JavaScript 網頁程式設計
Module 0 背景知識
預備知識
- 基礎的程式識讀 ( Python )
- Chrome
課程大綱
-
Module 1. 測試及除錯工具
-
Module 2. 使用 script 標籤
-
Module 3. 常數和變數宣告
- Module 4. 基本類型
- Module 5. 運算子
- Module 6. String
課程大綱
- Module 7. 取得標籤元素
- Module 8. 流程控制
- Module 9. Object類型
- Module 10. Array類型
- Module 11. JSON
- Module 12. 函式的定義
課程大綱
- Module 13. Scope變數領域
- Module 14. 時間與計時器
- Module 15. 數學物件
- Module 16. window物件
- Module 17. 事件處理
- Module 18. AJAX
Module 1: 測試及除錯工具
Module 1: 測試及除錯工具
1-1: Chrome開發者工具 1-2: Console面板 1-3: Network面板
Javascript 是什麼?
- 原名: LiveScript,因為一開始 Java 很流行,取個相近的名稱
- Chrome 將 Js 效能提高 20幾倍
- 在2008年到2009年的第二次瀏覽器大戰之前,JavaScript引擎僅簡單地被當作能閱讀執行JavaScript原始碼的直譯器。
1-1: Chrome開發者工具
- 在 Chrome 按右鍵 Inspect Element / Inspect
- 在 Chrome 的 Menu 選單 -> View -> Developer -> Developer Tools
1-1: Chrome開發者工具
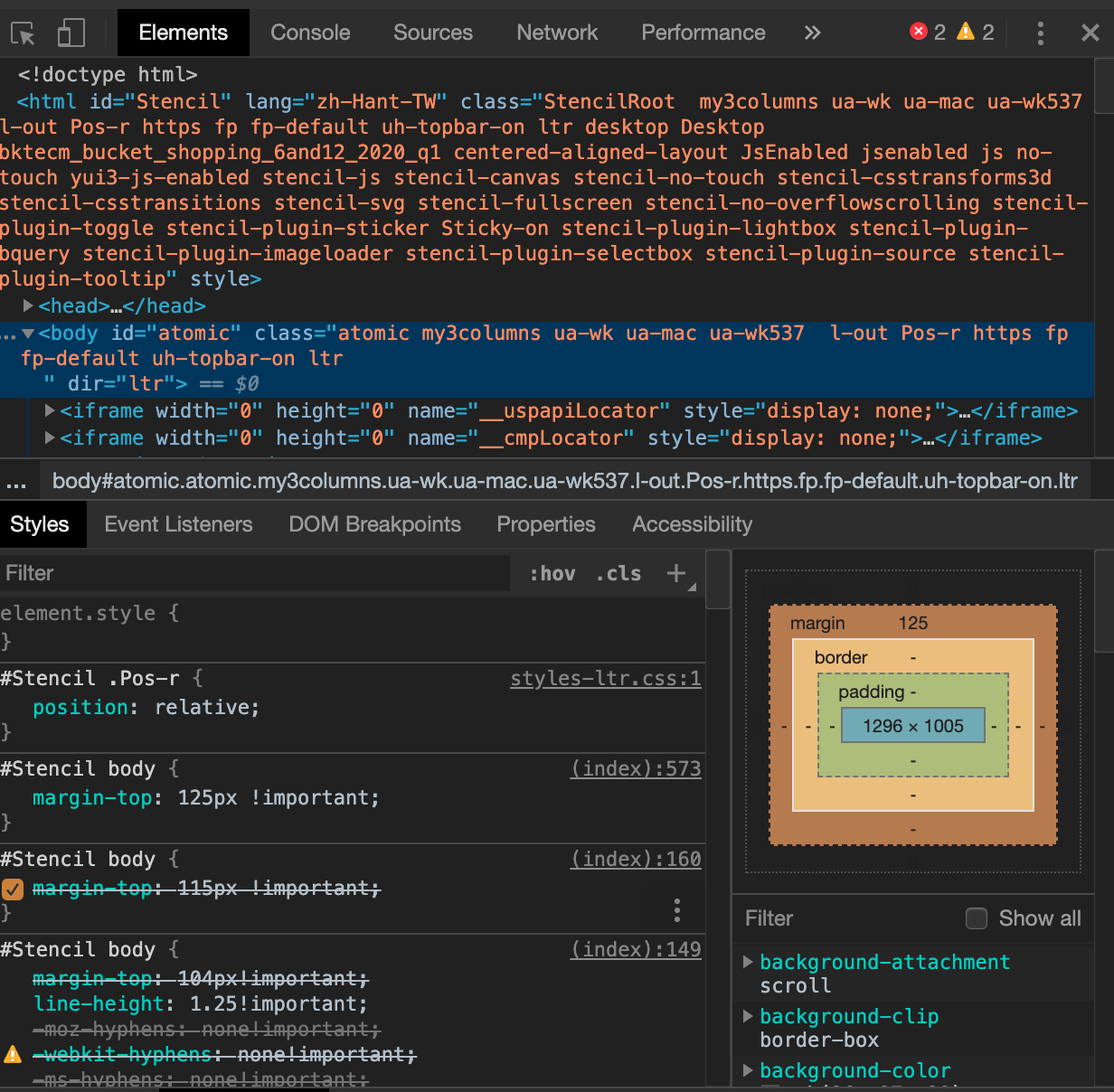
- Elements: 查詢 HTML 網頁原始碼的元素。若手動修改一元素的屬性和樣式,可直觀的看見瀏覽器頁面也相對應改變。
- Console: 顯示開發過程的日誌資訊 ( log ) 與警告。是可與 Js 進行互動的命令列 ( Shell ),Js 除錯時常用。
- Sources: 可見頁面的檔案來處。
-
Network: 自發起頁面請求 ( Request ) 後,分析各個請求資源資訊(包括狀態、資源型別、大小、所用時間等)。可以根據這些資料條件進行網頁效能優化。
1-2: Console面板
- 能在這邊直接看到 Console.log 的結果
- 與網頁的變數與功能進行互動
- 測試一些 Js Code
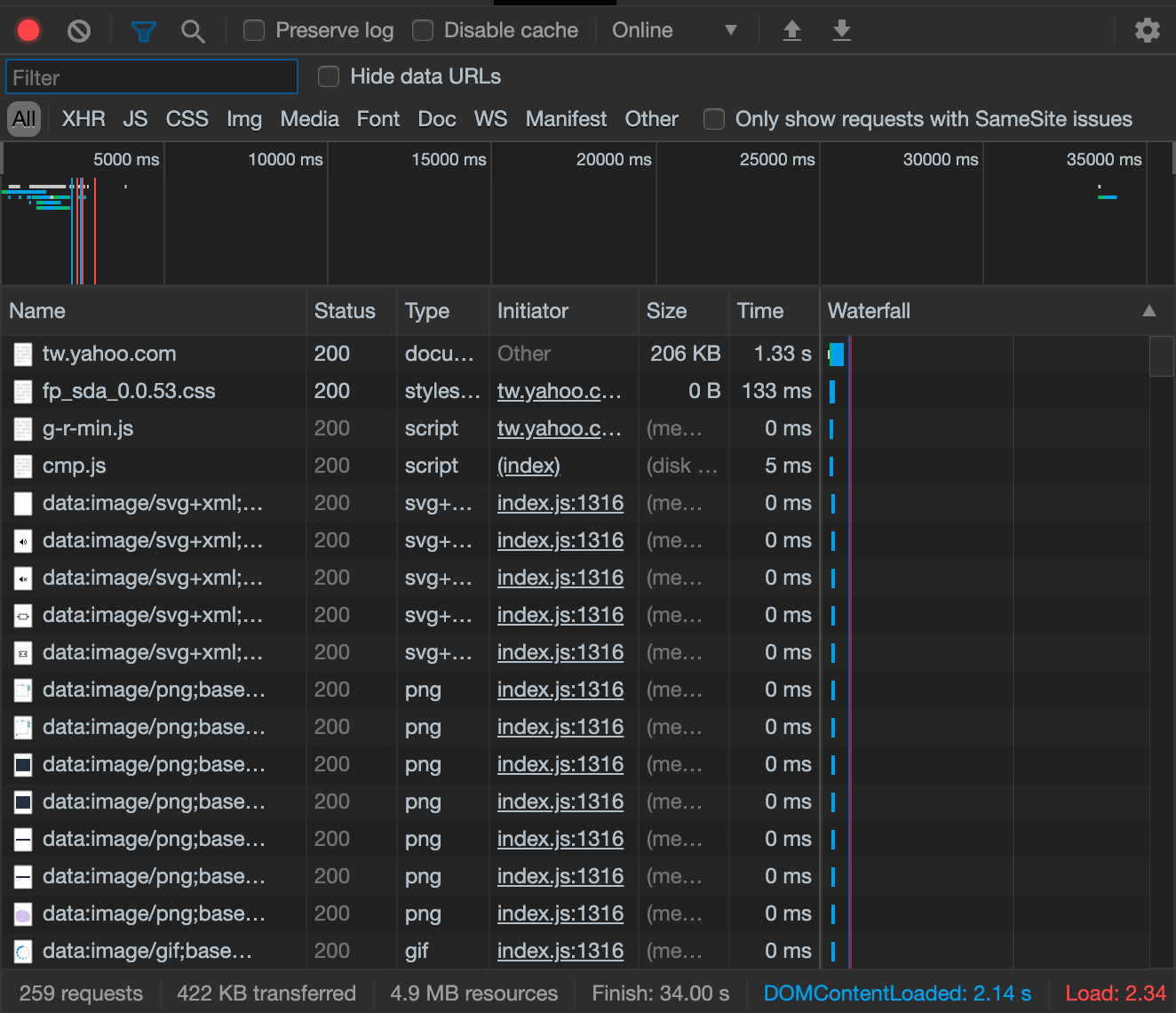
1-3: Network面板
- 使用瀑布流看到檔案載入的結果
- 左上角的紅色鈕可以錄製 request
- Disable cache 可以暫停暫存
- Filter 可以搜索你要的資料關鍵字
- 各型態可以選擇你想關注的檔案類型。
Module 2. 使用 script 標籤
Module 2. 使用 script 標籤
2-1: DOM簡介
2-2: 動態新增頁面標籤內容
2-3: 取得標籤元素
2-1: DOM 簡介

2-1: DOM 簡介
-
document.head
回傳 <head> 元件
-
document.body
回傳 <body> 元件
-
document.scripts
回傳 <scripts> 元件
-
document.title
回傳 <title> 元件
2-2: 動態新增頁面標籤內容
2-3: 取得標籤元素
Coding Style 程式的命名規則
Camel Case 駝峰式 :
-
lower camel case 小駝峰, 首字母小寫
- 例如: firstName, lastName
- 常用在 Javascript 系列語言
- upper camel case 大駝峰, 首字母大寫
- 例如: FirstName, LastName
- 常用在 ReactJs 的元件
Snake Case 蛇式 :
- 字與字之間用下劃線連接
- 例如: first_name, last_name
Module 3. 常數和變數宣告
3-1: var、let 和 const
var: 變數
- ES5
let: 變數
- ES6
const: 常數 -> 不會重新被定義
- ES6
Demo on nb or DevTools
常數表示法
- // console.log(0o23) // 舊的 8 進位用法, 不建議使用 - console.log(0o23) // 8 進位 - console.log(0x23) // 16 進位 - console.log(0b1111) // 2 進位 - console.log(2e5) // 科學表示法
Let's Test on DevTools or Appendix on nb
3-2: 識別字的規則
3-3: var 和 let 的主要差異
1. 域不一樣!
- var的作用域在函數 (function) 裡
- let的作用域則是在區塊 (block) 裡。
2.
- var 會改到原本的 window
- 但,let 不會
- eg. alert() function
Let's test on DevTools
if(true){
//Start of the Block scope
let b = 'Hi I am in the Block';
//End of the Block scope
}
console.log(b);
//ReferenceError
(function(){
var s = 'Hi I am in the Function';
}())
console.log(s)
//ReferenceError Module 4. 基本類型
4-1: Number、Boolean和String
- Boolean // 布林 - Number // 數字 - String // 字串 - null // 空值 - undefined // 空值,也可視為一個型態 - true // 常數,不可作為變數名稱 (Js 開頭為小寫,與 Python 不同) - false // 常數,不可作為變數名稱 (Js 開頭為小寫,與 Python 不同)
4-1: Number、Boolean和String
我們來在 DevTools 測試 - true = 100
- 12 = 33 // 不能使用 因為 12 不是變數
- 0xFF0000 //色碼 RGB 所以這個是紅色
- 2e3
- 2E3 //大小寫皆可
- 2E-3 //後面是負的代表示 10^-3次方 2*0.001
- Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER //Type in DevTools
- Number.MAX_VALUE //Type in DevTools
- Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY //Type in DevTools
4-2: 轉換為Number
Number("123") // 123 Number("12.3") // 12.3 Number("") // 0 Number("0x11") // 17 Number("0b11") // 3 Number("0o11") // 9 Number("foo") // NaN Number("100a") // NaN
parseInt() 函式能將輸入的字串轉成整數。
parseFloat() 函式能將輸入的字串轉成浮點數。
!!n 轉換為 Boolean
4-3: 轉換為String
.toString()可以將所有的的資料都轉換為字串,但是要排除null 和 undefined
toString() 括號中的可以寫一個數字,代表進位制,對應進位制字串
二進位制:.toString(2);
八進位制:.toString(8);
十進位制:.toString(10);
十六進位制:.toString(16);
4-3: 轉換為String
String()可以將null和undefined轉換為字串,但是沒法轉進位制字串
example:
var str = String(null);
console.log(str, typeof str);
var str = String(undefined);
console.log(str, typeof str);Module 5. 運算子
5-1: 算術運算子
| 運算子 | 例子 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
| + | x + y | x, y 相加 |
| - | x - y | x,y 相減 |
| * | x * y | x, y 相乘 |
| / | x /y | x,y 相除 |
| % | x % y | x,y 取餘數 |
| ** | x **y | x 的 y 次方 |
| & | x &y | x y 做位元 AND 運算 |
| ^ | x ^ y | x y 做位元 XOR 運算 |
| | | x | y | x y 做位元 OR 運算 |
5-2: 關係運算子 relational operators
10 > 5 //true 10 是否大於 5
10 >= 5 //true
10 < 5 //false
10 <= 5 //false
10 == 5 //false 值是否相同
10 != 5 //true
10 === 5 //false 值是否相同, 型態也要相同
10 !== 5 //true 值是否不同, 嚴謹
////陣列
'a' in ['a','b'] //false
0 in ['a','b'] //true
//陣列是看索引位置的
var people = { firstName: 'Andy', lastName: 'Tseng', gender: 'M' };
'firstName' in people; //true5-3: 邏輯運算子
//邏輯 AND -> &&
let fruit = 'Apple' && 'Banana'
//邏輯 OR -> ||
let fruit = 'Apple' || 'Banana'
//邏輯 NOT -> !
let notTrue = !(true && true)Module 6. String
6-1: 字串的標示方式
var str = 'This is string text';
var str = "This is string text";
var str = `This is string text` ;可以使用 單引' 雙引" 與反引號` example:
6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
這樣會發生錯誤 example:
var str = 'Andy's hat.';
var str = "This is a "cat".";6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
這樣可以解決 example:
var str = "Andy's hat."; // 雙引內放單引
var str = 'This is a "cat".'; // 單引內放雙引6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
用跳脫字元 (escape character) 反斜線 (backslash) \
來處理引號
example:
var str = 'Andy \'s hat.';
var str = "This is a \"cat\"."; // 單引內放雙引6-2: 字串的跳脫表示法
跳脫字元 \ 還可以處理以下這些
| 特殊符號 | 表示的符號 |
|---|---|
| \0 | NULL 字元 |
| ' | 單引號 |
| " | 雙引號 |
| \ | 反斜線 |
| \n | 換行符號 |
| \r | return 回車鍵 |
| \t | tab |
| \v | vertical tab |
| \b | backspace |
| \f | form feed |
| \uXXXX | unicode codepoint |
6-3: 字串的常用方法
字串相加
let a = 'hel'+'llo'
//'hello'
let name = 'Andy'
//'Andy'
let greetings = a + ' ' + name
// 'hello Andy'
let greetings += '!'
//'hello Andy!'多行字串
let a = 'hel' +
'llo ' +
'Andy' +
//'hello Andy'
//Or,
let a = 'hel \
llo \
Andy'
//'hello Andy'
6-3: 字串的常用方法
let name = 'Andy'
let greetings = `Hello ${name}, How are you?`
// Length
console.log(greetings.length)
//split
console.log(greetings.split(""))
//(24) ["H", "e", "l", "l", "o", " ", "A", "n", "d", "y", ",", " ", "H", "o", "w", " ", "a", "r", "e", " ", "y", "o", "u", "?"]
console.log(greetings.split(" "))
//(5) ["Hello", "Andy,", "How", "are", "you?"]
console.log(greetings.split(","))
//["Hello Andy", " How are you?"]
var str = "This is an 'ant'";
var index = str.indexOf("an");
console.log(index)
// 8
Module 7. 取得標籤元素
Get script tag
Module 7. 取得標籤元素
7-1: 使用ES3的方法
7-2: querySelector()
7-3: querySelectorAll()
7-1: 使用ES3的方法
- getElementById
- getElementsByTagName
- getElementsByName
- getElementsByClassName
7-1-1 範例
7-2&3: querySelector() & querySelectorAll()
document.querySelector('#my_id') // 抓單一物件 抓 id
document.querySelector('.my_class') // 抓第一物件 抓 class
document.querySelectorAll("p") // 抓所有的 p
document.querySelectorAll("a[target]")// 抓有target屬性的aModule 8. 流程控制
Module 8. 流程控制
8-1: 選擇敘述
8-2: 迴圈
8-3: break和continue
8-1: 選擇敘述
if(條件式){
//條件式為 true 執行
}if: 依條件執行某程式區塊 ( block )
if/else: 條件式為 true 執行 block 1 否則 block 2
8-1: 選擇敘述
if(條件式一){
//條件式為 true 執行
}else{
if(條件二){
}else{
if(條件三)
}
}if(條件式一){
//條件式為 true 執行
}else if(條件二){
}
else if(條件三){
}8-1: 選擇敘述
8-1: 選擇敘述
switch(變數){
case 值一:
//變數為值一時
break
case 值二:
//變數為值二時
break
case 值三:
//變數為值三時
break
default:
// 預設值
}switch/case
8-1: 選擇敘述
switch/case
8-2: 迴圈
for(起使值;條件式;步進式){
//迴圈內容
}
// Example
for(i=0; i<8; i++){
console.log(i)
}for 迴圈
a++
++a
8-2: 迴圈
8-2: 迴圈
8-2: 迴圈
8-2: 迴圈
8-2: 迴圈
8-2: 迴圈
let i = 0
while(條件式){
//迴圈內容
i++
}
// Example
let i = 0
while(i<5){
console.log(i)
i++
}while 迴圈
8-2: 迴圈
8-2: 迴圈
let i = 0
do {
//迴圈內容
i++
}while(條件式)
// Example
let i = 0
do {
console.log(i)
i++
}while(i<5)do while 迴圈: 先跑一次再說
8-3: break和continue
break 用來跳出迴圈
continue 跳到檢查條件繼續跑
Module 9. Object類型
Module 9. Object類型
9-1: Object類型的特點
9-2: Object表達式
9-3: for/in迴圈
9-1: Object類型的特點
var str = {firstName: 'Andy', lastName: 'Tseng'}
var list1 = ['apple', 'banana', 'cat']
str['firstName'] // Andy
str.firstName // Andy
delete str.firstNameObject: 是一個物件包含 key and value 用{} 表示
Array: 是一個有序的資料集合
9-2: Object表達式
Object: 一個 名稱 對應一個 值
也叫 hash table
key 為字串不重複,也稱做 字典 Dictionary
value 也可以是 function
key 沒有順序
let obj = {}
let obj1 = Object()9-3: for/in迴圈
for/in 列舉變數 用於 Object
也可以用在 Array
Object 拿到 key
Array 拿到位置
9-3: for/in迴圈
Module 10. Array類型
Module 10. Array類型
10-1: Array類型的特點
10-2: Array表達式
10-3: Array的方法
for/of 用法
for/of 用於迭代的(iterable)物件上,例如 Array,String
for in vs for of
主要差別如下:
- for in是ES5標準;for of是ES6標準。for of修復for in的不足
- 用object來說的話,for in遍歷的是key;for of遍歷的是value。不過JavaScript中object本身不是可迭代對象,for of會直接報錯(object迭代寫法後面再說明)
- for of不能遍歷一般物件,主要是針對數組(即array、arguments等可迭代的對象)使用,會忽略掉不可遍歷的對象
- for of可使用的對象有Array、Map、Set、String、TypedArray、arguments
- for in會遍歷自定義屬性,甚至原型鏈上的屬性也會遍歷到,反而又不是我們所想要的
Objects 如何用 for of
let obj = {
a:'apple',
b:'banana',
c:'cake'
}
for(let key of Object.keys(obj)){
console.log(obj[key]);
}
// 不如直接 for in
for(let id in obj){
console.log(obj[id]);
}10-1&2: Array類型的特點 & 表達式
var list1 = ['apple', 'banana', 'cat']
for(let i =0; i<list1.length;i++){
console.log(i+':'+ list1[i])
}
list1[2] = "cake"
Array: 是一個有序的資料集合 用 [] 表示
索引從 0 開始
有長度 .length
10-1&2: Array類型的特點 & 表達式
10-3: Array的方法
10-3: Array的方法
//Unicode 方式 sort
const slogan = '安迪TV:全民普及!'
const cutSlogan = slogan.split('')
cutSlogan.sort();
console.log(cutSlogan);
let follower = [ 6, 8, 10, 23, 8]
follower.sort()
console.log(follower);10-3: Array的方法
//由小到大
let follower = [ 6, 8, 10, 23, 8]
follower.sort(function(a,b){
return a-b
})
console.log(follower);10-3: Array的方法
//Splice 用法
//.splice(位置, 刪除幾項, items);
const months = ['Jan', 'March', 'April', 'June'];
months.splice(1, 0, 'Feb');
// inserts at index 1
console.log(months);
// expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "June"]
months.splice(4, 1, 'May');
// replaces 1 element at index 4
console.log(months);
// expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "May"]
10-3: Array的方法
//forEach 用法
let man = [
{ name: 'Steve', age: 25, id: 'A006' },
{ name: 'Dave', age: 27, id: 'A009' },
{ name: 'Andy', age: 3, id: 'A088' },
];
man.forEach(function(val, ind){
console.log( ind +': ' + val.name )
})10-3: Array的方法
//filter 用法
let words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant',
'destruction', 'present'];
let result = words.filter(function(word){return word.length > 6})
//let result = words.filter(word => word.length > 6);
console.log(result);
// expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
10-3: Array的方法
//map 用法
let array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
// pass a function to map
let map1 = array1.map(function(x){ return x * 2});
console.log(map1);
// expected output: Array [2, 8, 18, 32]
10-3: map 如何用 forEach實作
//map 的作法
let array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
// pass a function to map
let map1 = array1.map(function(x){ return x * 2});
console.log(map1);
// expected output: Array [2, 8, 18, 32]
let array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
let map1 = []
array1.forEach(function(x){
map1.push(x*2)
})
console.log(map1);Module 11. JSON
Module 11. JSON
11-1: JSON字串規則
11-2: Object和Array的複製
11-3: 編輯JSON檔
11-1: JSON字串規則
什麼是 JSON
JSON 是個以純文字為基底去儲存和傳送簡單結構資料,你可以透過特定的格式去儲存任何資料(字串,數字,陣列,物件),也可以透過物件或陣列來傳送較複雜的資料。一旦建立了您的 JSON 資料,就可以非常簡單的跟其他程式溝通或交換資料,因為 JSON 就只是純文字個格式。
JSON 的優點如下:
- 相容性高
- 格式容易瞭解,閱讀及修改方便
- 支援許多資料格式 (number,string,booleans,nulls,array,associative array)
- 許多程式都支援函式庫讀取或修改 JSON 資料
11-1: JSON字串規則
{
"orderID": 54101,
"shopperName": "John Doe",
"shopperEmail": "johndoe@example.com",
"contents": [
{
"productID": 46,
"productName": "Helmet",
"quantity": 1
},
{
"productID": 98,
"productName": "Gas",
"quantity": 3
}
],
"orderCompleted": true
}
11-1: JSON vs XML
<object>
<property>
<key>orderID</key>
<number>54101</number>
</property>
<property>
<key>shopperName</key>
<string>John Doe</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>shopperEmail</key>
<string>johndoe@example.com</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>contents</key>
<array>
<object>
<property>
<key>productID</key>
<number>46</number>
</property>
<property>
<key>productName</key>
<string>Helmet</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>quantity</key>
<number>1</number>
</property>
</object>
<object>
<property>
<key>productID</key>
<number>88</number>
</property>
<property>
<key>productName</key>
<string>iPad</string>
</property>
<property>
<key>quantity</key>
<number>3</number>
</property>
</object>
</array>
</property>
<property>
<key>orderCompleted</key>
<boolean>true</boolean>
</property>
</object>
XML 的資料量遠大於 JSON 資料量
11-1: JSON字串規則
var jsonString = ' \
{ \
"orderID": 54101, \
"shopperName": "John Doe", \
"shopperEmail": "johndoe@example.com", \
"contents": [ \
{ \
"productID": 64, \
"productName": "Helmet", \
"quantity": 1 \
}, \
{ \
"productID": 88, \
"productName": "iPad", \
"quantity": 3 \
} \
], \
"orderCompleted": true \
} \
';
11-1: JSON字串規則
// 從 JSON 字串 換回 js Object
let cart = JSON.parse ( jsonString );
console.log( cart.shopperEmail );
console.log( cart.contents[1].productName );
// 把物件 變成字串
let jsonStr = JSON.stringify(cart)
console.log(jsonStr) 11-2: Object和Array的複製
let arrayA = [28, 77, 'abc', ['John', 63, 'male'] ];
let arrayB = arrayA;
let arrayC = arrayA.slice(); // 單層
arrayA[3][0] = 'Mary';
arrayA[0] = 87;
console.log('arrayA:', arrayA);
console.log('arrayB:', arrayB);
console.log('arrayC:', arrayC);一般淺層複製,slice 深層複製
11-2: Object和Array的複製
let arrayA = [28, 77, 'abc', ['John', 63, 'male'] ];
let arrayB = arrayA;
let arrayJSON = JSON.stringify(arrayA)
let arrayC = JSON.parse(arrayJSON)
arrayA[3][0] = 'Mary';
arrayA[0] = 87;
console.log('arrayA:', arrayA);
console.log('arrayB:', arrayB);
console.log('arrayC:', arrayC);11-3: 編輯JSON檔
Let's try jsoneditoronline.org
Module 12. 函式的定義
Module 12. 函式的定義
12-1: 基本型函式
12-2: 暱名函式
12-3: 箭頭函式
12-1: 基本型函式
function 函式名稱(參數們) {
// 內容
return 回傳值
}
// Example
function myFunc() {
console.log('hi')
}
myFunc() // call myFunc function定義
12-1: 基本型函式
// 使用參數
function myFunc(a, b) {
console.log('a:' + a)
console.log('b:' + b)
console.log('arguments:' + arguments)
console.log(JSON.stringify(arguments))
}
myFunc(5, 8, 7);
// ES6
function myFunc2(a, ...b) {
console.log('a:' + a)
console.log('b:' + b);
}
myFunc2(5, 8, 7);12-1: 基本型函式
//舊
function multiply(a, b) {
b = (typeof b !== 'undefined') ? b : 1;
return a * b;
}
//ES6
function multiply(a, b = 1) {
return a * b;
}
multiply(3, 3); // 9
multiply(4, 6); // 24
multiply(7); // 712-2: 暱名函式
var square = function(num) {
return num**2;
};沒有名稱直接用
12-3: 箭頭函式
let square = (num) => {
return num**2;
}
let square = num => num**2
Module 13. Scope變數領域
Module 13. Scope變數領域
13-1: 全域變數
13-2: 區域變數
13-3: closure
13-1&2: 全域變數與區域變數
定義:
- 在最頂層範圍的變數
- 使用 var 來做全域變數會變成 window 的屬性,let 則否
- 區域變數的領域只會再函式 ( function ) 內,而在函式外,看不到此變數
- 參數是區域變數
- 若在某個區間,找不到該變數,則會往外一層區域尋找
13-1&2: 全域變數與區域變數
var a='apple'; //全域變數
function banana(){
var b='banana'; //區域變數
console.log('aInFunc:'+a)
console.log('bInFunc:'+b)
}
banana()
console.log('aNotInFunc:'+a)
console.log('aNotInFunc:'+b)13-3: closure
閉包,由內部函式居然能在外部執行,十分有趣!
13-3-1: closure
想一想!由 function 內往外推
Module 14. 時間與計時器
Module 14. 時間與計時器
14-1: Date 物件
14-2: setTimeout 用法
14-3: setInterval 用法
14-1: Date 物件
today = new Date() //無參數 今天
Xmas95 = new Date("December 25, 1995 13:30:00") //忽略為零
Xmas95 = new Date(1995,11,25,9,30,0) //多參數
//"set" 方法,用於設定 Date 物件的日期和時間的值。
//"get" 方法,用於取得 Date 物件的日期和時間的值。14-1: Date 物件
我們現在學會了用電腦來設定時間,
但,能不能夠用程式將時間設定成
使用者易讀的文字格式呢?
接著看下去..GO!
14-1-1: 建一個 function 來處理 Date
function JSClock() {
//存現在時間
let time = new Date()
//取得小時
let hour = time.getHours()
//取得分鐘
let minute = time.getMinutes()
//取得秒數
let second = time.getSeconds()
//將 0-24 小時制轉成 0-12 小時制
var temp = "" + ((hour > 12) ? hour - 12 : hour)
//如果是0點就是12點
if (hour == 0)
temp = "12";
//小於十要補零 其他不用
temp += ((minute < 10) ? ":0" : ":") + minute
//小於十要補零 其他不用
temp += ((second < 10) ? ":0" : ":") + second
//判斷上下午
temp += (hour >= 12) ? " P.M." : " A.M."
return temp
}那我們能不能夠 等一下!
再讓程式跑呢?.....
可以的!
接著看下去..GO!
14-1-1: 建一個 function 來處理 Date
14-2: setTimeout 用法
// 語法
setTimeout(function 函式,
milliseconds 毫秒,
param1 參數一,
param2 參數二,
...);
// 範例
setTimeout(function(){
alert("Hello");
}, 3000);接著看下去..GO!
14-2-1: setTimeout 很多次怎麼辦?
setTimeout(function(){ console.log("2 seconds") }, 2000);
setTimeout(function(){ console.log("4 seconds") }, 4000);
setTimeout(function(){ console.log("6 seconds") }, 6000);有沒有更好的作法?
14-3: setInterval 用法
// 語法
setInterval(function 函式,
milliseconds 毫秒,
param1 參數一,
param2 參數二,
...);
// 範例
let a = setInterval(function(){
console.log("Hello");
}, 3000);
//清掉 Interval
setTimeout(function(){
clearInterval(a)
},20000)
Module 15. 數學物件
Module 15. 數學物件
15-1: 亂數
15-2: 三角函數
15-3: 環狀排列物件
15-1: 亂數
Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 1;
// Math.floor 無條件捨去到整數
// 回傳一到十的亂數定義: 0-1的亂數,包括零,不包括一!
.
15-1-1: 指定範圍的亂數
function getRndInteger(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() *
(max - min) ) + min;
}
// 包括 min 不包括 max
.
function getRndInteger(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() *
(max - min + 1) ) + min;
}
// 包括 min 包括 max
15-1-2: 隨機排列物件
.
15-2: 三角函數
// 放一個 rad 數字 360度需轉換
// Math.PI * a角度 / 180
Math.sin(3); // 0.1411200080598672
Math.sin(-3); // -0.1411200080598672
Math.sin(0); // 0
Math.sin(Math.PI); // 1.2246467991473532e-16
Math.sin(Math.PI / 2); // 1
// cos, tan 依此類推.
15-3: 環狀排列物件
.
Module 16. window物件
Module 16. window物件
16-1: window物件的方法
16-2: window的子物件
16-3: document的常用屬性
16-1: window物件的方法Method
alert() // 跳出警示對話框
blur() // 視窗失焦
clearInterval() // 清除重複觸發某函式
clearTimeout() // 清除觸發一次某函式
close() // 關閉視窗
confirm() // 跳出確認對話框
focus() // 視窗取得焦點
print() // 執行列印
prompt() // 跳出詢問對話框
setInterval() // 間隔一段時間後重複觸發函式
setTimeout() // 間隔一段時間後觸發一次函式.
16-2: window的子物件
- navigator : 瀏覽器版本資訊
- screen : 螢幕顯示尺寸資訊
- history : 頁面上一頁或下一頁的歷史記錄
- location : url 相關資訊。
- document : 頁面 DOM 的物件
.
16-3: document的常用屬性
//指令 //類型 //說明
URL // String // 網址
anchors // HTMLCollection // Anchor集合
characterSet // String // 網頁使用的編碼,同charset
cookie // String // Cookies
doctype // DocumentType // 文件類型
domain // String // 網域名稱
forms // HTMLCollection // 表單集合
head // HTMLHeadElement // Head元素
images // HTMLCollection // 圖片集合
links // HTMLCollection // 連結集合
referrer // String // 從哪兒來
title // String // 標頭名稱Document 常用方法在7-1-1 有範例
.
Module 17. 事件處理
Module 17. 事件處理
17-1: 標籤內的事件處理器
17-2: addEventListener
17-3: onclick 與 addEventListener 比較
17-1: 標籤內的事件處理器
onclick // 當單擊
ondbclick // 當雙擊
onmousedown // 當鼠標按下
onmouseup // 當鼠標放開
onmousemove // 當鼠標在元素上移動
onmouseover // 當鼠標移入元素
onmouseout // 當鼠標移出元素
onkeydown // 當鍵盤按下 body 功能
onkeyup // 當鍵盤放開 body 功能
onkeypress // 當鍵盤按著(可持續) body 功能
17-1: 標籤內的事件處理器
onload // 當鍵盤按下 body,object 功能
onresize // 當文件調整長寬
onscroll // 當文件捲動
onblur // 當失焦
onchange // 當內容改變 input, select, textarea 功能
onfocus // 當聚焦
onreset // 當表單重置
onselect // 當選取 input, textarea 功能
onsubmit // 當送出表單
.
17-2: addEventListener
語法:
- 元素.addEventListener(event, function函式)
.
17-3: onclick 與 addEventListener 比較
.
Module 18. AJAX
Module 18. AJAX
18-1: 什麼是 AJAX
18-2: XMLHttpRequest
18-3: fetch()方法
18-1: 不刷新頁面更新內容
.
18-2: XMLHttpRequest
說明:
- 要拿資料必須送出一個 HTTP 請求(Request)
- XMLHttpRequest 將會回應一個 Response
.
18-3: fetch()方法
fetch API 讓 http 的處理更加簡單! 發送跟接收資料都可以!
.
JavaScript網頁程式設計
By txshon Tseng
JavaScript網頁程式設計
時數: 18hr 老師: Andy Tseng 曾郁翔
- 1,519



