C++
自我介紹
成電38th教學 吳承樺
講太快直接舉手問我
害羞的用slido也可以
有任何問題也都可以私訊問我

Index
- 電腦環境配置
- 基本架構
- 變數&&輸入輸出
- 運算子
- if else
- for while
- 陣列
- 函式
電腦環境
做好寫程式的準備
IDE
也就是你寫程式的地方
編譯器會將你寫的"人話"
翻譯成機器語言給電腦執行
1.Code::Blocks
優點:
1.APCS用
2.熟悉後好用
3.我常用
缺點:
1.在家安裝有點麻煩,要調設定
2. Visual Studio Code
優點:
除錯功能佳
缺點:
環境設定複雜

3.Dev-C++
優點:
非常容易使用
缺點:
老
舊

現在把Code::Blocks打開
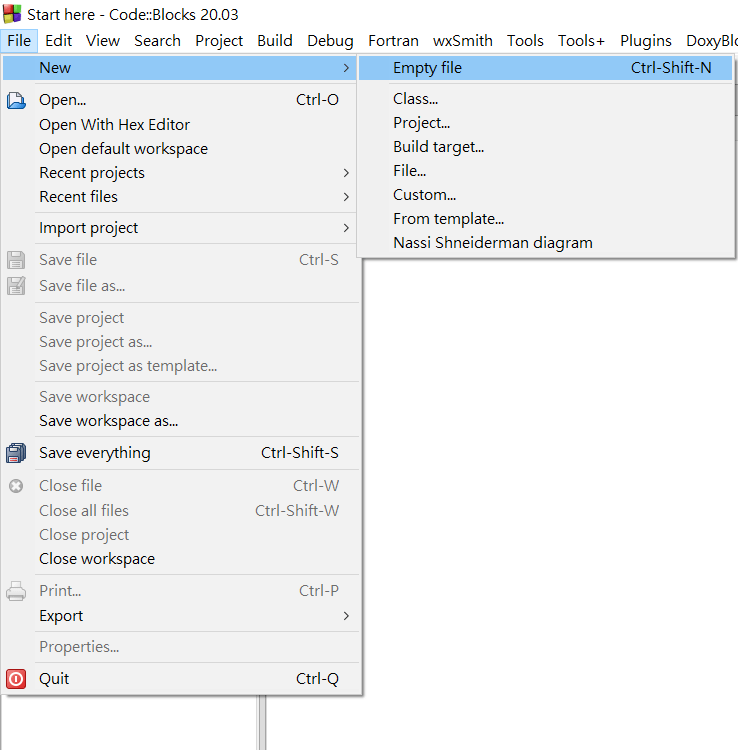
點左上角創立一個新檔案
現在把Code::Blocks打開
點擊這個來執行並存檔

建立檔案時記得要在檔名後加上.cpp
不然他預設是.c檔
前置作業完成!
基本架構
開始寫程式囉
第一個程式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "hello, world" << endl;
return 0;
}
第一個程式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "hello, world" << endl;
return 0;
}
2.設定命名空間
標準函式庫被放在std的命名空間
std::cout<<....
每一行都要打很麻煩
第一個程式
3.main函式
大括號內包著你要做的事
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "hello, world" << endl;
return 0;
}
第一個程式
4.輸出
讓程式印出結果
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "hello, world" << endl;
return 0;
}
第一個程式
5.return 0;
回傳0
程式的終點
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "hello, world" << endl;
return 0;
}
先去試試吧
有空的完成d483

成功之後應該長這樣
補充:
萬用標頭檔#include<bits/stdc++.h>
裡面包含競程99%要用的工具
強烈建議熟讀
裡面有題目
都去寫一次
變數&&輸入輸出
開始寫程式囉
變數Variable
用來存放資料的空間
就像數學的x,y一樣
在程式執行的時候可做運算和更改
資料型態
| 變數型別 | 中文說明 | 舉例 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 整數 | 1、2、3 |
| long long | 長整數 | 1000000000000000000 |
| float(不要用) | 小數(浮點數) | 3.14 |
| double | 長小數(雙精度浮點數) | 3.14159 |
| char | 字元 | 'a'、'b'、'c' |
| string | 字串 | "hello world" |
| bool | 布林 | true、false |
非零即為真
宣告
創造一個變數
方式:
資料型別 變數名稱=值;
宣告
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;//先宣告一個叫做a的整數型態變數
a=1;//再賦值
int b=1;//宣告b即賦值
}
在程式世界中"="不是等於的意思
而是指派
如上例:將1(值)指派給a(變數)
變數名稱
不能使用保留字(int,char),特殊字(&,%)
字元用' '
字串用" "
不能使用數字當開頭(123a)
大小寫是不一樣的(Apple!=apple)
盡量與變數意義相關(不然其他人可能看不懂)
輸入input
cin>>變數;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
cin>>a;//將輸入的值賦予a
}
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c//連續輸入3個每個輸入值以空格或換行分開
輸出output
cout<<變數;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=1;
cout<<a<<'\n';
}
輸出
變數
換行
換行有endl跟"\n"兩種
"\n"較快 競程用
endl可以清緩存 大專案用
小試身手
AC code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
cin>>s;
cout<<"hello, "<<s;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s1,s2;
cin>>s1>>s2;
cout<<s1<<" and "<<s2<<" "<<"sitting in the tree";
}
a001
c726
運算子
+ - * / %
1.指派運算子
int a=7,b;
b=a+3;
b=b+a;把等號右邊的值指派給左邊的
先計算右邊的算式的值
再指派給左邊的變數
2.算術運算子
| 運算子 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| + | 加 |
| ++ | 遞增 1 |
| - | 減 |
| -- | 遞減 1 |
| * | 乘 |
| / | 整除(無條件捨去) |
| % | 取餘數 |
先乘除後加減
()內先算
2.算術運算子
來搞懂++ --
int a=5;
cout<<a++<<'\n';
cout<<a<<'\n';int a=5;
cout<<++a<<'\n';
cout<<a<<'\n';5
6
6
6
6
int a=5;
cout<<a--<<'\n';
cout<<a<<'\n';int a=5;
cout<<--a<<'\n';
cout<<a<<'\n';5
4
4
4
4
++ --放後面 先用變數再改值 放前面則反之
2.算術運算子
來搞懂+= -=
int a=5;
a+=1;
cout<<a<<'\n';
6
int a=5;
a-=1;
cout<<a<<'\n';4
"a+=b" = "a=a+b"
3.比較運算子
| 運算子 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| == | 等於 |
| != | 不等於 |
| > | 大於 |
| < | 小於 |
| >= | 大於或等於 |
| <= | 小於或等於 |
!是不的意思
出來的結果為true/false
4.邏輯運算子
結果也是true/false
| A && B | B = true | B = false |
|---|---|---|
| A = true | true | false |
| A = false | false | false |
1.&& 且
2.|| 或
| A || B | B = true | B = false |
|---|---|---|
| A = true | true | true |
| A = false | true | false |
3.! 反
| A = true | A = false | |
|---|---|---|
| !A | false | true |
5 && 3 -> true
5 && 0 -> false
5 || 3 -> true
5 || 0 -> true
!0 -> true
!1 -> false
做做題目
AC code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<a+b;
}
a002
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int p;
cin>>p;
cout<<p/12*50+p%12*5;
}
d827
幾打+幾枝
if else
條件判斷
該如何解決此問題
如果分數為100分 輸出good
否則如果60分以上輸出pass
否則輸出bad
翻譯成程式語言
int score;
cin>>score;
if(score==100){
cout<<"good\n";
}
else if(score>=60){
cout<<"pass\n";
}
else{
cout<<"bad\n";
}如果
否則 如果
否則
if
if(判斷式){
要做的事;
}
如果判斷式成立(結果為真)
則執行大括號內的程式碼
如果只有一行可以省去大括號
if(判斷式)要做的事;
else if
else if(判斷式){
要做的事;
}
如果if判斷式不成立
會接著判斷()內
如果結果成立
則執行大括號內的程式碼
else
else{
要做的事;
}
如果上面所有判斷式皆不成立
會直接執行大括號內的程式碼
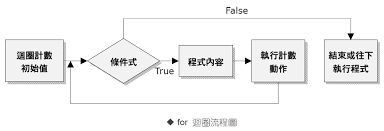
流程圖
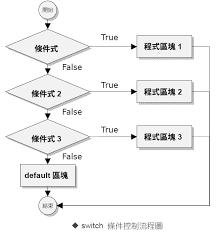
if
else if
else
else if
現在看得懂這段在幹嘛了吧
int score;
cin>>score;
if(score==100){
cout<<"good\n";
}
else if(score>=60){
cout<<"pass\n";
}
else{
cout<<"bad\n";
}score 100 70 30
if
else if
else
good
X
X
pass
X
X
X
X
bad
題目
AC code
a799
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n<0)n=-n;
cout<<n;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<abs(n);
}
補充:abs(數字) 是絕對值的意思
AC code
d064
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n%2){
cout<<"Odd";
}
else{
cout<<"Even";
}
}
AC code
a003
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m,d;
cin>>m>>d;
int s=(m*2+d)%3;
if(s==0){
cout<<"普通";
}
else if(s==1){
cout<<"吉";
}
else{
cout<<"大吉";
}
}
AC code
d068
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int w;
cin>>w;
if(w>50)w--;
cout<<w;
}
AC code
m286
有點難
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
if(n%m==0){
cout<<"整數 "<<n/m;
}
else if(n<m){
cout<<"真分數 "<<n<<"/"<<m;
}
else{
cout<<"帶分數 "<<n/m<<' '<<n%m<<"/"<<m;
}
}
for while
迴圈
輸出1到5?
簡單啊
cout<<1<<'\n';
cout<<2<<'\n';
cout<<3<<'\n';
cout<<4<<'\n';
cout<<5<<'\n';太過繁瑣
如果要你輸出1到100呢?
用for!!!
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
cout<<i<<'\n';
}
for(設定計數器;進入迴圈條件;改變計數器){
每次要做的事;
}
順序
for(A;B;D){
C;
}
1.迴圈一開始執行A
2.判斷B是否為真
3.執行C
4.執行D
5.接下來重複234
6.B為false 結束迴圈
for(設定計數器;進入迴圈條件;改變計數器){
每次要做的事;
}
順序
for(A;B;D){
C;
}
A B C D
手動看一次
for(A;B;D){
C;
}
1.迴圈一開始變數i=1
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
cout<<i<<'\n';
}
2.判斷i<=5是否為真
3.執行cout<<變數i
4.執行i遞增
5.重複234
6.i>5結束迴圈
注意事項
for(初始條件;終止條件;每次結束要做的事){
每次要做的事;
}
1.中間是用分號
2.注意終止條件要達成
迴圈才會停止
否則無窮迴圈
停不下來
視覺化
可以看得更清楚
while
在判斷式成立下執行
當判斷式成立時
執行大括號內的程式碼
直到判斷式變false
while(條件式){
每次要做的事;
}
範例
印出1到5
注意while迴圈中要有能讓迴圈停止的條件
否則會while true
無窮迴圈
int i=1;
while(i<=5){
cout<<i<<'\n';
i++;
}
特殊用法
用來讀取不等的數
當變數收到輸入值後會回傳true
迴圈就會執行
如果沒辦法收到符合變數的值則為false
int 變數
while(cin>>變數){
執行的事;
}
continue
結束此次迴圈
for while皆可用
用一道題目來解釋
印出1到5 但不要印4
continue
可以自己試著用while寫寫看
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
if(i==4)continue;
cout<<i<<'\n';
}當i等於4 跳過迴圈
break
for while 皆可用
強制結束此層迴圈
範例
for(int i=1;i<10;i++){
if(i==6)break;
cout<<i<<'\n';
}當i等於6 迴圈終止
學到這裡
有寫不完的題目等著你
AC code
a147
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin>>n && n){
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(i%7==0)continue;
cout<<i<<' ';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
}
AC code
b971
這題有點難
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int st,ed,d;
cin>>st>>ed>>d;
for(int i=st;i!=ed+d;i+=d){
cout<<i<<' ';
}
}
AC code
d074
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int mx=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int s;
cin>>s;
if(s>mx)mx=s;
}
cout<<mx;
}
AC code
a038
這題難
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
if(!n)cout<<n;
while(n){
if(n%10)break;
n/=10;
}
while(n){
cout<<n%10;
n/=10;
}
}
%10可以取最後一位數字
進階
AC code
c418
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
cout<<'*';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
}
AC code
c419
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n-i-1;j++){
cout<<'_';
}
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
cout<<'*';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
}
AC code
c420
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n-i-1;j++){
cout<<'_';
}
for(int j=0;j<=i*2;j++){
cout<<'*';
}
for(int j=0;j<n-i-1;j++){
cout<<'_';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
}
陣列
如何存5個東西?
int a,b,c,d,e;拿5個變數再把值存進去
但是
如果5改成5000呢?
陣列
一段連續的記憶體
變數->箱子
陣列->一堆連起來的箱子
宣告
資料型態 陣列名稱[長度];
int arr[1005];
//宣告長度1005的陣列
int abc[4]={0,2,1,3};
//宣告長度4 分別為0,2,1,3
int ccc[4]={1,2};
//只賦值前兩個 其他補0
char b[114514];
//宣告字元陣列
陣列取值
陣列名稱[位置]
int arr[4]={0,1,2,3};
cout<<arr[1];輸出多少?
1
陣列的編號是從0開始
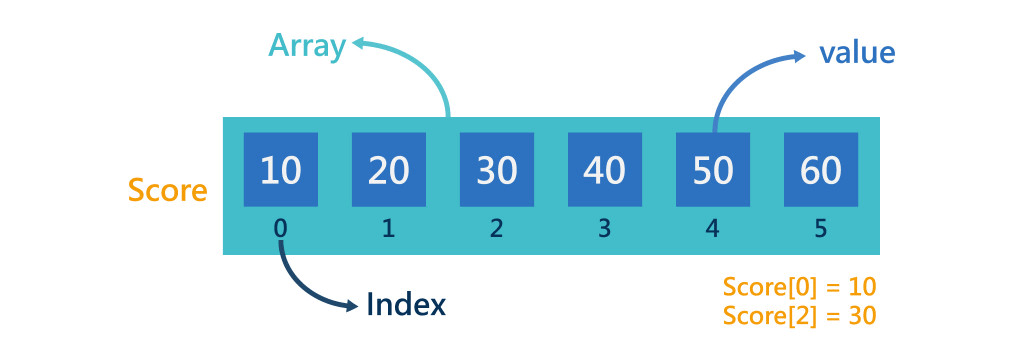
取值與修改
'=' 是指派的意思
把右邊的值放進陣列的格子中
int arr[4]={0,1,2,3};
cout<<arr[0]<<'\n';
arr[0]=4;
cout<<arr[0]<<'\n';
arr[0]+=9;
cout<<arr[0]<<'\n';
RE

練習題目常常遇到這種問題?
為什麼會發生
存取了超過陣列範圍的元素
int arr[4];
arr[-1]=5;
//不可是負的
arr[4]+=3;
//陣列大小是4 編號0~3在自己編譯器裡測試可能不會出錯!
(題目給的測資太大 陣列放不下)
競賽慣例
全域變數-可以暫時先理解成
在main()函式外的變數
有全域當然也有相反的
區域變數
int a;
//放在全域
int main(){
int b;
//放在區域
}競賽慣例
全域變數會自動初始化
數字=0,字串=""(空字串)
int a;
//a=0
int main(){
int b;
//b的值不一定
}可以有效避免很多錯誤
在全域可以開到幾千萬(1e8)的大小
但在區域只能幾百萬
競賽慣例
但是不是說開就開
他就算是免錢的電腦也會把它擋下來
通常我會設陣列的大小為題目的最大值+5
如果寫題目遇到RE
看看題目的範圍吧
或有沒有不小心戳到-1格了
多維陣列
陣列可以開多維
要取用裡面的值
int arr[3][3];//二維cin>>arr[0][0];
cout<<arr[1][2];假如有n列m行
[0][0] ~ [0][m-1]
...
[n-1][0] ~ [n-1][m-1]
題目時間
f345
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int arr[1000005];
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>arr[i];
}
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)cout<<arr[i]<<' ';
}
函式
函式
一台機器
可以接收輸入
回傳輸出
使用函式可以讓程式碼更簡潔
可讀性更高
函式
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//一般寫在main函式前
int add(int a, int b){
return a+b;
}
int main(){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
cout << add(x, y) << '\n';
}語法:
回傳值型態 函式名稱(參數) {
return 回傳值
}
函式
回傳值型態:
函式最前方 代表此函式回傳的東西是什麼樣的資料型態
任何型態都行 例:int char string bool...
int add(int a, int b){
return a+b;
}函式命名規則:
和變數一樣 不能用關鍵字
函式
回傳值:
return後面放回傳值
像上面的程式碼 是回傳a+b這個值
int add(int a, int b){
return a+b;
}不過 如果你只想讓函式做一些事
但不想有回傳值
函式
void:
不需要回傳值的函式
void print(int a, int b){
cout<<"a="<<a<<"b="<<b;
return;//可省略
}參數:
用括號包起來的部分
沒數量限制(也可以沒有)
但使用的時候數量要相同
函式主體
函式可以使用的變數
只有全域變數 參數 在函式內宣告的變數
在其他函式中宣告的不能用
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//一般寫在main函式前
int p=3;
void print(int a, int b){
int c=a+b;
cout<<p<<'\n';//全域變數
cout<<a<<'\n';//參數
cout<<c<<'\n';//函式內宣告
return a+b;
}
int main(){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
cout << print(x, y) << '\n';
}如何知道 變數使用什麼值
往上找第一個遇到的
變數的存活範圍:大括號
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a=1;
void print(int a){
cout<<a<<'\n';
}
void printt(){
cout<<a<<'\n';
}
int main(){
int a=3;
cout<<a<<'\n';
print(2);
printt();
}使用時機
精簡程式碼
把大問題變小問題
進行遞迴
為什麼要學
先大概了解在幹嘛
到時候遞迴才聽得懂
課程到這裡
不管甚麼問題都歡迎
C++(社課)
By wuchanghualeo
C++(社課)
- 250



