From Magnetic Susceptibility Imaging
To Principled Learned Proximal Operators
Zhenghan Fang


Kavli NDI Breakfast Meeting
February 7, 2024
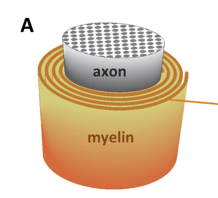
Imaging Tissue Magnetic Susceptibility in the Brain
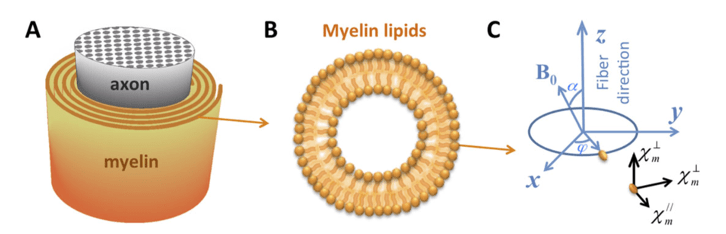
Susceptibility Anisotropy
- Fiber tracking
- Disease characterization
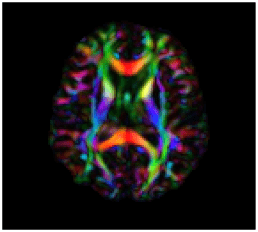
Susceptibility Tensor Imaging
Mean
Anisotropy
PEV

- Acquire data at multiple head orientations
- Time-consuming and uncomfortable
☹
Magnetic Susceptibility
- Degree to which a material is magnetized in an external magnetic field
DeepSTI: Towards STI Using Fewer Orientations
Solving the Inverse Problem
Fang Z, Lai KW, van Zijl P, Li X, Sulam J. DeepSTI: Towards tensor reconstruction using fewer orientations in susceptibility tensor imaging. Medical image analysis. 2023 Jul 1;87:102829.
Regularizer
Proximal Operator
DeepSTI
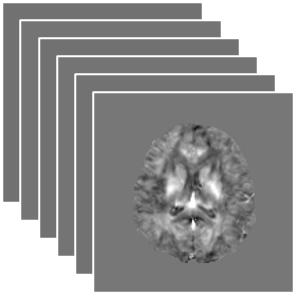
Dipole Inversion
MRI phase measurements
STI image
Inverse Problem in STI
Dipole Convolution
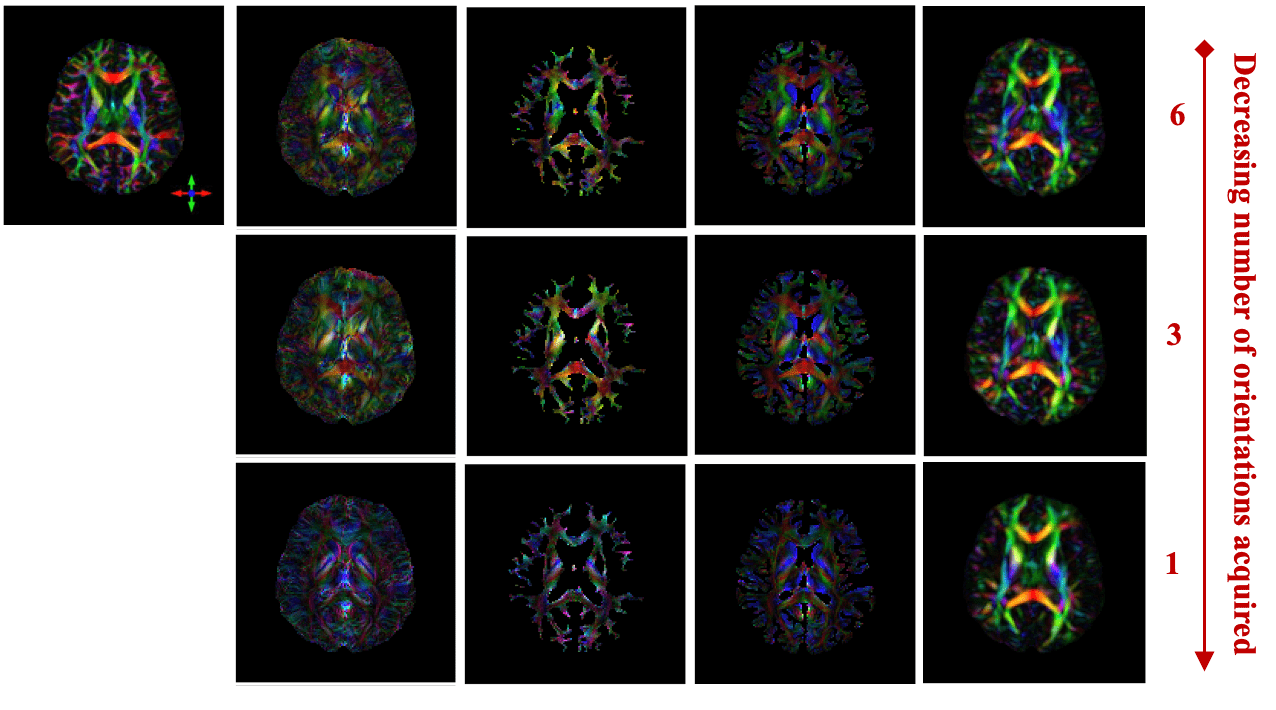
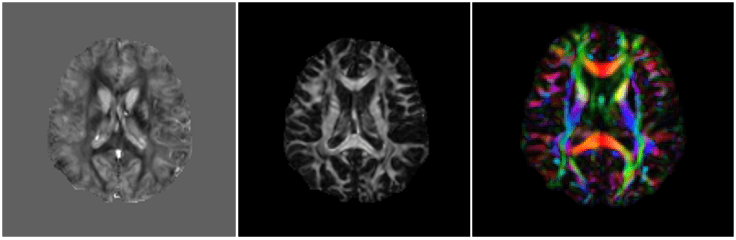
In Vivo Tensor Reconstruction using DeepSTI
DTI
STIimag
[Li et al.]
MMSR
[Li and Van Zijl]
aSTI+
[Shi et al.]
DeepSTI
(ours)
[1] Li et al, NMRB 2017; [2] Li and van Zijl, MRM, 2014;
[3] Cao et al., MRM, 2021; [4] Shi et al., IEEE JBHI, 2022
[5] Fang et al. Medical Image Analysis, 2023
In Vivo Fiber Tractography using DeepSTI
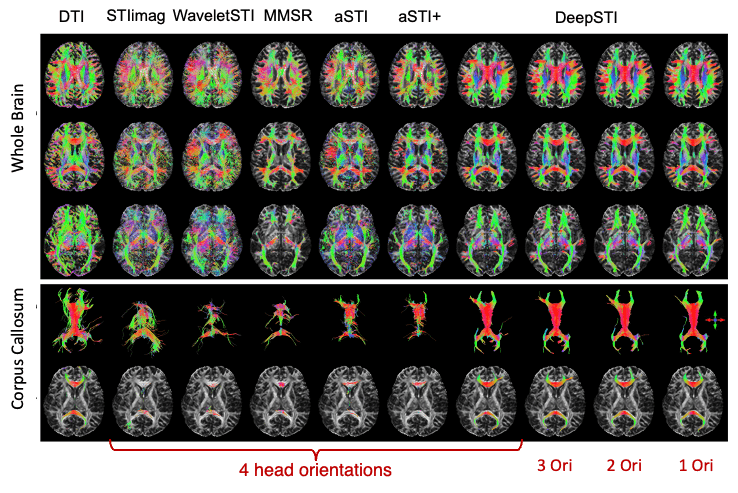
[1] Li et al, NMRB 2017; [2] Li and van Zijl, MRM, 2014;
[3] Cao et al., MRM, 2021; [4] Shi et al., IEEE JBHI, 2022
[5] Fang et al. Medical Image Analysis, 2023
Susceptibility Source Separation

Susceptibility Source Separation: WaveSep and DeepSepSTI


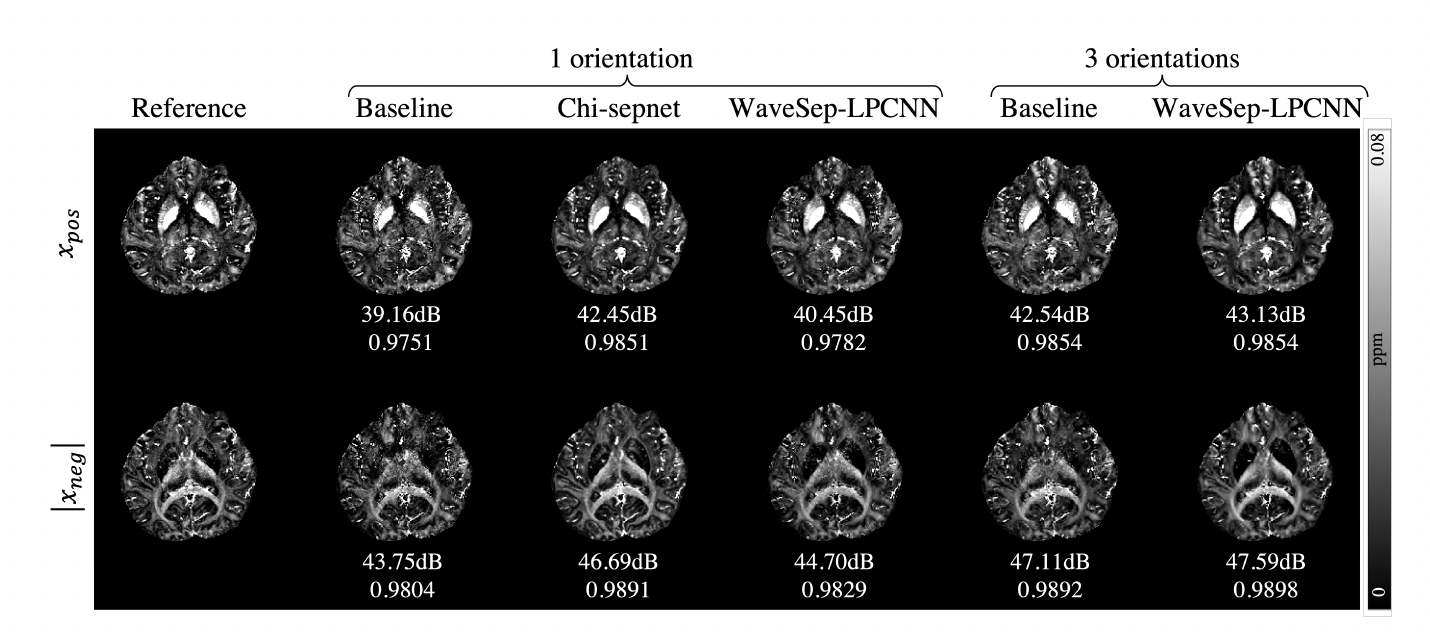
In vivo Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) Separation Result from WaveSep
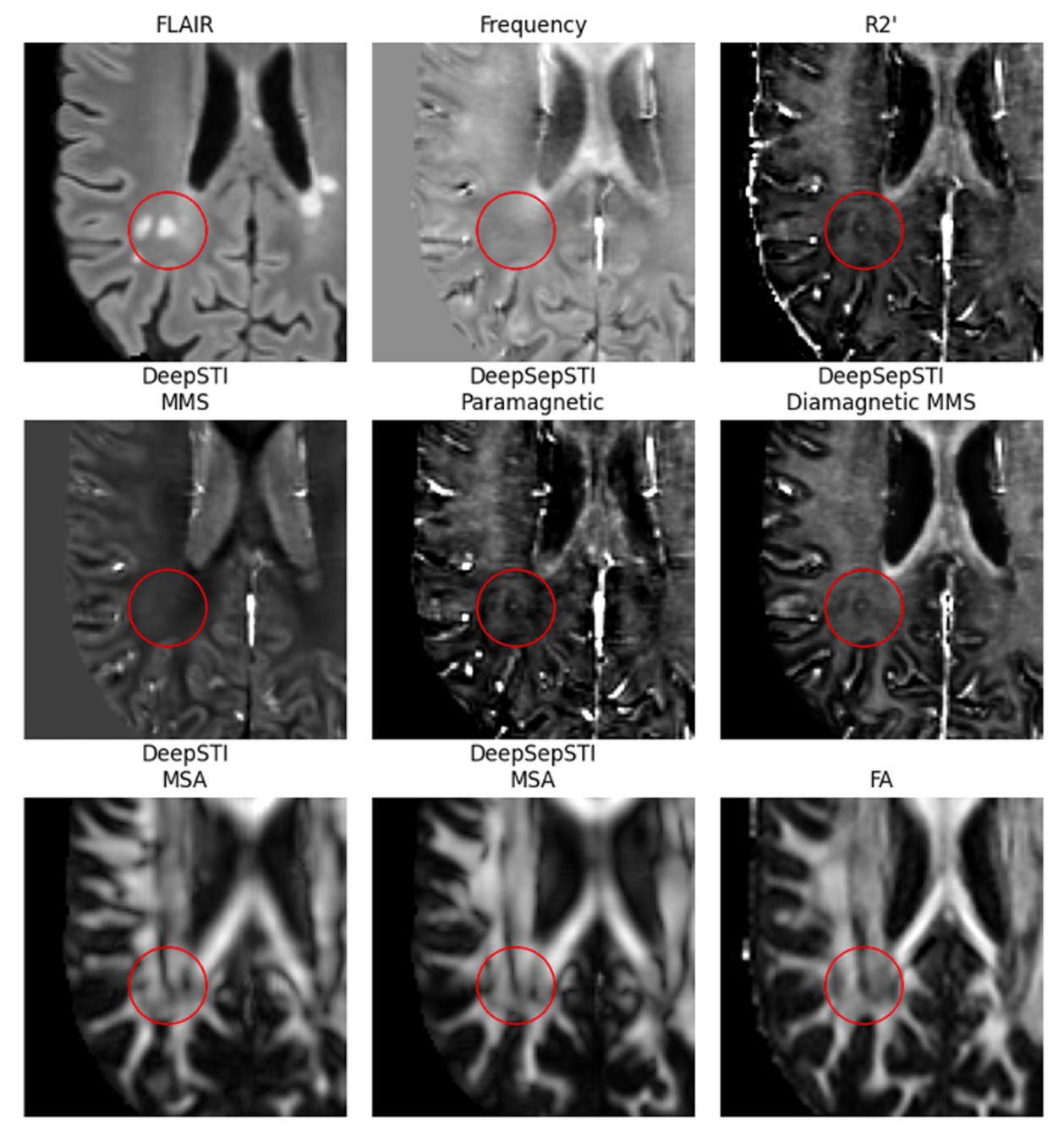
In vivo STI Separation Result from DeepSepSTI on a Multiple Sclerosis Patient
- WaveSep: decouple susceptibility estimation and source separation
- DeepSepSTI: joint susceptibility estimation and source separation
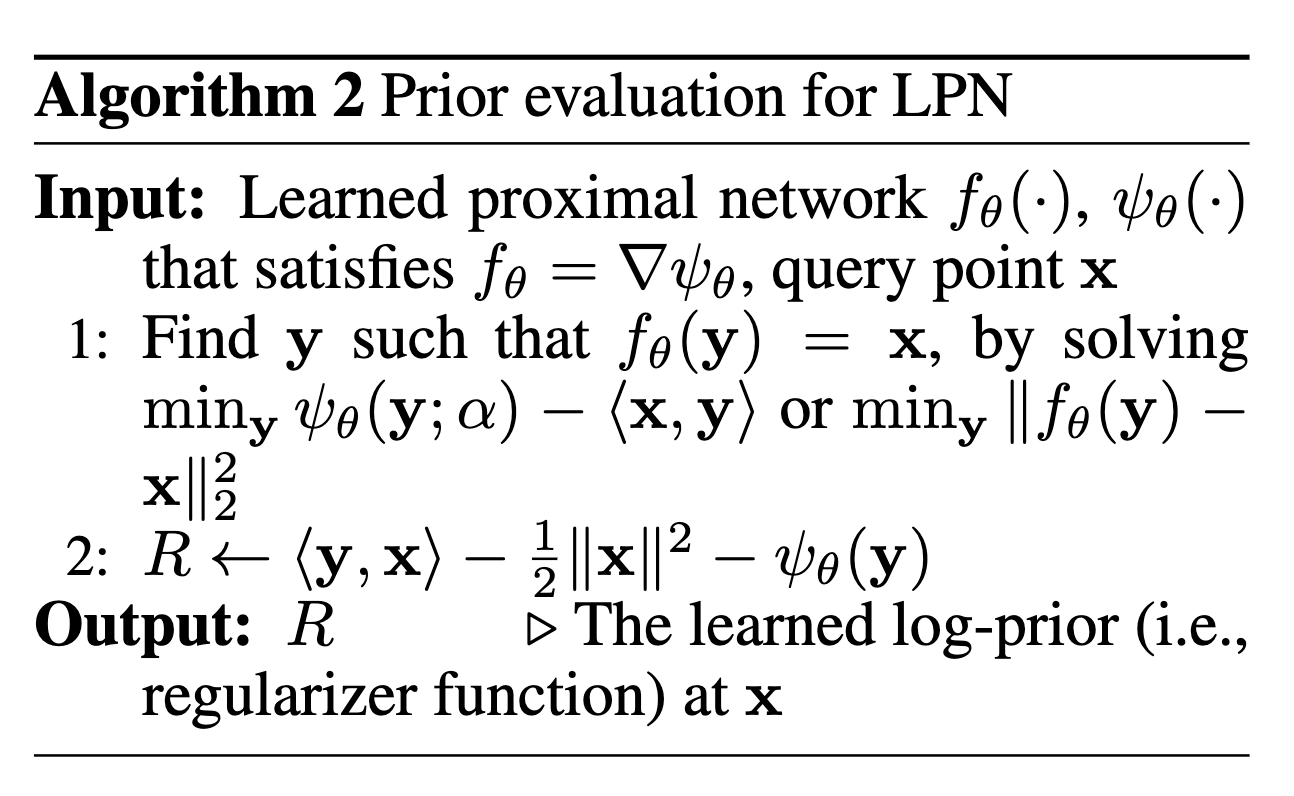
What's in a Prior? Learned Proximal Networks for Inverse Problems
- Is there an \(R\) such that \(f_\theta = \mathrm{prox}_{\eta R}\)?
- What is the regularizer/prior \(R\) learned by the neural network?
Proposition (Learned Proxima Networks). Let \(\psi_\theta: \R^{n} \rightarrow \R\) be defined by \(z_{1} = g( \mathbf H_1 y + b_1), z_{k} = g(\mathbf W_k z_{k-1} + \mathbf H_k y + b_k), \psi_\theta(y) = \mathbf w^T z_{K} + b\) with \(g\) a convex, non-decreasing nonlinear activation, and all \(\mathbf W_k\) and \(\mathbf w\) non-negative. Let \(f_\theta = \nabla \psi_{\theta}\). Then, there exists a function \(R_\theta\) such that \(f_\theta(y) = \mathrm{prox}_{R_\theta}(y)\).
What's in a Prior? Learned Proximal Networks for Inverse Problems
Fang Z, Buchanan S., Sulam J. What's in a prior? Learned proximal networks for inverse problems. ICLR 2024
Proposition (Learned Proxima Networks). Let \(\psi_\theta: \R^{n} \rightarrow \R\) be defined by \(z_{1} = g( \mathbf H_1 y + b_1), z_{k} = g(\mathbf W_k z_{k-1} + \mathbf H_k y + b_k), \psi_\theta(y) = \mathbf w^T z_{K} + b\) with \(g\) a convex, non-decreasing nonlinear activation, and all \(\mathbf W_k\) and \(\mathbf w\) non-negative. Let \(f_\theta = \nabla \psi_{\theta}\). Then, there exists a function \(R_\theta\) such that \(f_\theta(y) = \mathrm{prox}_{R_\theta}(y)\).
What's in a Prior? Learned Proximal Networks for Inverse Problems
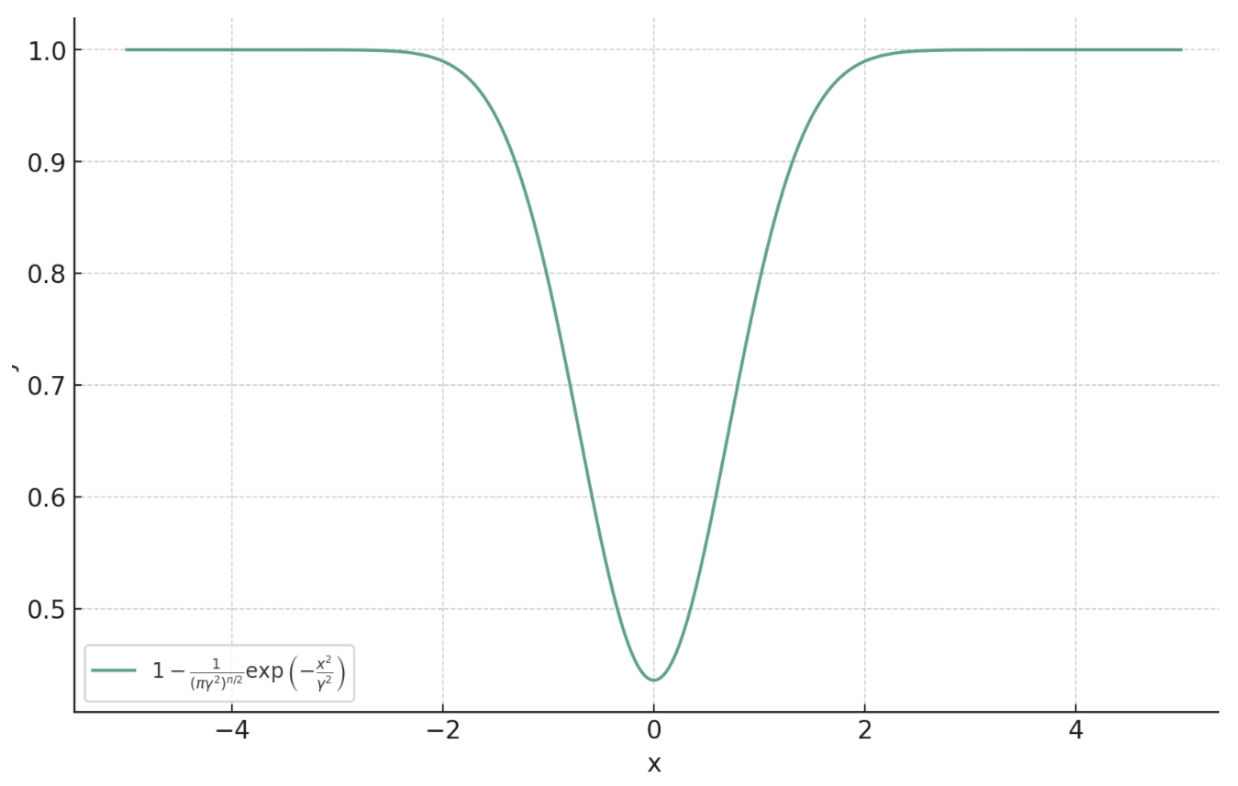
Theorem (Proximal Matching). Let
\[f^* = \argmin_{f} \lim_{\gamma \searrow 0} \mathbb{E}_{x,y} \left[ m_\gamma \left( \|f(y) - x\|_2 \right) \right].\]
Then, almost surely (for almost all \(y\)),
\[f^*(y) = \argmax_{c} p_{x \mid y}(c) = \mathrm{prox}_{-\sigma^2\log p_x}(y).\]
\(m_{\gamma}(x) = 1 - \frac{1}{(\pi\gamma^2)^{n/2}}\exp\left(-\frac{x^2}{\gamma^2}\right)\)
Prox Matching Loss
Fang Z, Buchanan S., Sulam J. What's in a prior? Learned proximal networks for inverse problems. ICLR 2024
What's in a Prior? Learned Proximal Networks for Inverse Problems
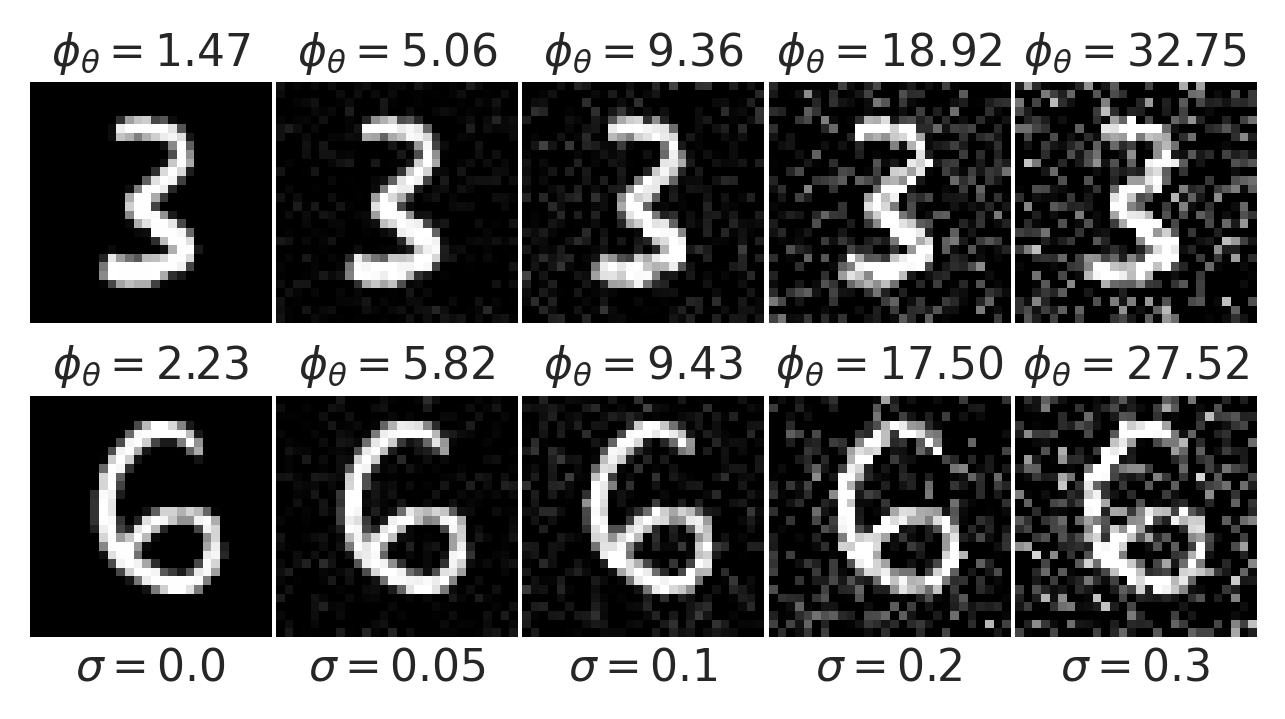
Gaussian noise
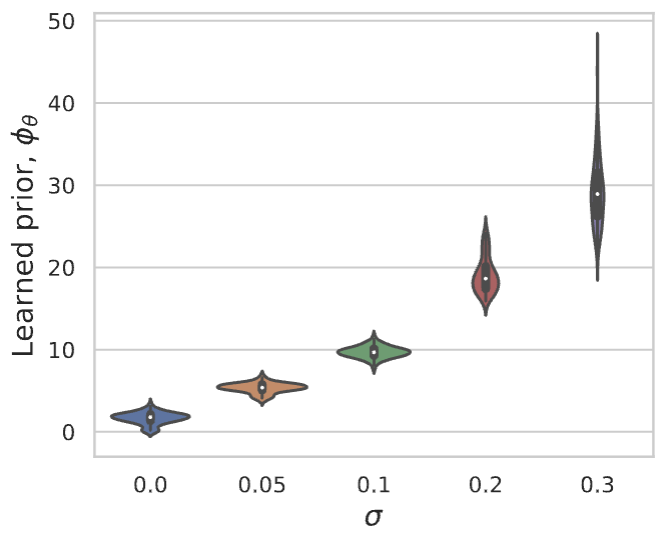
LPN faithfully captures distribution of natural images
Fang Z, Buchanan S., Sulam J. What's in a prior? Learned proximal networks for inverse problems. ICLR 2024
What's in a Prior? Learned Proximal Networks for Inverse Problems
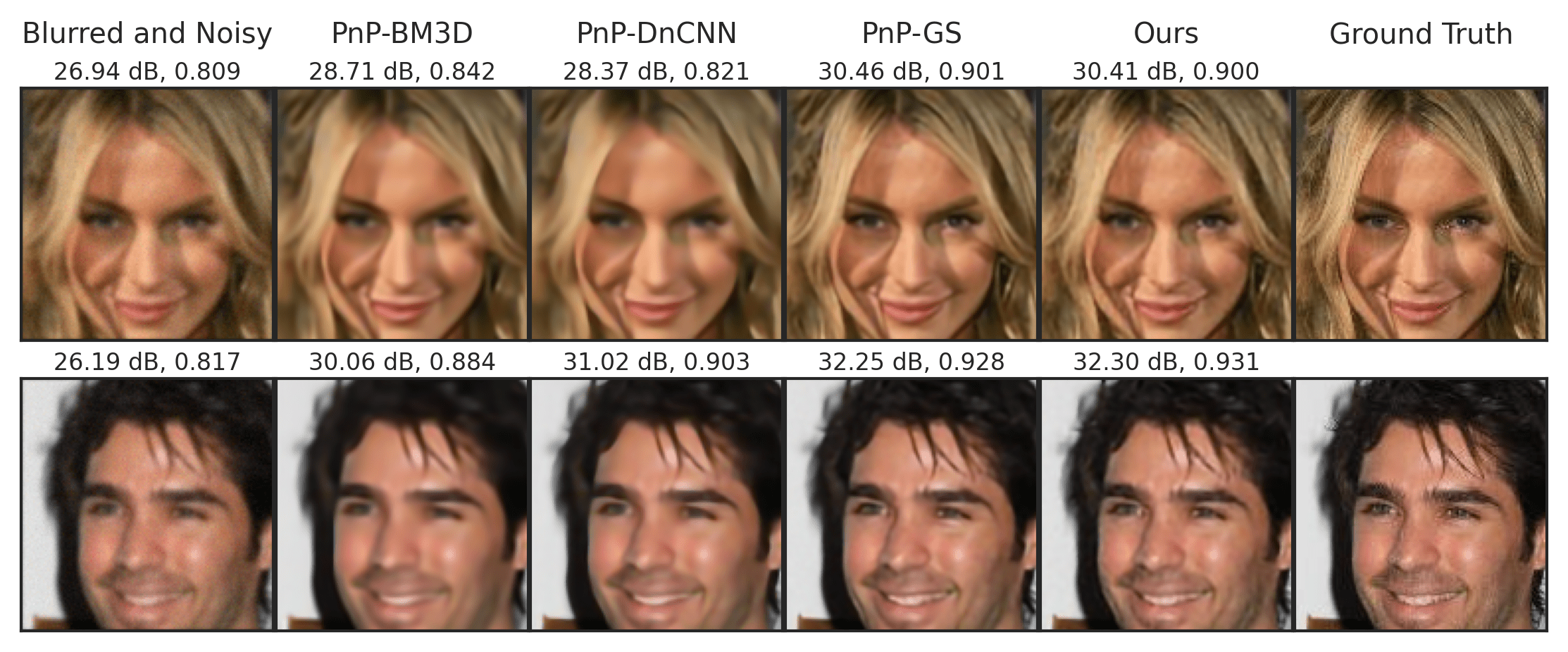
Deblurring on CelebA images
Fang Z, Buchanan S., Sulam J. What's in a prior? Learned proximal networks for inverse problems. ICLR 2024
Summary
- DeepSTI enables in vivo magnetic susceptibility tensor reconstruction using much fewer orientations
- WaveSep and DeepSepSTI achieves separation of paramagnetic and diamagnetic sources
- Learned proximal networks (LPN) presents a principled and interpretable machine learning algorithm for inverse problems






- NIH NIBIB (P41EB031771)
- Distinguished Graduate Student Fellows program of the KAVLI Neuroscience Discovery Institute
Acknowledgements
Kavli 5min
By Zhenghan Fang
Kavli 5min
- 170



