
Building a Scalable and Reliable Payment System
@timrossinfo
What is a payment system?
A payment system is any system used to settle financial transactions through the transfer of monetary value. This includes the institutions, instruments, people, rules, procedures, standards, and technologies that make its exchange possible https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Payment_system
Why payments are hard
A small mistake can potentially cause significant revenue loss and destroy credibility among users.
We can reduce risk by making sure every cent is accounted for and every state transition explainable.
Can be complex and intimidating to work on.

First paid booking made in Feb 2018
A platform for discovering and booking short nature escapes
Accommodation, adventures and stories
Australia (VIC, NSW), NZ (North Island), US (WA, OR)
Two-sided marketplace
Hosts
Travellers
Storytellers

Architecture

Bookings
Payments
Payouts
Accounting
Tax
Stripe Connect
Managed connected accounts
Platform Stripe account





Separate Stripe instance per country
Booking Workflow
Early Challenges
- Direct charges only
- Stripe only holds funds for 90 days
- Irregular payouts of commission
- Vouchers charged to a company debit card
incurring double fees from Stripe
To solve these issues and enable future growth,
we needed the ability to hold funds
Holding funds allows us to
- Use separate charges and transfers in Stripe
- Redeem vouchers from a holding balance to avoid double Stripe fees
- Create internal vouchers (support, team perks, corporate) and track the liability
- Pay for Storyteller bookings on account (future revenue)
But, we need to know what funds are being held and where
Double-entry accounting
Provides a more accurate and complete view of financial health and growth
Involves recording every transaction twice, once as a credit and once as a debit
The accounting equation
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Dividends + Expenses + Assets
=
Liabilities + Equity + Revenue
Debit (destination)
Credit (source)
DEALER
Debits add to expense and asset accounts, and subtract from liability, revenue and equity balances
Credits subtract from expense and asset balances, and add to liability, revenue and equity accounts
| ACCOUNT TYPE | DEBIT | CREDIT |
|---|---|---|
| Dividends | + | − |
| Expense | + | − |
| Asset | + | − |
| Liability | − | + |
| Equity | − | + |
| Revenue | − | + |
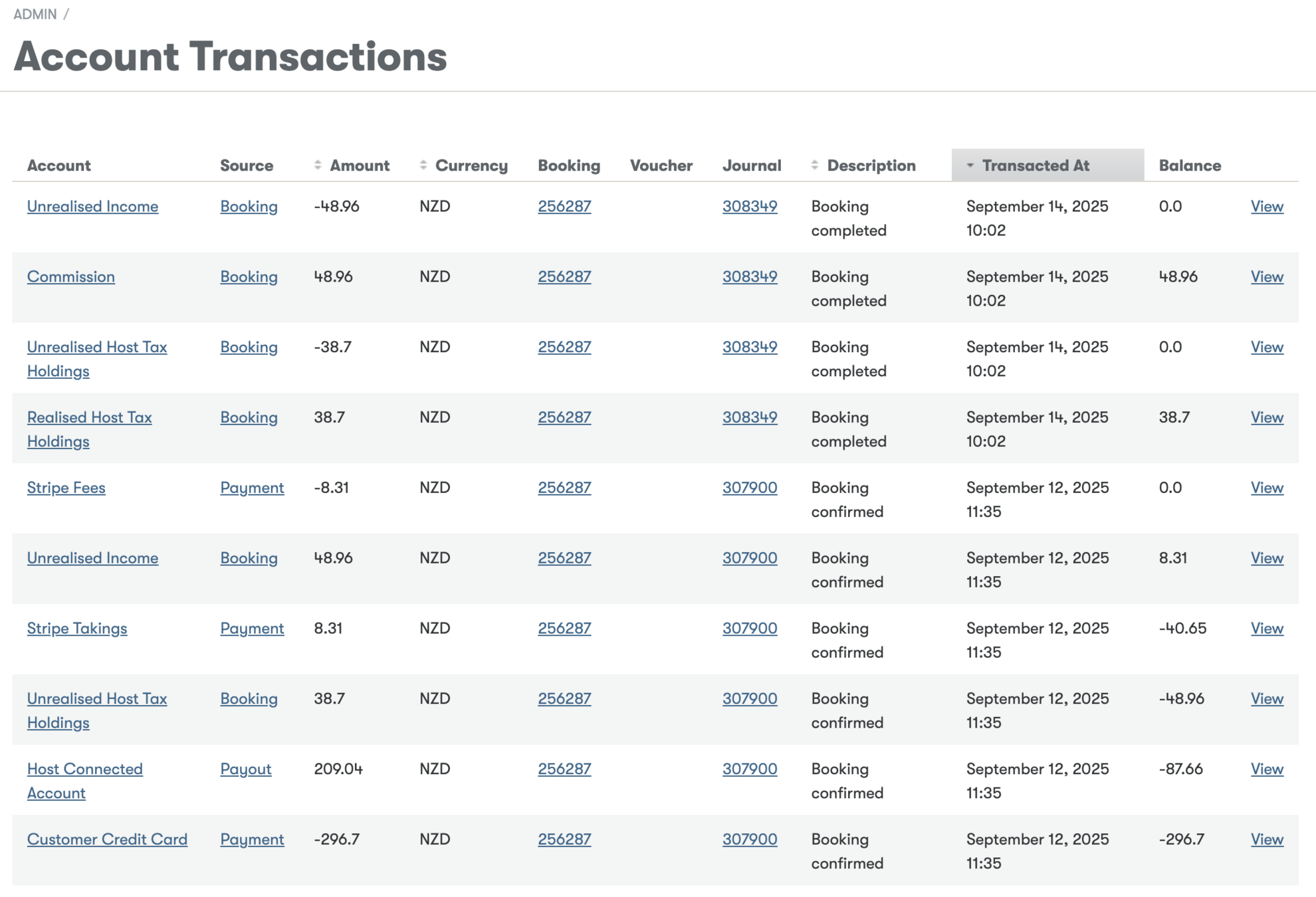
Journal Entries
Record of a business transaction using a double-entry system
Includes transactions for two or more accounts
Debits and credits must balance in each journal entry
Triggered by accounting events
Booking Confirmed
| ACCOUNT | DEBIT | CREDIT |
|---|---|---|
| Customer credit card | 100 | |
| Stripe fees | 5 | |
| Host holdings liability | 90 | |
| Unrealised income | 10 | |
| Stripe takings | 5 |
Accounting::Journal.create!(
narration: 'Booking confirmed',
posted_at: booking.confirmed_at,
booking: booking
) do |journal|
journal.add_line(
account: 'customer_credit_card',
source: payment,
debit: payment.amount
)
journal.add_line(
account: 'host_holdings_liability',
source: payout,
credit: payout.amount
)
journal.add_line(
account: 'unrealised_income',
source: booking,
credit: booking.expected_revenue
)
endBooking Completed
| ACCOUNT | DEBIT | CREDIT |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealised income | 10 | |
| Commission | 10 |
Accounting::Journal.create!(
narration: 'Booking completed',
posted_at: booking.completed_at,
booking: booking
) do |journal|
journal.add_line(
account: 'unrealised_income',
source: booking,
debit: booking.unrealised_income_balance
)
journal.add_line(
account: 'commission',
source: booking,
credit: booking.unrealised_income_balance
)
endmodule Bookings
# Complete a confirmed booking after booking ends.
class Complete
include AfterCommitEverywhere
include Service
def initialize(booking)
@booking = booking
end
def call
booking.transaction do
return if booking.completed?
raise Error, 'Booking cannot be completed' unless booking.confirmed?
booking.complete!
Accounting::Journals::BookingCompleted.call(booking)
end
after_commit do
AnalyticsEvents::TrackBooking.new(booking).completed
end
end
...
end
end
Booking Cancelled
| ACCOUNT | DEBIT | CREDIT |
|---|---|---|
| Customer credit card | 90 | |
| Host holdings liability | 90 | |
| Unrealised income | 10 | |
| Commission | 10 |
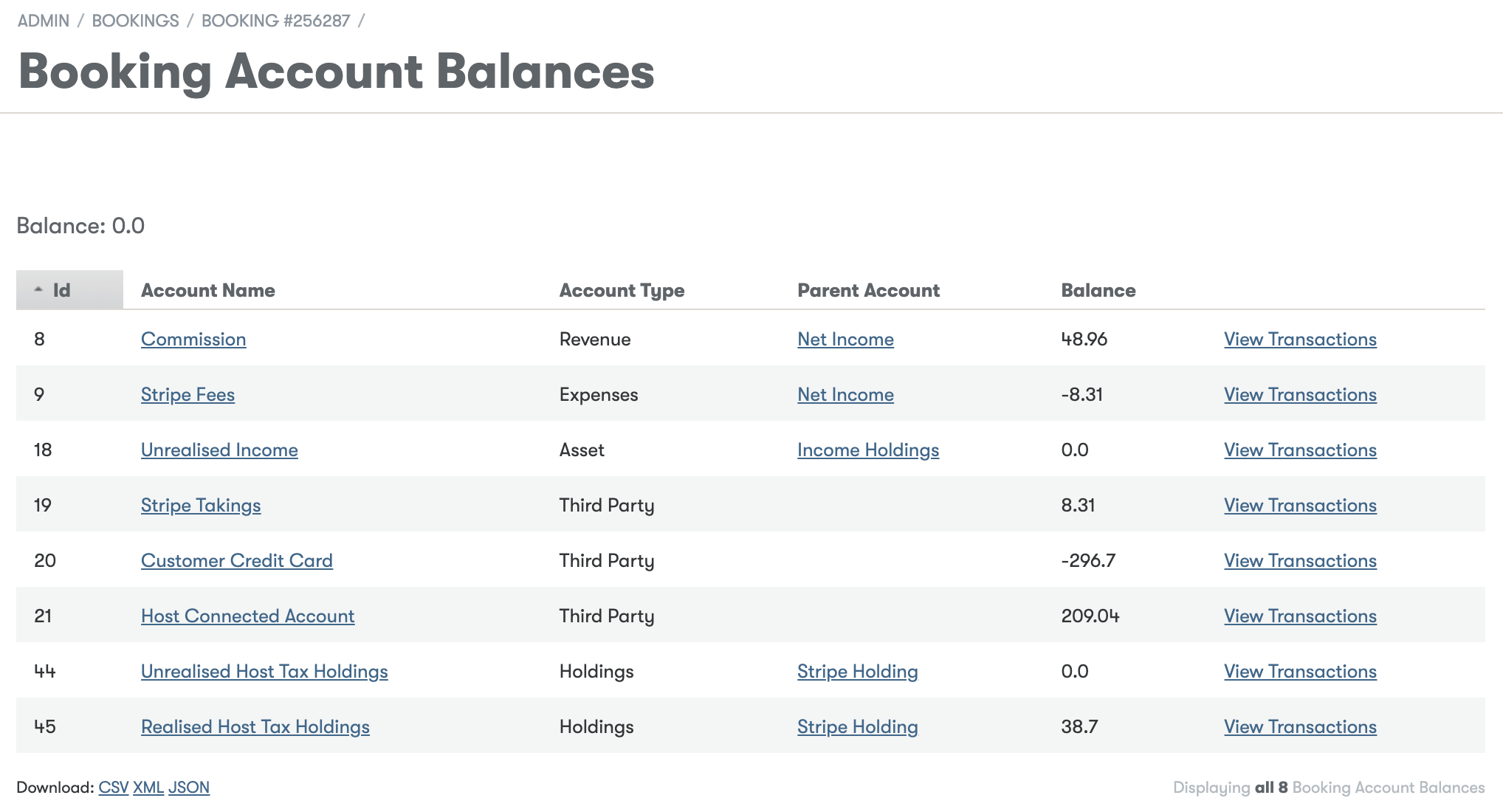
Chart of Accounts
Accounts can belong to a parent and have child accounts
Set an opening balance
The balance of child accounts contribute to the balance of the parent account
Net Income
Commission
Internal
Vouchers
Expired
Vouchers
$100
-$50
$20
$70
Nightly transfer
Multi-currency
Accounting transactions have a currency
Accounting system is partitioned by currency
No currency conversion
Stripe customers are synced across instances
Reliability practices
✅ Single source of truth
🔒 Locks
🔁 Idempotency
📊 Reconciliation and monitoring
Single source of truth
Ensure you can always recreate a computed value
Only use one way to compute a value (e.g. pricing, tax)
Transactional locks
Prevent multiple requests from accessing a database row at the same time, ensuring data integrity and consistency
If an error occurs, the transaction is rolled back, discarding any data changes
module Bookings
# Requests a booking and creates a conversation with the host.
class Request
include AfterCommitEverywhere
include Service
def call
# Use a lock to prevent double requesting the booking.
booking.with_lock do
return if booking.requested?
booking.request!
booking.request_dates!
conversation = find_or_create_conversation
create_message(conversation)
end
# Trigger background jobs after the transaction is committed.
after_commit { Requested.call(booking) }
end
end
end
Advisory locks
Advisory locks are locks provided by the database that you can control via your application
Helps you to manage concurrency while preventing data being rolled back if transaction fails
module Bookings
class Confirm
include Service
def call
# Use a lock to prevent double charging the booking.
booking.with_advisory_lock('confirm') do
return if booking.confirmed?
# Guard against unexpected state.
unless booking.requested?
raise Error, 'Booking cannot be confirmed'
end
# Charge the booking inline so we can provide immediate
# feedback to host.
charge_booking
# If an error occurs while confirming, we don't lose the
# fact the booking was charged.
confirm_booking
end
end
end
end
Idempotency
Guarantees that performing an operation multiple times will yield the same result without side-effects
Use guards to check state before performing an operation
Helps to maintain consistency and integrity if operations are retried
Avoids double-charging
Reconciliation and monitoring
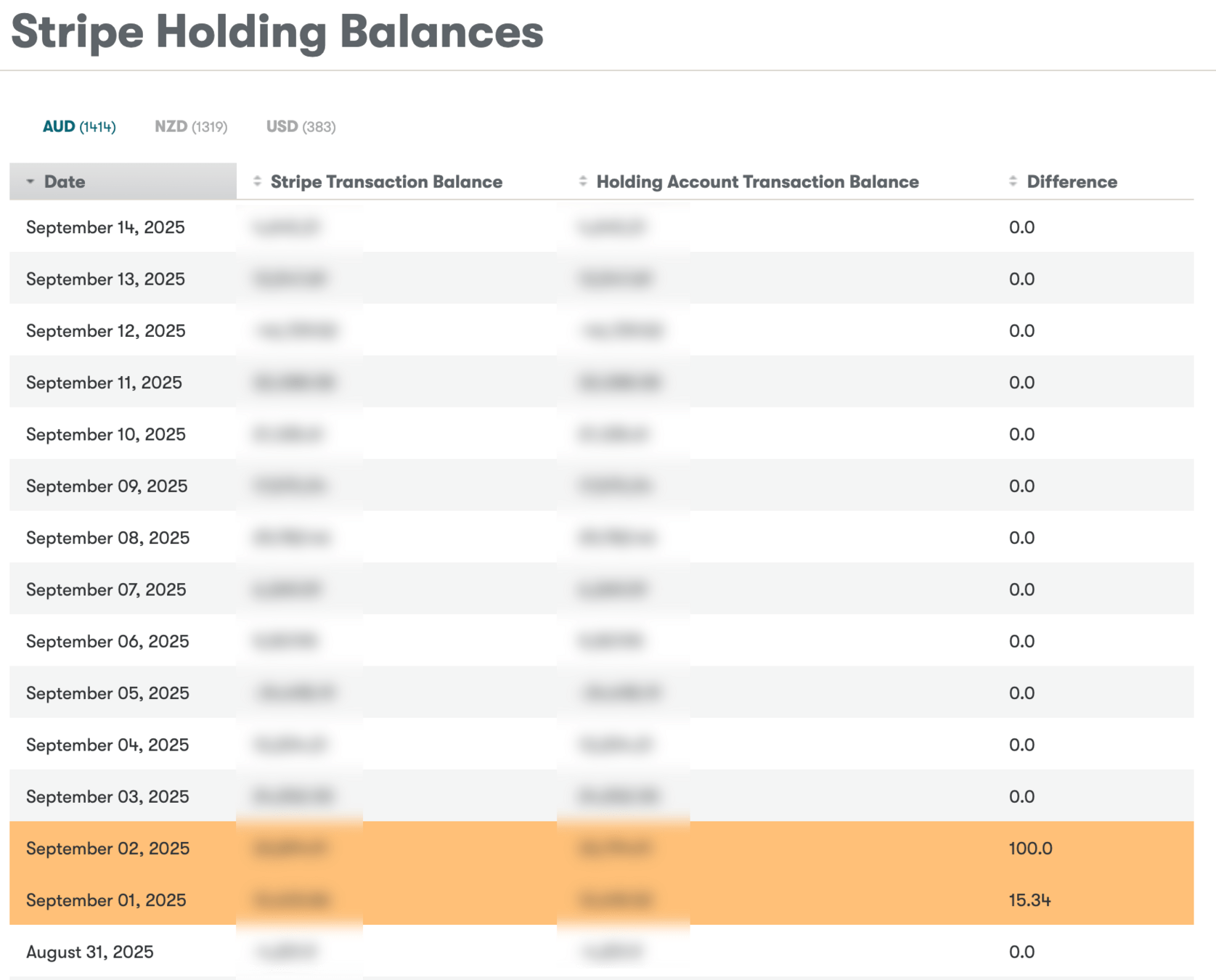
Daily balance reconciliation with Stripe
Accounting dashboard to show any discrepancies between internal records and accounting balance
Accounting balance for each booking
Five takeaways
Double-entry early
Partition by currency
Use idempotency + locks
Reconcile daily
Record everything
Further information
Tracking the Money — Scaling Financial Reporting at Airbnb
https://medium.com/airbnb-engineering/tracking-the-money-scaling-financial-reporting-at-airbnb-6d742b80f040
Engineers Do Not Get To Make Startup Mistakes When They Build Ledgers
https://news.alvaroduran.com/p/engineers-do-not-get-to-make-startup
Designing a Payment System
https://newsletter.pragmaticengineer.com/p/designing-a-payment-system
Building a Scalable and Reliable Payment System
By timrossinfo
Building a Scalable and Reliable Payment System
The goal of this talk is to look back at the role of Javascript in Rails and to look ahead at the choices for integrating JavaScript in Rails 7 and beyond.
- 65



