Medieval Cities
in Europe
Unit 3
11th to 14th Century
Trade increased
between European Kingdoms, Muslim World,
Byzantine Empire
and Far East
Agriculture improved
new techniques were introduced
and
population grew
a time of growth and change
High Middle Ages
11th and 13th Century
Beginning of Banking
appeared to manage
money in trade
Improvements in Agriculture
Better tools and techniques = More food
Less famine = healthier population
More food = Less famine
Healthier population = Less deaths, more births
Population grew from 42 million to 73 million in 300 hundred years

Better tools = more production, less work

Roman plough
10th Century
Mouldboard/Heavy plough
- 12th Century
Which was more efficient??????
Better Tools
Improvements Agricultural Techniques
Irrigation

New methods from Muslim territories

= More food
= more people
Three Year Crop Rotation
Better methods ...
Did the work for 40 people

Windmills and Watermills

Increase in Trade
and
Why????
Population increased ...
people left fiefs/villages and moved to cities ...
trade between
cities and the kingdoms/empires increased
less manual work in agriculture ...
so
and
Trade Routes

Mediterranean route
Joined
SPANISH and ITALIAN cities to
ISLAMIC and BYZANTINE ports
Important Trade Routes

Atlantic and Baltic route
Joined
PORTUGUESE and CANTABRIAN
with
FLEMISH,
GERMAN and RUSSIAN ports
Important Trade Routes
What was traded?
From the West to East
-
wool/leather
-
grains (wheat,oats)
-
salt/wine
-
wood
-
weapons/iron
From the East to West
-
spices/perfume
-
honey
-
porcelain
-
cotton/cloth/furs/silk
-
rugs
-
dyes

Merchants bought and sold in TRADE FAIRS
Creation of Banking
Gave credit and changed money
Bills of exchange
Made buying
and selling easier
CREDIT
MONEY CHANGER
Lent money with interest
exchanged different coins
with different values


BILLS OF EXCHANGE
Paper/bills replaced coins

GUILDS
and
ARTISANS
13th Century
people in cities
needed more products


Different artisans formed guilds
Ironsmith
Hatmaker
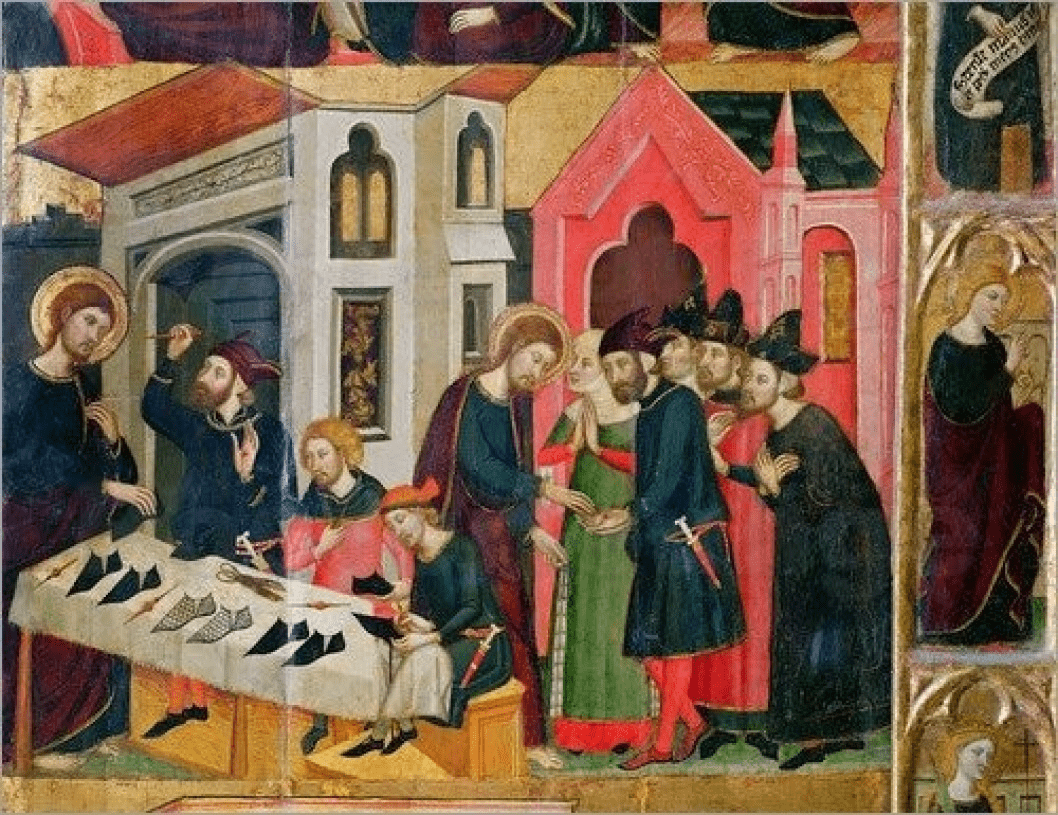
Shoemaker
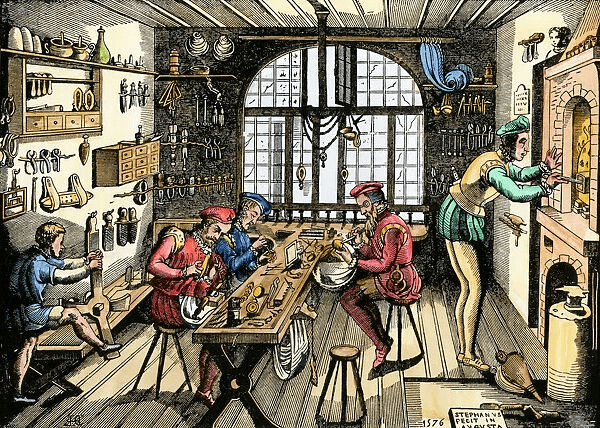
Goldsmith
An association or group of artisans.
Only the qualified artisans in a guild
could practise a trade
- wages/money earned
- how many hours artisans worked
- checked the quality
- prices of goods
Support
What was a guild?
- Helped families whose father had died
- created hospitals
Benefits/Aid

Artisans
made and sold
their products
in workshops
where they lived
The same artisans in a guild worked on the same street
Calle Zapateria
Calle Tejeria
Calle Caldereria
The role of an Artisan
made OBJECTS from
METAL WOOD CERAMIC
LEATHER COTTON
became important
because society changed from...
tools
weapons
furniture
bowls, cups
a self-sufficient society (rural)
a commercial society (urban)
clothes
shoes
to
MASTER CRAFTSMAN
Owned and lived with family in the workshop
Apprentices lived and learned trade
Journeymen worked for Master Craftsman
Three categories of a ARTISAN

How to become a MASTER CRAFTSMAN
1) AN APPRENTICE
Young teenaged boy
learned the trade
Didn't earn wages
Lived and worked
in a Master Craftsman's
Workshop

next

2) JOURNEYMAN
Skilled artisan worked for master craftsmen
Recieved wages
Could move from workshop to workshop
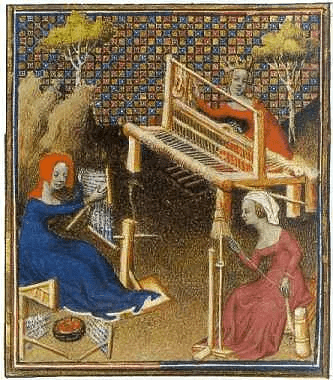
Women often made clothes in workshops

Spinner, weavers
and carpenters

Let´s watch the video
and answer these questions...
What was a guild?
What benefits did craftsman have
when they belonged to a guild?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vnQlHeee9Dw&feature=share&list=PL924AC0143DD06D38&index=38
A better life for peasants who
could work and move freely
Merchants wanted the protection of the walled cities
Medieval Cities grew because...
More people and less work in villages/fiefs
Cities were located
near the coast
an
important river
or
Genoa, Italy
Old cities expanded and
new cities started

Bruges, Low Countries

Each city received a
CHARTER or FUEROS
Self-government
with rights and privileges
(freedom from feudal lords)

Cities were the centre of
RELIGIOUS, POLITICAL and
ECONOMIC activity

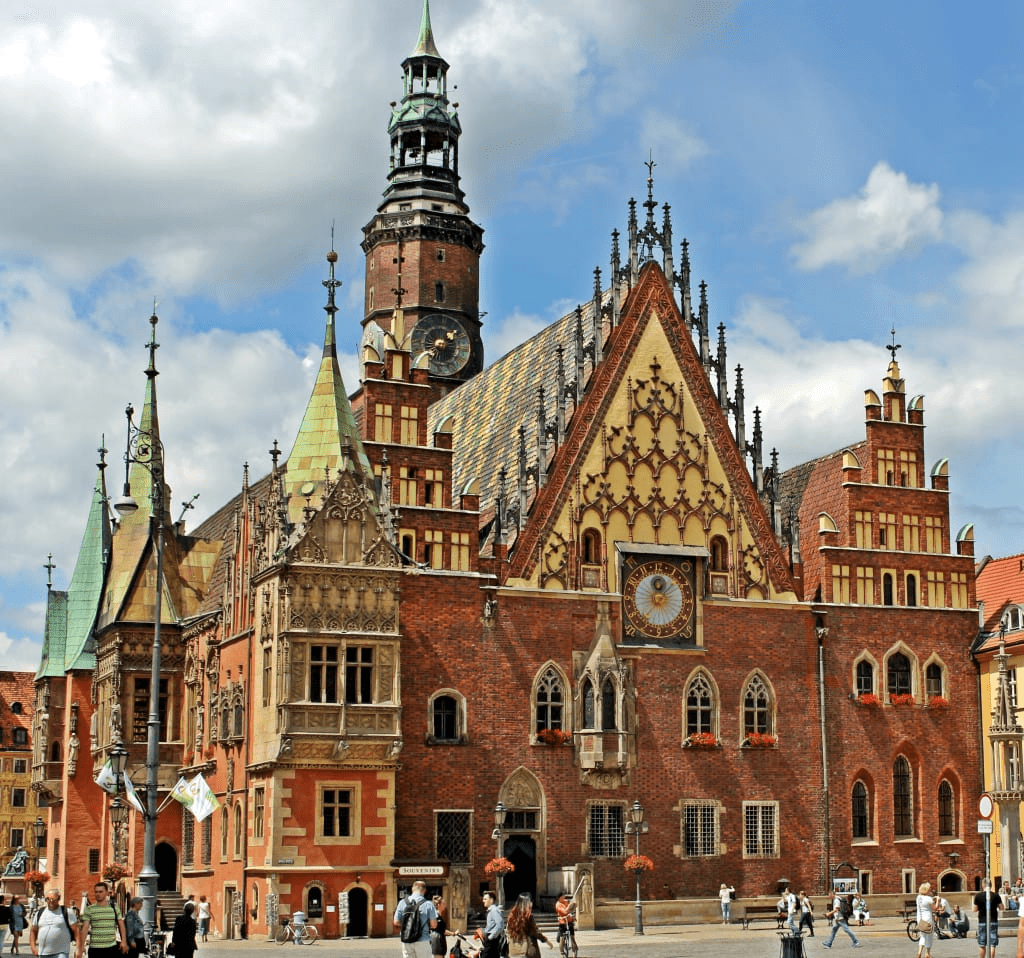
City Halls
Wealthy families
controlled
the city hall
...defended the city, collected taxes
and maintained
of the city walls
King /
Pope
Clergy / Nobility
Rich artisans, merchants
and bankers
Merchants, craftsmen,
shopkeepers,
house servants and students
Peasants (no work) begged or stole
New classes that appeared during the 12th Century
Bourgeoisie
New social structure
Urban Society
Elite
Christians - majority
Multicultural cities
Muslims -usually craftsmen
only found in Iberian Peninsula
lived in separately outside
city walls.
Jews - usually merchants, bankers
lived in together in separate parts of cities called 'ghettoes'
In Spain lived in JUDERIAS

Tudela
Segovia

Medieval Cities
Pamplona



Walls the protected the city
Moat protected against invasions
Gate/door
closed at night


CITY HALL
COVERED MARKET
CATHEDRALS


Organised in neighbourhoods
Narrow streets, crowded, dirty and unhealthy
Market square - farmers and merchants sold products
and festivals / executions
Cities were dirty,crowded unsafe.
11th-13th Century Renaissance
Education
Cathedral schools
controlled by the bishop
taught religion
Urban/municipal schools
educate weathly people living
in cities
taught reading, writing, maths ...
First universities
were built to teach
Liberal Arts, Medicine, Law
and Theology


Find the oldest universities in Europe
Architecture

Explosion of public buildings
Cathedral, churches, market place
and city hall
Palaces decorated built by weathly nobles and merchants


Art
Paintings and sculptures
were commissioned
by private people
Literature
New literary styles appeared

Greek philosophers
rediscovered

Most people couldn't read so ...
MINSTRELS - travelled an played music and
recited poetry
City charters

Gave cities charters/fueros
= privileges and autonomy
In exchange for
economic support = taxes
Rise of the Monarch
Economic growth
Growth of cities
Collected more taxes from cities
Created private armies
Less dependence on nobility

Rise of the Monarchy
BOURGEOISIE became more important
than the NOBILIT Y
Supported the kings
Kings gave their cities CHARTERS
Rise of the Monarchy

Studied Law
Royal adminstration - professional
restored Roman Law
Growth of Universities
Late Middle Ages
Agriculture
Economic - Social Tensions
bad weather, lost crops
unfertile soil
famine
Peasants forced to fight in wars
rebelled
City dwellers forced to pay high taxes
rioted
Time of Crisis
1350-1400's
Demographic
Black Plague
killed 1/3 of the population
Black Death 1347 - 1351
What were the symptoms of the Black Plague?
Explain where it came from and why it killed so many people
How many people died?
Copy of MEDIEVAL CITIES IN EUROPE
By txecor
Copy of MEDIEVAL CITIES IN EUROPE
UNIT 3
- 672


