Web development & API design
L10: Data!
Assignment 1
- Not completely done…
- Lots of good stuff!
- Issues with data and reloading
The URL
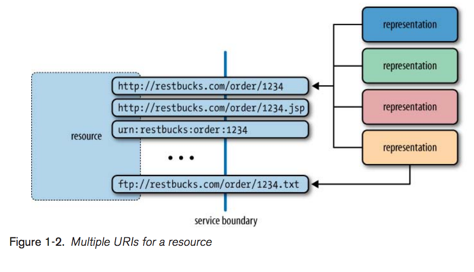
The Richardson maturity model
React state
export default class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
colors: [],
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch('http://localhost:2466/colors')
.then(res => res.json())
.then(colors => this.setState({colors}));
}
render() {
return <div>
{this.state.colors.map(
color => <Color
key={color.color}
color={color.color}
hex={color.hex}/>
)}
</div>;
}
}
Demo: display & create
- What does "without needing to refresh" mean?
Pros
- State is natively supported
- Well-documented
- Well-known
- Triggers automatic rerendering
Cons
- State is spread around the app
- Callbacks get weird and bloaty
- State makes debugging hard
- State is hard to test
- "Undo" and "Redo"
React state
Redux

A Redux store is a single object
{
messages: [
// ...
],
contactInfo: {
// ...
}
}- Not directly mutable
- Just like setState(…)
- But for everything
- EVERYTHING is stored here
- Bad practise…?
- Handles rerendering
Get started!
// Can be used with any view lib (not just React)
npm install --save redux
1: Create a reducer
function reducer(
state = {
messages: [],
contactInfo: {}
}, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD_MESSAGE':
return {
messages: [...state.messages, action.data],
contactInfo: state.contactInfo,
};
case 'UPDATE_CONTACT_INFO':
return {
messages: state.messages,
contactInfo: action.data,
};
default: return state;
}
}
- (oldState, action) => newState
- A pure function
- Accepts
- current state
- an action
- Returns the new state
- Accepts
2: Create a Redux store
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import theReducer from './reducer.js';
const store = createStore(reducer);- Pass the reducer to createStore(…)
- Done!
3: Dispatch an action
// from the reducer
case 'ADD_MESSAGE':
return {
messages: [...state.messages, action.data],
contactInfo: state.contactInfo,
};
// updating the state
store.dispatch({
type: 'ADD_MESSAGE',
data: {name: 'A', email: 'b@c.d', message: 'fghijklmn'},
});- Actions = plain objects
- Like Intent in Android
- Like Intent in Android
- Passed as argument #2 to the reducer
3: Connect to React
// React bindings
npm install --save react-reduximport { connect } from 'react-redux'
// ...
class App extends React.Component {
// ...
}
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return {};
}
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {};
}
const ConnectedApp = connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(App);
export default ConnectedApp;- Properties from mapXToProps become available as props
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
// ...
render((
<Provider store={store}>
<App .../>
</Provider>
), document.getElementById('container'));
Map state & Dispatch
to props
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return {
messages: state.messages,
};
};
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {
addMessage: message => dispatch({
type: 'ADD_MESSAGE',
data: message
}),
};
};// render
<AdminPanel title="All messages"
messages={this.props.messages}/>
// elsewhere
.then(message => {
this.props.addMessage(message);
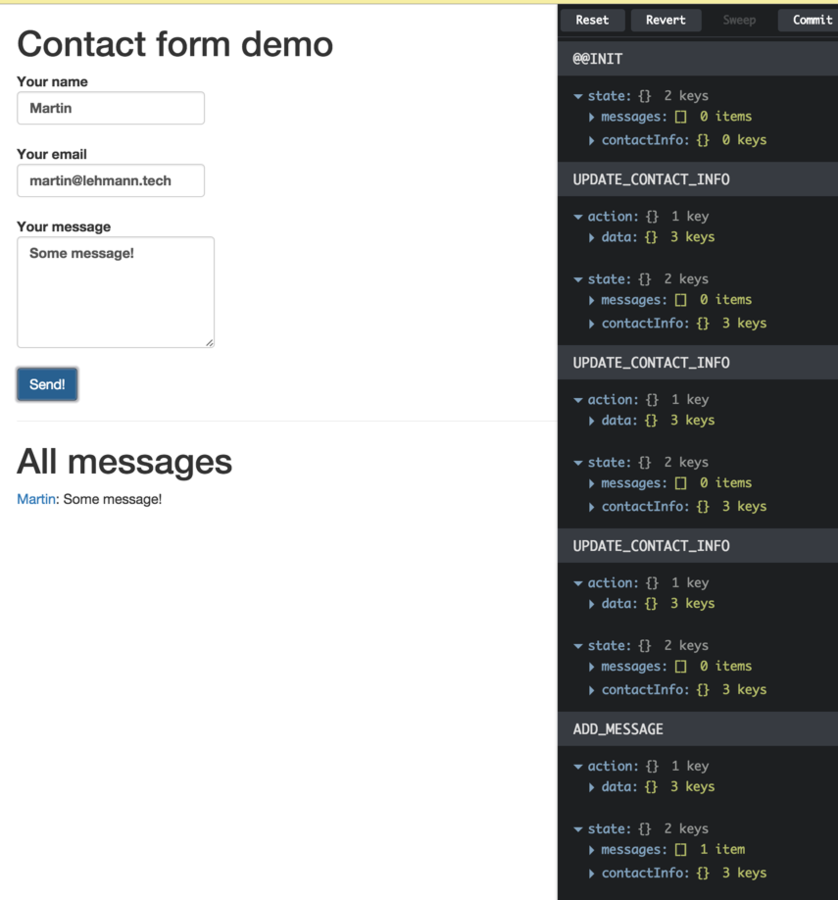
})Small bonus: React Devtools
Database!

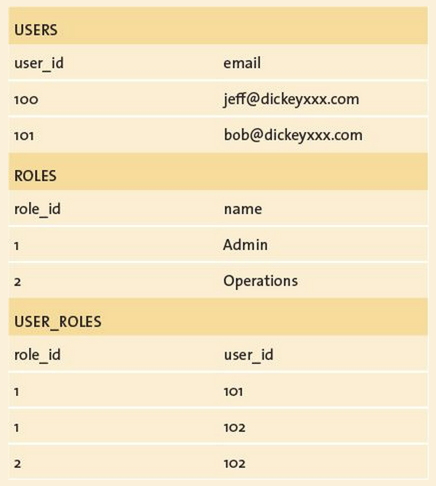
Relations vs. Documents


Storage format: BSON
- Binary JSON
- ObjectId based on timestamp
- Documents "=" objects
Joins
Express <3 Mongoose
var app = require('express')();
var mongoose = require('mongoose');
app.use(require('body-parser').json());
var personSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true }
});
var Person = mongoose.model('Person', personSchema);
app.get('/person', function(req, res) {
var person = new Person({
name: 'Martin'
});
res.send(person);
});
app.listen(1234);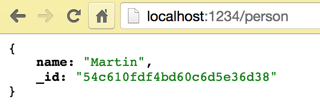
Embedded docs (sub docs)
- Ownership between types
-
Example code
- /series
- /series/:seriesId
- /series/:seriesId/books
- /series/:seriesId/books/:bookId
- /books?
PG6300-17-010: Data!
By theneva
PG6300-17-010: Data!
Lecture 010 in PG6300-17 Webutvikling og API-design
- 576



