Python Basics
What is Python and what is it used for?
- Python is a general purpose programming language created in the late 1980s and named after Monty Python.
- People use python to make games, create web applications, compile data, solve business problems, etc.
Python Keywords
Keywords are reserved words that cannot be used as a variable name, function name or any other identifier.
Your code editor will highlight (most) keywords
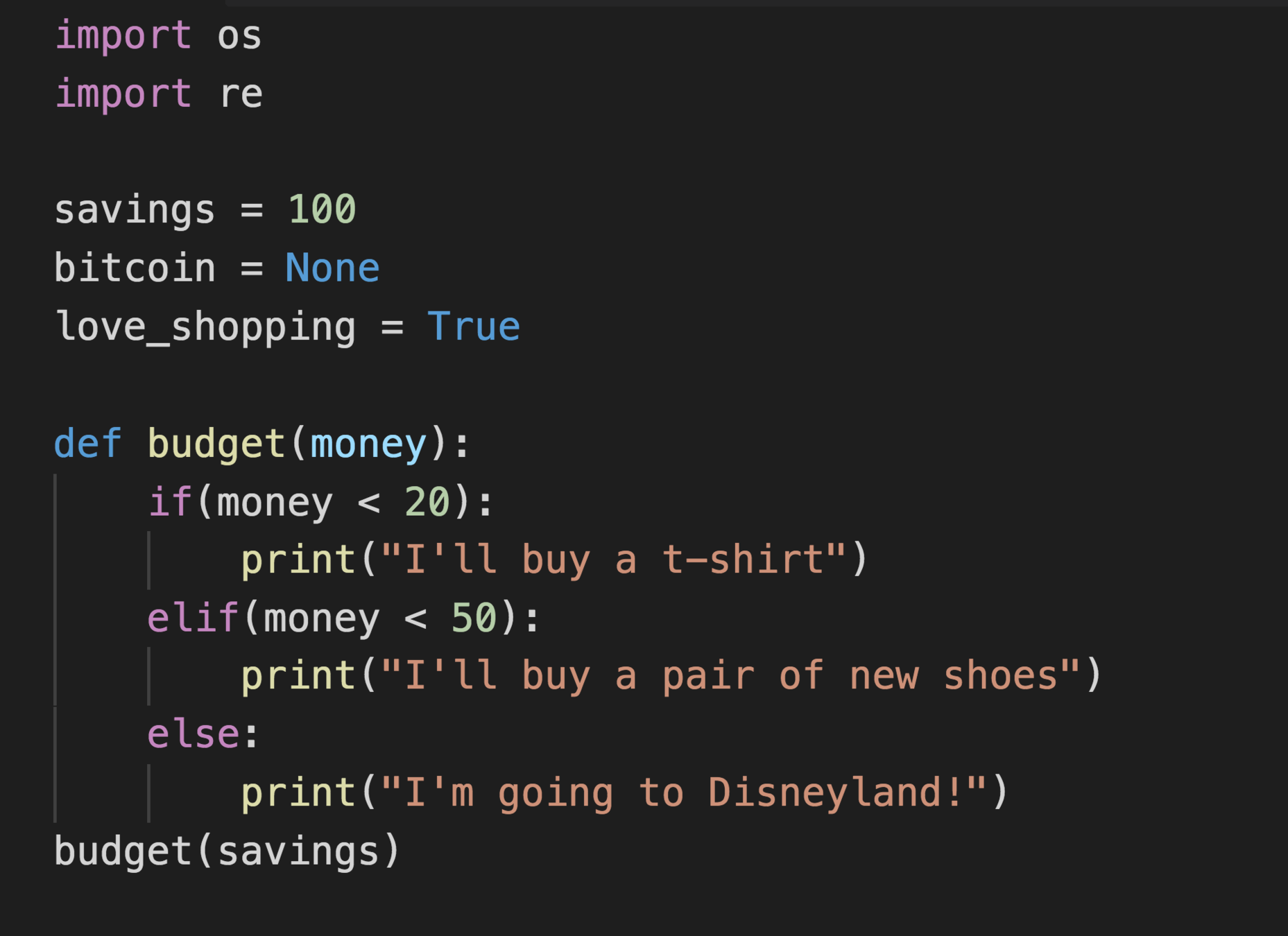
Variables
- Variable names can contain only letters, numbers and underscores. They can start with a letter or an underscore, but not with a number.
- Spaces are not allowed in variable names, but underscores can be used to separate words in a variable names.
- DO NOT use keywords and function names as variable names
- Variable names should be short but descriptive
Variables are 'containers' for data. It holds a value. Basically they are Pointers (references) to data stored in Memory (RAM)
Creating a variable
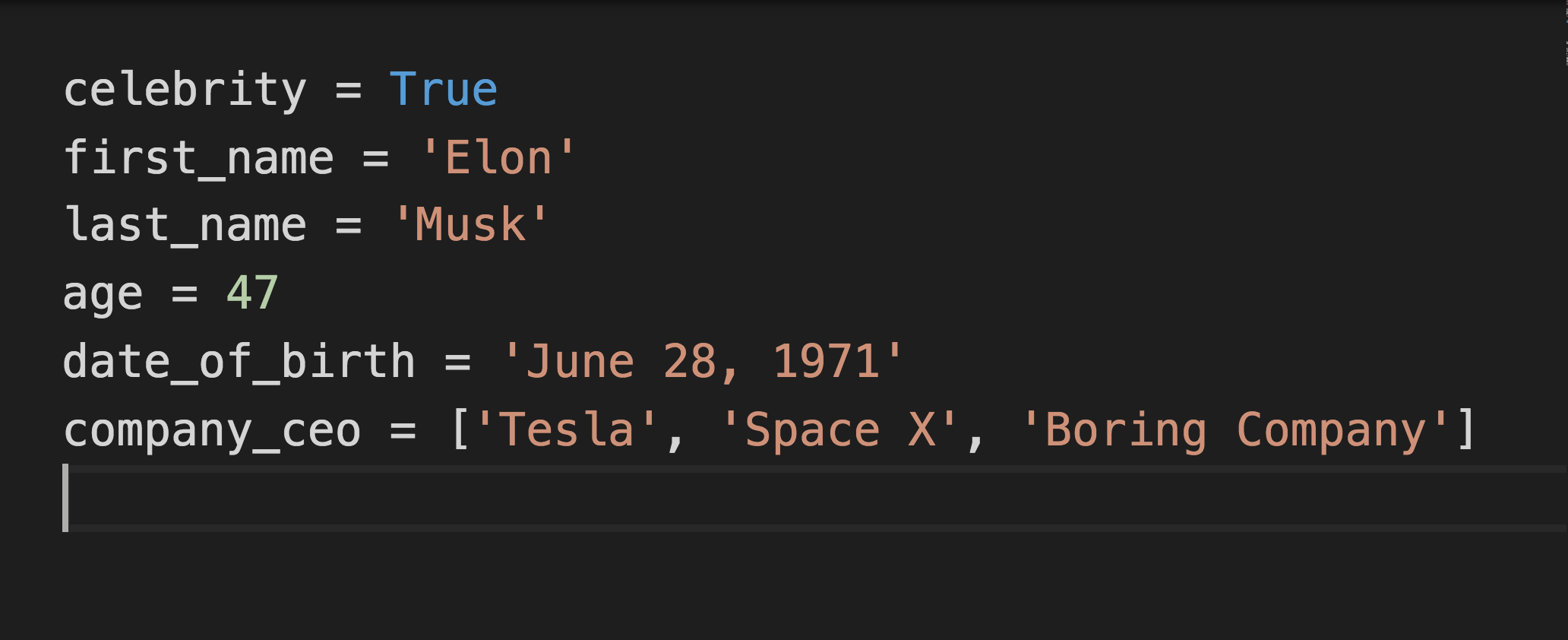
Data Types
- String
- Number
- List
- Dictionary
- Tuple
- Boolean
String Data Type
A series of characters wrapped in 'quotes'
// Strings are wrapped between double quotes
"Hello World"
// or single quotes
'Hello Solar System'
// wrap literal single quotes in double quotes
"Hello Local Interstellar Cloud, i'm fine"
// wrap literal double quotes in single quotes
'Hello "Local Bubble", how are you?'
// or escape double quotes with a backslash \
"Hello Orion's \"Arm\""
// or escape single quotes with a backslash \
'Hello Virgo\'s Supercluster'
// concatenate strings
"Observble" + "universe"
// concatenate with a space
"Observble" + " " + "universe"
String Concatenation
Adding or combining strings together
// Strings are wrapped between double quotes
"Hello World"
// or single quotes
'Hello Solar System'
// wrap literal single quotes in double quotes
"Hello Local Interstellar Cloud, i'm fine"
// wrap literal double quotes in single quotes
'Hello "Local Bubble", how are you?'
// or escape double quotes with a backslash \
"Hello Orion's \"Arm\""
// or escape single quotes with a backslash \
'Hello Virgo\'s Supercluster'
// concatenate strings
"Observble" + "universe"
// concatenate with a space
"Observble" + " " + "universe"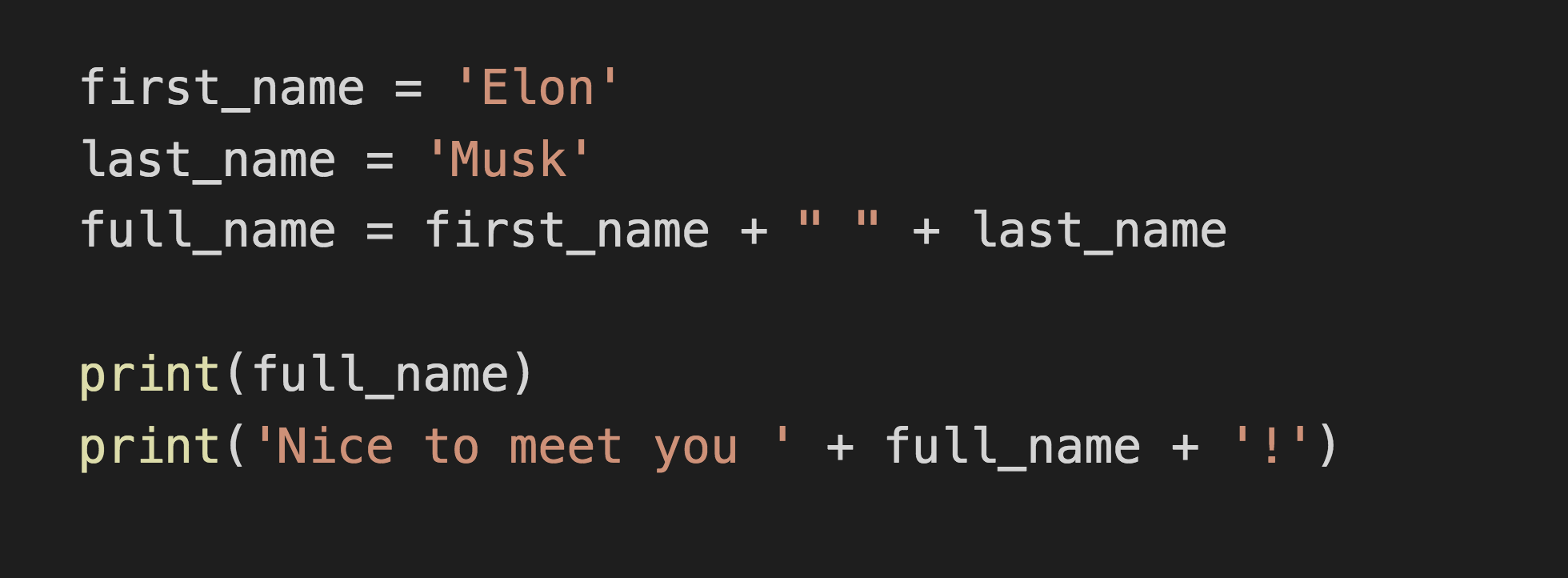
Spacing with Tabs or Newlines
Using whitespace to organize your output
// Strings are wrapped between double quotes
"Hello World"
// or single quotes
'Hello Solar System'
// wrap literal single quotes in double quotes
"Hello Local Interstellar Cloud, i'm fine"
// wrap literal double quotes in single quotes
'Hello "Local Bubble", how are you?'
// or escape double quotes with a backslash \
"Hello Orion's \"Arm\""
// or escape single quotes with a backslash \
'Hello Virgo\'s Supercluster'
// concatenate strings
"Observble" + "universe"
// concatenate with a space
"Observble" + " " + "universe"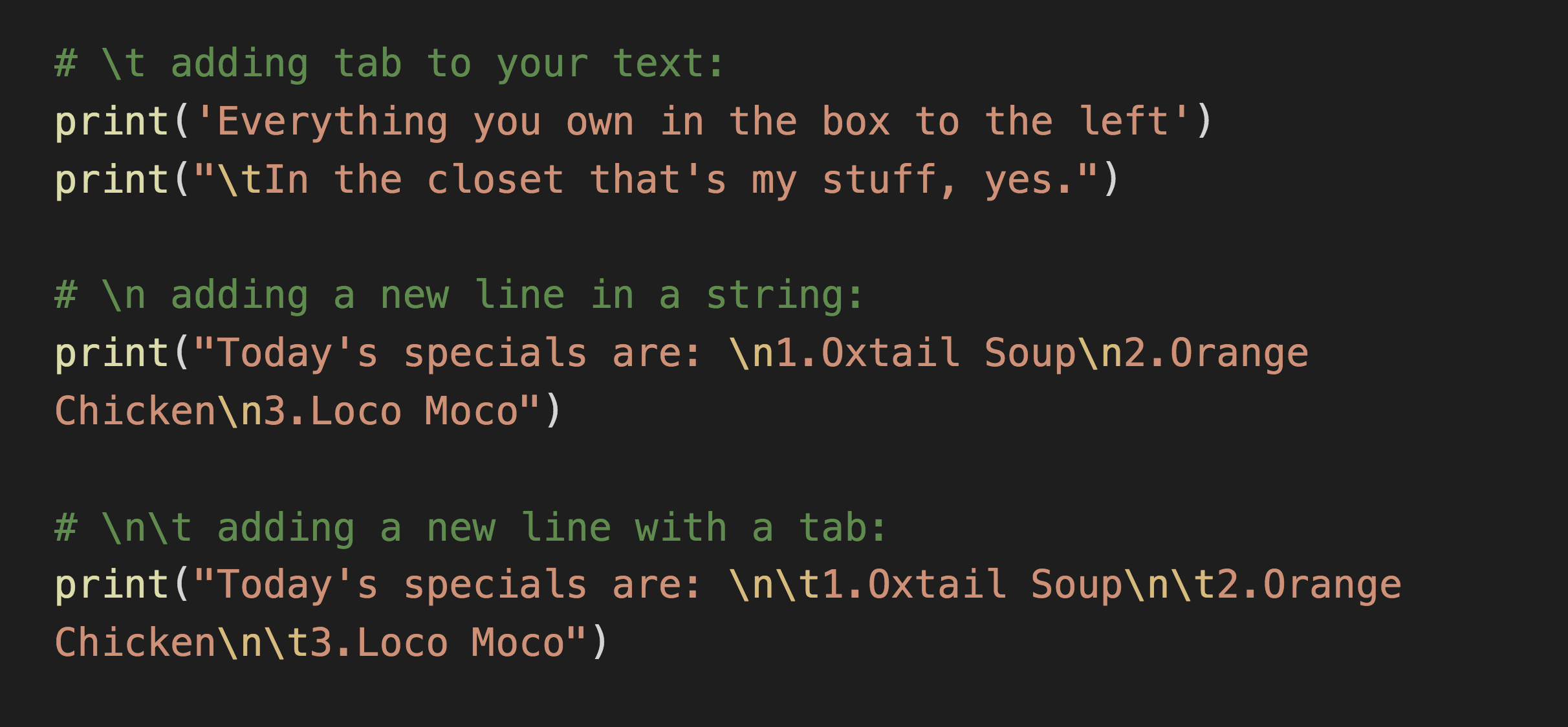
Number Data Type
Number as Strings
Sometimes you'll use a variable's integer value within a message.

But Python isn't too sure how to interpret the number value. Hence you'll need to convert the integer as a string of characters.

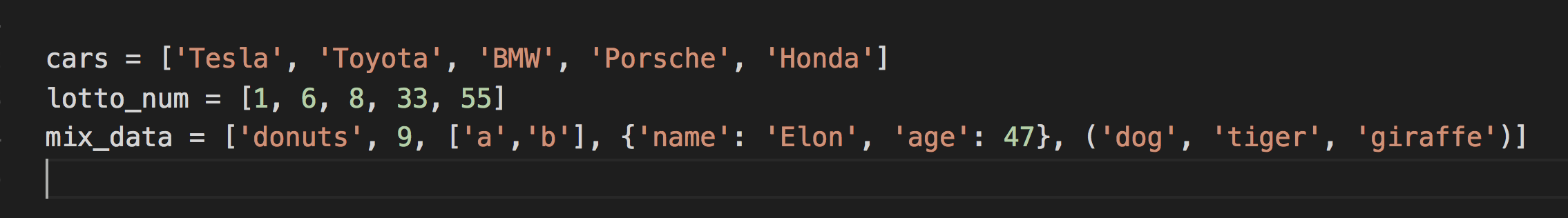
List Data Type
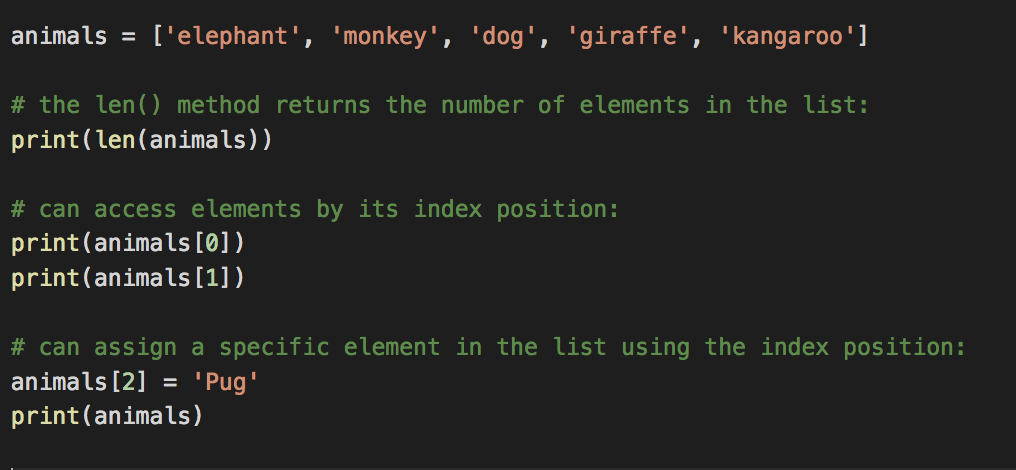
A list is a collection of items in a particular order.
- A list is wrapped in brackets [ ]
- List can contain any data type
- List are zero-based indexed (starts from 0 )
- List will always have a length (number of elements in the list)
- Can access elements in the list by its index position
- Can assign specific element of the list using an index into the list
- List have methods that can modify or access values within the list
Accessing Elements in a List
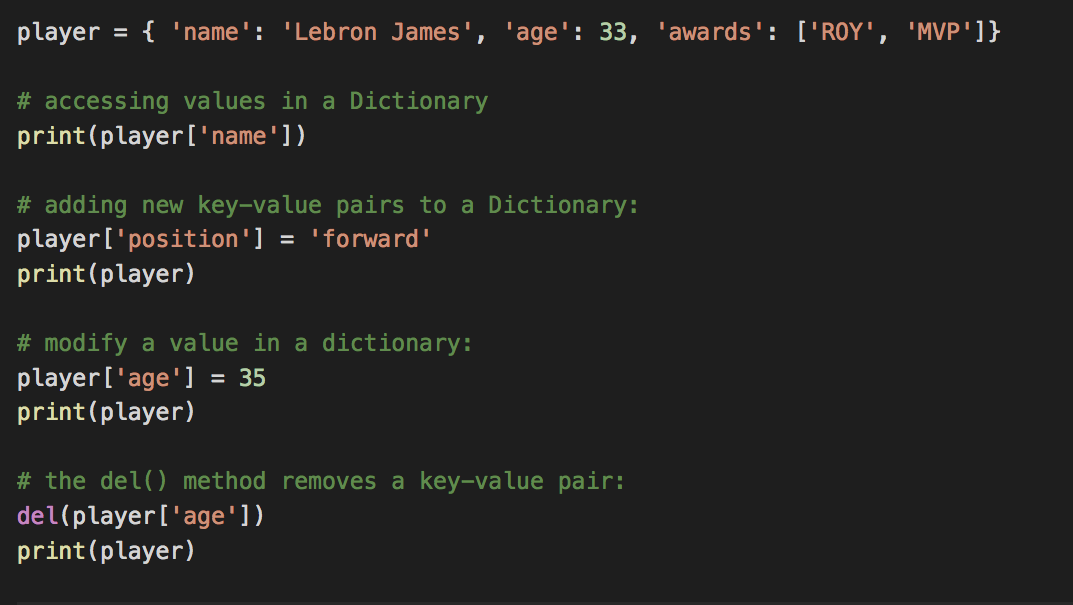
Dictionary Data Type
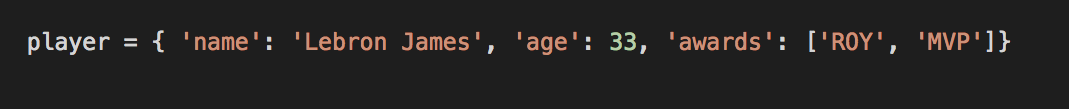
A collection of key-value pairs.
- A dictionary is wrapped in braces { }
- Each key is connected to a value by a colon
- Each key-value pair is separated by a comma
- Dictionaries are dynamic, you can add new key-value pairs at any time
Accessing Values in a Dictionary
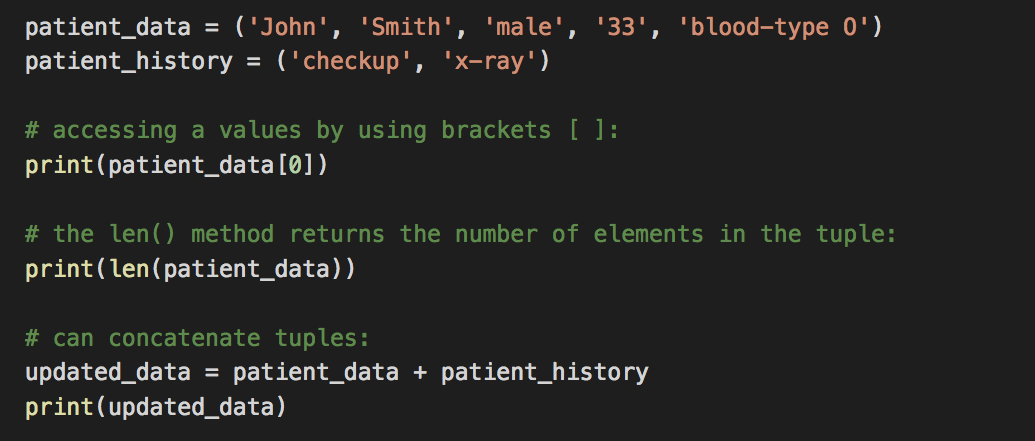
Tuple Data Type
A group of values similar to list but cannot be changed.
- A tuple is wrapped in parenthesis ( ) .
- Tuples are immutable, values cannot be updated or changed
- Tuples can contain any data type
- Tuples are also zero-base indexed
- Tuples are faster than lists

Accession Values in a Tuple
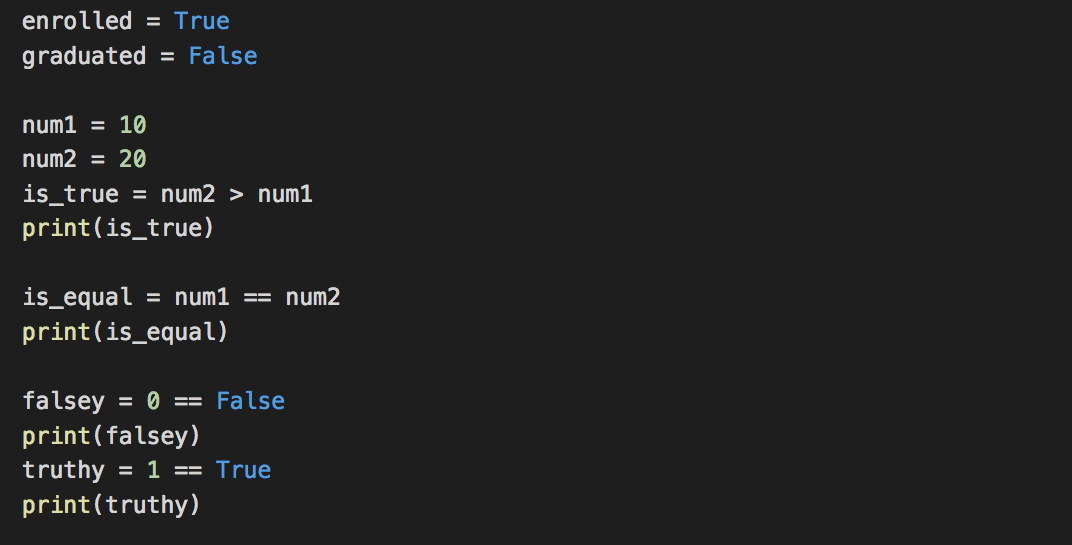
Boolean Data Type
Represent a True or False value.
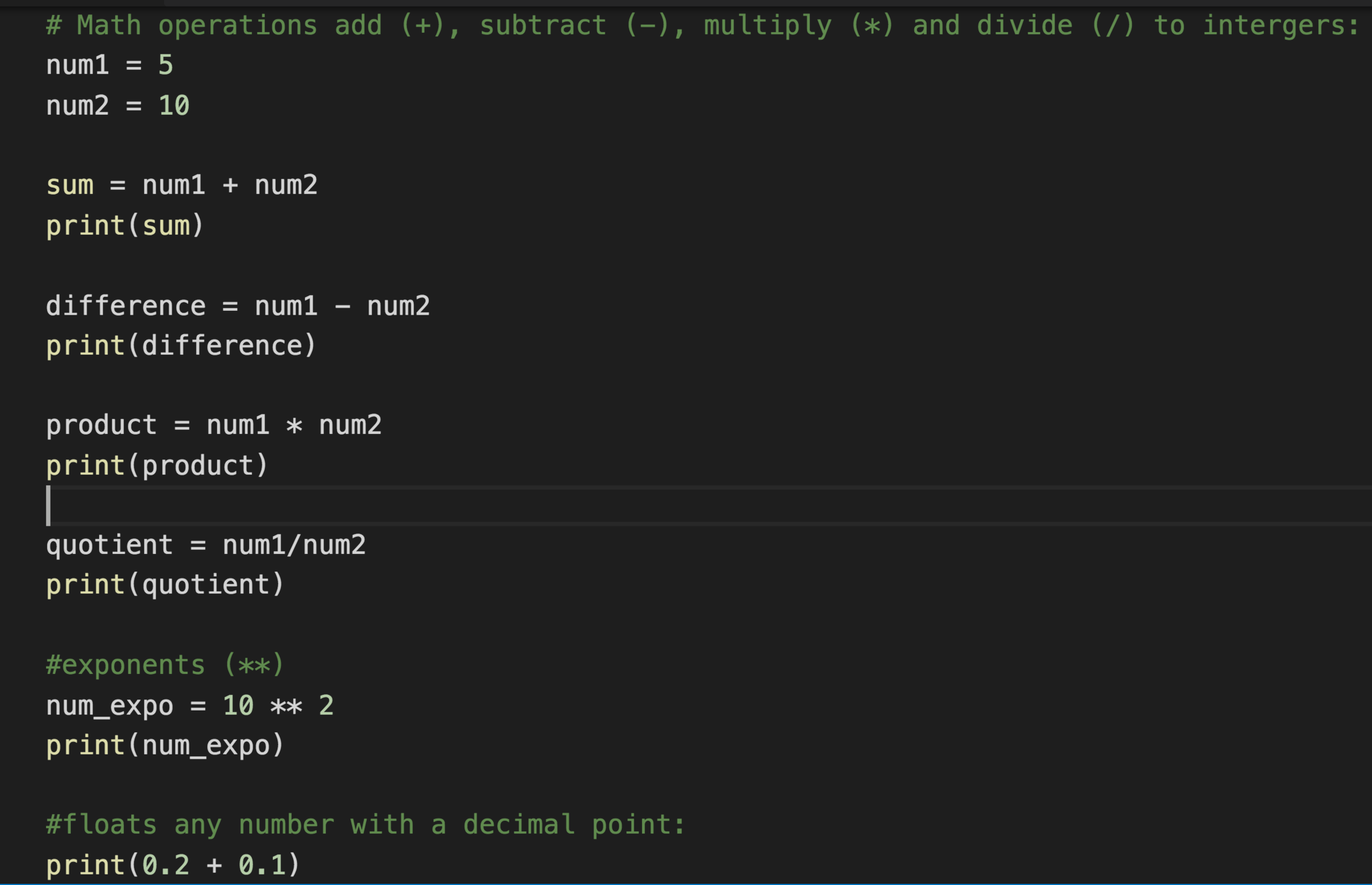
Python Arithmetic Operators
+ Addition
- Subtraction
* Multiplication
/ Division
% Modulus
** Exponent
// Floor Division
Python Comparison Operators
== equality
!= inequality
> greater than
< less than
>= greater than or equal to
<= less than or equal to
Python Assignment Operators
= Assignment
+= Increment and Assign
-= Decrement and Assign
*= Multiply and Assign
/= Divide and Assign
%= Modulus and Assign
**= Exponent and Assign
//= Floor Division and Assign
Python Basics
By vic_lee
Python Basics
- 787



