Welcome to VueJS workshop


Independent consultant
Web / Mobile / VR / AR / IoT
GDE, author, engineer
What is Vue?
Vue is a progressive framework for building user interfaces that is designed to be incrementally adoptable
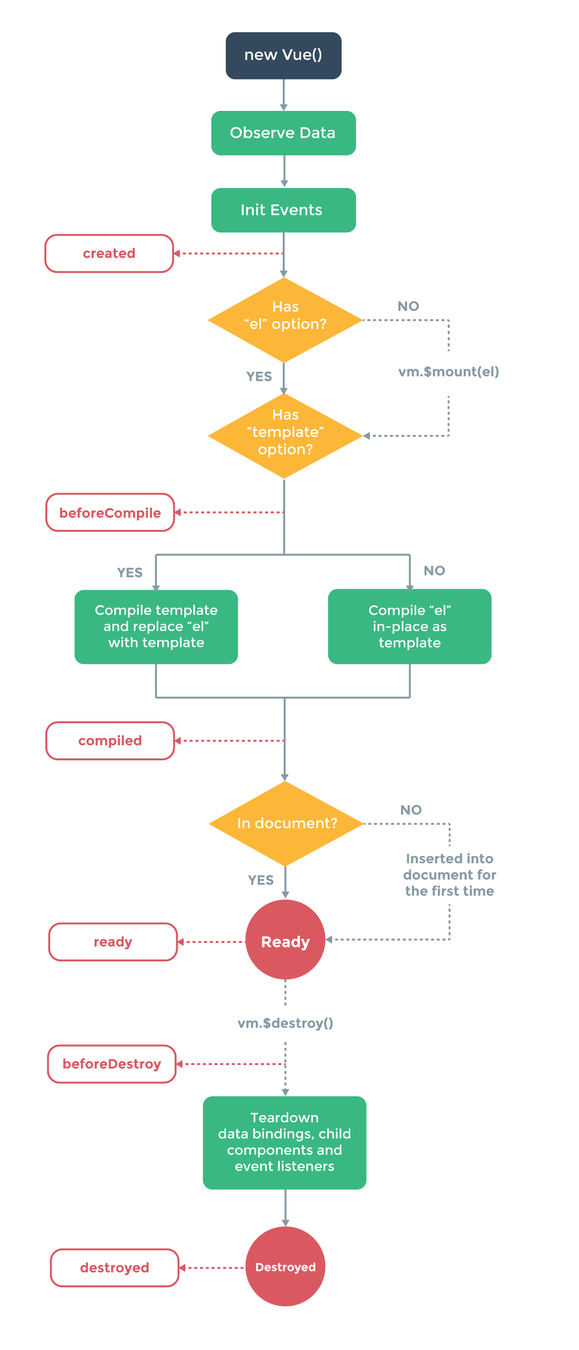

Lifecycle of Vue instance
Vue Devtools
Template syntax
you can put one single expression in {{ }}. Everything that is on this will be available in mustache syntax
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span>
{{ var a = 1 }}
{{ number + 1 }}{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}{{ if (ok) { return message } }}Directives
Special attributes with v- prefix
Directives reactively apply changes to DOM when a value of its single expression changes
Directives can take an argument using : syntax
v-text
v-html
v-show
v-if
v-else
v-else-if
v-for
v-on
v-bind
v-model
v-slot
v-once
used instead of {{ }} syntax
render raw HTML (dangerous)
hides element (display: none)
conditionally render element based on predicate (Don't use together with v-for)
previous sibling must be v-if or v-else-if
restrictions the same as on v-else, but accepts expression as v-if
loops over collection
accepts event name as an argument and invokes a function/statement
dynamically binds one or more attributes or props to expression
creates two way binding on a form input element
v-cloak
pass properties to slots
can be used to hide mustache bindings until Vue instance is ready
v-pre
removes mustache syntax and renders as is
render element only once
shorthands
v-bind shorthand :
v-on shorthand @
some directives are so common that they have shorthands
styles
<div v-bind:class="{ active: isActive }"></div><div v-bind:class="[activeClass, errorClass]"></div><div v-bind:style="{ width: withVariable }"></div><div v-bind:style="[activeStyle, otherStyle]"></div>Object syntax
Array syntax
inline styles
Object syntax
Array syntax
Listening to events
We can listen to any event by using @
<a v-on:click.stop="doThis"></a>And we can use so-called modifiers
.stop
stopPropagation()
preventDefault()
addEventListener(event, function, useCapture);
will trigger only if target is self
will be triggered only once (also on component events)
indicates that the function specified by listener will never call preventDefault()
.prevent
.capture
.self
.once
.passive
Keyboard events
we can pass key modifiers to map to target keys
<input v-on:keyup.page-down="onPageDown">.enter
.tab
.delete
.esc
.space
.up
.down
.left
.right
you can use keycodes as well (not consistent in IE9)
<input @keyup.13="submit"></input>or configure your own mappings
Vue.config.keyCodes.f1 = 112System modifiers
They work both for mouse and keyboard events
.ctrl
.alt
.shift
.meta
<input v-on:keyup.alt.67="clear">.exact
used to control exact combination of system modifiers
Mouse modifiers
.left
.right
.middle
Methods
this anywhere in Vue instance is proxied and has everything on data and methods available
Computed
computed properties are cached based on their reactive dependencies.
computed: {
priceWithCurrencySymbol: function () {
return this.price + this.currencySymbol
}
}computed: {
priceWithCurrencySymbol: {
get: function () {
return this.price + currencySymbol
},
// setter
set: function (priceString) {
this.currencySymbol = currencySymbolsDict[priceString[priceString.length - 1]] || "$"
this.price = priceString.slice(0, -1)
}
}
}Computed
If you need to change data -> Use data
When you need to change data presentation -> use computed properties
Watchers
Vue provides a way to "watch" data and react to its change
watch: {
firstName: function (val) {
this.fullName = val + ' ' + this.lastName
},
lastName: function (val) {
this.fullName = this.firstName + ' ' + val
}
}Don't use watchers unless you really need to. In most cases you need computed prop
Use watchers if you need to run side effect on data change
Filters
filters work mustache interpolations and v-bind expressions
filters: {
capitalize: function(value) {
if(!value) return '';
value = value.toString();
return value.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + value.slice(1)
}
}{{ message | filterA | filterB }}Exercise time
Components
Collection of elements encapsulated in container and can be referred as a single element
Vue.component('click-counter', {
template: '<button @click="count++">{{count}}</button>',
data(){
return {
count: 0
}
}
});Note: data must be a function
Components
Component template can be defined both as string and as script tag
Vue.component('click-counter', {
template: '#click-counter-template', // inside html: <script type="script/x-template"></script>
data(){
return {
count: 0
}
}
});Components
Component can accept props
Vue.component('TodoList', {
template: '#todo-list',
props: ['todos']
});Vue.component('TodoList', {
template: '#todo-list',
props: {
todos: {
type: Array,
required: true, //required
validator: value => { //custom validation
return true;
}
}}
});bad
good
Components
props can be assigned default values as well as custom validation
Vue.component('TodoList', {
template: '#todo-list',
props: {
todos: {
type: Array,
required: true, //required
default(){
return [] // Arrays, objects should be passed default function
},
validator: value => { //custom validation
return true;
}
}}
});Passing data to component
<todo-list :todos="todos"></todo-list>v-bind to pass data down via props
Component naming
- Always multi word to prevent conflicts
- Base components - used globally - they shoud start with Base, App or V
- Single instance component names - "The"
- Tightly coupled component names - make relationships clear
- Order of the words - start with highest level (general) words and end with descriptive and modifying words
- Using full worlds - use full worlds instead of abbreviation and shorthands
Component naming
<todo-list :todos="todos"></todo-list>Pascal or camel case converts to kebab-case
Vue.component('TodoList', {
template: '',
props: ['todos']
});Component registration
const TodoList = {
template: '#todo-list',
props: {
todos: Array
}
};
new Vue({
...
components: {
TodoList
}
})Vue.component('TodoList', {
template: '',
props: ['todos']
});Global registration
Local registration
Events communication
<todo-list :items="items" @update="updateItemArray"></todo-list>items array on data is passed down as prop
custom event emitted from todo-list component method
this.$emit("update", this.items.map((item, index) =>
index === itemIndex ? value : item
));Component v-model
v-model on a component in order to work expects component to emit input event and get value as a prop
You can change that:
Vue.component('base-checkbox', {
model: {
prop: 'checked',
event: 'change'
},
props: {
checked: Boolean
},
template: `
<input
type="checkbox"
v-bind:checked="checked"
v-on:change="$emit('change', $event.target.checked)"
>
`
})Exercise 1.1
convert exercise 1 to components
Single file components
in Vue we have .vue files which contain both template, code and styles and which we can load with vue-loader and relevant style loader
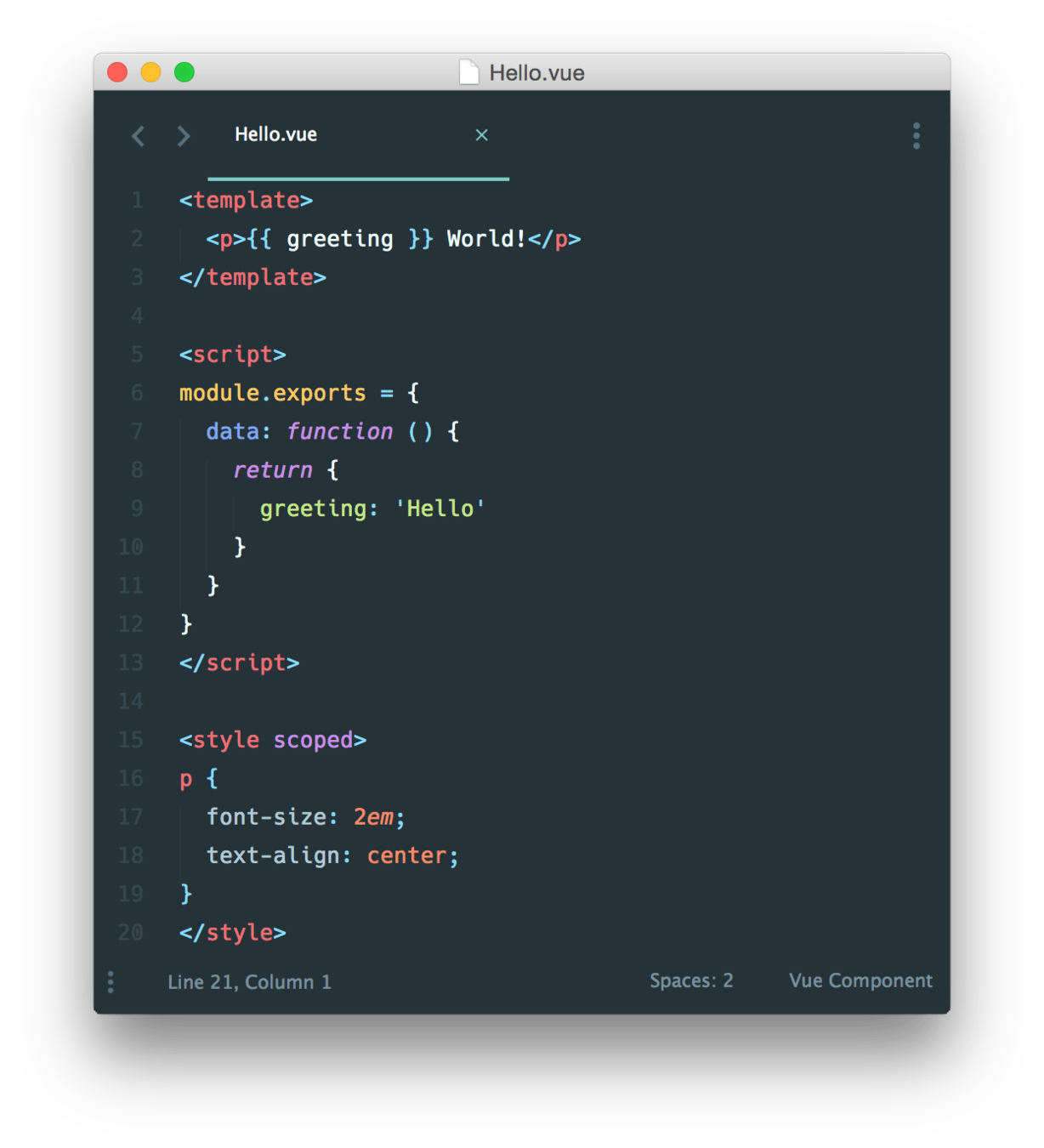
template
code
styles that are applied through assigning data-v-hash attribute
Let's convert our todo app to webpack
install webpack
yarn add --dev webpack webpack-cli vue
create src/index.js and src/App.vue files
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
})<template>
<div>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
</div>
</template>index.js
App.vue
create basic webpack config
'use strict'
const { VueLoaderPlugin } = require('vue-loader')
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
use: 'vue-loader'
}
]
},
plugins: [
new VueLoaderPlugin()
]
}yarn add --dev vue-loader vue-template-compiler vue-style-loader css-loaderadd build script
"build": "webpack --config build/webpack.config.dev.js"package.json
include script in index.html
<script src="dist/main.js" type="text/javascript"></script>Hot reload
"dev": "webpack-dev-server --config webpack.config.dev.js"package.json
add HMR and HTML plugins to webpack config
yarn add --dev webpack-dev-server html-webpack-pluginnew webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'index.html',
template: 'index.html',
inject: true
})remove dist script reference from index.html
Styles
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin')
// ...
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'main.css'
})
]add mini-css-extract plugin (nice to have)
yarn add --dev css-loader vue-style-loader mini-css-extract-pluginolder browsers
{
test: /\.js$/,
use: 'babel-loader'
}add loader
yarn add --dev @babel/core babel-loader @babel/preset-envadd .babelrc file
{
"presets": [
["@babel/env", {
"modules": false,
"targets": {
"browsers": ["> 1%", "last 2 versions", "not ie <= 8"]
}
}]
]
}Static files
yarn add --dev copy-webpack-pluginadd plugin to webpack.config
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
//..
const path = require('path')
function resolve (dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
plugins: [
new CopyWebpackPlugin([{
from: resolve('static/img'),
to: resolve('dist/static/img'),
toType: 'dir'
}])
]Excercise 2

Vue CLI
A must CLI for prototyping, maintaining Vue projects, installing plugins etc
@vue/cli
@vue/cli-service
@vue/cli-plugin-
CLI tool with scaffolding commands and vue ui command
based on webpack and webpack-dev-server
set of plugins that are loaded automatically by @vue-cli-service
Vue CLI
vue serve
vue create
vue ui
Recommended to use only for prototyping - loads .vue files with zero config
Creates new Vue project prompting for different plugins etc. You can use it on an existing directory.
Present neat ui to manage your vue projects
npm install -g @vue/cli-service-global
# or
yarn global add @vue/cli-service-global
vue add plugin-name
invokes plugin generator and resolves vue plugin
How to change Vue CLI configuration
vue-cli-service automatically loads optional vue.config.js file where you can override any configuration
publicPath - equivalent to webpacks output.publicPath
outputDir - equivalent to webpacks output.path
assetsDir - directive related to outputDir to nest generated static assets
indexPath - path of index.html relative to outputDir
pages - run in multipage mode
runtimeCompiler - to use template options in components (increase 30% bundle size)
configureWebpack - object that will be merged into webpack.config
chainWebpack - powered by webpack-chain and allows more fine grained control
devServer - all options of webpack dev server
chainWebpack: config => {
config
.plugin('html')
.tap(args => {
args[0].template = path.join(__dirname,'index.html')
return args
})
}Vue in VSCode
Vetur extension
Single file components

template need to have one wrapping element
data must be a function
scoped styles that are applied through assigning data-v-hash attributes. not scoped are applied globally
Styles gotchas
use <style scoped> in your components
classes and styles passed to components are applied to wrapping element
Excercise 2.1
change our Todo app to Vue CLI
chainWebpack: config => {
config
.plugin('html')
.tap(args => {
args[0].template = path.join(__dirname,'index.html')
return args
})
}Nested components
import component and register it locally
use base component
Automatic global registration
import Vue from 'vue'
import upperFirst from 'lodash/upperFirst'
import camelCase from 'lodash/camelCase'
const requireComponent = require.context(
// The relative path of the components folder
'./components',
// Whether or not to look in subfolders
false,
// The regular expression used to match base component filenames
/Base[A-Z]\w+\.(vue|js)$/
)
requireComponent.keys().forEach(fileName => {
// Get component config
const componentConfig = requireComponent(fileName)
// Get PascalCase name of component
const componentName = upperFirst(
camelCase(
// Gets the file name regardless of folder depth
fileName
.split('/')
.pop()
.replace(/\.\w+$/, '')
)
)
// Register component globally
Vue.component(
componentName,
// Look for the component options on `.default`, which will
// exist if the component was exported with `export default`,
// otherwise fall back to module's root.
componentConfig.default || componentConfig
)
})We want to have BaseComponents as global and the rest as local
Slots
in child component use <slot></slot> as a placeholder
In the parent component use v-slot directive on an element to put inside the slot
named slots
<slot name="slotName"></slot>
v-slot:slotName
in ParentComponent
ChildComponent
v-slot can be used only on template or component
default content
<slot name="slotName"> Default </slot>
v-slot:slotName
ParentComponent
ChildComponent
scoped slots
<slot name="slotName">
</slot>
v-slot:slotName="slotProps"
ParentComponent
ChildComponent
give parent access to child data
<slot :author="author" >
</slot>
v-slot:default="defaultSlotProps"
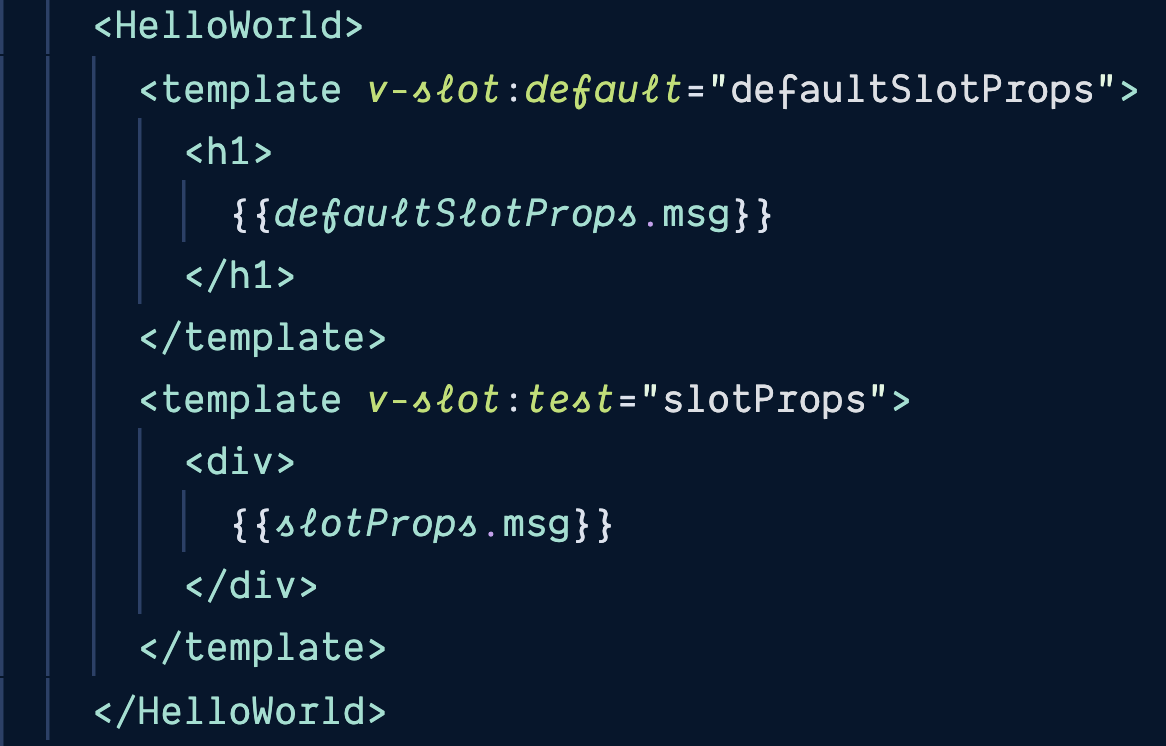
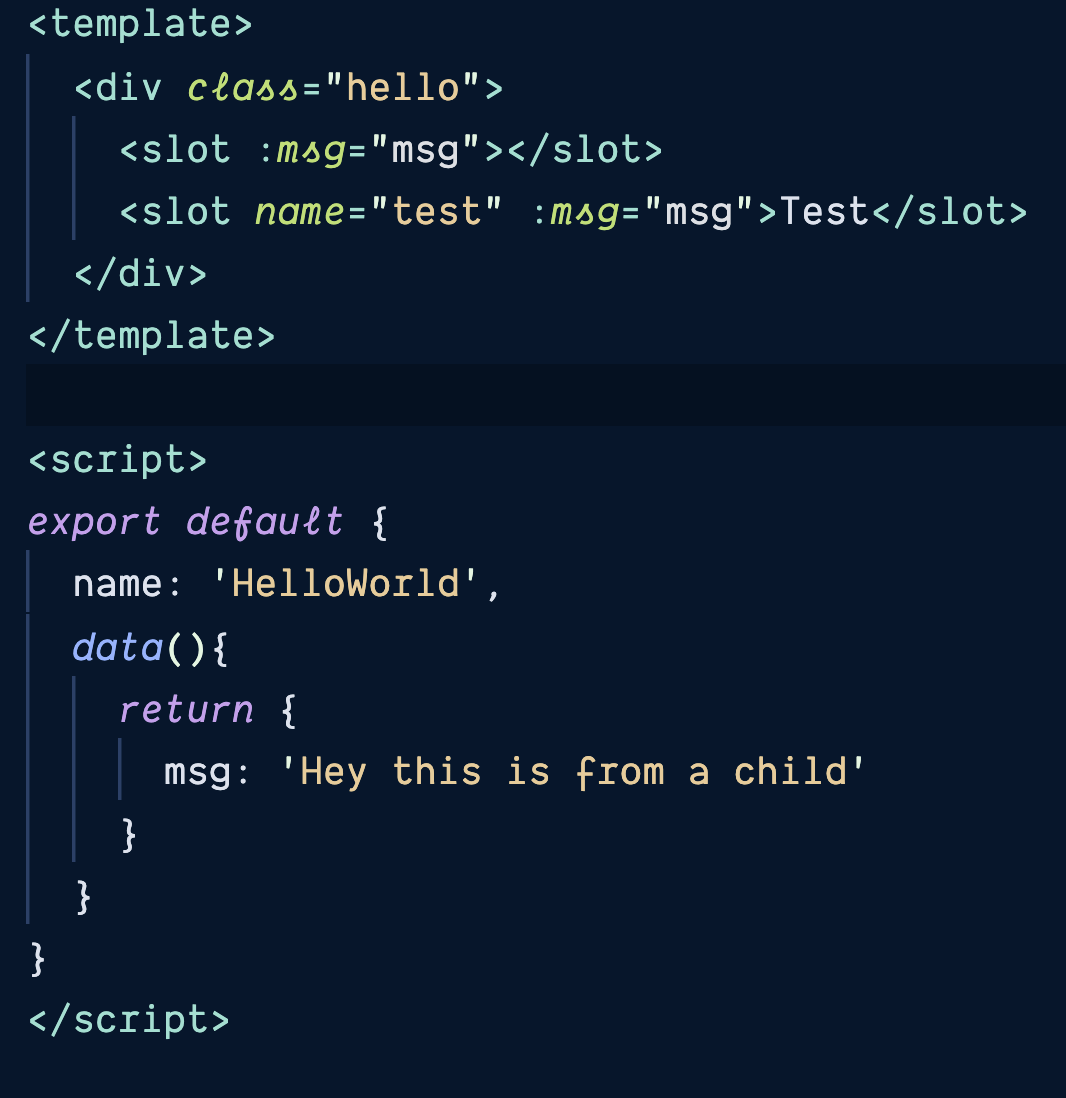
msg from child data
msg from child data
destructuring
<slot name="slotName">
</slot>
ParentComponent
ChildComponent
<slot :author="author" >
</slot>
v-slot:default="{ author }"
shorthand #
<slot name="slotName">
</slot>
ParentComponent
ChildComponent
<slot :author="author" >
</slot>
<template #default="{ author }">
<template #slotName>Content</template>
Components communication
EventBus.$emit('eventName', payload);
EventBus
emit event
export const EventBus = new Vue();
EventBus.$on('eventName', handler);
subscribe
EventBus.$off('eventName', handler);
remove listener
you can use $once to trigger event only once
Dynamic components
You can pass components dynamically in the following manner:
build in Vue component
<component is="componentPropertyObject"></component>
bind to component property object
keeping components alive
Dynamic components are destroyed and recreated when new component is passed to is prop. Use <keep-alive></keep-alive> to keep components alive
<keep-alive> <component is="componentPropertyObject"></component>
</keep-alive
keep-alive also introduces activated and deactivated lifecycle hooks
Async components
components can be loaded asynchronously using the following syntax
const BelowFold = () => import(
/* webpackChunkName: "below-fold" */ './BelowFold.vue'
);
const AboveTheFold = () => import(
/* webpackChunkName: "modal" */ './AboveTheFold.vue'
);
//....
//
{
components: {
AboveTheFold,
BelowFold
}
}Lifecycle hooks patterns
beforeCreate() - runs before initialization data is not reactive yet, events hasn't been set up
created() - data is reactive, events can be accessed, templates and VDOM not mounted or rendered (API calls are usually done here)
beforeMount() - almost not used - do something before initial render
mounted() - component is rendered - you have access to reactive component, templates and VDOM (this.$el)
using it for API calls it's antipattern
use it for DOM access or integrating non Vue libs
beforeUpdate() - runs before update happens just before DOM rerenders. You can get there a new state of your reactive data before it rerenders
updated() - runs after DOM is rerendered (use if you need to access DOM after the change)
beforeDestroy() - runs just before component destruction. Used to get rid of any subscriptions. Component still presents here and fully working
destroyed() - everything is destroyed. Used for any last-minute cleanup
API
fetch / axios / vue-resource
create services/apiService.js
The main purpose is to encapsulate api calls in one single file and expose methods that will be accessed through components
import axios from 'axios'
const apiClient = axios.create({
baseURL: `http://localhost:3000`,
withCredentials: false, // This is the default
headers: {
Accept: 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
})
export default {
getEvents() {
return apiClient.get('/events')
}
}Excercise 3
Create a new project using vue-cli without vue-router or VueX
Create /views directory and inside Home and Blog component
Create BaseLayout component that will have header, footer and content slot and register it globally.
Create DummyNavigator component
navigator will get routes object prop
when routeChange event triggered navigator will switch displayed component based on provided prop
navigator will use history api to change browser url
Thanks and see you tomorrow
@VladimirNovick
Vue Workshop Day 1
By Vladimir Novick
Vue Workshop Day 1
VueJS Syntax, Bindings, Directives, Modifiers, Event Handling, Forms, Components, Webpack, Vue CLI,
- 97

