UE JS

! IMPORTANT !
Each green text is a LINK
Be sure to check it out
I figured, what if I could just extract the part that I really liked about Angular and build something really lightweight
Evan You
- Open-source JS framework;
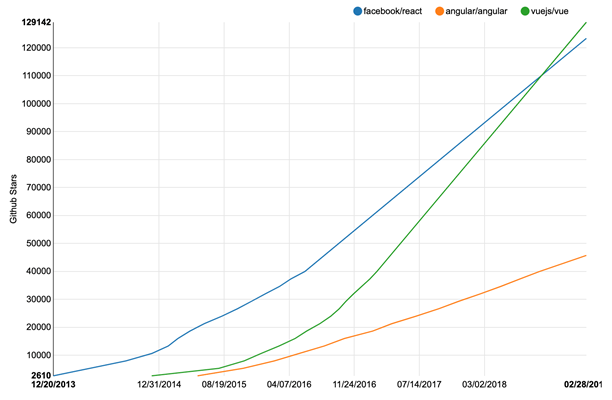
- First Vue.js release – February 2014 (React was released in March 2013);
- According to SimilarTech, Vue is in use on 26,000 unique domains. Growing at 3.34% per month;
- The goal is — or at least should be — to build incredibly capable and robust single-page (SPA) applications;
- Tries to simplify most common things developer faces during development and focus on bringing the value faster.
- Simple and good documentation
First look info
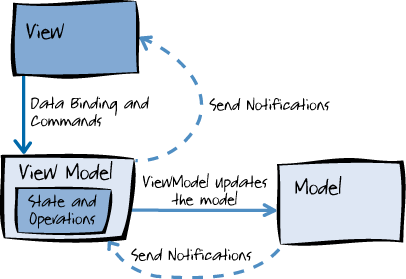
Model-View-ViewModel
User
- Flexibility and Modularity
- Integration
- Components
- Library size
- Learning curve
- Runtime Performance
- Scaling Up/Down
VUE benefits
How to start?
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create hello-world
npm install -g @vue/cli-service-global
vue serve MyComponent.vue
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>vue ui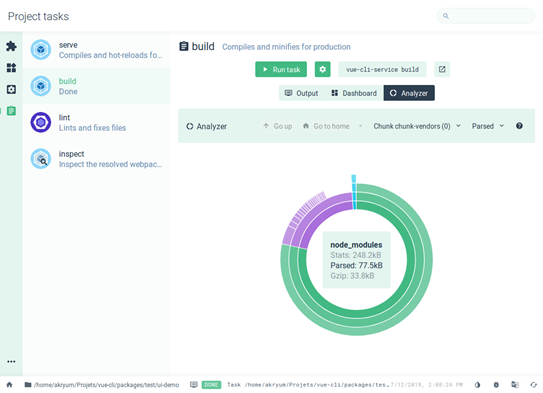
How it works?

How to define a component?

Vue.component('component-a', { /* ... */ })
Vue.component('component-b', { /* ... */ })
Vue.component('component-c', { /* ... */ })
new Vue({ el: '#app' })Component global registration
const ComponentA = { /* ... */ }
const ComponentB = { /* ... */ }
const ComponentC = { /* ... */ }
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'component-a': ComponentA,
'component-b': ComponentB
}
})Component local registration
const ComponentA = { /* ... */ }
const ComponentB = {
components: {
'component-a': ComponentA
},
// ...
}Nesting
<template>
<p>{{ greeting }} World!</p>
</template>
<script>
module.exports = {
data: function () {
return {
greeting: 'Hello'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
p {
font-size: 2em;
text-align: center;
}
</style>How to describe a component?
Component options
import ChildComponent from './../ChildComponent';
export default {
name: 'YourNewComponent',
data() {
return {
dataName: ...,
...
};
},
components: {
ChildComponent,
...
},
props: {
propName: {
type: ... , // type object (ex. String, Number ...)
required: ... , // boolean (ex. true)
validator: function (value) { ... }, // optional for props
default() { // if prop type - object (array, function...)
return { ... }
},
default: ... , // if prop type - primitive (boolean, string...),
},
},
computed: {
something() { return ... ; },
},
methods: {
someMethod() { ... },
},
...
};Directives
<input v-model="message" placeholder="edit me">
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>...
methods: {
login () {
this.$emit('login', {
email: this.email,
password: this.password
})
}
}
...child.vue
<child @login='onLogin' />
methods: {
onLogin (data) {
console.log('child component said login', data)
// email:..., password:...
}
}parent.vue
How to expand a component?

const mixin = {
data: function () {
return {
message: 'hello',
foo: 'abc'
}
}
}
new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
data: function () {
return {
message: 'goodbye',
bar: 'def'
}
},
created: function () {
console.log(this.$data)
// => { message: "goodbye", foo: "abc", bar: "def" }
}
})<!-- in mustaches -->
{{ message | capitalize }}
<!-- in v-bind -->
<div v-bind:id="rawId | formatId"></div>//local
filters: {
capitalize: function (value) {...}
}
//global
Vue.filter('capitalize', function (value) {...})
new Vue({
// ...
})<a v-bind:href="url" class="nav-link">
<slot name="test"></slot>
</a><child>
<template v-slot:test>
<h1>Here might be a page title</h1>
</template>
</child>child.vue
parent.vue

<div id="app">
<h1>Hello App!</h1>
<p>
<router-link to="/foo">Go to Foo</router-link>
<router-link to="/bar">Go to Bar</router-link>
</p>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>index.html
const Foo = { template: '<div>foo</div>' };
const Bar = { template: '<div>bar</div>' };
const routes = [
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo },
{ path: '/bar', component: Bar }
];
const router = new VueRouter({ routes });
const app = new Vue({
router
}).$mount('#app');
index.js
export default {
computed: {
username () {
return this.$route.params.username
}
},
methods: {
goBack () {
window.history.length > 1
? this.$router.go(-1)
: this.$router.push('/')
}
}
}
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
components: { Counter },
template: `
<div class="app">
<counter></counter>
</div>
`
})const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
],
count: 1,
},
getters: {
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
},
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
commitIncrement (context) {
// AJAX
context.commit('increment')
}
}
});State structure
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed:
...mapState({
countAlias: 'count', // also true for all bellow
count: state => state.count,
countPlusLocalState (state) {
return state.count + this.localCount
}
}),
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
]),
...mapMutations([
'increment',
'incrementBy'
]),
...mapActions([
'increment',
'incrementBy'
]),
}const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> `moduleA`'s state
store.state.b // -> `moduleB`'s state
Thanks
links
Useful Links
For the most curious...
VUE JS
By Victoria Budyonnaya
VUE JS
- 1,020



