Political and Economic
Changes in Europe
UNIT 8
Europe
12th-13th Century
Feudalism began to disappear
Cities became more populated,
dirty and crowded
Bubonic Plague
or
the Black Death
These are the clothes the
doctors wore
who treated the sick

click to watch video

From 1400’s to 1500’s population began to increase
In 16th Century the population had almost recuperated.

Banking system improved.
Financial transactions easier.
Lent money
Found new ways to pay borrowed money.
Cities with artisans and trade
became
the centre of economic power.
Most Important cities were
VENICE, FLORENCE, ANTWERP,
LISBON, SEVILLE
and LONDON.
Changes in Society
Three Estates
Nobles and clergy
Merchants,craftsman, shopkeepers,
farmers, domestic help
and
peasants
but with some changes...
Nobles and clergy
Privileged estates
Didn’t pay taxes
Most important positions


Bourgeoisie
Rich and powerful
merchants and bankers.
Increased in number and power.
Often married into nobility.
Had important connections
with the monarchy.
Lent them money
and received privileges in exchange.

Peasants
Bad conditions, poor but free from serfdom
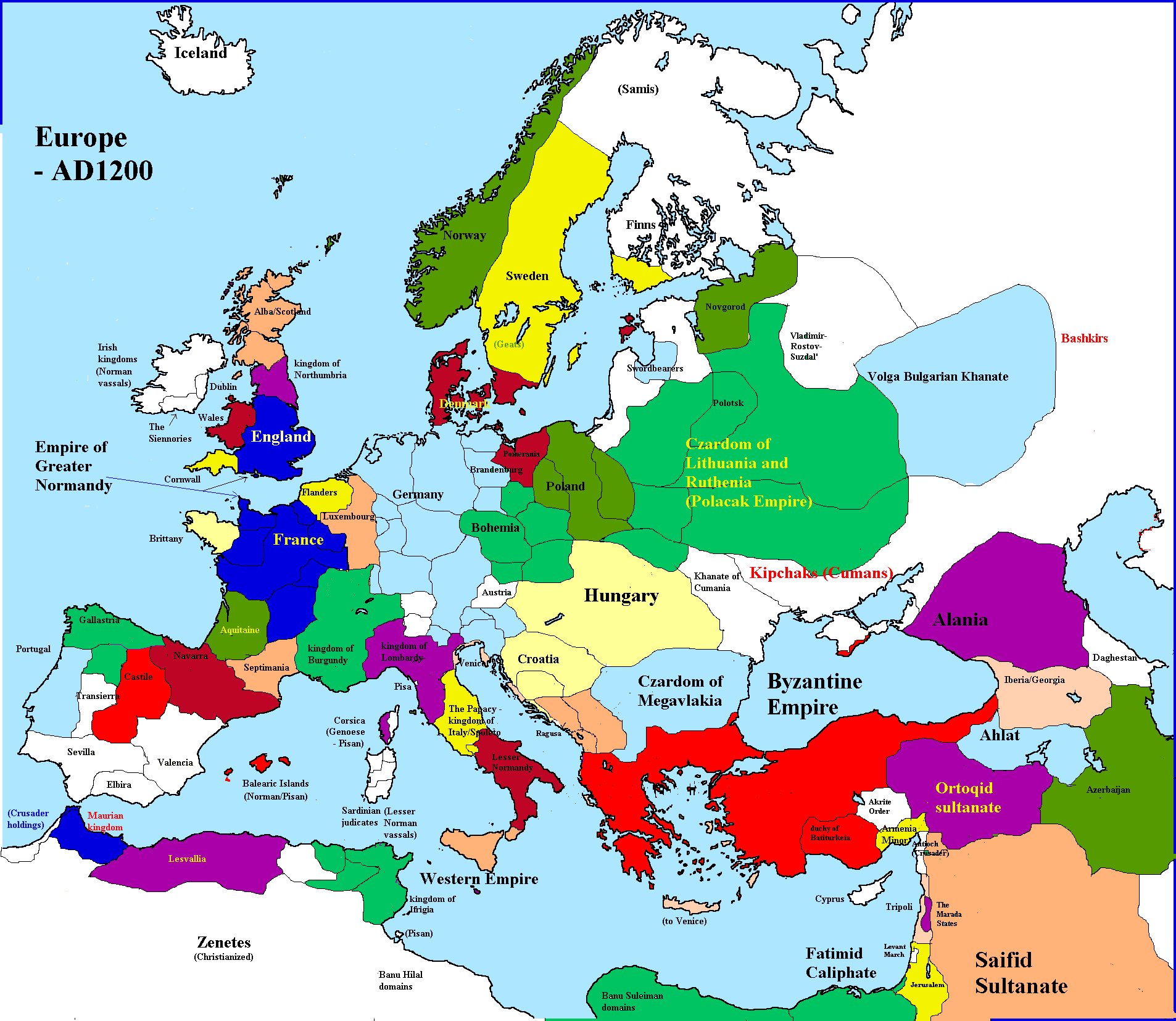
In the 11th and 12th Century
Authoritarian Monarchies
Europe was divided
into small states.
In the 15th Century
Great kingdoms formed
through marriage alliances or conquest.
Beginning of present day countries.
Most of these kingdoms were Authoritarian.



England
France
Russia
FRANCE was united after the 100 Years War (between France and England)
The country was united
from the reign of
Charles VII to Francis I.


ENGLAND
Civil war during the 15th century
(The War of the Roses between York and Lancaster)
made the monarch weak.
The Tudors won and Henry VIII reigned in the 16th Century

RUSSIA Ivan the Great unified the country and annexed territories (Ukraine, Lithuania and north of Moscow)
Became Czar/Emperor of Russia.

The Catholic Monarchs
unified
the Iberian kingdoms
except Portugal.
Text
SPAIN
Authoritarian Monarchy
- Reduced the power of the NOBILITY and the CHURCH.
- Created a centralized government
- Built a private army
- Raised taxes to pay for army.
- Created diplomatic system with Ambassadors
increased their power by...

Early 1400’s
Five main kingdoms :
CROWN OF CASTILE,
CROWN OF ARAGÓN,
KINGDOM OF NAVARRA (1512),
KINGDOM OF PORTUGAL (1385/1580)
and
NASRID KINGDOM OF GRANADA (1492)
Spanish Kingdoms

Foreign Policies
From1492 to 1512
- Annexed Kingdom of Granada
- Began to conquest America
- Conquered cities such as Melilla
- Annexed Kingdom of Naples
- Oran – North Africa
- Canary Islands and Tripoli
1512 – Annexed Kingdom of Navarra
While Henry IV was king,
there was a civil war
between...
THE CROWN OF CASTILE

...the supporters of his daughter,
Joanna La Beltraneja (believed to be illegitimate)
and
supporters his half-sister Isabella I of Castile (La Catolica).

When Henry IV died
in 1474,
Isabella I
became Queen of Castile

Crown of Aragón
Ferdinand of Antequera
from the
Trastamara Dynasty in Castile
became
king of Aragón.


In 1410,
the King of Aragon,
Martin I
died with no hiers

In 1479 his grandson,
Ferdinand II
became King of Aragon
Trastamara Dynasty (governed Castile)

In 1476 Isabella I of Castile secretly married
her second cousin Ferdinand II.
In 1479, Ferdinand II became King of Aragón.

Isabel and Ferdinand
asked the Pope
to recognize their marriage.
They ruled
Crown of Aragón and the Crown of Castile together.
They were called the Catholic Monarchs.
They governed the two territories,
but each territory kept
its institutions and laws.


Created several institutions
to provide peace and unity
to Castile and Aragón.
The Catholic Monarch
Reyes Católicos
Isabella I of Castile
Ferdinand II of Aragón

1) Holy Brotherhood (Santa Hermandad)
A police force.
to fight thieves and control nobility
Domestic Policies

2) Royal Council – highest law makers
3) Corregidores – represented
the monarches authority in cities
and towns

4)Treasury – collected taxes and took economic privileges away from the nobility
5) Professional Army
permanent and one of the best in Europe.
Religious Unification
In 1478 founded the Tribunal of the Inquisition to find and punish non Catolics
In 1492 Expulsion or conversion of Jews.
Approximately 80,000 people left Spain in a short period of time.
Some converted and stayed – conversos/marranos
In 1512 Mudejars (Spanish Muslims)
whose religious belief was protected
after the annexation of Granada
were also forced to convert or leave.
The converts were called MORISCOs
In 1504 Isabella died,
JOANNA the MAD (Juana la Loca)
her daughter
was heir to the throne of Castile.
Ferdinand II continue as
King of Aragón.
Joanna the Mad was unable to rule and Ferdinand II ruled
the Crown of Castile in her name.

Dynastic Union

and...
In 1516
Ferdinand II died
Joanna the Mad’s son
Charles I
(also called Charles V)
unified and controlled
Crown of Castile
and
Crown of Aragón.
Joanna the Mad
married
Philip the Handsome from the
Hapsburg Dynasty
of Austria.
This was a
marriage alliance
to gain more territories.

POLITICAL AND ECONOMIC CHANGE IN EUROPE
By txecor
POLITICAL AND ECONOMIC CHANGE IN EUROPE
Unit 8
- 2,417


