Web development & API design
011: Testing!
Automated Testing!
- Code that tests other code
- Automatically run (on build?)
- Can be run on file changes
- Like webpack, but for QA
- Verifies that the program works as intended
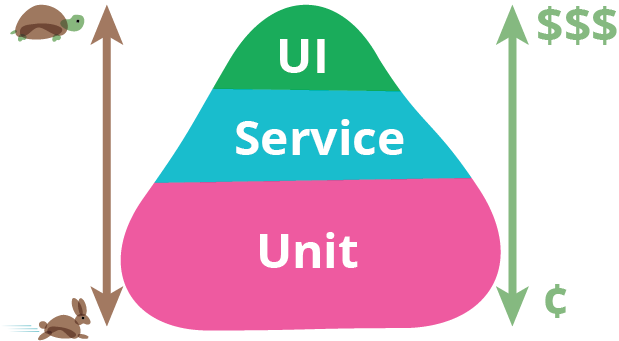
Three types (+++)
Jest
- Framework, test runner, mocking, assertions
- describe & it (BDD)
describe('GET /messages', () => {
it('should require a token', (done) => {
// do something
});
});const greet = require('../Greeting');
describe('Greeting', () => {
it('has correct form', () => {
const result = greet('Liam');
const expected = 'Hello, Liam!';
// assertions
});
});
Simple JS module
API endpoint
Assertions with Jest
const greet = require('../Greeting');
describe('Greeting', () => {
it('has correct form', () => {
const result = greet('Liam');
const expected = 'Hello, Liam!';
expect(result).toEqual(expected);
});
});
Some details
- Run tests with $ jest
- Recursive by default
- **/__tests__/*.js
- **/*.test.js
Installation
- Already included with create-react-app
- $ yarn add --dev jest
Quick demo!
Server-side testing
- Let's just test the API endpoints
- Not really unit tests
- Make the API available
- Send a request
- Verify the response
- (Notify that you are done)
Server-side testing
const express = require('express');
const request = require('supertest');
const app = express();
const api = require('../api')
// make api available
app.use(api);
describe('/person', () => {
it('should return a JSON person', () => {
// send a request
return request(app)
.get('/person')
-
supertest
- Based on superagent
- Popular HTTP lib
- Before fetch
- $ yarn add --dev supertest
Server-side testing
const express = require('express');
const request = require('supertest');
const app = express();
const api = require('../api')
// make api available
app.use(api);
describe('/person', () => {
it('should return a JSON person', () => {
// send a request
return request(app)
.get('/person')
// verify response
.expect(200)
.expect('Content-Type', 'application/json; charset=utf-8')
.expect(res => {
const person = res.body;
expect(person.name).toEqual('Liam');
expect(person.age).toEqual('22');
});
});
});
Server-side testing
const express = require('express');
const request = require('supertest');
const app = express();
const api = require('../api')
// make api available
app.use(api);
describe('/person', () => {
it('should return a JSON person', () => {
// send a request
return request(app)
.get('/person')
// verify response
.expect(200)
.expect('Content-Type', 'application/json; charset=utf-8')
.expect(res => {
const person = res.body;
expect(person.name).toEqual('Liam');
expect(person.age).toEqual('22');
});
});
});
- Notify you're done
Useful things to note
- app.use(api) doesn't need to be the ENTIRE api
- tests actually run api file
- External dependencies must be present
- db…
Jest <3 React
- From create-react-app
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
it('renders without crashing', () => {
const div = document.createElement('div');
ReactDOM.render(<App />, div);
});
// package.json
"test": "react-scripts test --env=jsdom",
Meh, just use Mocha
import React from 'react';
import TestUtils from 'react-addons-test-utils';
import EmailInput from '../../../src/web/components/EmailInput.jsx';
describe('EmailInput', () => {
it('is a div that contains a label', () => {
// ...
});
});-
Pure functions are easy to test
- Redux => everything is a prop
- Components are functions of props
- Small components are easiest
Snapshot testing
it('renders correctly', () => {
const tree = renderer.create(
<Link page="http://www.instagram.com">Instagram</Link>
).toJSON();
expect(tree).toMatchSnapshot();
});Demo
Exercise
- Add tests to assignment!
- (Will be required in A11)
PG6300-17-011 Testing!
By theneva
PG6300-17-011 Testing!
Lecture 011 in PG6300-17 Webutvikling og API-design
- 669



