SmotherSpectre
Exploiting Speculative Execution through Port Contention

The 2018 Shock
Meltdown Leaks Kernel Memory
Spectre leaks arbitrary memory outside bounds and even sandboxes
Detour to a quick crash course on Meltdown and Spectre
Genesis
- There are two key steps in Meltdown & Spectre
- Source of the attack (OoO andSpeculative Execution)
- Medium of leak (predominantly Caches)
- Umpteen works on sealing the medium of leakage (Caches, BPU, etc.)
- But how do we know there are only a finite number of mediums? And sealing a medium kills the attack?
- This work shows that there's yet another medium that's the source of leakage
- (What does it tell us?) - It might be more worthwhile to go behind the source than behind the medium
Another disadvantage with Cache side channels
- Consider Spectre V2 - Branch Target injection
- Pollute BTB - speculate target to branch to a gadget code and execute it (gadget code with loads from critical memory)
- But finding a gadget code that gets the data to the cache is very hard except in a few cases such eBPF (Berkeley's Packet Filter)
- Hence, costly solutions like Retpoline (indirect branches don't speculate) is not applied widely
- However, the current work claims to make V2 more practical - since we are not limited to load gadgets alone!
Idea
SMoTher
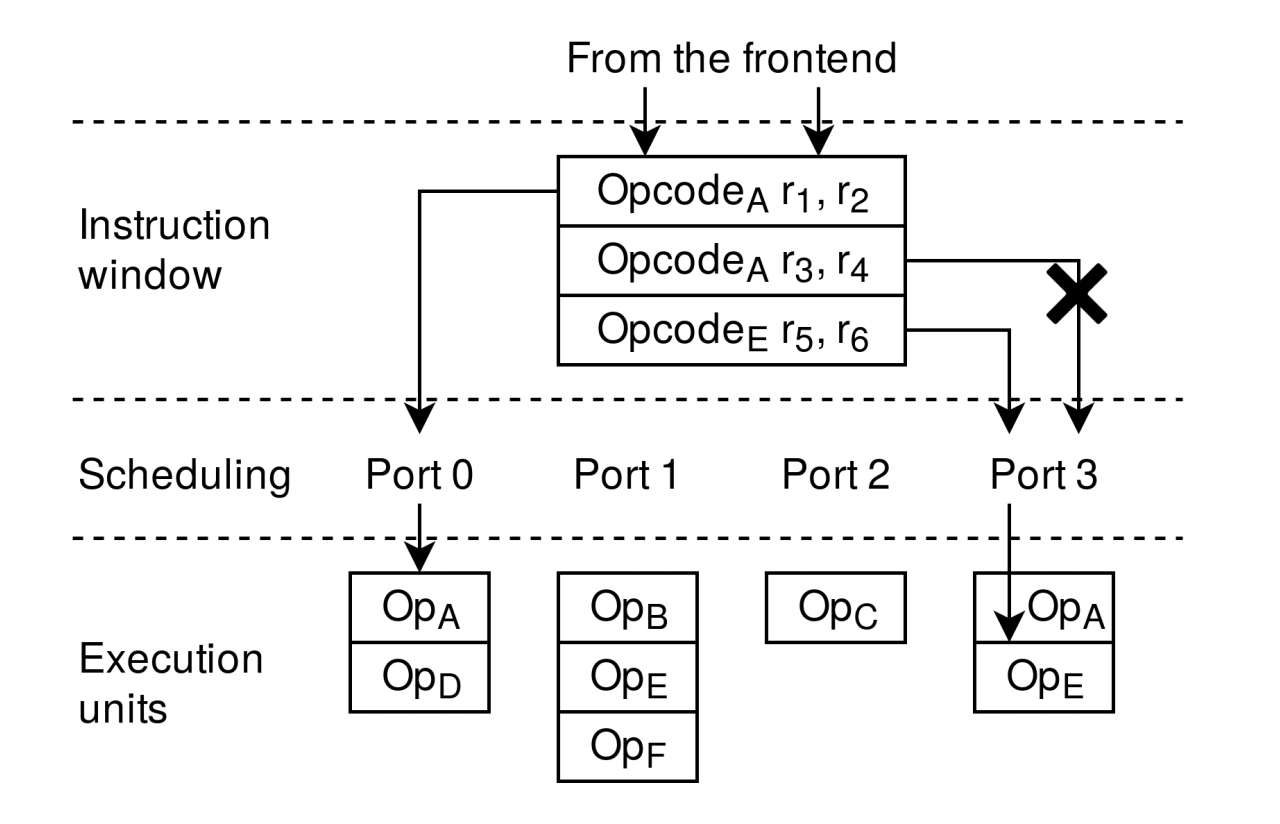
- The attack is based on the following observation
- Two SMT threads share Execution units
- Instructions that are scheduled to execute on the same port will contend
SMoTher Differentiability
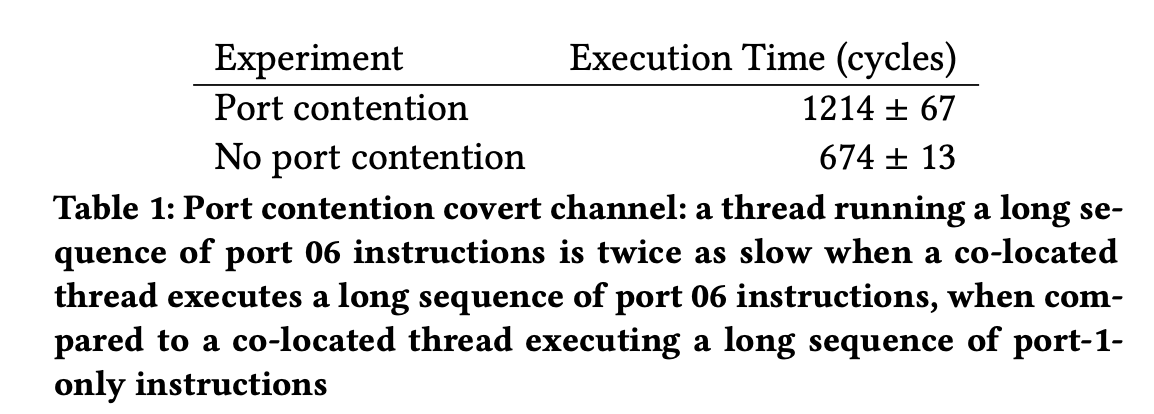
- Let one SMT thread run a set of instructions \( V = \{V0, V1, V2,...\} \)
- Attacker runs a set of instructions A
- If Attacker can infer some \( V_i \in V\) the sequences in V are said to be SMoTher Differentiable
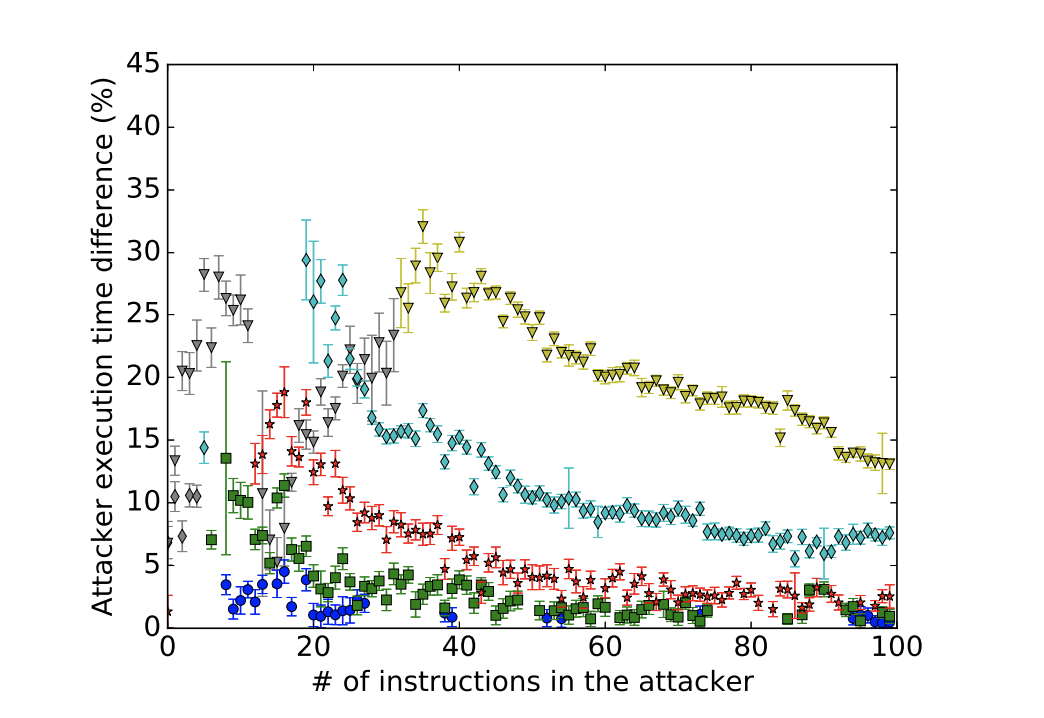
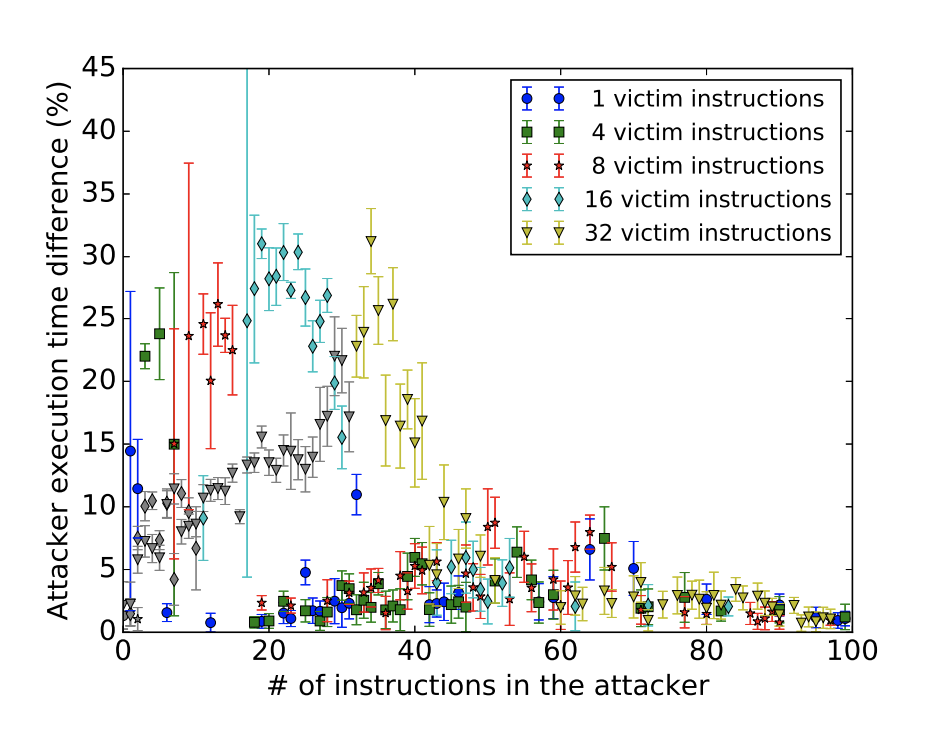
Victim: Either popcnt (port 1) or ror (port 6)
Attacker: Contending and timing port 1
Victim: Either cmovz (port 6) or popcnt (port 1)
Attacker: Contending and timing port 6 using bts
Pitfalls
- Synchronization of attacker and victim is crucial. If the code sequence is short, this is hard to achieve
- Pipeline bottlenecks other than port contention can overshadow the side channel (e.g. RAW hazards)
- The CPU may eliminate the execution of some instructions (zero idioms). This removes contention
- Some instructions (e.g. SSE and AVX) are subject to aggressive power-saving features on modern CPUs. This makes measuring very difficult
SMoTherSpectre
- Leverages BTI to poison BPU making one SMT thread jump to an address upon an indirect jump to execute a code with SMoTher Differentiable code
- Unlike cache side channels, you don't need a measurable change in the micro-architectural state here
- Apparently, SMoTher differentiable gadgets are easy to find unlike cache load gadgets
- libcrypto in OpenSSL has 12,000 such gadgets readily available
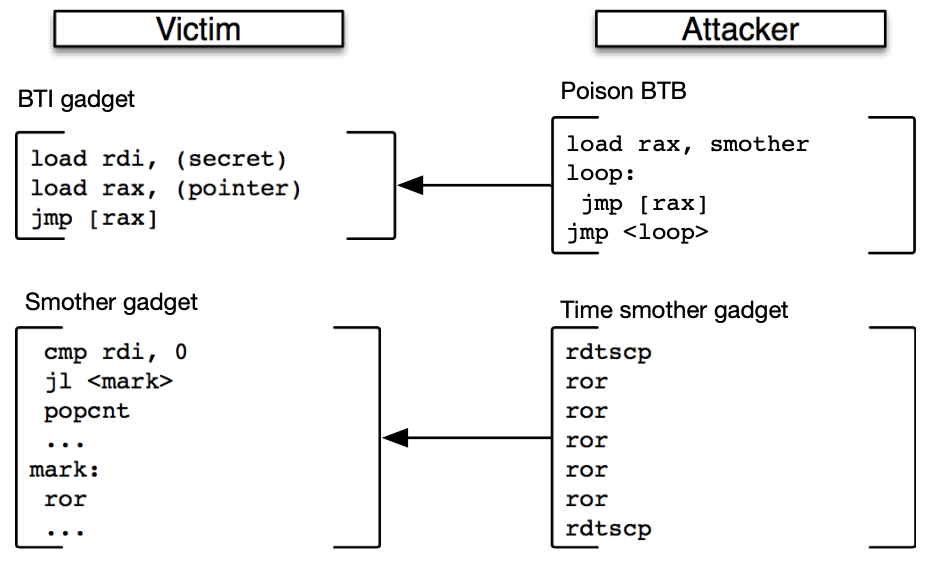
Key Assumptions
- To maximize the success rate
- Introduce N taken branches before indirect branch
- Disable ASLR
- Evict cache line containing indirect jump pointer
- Know if BTI worked using performance counter
- BR_MISP_EXEC.TAKEN_INDIRECT_JUMP_NON_CALL_RET
Gadgets
- There are two types of gadgets that's required to make SMoTherSpectre successful i.e. BTI gadget and SMoTher gadget
BTI Gadgets
- Pass a secret through a register to an arbitrary code in the same process
- Ideal BTI targets are virtual function calls in C++ that happens through a vtable and dynamically linked ELF calls that will go through GOT
- If we evict vtable and GOT from cache, it gives around ~200 cycles to reliably mount the attack
SMoTher Gadgets
- The gadget is either a part of the victim or an additional attack vector by the attacker
- The gadget consists of,
- Instruction comparing the secret register to a known value
- Followed by a conditional-flow transfer depending on the comparison
- The instructions should have distinct port fingerprint
- Port fingerprinting is the task of ranking two instruction sequences based on their port utilization
- Instructions should not have other memory references to caches - that will inject noise
Real World OpenSSH attack

This calls bzero function using a volatile pointer
Chosen BTI gadget
This ins checks if 8th bit is set in address location within (rdi) - secret
This code times the addl and checks for port contention with sub
Secret
Mitigations
- Disable SMT entirely (15% overhead on Intel machines)
- OS can employ side-channel aware strategy i.e. colocate only threads from the same user on same SMT threads
- Can explore the utilities of coarse-grained or interleaved Multithreading as viable alternatives for SMT
- Figure out a solution for BTI (such as Retpoline)
- But it should have very low overheads (<Disabling SMT obviously)
- However SMoTherspectre can also employ other Spectre Variants (e.g. RSB overflow) to mount the attack
SmotherSpectre
By Vinod Ganesan
SmotherSpectre
- 265



