How does NodeJS works?
What is NodeJS
and why it is so different
JavaScript runtime built on Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine. Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient.
Background
- Released in 2009
- Nearly a commit a day
- Created by Ryan Dahl, for interactive web app with maximum throughput and efficiency
- Sponsored by Joyent, specialized in high-performance cloud computing
- Used by LinkedIn, eBay & PayPal
The Architecture
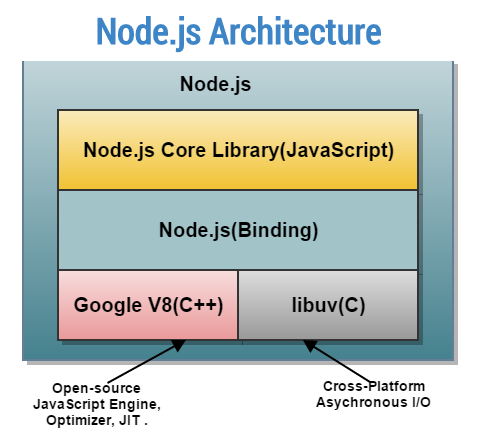
NodeJS is ..
- Very Fast in code execution
- Asynchronous & Event-driven
- Single-threaded, Non-blocking I/O calls
- High scalability
Single-threaded?
Isn't multi-threaded faster?
Not exactly!
Single vs Multi threaded
Clients
Threads
I/O operations
Assuming that each thread potentially has an accompanying 2 MB of memory with it, running on a system with 8 GB of RAM puts us at a theoretical maximum of 4000 concurrent connections, plus the cost of context-switching between threads.
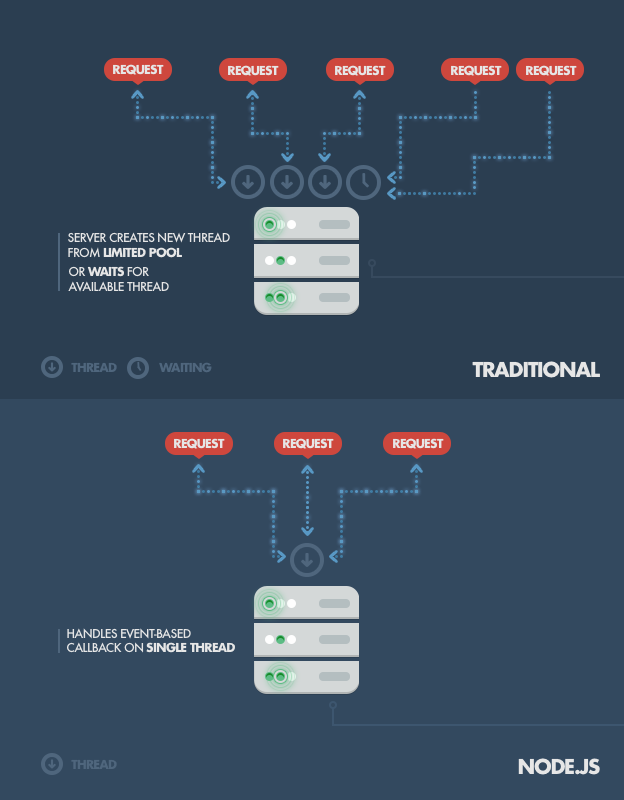
By avoiding all that, Node.js achieves scalability levels of over 1M concurrent connections.
Node Async
Call Stack & Event Loop
The Stack

Sync in browser is bad..
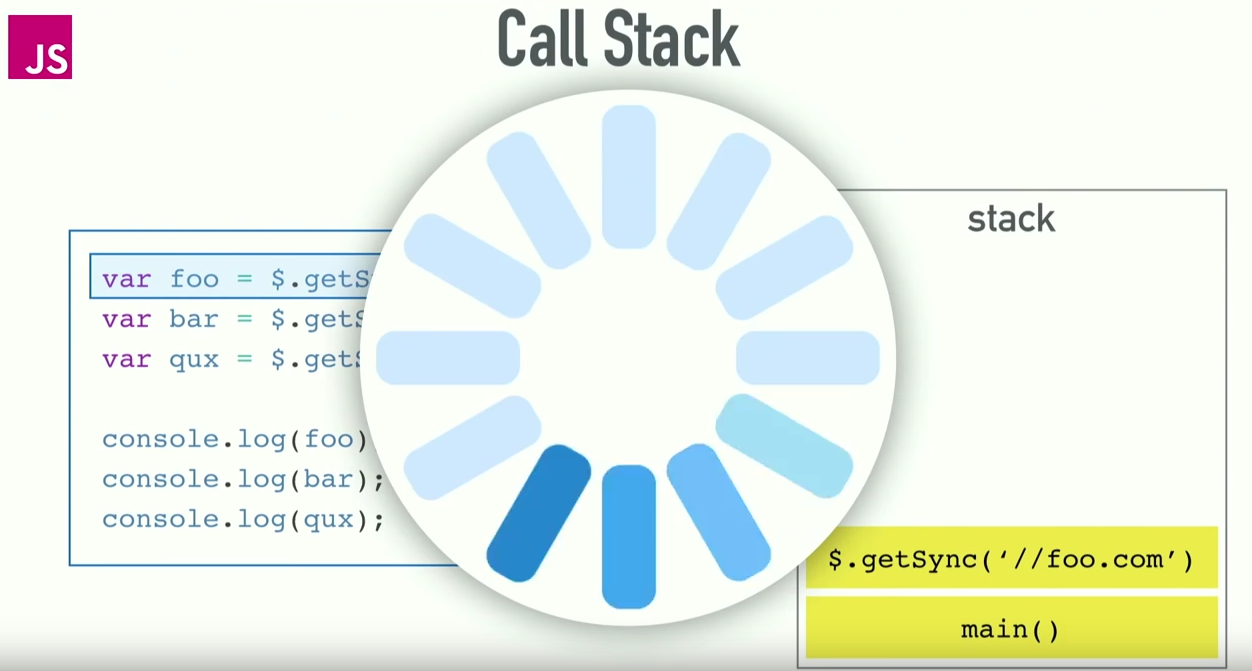

The solution?
Asynchronous Callbacks

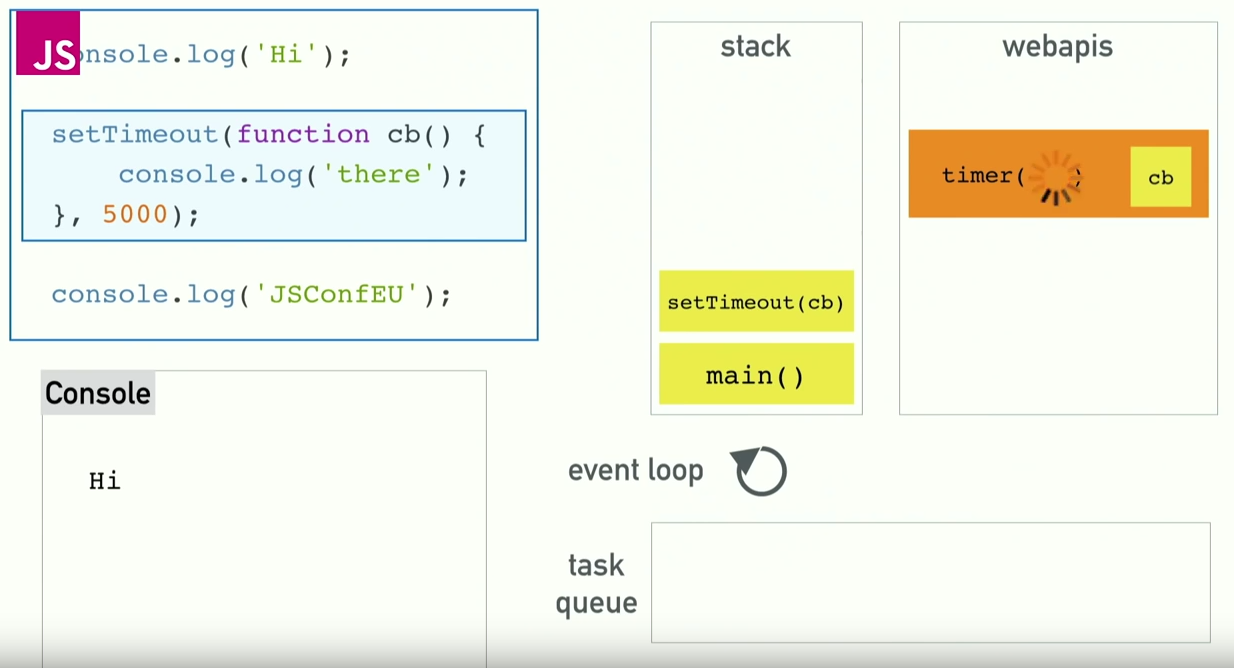
The Event Loop
When to use NodeJS
..and when not to?
NodeJS is perfect for
- I/O bound Applications
- Data Streaming Applications
- Data Intensive Real time Applications (DIRT)
- JSON APIs based Applications
- Single Page Applications
NodeJS is not for
CPU intensive applications
How does NodeJS works?
By Wan Mohd Hafiz
How does NodeJS works?
- 527




