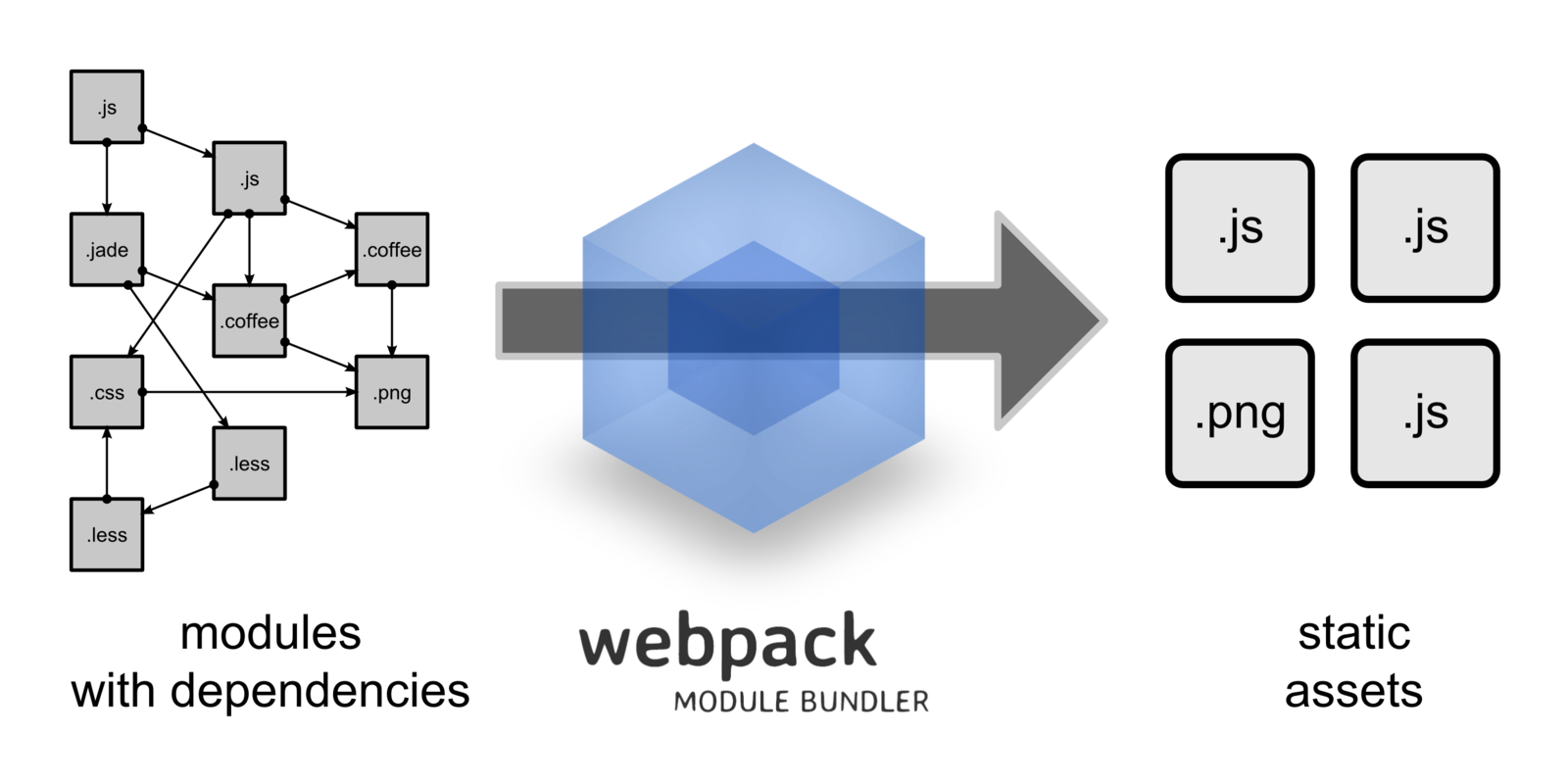
Tying
it
To-gether
webpack...
-
Loads your source files using loaders
- babel-loader for ES2015 and JSX
-
stylus-loader for Stylus (to CSS)
- "Bundles" them together into a single file bundle.js
- … which is the only file you include in index.html
- … which is the only file you include in index.html
- Lets you import modules ES2015-style
- (or require CommonJS or AMD-style)
webpack.config.js
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Webpack demo!</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container"></div>
<script src="bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>- Node script!
- Decides what Webpack does.
export default class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
import Person from './Person';
const liam = new Person('Liam');
console.log(liam);{
"name": "webpack-demo",
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --config webpack.config.js"
},
"devDependencies": {
"babel-loader": "^6.2.1",
"webpack": "^1.12.12"
}
}
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const srcDir = path.join(__dirname, 'src');
module.exports = {
entry: path.join(srcDir, 'index.js'),
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'output'),
filename: 'bundle.js',
},
module: {
loaders: [
{ test: /\.jsx?$/, loader: 'babel', include: srcDir },
],
},
};
index.html
src/Person.js
src/index.js
package.json
webpack.config.js
Hot module replacement
Exercise
- Install Node (and run node and npm from terminal)
- Install nodemon globally with npm install -g nodemon
- Build https://github.com/theneva/webutvikling-og-api-design/tree/master/f03/exercise with Webpack
- Add hot module reloading & fly!
PG6300-15-03 Tooling: npm, Babel, Webpack, ES2015
By theneva
PG6300-15-03 Tooling: npm, Babel, Webpack, ES2015
Lecture 3 in PG6300-15 Webutvikling og API-design
- 767



