Computational Linguistics
What is linguistics?
-
The study of language and its structure
-
Includes the study of phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, pragmatics, etc.
Uses
- Sociolinguistics - sociology
- Historical linguistics - history
- Neurolinguistics - neurology
- Forensic linguistics - forensics
Computational Linguistics
-
Modeling natural language from a computational perspective
-
Letting a computer make sense of human language

How important is computational linguistics?



Syntax Trees
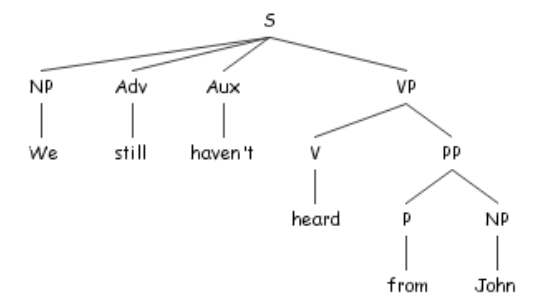
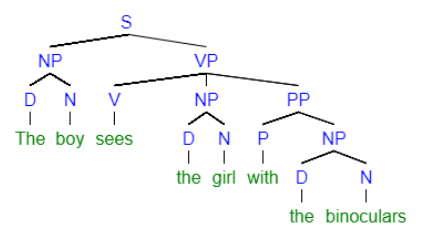
What is a syntax tree?
- Aka parse tree aka parsing tree aka derivation tree
- Represents the syntactic structure of a sentence
Uses
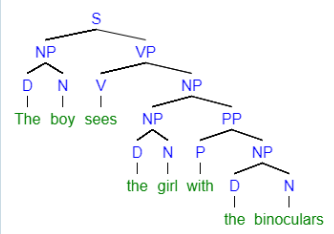
- Clears up ambiguity in meaning
- “The boy sees the girl with the binoculars”
- Determine syntactically correct sentences
- Computational linguistics: processing sentences / generating sentences
Syntax vs Grammar
Syntax
the rules of sentence structure
Grammar
the rules of a language in general, including syntax, morphology (rules of a word), etc.
Making a syntax tree
Define a set of syntax rules
- S → NP VP
- NP → (D) (AP) N (PP)
- NP → NP Conj. NP
- VP → V (NP) (PP)
- AP → Adj.
- AP → AP Conj. AP
- PP → P (NP)
Categorize words
- N: cat
- N: dog
- N: bone
- V: sees
- D: the
- D: a
- Adj.: big
- P: with
- Conj.: and
S - sentence NP - noun phrase VP - verb phrase
AP - adjective phrase PP - preposition phrase
N - noun V - verb D/Det. - determiner Adj. - adjective
P/Prep. - preposition Conj. - conjunction
"The gigantic yellow bee worried Maxine."
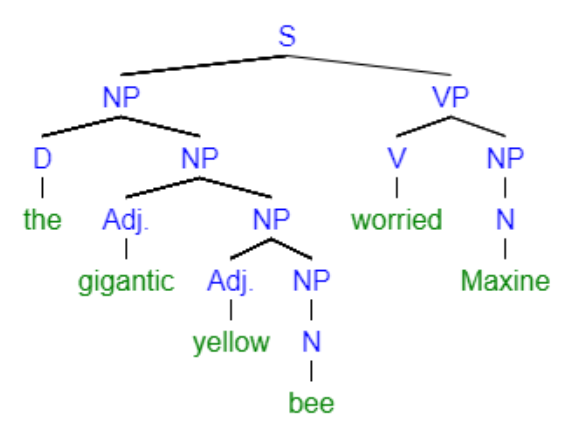
Recursion
Recursion:
Defining a term in terms of itself

Allows sentences to be extended infinitely
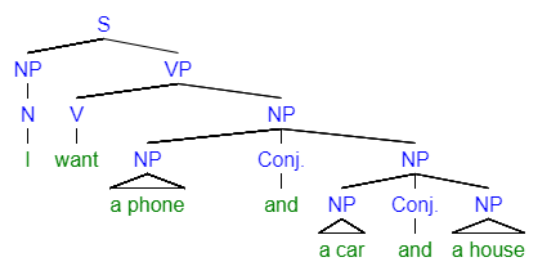
Pirahã: a language with no recursion
- No embedding: impossible to make sentences like "He really knows how to talk about making arrows"


Computational Linguistics
By Willie Jeng
Computational Linguistics
- 240



