Spring Framework 4.x
Revolution or evolution?
Yegor Bondar
About the Presenter
Yegor Bondar
-
NIX Solutions Ltd.
-
Java Developer, Group Lead
-
Spring Framework fan :)
key Notes
In this talk We will try to cover:
-
Review new era of Spring Framework as a Platform
-
Provide steps to migrate your app from Spring 3.x to 4.x
-
Analyze and try new Spring Core and Web enhancements
- Java 8 and Spring 4.x

Spring.io
Spring INITIALIZR
Spring.IO platform provides easy-to-use portal to bootstrap new application from scratch
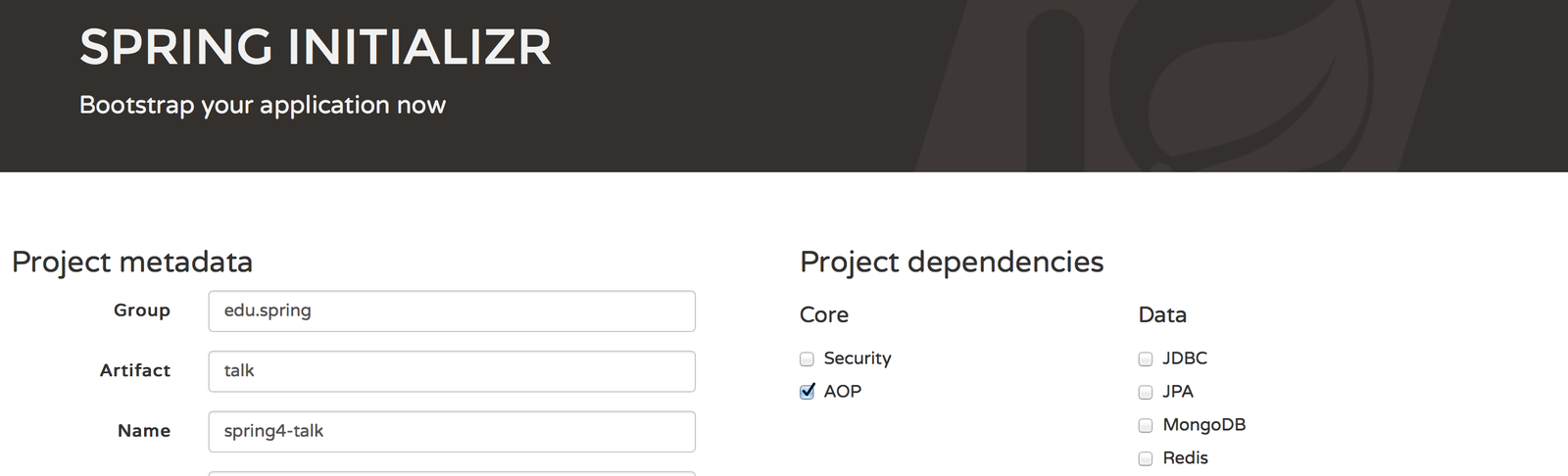
New environment - forget about legacy
-
Release Date: 01.10.2014
-
Current Release Version: 4.1.1.RELEASE
-
Latest Version: 4.1.2-SNAPSHOT
A new Java baseline
Java SE 6+ (minimum API level: JDK 6 u18, early 2010)
Java EE 6+ (Servlet 3.0 focused, Servlet 2.5 compatible in runtime)
All @Deprecated were removed
NEW ENVIRONMENT - FORGET ABOUT LEGACY
Common server generation
-
Tomcat 6.0.33+ (WebSocket support for 7.0.47 and 8.x)
-
Jetty 7.5+ (WebSocket support for 9.x)
-
JBoss 6.1+ (WebSocket support for WildFly 8.x)
Support for 3rd party libraries version 3 years back
Hibernate 3.6.9+, Ehcache 2.4.7+, Quartz 1.8.6+, Apache Tiles 2.2.2+, Hibernate Validator 4.3+
key Framework updates
New Spring sub-projects
-
spring-websocket & spring-messaging
-
spring-boot (makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that can you can "just run")
Java 8 support
-
lambdas and method references in Spring API (JdbcTemplate, MessagingTemplate)
-
new DateTime package support (@DateTimeFormat)
-
@Repeatable annotations
- method parameter names handling( javac -parameters )
KEY FRAMEWORK UPDATES
Support for key JavaEE 7 technologies (like JMS 2.0, JPA 2.1, Servlet 3.1, JCache etc.)
Kill an XML: Groovy Bean Definition DSL
Core container enhancements:
-
generic types as qualifier
-
meta-annotations
- @Conditional
- Objenesis library is included for proxies creation
- @Order annotation for bean collection injection
Spring web Updates
Spring MVC enhancements
-
@RestController
-
AsyncRestTemplate for developing non-blocking REST clients.
- New static resource handling in Spring 4.1
How to Migrate Your Project?
1. Increase version of Spring dependencies
If you already have Spring 3.1.x/3.2.x then just change version to 4.x AND make sure that you added spring-context dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>HOW TO MIGRATE YOUR PROJECT?
2. Update xml configuration namespaces
Make sure that you update your Spring.XSD namespaces:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">HOW TO MIGRATE YOUR PROJECT?
3. Ensure that your 3rd party libs are compatible with Spring 4.x
E.g. Update Jackson dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0</version>
</dependency>Spring core - new configuration
From Spring 3.x you can configure your beans and context with aim of Java (@Configuration, @Beans)
In Spring 4.x you can configure your beans and context with aim of Groovy
Spring 4.x provides new Groovy Bean DSL
Main entry point classes:
-
Bean definition reader: GroovyBeanDefinitionReader
-
Application Context: GenericGroovyApplicationContext
Groovy Bean Dsl - import
XML config:
<import resource="classpath:/context/gbeans.groovy">@Configuration
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource(value = "config.properties"),
@PropertySource(value = "config_repeat.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
})
@ImportResource(value = "classpath:/context/gbeans.groovy")
public class ApplicationConfiguration {...}<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:/context/gbeans.groovy</param-value>
</context-param>Spring xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="gdbean" class="edu.spring.talk.gbeans.GDBean">
<property name="name" value="testname"/>
<property name="desc" value="testdesc"/>
</bean>
</beans>Groovy bean dsl
package edu.spring.talk.gbeans import edu.spring.talk.gbeans.inner.IGADrivenBean beans { gdbean GDrivenBean, name:'testname', desc:'testdesc' gdbeanprops(GDrivenBean){name = 'propname' desc = '${test.desc}' //properties file driven } igadbean(IGADrivenBean) {bean -> bean.scope = 'prototype' reference = ref 'gdbeanprops' s_reference = gdbean } }
Bean definition: beanName(type, constructor-args)
Advanced Groovy Bean DSL
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource def defaultScope = 'prototype' def properties = new Properties() properties.load(new ClassPathResource('application.properties').inputStream); beans { xmlns([ctx:'http://www.springframework.org/schema/context']) ctx.'component-scan'('base-package':properties.basePackage)igadbean(IGADrivenBean) {bean -> bean.scope = defaultScope } }
Advanced groovy Bean dsl
-
You can use all common Groovy constructions
- Groovy DSL has an access to the all GroovyBeanDefenition fields
beans {
if (environment.activeProfiles.contains("dev")) {
gdbean GDrivenBean, name:'testname', desc:'testdesc'
} else {
gdbean GDrivenBean, name:'prodname', desc:'proddesc'
}
}protected GroovyBeanDefinitionReader invokeBeanDefiningClosure(Closure callable) {
callable.setDelegate(this);
callable.call();
finalizeDeferredProperties();
return this;
}Spring contexts - PERFORMANCE
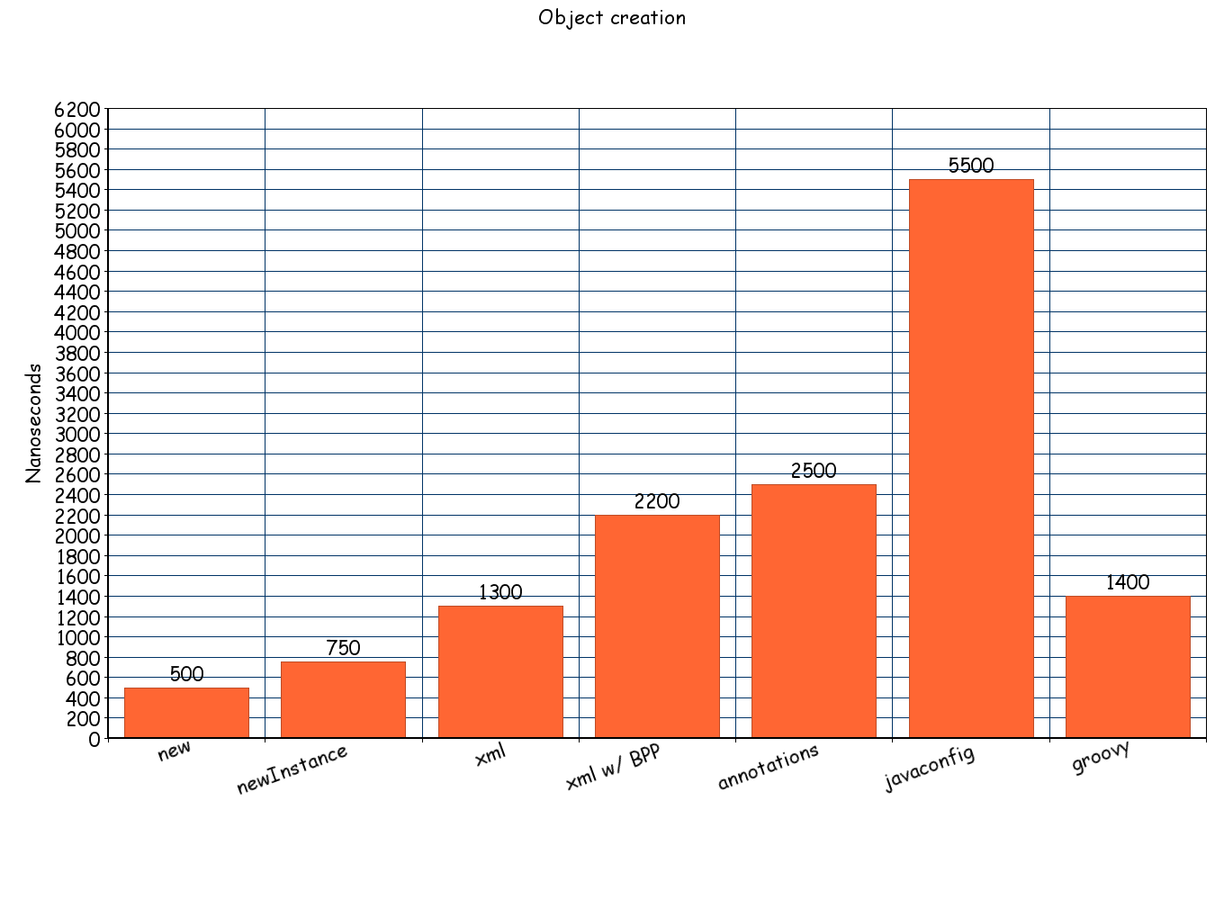
Spring 4.x & java 8
Spring 4.x has a lot of Java 8 Lambdas-ready interfaces in Templates helpers like:
-
JdbcTemplate (RowMapper, PreparedStatementSetter)
-
JmsTemplate (MessageCreator)
- TransactionTemplate (TransactionCallback)
JdbcTemplate jt = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
jt.query("SELECT name, age FROM person WHERE dep = ?",
ps -> {
ps.setString(1, "Sales");
},
(rs, rowNum) -> {
return new Person(rs.getString(1), rs.getInt(2));
});Spring 4.x & Java 8
Before Java 8
@PropertySources({ @PropertySource(value = "config.properties"), @PropertySource(value = "config_repeat.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = true) })public class Configuration {...}
Now w/ Java 8
@PropertySource("config.properties") @PropertySource("config_repeat.properties",ignoreResourceNotFound = true)public class Configuration {...}
Spring 4.x & java 8
Optional Controller handler parameters
@RequestMapping(value = "/bean/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public GDrivenBean getBean(@PathVariable Optional<String> name, @RequestParam Optional<String> desc){
bean.setName(name.orElseGet(() -> bean.getName()););
bean.setDesc(desc.orElse("default"));
return bean;
}@Bean
JDrivenBean jDrivenBean(@Qualifier("gdbean")Optional<GDrivenBean> gdbean){
return new JDrivenBean("t");
}Spring core - generic @Autowired
Input Case:
public class JDrivenBean<T> { T value; }@Component("jstringbean") public class JADrivenBean extends JDrivenBean<String> {...} @Component("jlongbean") public class JLongBean extends JDrivenBean<Long>{...}
<alias name="jbean" alias="jlongbean">
@Autowired
@Qualifier("jbean")
private JLongBean bean; @Autowired private JDrivenBean<String> genericBean; Spring core - metannotations
With the exception of value(), meta-annotated types may redeclare attributes from the source annotation to allow user customization.
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@RequestMapping("/webservice")
@RestController
@Scope("request")
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT)
public @interface WebServiceController {
Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW;
String [] headers() default {};
}
@WebServiceController
public class BeanRestController {...}Spring web Updates
@RestController - @Controller + @ResponseBody
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {...}
@RestController
public class BeanController{
@RequestMapping(value = "/get/bean", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public TestBean get(){...}
}
Spring web - Groovy templates
yieldUnescaped '<!DOCTYPE html>' html(lang:'en') { head { meta('http-equiv':'"Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"')title('My page') } body { p('This is an example of HTML contents') } }
The same as Freemarker and Velocity:
GroovyMarkupView/ViewResolver/Configurer

Spring web - Static resources handling (Teaser)
Major Spring Framework 4.1 feature
• Evolve existing ResourceHttpRequestHandler mechanism
• ResourceResolver and ResourceTransformer chains
• arbitrary resolution (version in URL path)
• ResourceUrlProvider
• prepare “public” resource URL (e.g. insert version)
Now you can do this:
/images/background-7fbe76cdac.png
conclusions
-
Spring 4.X is Production Ready - Migrate & Enjoy it!;
-
Groovy Bean DSL is killer of XML Configs;
-
You HAVE TO try new Spring projects: Spring Boot & Spring Messaging/WebSockets.
Useful resources:
Source code: https://bitbucket.org/yegorbondar/spring-4.x
Q & a
Thank you!
spring-4.x
By Yegor Bondar
spring-4.x
ThinkJava #1 Spring 4.x talk
- 4,699




