Ancient Rome
Unit 11
What do you know about Ancient Rome?
GLADIATORS
AQUADUCTS
- the three time periods of Ancient Rome and the main differences between them
- what was important about each period
- why each period ended
- Basic characteristics of the Roman society.
We are going to learn :


Etruscans - in the north
Greeks - colonies in the south
Latins - in the centre
Three main cultures
on the Italian Pennisula
Etruscans
Conquered ROME in 6th Century
Ruled for 250 years.
The Roman World
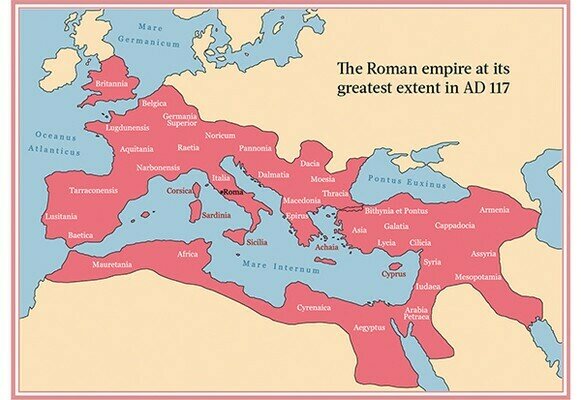
Mare Nostrum

There were seven hills around the Tiber River.
Etruscans, people from the north of the Italian Península
united the seven hills
into one city
and declared
themselves king.
Monarchy 753-509BC
The Monarchy 735-509BC
The king chosen by the richest people
Elected for life
King controlled
religious ceremonies,
the army
and the justice



The Romans defeated the Etruscans
and changed the Monarchy to Republic
The Republic
509-27 BC
What does REPUBLIC mean to you?
Is there only ONE person who rules????
Do the people participate in the government?
Which people? All the people? Some people? Who participates?

Three institutions:
Assemblies /comitias - a place where citizens
(patricians & plebeians) VOTED for laws.
Magistrates - made political decisions AND created laws.
Consuls - There were 2 consuls,
the most powerful politicians,
elected for one year.
Senate - A group of senators
Gave advice to the consuls
(retired magistrates)
Government in the REPUBLIC
Roman Society
Patricians - important, wealthy people in society.
Only people who had political power.



Plebeians - craftsmen, merchants peasants
Slaves -
Prisoners of war
owned by the masters

Roman Women - male guardians, no political rights,
take care of children and house, work in the fields or shops

Can defend their rights in the Senate in TRIBUNES
WOMEN had no political rights and
couldn't vote
Non-Citizens
Citizens
Roman Society
Tribune of the Plebians

5th Century
Fought to attend the Senate
Became magistrates and senators

500 BC - 250 BC - Italian Peninsula
Expansion of the REPUBLIC
Italian Peninsula
3rd and 2nd Centuries BC
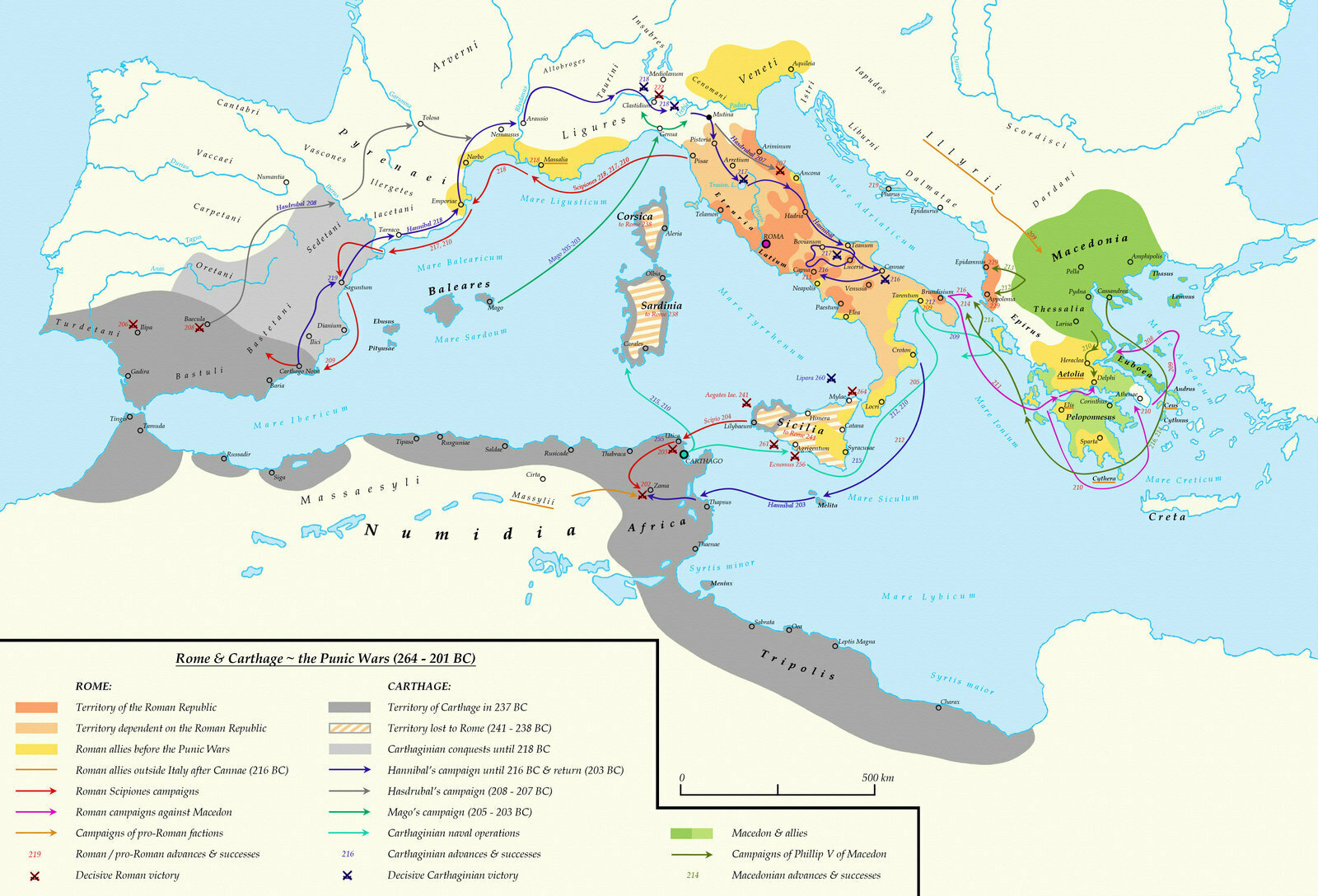
Punic Wars (264-146 BC) between Rome and Carthage

2nd and 1st Centuries
Eastern Mediterranean

Army expanded the Roman territory
organised in LEGIONS that formed LEGIONARIES (soldiers)
Roman Legions
Conquered land and people.
Cities were destroyed
people who resisted became slaves

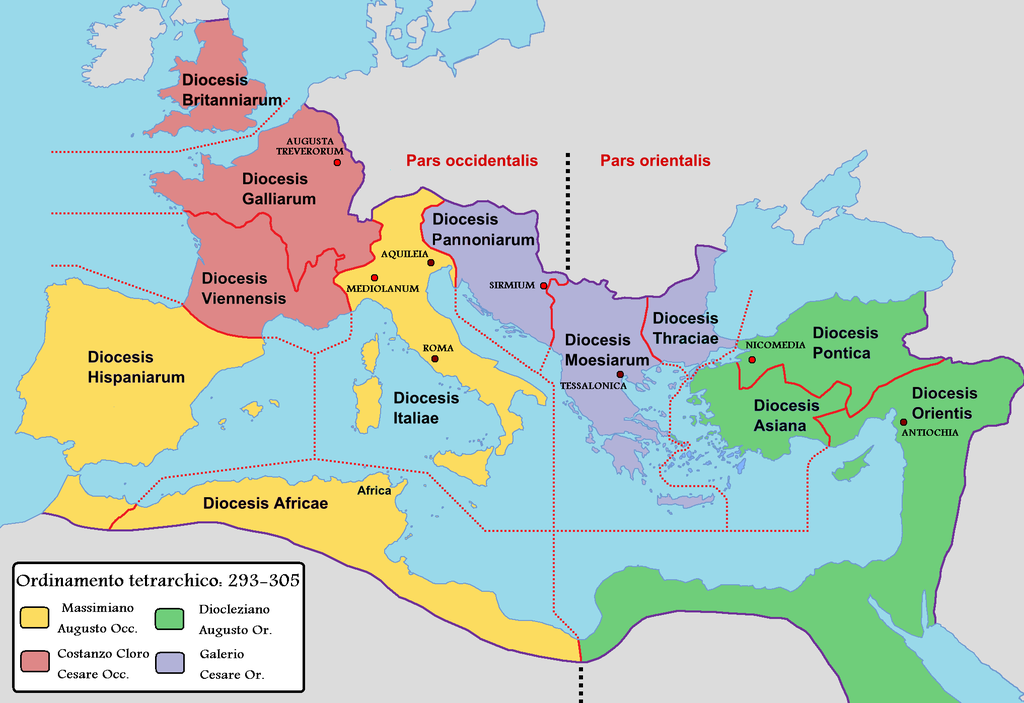
The conquered territories organised in PROVINCES
Each province ruled be GOVERNOR
Expansion of the Republic
Economy - Improved
- Trade increased = more products and slaves
- Collected more taxes from conquered territories
Politics - Created PROVINCES.
- Each province had a GOVERNOR
Society - Inequality between people
- Only a few people had most of the wealth
Decline of the Republic
1st Century BCE - 27 BC
PROBLEMS
Large territories - difficult to control
Generals became more important
Solution ????
Inequality between rich and poor
Corruption
Social unrest
Internal conflicts
Fighting between different provinces and Rome = Civil Wars

WHY??????
JULIUS CAESAR A consul and general.
The most famous and victorious.

Stopped the invasion
of Roman territories in
France and Belgium
by Germanic tribes
Julius Caesar
declared himself
PERPETUAL DICTATOR.
He wanted to change Rome
from a REPUBLIC
to
an EMPIRE

DO YOU THINK THE SENATE
WAS HAPPY????

He was killed by 60 senators in the Senate
on the Ides (15) of March 44BC
Subtitle
Roman Empire
27BC - 476AD
Many people and politicians
liked and supported Caesar
a CIVIL WAR started
Octavian (Caesar's nephew)
won the war
He started the EMPIRE
and became
the 1st EMPEROR


Octavian
changed his name to
which means
CHOSEN BY THE GODS
As EMPEROR
he controlled the army
government and
was the highest
religious leader
AUGUSTUS

Romanisation
UNIFIED new territories with
Roman laws/customs,
religion and language (Latin)
1st and 2nd Centuries
- Conquered new lands
- Territories well defended
- Social rest
PAX ROMANA
PAX ROMANA
1st and 2nd Centuries
Important buildings were built

Puga, Croatia
PAX ROMANA
1st and 2nd Centuries

Bath, England
PAX ROMANA
1st and 2nd Centuries
Segovia, Spain

Romanisation
Conquered lands/people adopted
LAWS
TRADITIONS/
RELIGION
LANGUAGE - Latin



Crisis in the Empire
3rd Century
Internal conflict
- Bad Emperors caused ANARCHY
External conflict
Germanic tribes from
the north,
Persians from the east, and pirates from coast of Africa
attacked cities in the empire
There were revolts and invasions
so
Cities unsafe
People left cities
and
went to the countryside
Trade decreased
Economic crisis

TRADE COLLASPED
Cities were dangerous
People left cities
and moved to the country
and
RURALISATION

All MEN living in Roman territory became CITIZENS
Except for slaves
- This gave them political representation
Roman Society
Non-Citizens
Roman Society

WOMEN had no political rights and
couldn't vote
Wealth landowners
Text
Merchants, craftsmen, and peasants
Text
Prisoners of war
Not free
A Roman Teenager
Roman houses

Wealthy Romans lived here.
One floor
Centered around a courtyard
Had paintings on the walls
Mosaics on the floor
Domus

Insula
Block of small apartments
Bad construction - brick and wood
No running water
Dangerous in fires
Poor people lived there
Roman Houses

Roman Houses
A large farm
One family lived in the big house
Slaves and peasants worked on the farm
Villas
Roman Cities
Virtual Tour of ANCIENT ROME


Roman Baths
Roman culture & religion
The Empire Recovers
4th Century
CONSTANTINE
Two important Emperors
THEODOSIUS



- Moved the capital from Rome to Constantinople
- Tolerated Christianity
In 313 AD
- Unified territories
Emperor CONSTANTINE

Western Roman Empire couldn't defend itself against
Germanic tribe invasions
Emperor
THEODOSIUS
Declared CHRISTIANITY
the official religion
in Roman Empire.
In 380 AD


Eastern Empire lasted another 1000 years
It was called Byzantine Empire
In 395, after Theodosius died
the empire was divided in two
Western and Eastern Roman Empire
Fall of the Roman Empire
In 476AD
Title Text
Ancient Rome 2023-34
By txecor
Ancient Rome 2023-34
- 373


