Videos and data
Goal: model
Main lines of the model
- 2 groups
heading to the food
heading to the nest
- agents \(i\) with position \(X_i \in \mathbb{R}^2\) and velocity \(V_i \in \mathbb{R}^2\)
- Model of evolution :
- Visual field \(\mathcal{V}_i\)
Visual field \(\mathcal{V}_i\)
orientation
Forces
1. Self-propulsion
\(\nu > 0\) strength of the force
\(\xi > 0\) target velocity magnitude
3. Interaction
2. Drive
drives to the right if \(g_i = 1\)
drives to the left if \(g_i = -1\)
controls the velocity magnitude
drives towards the objective
deals with the other agents
Forces
1. Self-propulsion
\(\nu > 0\) strength of the force
\(\xi > 0\) target velocity magnitude
controls the velocity magnitude
drives towards the objective
deals with the other agents
Force self-propulsion
The parameters \(\nu\) and \(\xi\) chosen according to the situation:
depends on the visual field \(\mathcal{V}_i\)
1. No obstacles
2. Head-on contact with another agent
3. Generic contact with another agent
cruising
braking
sliding
or
Forces
1. Self-propulsion
\(\nu > 0\) strength of the force
\(\xi > 0\) target velocity magnitude
3. Interaction
2. Drive
drives to the right if \(g_i = 1\)
drives to the left if \(g_i = -1\)
controls the velocity magnitude
drives towards the objective
deals with the other agents
Force \(F_{\text{interact}}\)
Depends on the visual field \(\mathcal{V}_i\)
\(\mathrm{I}\). Same group
attraction
repulsion
\(\mathrm{II}\). Other group
attraction
steer (avoid)
1/2
nothing
Force \(F_{\text{interact}}\)
Depends on the visual field \(\mathcal{V}_i\)
\(\mathrm{I}\). Same group
attraction if
\(|X_j - X_i|> d_{\text{ref}}\)
repulsion if
\(|X_j - X_i|< d_{\text{ref}}\)
\(\mathrm{II}\). Other group
attraction
steer (avoid)
2/2
If \(\Theta_j \cdot \sigma^{\perp}_+ \leq 0 \) :
Then
\(\sigma^\perp_+\) chosen such that
\(\Theta_i \cdot \sigma^{\perp}_+ \geq 0\)
If \(\Theta_j \cdot \sigma^{\perp}_+ \geq 0 \) :
If \(|\Theta_i \cdot \sigma| \geq |\Theta_j \cdot \sigma|\) then
Else
Steering force \(F_{\text{steer}}\)
Videos
Quantitative properties: velocity magnitudes
Comparison with data
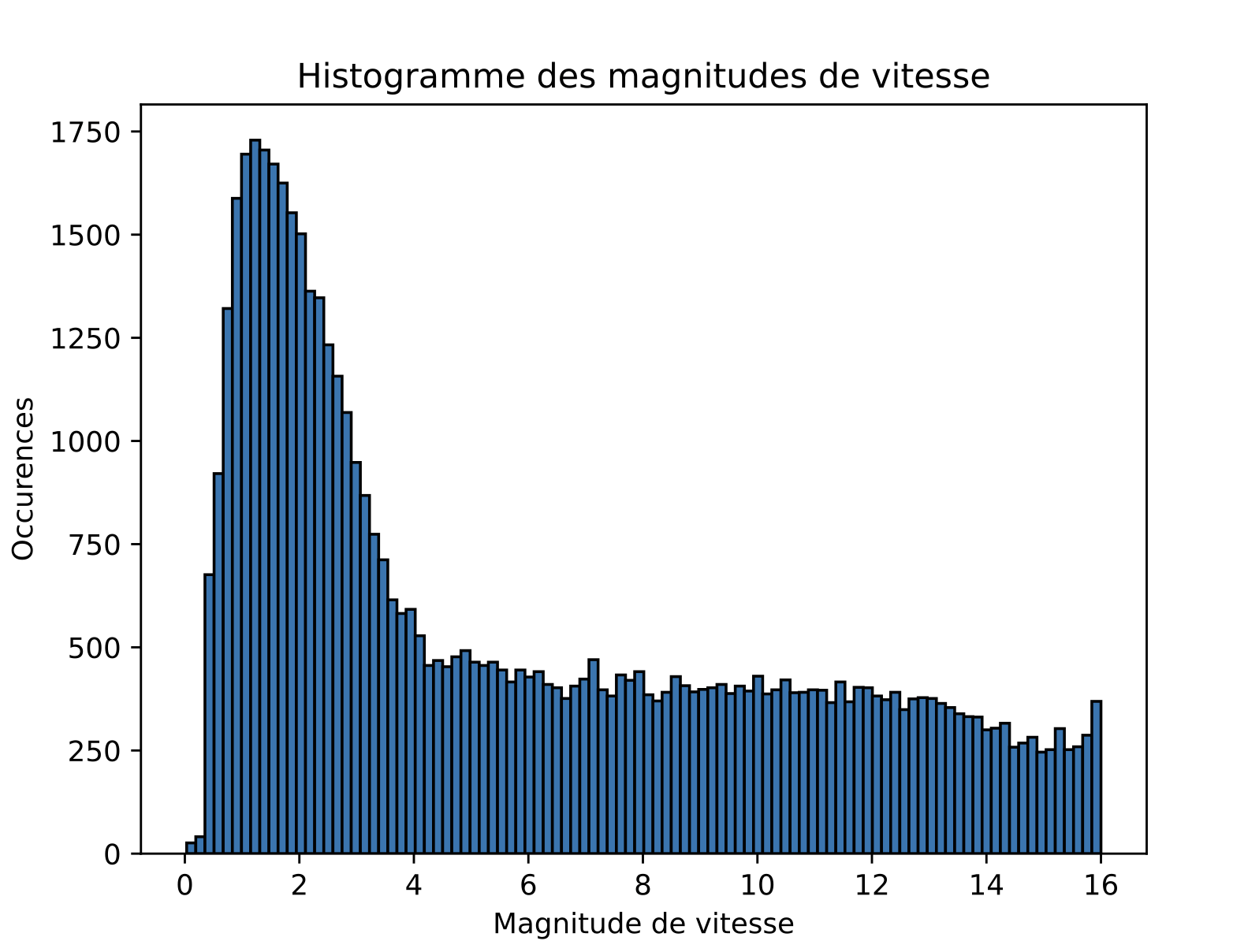
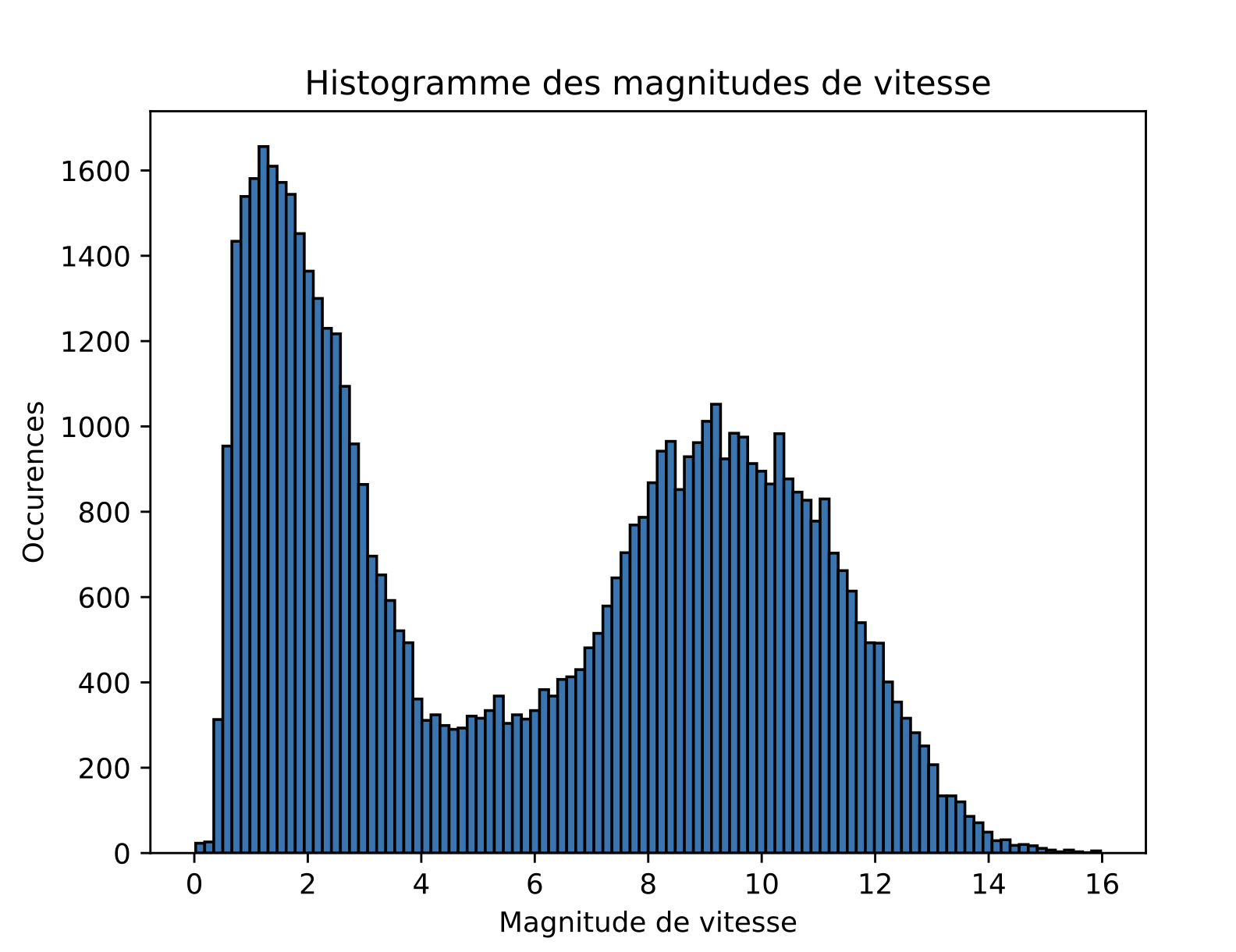
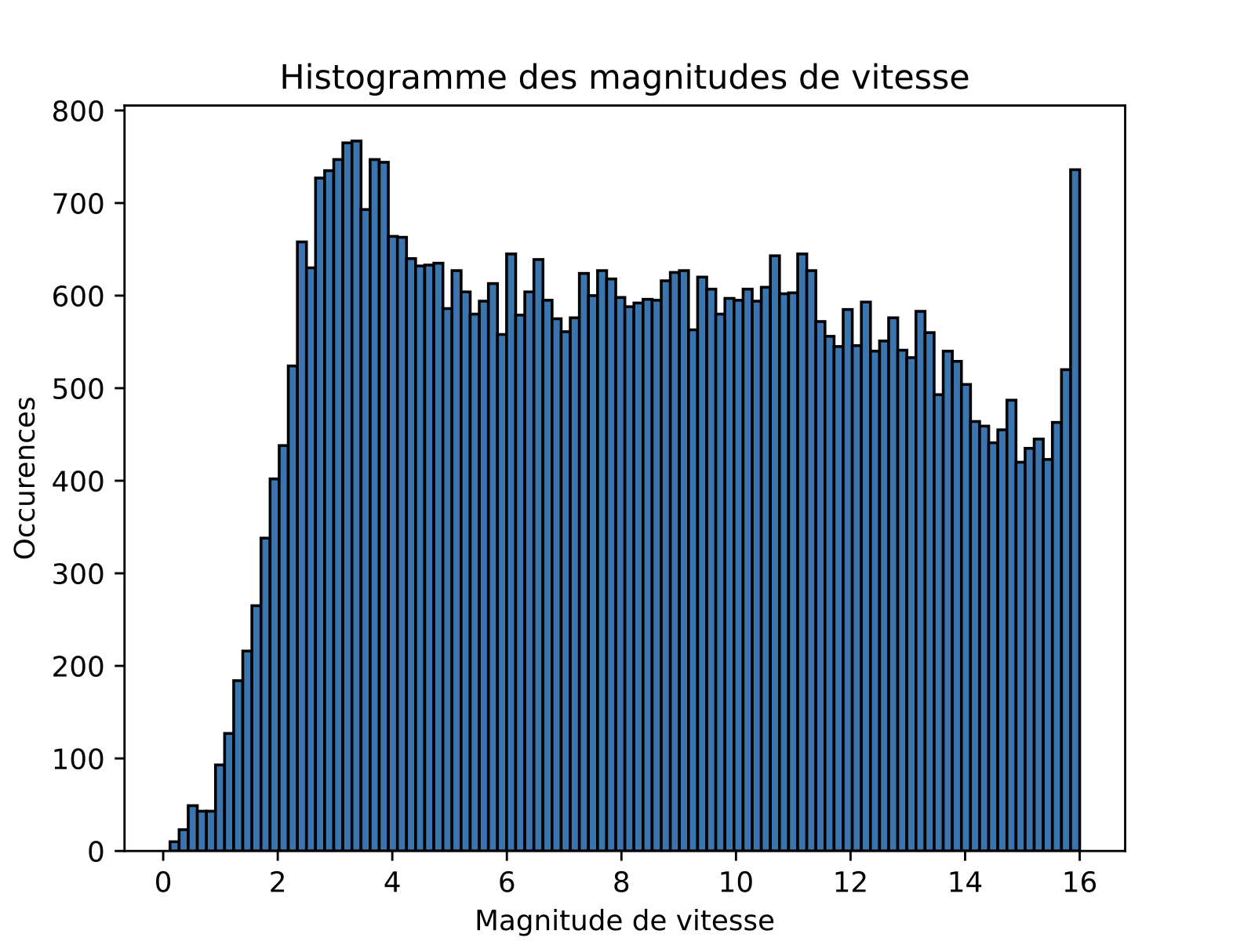
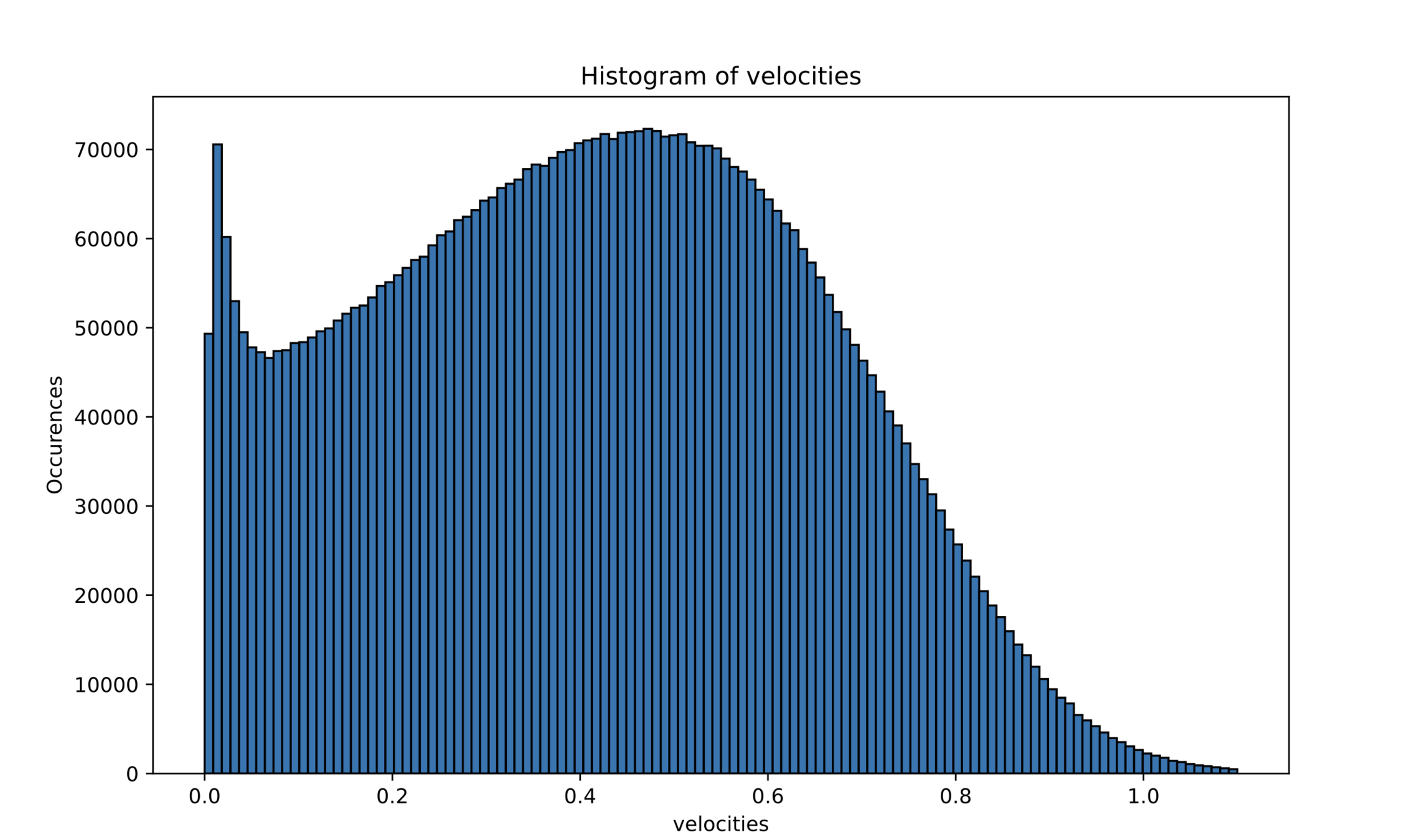
Experimental data:
Simulation:
Sim 2 : smaller \(\nu_{\text{cruise}}\)
Reference simulation
Sim 3 : smaller \(\nu_{\text{cruise}}\) and bigger steering force
Quantitative properties
Two-phase flow?
Simulated flow
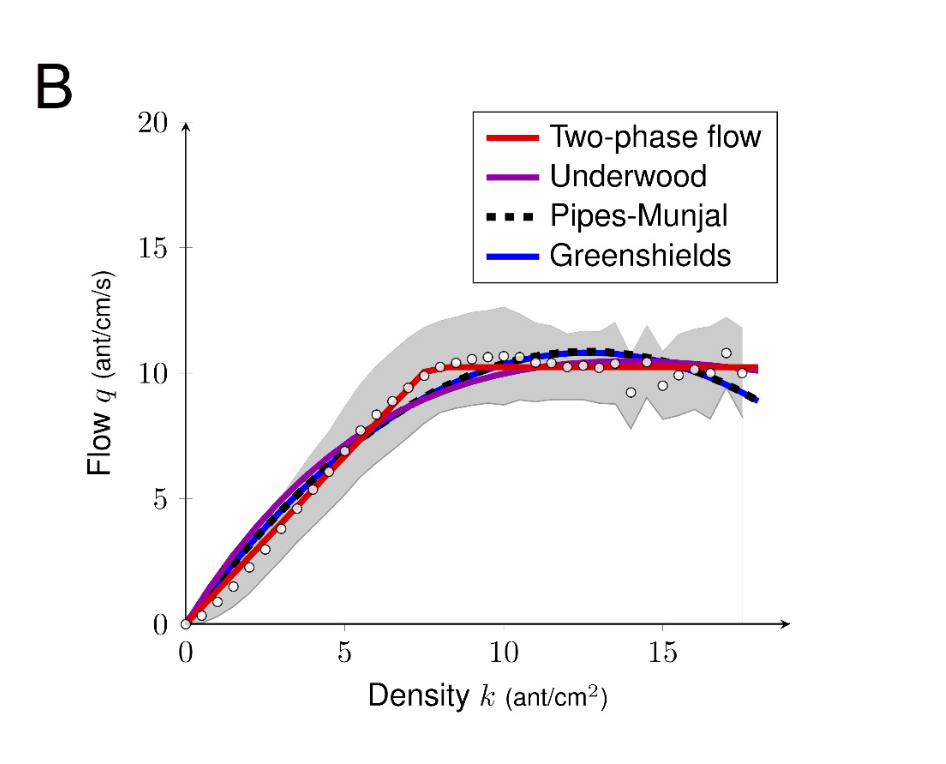
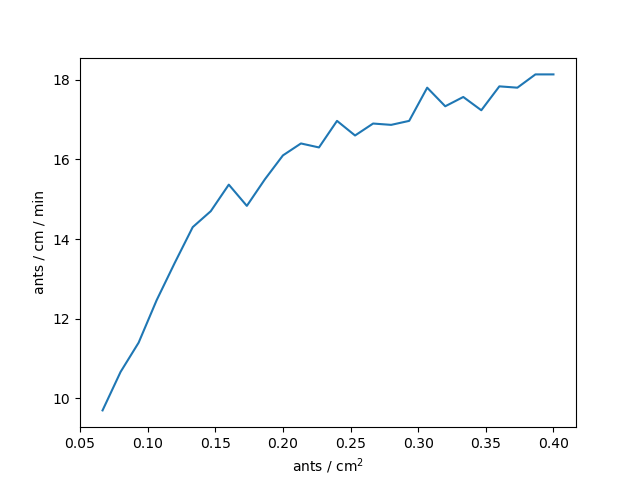
Experimental flow
(Experimental investigation of ant traffic
under crowded conditions)
* En fait la fourmi aime le bord. Suivi de bord "thygmotactisme"
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thigmotactisme
Seul à 5, 10 mm, on ne voyait pas trop le bord. A 20 mm, on n'a jamais réussi à avoir un flux suffisant pour occuper tout le pont.
* Elle aime bien l'idée d'une vitesse de croisière. Peu de variabilité individuelle.
* Champ visuel plus large (un peu plus de 180°). (différent du cône de la phéromone qui est plutôt de 60°)
Les fourmis "oscillent" --> osmothropotaxie
* Faible flux: interaction douce, attraction (elles vont l'une vers l'autre, les deux modifient leurs trajectoires) [attraction plutôt 2 fourmis]
Fort traffic: interaction non choisie, contact, arrêt brusque (il y en a une qui finit par se pousser)
Finteract: répulsion que quand elles sont vraiment proches, attraction à une longueur de 2 fourmis
--> La force d'interaction entre fourmis du même groupe est à revoir...
* Analyse spatiale du flux
That would bring some novelty on this data set
"Ces flux bidirectionnels qui se rencontrent, c'est assez rare: fourmis et piétons"
Quel est le modèle minimal qui donne le même résultat
Dirk Helbing Mehdi Moussaid
http://www.mehdimoussaid.com/laRecherche0311.pdf
https://www.complexity-explorables.org/explorables/the-walking-head/
Fouloscopie
Notes réu Tony
1 - Gestion des murs
Les murs seraient plutôt attractifs que répulsifs, avec une no-flux BC (projection de l'orientation). cf thigmotactisme
2 - Champ visuel
- le cône est bien adapté aux mouvements de détection avec antennes (osmotropotaxie)
- le champ visuel est très large mais très court et très flou
d_ref,same ~ 2 longueurs de fourmi
d_ref,other ~ 3 longueurs de fourmi
3 - Types de contacts
Choisis (attraction puis freinage smooth) ou non choisis (freinage brusque). À voir si on l’inclut dans le modèle.
4 - Analyse du modèle et utilité
Biologistes intéressés par l’analyse spatiale du flux / à voir si l’on peut trouver une sorte de loi sur les données, et comparer avec les simulations.
—> comprendre l’organisation spatiale.
Notes réu Thomas
Model simplification / compactification
1. Self-propulsion
\(\nu > 0\) strength of the force
\(\xi > 0\) target velocity magnitude
3. Interaction
2. Drive
drives to the right if \(g_i = 1\)
drives to the left if \(g_i = -1\)
lots of redundancy
Goal: model
Model
We take inspiration from the previous model to built a simpler and more precise one
Model
constant
cruising
constant
drive
not constant
braking
not constant
attraction and steering
constant
noise
Model
constant
cruising
constant
drive
not constant
braking
not constant
attraction and steering
constant
noise
corresponds to
comes from
(\(\hat{\Theta}_i\) part)
(\(\hat{\Theta}^\perp_i\) part)
Expression of \(\nu_b\)
Cruising and braking
pilot the range of interaction
pilots the window of braking
\(\alpha \sim 2 \implies\) term negligible when \(|X_j - X_i|\gtrsim 3 \, l_{\rm b} \)
\(\alpha \sim 3 \implies\) term negligible when \(|X_j - X_i|\gtrsim 2 \, l_{\rm b} \)
Expression of \(A\) and \(B\)
Attraction and steering
- the more aligned, the stronger the steer
- the more perpendicular, the stronger the attraction
- linear decrease of the strength of the steer
- linear decrease of the strength of the attraction
Equation in orientation
Attraction, steering and drive
Observed use of each term
drive
blend lines
make more lines /
more collisions
less lines head-to-back
less lines head-to-back
faster to get out
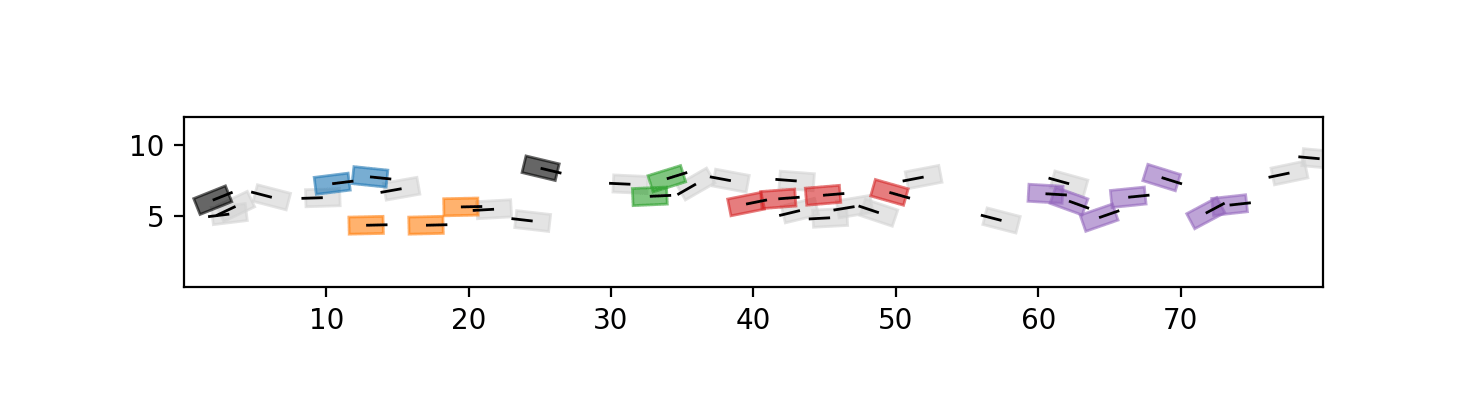
- closeness
- following
Lane detection
- Group by group (right and left)
- Sort agents by their \(x\)-position : \((i_1, i_2, \dots, i_N)\)
- Local criterion: \(i_{m}\) follows \(i_{n}\) if \(m \leqslant n\), \(\left|X_j - X_i \right| \leqslant l_1\) and \[\left( 1 - \cos \left(\theta_i - \varphi_{ij} \right) \right) \left|X_j - X_i \right|^\beta \leqslant \varepsilon \, l_1^\beta,\]
- \(\varepsilon > 0\), \(l_1 > l_0 > 0\) and \(\beta = \frac{-\log \varepsilon}{\log \frac{l_1}{l_0}}\)
- if \(i_m\) follows \(i_{n_1}, i_{n_2},\dots, i_{n_d}\), we group \(i_{m}\) with \(i_{n_1}, i_{n_2},\dots, i_{n_d}\) and all indices that any \(i_{n_k}\) follows
asks for \(i_m\) to head towards \(i_n\) and to be close to them. The closer, the less alignment is required, until \(|X_j-X_i|\leqslant l_0\) from which alignment no longer plays a a role
reunion fourmis
By Thomas Borsoni
reunion fourmis
- 37



