Linux part 1: Introduction
Background
What is Linux
Linux is, in simplest terms, is a freely distributed, cross-platform operating system based on Unix
Why Linux?

For developers
- Many open source applications/libraries are developed natively for Linux.
- Many development tools like GIT is developed natively for Linux
- Better command line
- Better window management & virtual desktops
- Environment variable
- Package managers apt-get | rpm
- Many different flavors of Linux that there's bound to be one you fall in love with.
Why let Microsoft give you a window, when Linux can give you a House?

For servers
- Stability
- Secure
- Performance
- Cost effective
- Distributed Apps
- PaaS

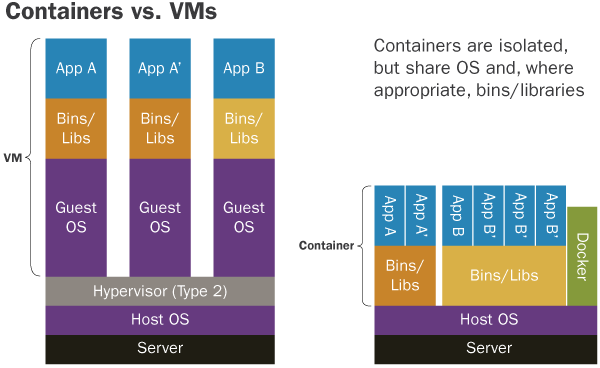


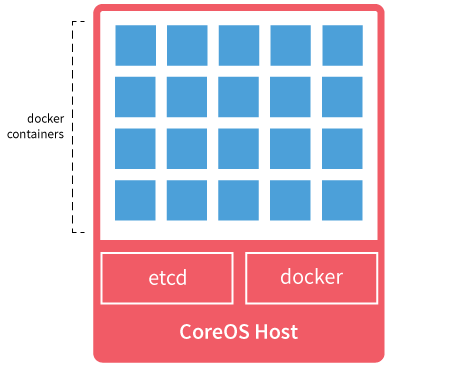
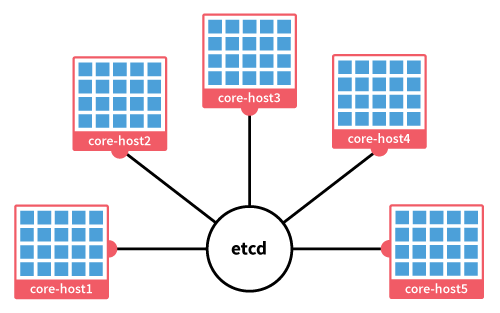

- A minimal Operating System
- Manage high availability of docker containers
- Clustered by default
- Painless auto updating
Desktop Environment
Unity
kde
Gnome
KDE
Cinnamon
Mate
xfce
Popular Distro
ubuntu
redhat/centOS
openSUSE
linux mint
elementary OS

Getting started
Installation: Dual boot
- Install Windows first
- Backup your files into external (just in case!)
- Create new partition for Linux (take note of the size)
- Create a bootable usb of your chosen linux distro
- Boot into USB & click install now -> 'Something else'
- Delete the new partition
- Create 3 new partitions:
- root (for root user): 10~20gb
- swap space: double the amount of your RAM
- home (for your Documents etc): all your remaining
- Once installed, if Windows is not detected, open a terminal window and run:
sudo update-grub
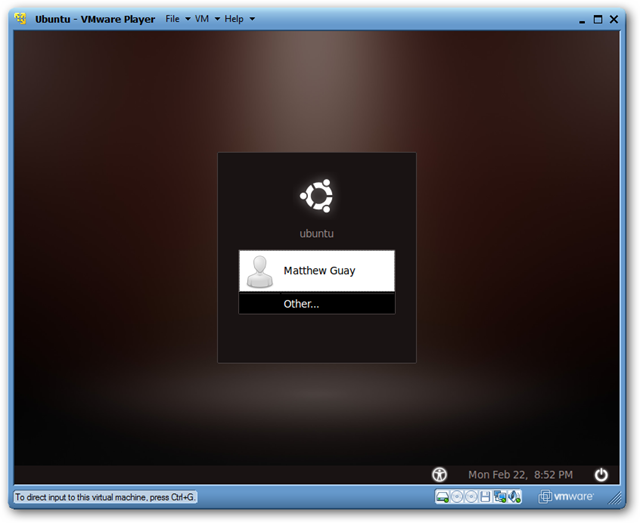
Installation: Virtualization
- Download & Install VM Player
- Open VMware Player, and choose “Create a New Virtual Machine.”
- Choose ISO image
- Create user
- Specify disk capacity
- Finish

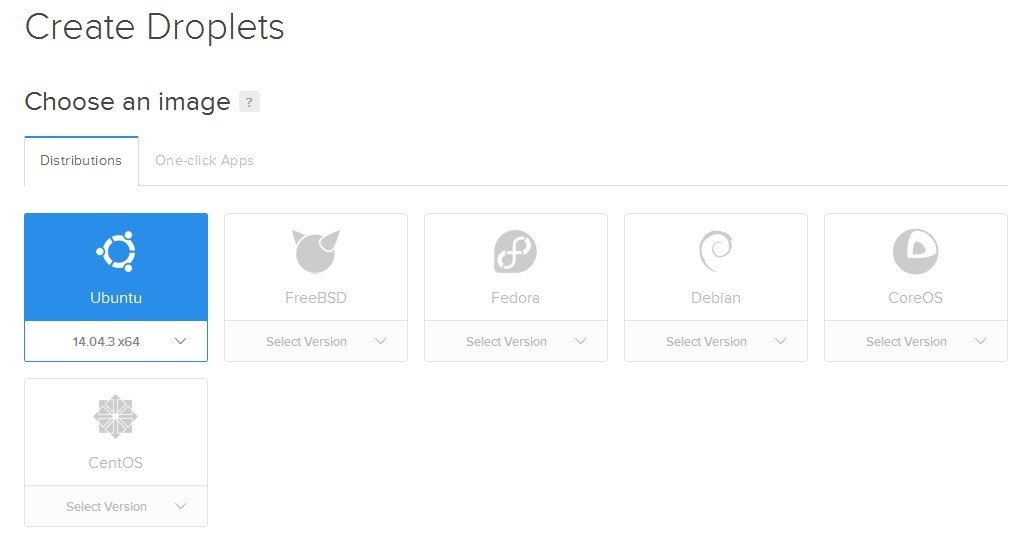
Installation: Cloud Hosting
- If you're not a member yet, use this link to get free $10 credit: Register
- Activate account & complete billing details
- Create a new droplet by choosing distro, size & data center
- Wait 55 seconds
- ???
- Done!

Basic Concept
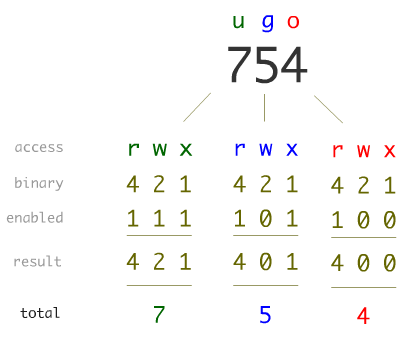
File Permission
Groups
- u : User: owner
- g : Group: other users in the same group
- a or o : Other: other users outside of the group
Types
- r : Read: 4
- w : Write: 2
- x : Execute: 1
Example

Option 1
To get 2nd output:
chmod u+x file1
chmod g-w file1
chmod a-r file1
To revert back to 1st:
chmod u-x file1
chmod g+w file1
chmod a+r file1
Option 2
To get 2nd output: chmod 740 file1
To revert back to 1st:
chmod 640 file1
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user group 1 2016-02-19 file1
-rwxr----- 1 user group 1 2016-02-19 file1
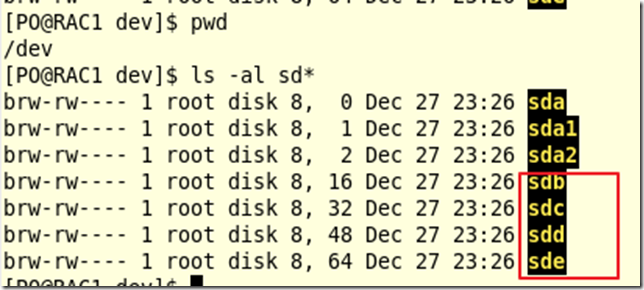
Devices Files
Working with files
Directory Operations
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| pwd | Print current directory |
| mkdir <dir> | Create a new directory |
| cd <dir> | Change directory |
| cd .. | Go up a directory |
| cd - | Toggle between last 2 directories |
| ls | List files in current directory |
ls options
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| -a | Show all including hidden |
| -R | Recursive list |
| -r | Reverse order |
| -t | Sort by last modified |
| -S | Sort by file size |
| -l | Long listing format |
| -h | Human readable format |
| -1 | One file per line |
| -m | Comma-seperated output |
| -Q | Quoted output |
File Command
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| rm <file> |
Delete file |
| rm -r <dir> |
Delete directory |
| rm -f <file> |
Force delete file |
| mv <file1> <file2> |
Rename or move file |
| cp <file1> <file2> |
Copy file 1 to file 2 |
| touch <file> |
Create or update file |
| cat file1 > logfile |
Standard |
| cat > <file> | Find all empty files in home directory |
Search Files
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| grep <string> <file> | Search for a given string in a file, with the following options: |
| -i | Case insensitive |
| -r | Recursive search |
| -v | Inverted search |
| -o | Show matched part of file only |
| find -iname "MyFile.c" | Find files in directory matching file name (case insensitive) |
| find -iname "MyFile.c" -exec md5sum {} \; | Execute commands on files found by the find command |
| find ~ -empty | Find all empty files in home directory |
Compression
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| tar cvf file.tar directory/ | Create a new tar archive |
| tar xvf file.tar | Extract from a tar archive |
| gzip test.txt | Create a *.gz compressed file |
| gzip -d test.txt.gz | Extract from a *.gz file |
| unzip test.zip | Extract a *.zip compressed file |
Pipes & IO Redirection

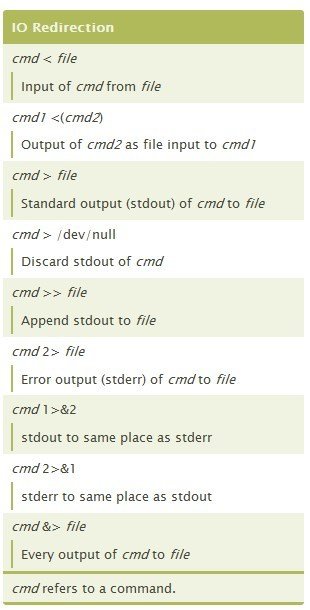
Cheat sheets:
Quiz Time!
Q1: Which of the following are Linux Distro ?
- A: Linux Mint
- B: KDE
- C: CoreOS
- D: Unity
- E: elementary OS
Q1: Which of the following are Linux Distro ?
- A: Linux Mint
- B: KDE
- C: CoreOS
- D: Unity
- E: elementary OS
Q2: How to set a file permission
-
owner: read, write & execute - group : read & execute only
- other: execute
Linux Introduction
By Wan Mohd Hafiz
Linux Introduction
- 653



