Anatomy Lab Checklist QQ
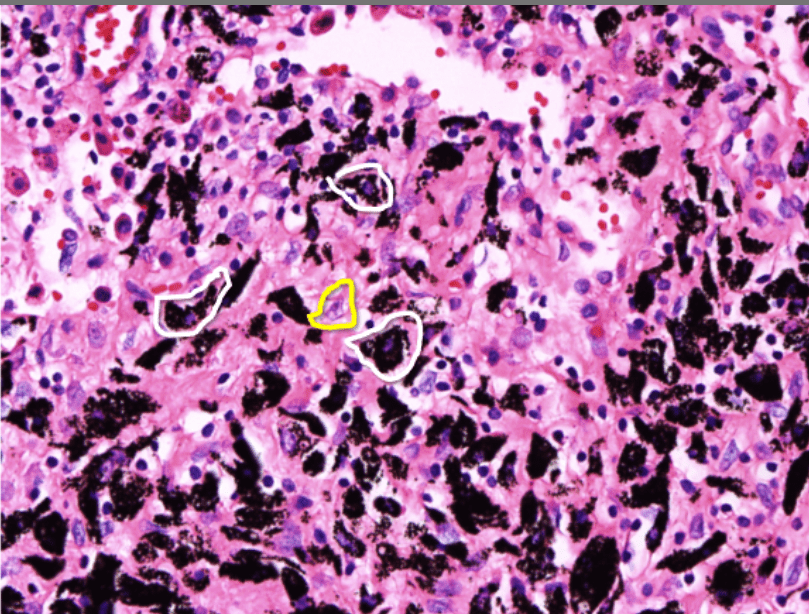
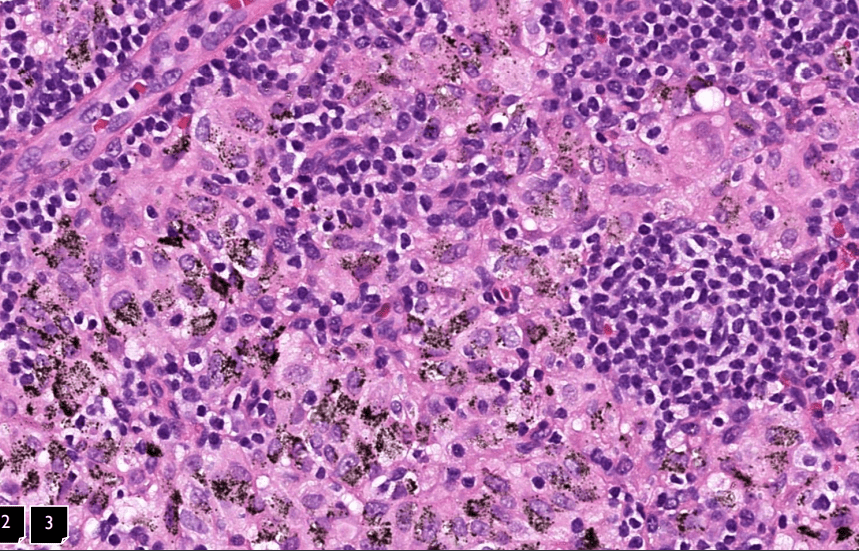
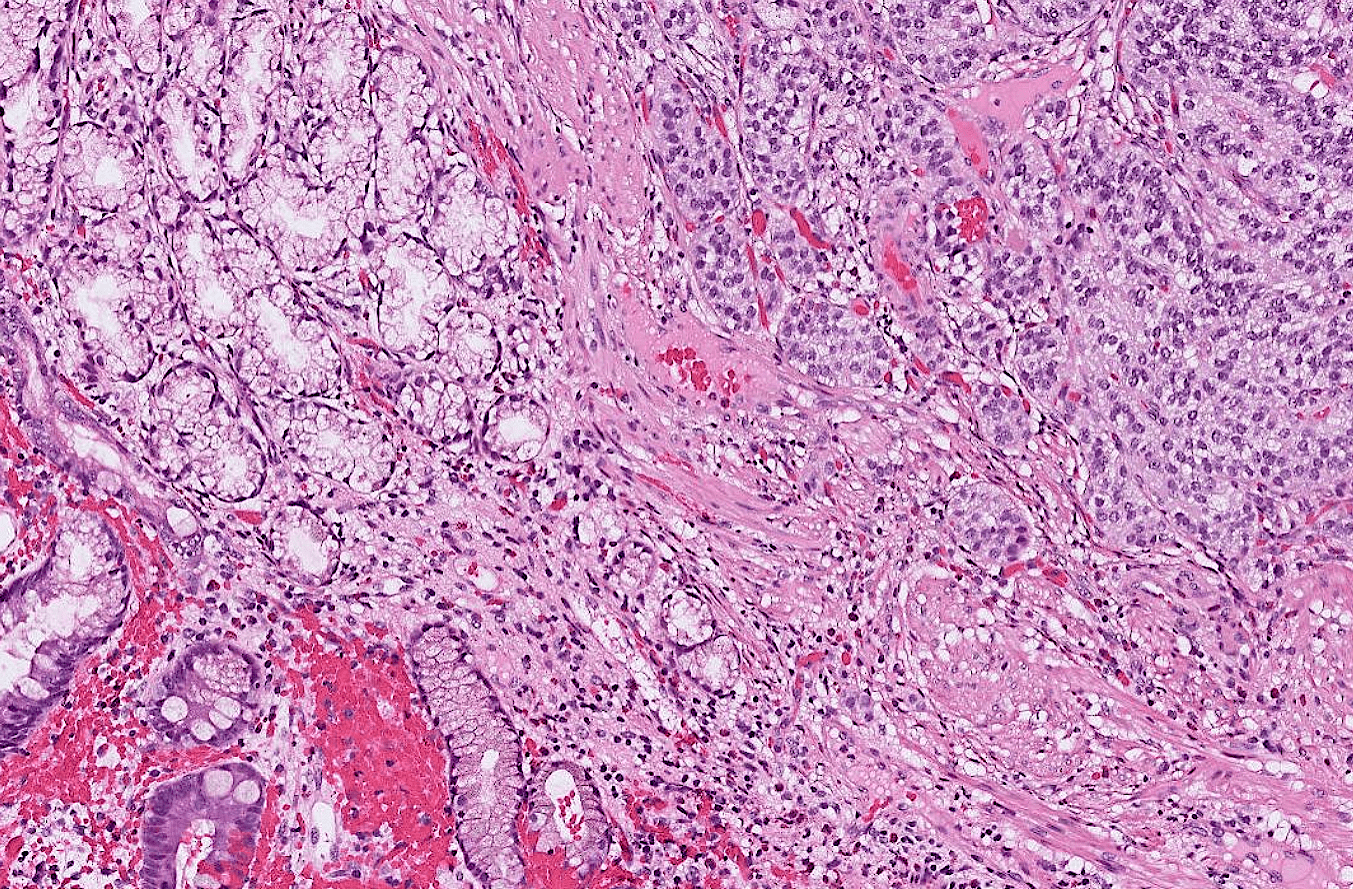
lung adenocarcinoma
lung adenocarcinoma
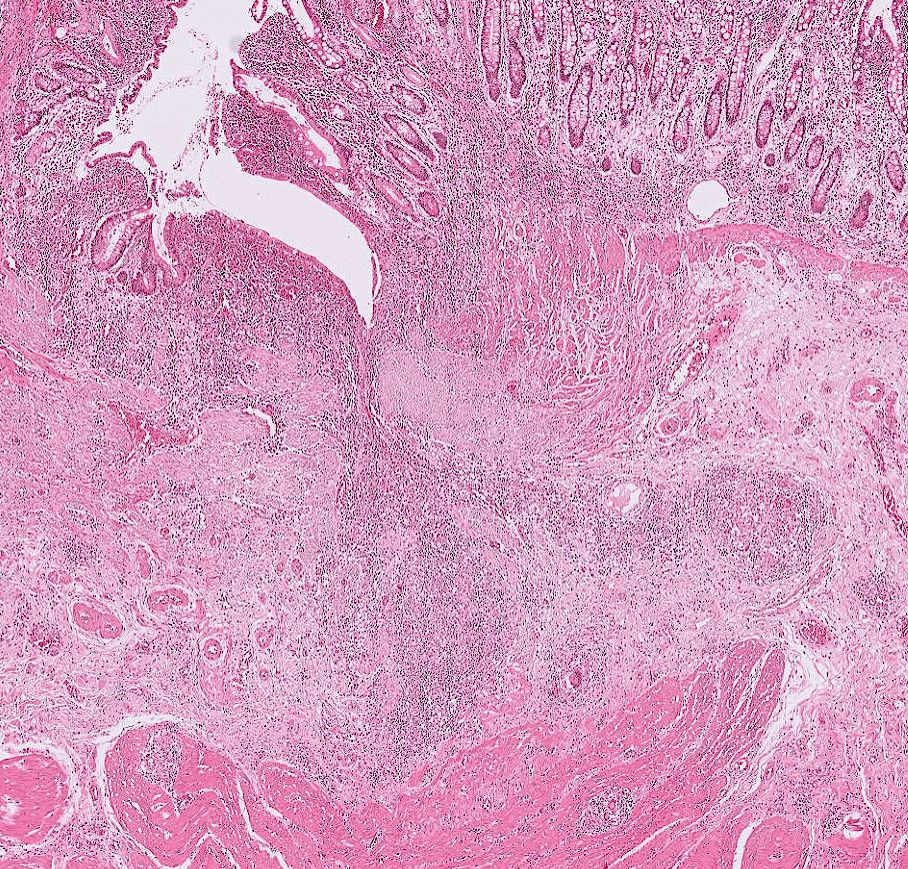
colon cancer
endometrial cancer
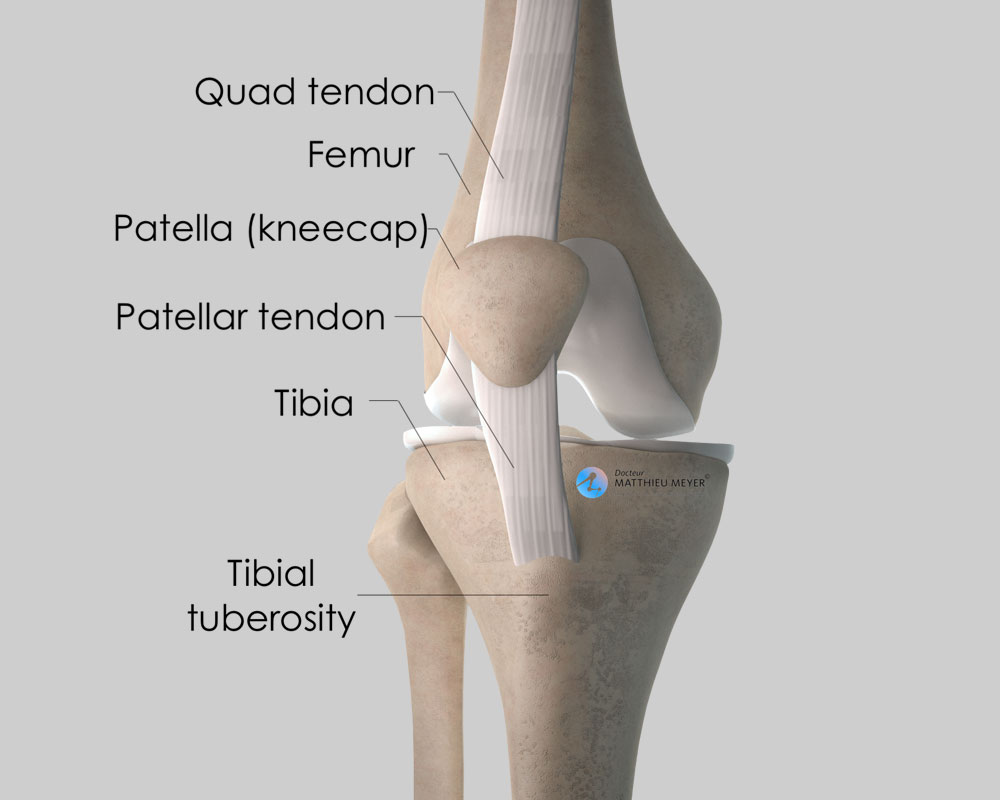
Upper Limb
Clavicle(left)
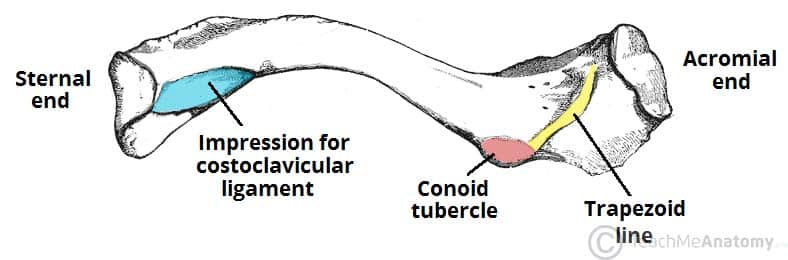
Clavicle
spinoglenoid notch
(suprascapular notch)
(intertubercular sulcus)
obique line
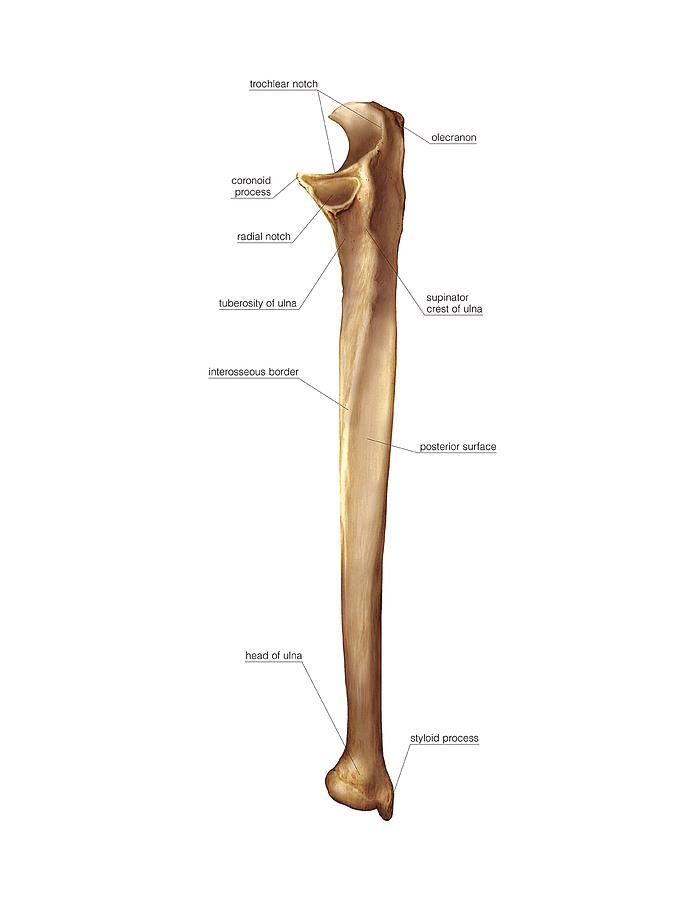
Ulnar(left?)
(Palmar view of left hand)
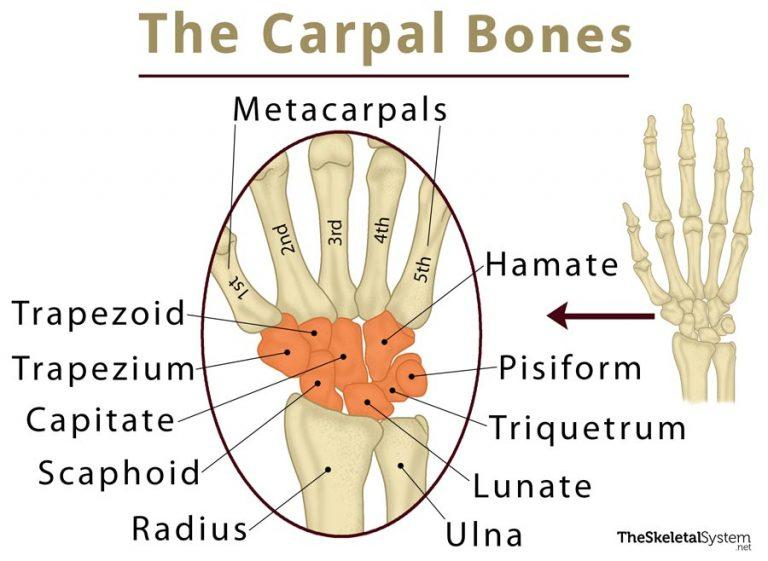
carpal arch(tunnel)
Lower Limb
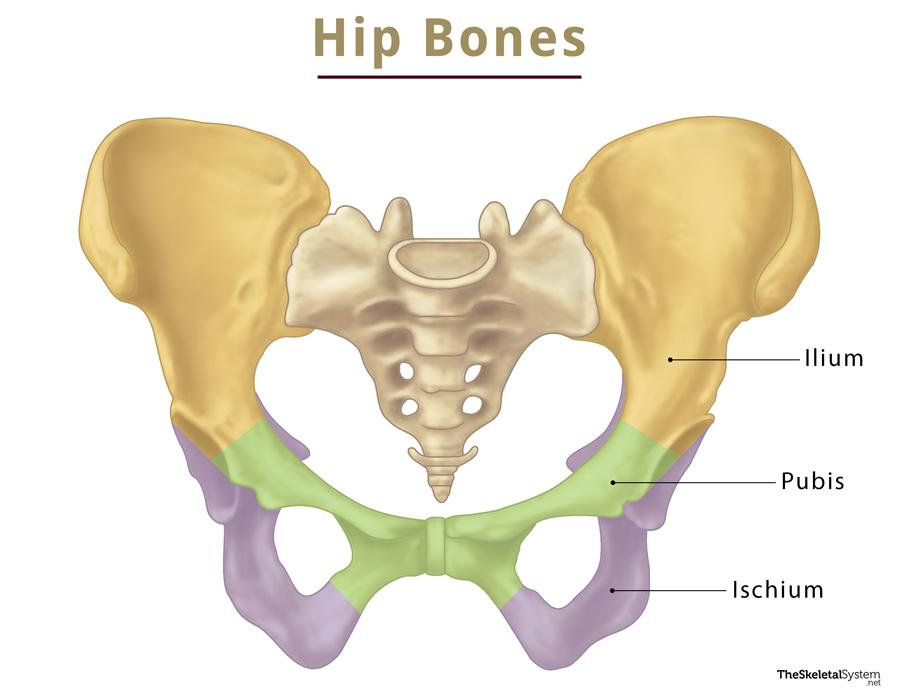
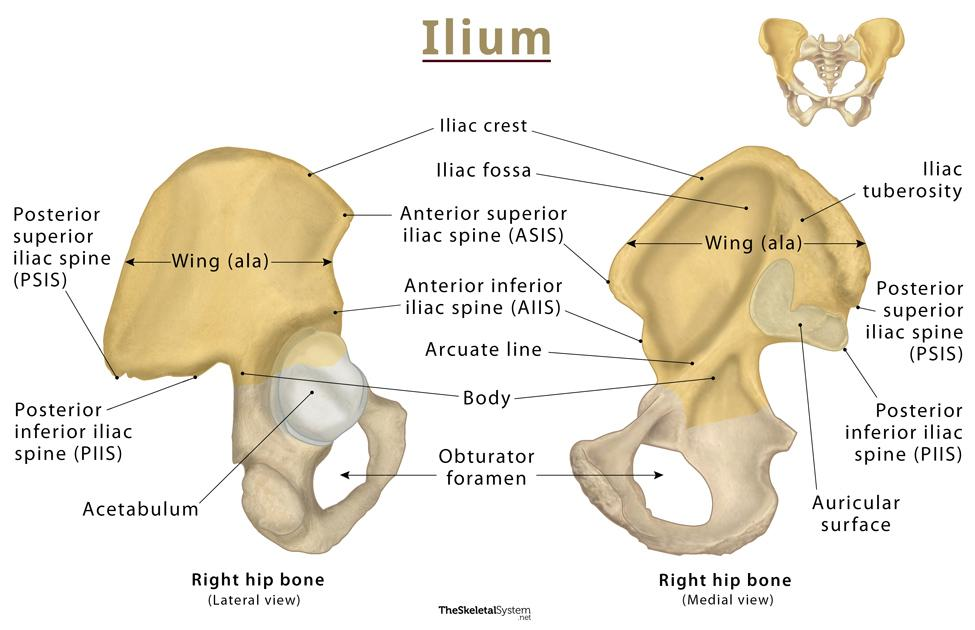
tubercle of the crest
posterior
anterior gluteal line
inferior
感覺iliopubic eminence在pubis?
Greater Sciatic Notch
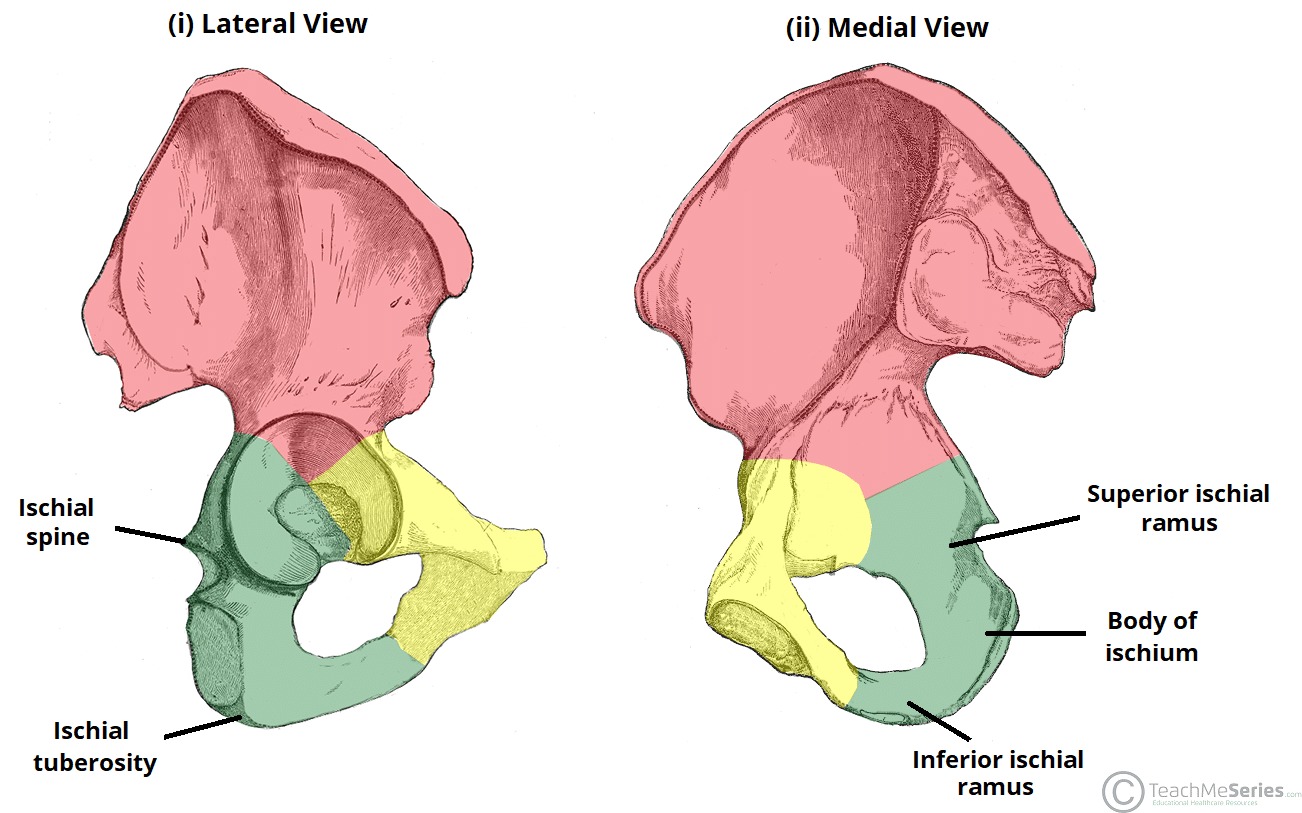
Ischium
lesser sciatic notch
Acetabular Fossa
Acetabular Notch

pubis(medial view)
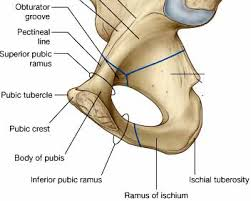

pubic symphisis
iliopubic eminence?
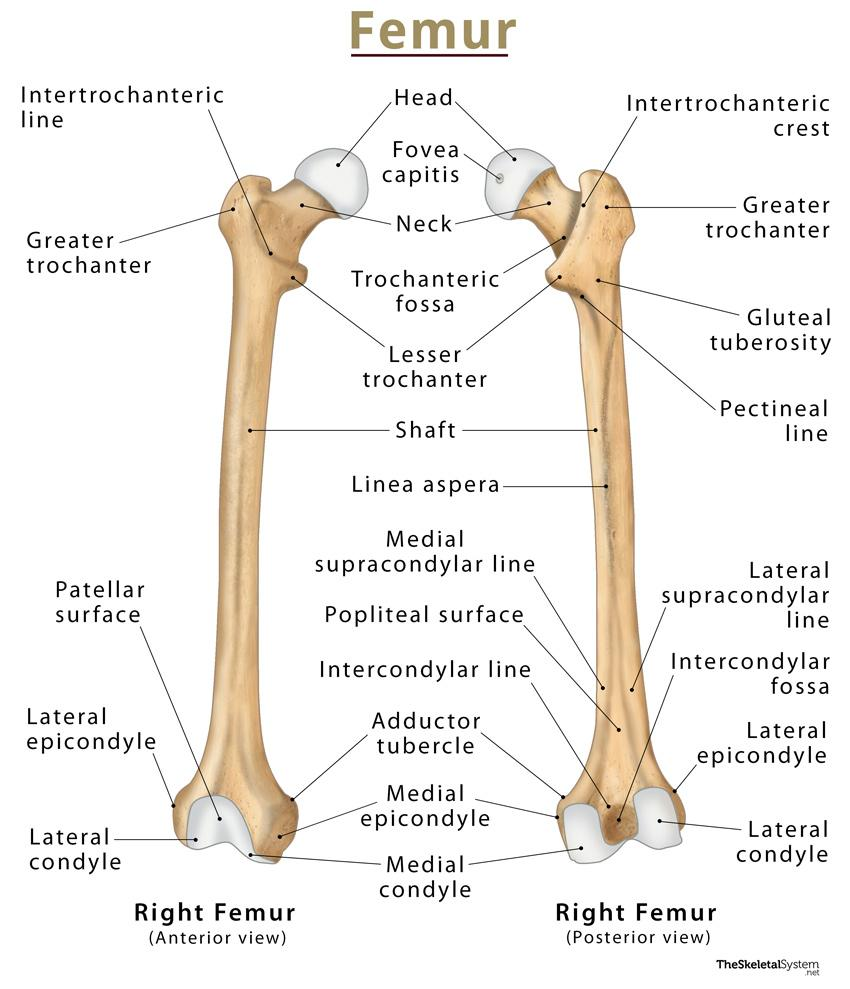
quadrate tubercle
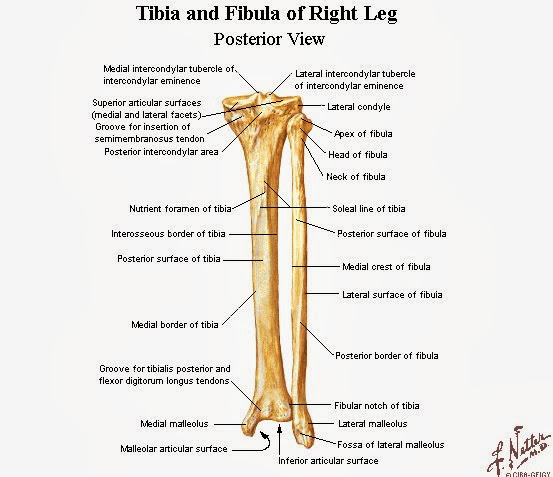
malleolar fossa
intercondylar eminence
styloid process
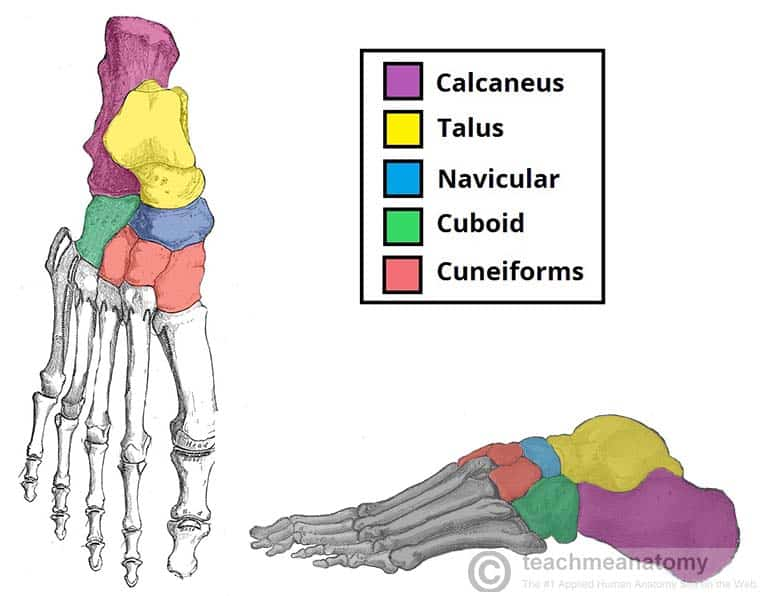
Tarsal Bones
Skull and Facial Skeleton
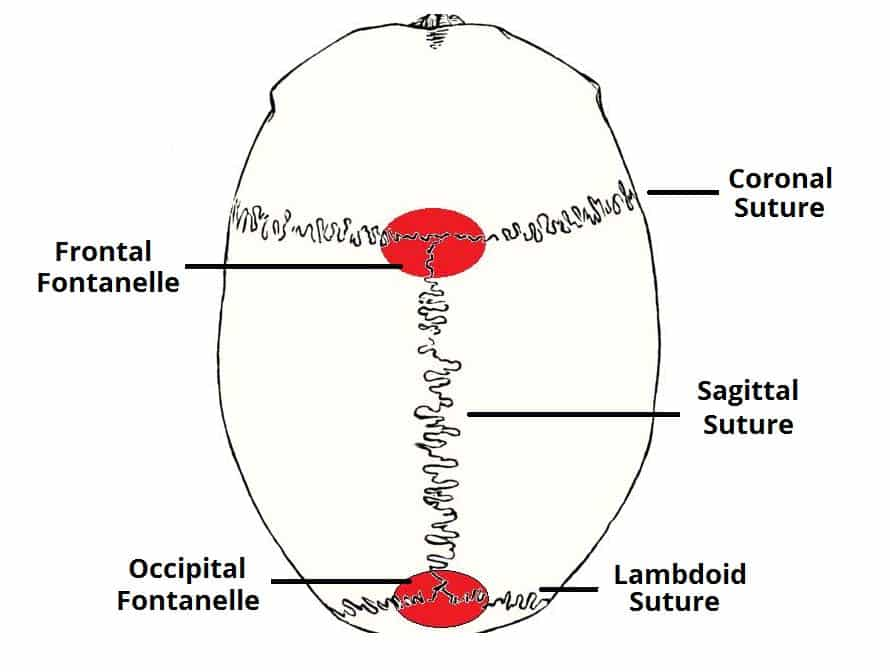
Sutures
(Bregma)
(Lambda)
External
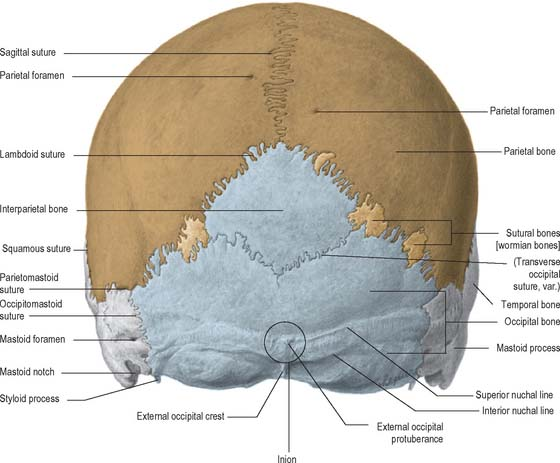
Lateral
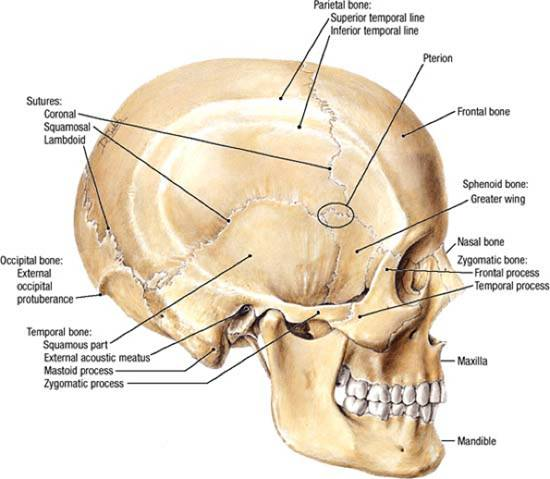
Frankfurt Plane
(zygomatic arch)
styloid process
Anterior
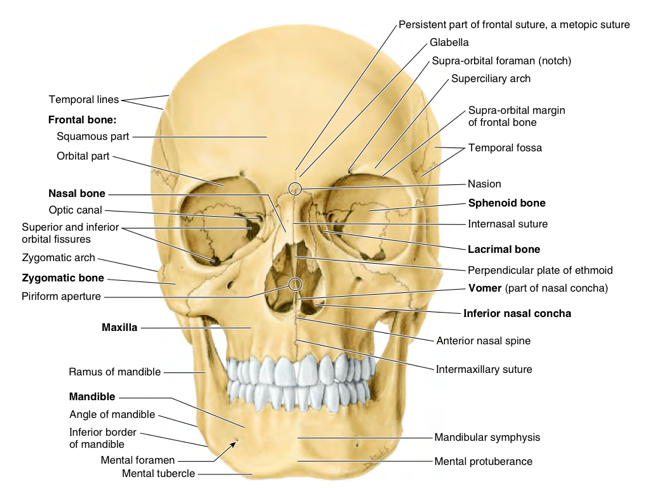
infraorbital foramen
Mandible
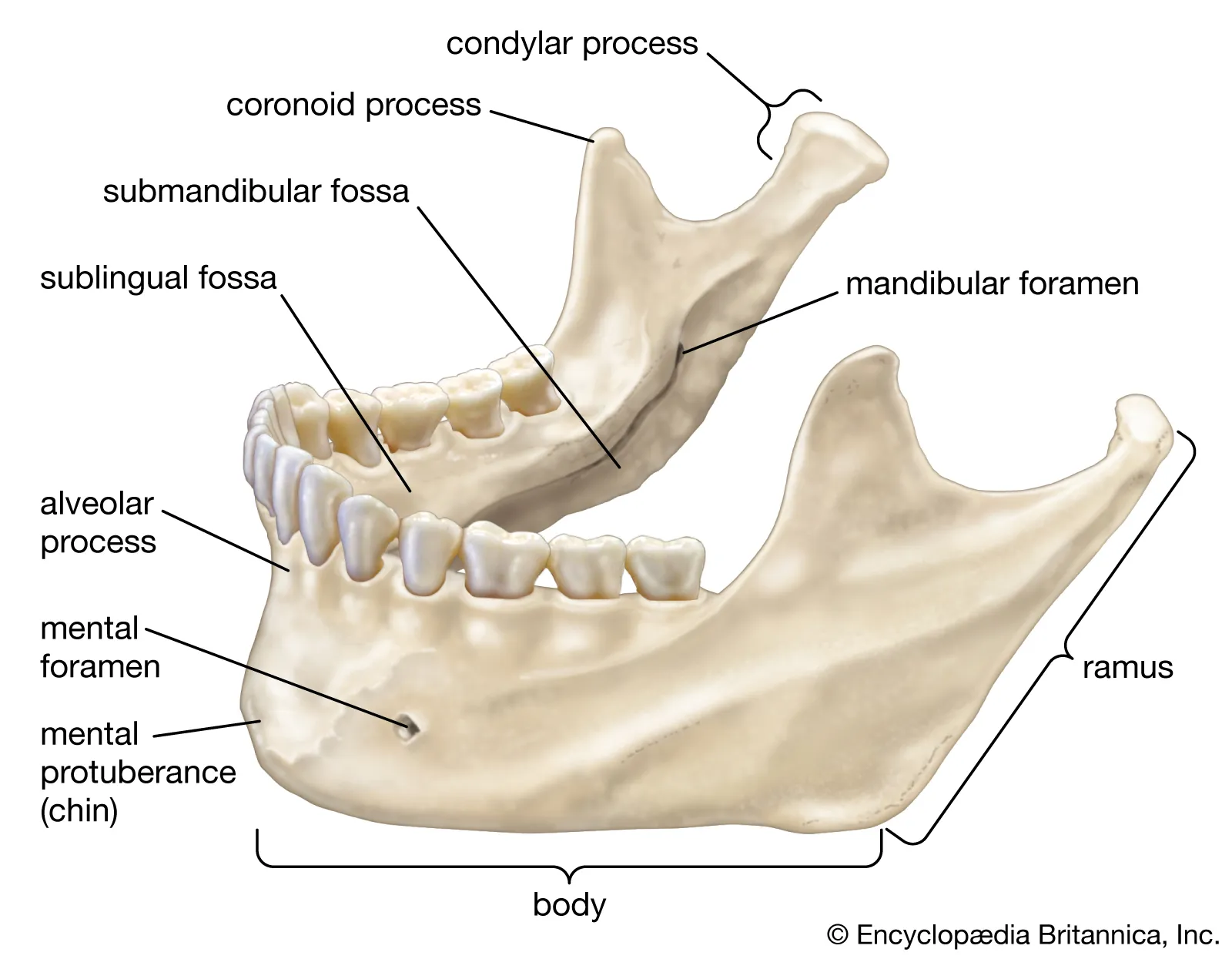
lingula
mylohyoid line
mylohyoid groove
Inferior
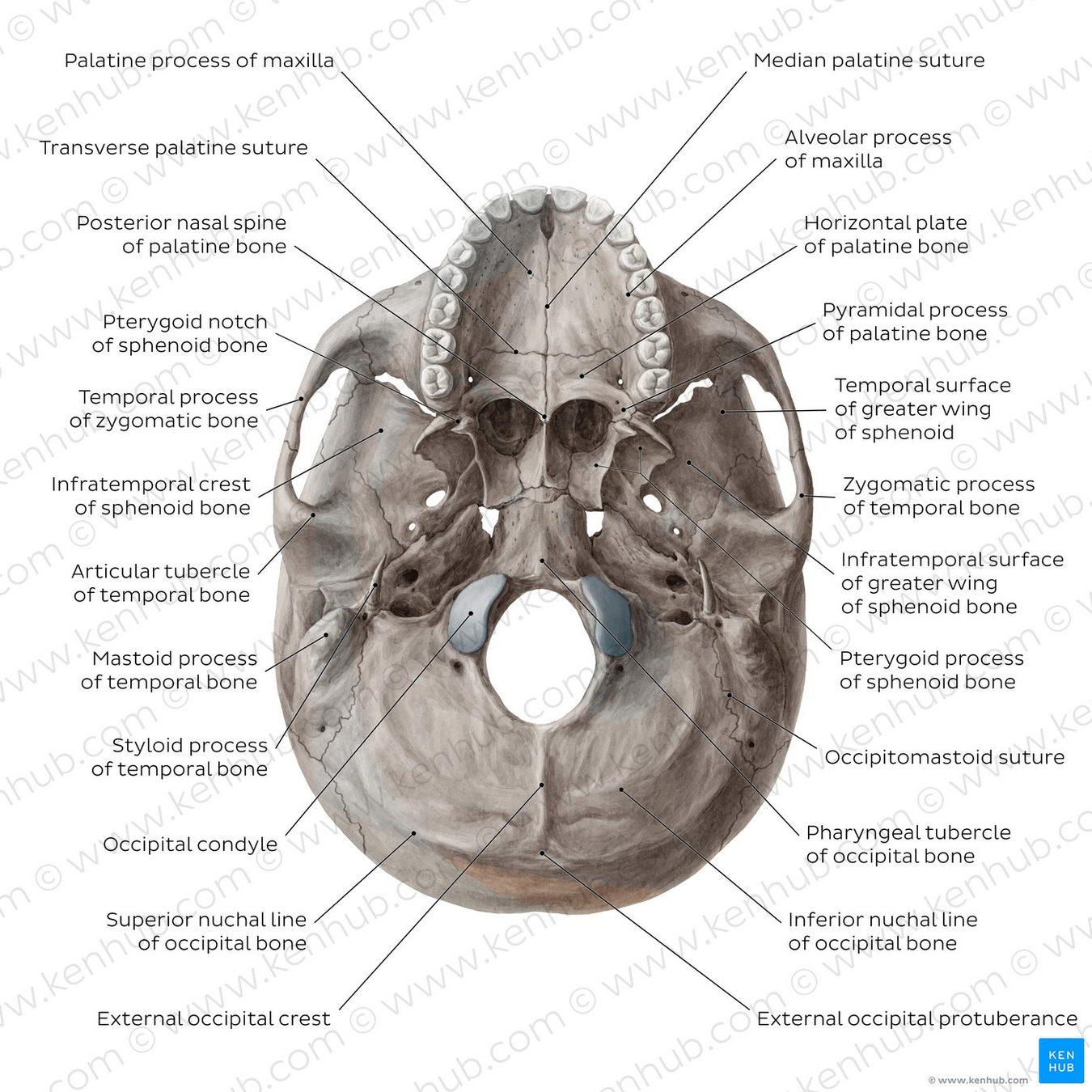
hard palate
(intermaxillary suture)
incisive fossa(canals inside)
-pterygoid plate(medial, lateral)
pterygoid fossa
greater palatine fpramina
lesserer palatine fpramina
pterygoid hamulus
mandibular fossa
carotid canal
jugular foramen
Pharyngotympanic tube (auditory tube)
stylomastoid foramen
hypoglossal canal
cranial cavity roof
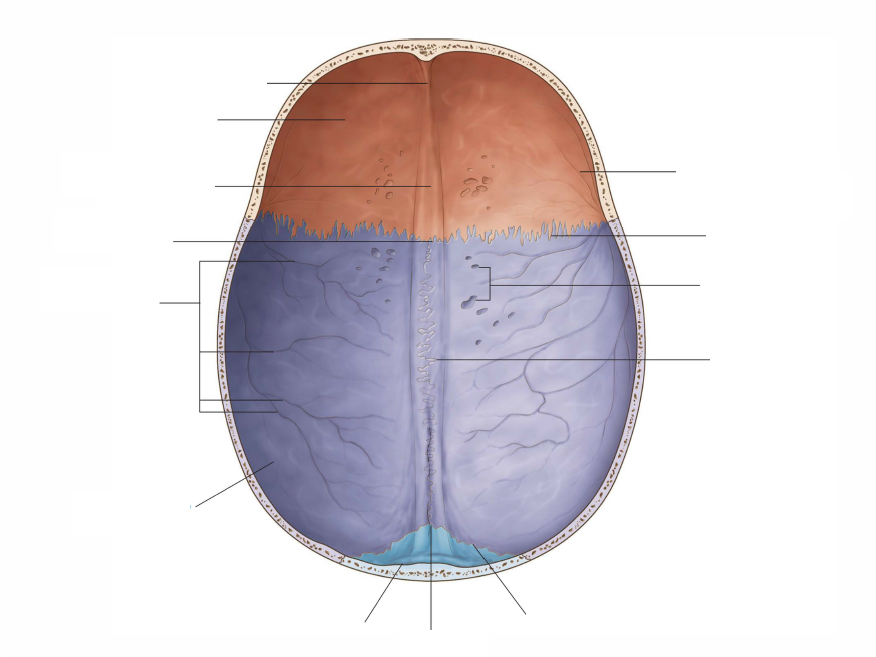
groove for SSS
frontal crest
cranial cavity floor
anterior clinoid process
tuberculum sellae(middle clinoid process)
hypophyseal fossa
dorsum sellae(posterior clinoid process)
clivus
crista galli
Skull and Facial Skeleton
9/19 小組討論
Questions
1. 根據病患抽血結果,請問病患較屬於哪一類型休克?
2. 休克復甦(resuscitation)時要注意哪些狀況?是否會併發其他器官功能異常,及其背後病理機轉為何?
抽血檢驗項目簡簡介
RBC: RBC concentration
HB: Hemoglobin concentration
HCT: volume percentage of RBC in blood
抽血檢驗項目簡簡介

MCV (mean corpuscular volume): \(\frac{HCT}{RBC}\), average volume of RBC
MCHC(mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration): \(\frac{HB}{HCT}\), average concentration of hemoglobin in RBC
抽血檢驗項目簡簡介

PLT: platelet concentration
RDW-CV: range of variation of RBC size
WBC: WBC concentration
抽血檢驗項目簡簡介

AST(GOT)/ALT(GPT): indicators of liver inflammation
抽血檢驗項目簡簡介

BUN(blood urea nitrogen)/Cre(creatinine): indicators of kidney health
抽血檢驗項目簡簡介

Lactic acid: increases due to hypoxia or impaired renal/hepatic function
hsCRP(high sensitivity-C reactive protein): a inflammation marker
Blood Test Results in Shocks
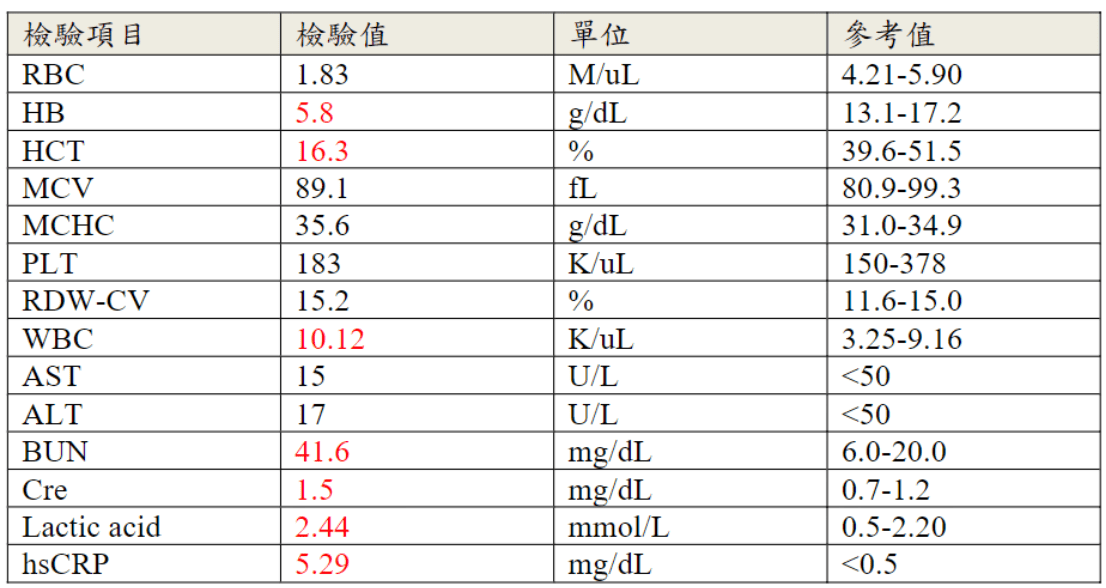
Blood Test Results in Shocks
- increased lactic acid \(\implies\) shock(hypoxia)
- increased BUN, Cre, ALT, AST\(\implies\)end-organ dysfunction related to shock
- increased WBC, left swift\(\implies\) infection?
- decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit\(\implies\)hemorrhagic hypovolemic shock



What kind of shock?

A. Distributive Shock
B. Cardiogenic Shock
C. Hypovolemic Shock
D. Obstructive Shock
What kind of shock?

A. Distributive Shock
B. Cardiogenic Shock
C. Hypovolemic Shock (with infection?)
D. Obstructive Shock
Questions
1. 根據病患抽血結果,請問病患較屬於哪一類型休克?
2. 休克復甦(resuscitation)時要注意哪些狀況?是否會併發其他器官功能異常,及其背後病理機轉為何?
Complications of Fluid Resuscitation
- Coagulation Disorders
- Reperfusion-Mediated Injury
- Pulmonary Edema/ARDS
Coagulation Disorders
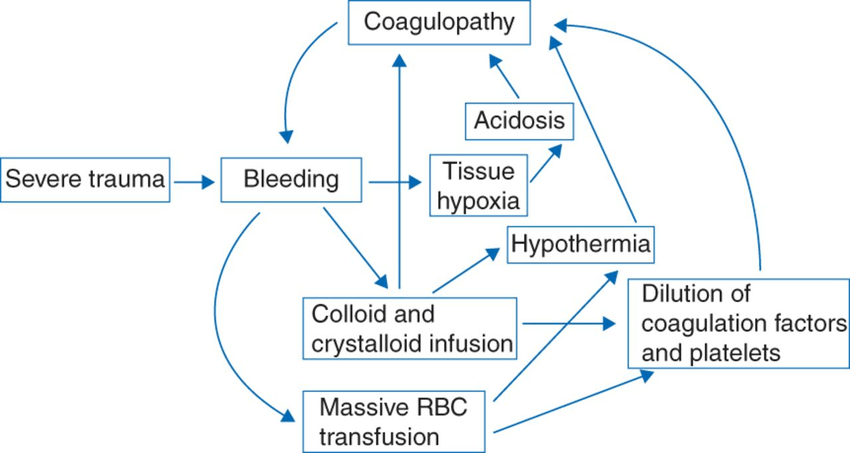
H.P. Pham, B.H. Shaz,Update on massive transfusion,British Journal of Anaesthesia,Volume 111, Supplement 1, 2013
Reperfusion-Mediated Injury
H.P. Pham, B.H. Shaz,Update on massive transfusion,British Journal of Anaesthesia,Volume 111, Supplement 1, 2013
- Cause general tissue injury/dysfunction
Oxygen-Derived ROS
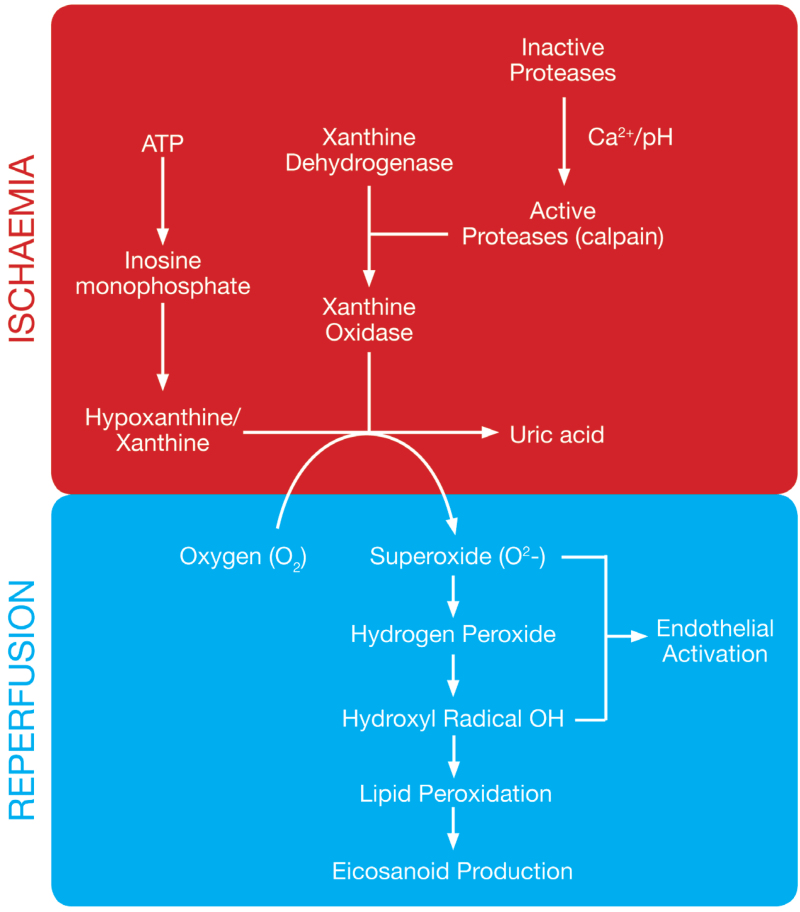
\(\implies\)
plasma membrane damage
Cytokines(IL-1,IL-6,IL-8,TNF-\(\alpha\))
neutrophil activation
\(\implies\)
More ROS
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
pulmonary edema
Lee J, Corl K, Levy MM. Fluid Therapy and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit Care Clin. 2021 Oct
\(\implies\)
ARDS
pulmonary edema
shock/inflammation
increased vascular permeability
fluid resuscitation
increased hydrostatic pressure
\(\implies\)
\(\implies\)
\(\implies\)
\(\implies\)
Other References
[1]Fluid Resuscitation: State of the Science for Treating Combat Casualties and Civilian Injuries. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Fluid Resuscitation for Combat Casualties; Pope A, French G, Longnecker DE National Academies Press (US); 1999.
[2]Huppert LA, Matthay MA, Ware LB. Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2019
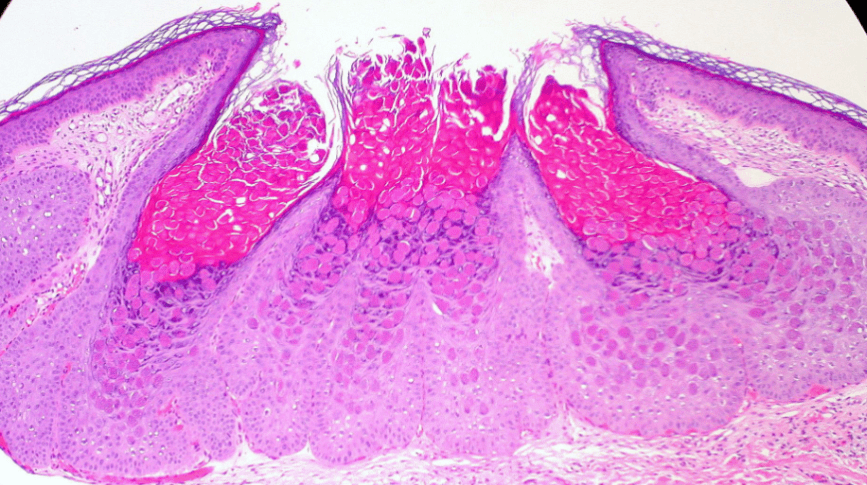
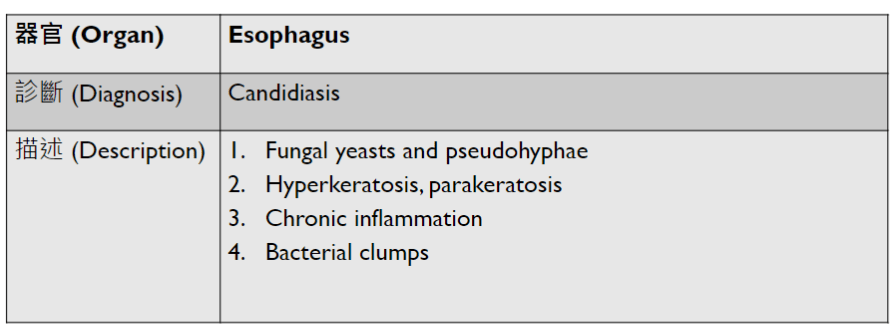
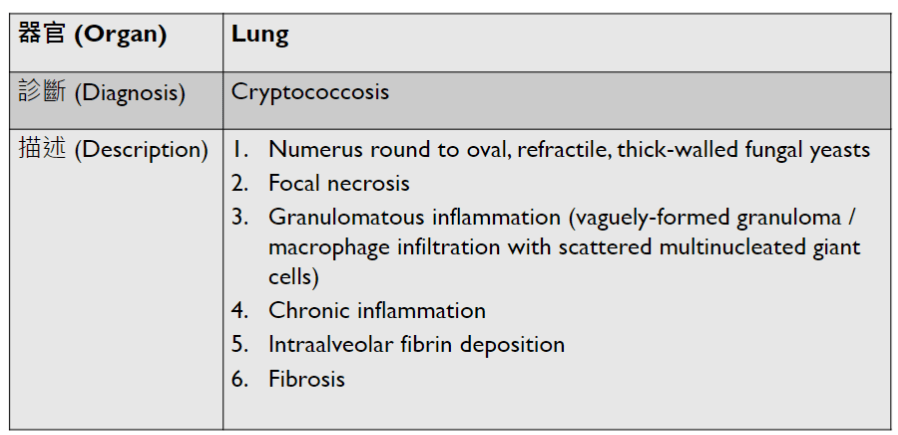
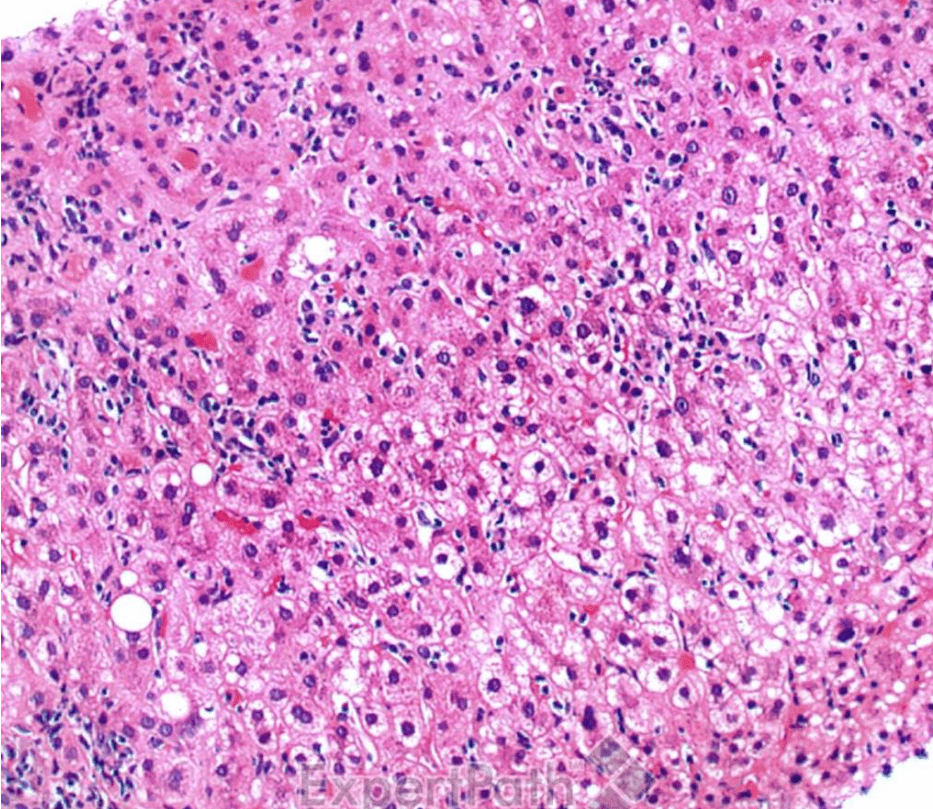
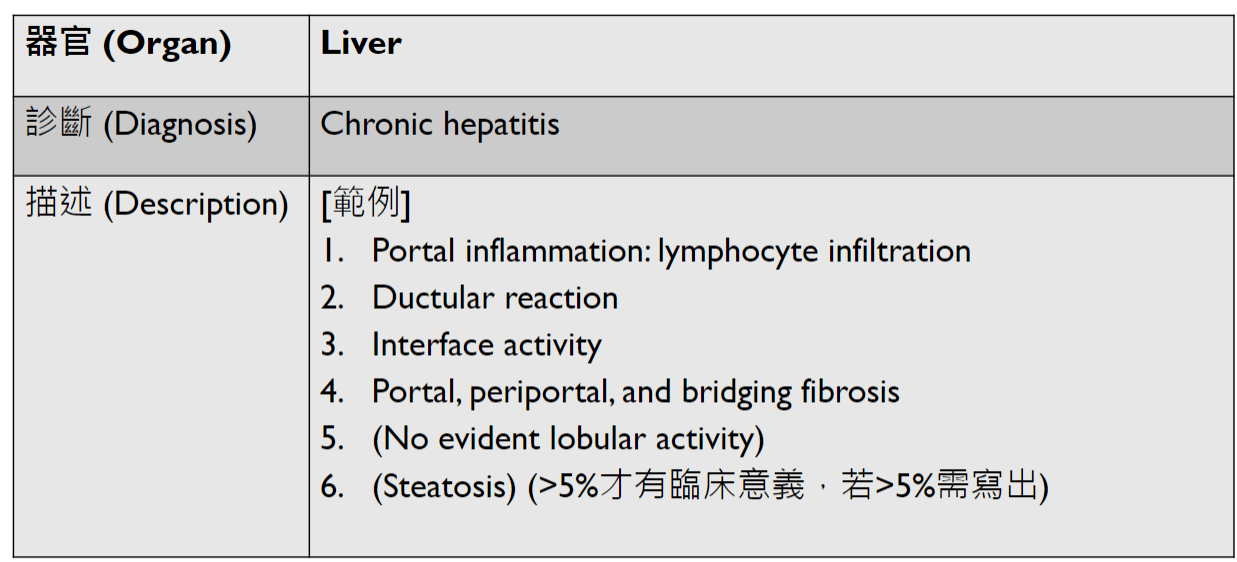
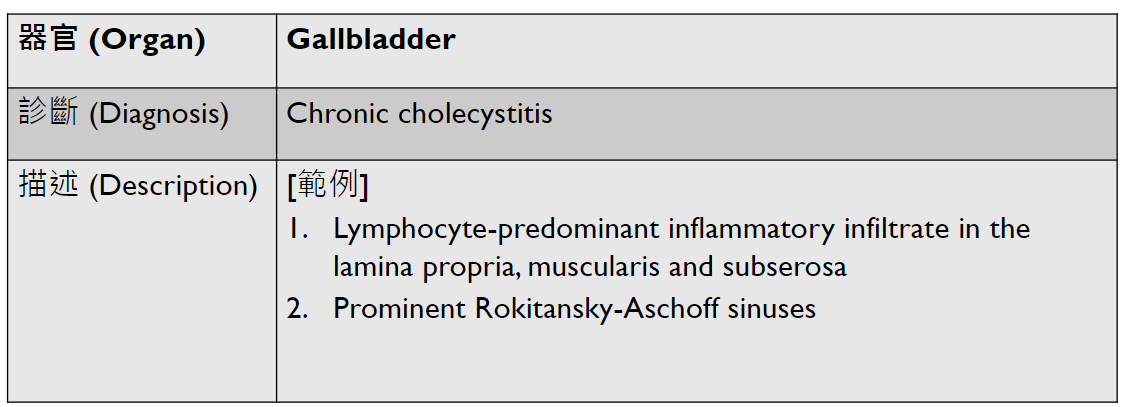
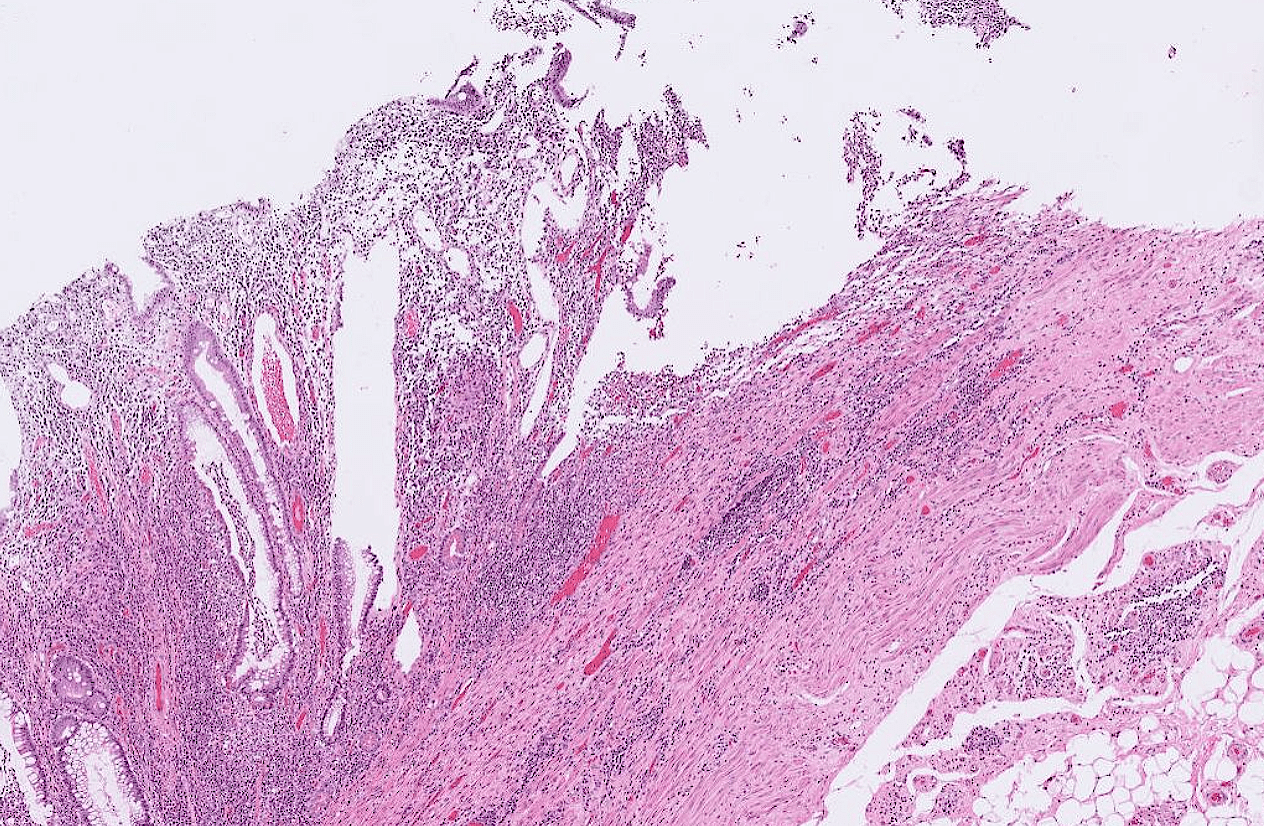
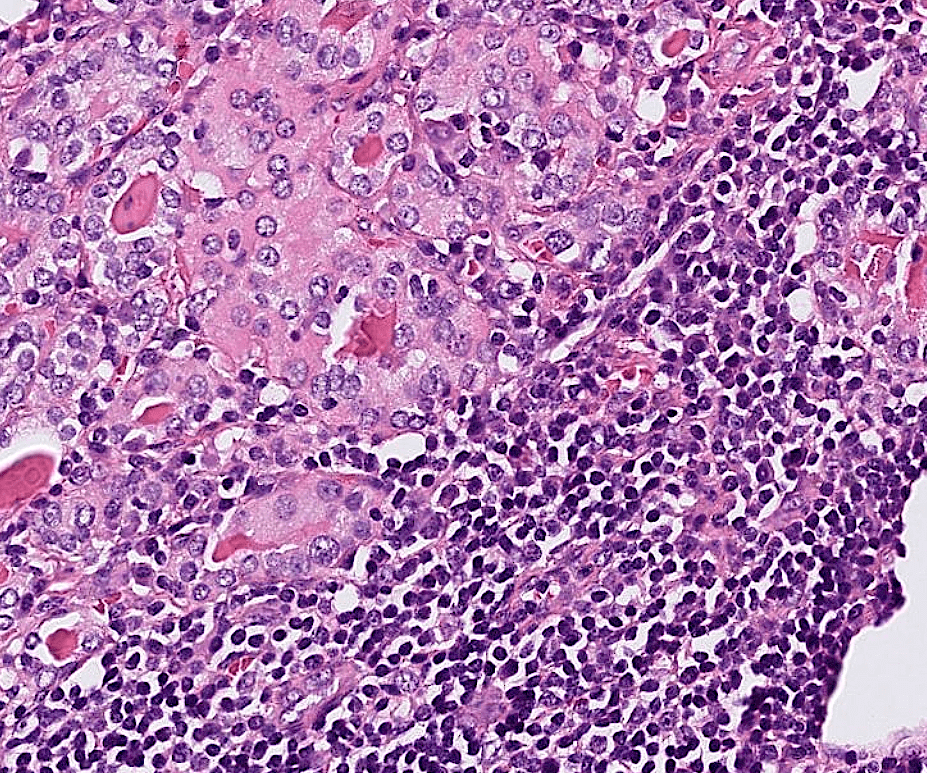
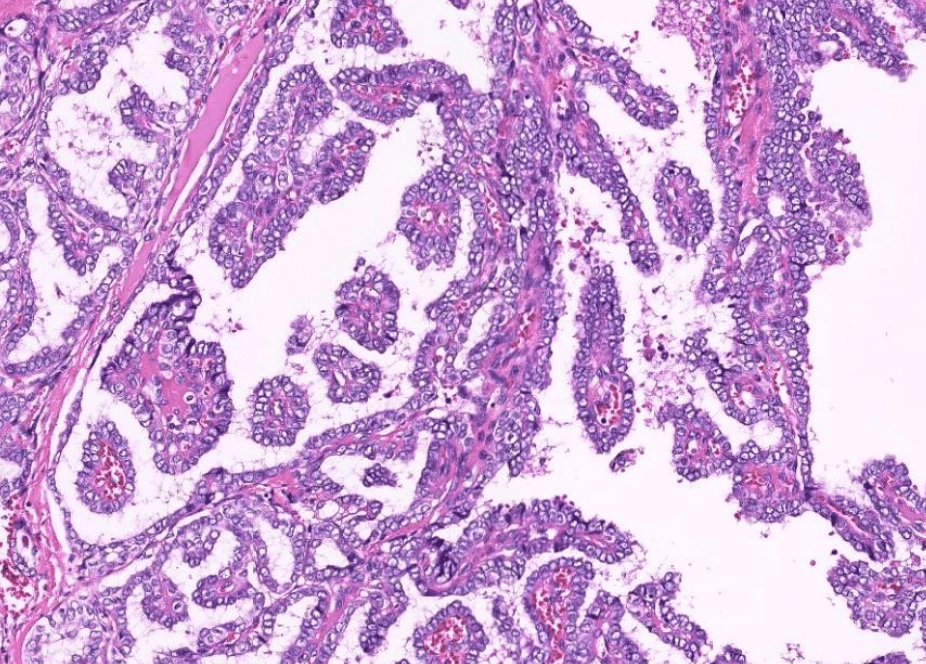
Pathology Lab 1
不太考
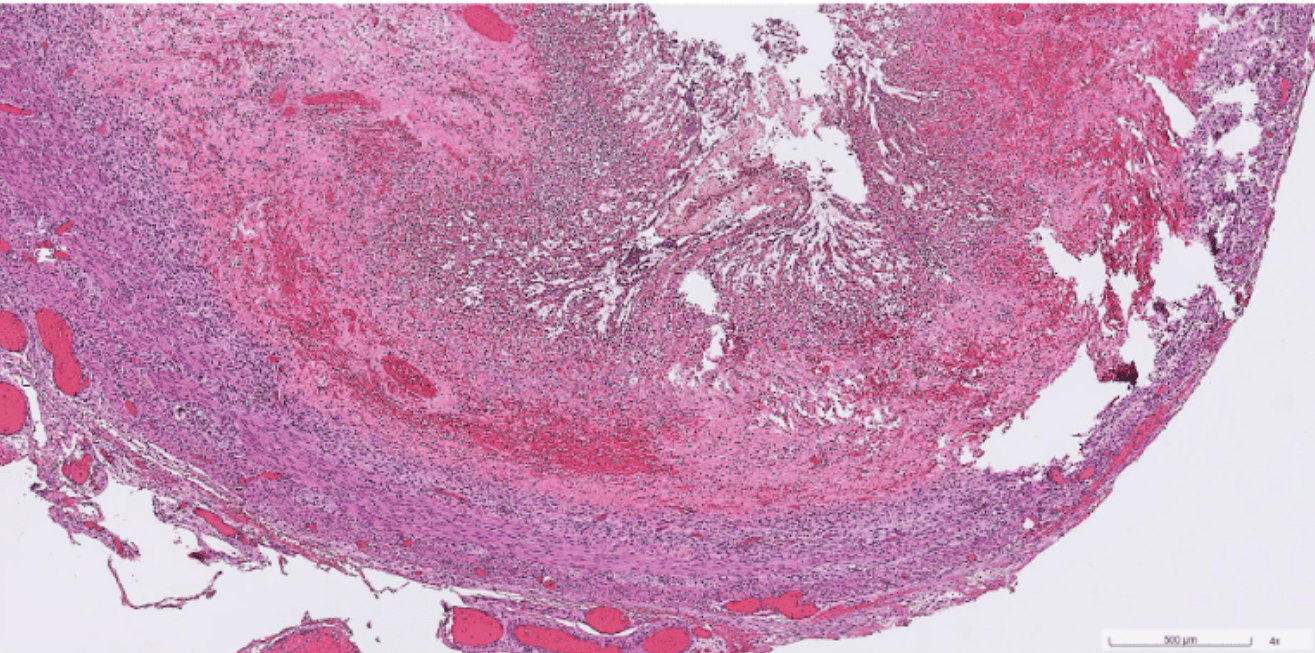
不太考
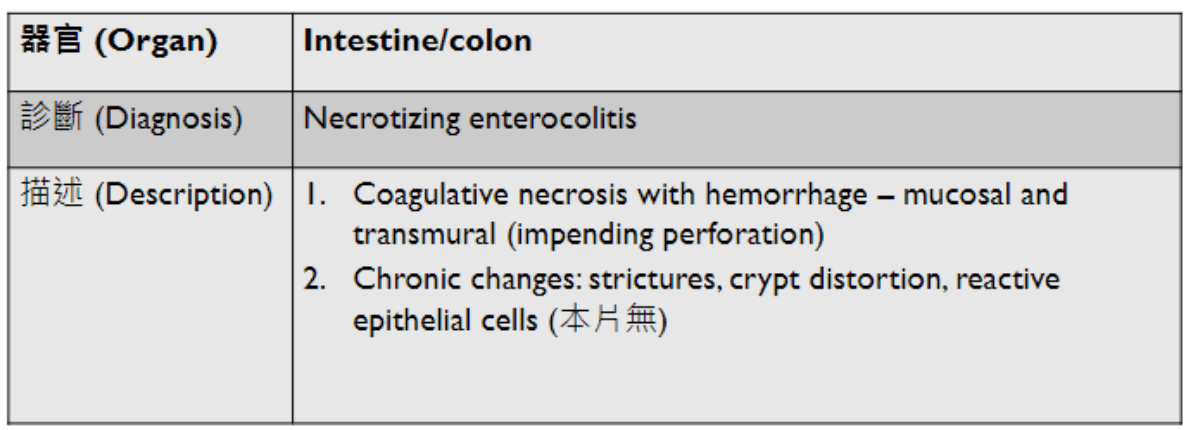
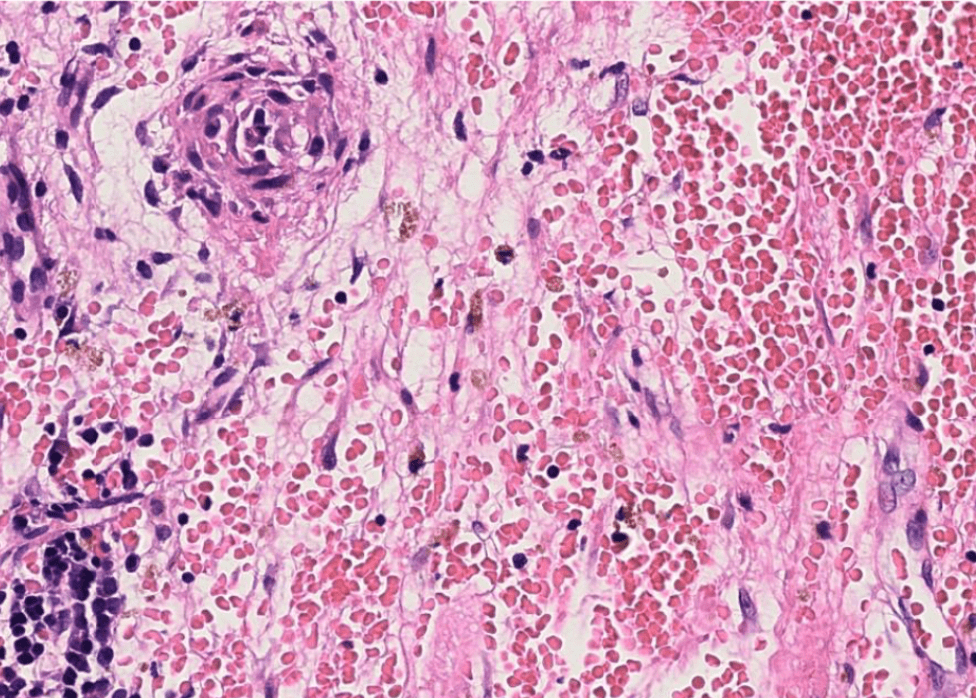
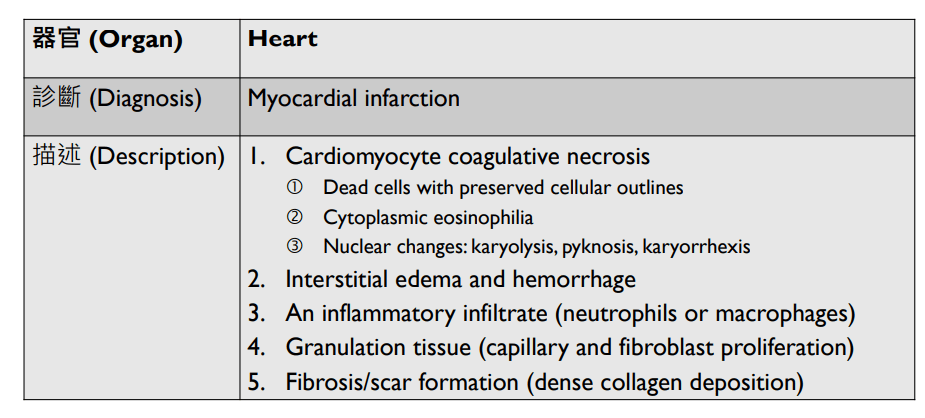
應該會考
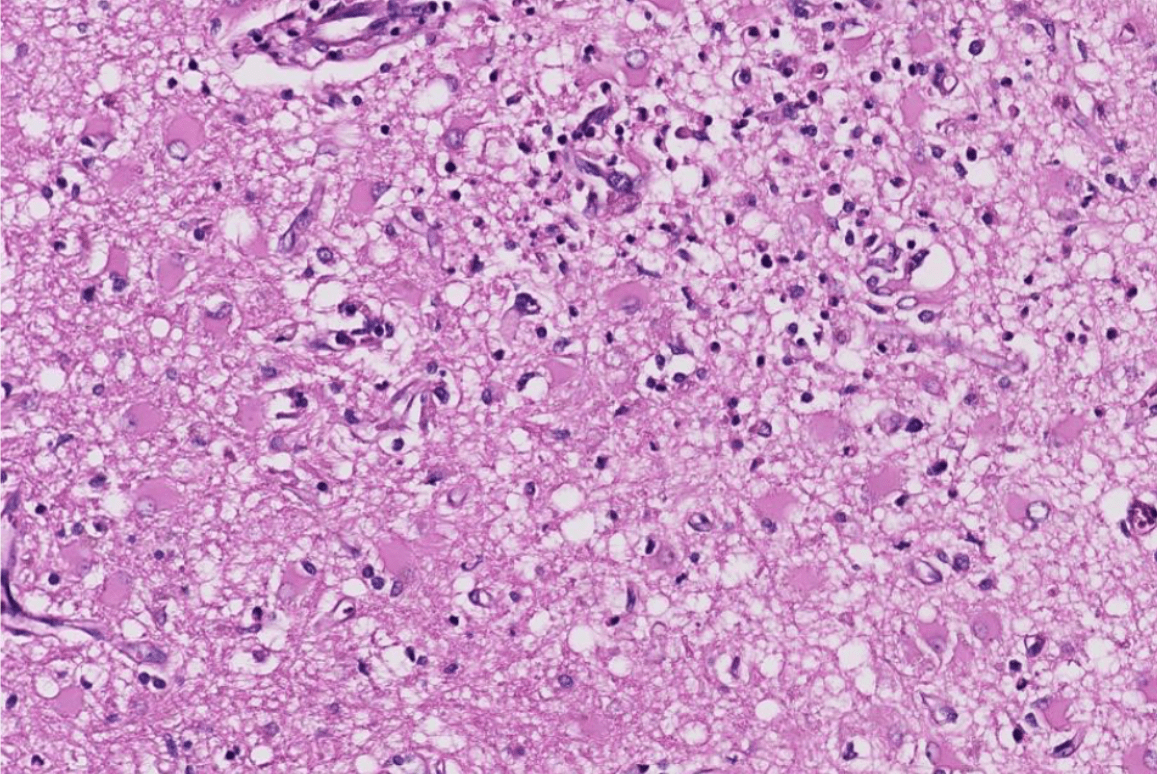
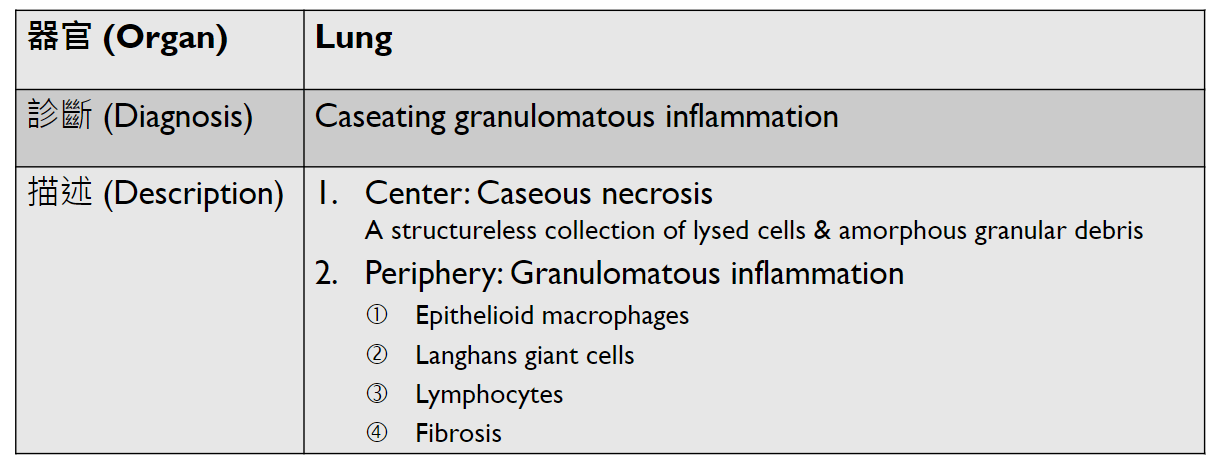
(plasma cell)

2. epithelial infoldings and papilla
不太考

不太考
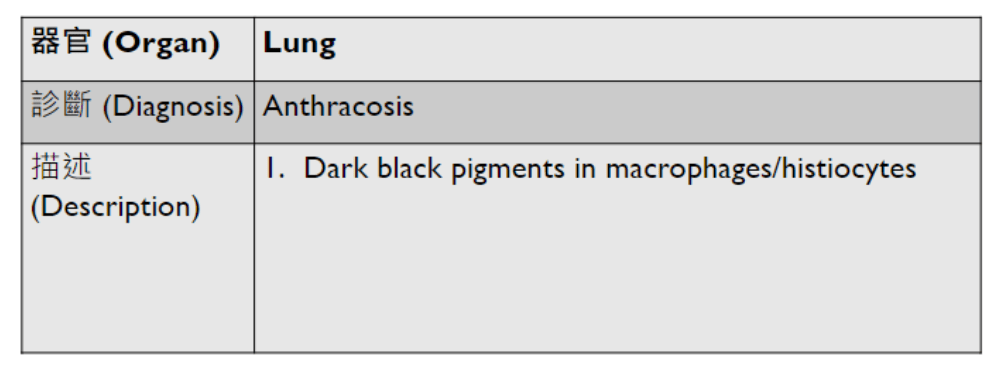
(or lymph node)
4. maturation with descent

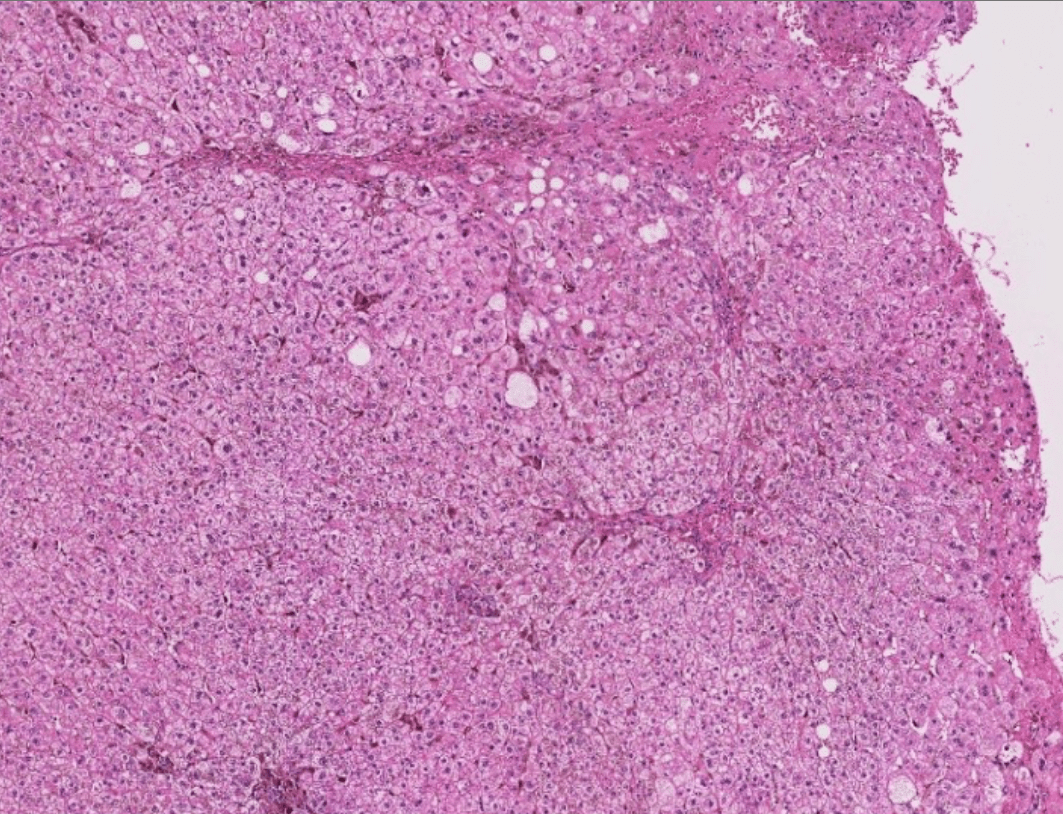

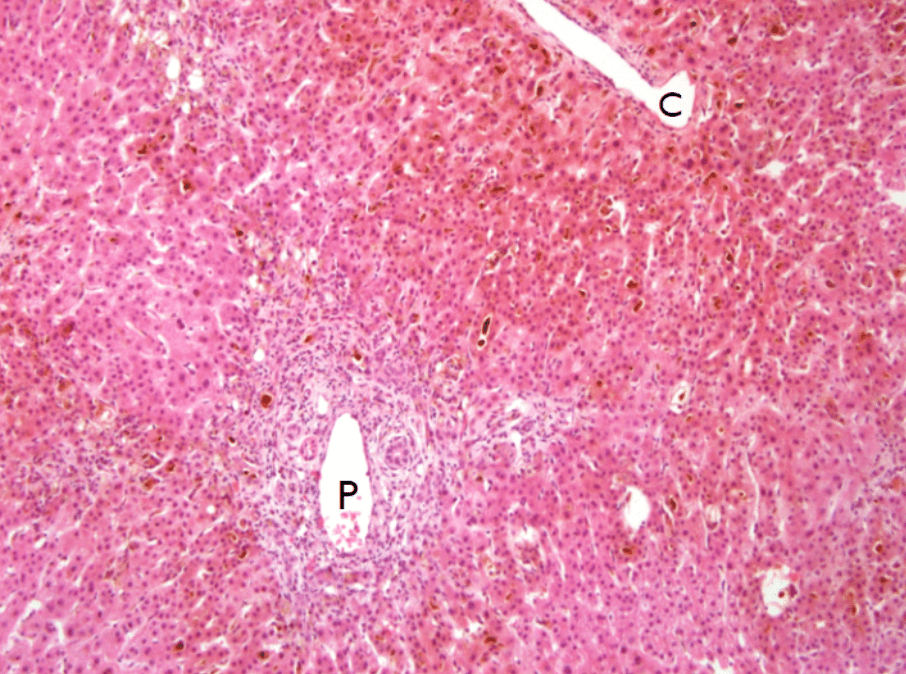
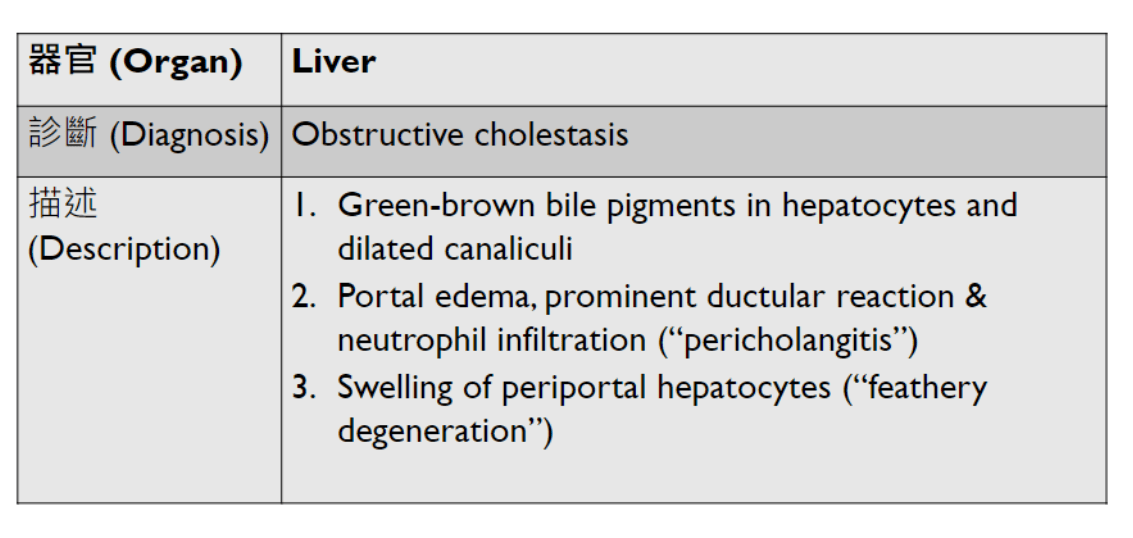
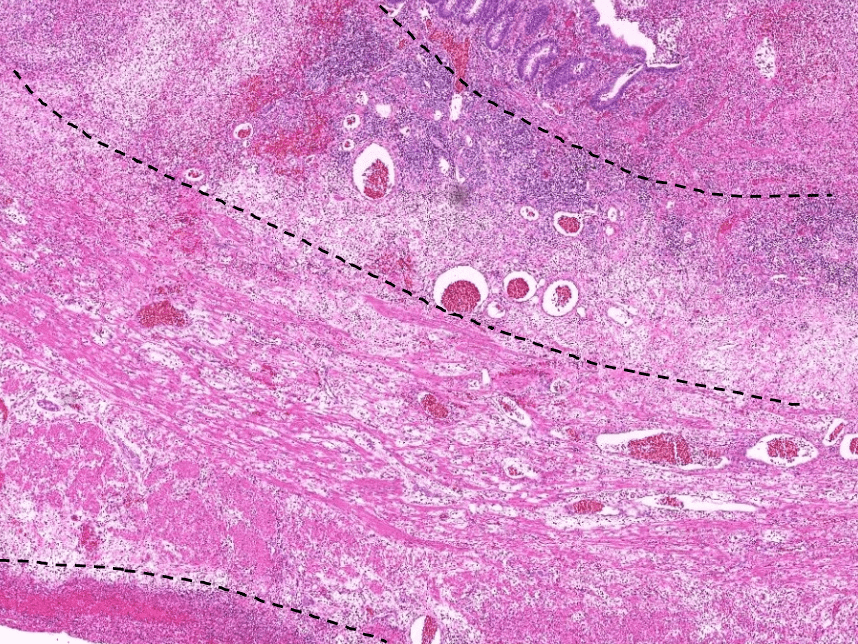
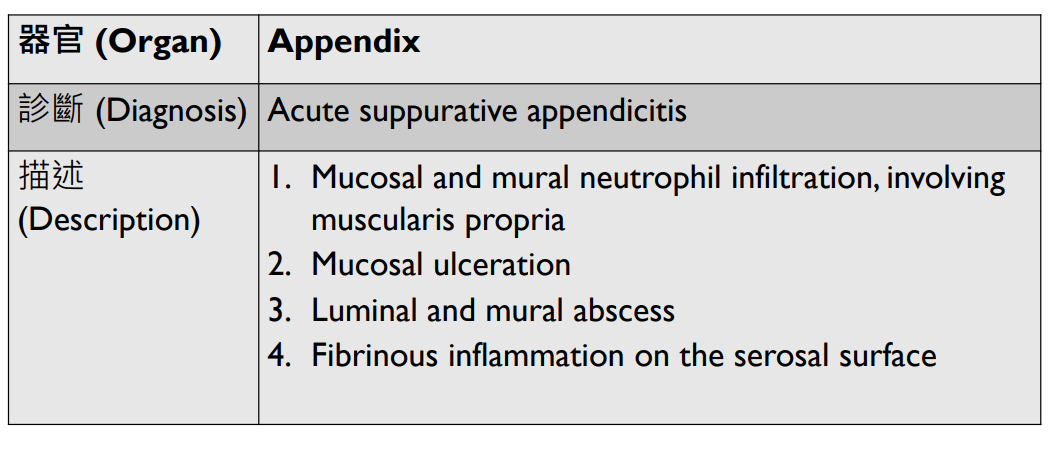
3. invaginated respiratory epithelium with cystic dilation
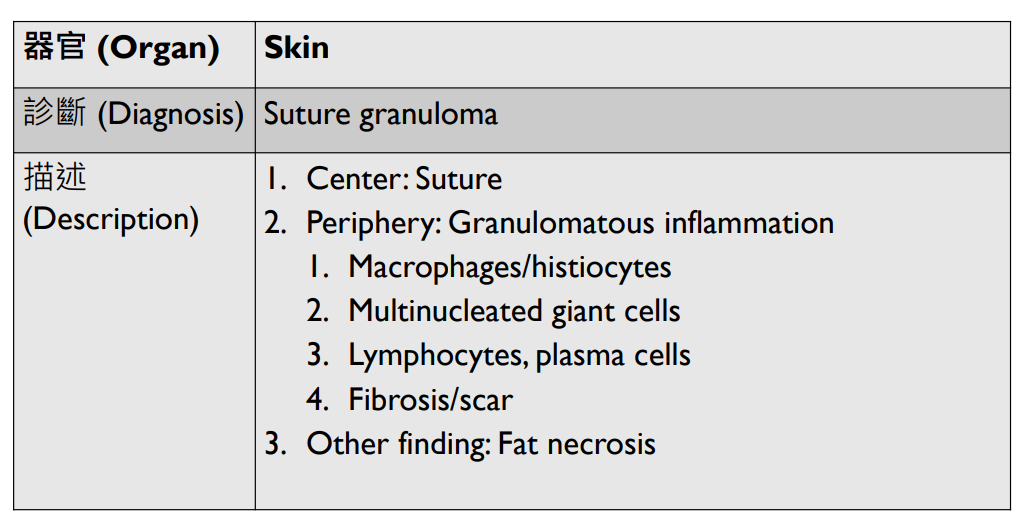
不太考
不太考
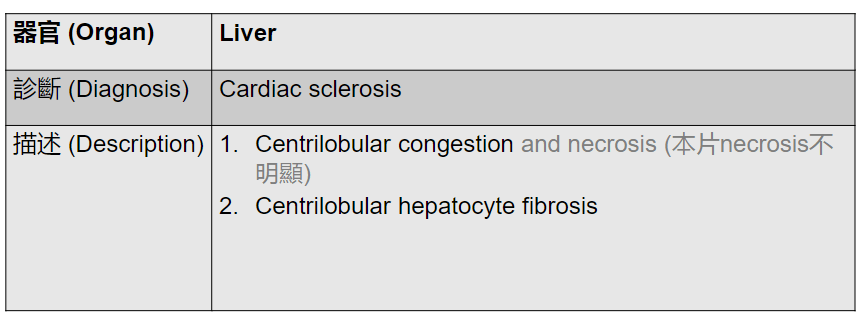
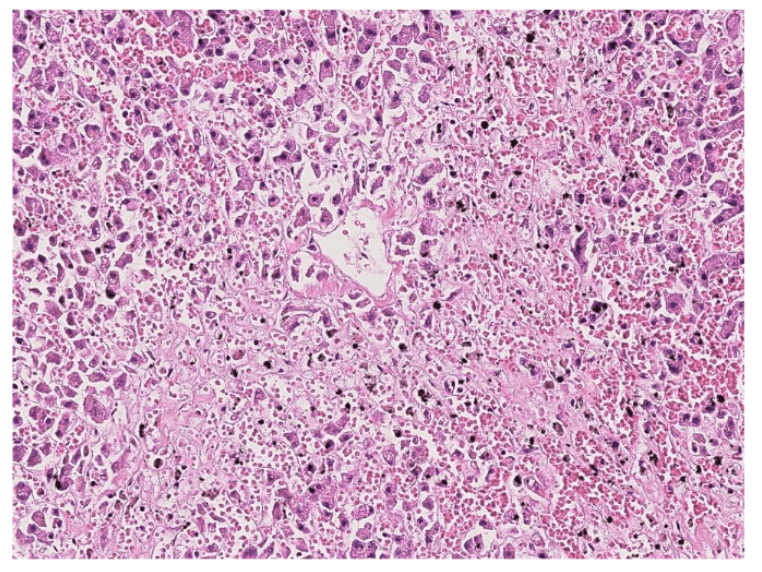
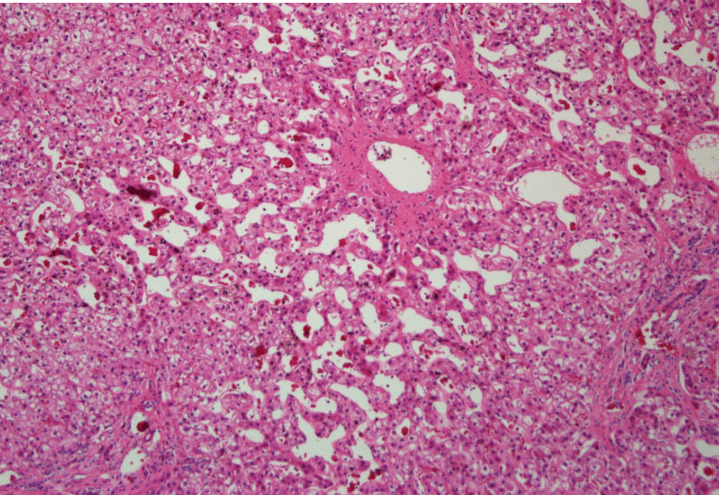
3. Dilation of central vein

(maybe with organization)
(including glomerulus)
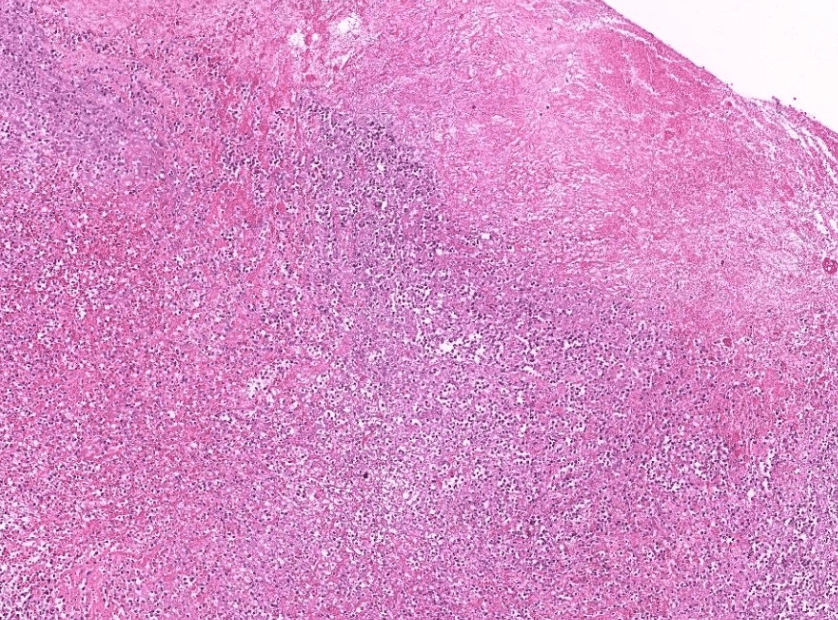
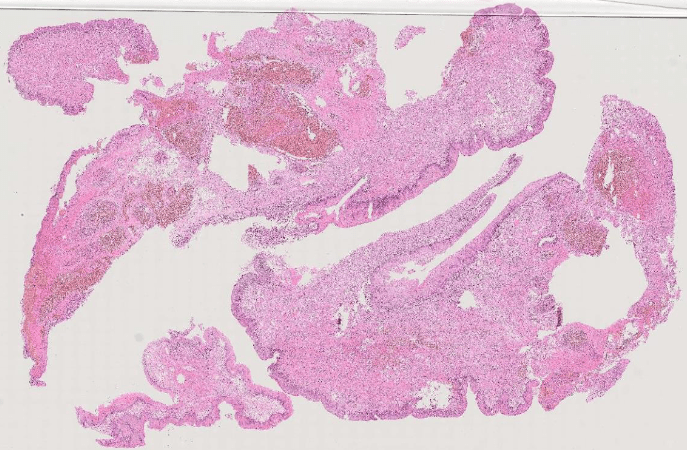
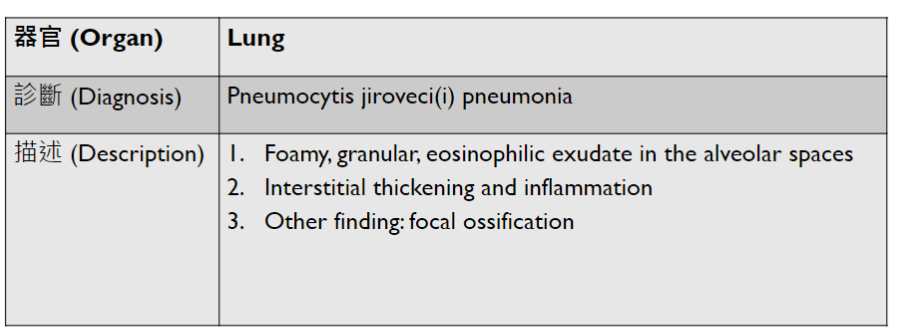
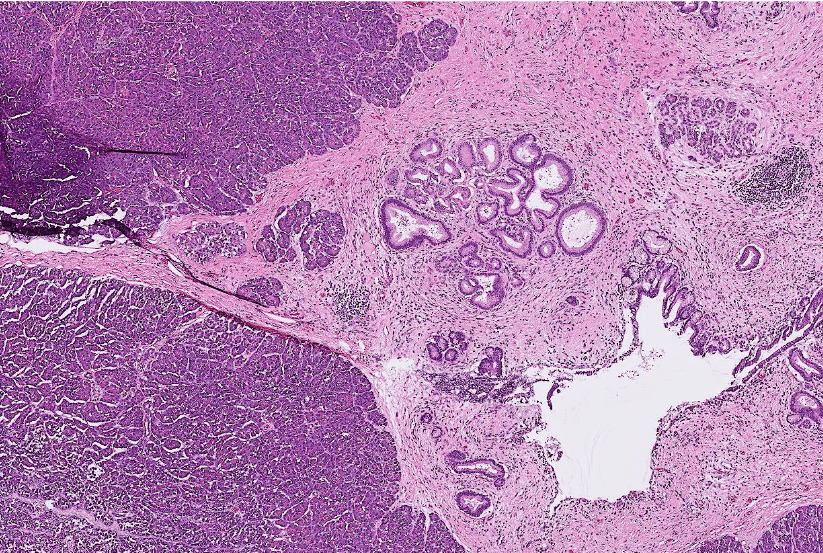
Pathology Lab 1-2
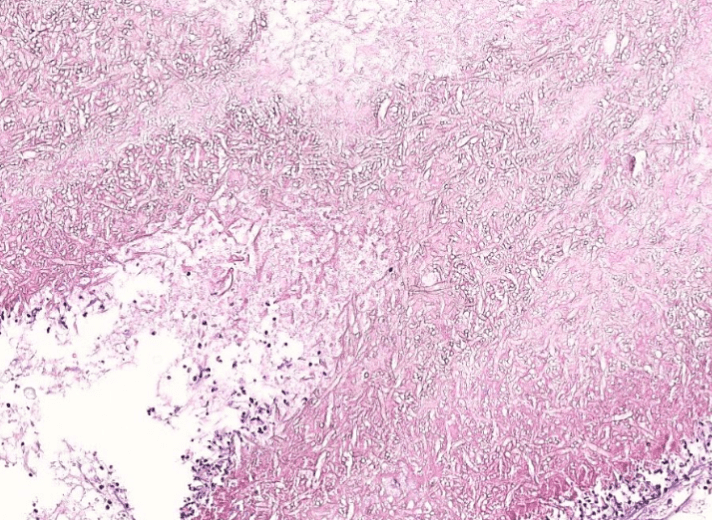
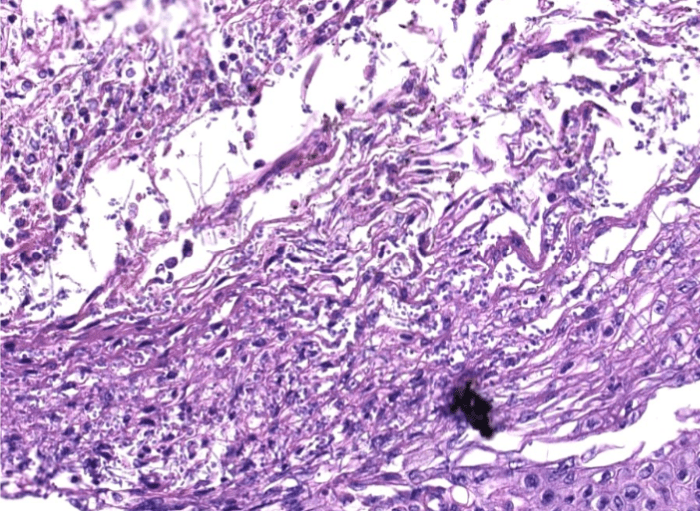
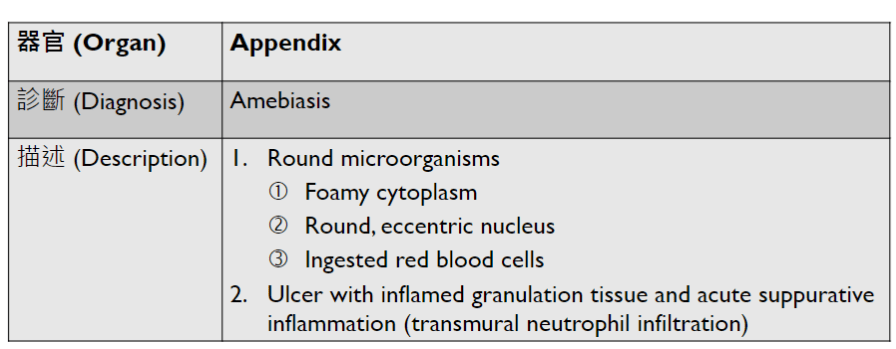
(Infection)

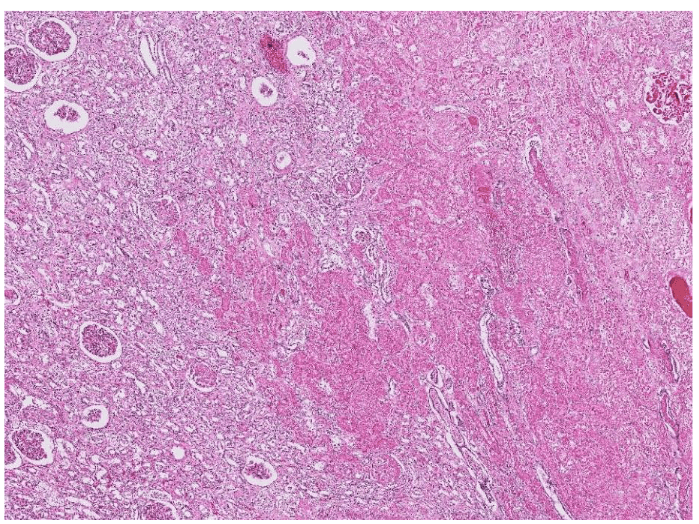
可能跟ulcer一起
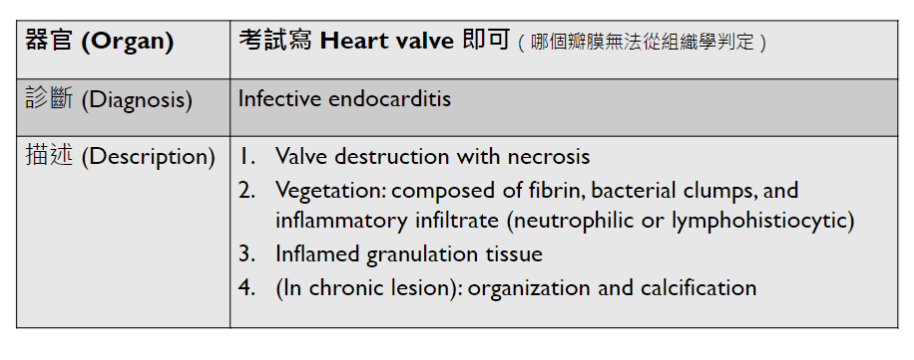

(可以寫多一些)

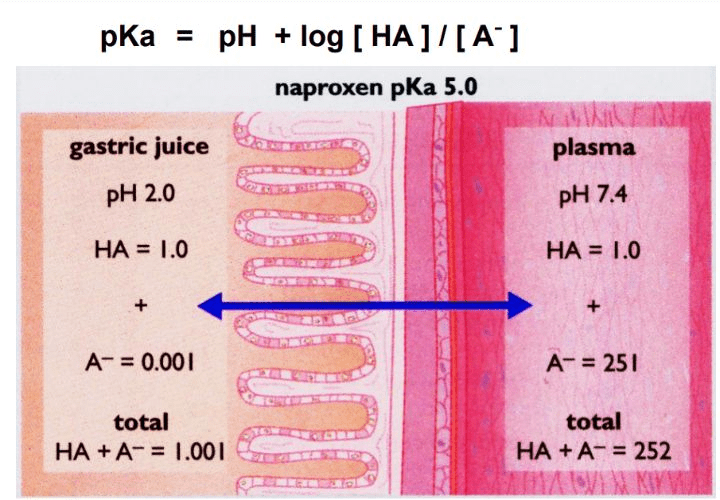
B Drug
4.0
0.01
1.01
2510
2511
breast cancer
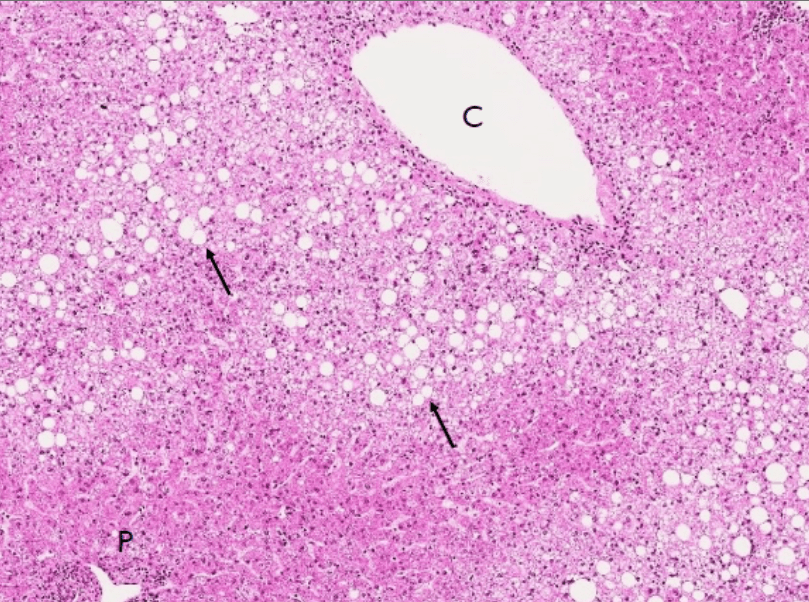
dyslipidemia
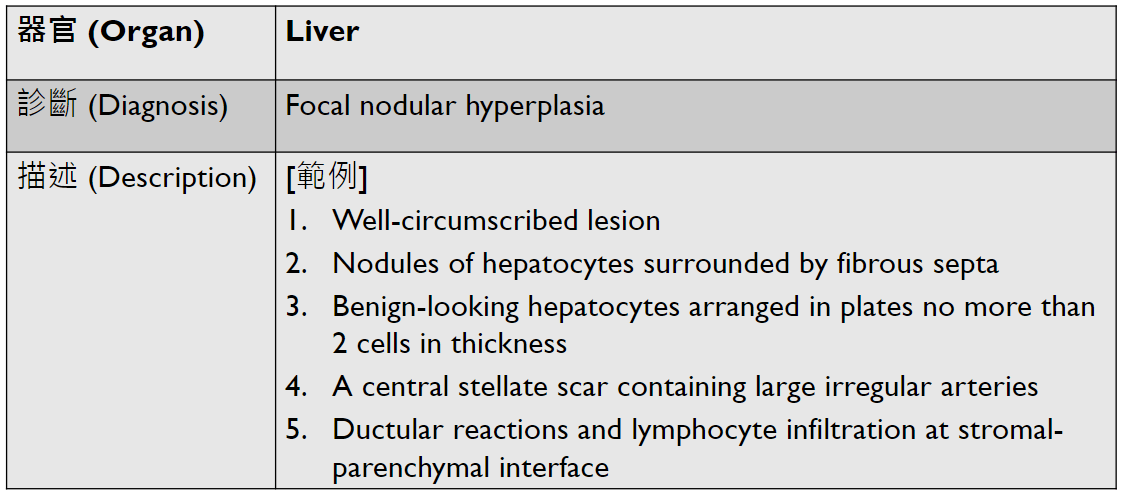
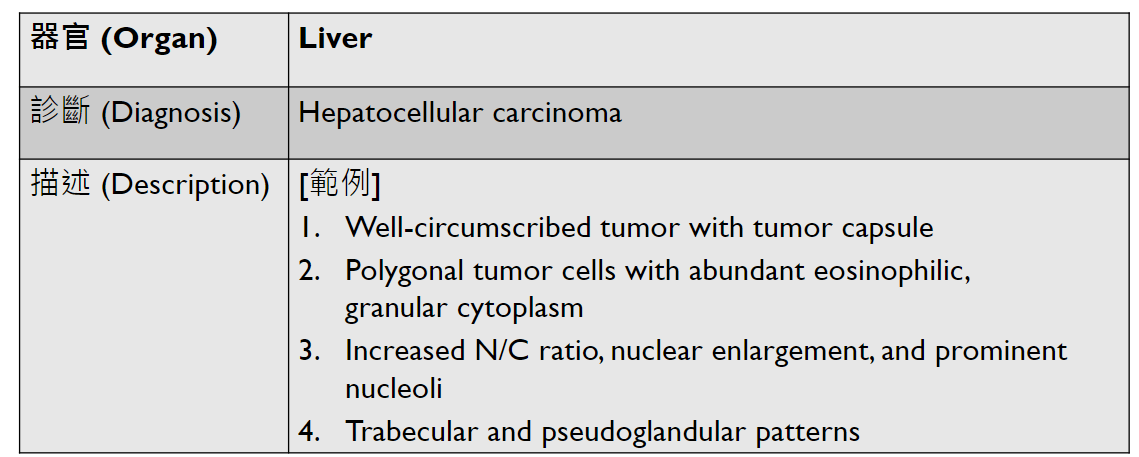
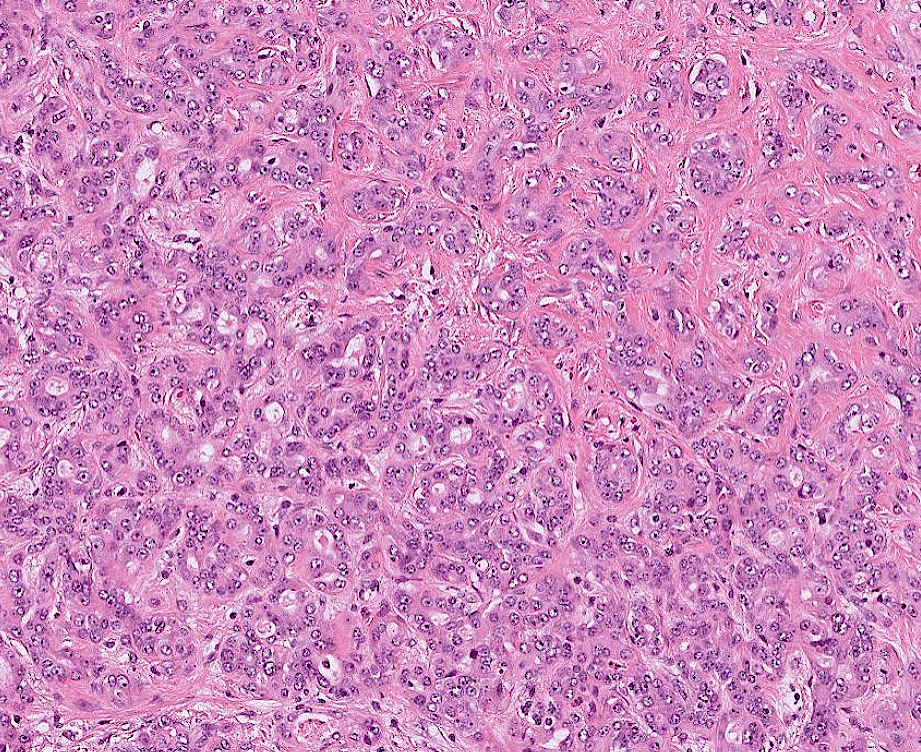
hepatocellular carcinoma
10/3 小組討論
Question
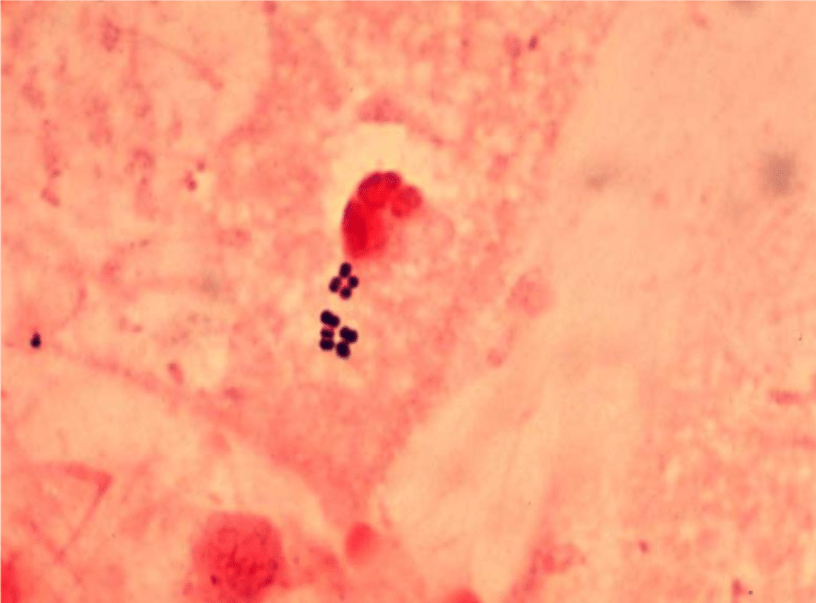
4. 呼吸道病毒感染後常見的細菌感染有哪些?初步的痰液染色如下圖,如何描述以及最可能的致病菌是什麼?
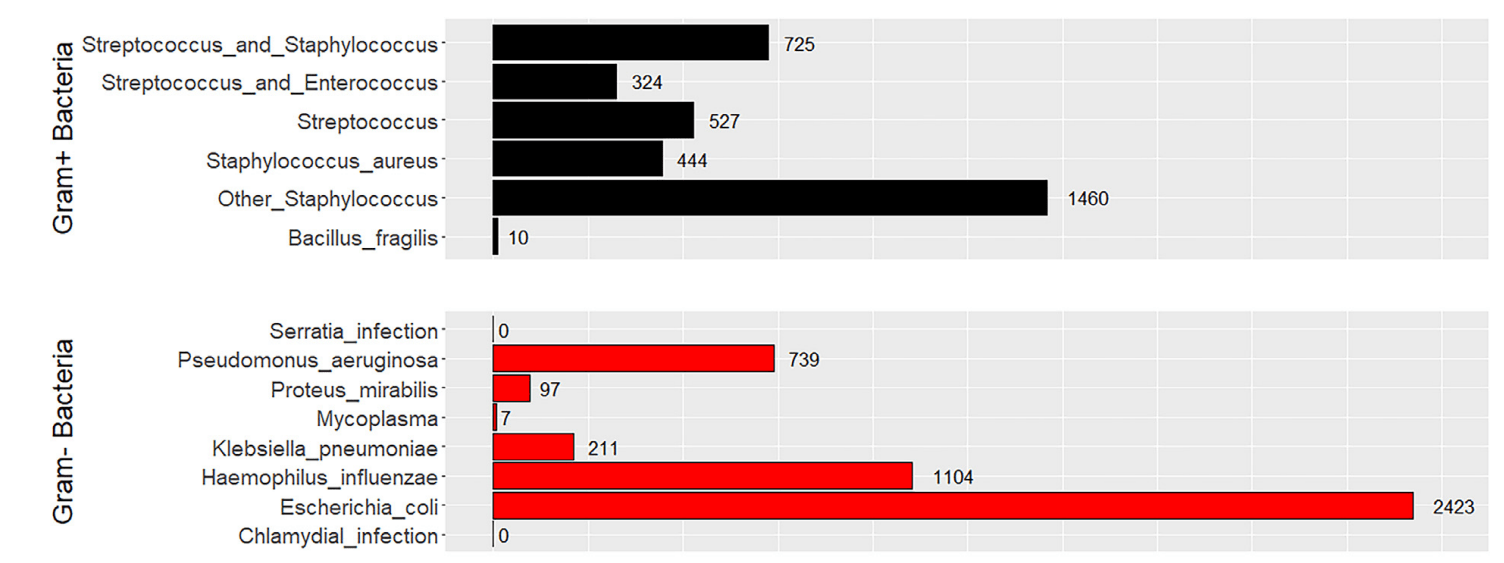
Common Secondary Bacterial Infections Associated to Viral Respiratory Tract Infections
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
Manna S, Baindara P, Mandal SM. Molecular pathogenesis of secondary bacterial infection associated to viral infections including SARS-CoV-2. J Infect Public Health. 2020
Common Secondary Bacterial Infections Associated to COVID-19
Hugh C. Murray, Michael Muleme, Darcie Cooper, Bridgette J. McNamara, Mohammad A. Hussain, Caroline Bartolo, Daniel P. O'Brien, Eugene Athan, Prevalence, risk factors, and outcomes of secondary infections among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 or post–COVID-19 conditions in Victoria, 2020-2023, International Journal of Infectious Diseases,2024
n = 194,660
How do secondary bacterial infections happen?
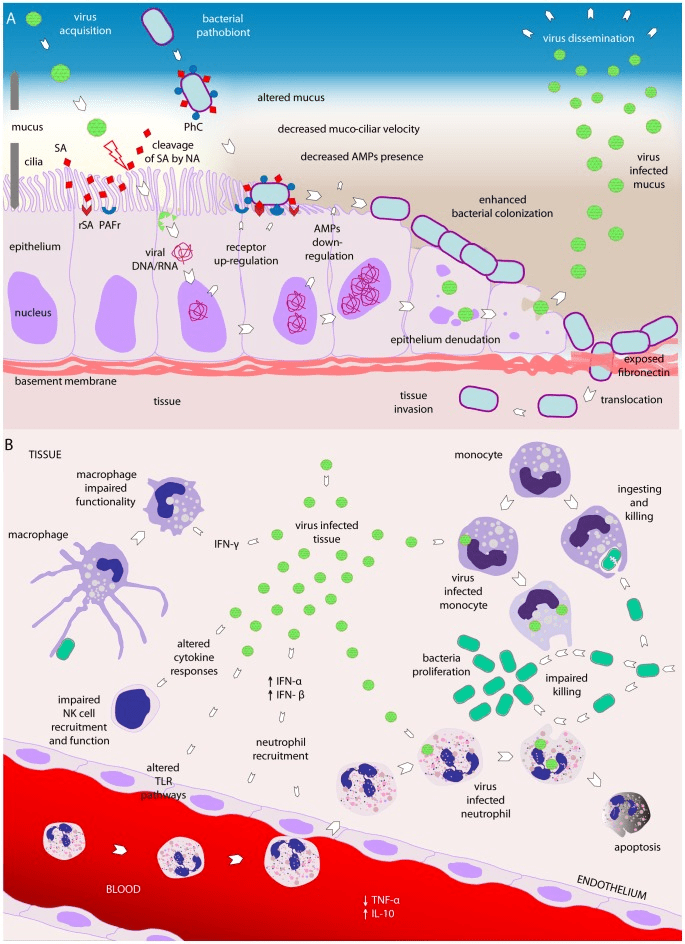
Bosch AA, Biesbroek G, Trzcinski K, Sanders EA, Bogaert D. Viral and bacterial interactions in the upper respiratory tract. PLoS Pathog. 2013
NA:neuraminidase
SA: sialic acid
How do secondary bacterial infections happen?
Bosch AA, Biesbroek G, Trzcinski K, Sanders EA, Bogaert D. Viral and bacterial interactions in the upper respiratory tract. PLoS Pathog. 2013
Those Pathogens in Sputum
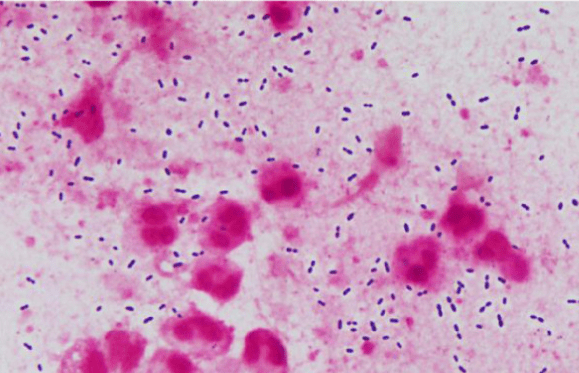
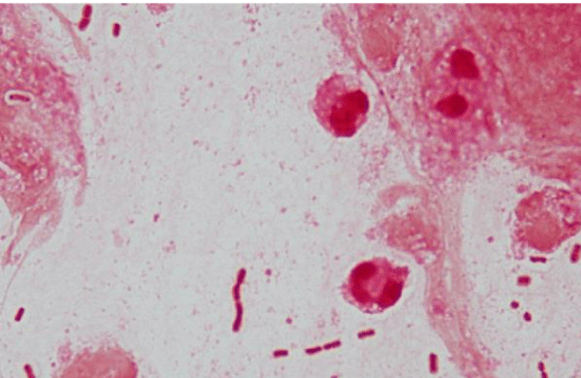
S. pneumoniae (Gram-positive lancet-shaped diplococci)
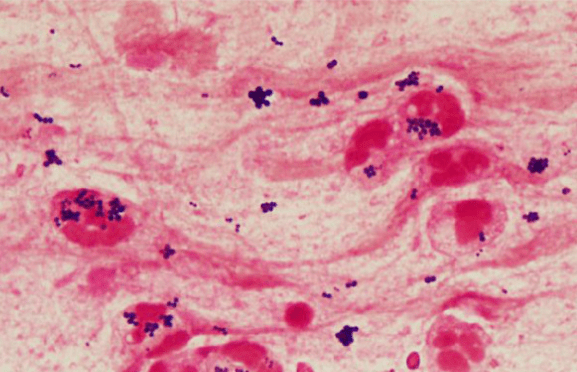
S. aureus (Gram-positive cocci in clusters)
Fukuyama H, Yamashiro S, Kinjo K, Tamaki H, Kishaba T. Validation of sputum Gram stain for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia and healthcare-associated pneumonia: a prospective observational study. BMC Infect Dis. 2014
Those Pathogens in Sputum
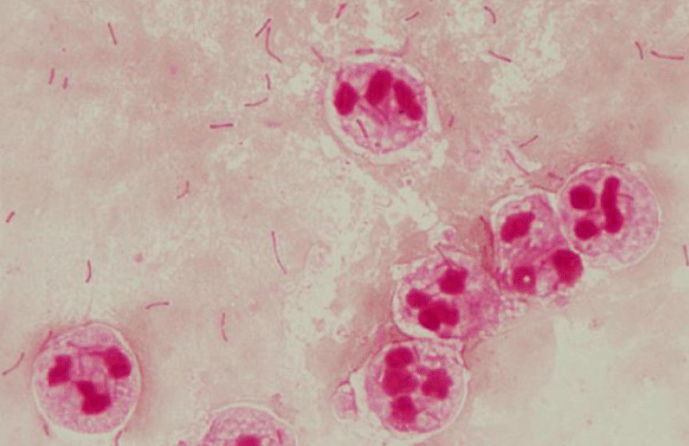
K. pneumoniae
(Gram-negative rods large sized)
Fukuyama H, Yamashiro S, Kinjo K, Tamaki H, Kishaba T. Validation of sputum Gram stain for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia and healthcare-associated pneumonia: a prospective observational study. BMC Infect Dis. 2014
P. aeruginosa
(Gram-negative rods small sized )
Those Pathogens in Sputum
?
Fukuyama H, Yamashiro S, Kinjo K, Tamaki H, Kishaba T. Validation of sputum Gram stain for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia and healthcare-associated pneumonia: a prospective observational study. BMC Infect Dis. 2014
H. influenzae
(Gram-negative coccobacilli )
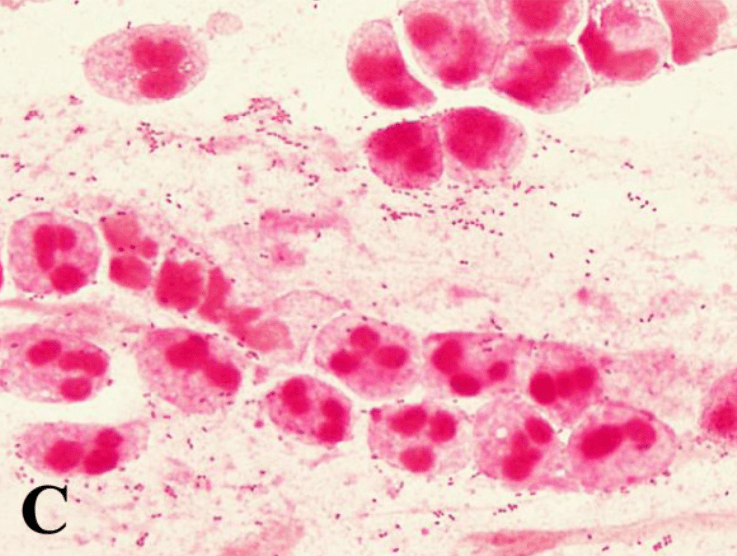


H. influenzae

K. pneumoniae

P. aeruginosa


S. pneumoniae

S. aureus
呼吸道病毒感染後常見的細菌感染有哪些?Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
初步的痰液染色如下圖,如何描述以及最可能的致病菌是什麼?
S. aureus (Gram-positive cocci in clusters)

Question
6. 年長者或免疫不全病患建議的呼吸道相關疾病疫苗有哪些?
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
- Influenza Vaccine
- DTap Vaccine(tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis)
- Pneumococcal Vaccine
- (Recombinant) Zoster Vaccine
- COVID-19
- RSV Vaccine
References:
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
- Influenza Vaccine
- Getting a flu vaccine is now more important than ever as patients are at higher risk of serious COVID-19 health outcomes.
- DTap Vaccine(tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis)
- Pneumococcal Vaccine
- (Recombinant) Zoster Vaccine
- COVID-19
- RSV Vaccine
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
- Influenza Vaccine
- DTap Vaccine(tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis)
- You should not miss an opportunity to vaccinate persons aged 65 years or older with Tdap. (CDC)
- 19歲以上,十年打一次(CDC)
- Pneumococcal Vaccine
- (Recombinant) Zoster Vaccine
- COVID-19
- RSV Vaccine
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
- Influenza Vaccine
- DTap Vaccine(tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis)
- Pneumococcal Vaccine
- recommended for all adults 65 years or older
- (Recombinant) Zoster Vaccine
- COVID-19
- RSV Vaccine
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
- Influenza Vaccine
- DTap Vaccine(tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis)
- Pneumococcal Vaccine
- (Recombinant) Zoster Vaccine
- Recommended for adults 50 years or older
- Varicella Pneumonia (rare)
- Hospitalized patients with HIV or AIDS with chickenpox are at high risk for developing varicella pneumonia.(7/12)
- COVID-19
- RSV Vaccine
Popara M, Pendle S, Sacks L, Smego RA, Mer M. Varicella pneumonia in patients with HIV/AIDS. Int J Infect Dis 2002;6:6–8
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
- Influenza Vaccine
- DTap Vaccine(tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis)
- Pneumococcal Vaccine
- (Recombinant) Zoster Vaccine
- COVID-19
- Recommended for everyone (CDC)
- RSV Vaccine
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
- Influenza Vaccine
- DTap Vaccine(tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis)
- Pneumococcal Vaccine
- (Recombinant) Zoster Vaccine
- COVID-19
- RSV Vaccine
- Recommended for everyone who ages 75 and older/ages 60-74 who are at increased risk of severe RSV disease. (CDC)
Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections

Vaccines for Respiratory Tract Infections
Live vaccines might be contra-indicated in immunocompromised patients!
- BCG Vaccine(卡介苗): always contraindicated
- Varicella-containing Vaccines: contraindicated in people who are significantly immunocompromised as a result of a medical condition
Q(A)/Discussion
Laureates of the Nobel Prize 2024
Zi-Hong Xiao
2024/10/17





Physiology or Medicine
Physics
Chemistry
Literature
Peace


Economic Science

Physiology or Medicine Prize
Before Their Research
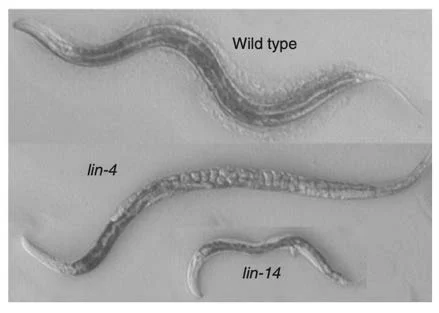
(lf)/lin-14(gf)
(lf)
[reiterated L1 stage growth]
[lack of L1 stage growth]
lin-4 negatively regulates lin-14
Victor Ambros
Gary Ruvkun
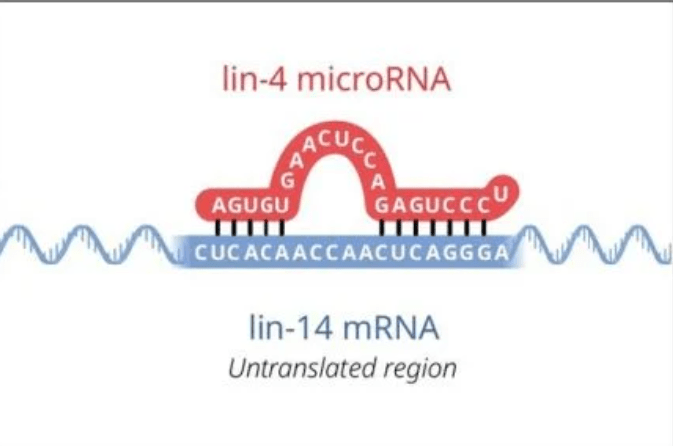
lin-4 is unlikely to encode a protein.
lin-4 encodes two small RNA transcripts.
There is partial complementarity between the lin-4 noncoding RNA and multiple elements in the lin-14 3’UTR.
Down-regulation of lin-14p occurs at a post-transcriptional step.
lin-4 and lin-14 3'-UTR is involved in the regulation.

John Hopfield: Hopfield Network
A network of "neurons" with memory.

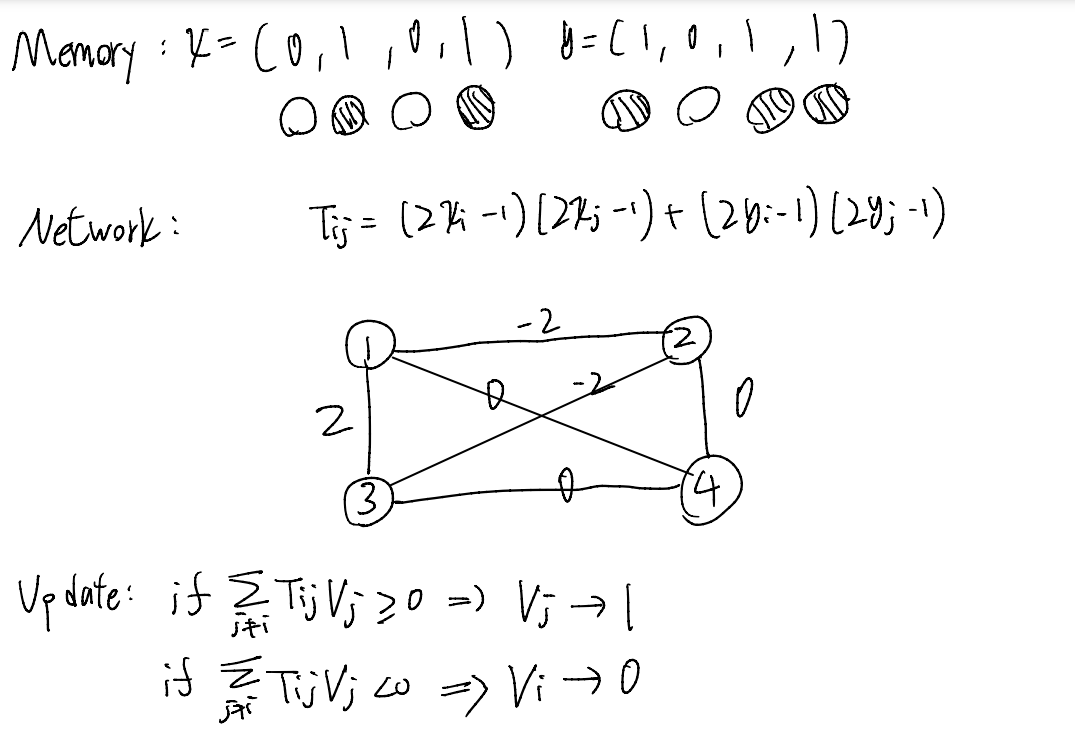
\(\sum\limits_{V_j = 1, j \neq i} T_{ij}\)
\(\sum\limits_{V_j = 1, j \neq i} T_{ij}\)
Geoffrey Hinton: Boltzmann Machine
An early generative model.
Pretty much like the Hopfield Network, but...
The edge weights are "trained" using gradient descent.
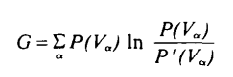
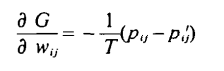
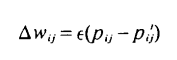
The update process is random.
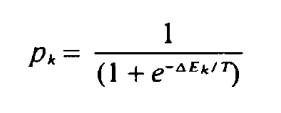
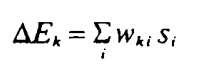


amino acid sequence
protein structure
structure prediction
protein design

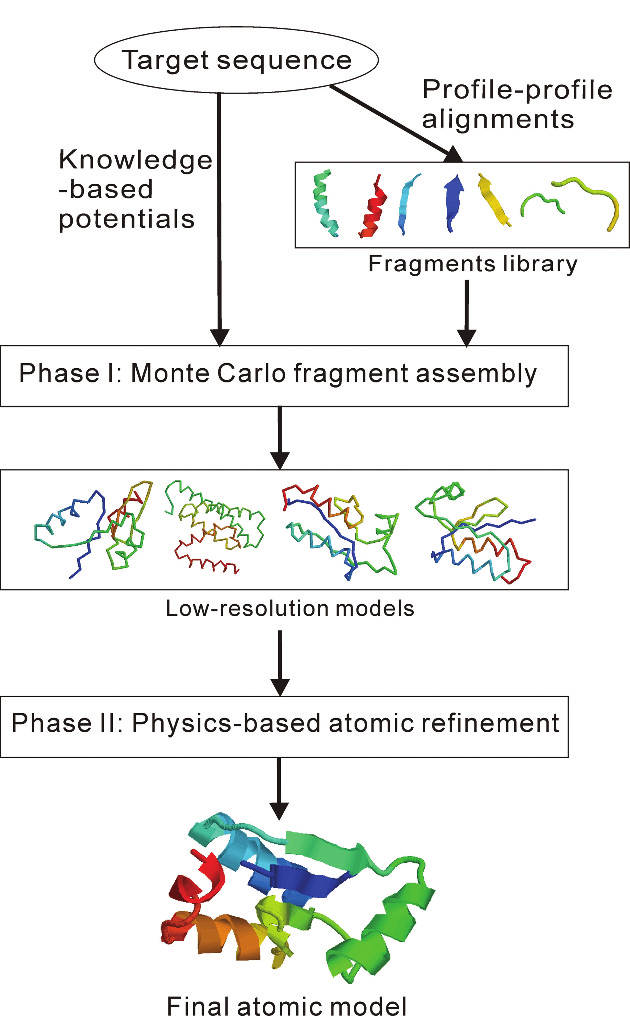
David Baker: Rosetta Algorithm
A useful tool for structure prediction and protein design.
(published in 2004)
......
Foldit

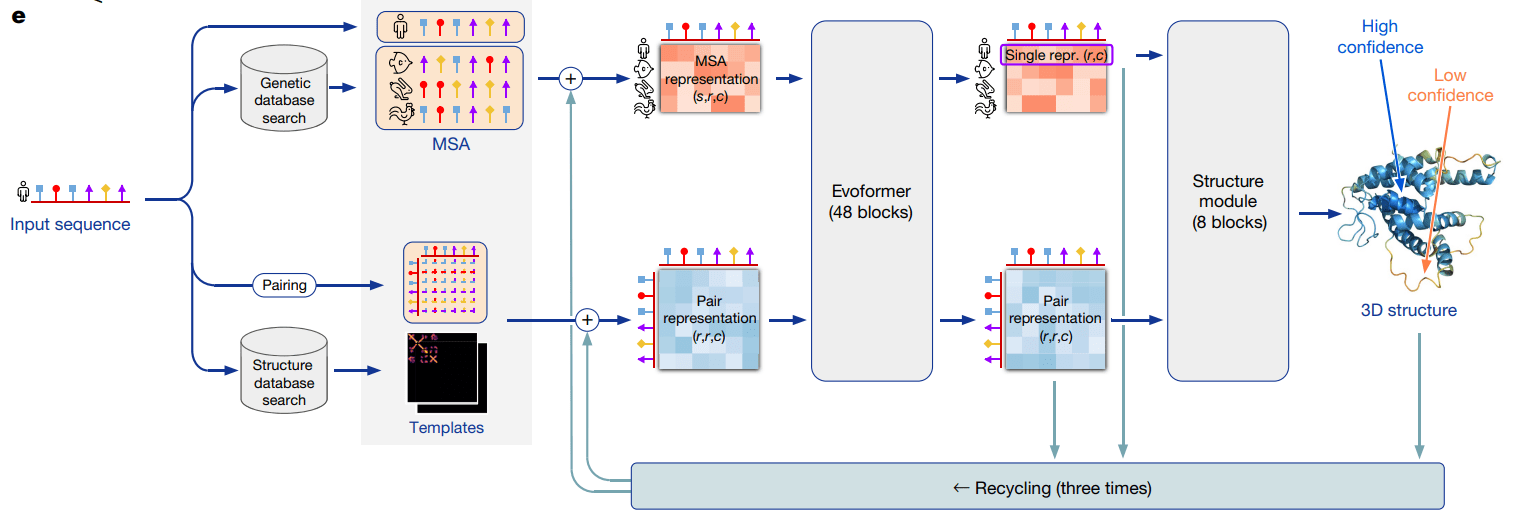
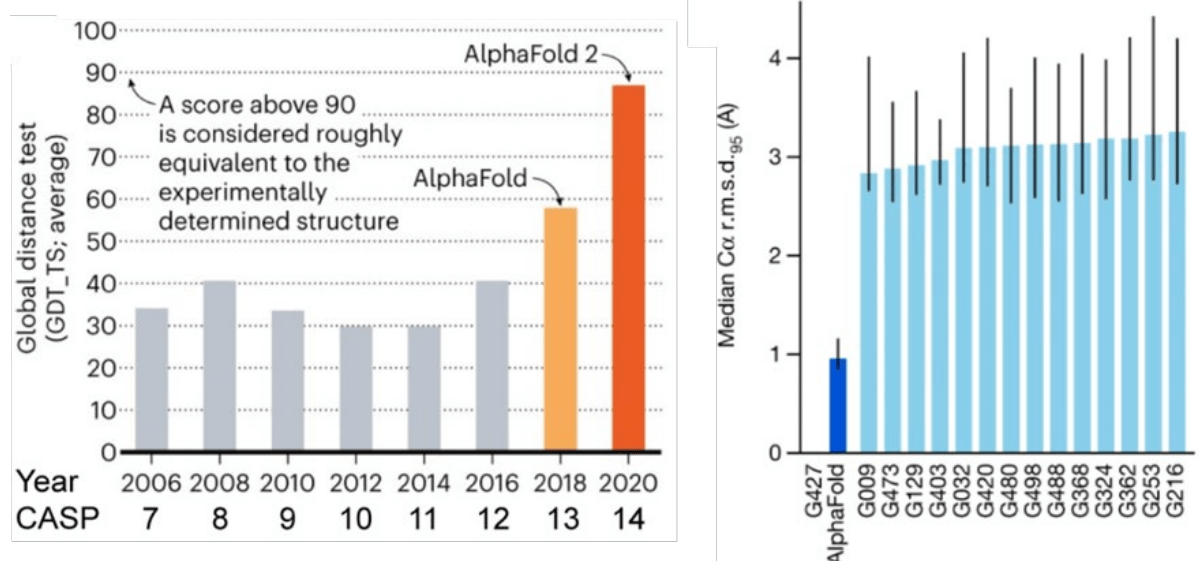
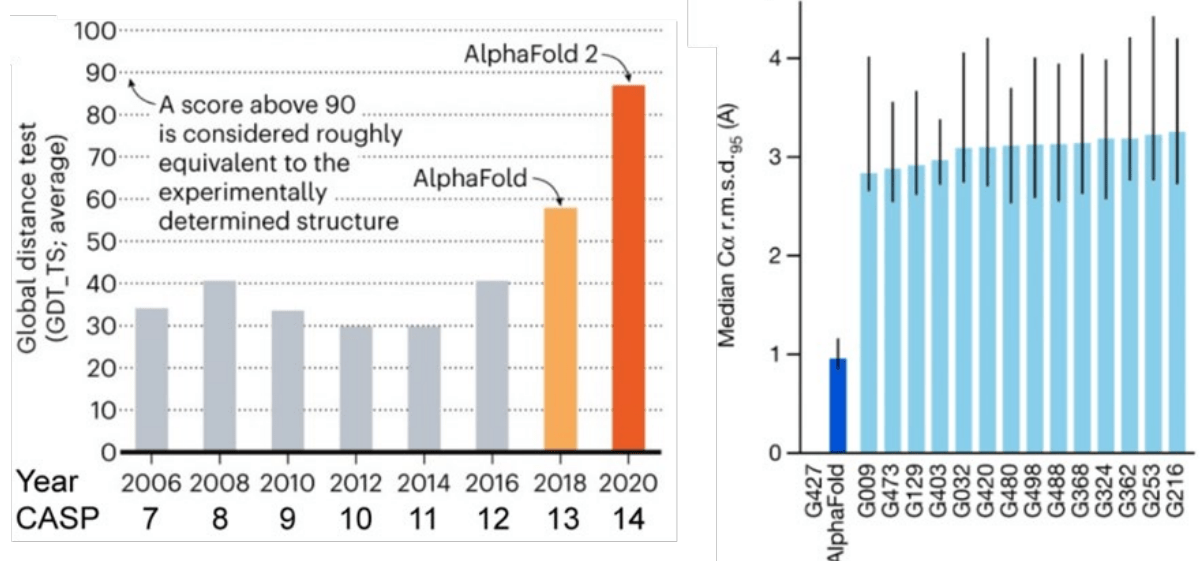
Demis Hassabis, John Jumper: Alphafold
A deep learning model that "solves the 50-year-old grand challenge in biology".



散文
- Born 1970 in a literary family
- Devoted to art and music
- Suffers from migraine

偏頭痛
Some Novels of Han Kang(韓江)
- The Vegetarian, 2007(素食者)
- Human Acts, 2014(少年來了)
- The White Book, 2016(白)
- We do not part, 2021(不做告別)



NIHON HIDANKYO
(日本原水爆被害者団体協議会,日本被団協)

- Founded in 1956
- Composed of Hibakusya(被爆者, atomic bomb survivors)
- Objectives
- Prevention of nuclear war and the elimination of nuclear weapons
- State compensation for the atomic bomb damages
- Improvement of the current policies and measures on the protection and assistance for the Hibakusya
制度
繁榮

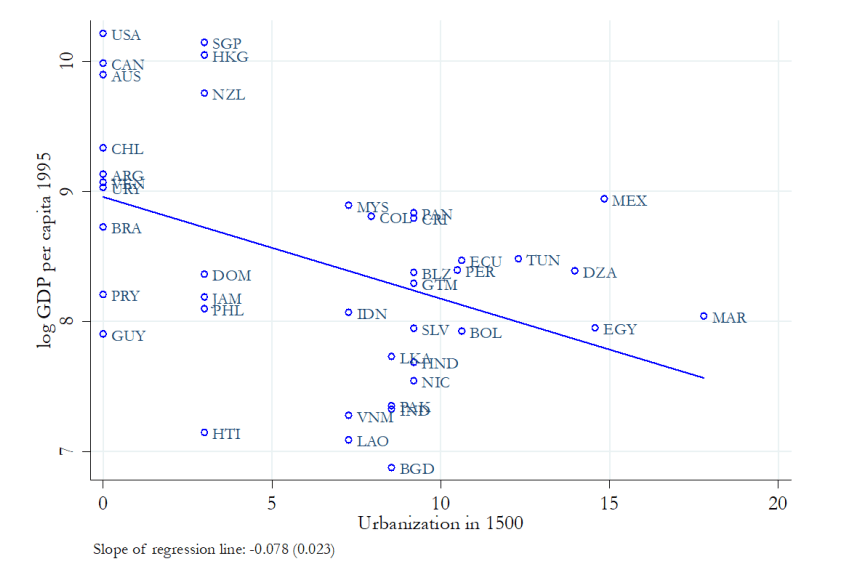
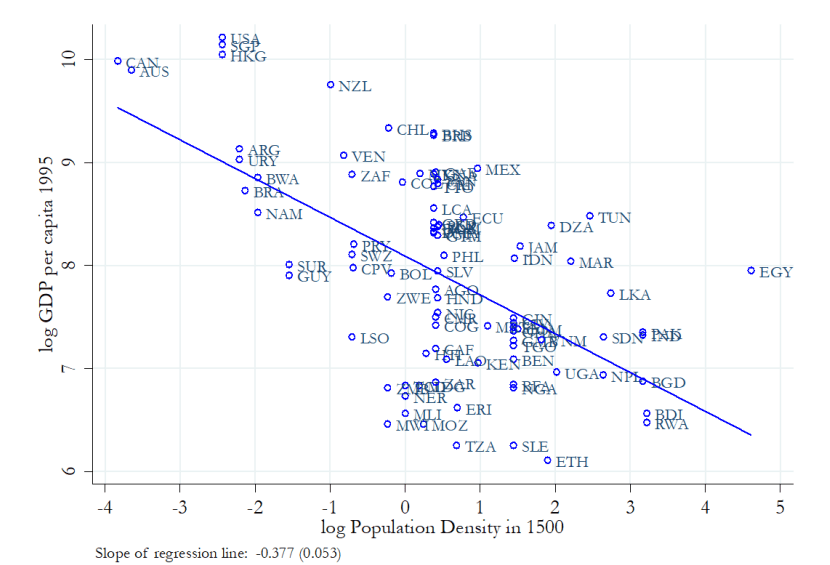
Reversal of Fortune?
1500
Richer regions
Densely populated
Less settlers
Extractive institutions
colonized
High tax
discourage investment
1995
Poorer countries
Poorer regions
Sparsely populated
More Settlers
Institutions of private property
More incentive for investment
better economic performance
Richer countries
Want to know more?
- Try out the Hopfield Network Simulator
- Play Foldit
- Read one of Han Kang's novels
- Take a look at nobelprize.org
Additional References
Pathology Micro-2
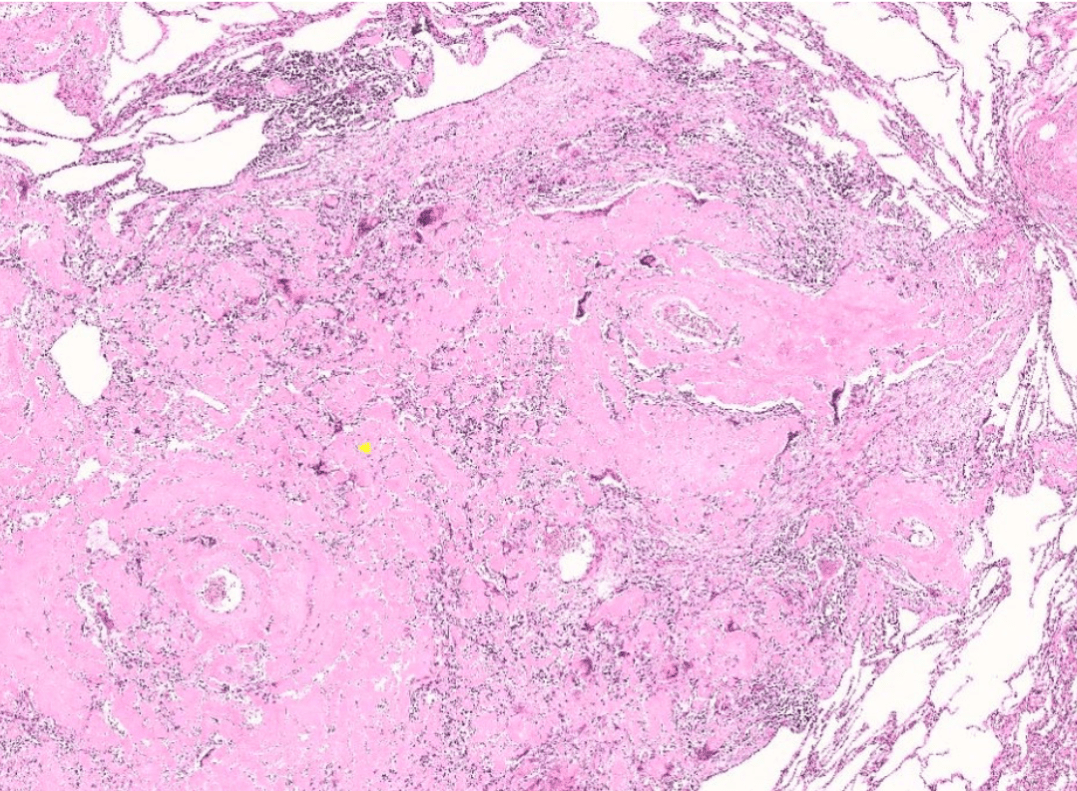

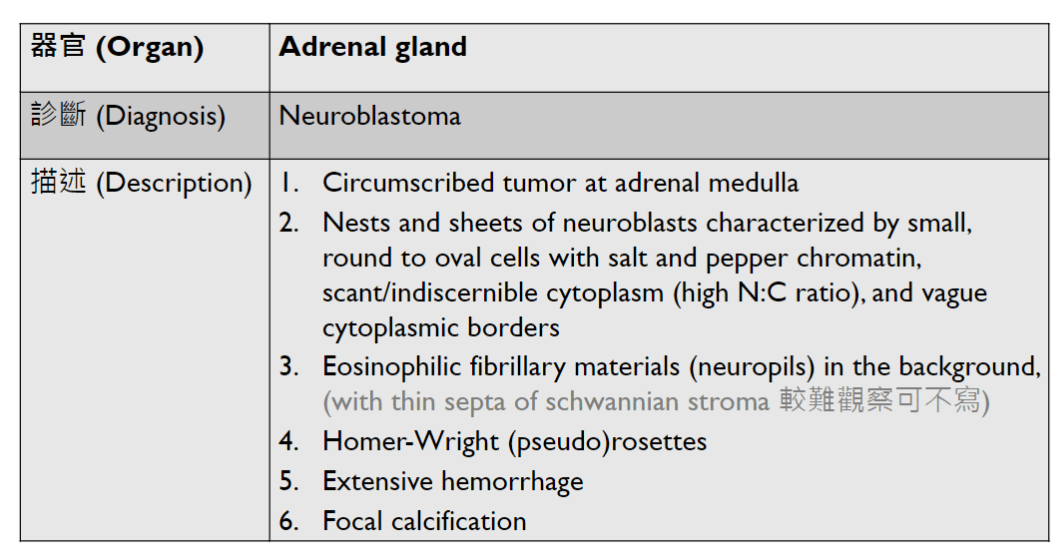
(heart, other organs)
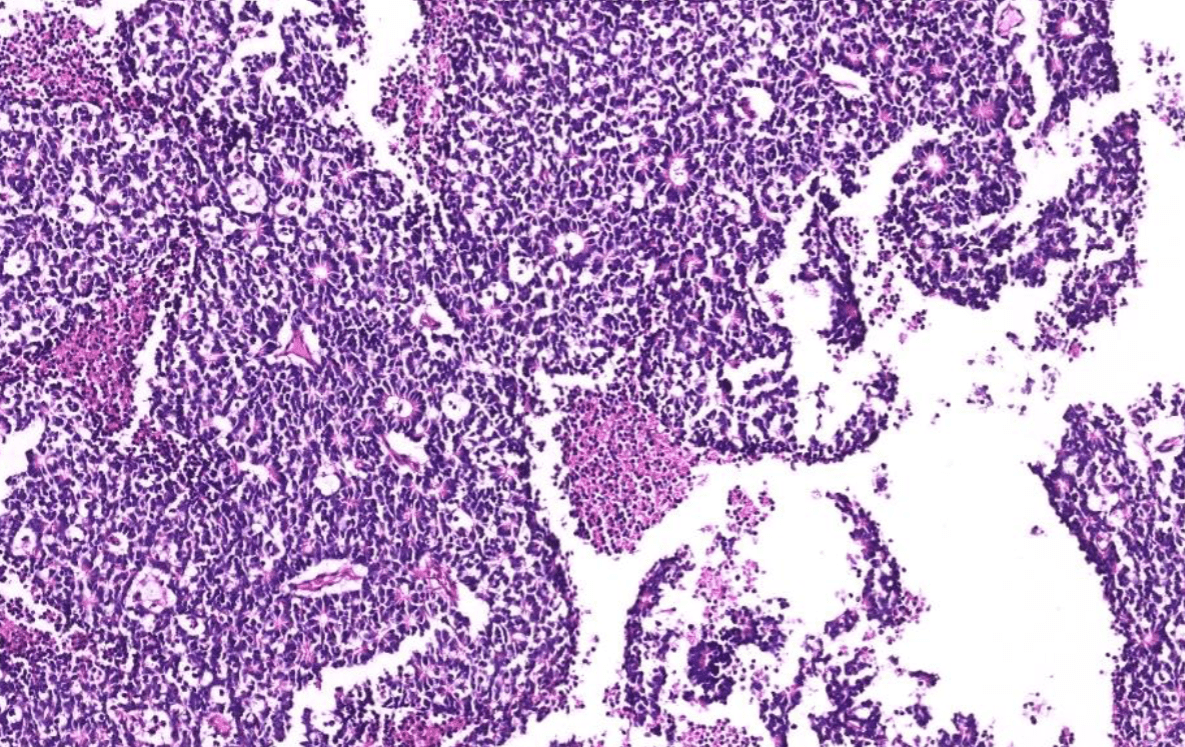

描述位置!
(may have heterologous elements, like cartilage or skeletal mescle)
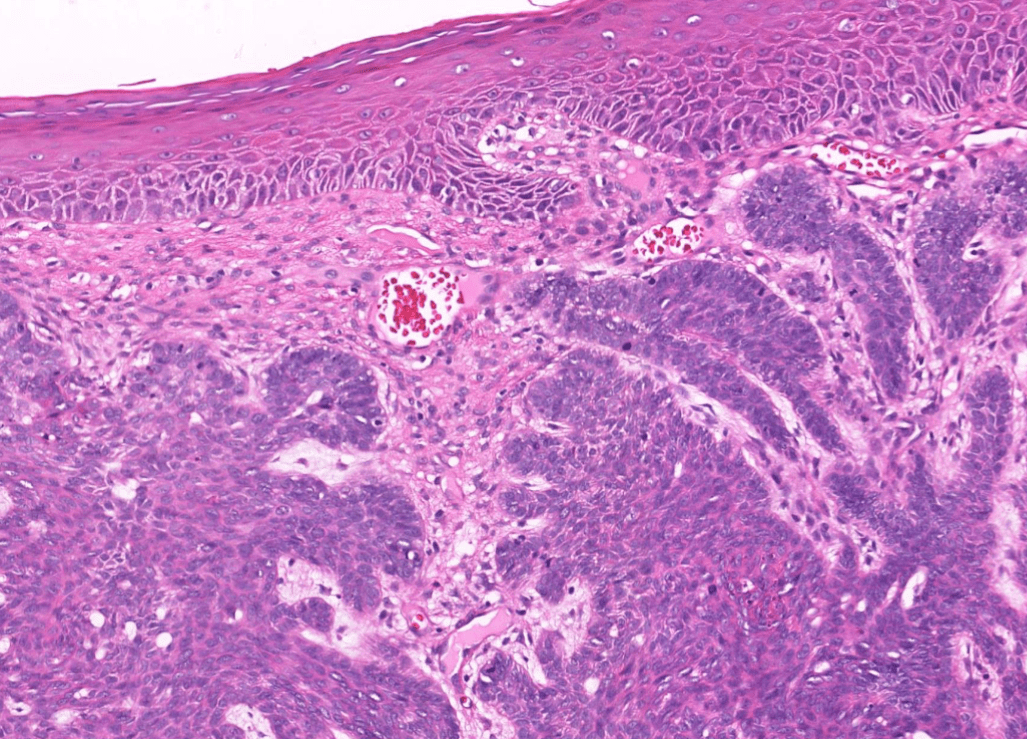
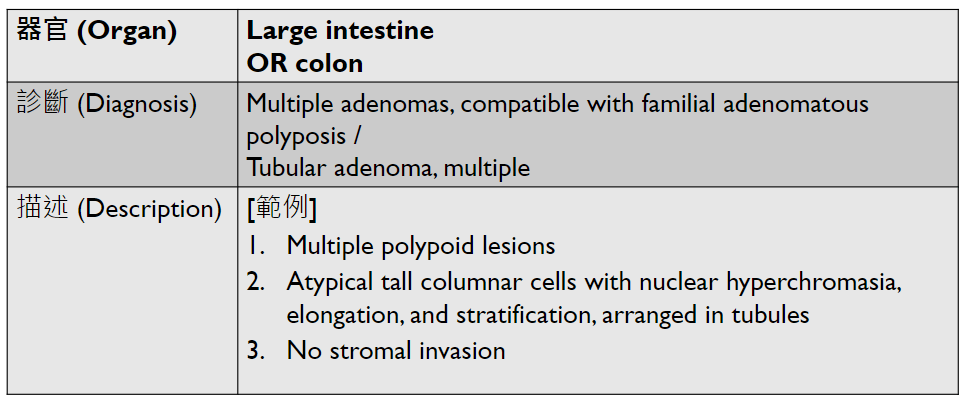
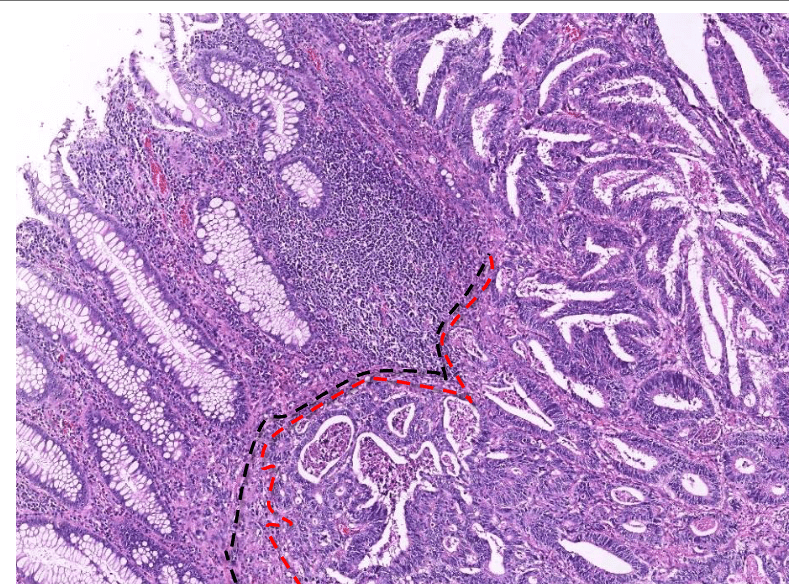
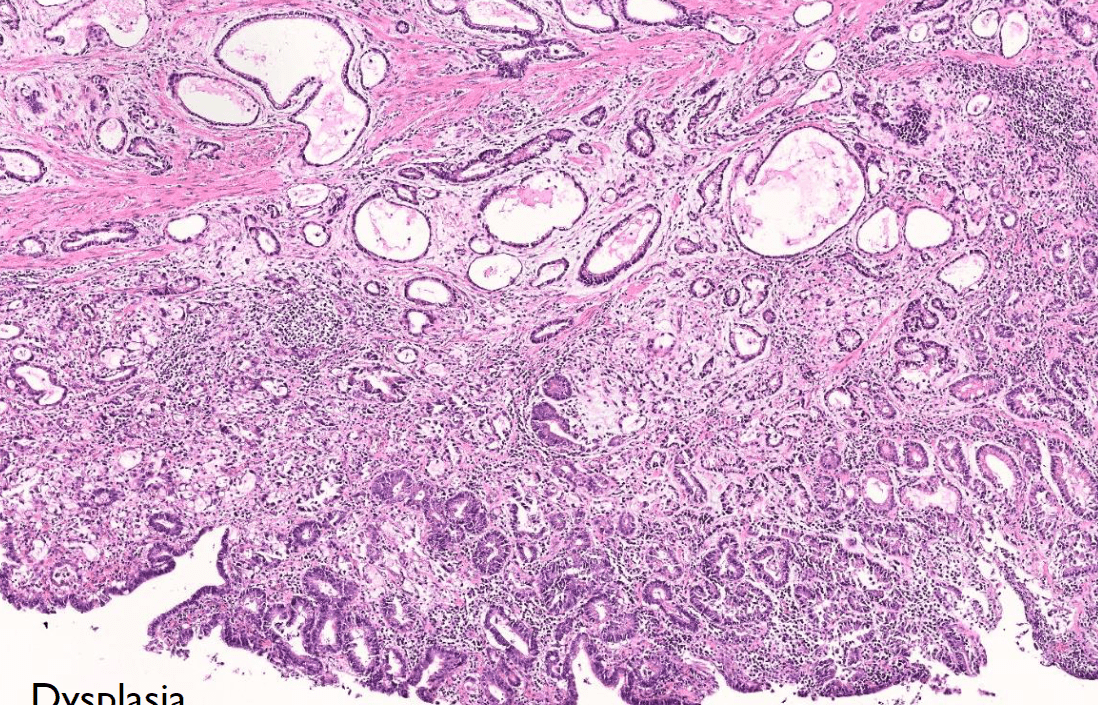
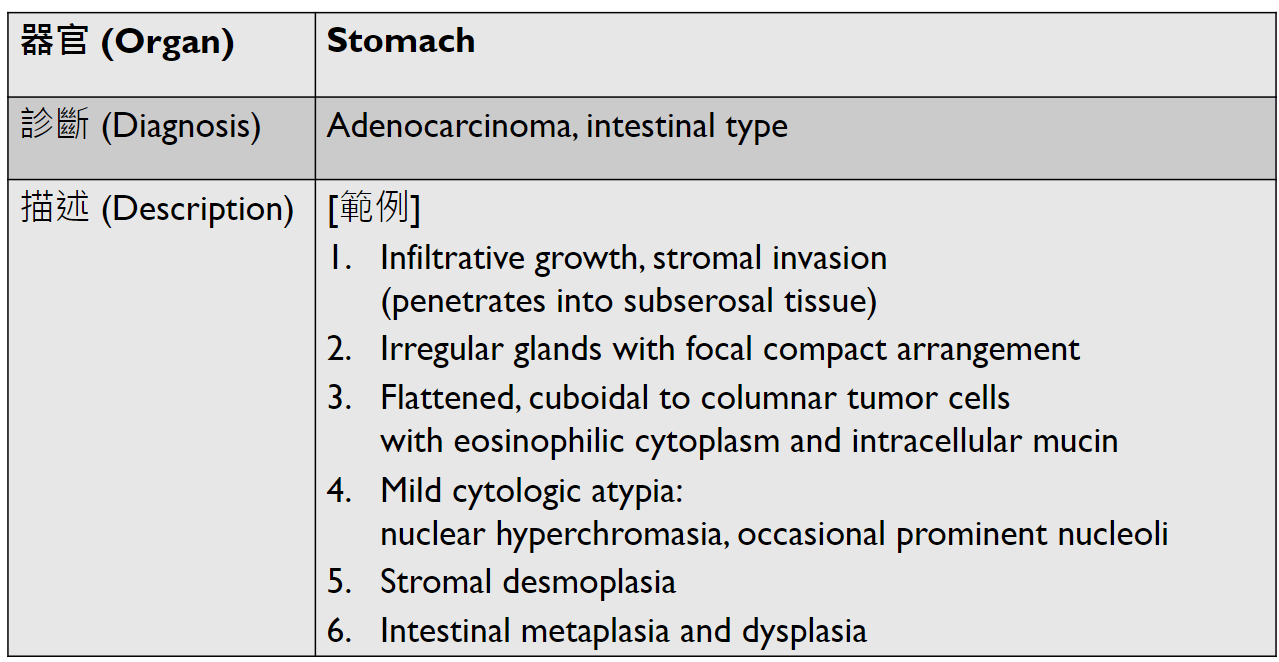
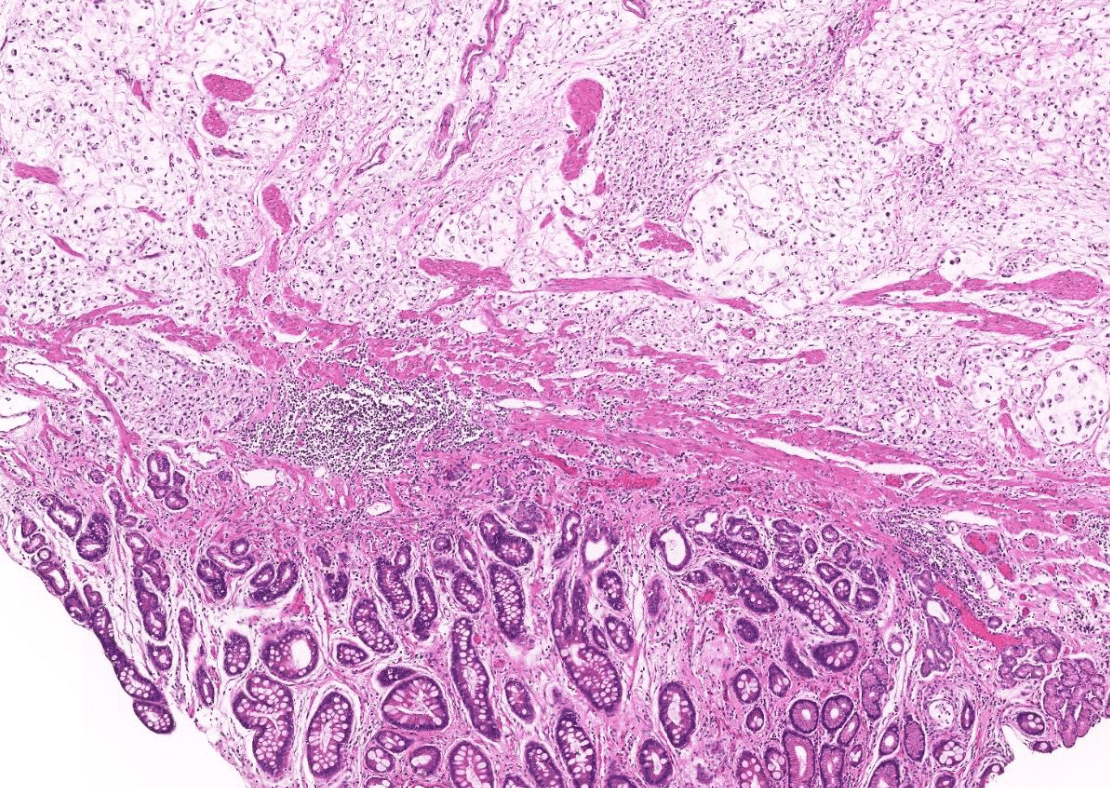
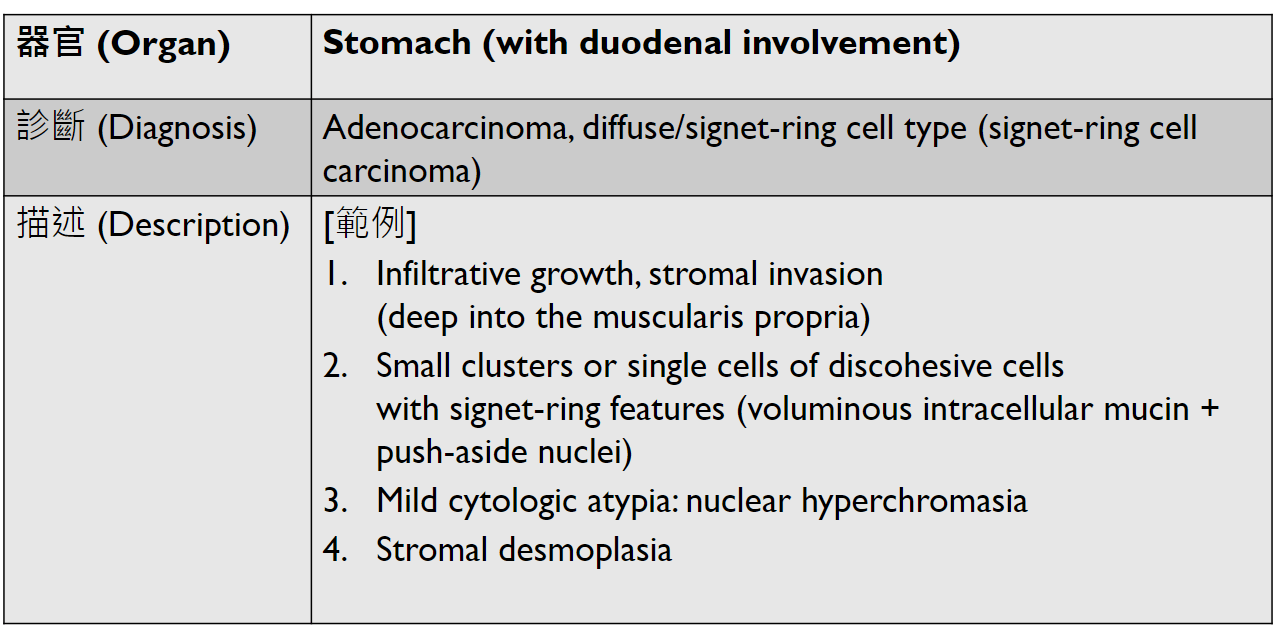
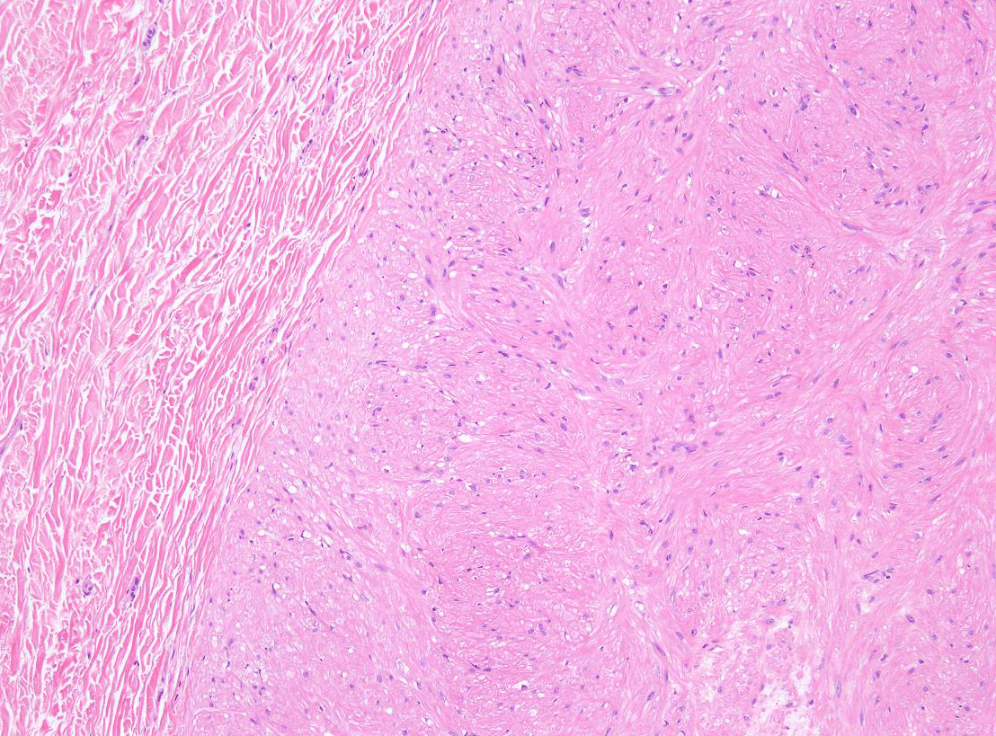
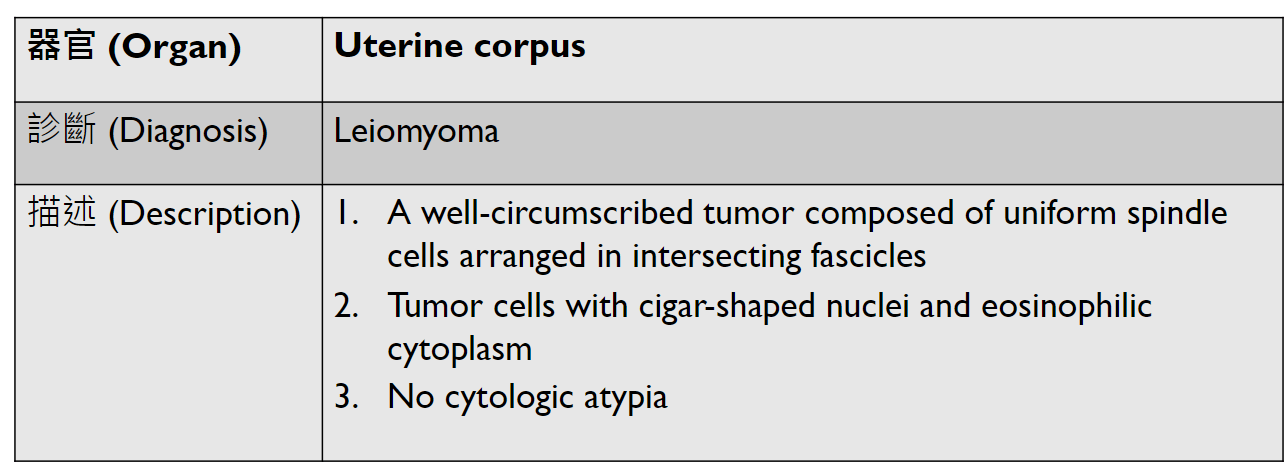
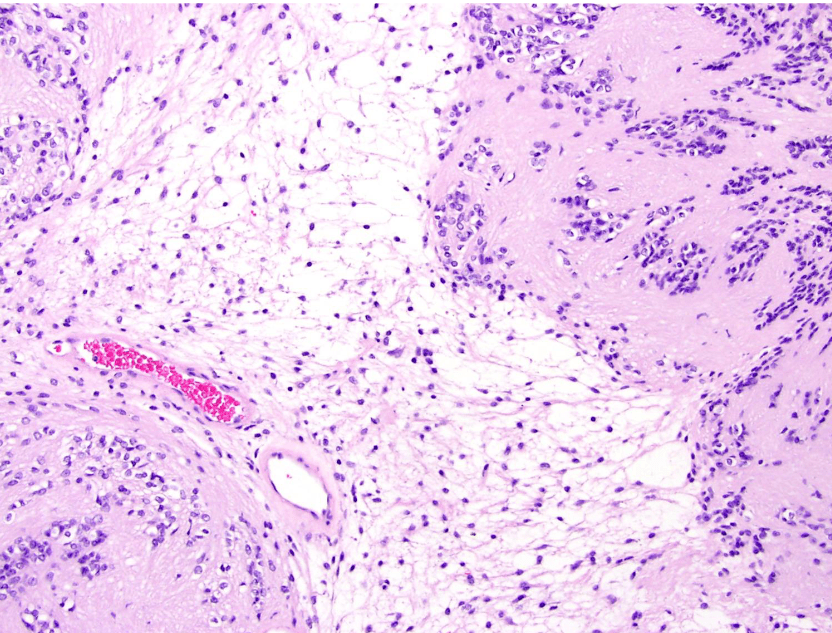
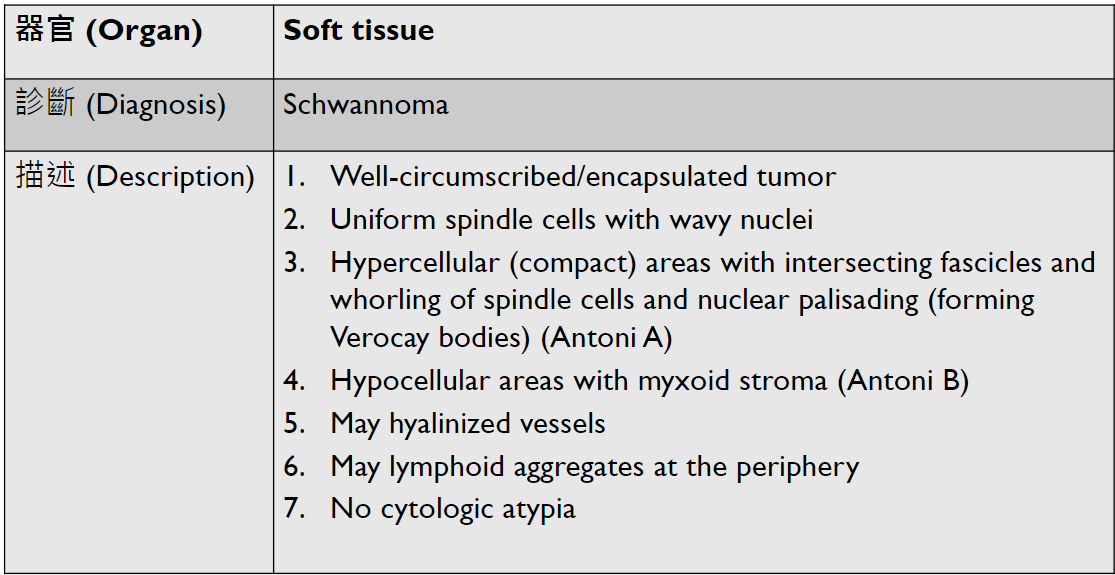
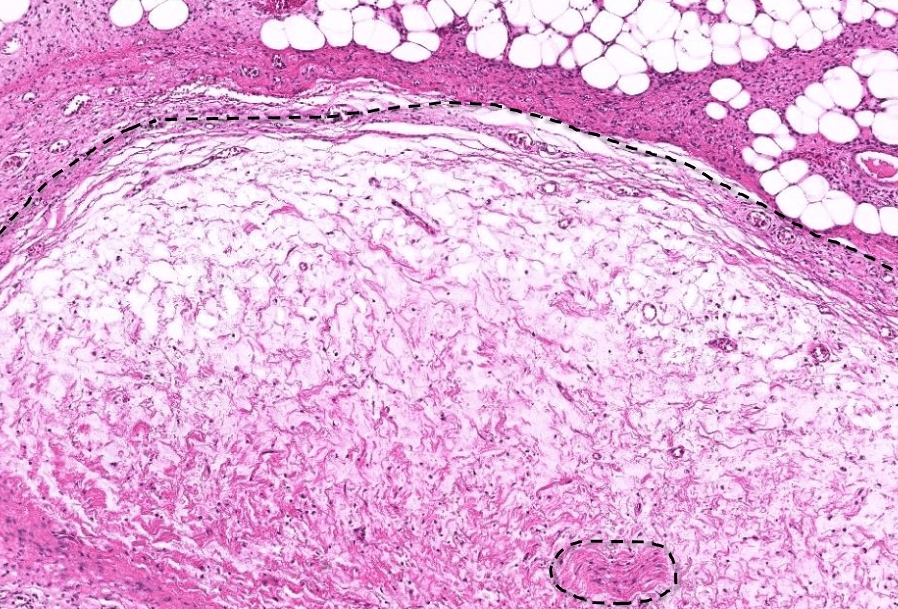
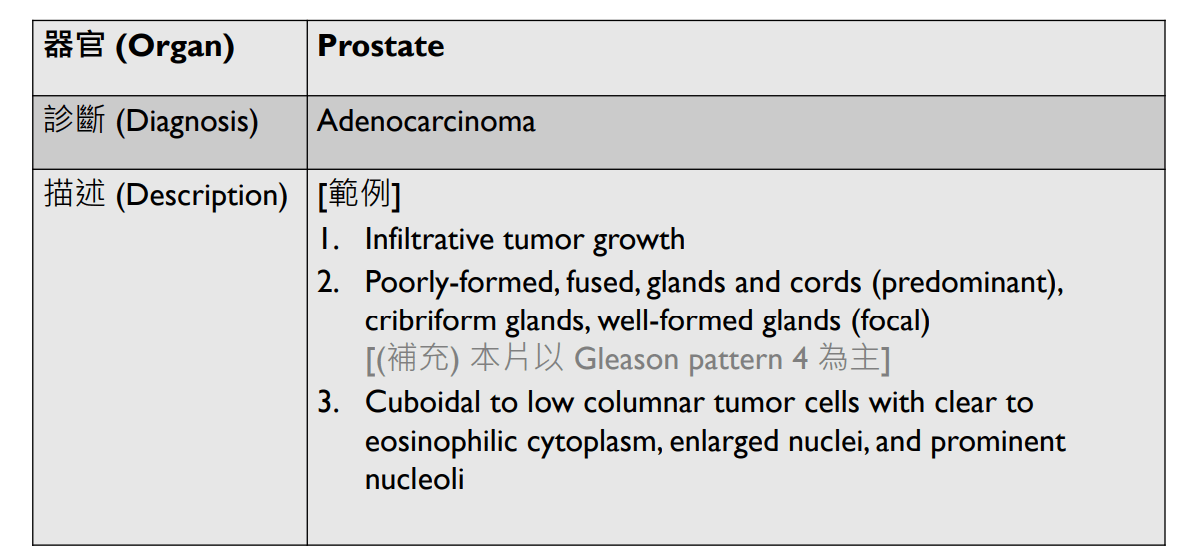
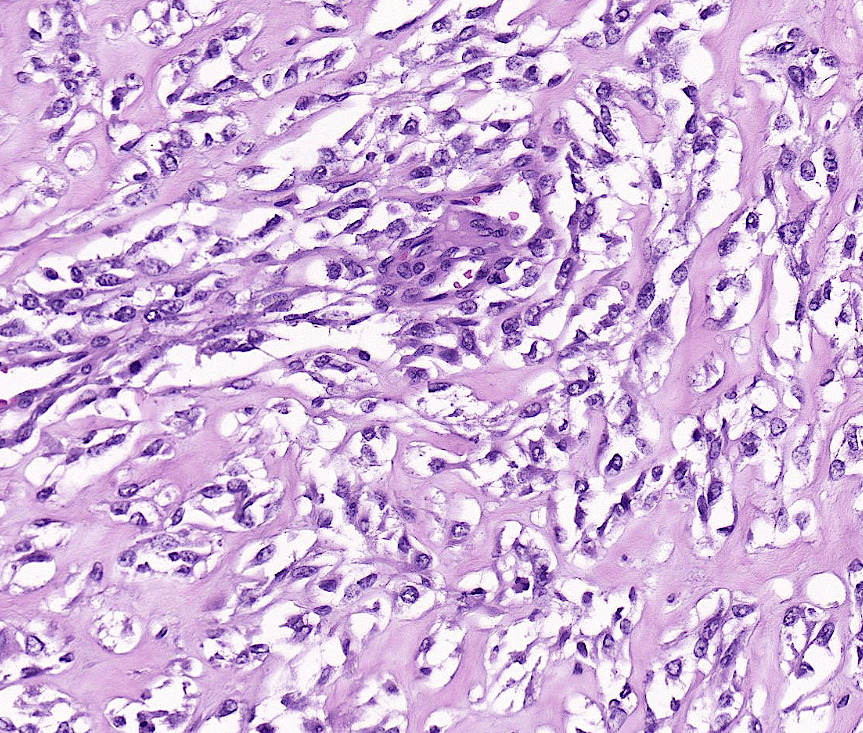
Tumor Description:
1. border(infiltrative到哪裡/circumscribed/capsule)
2. architecture
3. cell 長相
4. stroma
5. 其他周邊異常
5. stromal desmoplasia
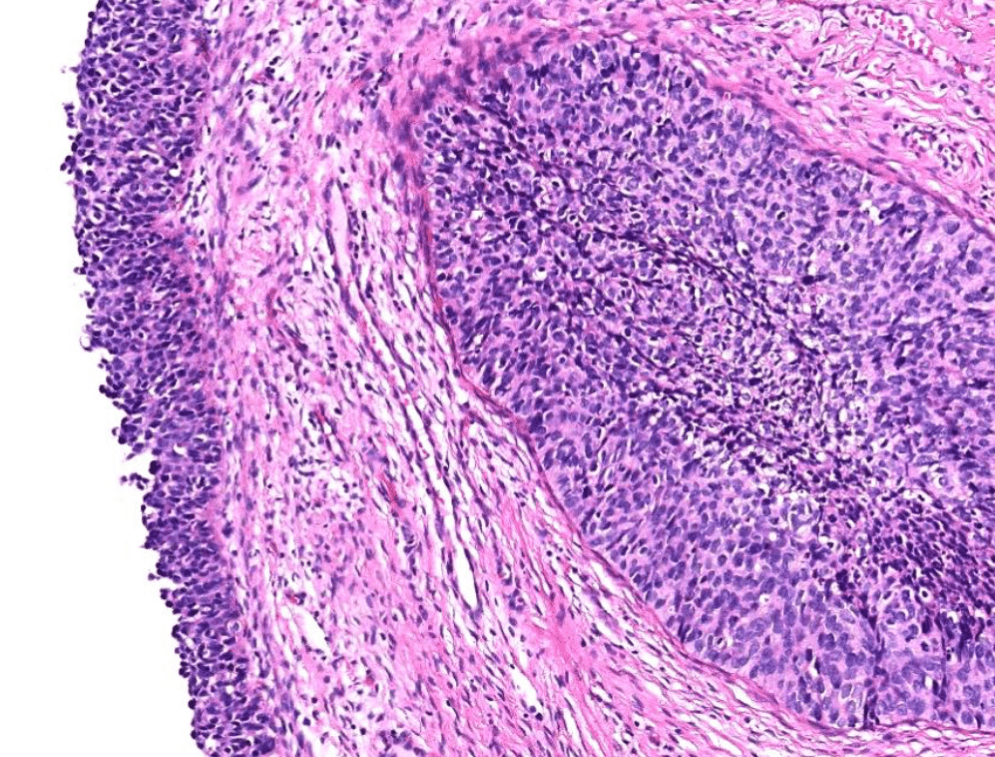
(Nabothian cyst)
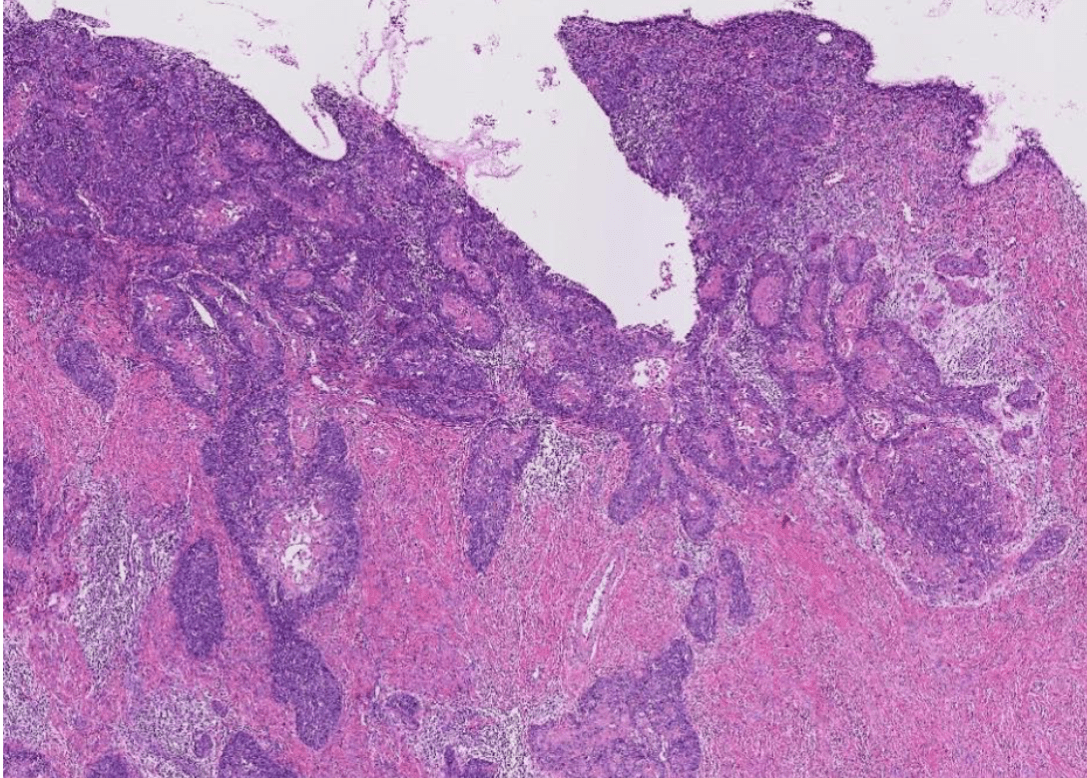
(apoptosis/prominent nucleoli)
(melanin pigment)
(circumscribed/infiltrative)
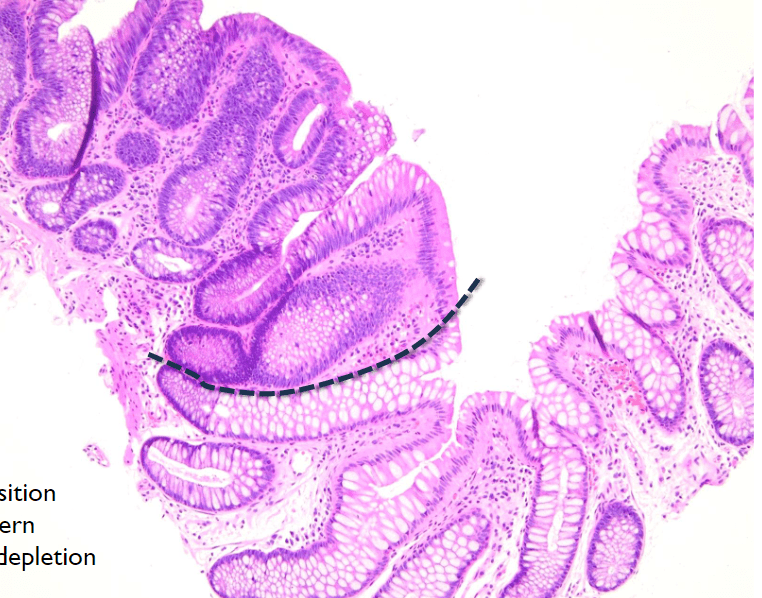
4. abrupt transition, depletion of goblet cell

(nuclear pleomorphism)
(elongated, tapered)
(cobweb structure)
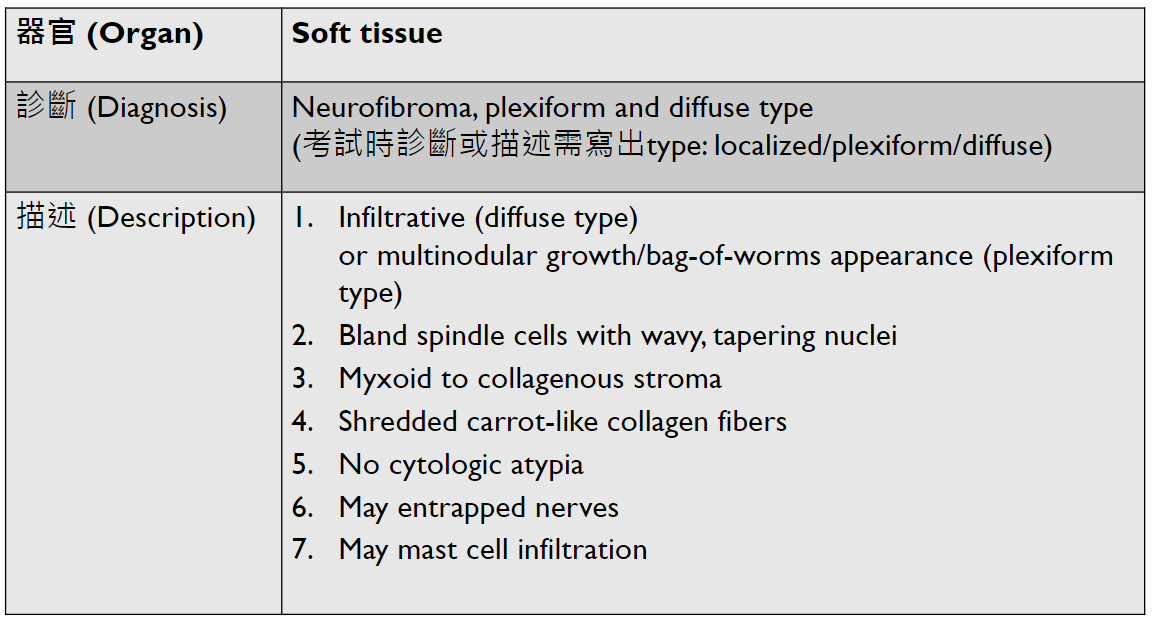
localized type: circumscribed
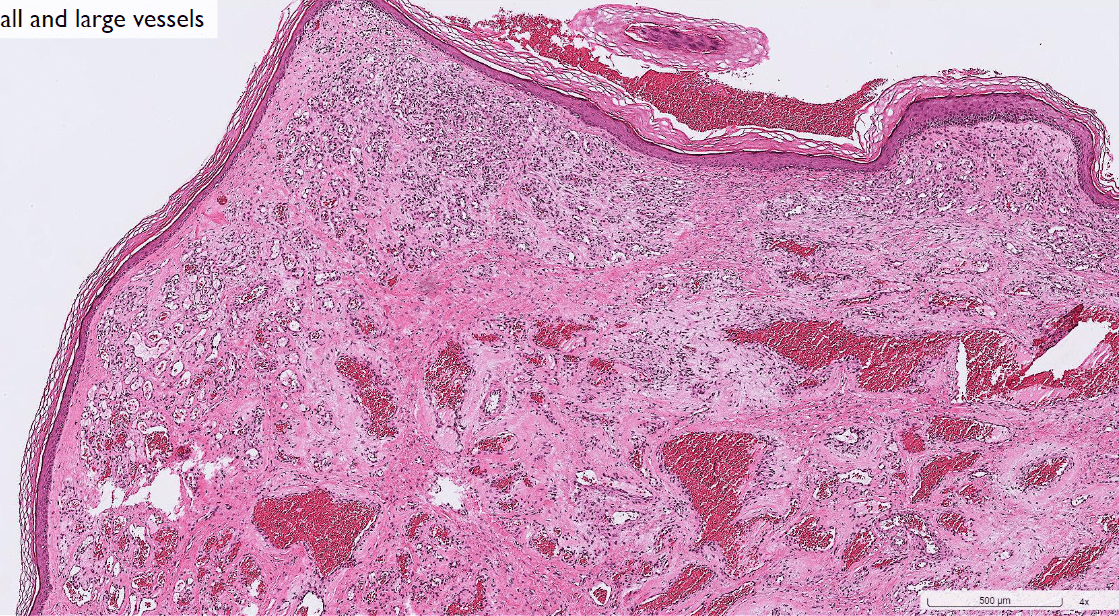
(maybe cavernous or capillary)
(tadpole, spider cell)
(cambium layer?)-TSC
(pagetoid spread)
(hyperchromatic也可)
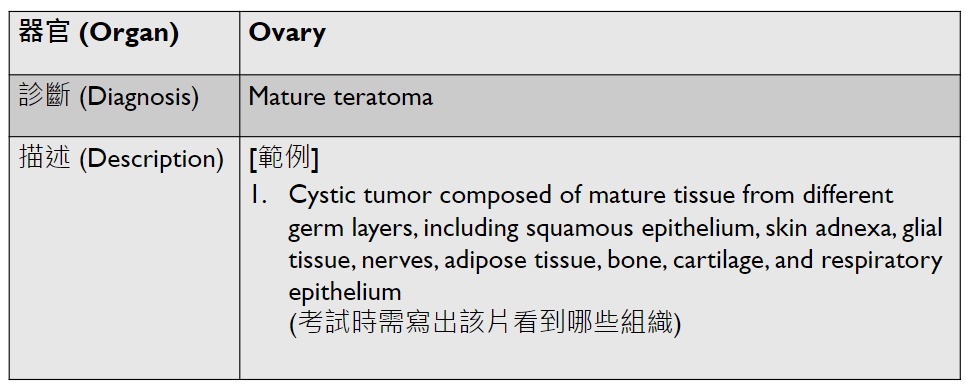
(只考在這)
(Gamna-Gandy body)
(HAM)

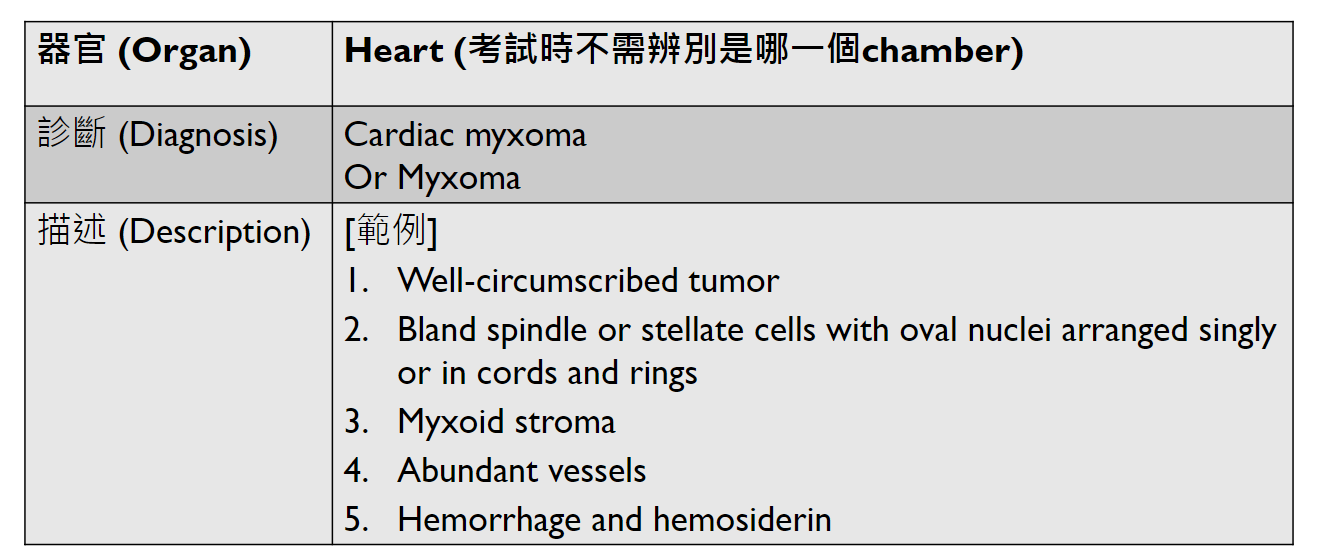
irregular lumen narrowing/intima thickening
11/7 小組討論
Question
4. 周邊動脈疾病的治療有哪些?對胡先生的周邊動脈疾病,在藥物治療上如何調整?
Treatment for PAD
- Lifestyle Modification
- Structured Exercise
- Medication
- Intervention/Surgery
2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
Treatment for PAD
-
Lifestyle Modification
- Smoking cessation
- Structured Exercise
- Medication
- Intervention/Surgery
2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
Treatment for PAD
- Lifestyle Modification
-
Supervised exercise program
- For patients with claudication
- Intermittent walking
- At least 30–45 min/session; 3 times/wk for 12 wk
- Medication
- Intervention/Surgery
2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
Medication for PAD
- Antiplatelet therapy(Aspirin or Clopidogrel)
- reduce MI, stroke, and vascular death
- Statin
- improves both cardiovascular and limb outcomes
- Antihypertensive therapy (patients with hypertension)
- reduce the risk of MI, stroke, heart failure, and cardiovascular death
- Cilostazol: Improve claudication symptoms
- Management of diabetes mellitus (patients with DM)
- Heparin for Anticoagulation (acute limb ischemia)
2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
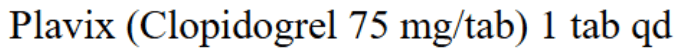
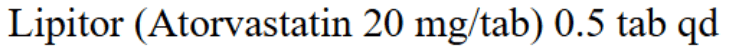

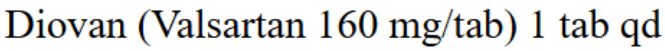
Contradicted in Heart Failure.
Intervention/Surgery for PAD (CLI)
- Revascularization
- Endovascular/Surgical
- Amputation
- should be performed as the first procedure in patients with a nonsalvageable limb
2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines.
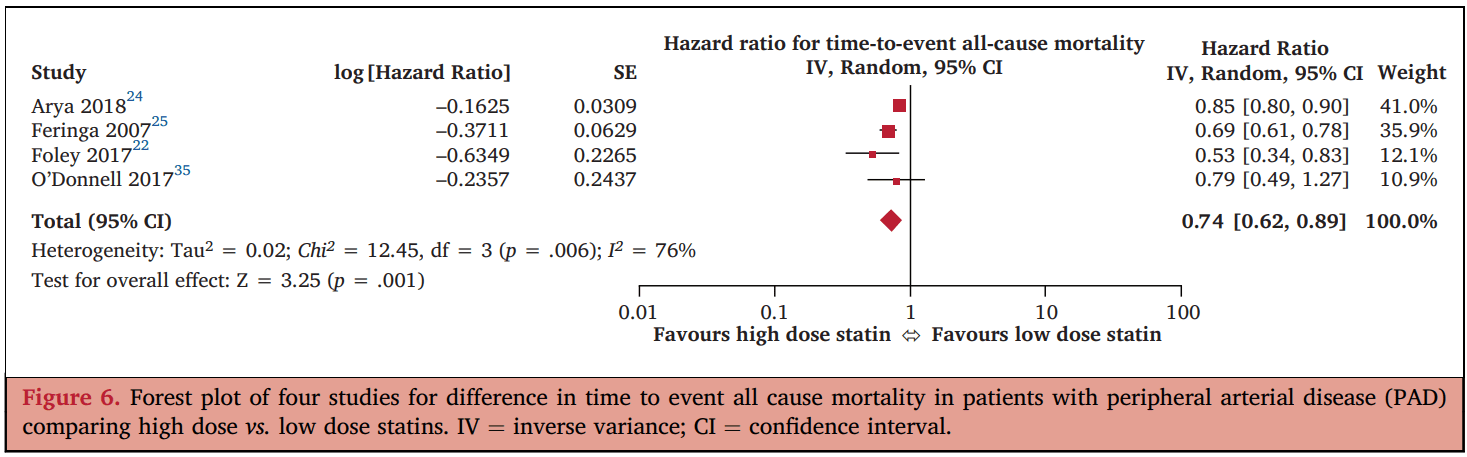
胡先生藥物治療上如何調整?
- 感覺該吃的都吃了?
- The other drugs (Pentoxifylline, Procaterol, Acetylcysteine) are also not contradicted in PAD?
- Atorvastatin for PAD pateint: standard dose is 80 mg/day.
Sofat S, Chen X, Chowdhury MM, Coughlin PA. Effects of Statin Therapy and Dose on Cardiovascular and Limb Outcomes in Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Sep;62(3):450-461. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.05.025. Epub 2021 Aug 10. PMID: 34389230.
Q(A)/Discussion
Question
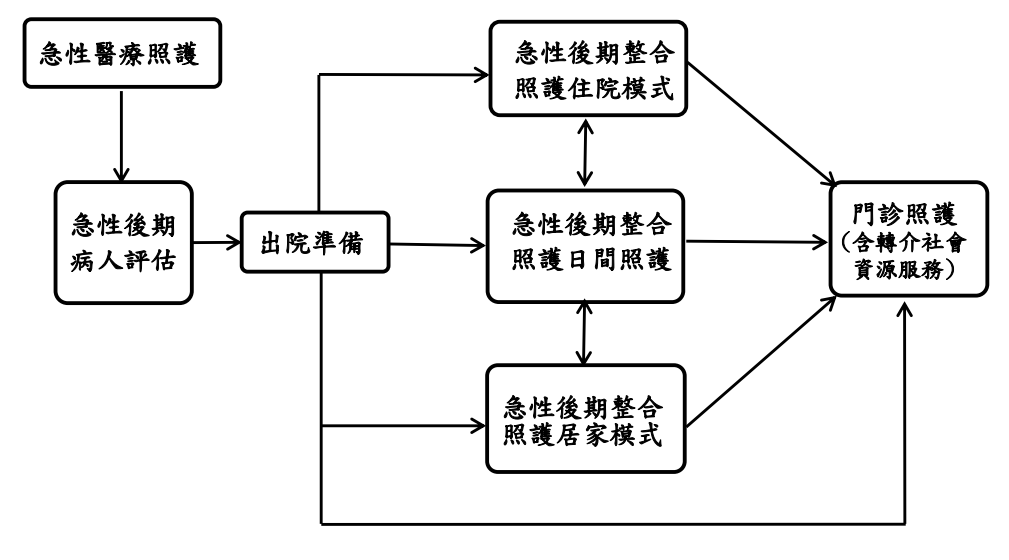
5. 何謂急性後期照護?胡先生是否符合健保署的「急性後期整合照護計畫」的收案標準?是否有其他出院後照護的選擇?
急性後期照護(Post-Acute Care)
林純聿、周怡君:衰弱高齡患者的急性後期照護。內科學誌。2019:30:7-13。
- 「對醫療狀況相對穩定、但仍有特殊照顧需求的病患提供周全的住院後照顧」
- 銜接急性醫療與較低強度之照護
- 重視功能
急性後期照護(Post-Acute Care)
健保署 全民健康保險急性後期整合照護計畫
Question
5. 何謂急性後期照護?胡先生是否符合健保署的「急性後期整合照護計畫」的收案標準?是否有其他出院後照護的選擇?
急性後期整合照護計畫
健保署 全民健康保險急性後期整合照護計畫
- 計畫推動範圍包含腦中風、燒燙傷、創傷性神經損傷、脆弱性骨折、心臟衰竭、衰弱高齡病患
心臟衰竭?
健保署 全民健康保險急性後期整合照護計畫


?
心臟衰竭?




(治療後)
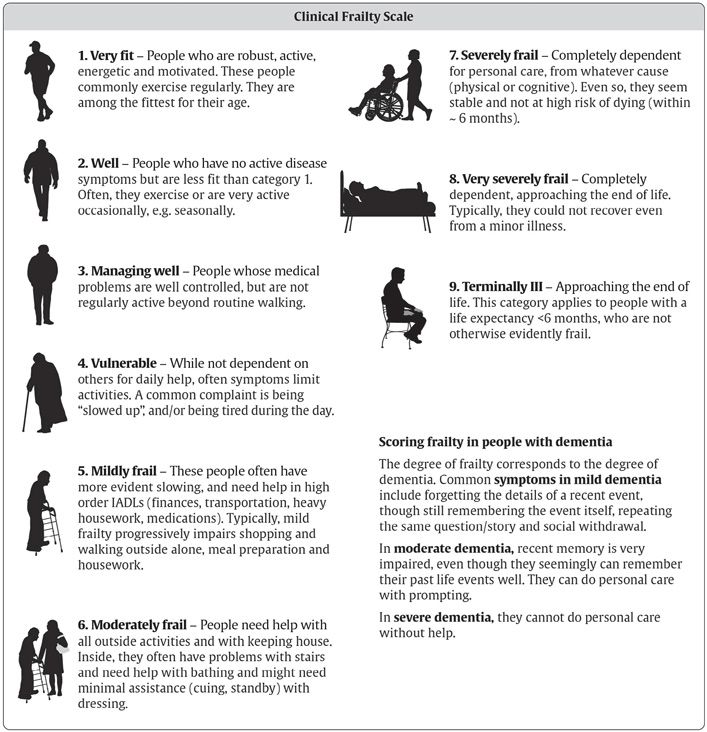
衰弱高齡?
衰弱高齡?
健保署 全民健康保險急性後期整合照護計畫

?
Question
5. 何謂急性後期照護?胡先生是否符合健保署的「急性後期整合照護計畫」的收案標準?是否有其他出院後照護的選擇?
出院後照護選擇
- 居家照顧
- 日間照護中心
- 長期照護機構
- 長照2.0
- 出院準備銜接長照服務
- 家庭醫師整合性照護計畫
- 居家醫療照護整合計畫
相關資源
Q(A)/Discussion
11/28 小組討論
Question
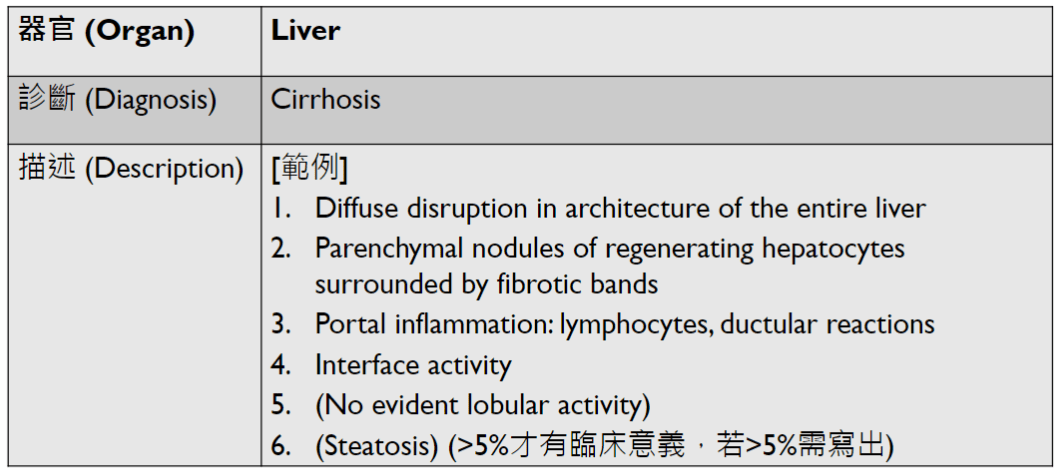
1. 以這位病人的入院診斷為例,如果你遇到一個病人肝硬化,你會再詢問他哪些病史,多做哪些理學檢查、實驗室診斷及影像學檢查,以進一步協助你做鑑別診斷,去判斷這位病人肝硬化的原因?肝硬化的成因有哪些?
Liver Cirrhosis: Etiology
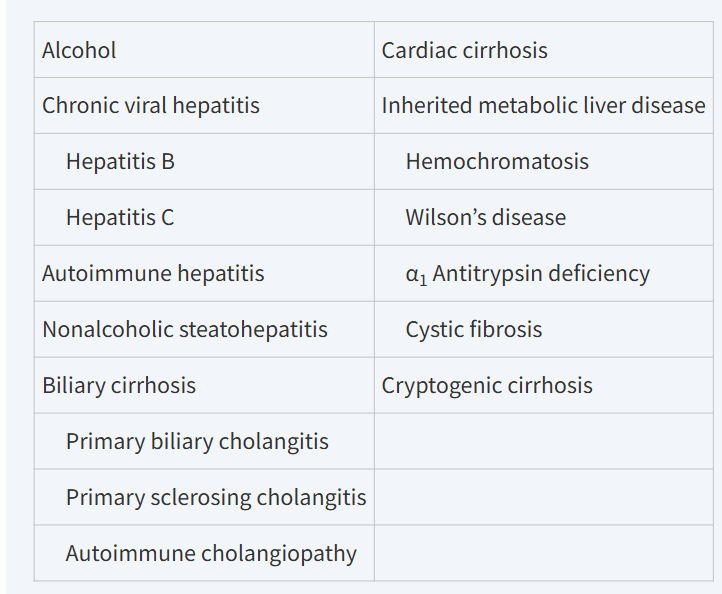
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 21st Edition
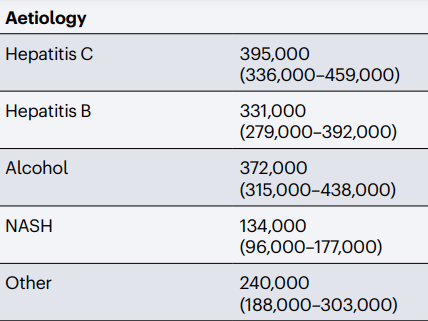
Global Deaths Associated with Cirrhosis in 2019
Huang, D.Q., Terrault, N.A., Tacke, F. et al. Global epidemiology of cirrhosis — aetiology, trends and predictions. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 20, 388–398 (2023).
Liver Cirrhosis: Differential Diagnosis
- History Taking
- Alcohol Use
- Travel, Sexual behaviors, Drug use
- Diabetes or Metabolic Syndrome
- Autoimmune Disorder
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
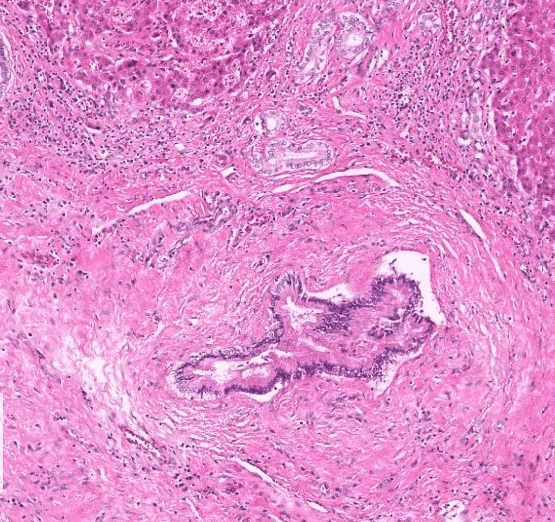
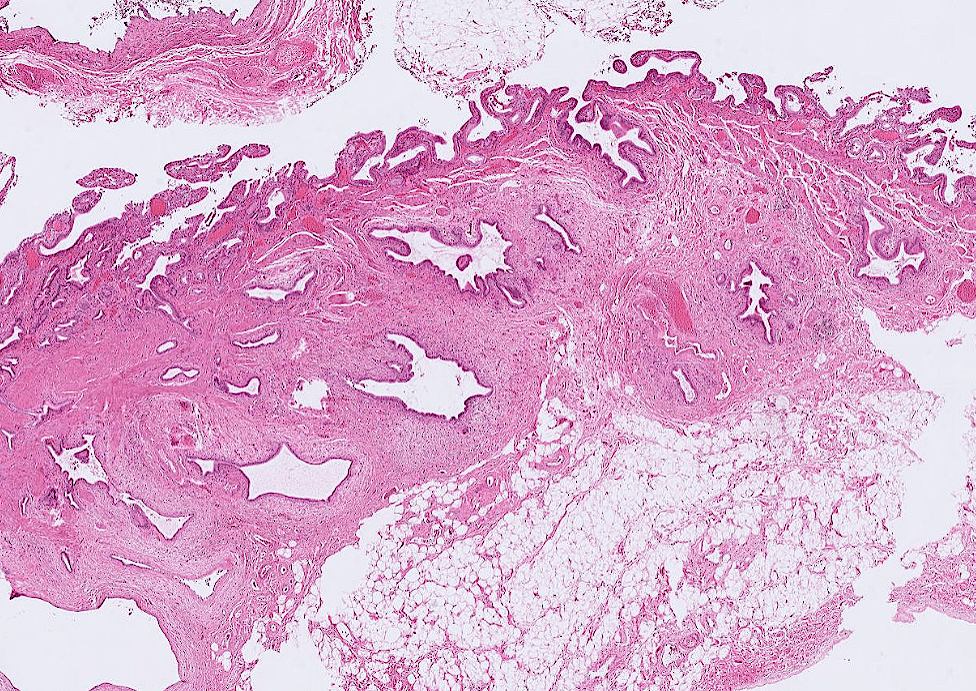
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Family History of Cirrhosis
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Anemia
Liver Cirrhosis: Differential Diagnosis
- Liver Function Tests
- AST, ALT: Hepatocyte Injury
- ALP, GGT: Cholestasis
- Alcohol: AST>ALT, high GGT
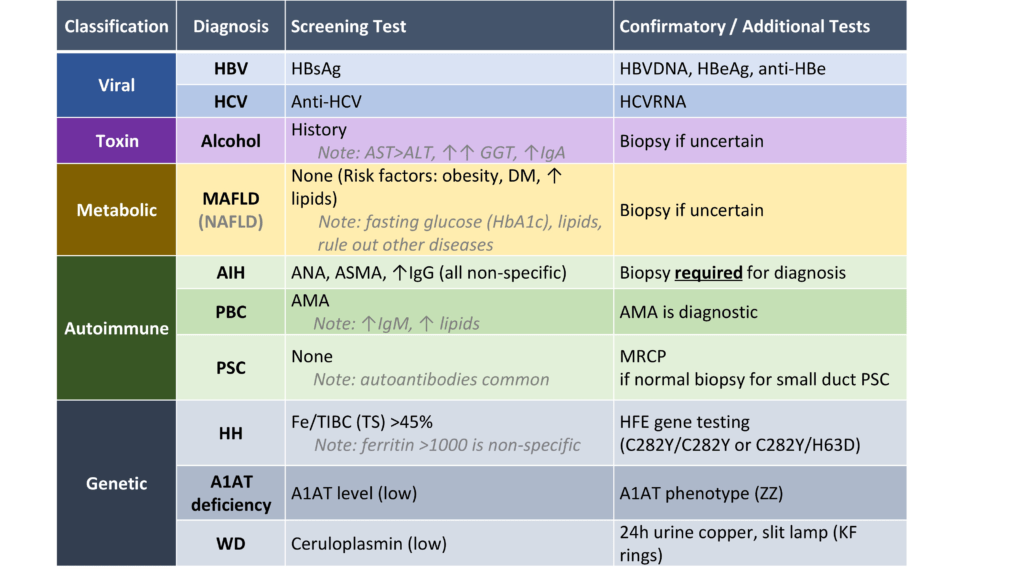
Liver Cirrhosis: Differential Diagnosis
- Other Laboratory Tests
https://cirrhosiscare.ca/cirrhosis-provider/work-up-the-etiology/
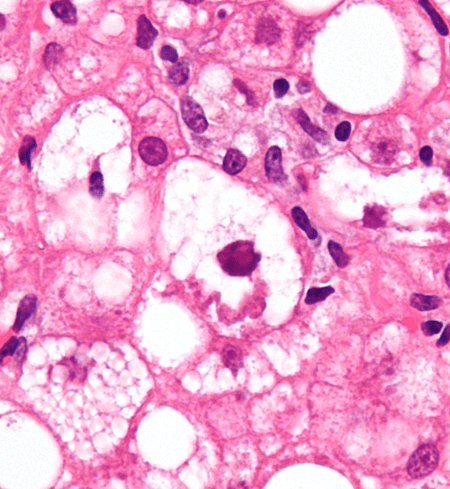
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mallory_body
Alcoholic Hepatitis/NAFLD
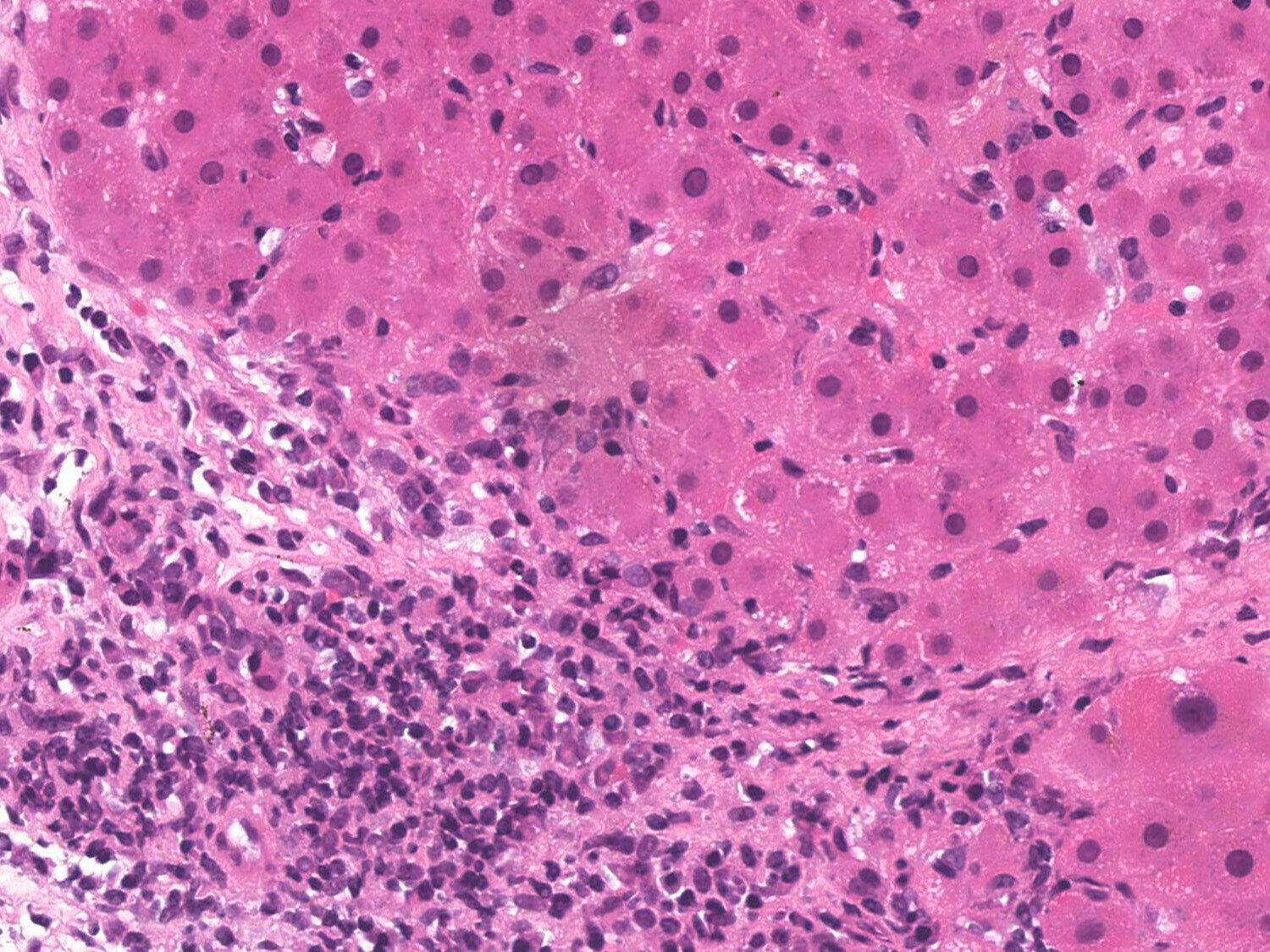
https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/liverautoimmune.html
AIH
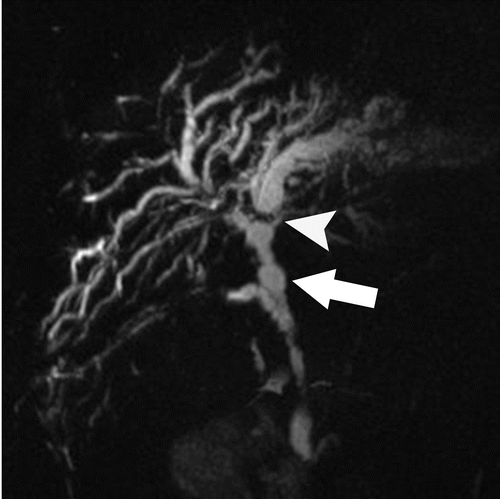
PSC
https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/epdf/10.1148/rg.2019180213
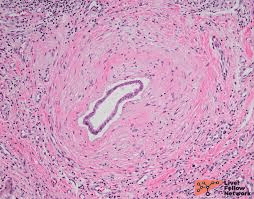
https://www.aasld.org/liver-fellow-network/core-series/pathology-pearls/pathology-pearls-post-8-primary-sclerosing
Q(A)/Discussion
Question
2. 請問腹水的成因如何?如何解釋她腹水檢驗的結果?
Ascites: Cause

Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 21st Edition
Why does Cirrhosis cause Ascites?
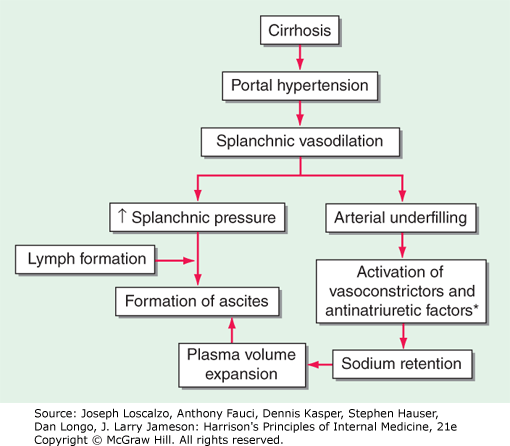
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 21st Edition
hypoalbuminemia
(RAAS, sympathetic)
serum-ascites albumin gradient (SAAG)
- SAAG: serum albumin - ascitic albumin
-
SAAG >= 1.1 g/dL: Ascites caused by portal hypertension
- Cirrhosis: ascitic protein < 2.5 g/dL
- SAAG < 1.1 g/dl: Other causes (TB, carcinomatosis, pancreatitis, ...)

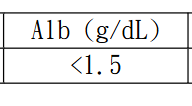
正常值
測量值
Serum
Ascites
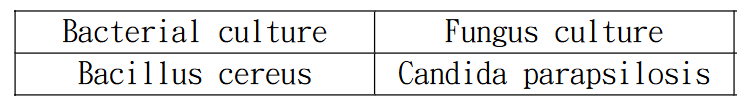
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis (SBP)
-
In hospitalized patients with cirrhosis and ascites, SBP can occur in up to 30% of individuals. (Harrison)
- Rare in patients without cirrhosis.
-
Pathophysiology: Bacterial Translocation
-
intestinal bacterial overgrowth, alterations of the intestinal mucosal barrier, deficiencies of the local immune response
-
Common Pathogen: E. coli, Klebsiella, Streptococcus
-
-
Diagnosis
- Ascitic PMN(neutrophils) >= 250/\(\mu L\)
- Positive culture result
- Absence of secondary causes of peritonitis
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 21st Edition
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment. Florin Alexandru Cãruntu , Loredana Benea, 2006
Ascitic Fluid Analysis
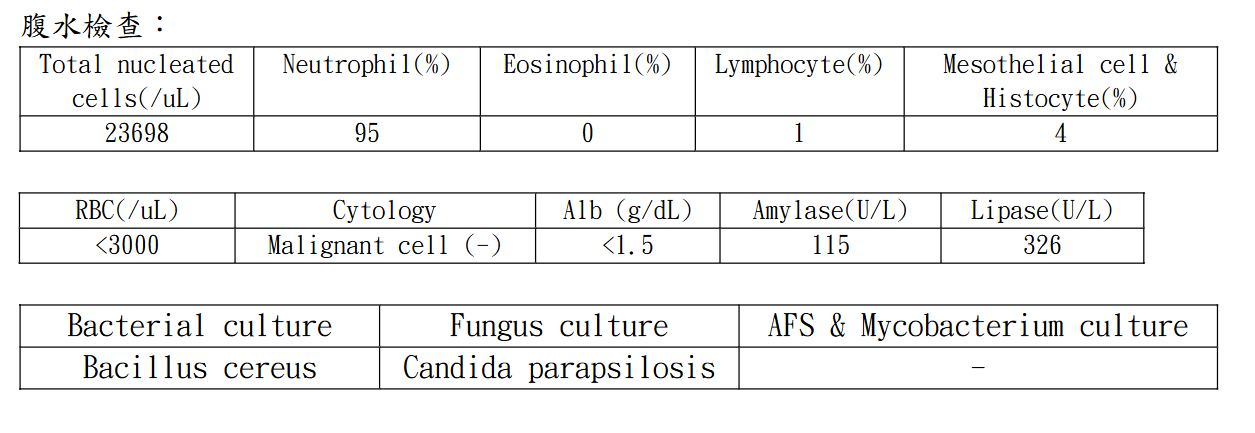
- Lymphocyte Predominant: TB
- Lipase/Amylase: pancreatic damage
- amylase > 1000 or 5x serum concentration
- Cytology: Malignancy
- RBC:
- High RBC: malignancy, trauma
- Substract 1 neutrophil/750 RBC
Conclusion?
The patient's ascites and SBP are complications of liver cirrhosis, where the SBP might contribute to the development of ascites.
Questions
1. Why did the ascites developed so quickly after the surgery?
2. Why were there two organisms cultured? May the peritonitis be secondary?
(Harrison : If more than two organisms are identified, secondary bacterial peritonitis due to a perforated viscus should be considered.)
Q(A)/Discussion
Complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
abscess (0.14 to 0.3 percent), bile leak (0.3 to 0.9 percent), biliary injury (0.26 to 0.6 percent), and bowel injury (0.14 to 0.35 percent)
12/8 小組討論
Question
1. 你是幫林小姐看診的消化內科醫師,請問你會如何跟林小姐解釋她眾多的消化系統問題,及建議她後續接受何種治療呢?
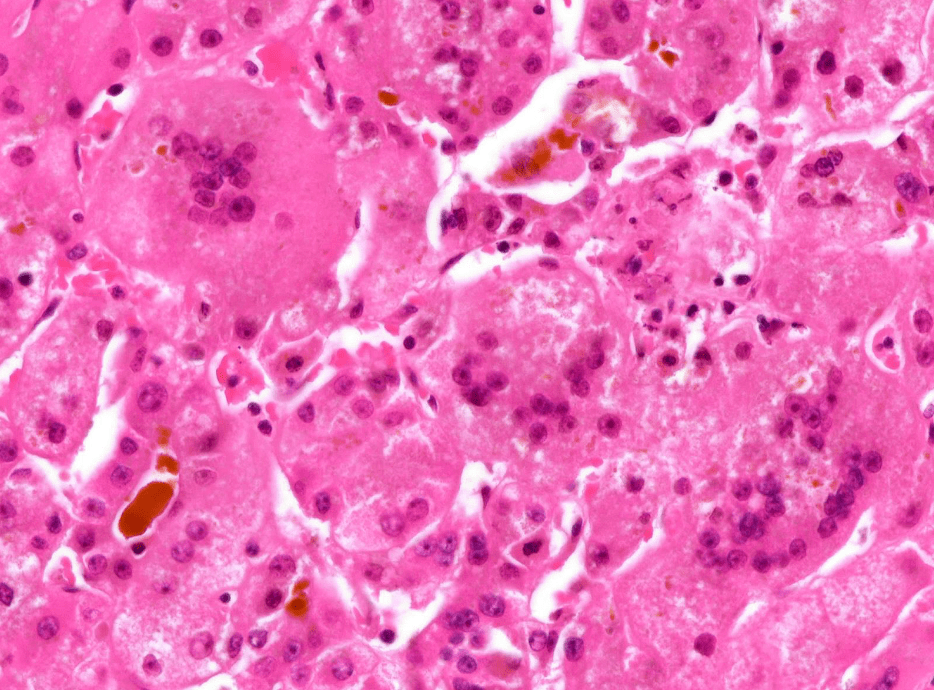
- 肝炎、脂肪肝(Steatohepatitis)
- 膽結石(Gallstones)
- 胃食道逆流(Gastroesophageal reflux disease, GERD)
- 良性大腸息肉(Colorectal Polyp)
Steatohepatitis
"脂肪在肝臟過度堆積,並且肝臟發炎"
- Metabolic dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis?
- No alcohol drinking
- Obesity, DM, hyperlipidemia
- Treatment:
- Hepatitis A,B vaccination, avoid alcohol
- lipid-lowering therapy, blood glucose control
- Weight loss
- diet, excercise
- bariatric surgery, drugs if goal not acheived after 6 months
- Many drugs in development
UpToDate, Management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) in adults
https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-treatment-patients-liver-scarring-due-fatty-liver-disease
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2309000
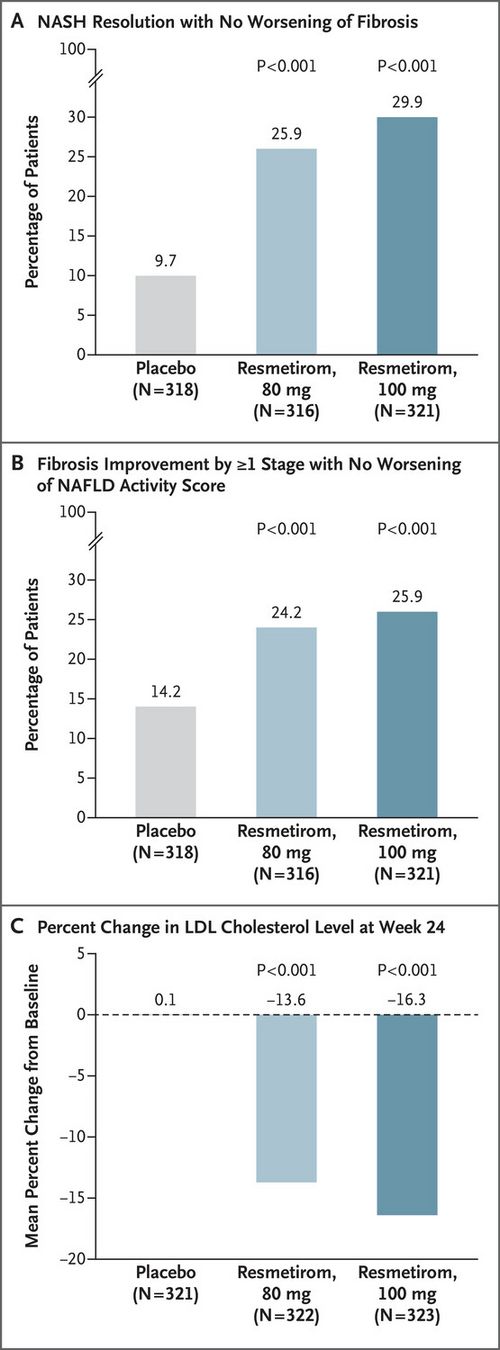

- Thyroid hormone excess is asscociated with lowered cholesterol and increased heart rate.
- Thyroid Hormone receptors
- THR\(\alpha\) : heart/bones
- THR\(\beta\) : liver
- Resmetiro is a partial agonist of THR\(\beta\).
Gallstones
"膽囊中有結石"
- Treatment
- Most do not require treatment if asymptomatic
-
Prophylactic cholecystectomy in selected patients
-
Increased risk of gallbladder cancer
- Stone > 3 cm
- Gallbladder Adenoma
- ...
- Hemolytic disorders
-
Increased risk of gallbladder cancer
UpToDate, Approach to the management of gallstones
GERD
"胃酸從胃跑到食道,食道因此有發炎及黏膜受損"
https://www.grepmed.com/images/13202/egd-losangeles-esophagitis-diagnosis-grading
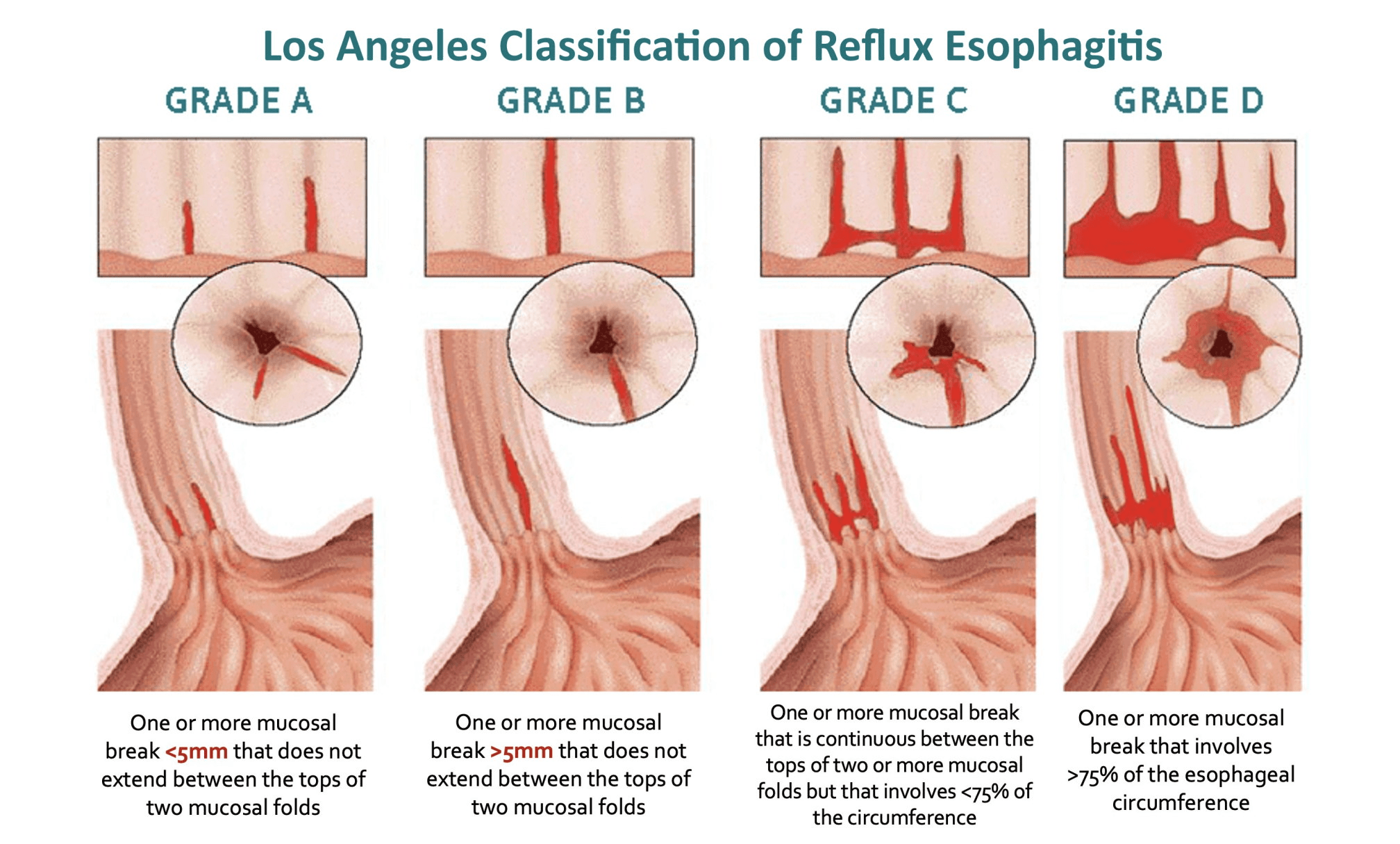
GERD
- Treatment:
- Weight loss
- Drugs
- Proton Pump Inhibitors(PPI)
- Lifestyle modification
- Avoiding meals within 2–3 hours of bedtime
- Avoid Trigger Foods
- ...
Katz, Philip O. MD, MACG1; Dunbar, Kerry B. MD, PhD2,3; Schnoll-Sussman, Felice H. MD, FACG1; Greer, Katarina B. MD, MS, FACG4; Yadlapati, Rena MD, MSHS5; Spechler, Stuart Jon MD, FACG6,7. ACG Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 117(1):p 27-56, January 2022. | DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001538
Colorectal Polyp
- Treatment:
- Remove by colonoscopy or surgery
"大腸長了良性的腫瘤,其中有些可能有機會發展成大腸癌"
"為什麼我的身體會有這些問題?"
"這些情形跟遺傳、環境、生活型態等因子都有關係,但..."
"可能跟肥胖有關"
Camilleri M, Malhi H, Acosta A. Gastrointestinal Complications of Obesity. Gastroenterology. 2017 May;152(7):1656-1670. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.052. Epub 2017 Feb 10. PMID: 28192107; PMCID: PMC5609829.
OR:1.94
OR:1.87
OR:1.44
RR:4.66
RR
M: 2.51
F: 2.32
Colorectal polyp/CRC
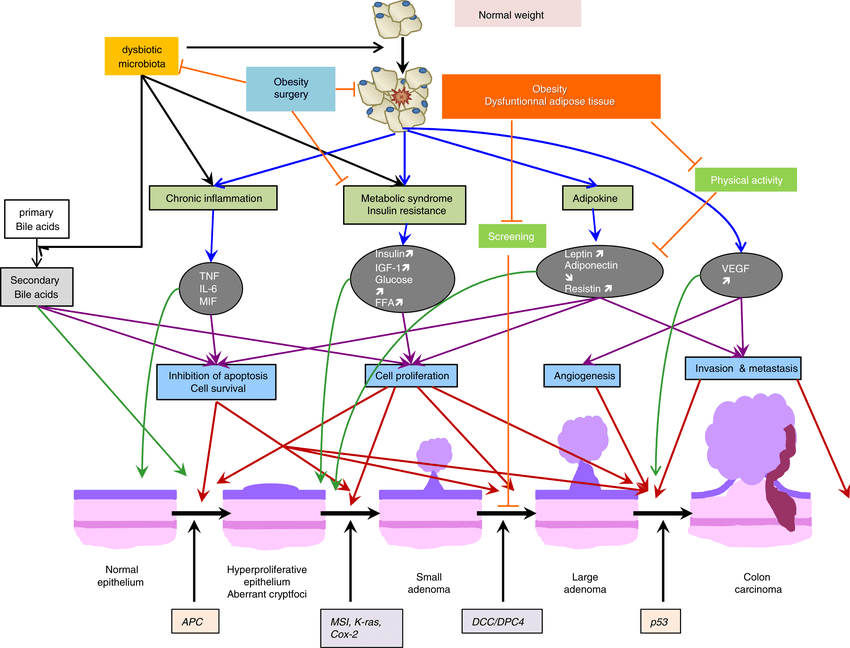
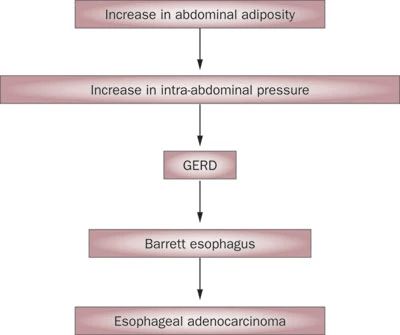
Mechanisms?
GERD
Lagergren, J. Influence of obesity on the risk of esophageal disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8, 340–347 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2011.73
Bardou M, Barkun AN, Martel M. Obesity and colorectal cancer. Gut. 2013 Jun;62(6):933-47. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-304701. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PMID: 23481261.
"因此除了以上針對各種狀況的治療之外,或許也可以試試看減重治療"
Q(A)/Discussion
Question
3. 什麼是傾倒症候群? 發生的原因為何? 要如何預防和治療? 和術後血糖的改善有關嗎?
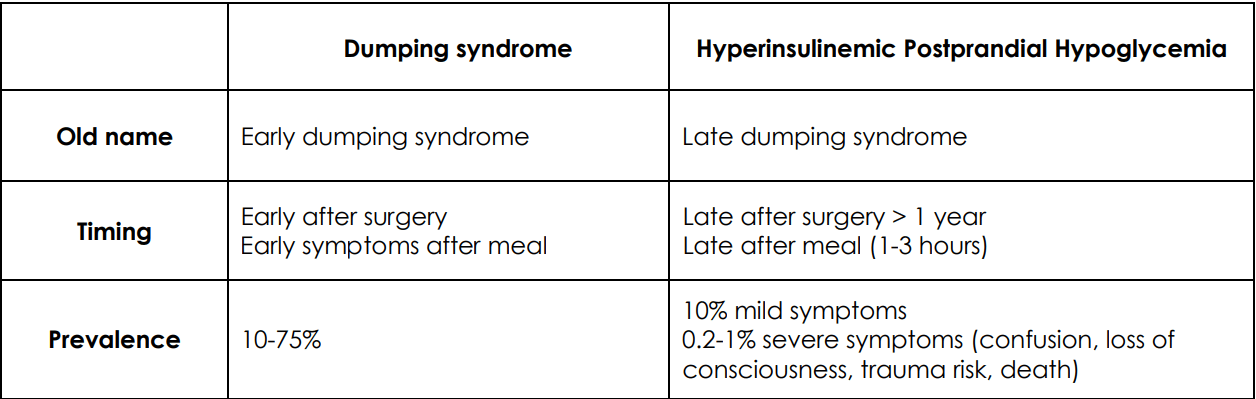
Dumping Syndrome 傾倒(ㄉㄠˋ?)症候群
a complication of bariatric surgery
symptoms
abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea
fatigue, the need to lie down after meals, tachycardia, flushing
hypoglycemia
(palpitaion, fatigue, sweating, ...)
Alexandre Nuzzo, Sebastien Czernichow, Alexandre Hertig, Séverine Ledoux, Tigran Poghosyan, Didier Quilliot, Maude Le Gall, André Bado, Francisca Joly. Prevention and treatment of nutritional complications after bariatric surgery. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Mar;6(3):238-251. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30331-9.
(Postbariatric Surgery Hypoglycemia)
Pathophysiology
Alexandre Nuzzo, Sebastien Czernichow, Alexandre Hertig, Séverine Ledoux, Tigran Poghosyan, Didier Quilliot, Maude Le Gall, André Bado, Francisca Joly. Prevention and treatment of nutritional complications after bariatric surgery. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Mar;6(3):238-251. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30331-9.
Scarpellini, E., Arts, J., Karamanolis, G. et al. International consensus on the diagnosis and management of dumping syndrome. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16, 448–466 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-020-0357-5
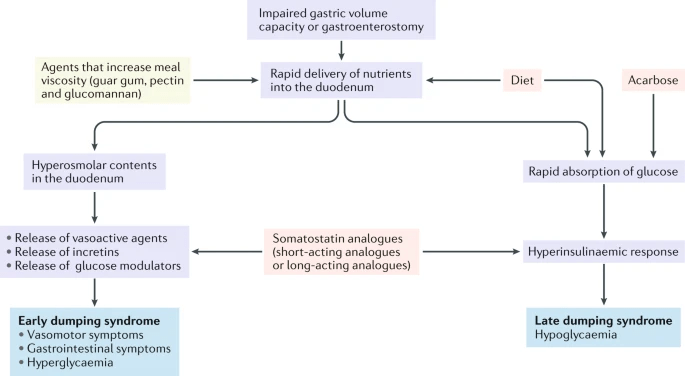
- fluid shift in small intestine
VIP
GIP
GLP-1
- hypovolemia
GLP-1
Treatment: Diet
Similar for early/late dumping syndromes
- Small, frequent meals
- Liquids should be withheld until 30 minutes after the meal
- Avoid simple sugar and milk products
- Low GI, fiber-rich food
- Adequate protein intake
Hui C, Bauza GJ. Dumping Syndrome. [Updated 2023 Jun 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470542/
Treatment: Octreotide
a somatostatin analog
- inhibit secretion of insulin, glucagon, gastrin, secretin, VIP,...
- reduce secretion of fluids by the intestine and pancreas
- reduce gastrointestinal motility
Hui C, Bauza GJ. Dumping Syndrome. [Updated 2023 Jun 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470542/
Treatment: Acarbose
\(\alpha\)-glucosidase inhibitor
Rosak C, Mertes G. Critical evaluation of the role of acarbose in the treatment of diabetes: patient considerations. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012;5:357-67. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S28340. Epub 2012 Oct 12. PMID: 23093911; PMCID: PMC3476372.
Cadegiani FA, Silva OS. Acarbose promotes remission of both early and late dumping syndromes in post-bariatric patients. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2016 Dec 7;9:443-446. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S123244. PMID: 27994477; PMCID: PMC5153290.

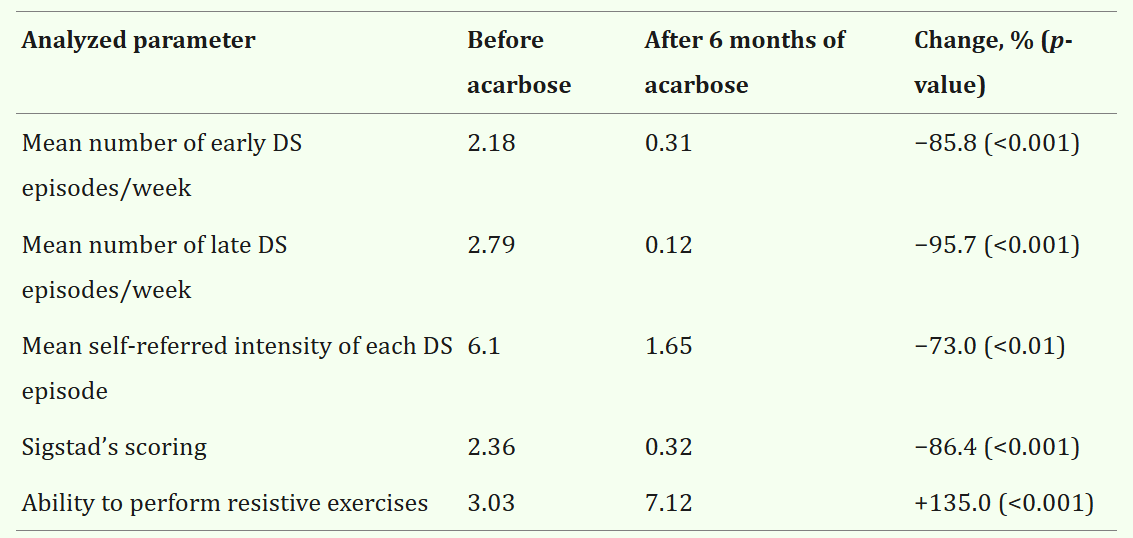
Question
3. 什麼是傾倒症候群? 發生的原因為何? 要如何預防和治療? 和術後血糖的改善有關嗎?
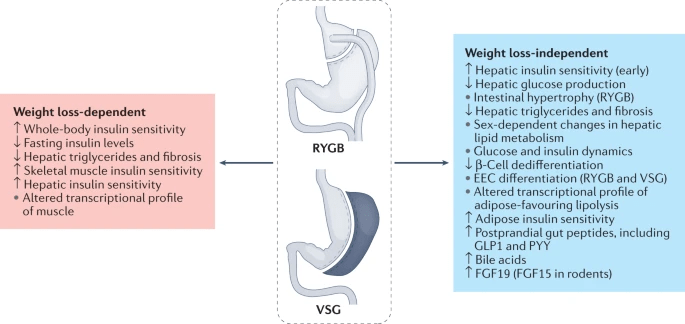
Glucose Metabolism After bariatric surgery
Sandoval, D.A., Patti, M.E. Glucose metabolism after bariatric surgery: implications for T2DM remission and hypoglycaemia. Nat Rev Endocrinol 19, 164–176 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-022-00757-
Q(A)/Discussion
Pathology-Micro 3
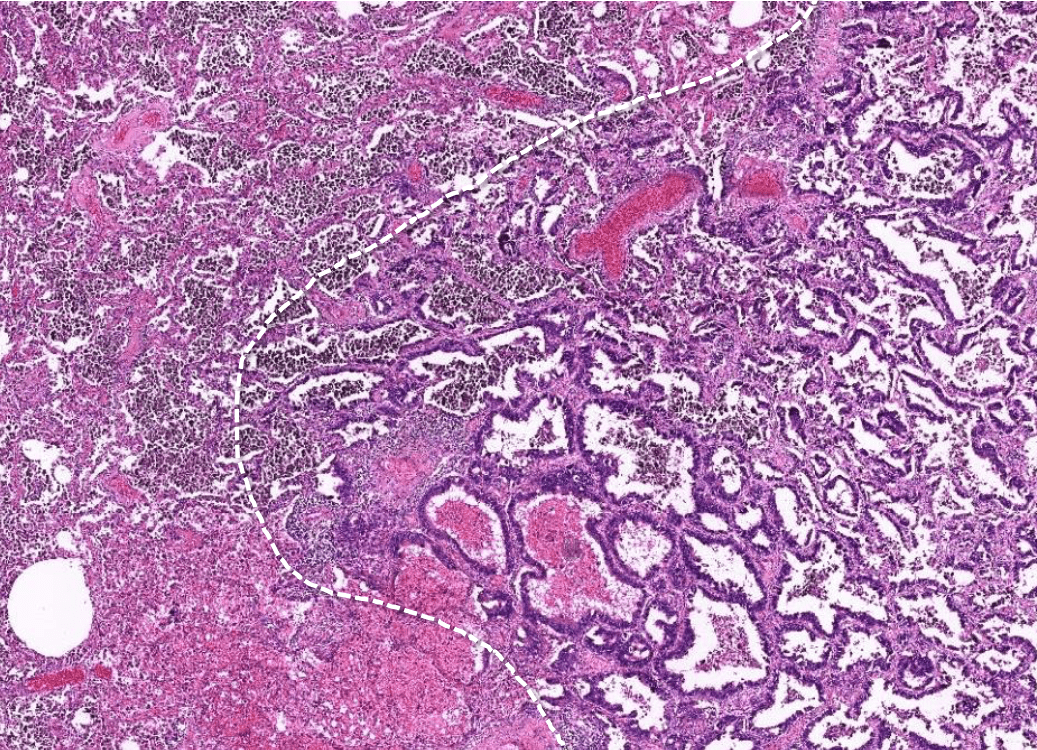
(or solid/micropapillary)
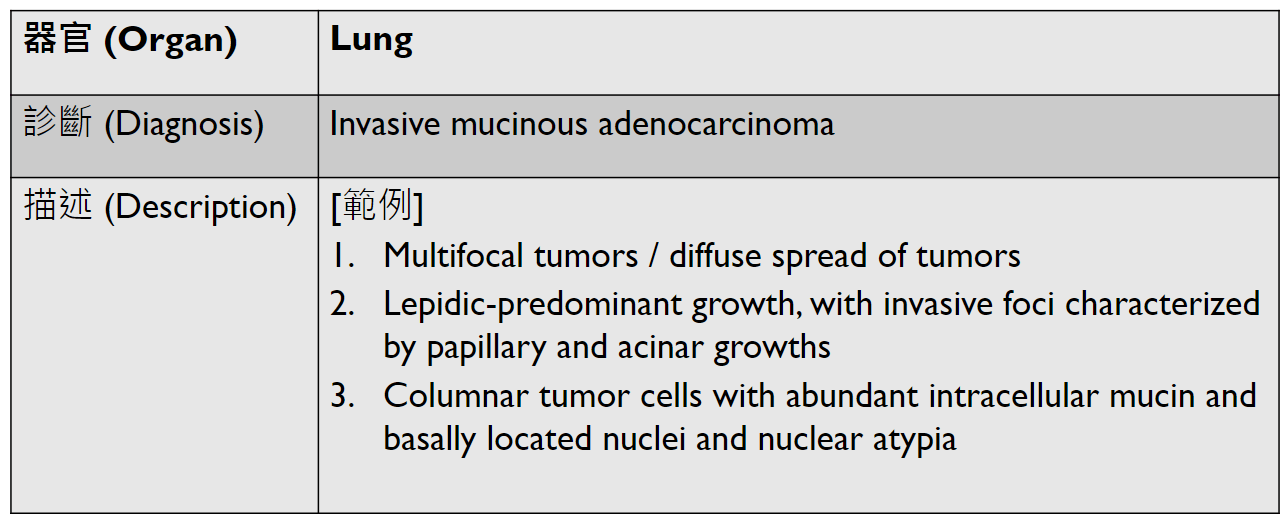
( )
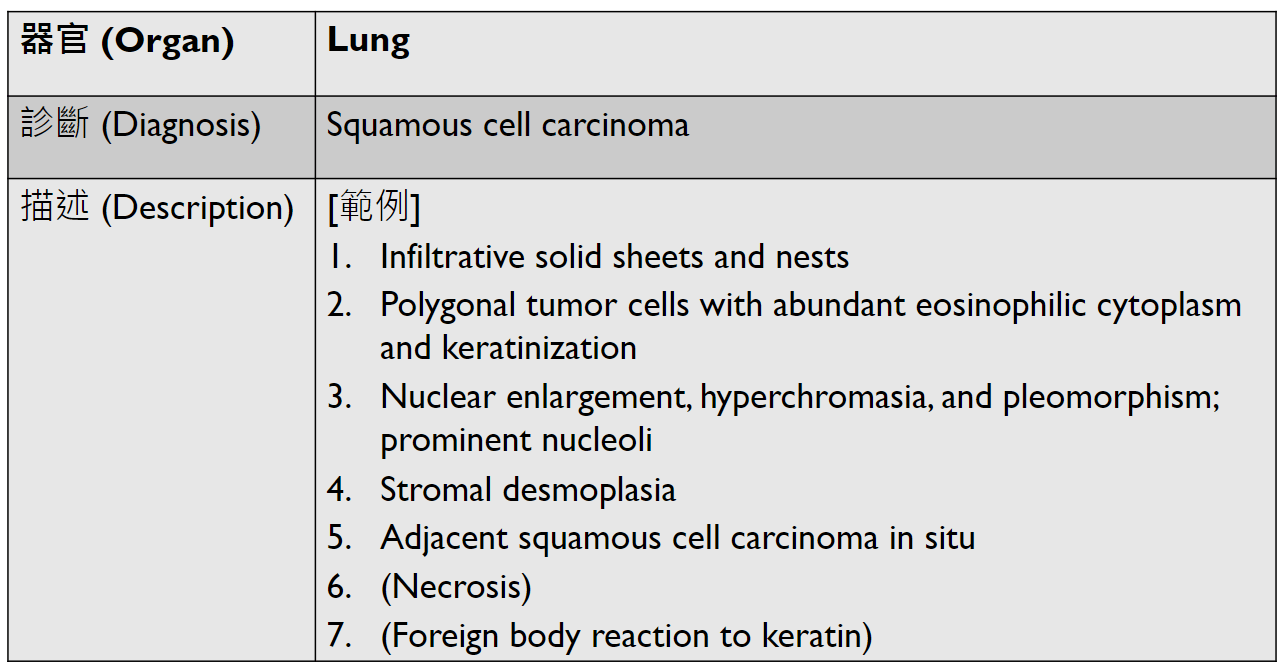
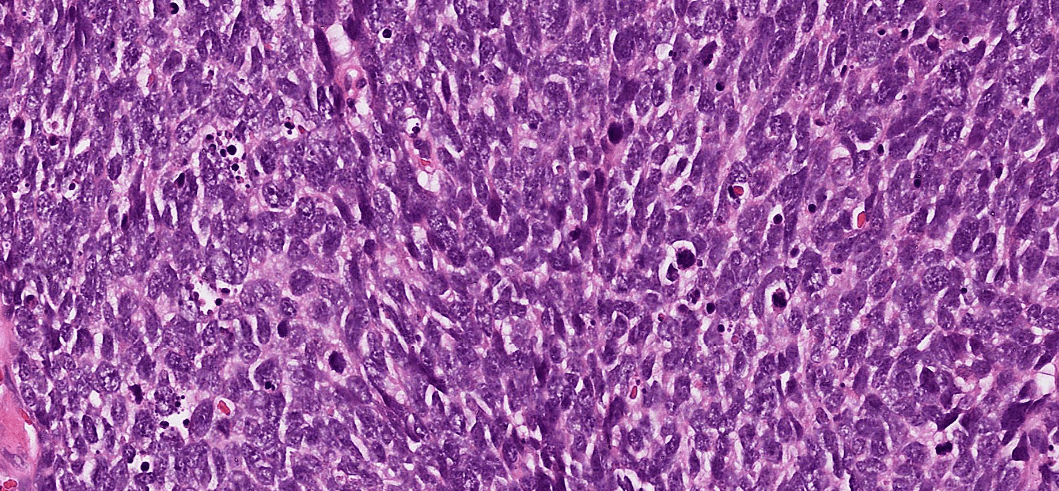
(keratin pearl/intercellular bridges)
在氣管旁要找,有要寫
(multinucleated giant cell)
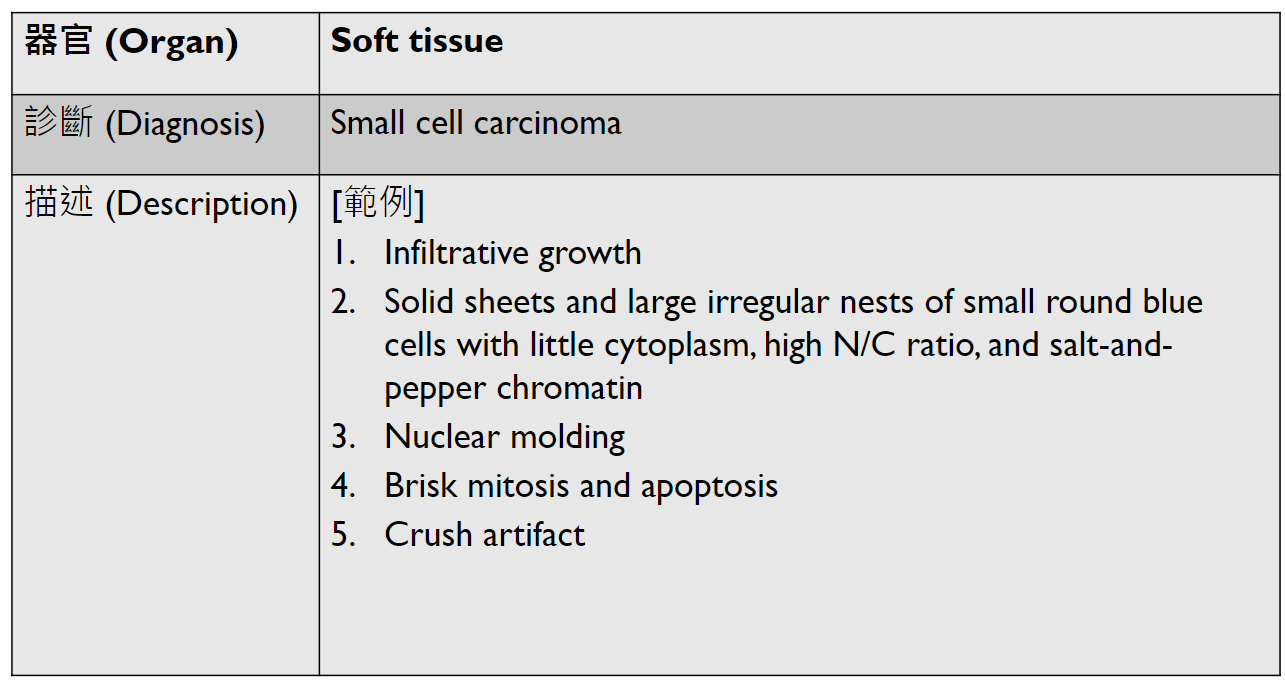
lung
(may have necrosis)
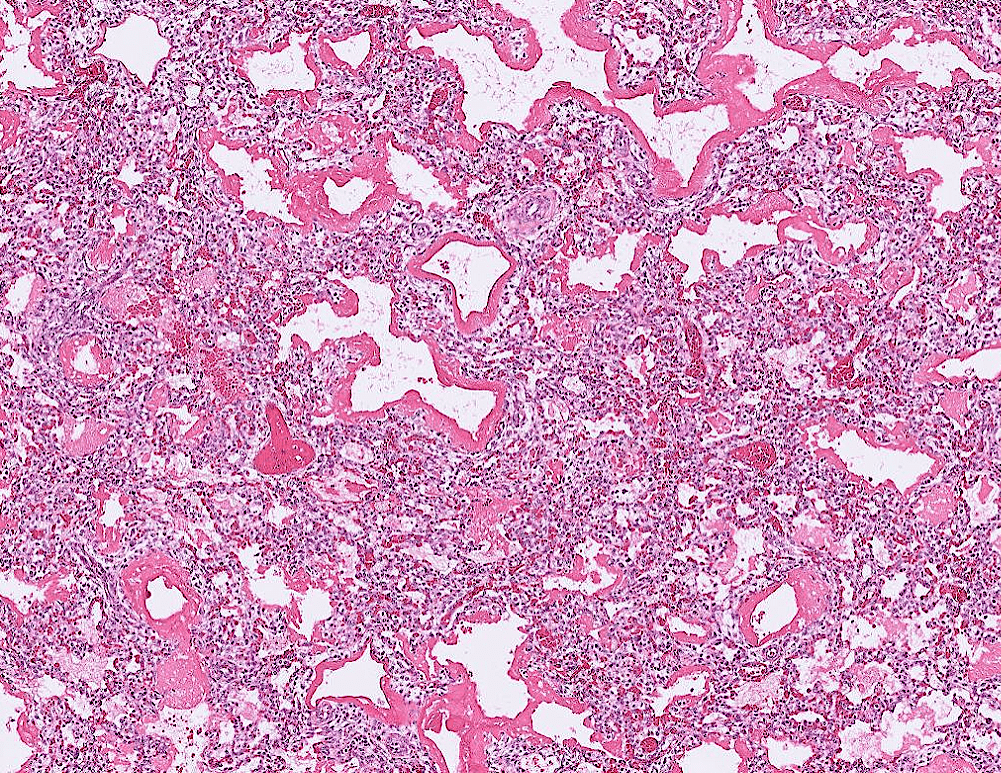
(may have exudate)
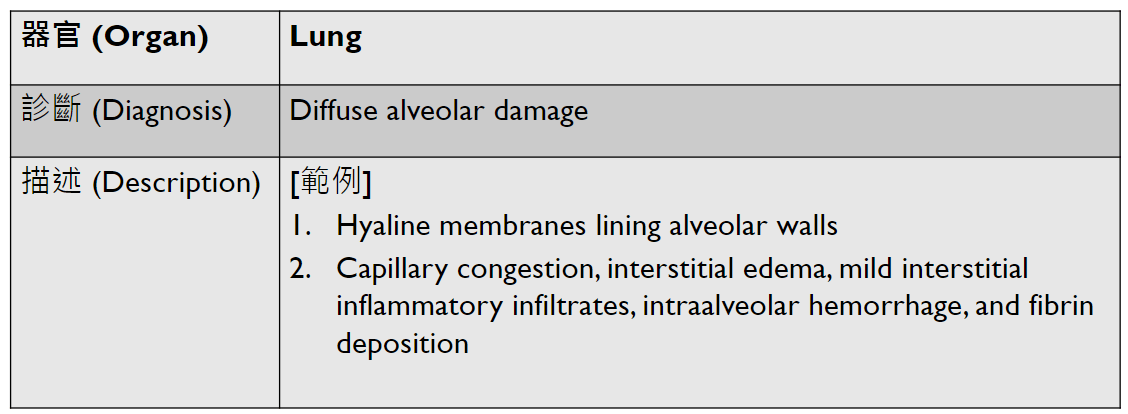
(難出)
(page)!!!
(plasma cell看到要寫)
不高機率考
(DIPCF)
PPOD

可能沒有!
(USRP)
(TING)
[ ]
may have granulation tissue
(PACCF)
may have autolysis/fat necrosis
Pathology-Micro 3
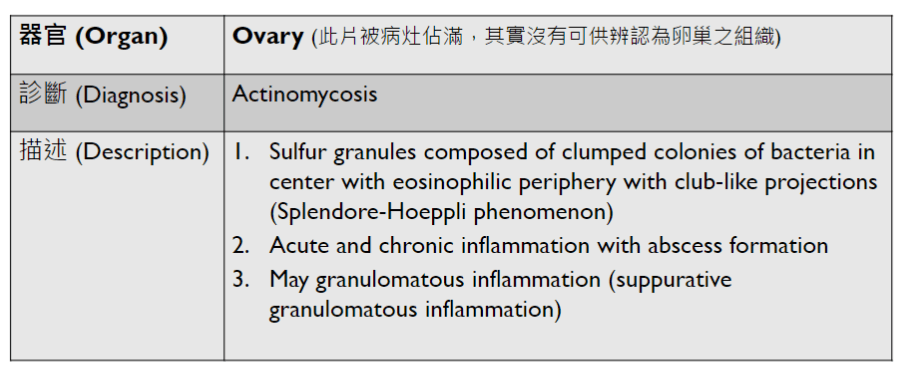
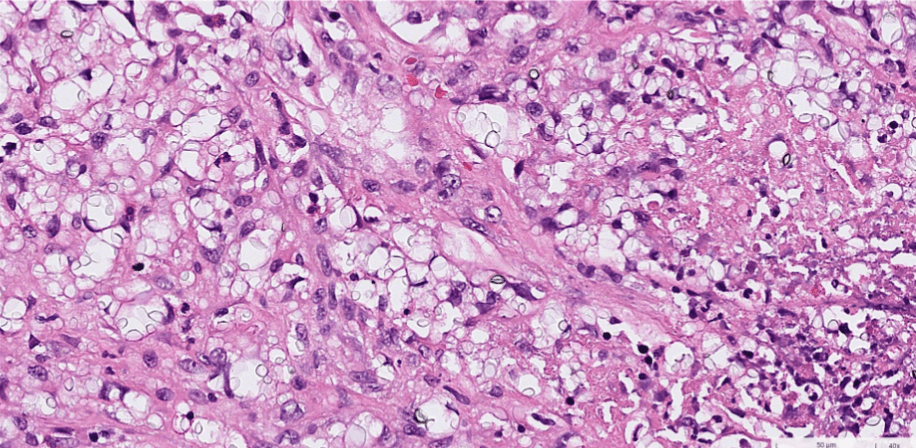
猜題


(plasma cell)



sulfur granules: actinomycosis

mucormycosis: aspeptate hyphae with wide-angle branching

aspergillosis: fungal hyphae with septa and acute angle branching

candidiasis: fungal yeasts and pseudohyphae



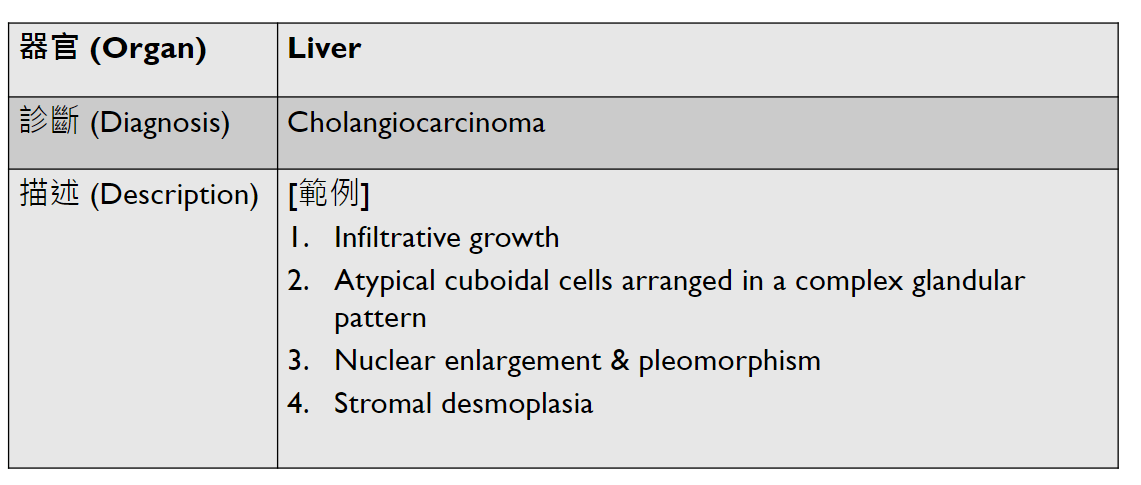
5. stromal desmoplasia
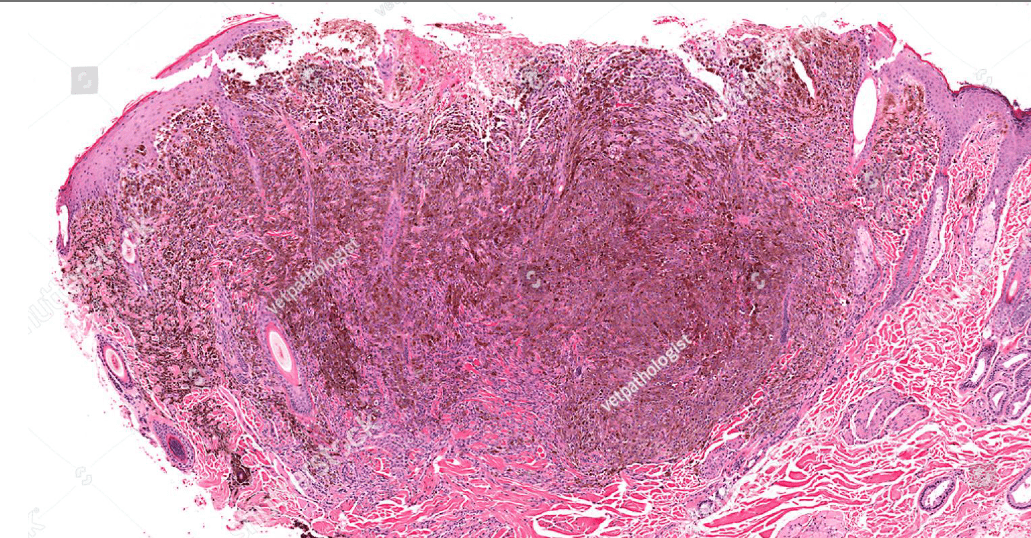
skin?


(melanin pigment)
(circumscribed/infiltrative)


(POV)


Pathology-Micro 4 Review


(may have heterologous elements, like cartilage or skeletal mescle)


2. epithelial infoldings and papilla


(Nabothian cyst)


(apoptosis/prominent nucleoli)




Pathology-Micro 4
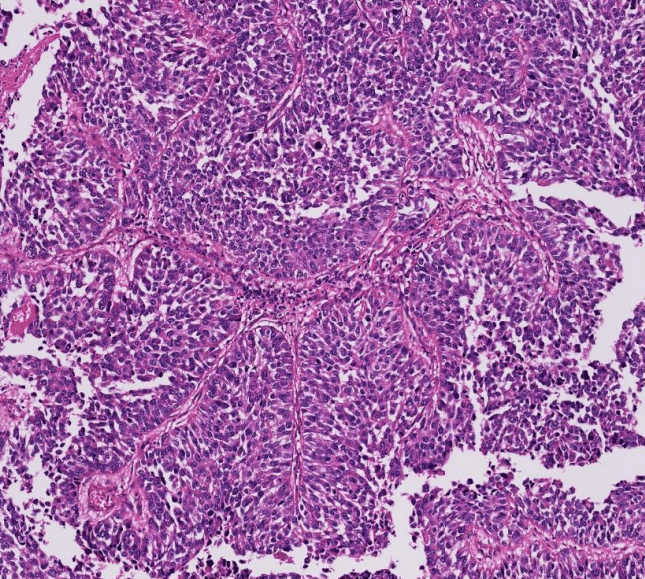
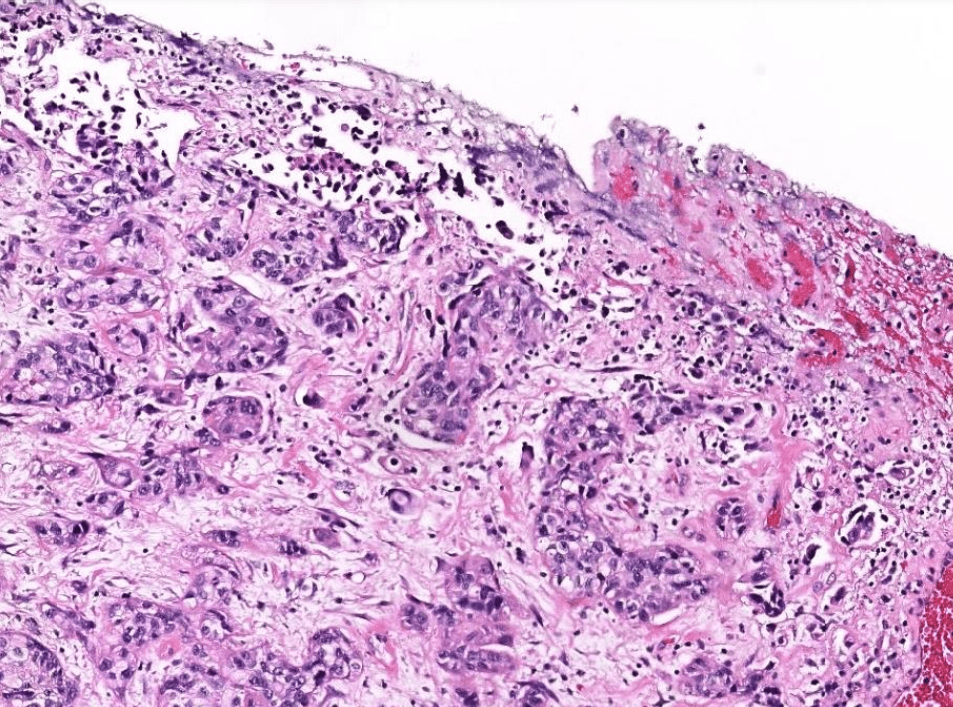
urothelium
may have squamous differentiation
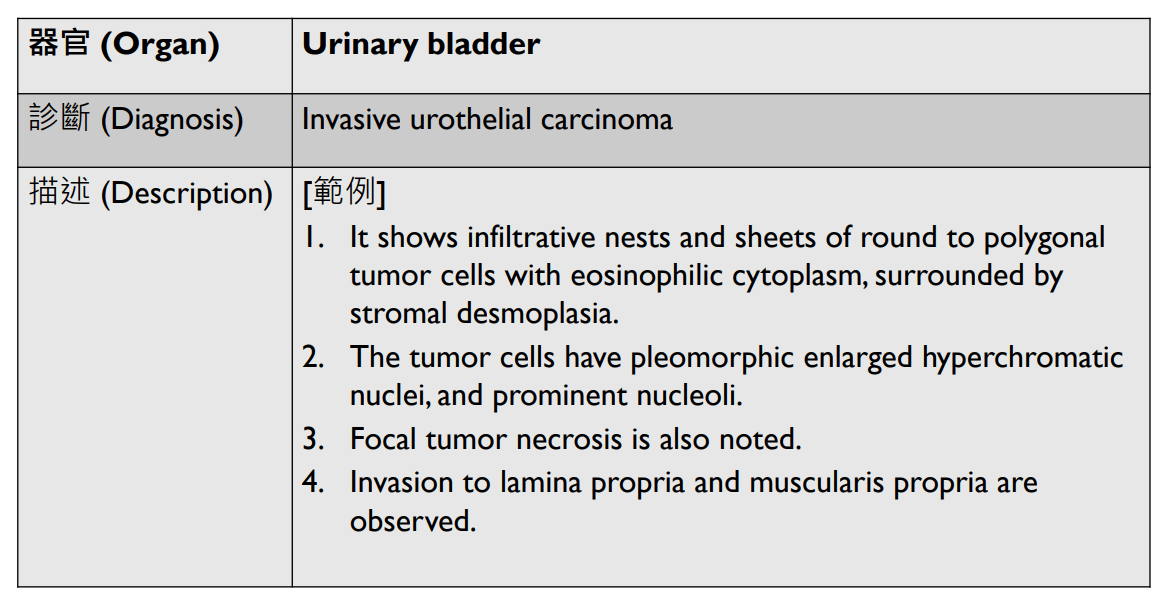
loss of basal cells
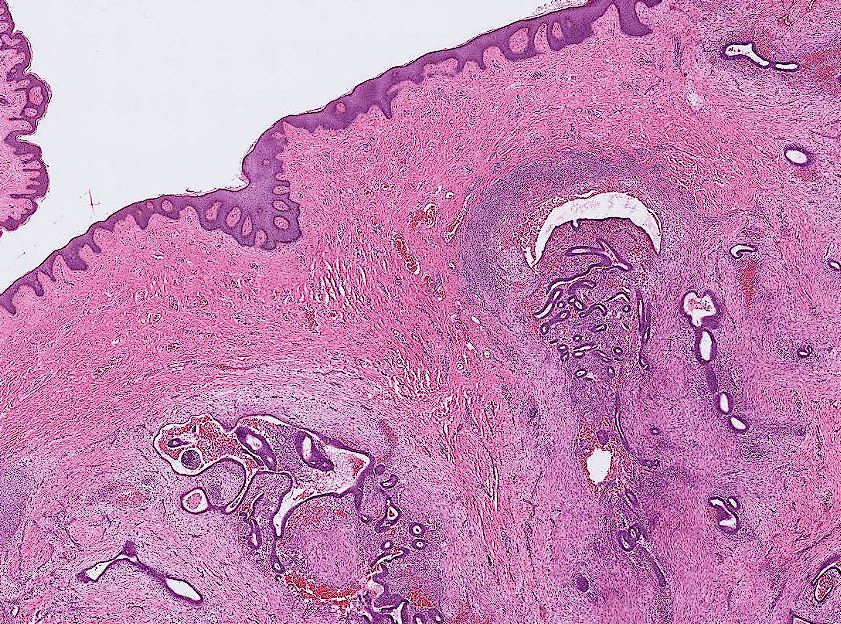
or other places (skin)
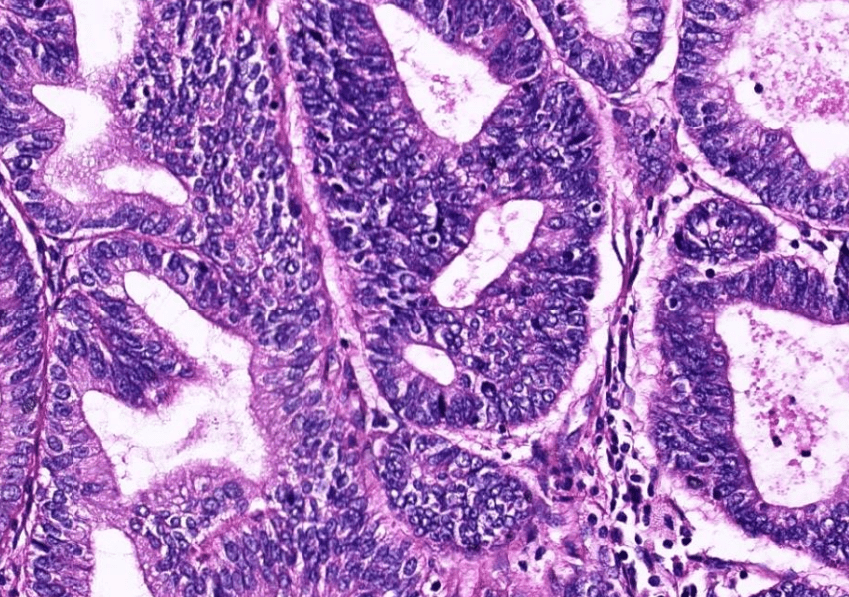
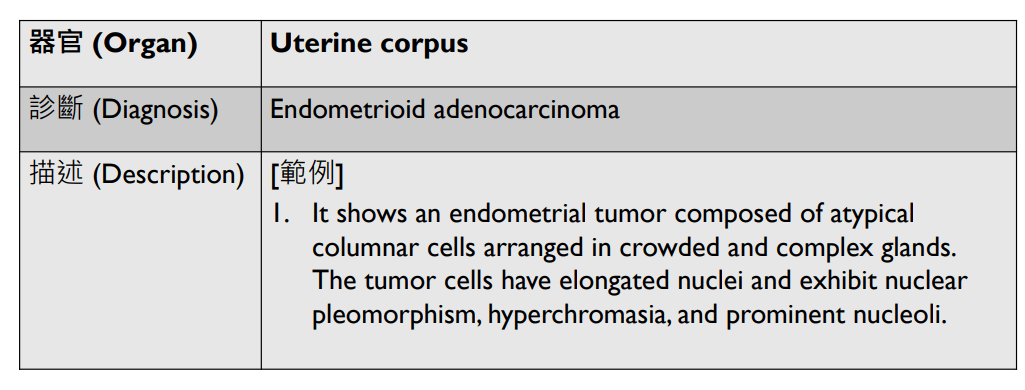
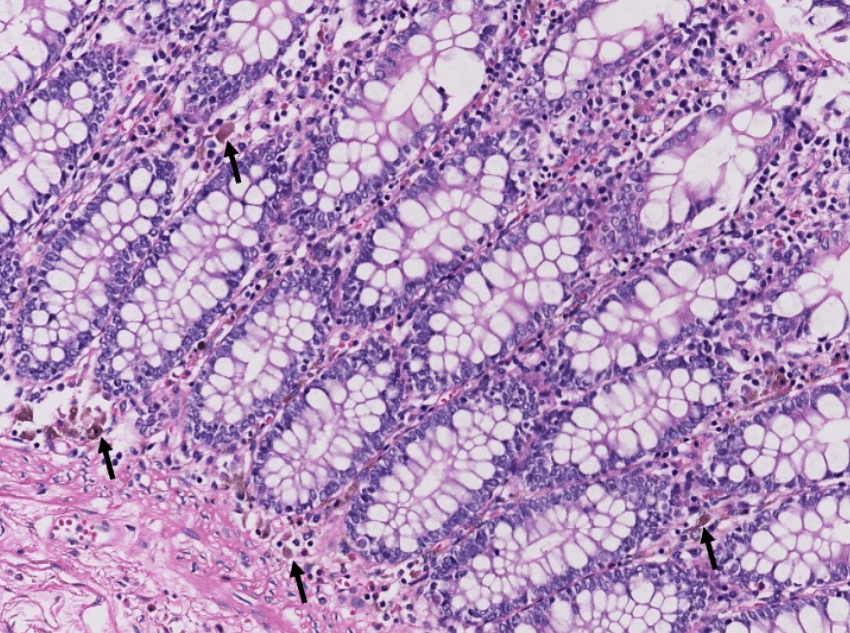
1. infiltrative/non-infiltrative endometrial tumor
2. atypical columnar cells arranged in crowded and complex glands, loss of intervening stroma
3. hyperchromatic elongated pleomophic nuclei, prominent nucleoli
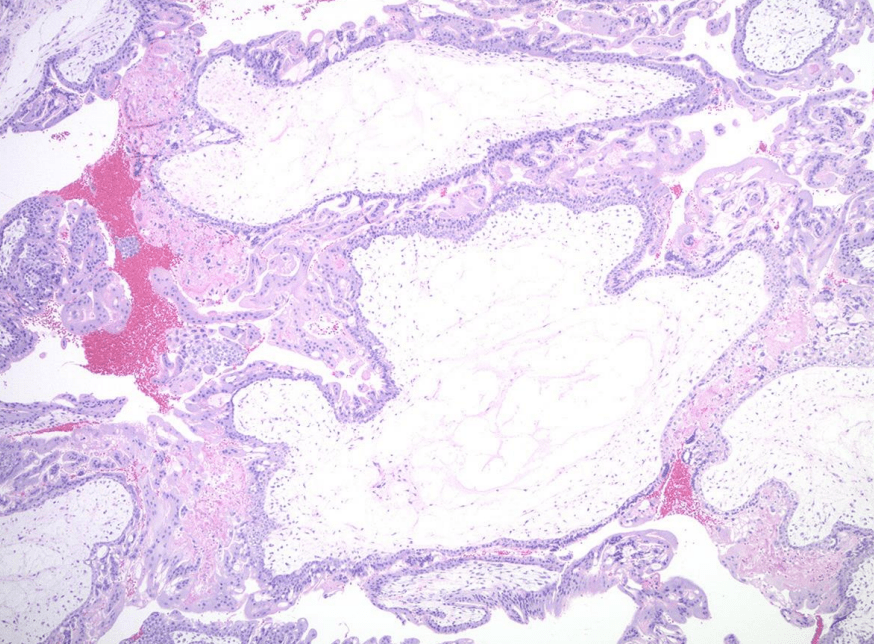
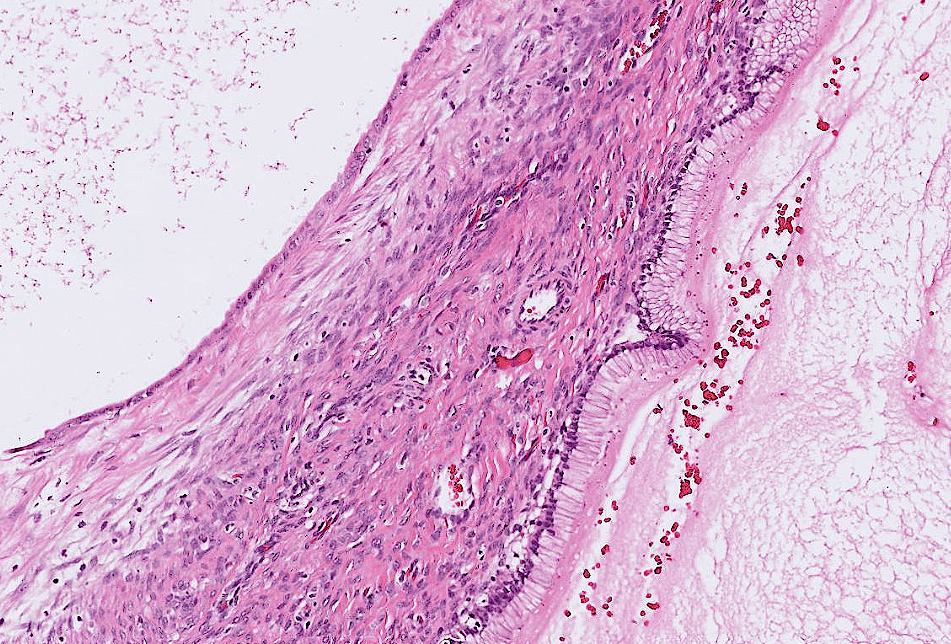
1. Avascular hydropic villi with central cisterns
2. Diffuse trophoblast hyperplasia with focal cytologic atypia
3. Endometrial decidual change and Arias-Stella reaction
唯一有villi的!
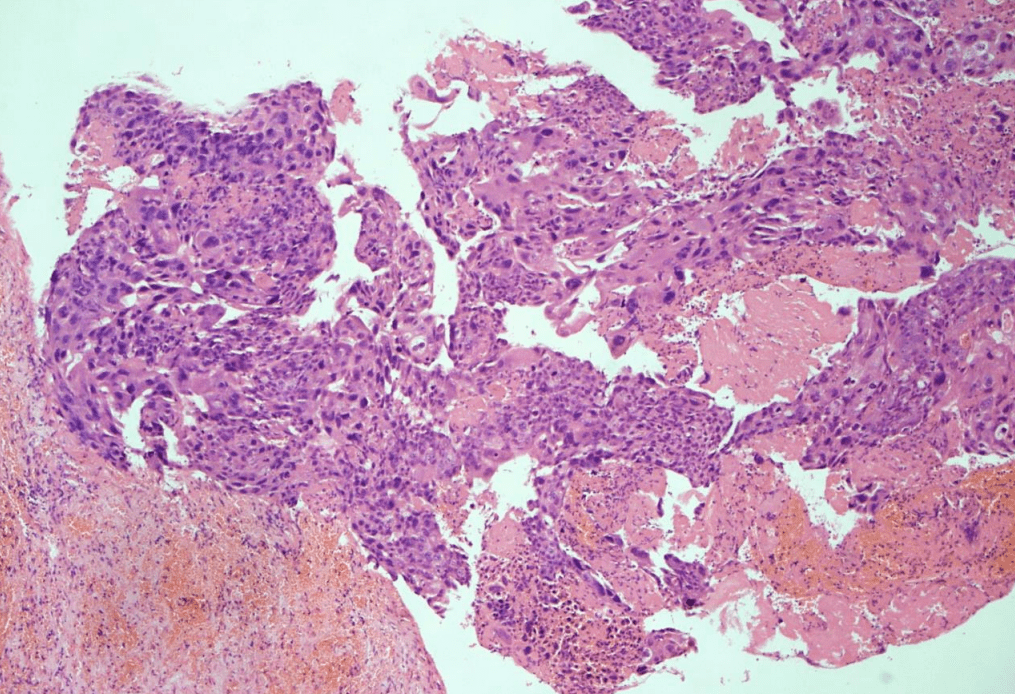
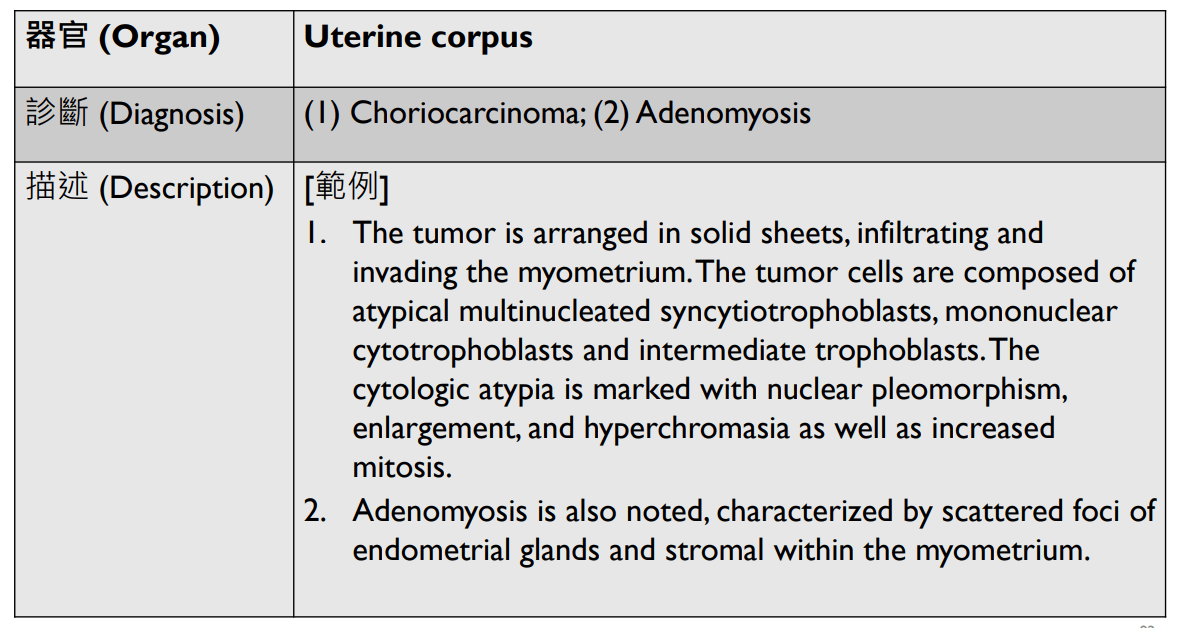
1. Infiltrative tumor invading the myometrium.
2. solid sheets of atypical multinucleated syncytiotrophoblasts, mononuclear cytotrophoblasts, and intermediate trophoblasts.
3. Marked cytologic atypia: hyperchromatic enlarged pleomorphic nuclei, increased mitosis.
4. may have necrosis/hemorrhage
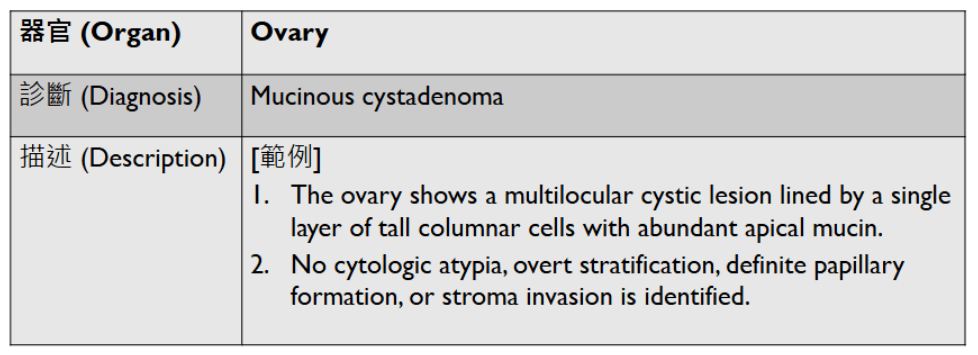
1. Multilocular cystic lesion lined by a single layer of tall columnar cells with abudant apical mucin
2. No definite cytologic atypia, stratification, papillary formation, or stromal invasion.
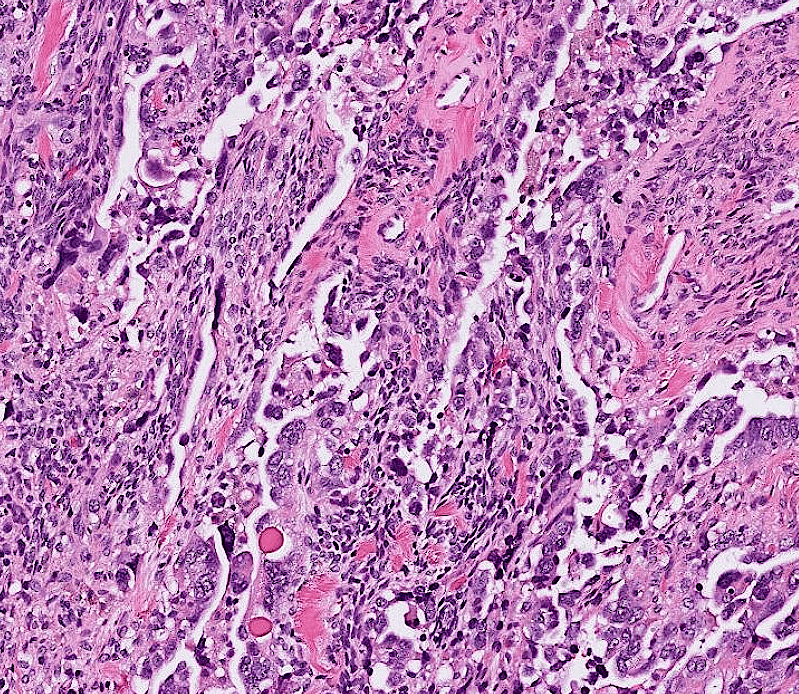
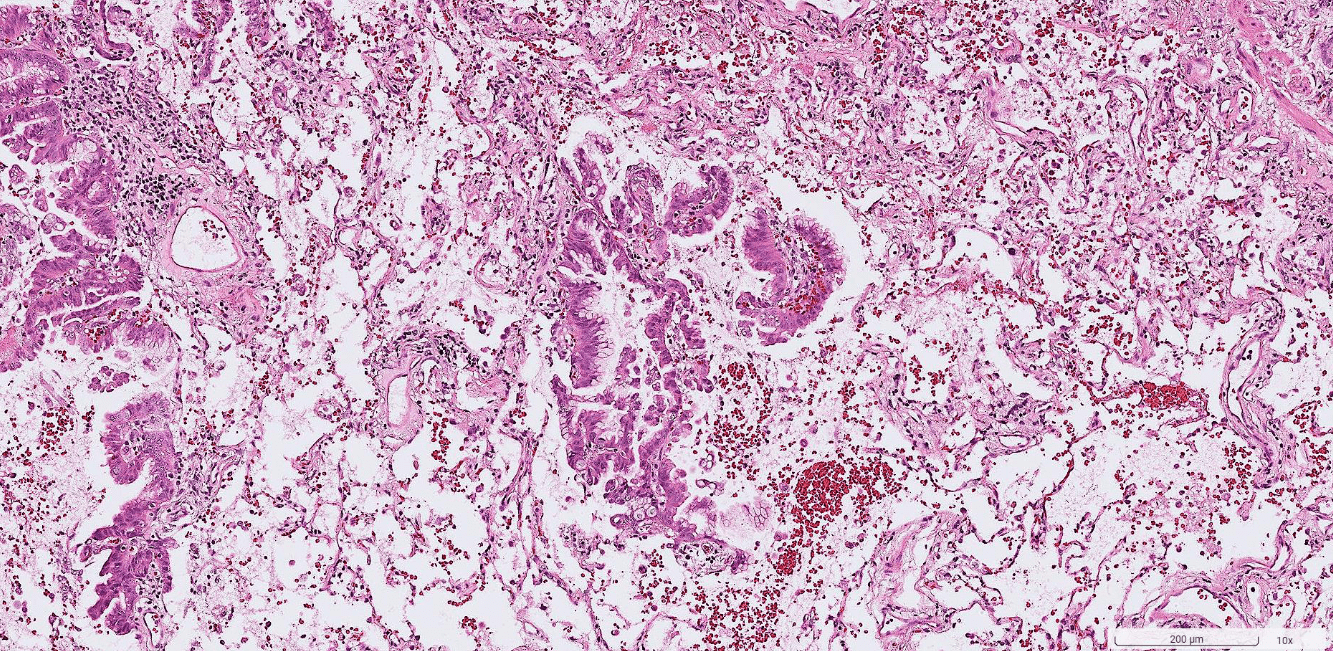
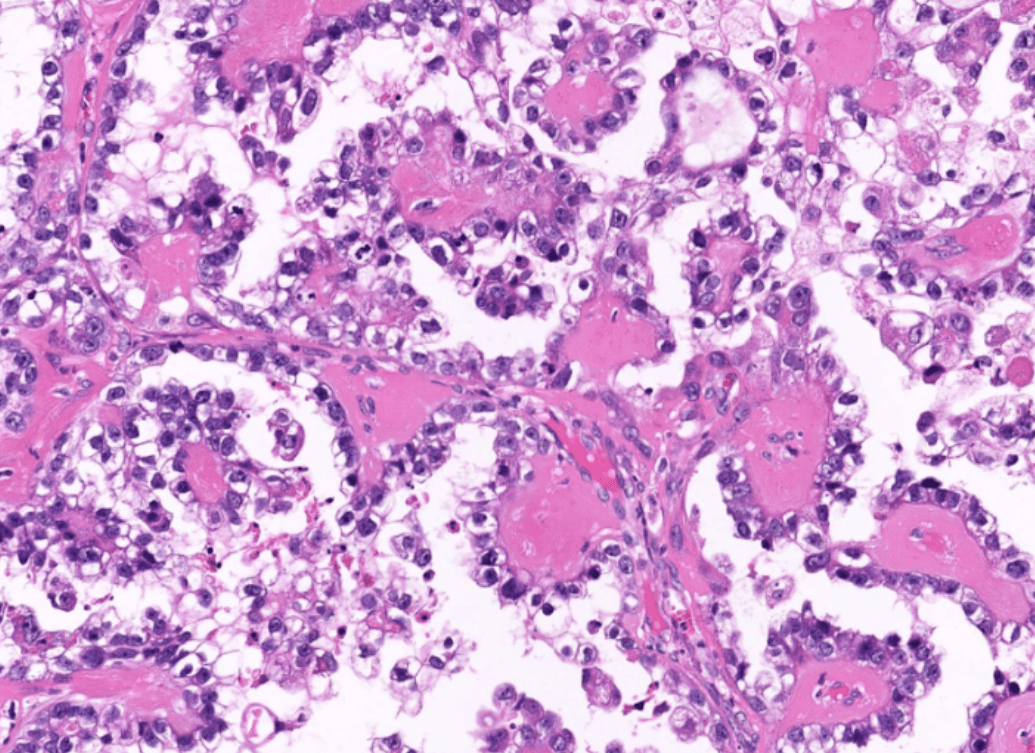
1. Infiltrative border
2. Papillary and solid growth of columnar to cuboidal tumor cells with eosinophilic cytoplasms.
3. Slit-like spaces between papillae.
4. Marked cytologic atypia: pleomorphic nuclei, prominent nucleloli, and frequent mitosis
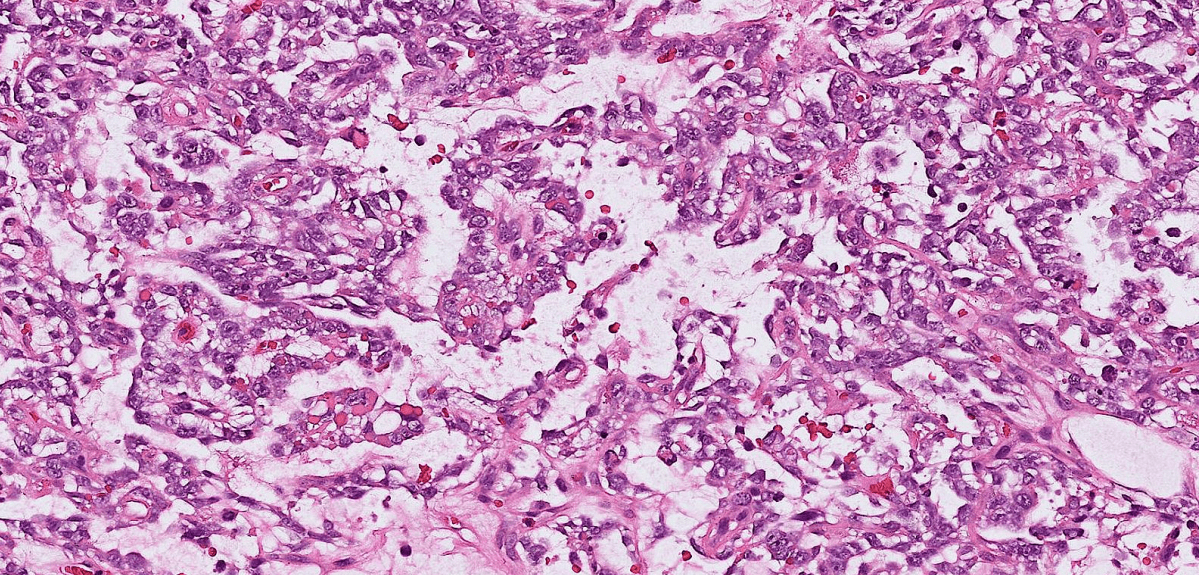
1. Tubulocystic and papillary structures lined by cuboidal, polygonal, or round cells with clear cytoplasm.
2. Papillae have hyalinized fibrovascular core.
3. Cells with hobnail-appearance.
4. Hyperchromatic pleomorphic nuclei, prominent nucleoli
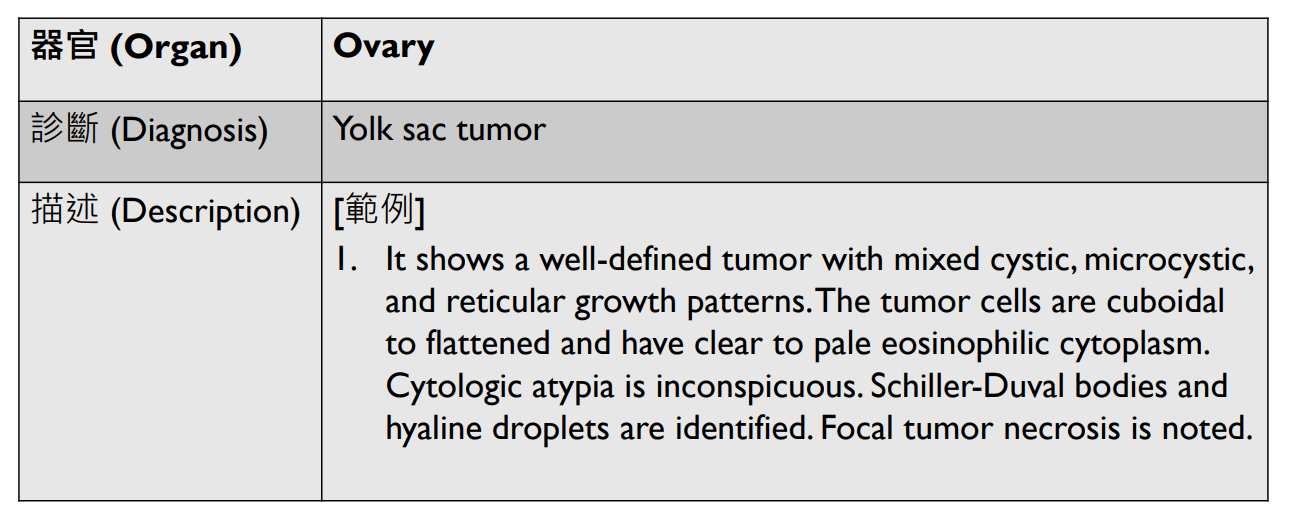
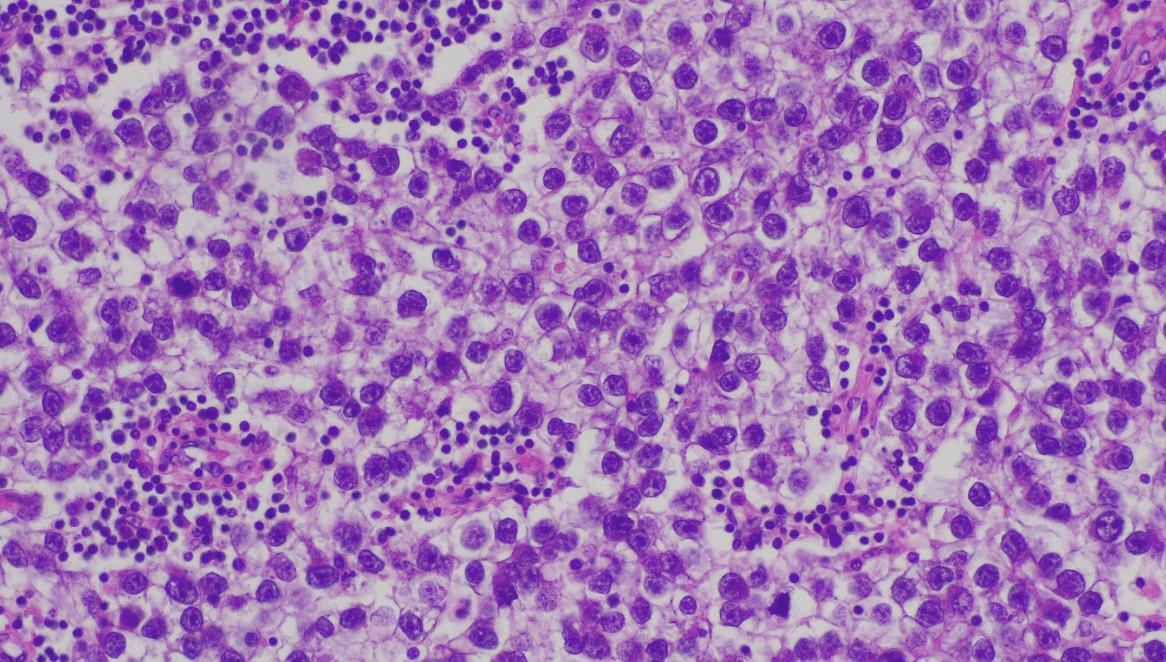
1. Well-defined tumor with mixed cystic / microcystic/ reticular pattern.
2. Cuboidal to flattened tumor cells with clear to pale eosinoplilic cytoplasm.
3. Schiller-Duval bodies and hyaline droplets.
4. Inconspicious cytologic atypia.
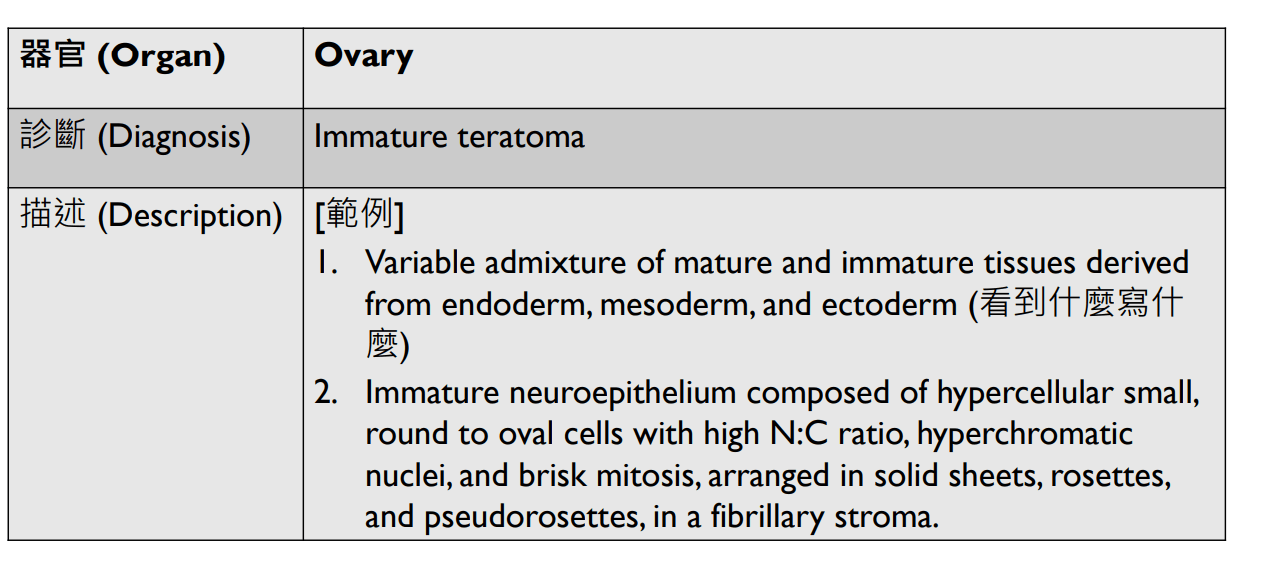
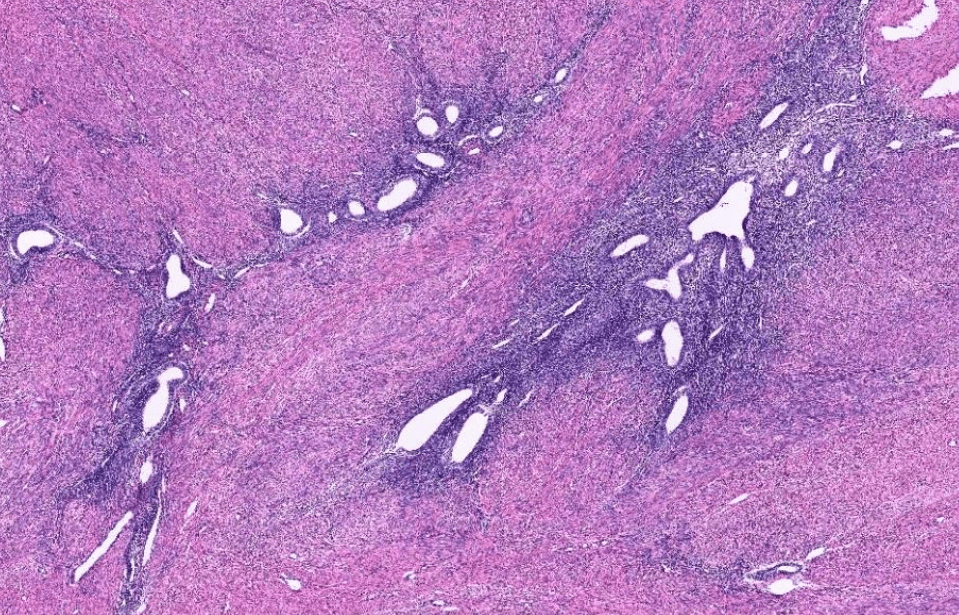
2. Immature neuroepithelium composed of dense small blue round cells with brisk mitosis, arranged in sheets, rosettes, pseuorosettes in a fibrillary background.
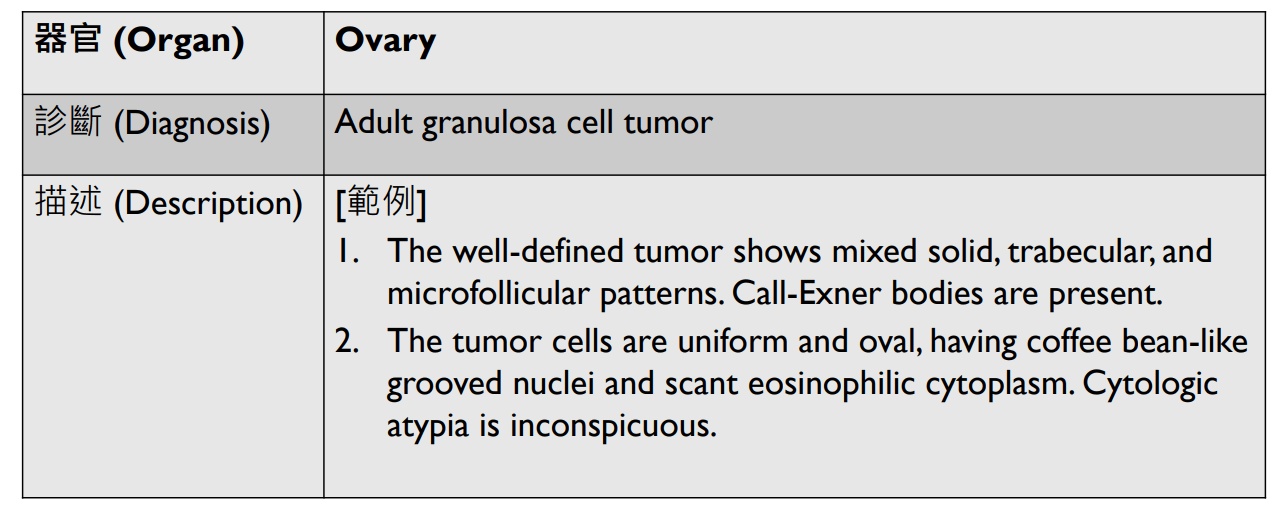
1. Well-defined tumor with mixed solid /trabecular /microfollicular patterns.
2. Call-exner bodies.
3. Uniform oval tumor cells with coffee bean-like grooved nuclei and scant eosinophilic cytoplasm.
4. Inconspicuous cytologic atypia.

感覺低機率考
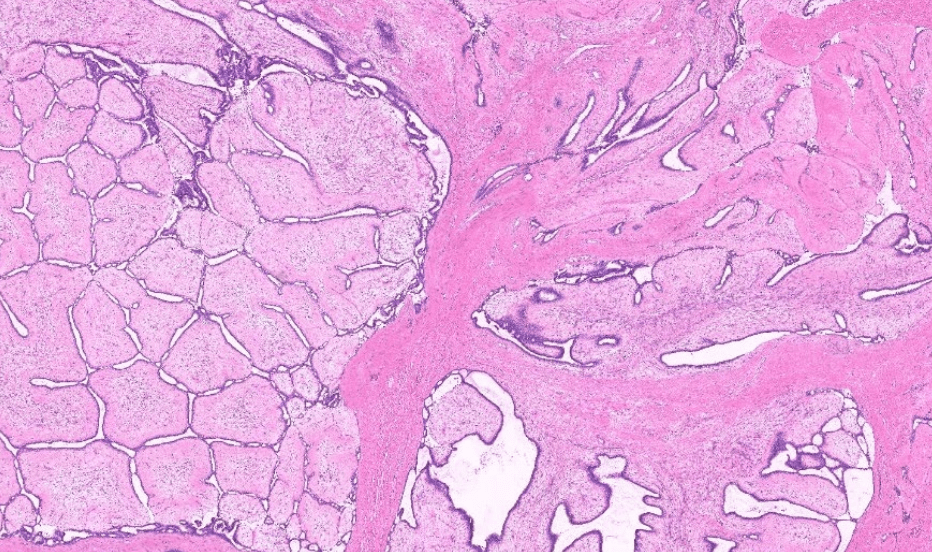
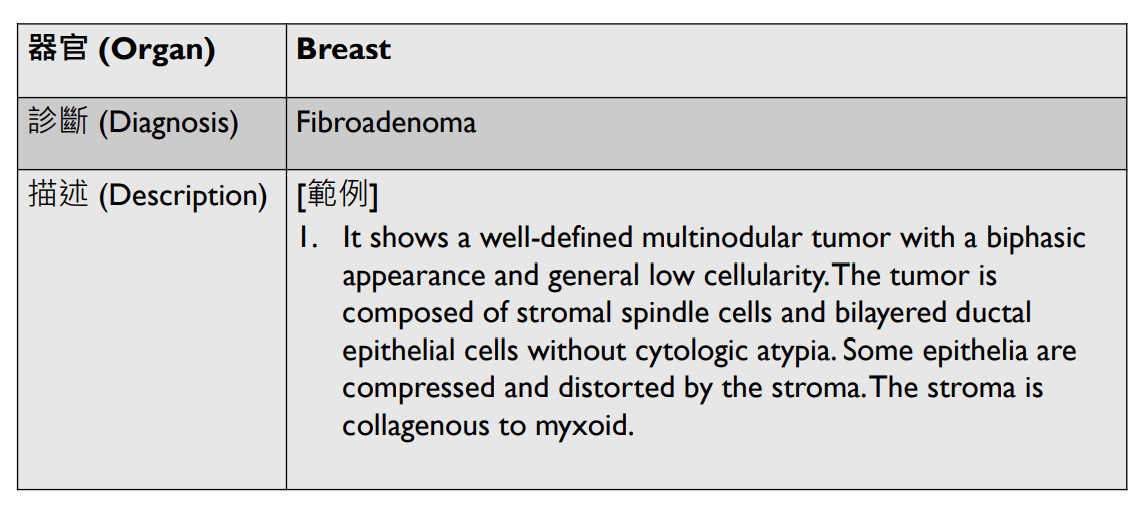
1. Well-defined multi-nodular biphasic tumor and generally low cellularity.
2. Stromal spindle cells and bilayered epithelial cells without atypia.
3. Some epithelium is compressed and distorted by the collagenous to myxoid stroma.
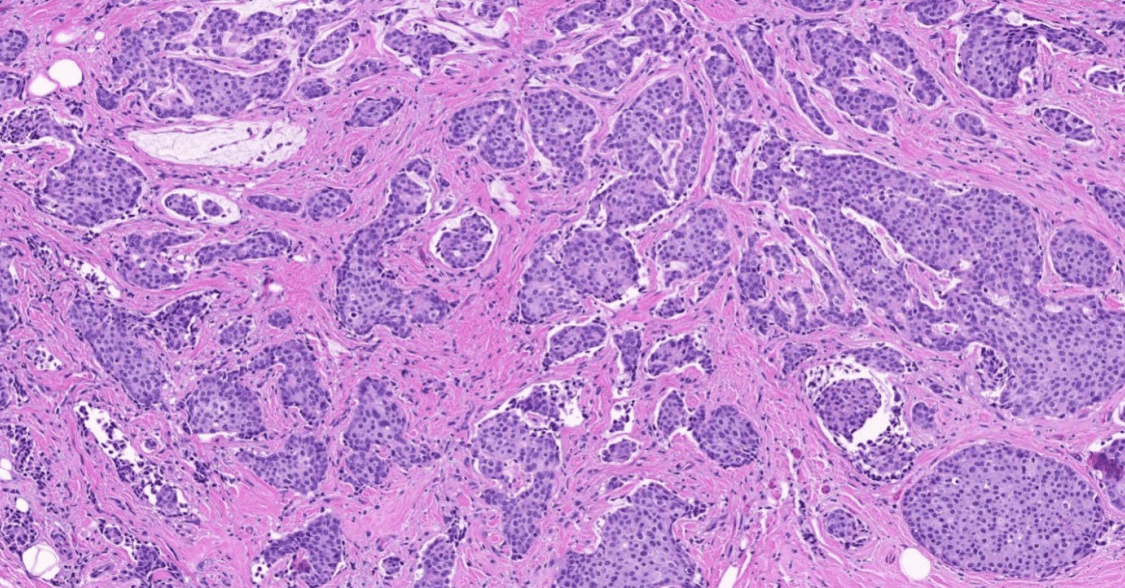
1. Infiltrative tubules.
2. Atypical cuboidal to columnar epithelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged pleomorphic nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and increased mitosis.
3. cribriform (or other types of) DCIS
4. stromal desmoplasia
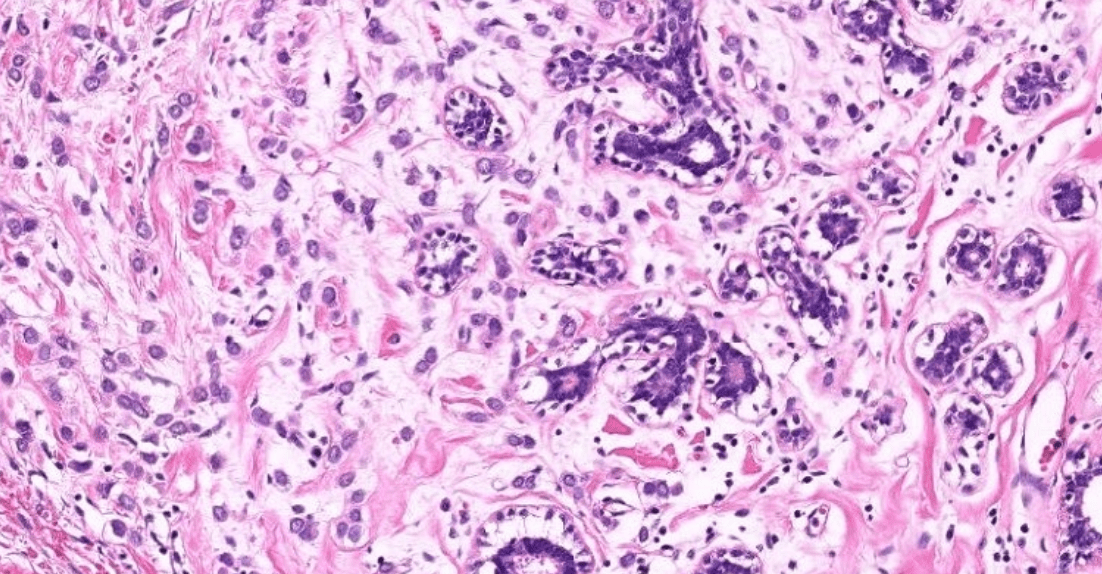
1. Infiltrative discohesive tumor cells arranged in a single-cell or single-file pattern.
2. Uniform, small, round tumor cells with minimal cytologic atypia.
3. No stromal desmoplasia.
4. LCIS
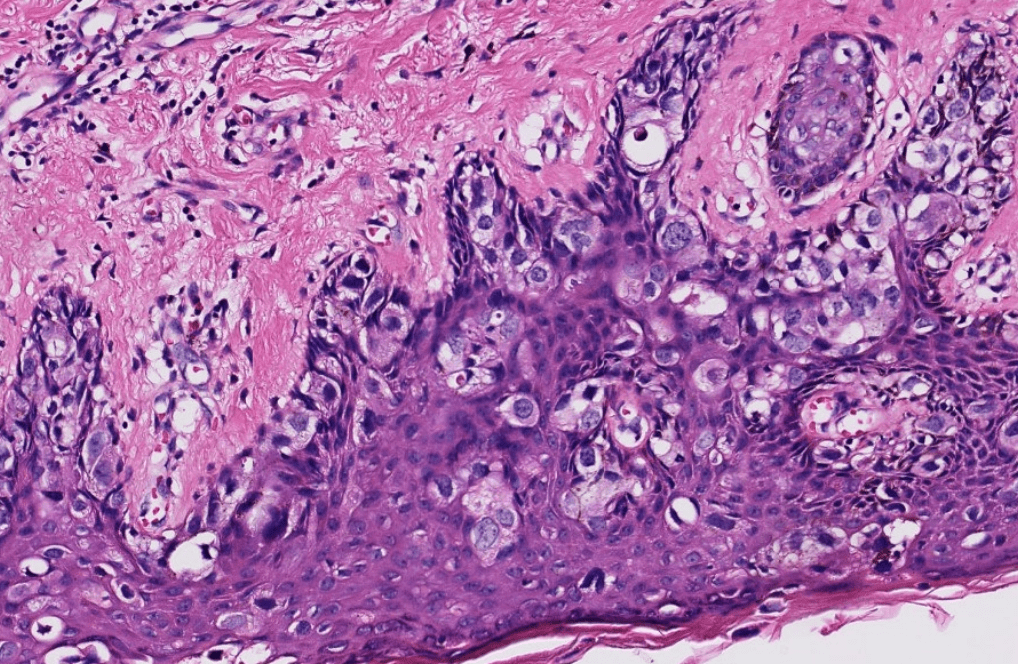
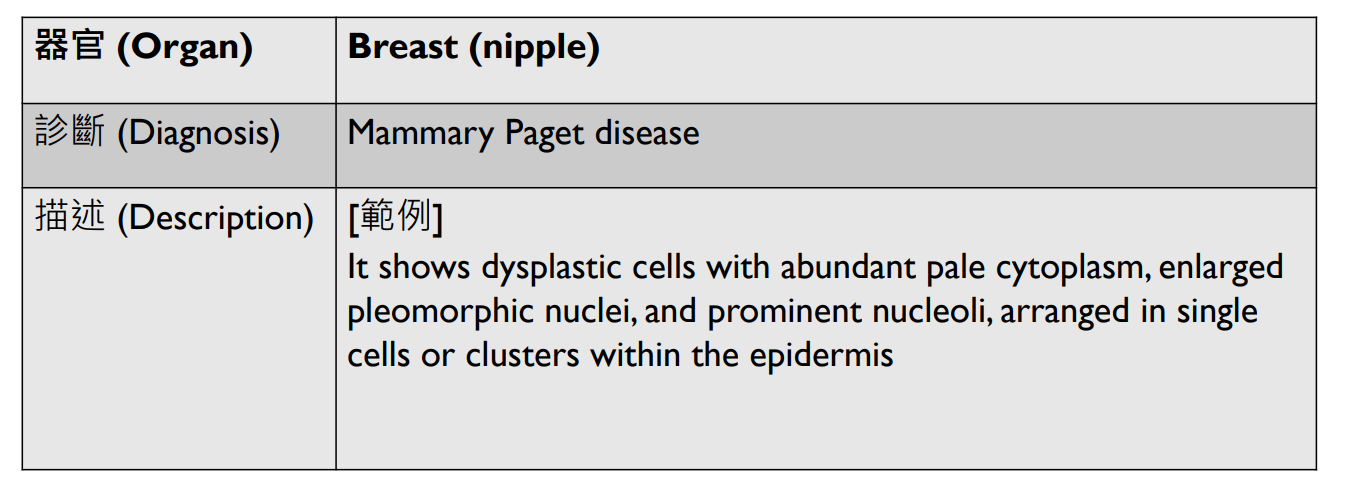
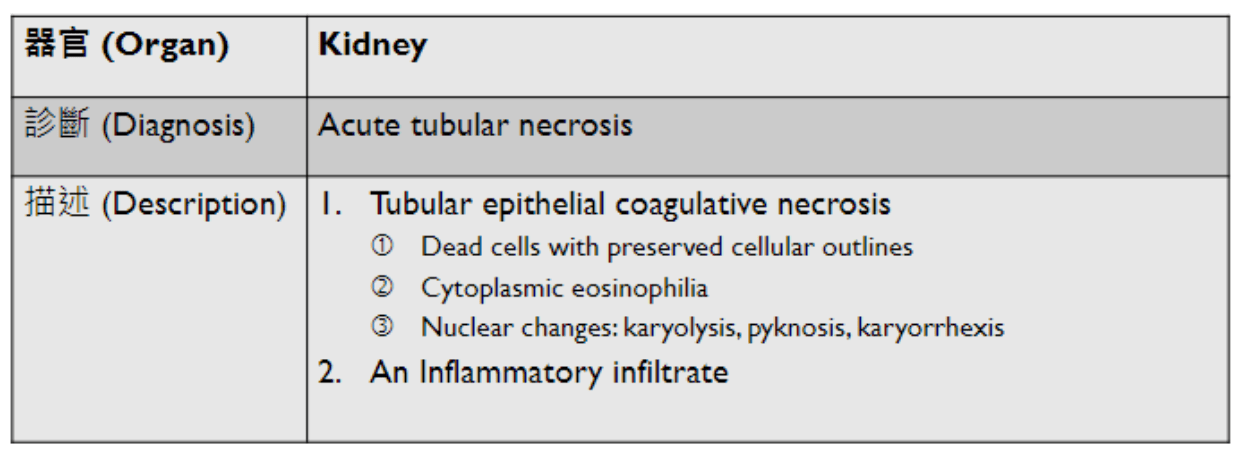
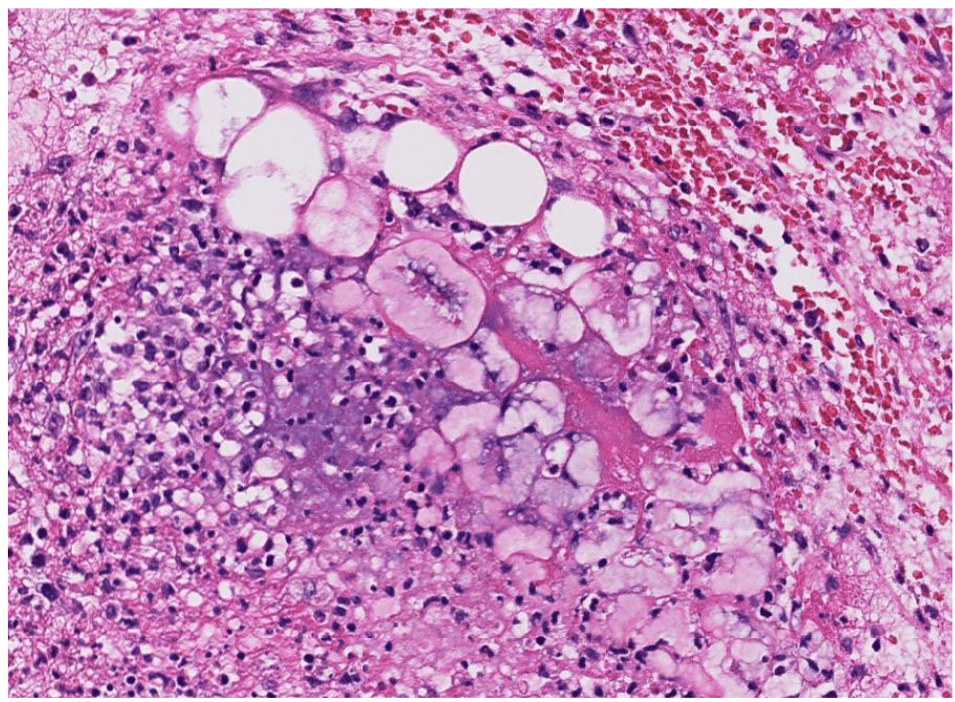
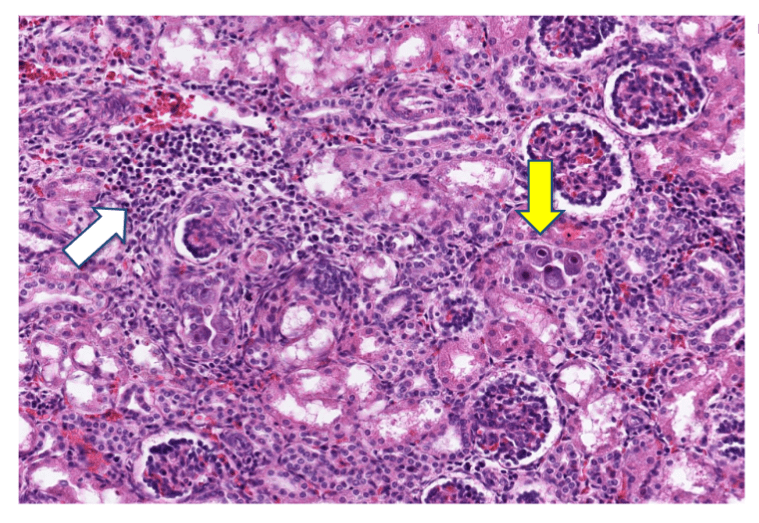
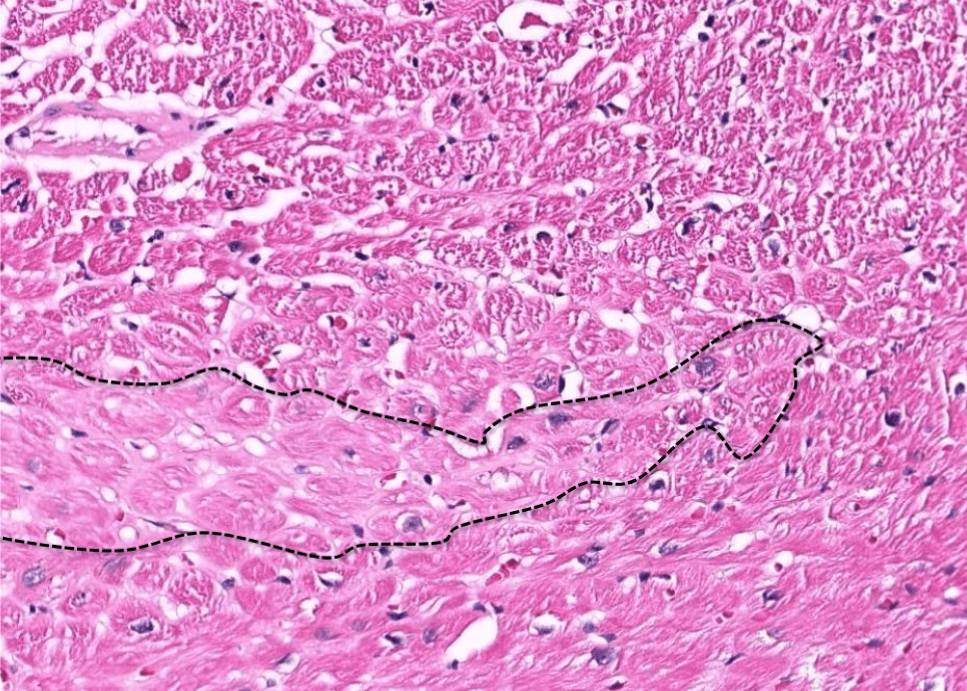
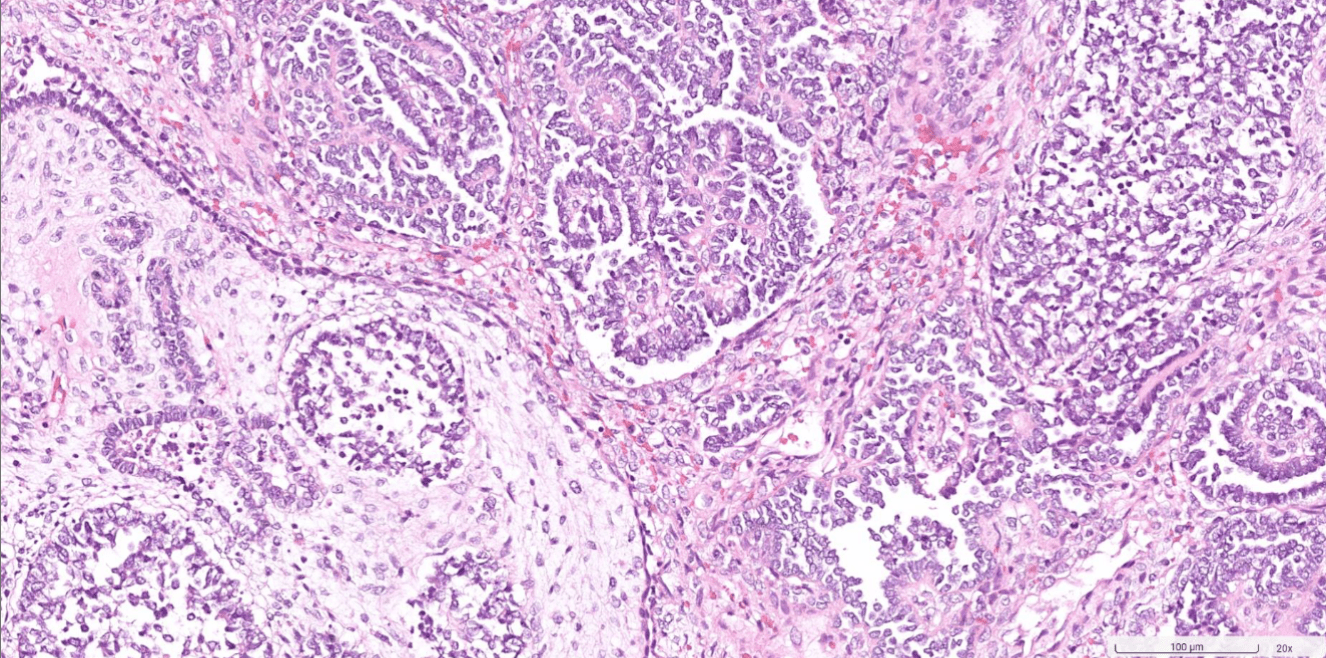
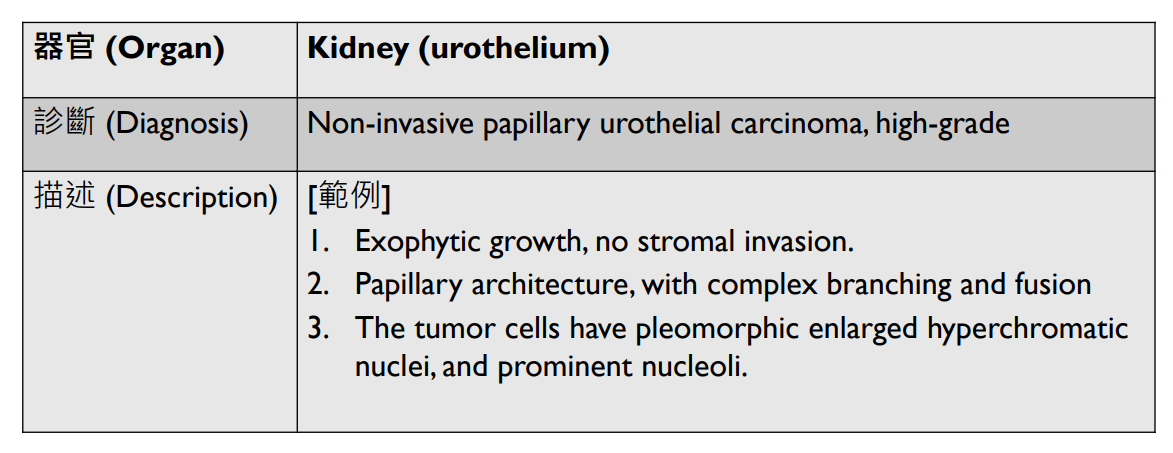
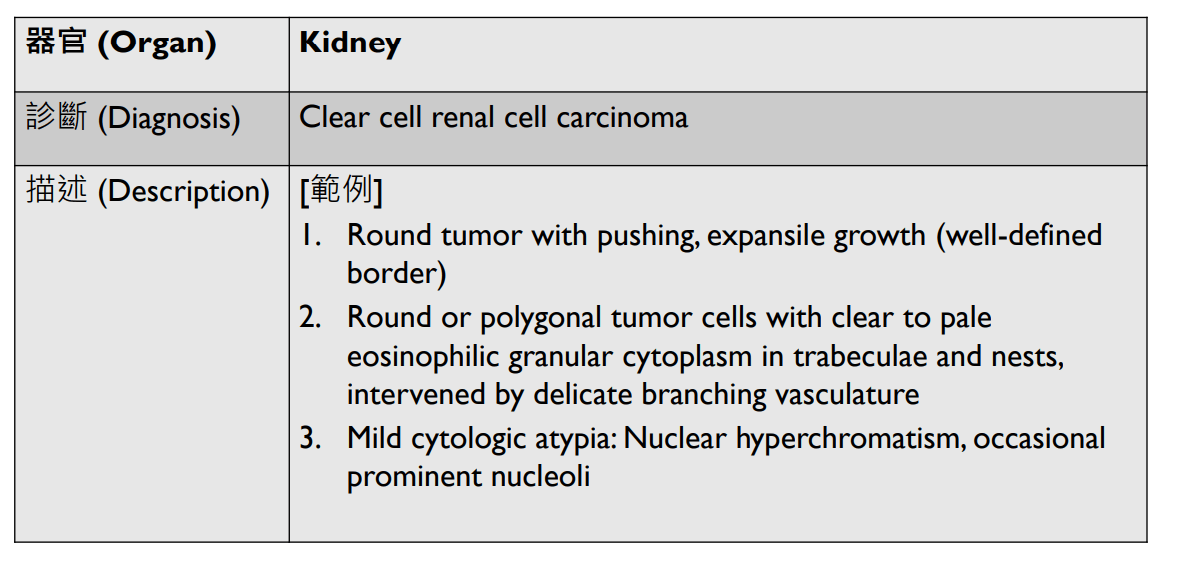
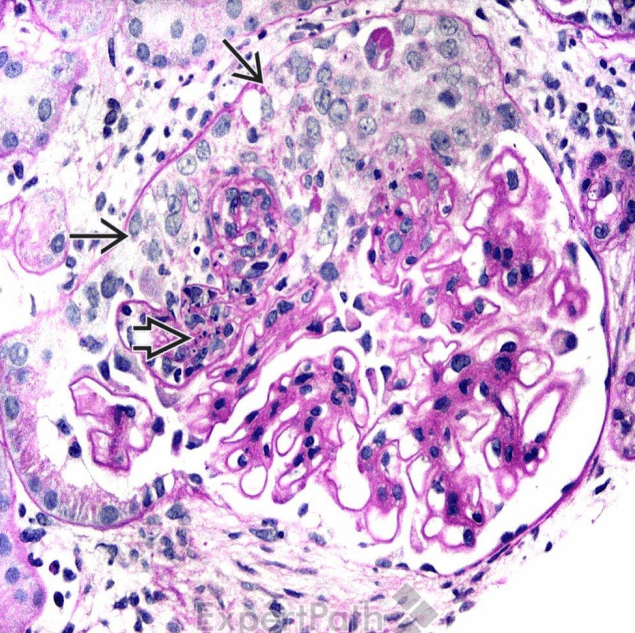
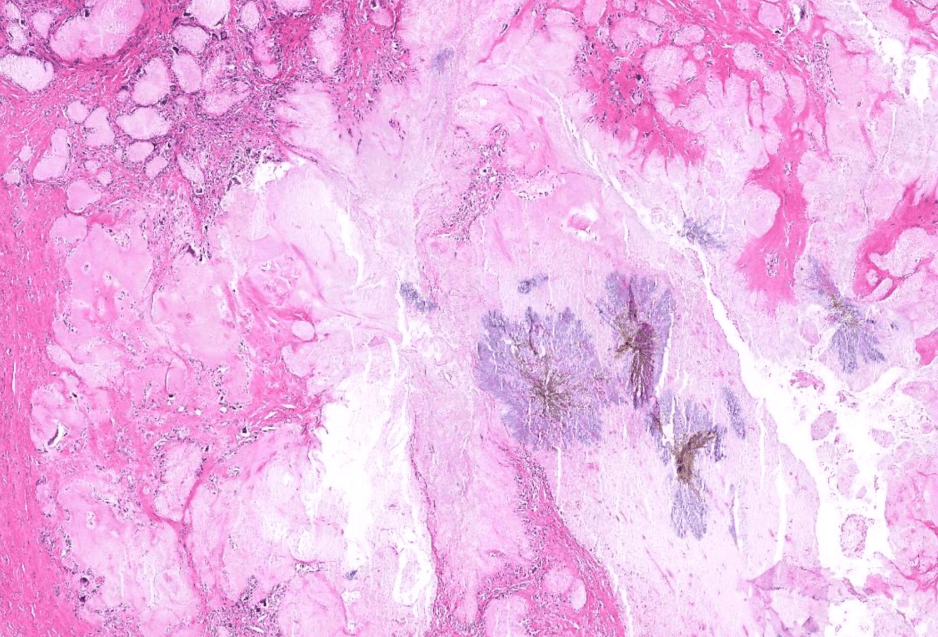
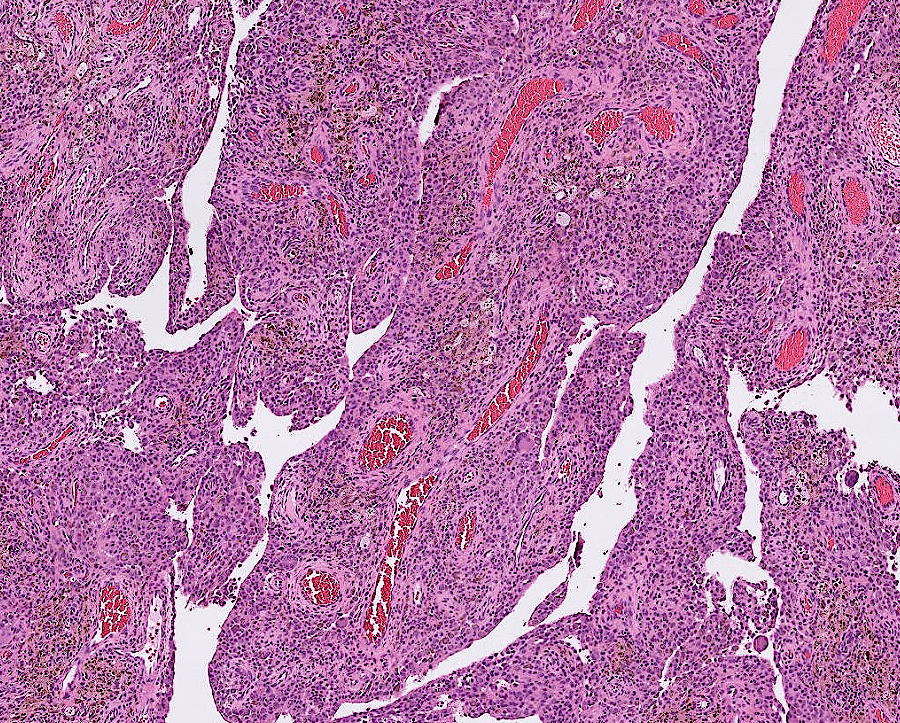
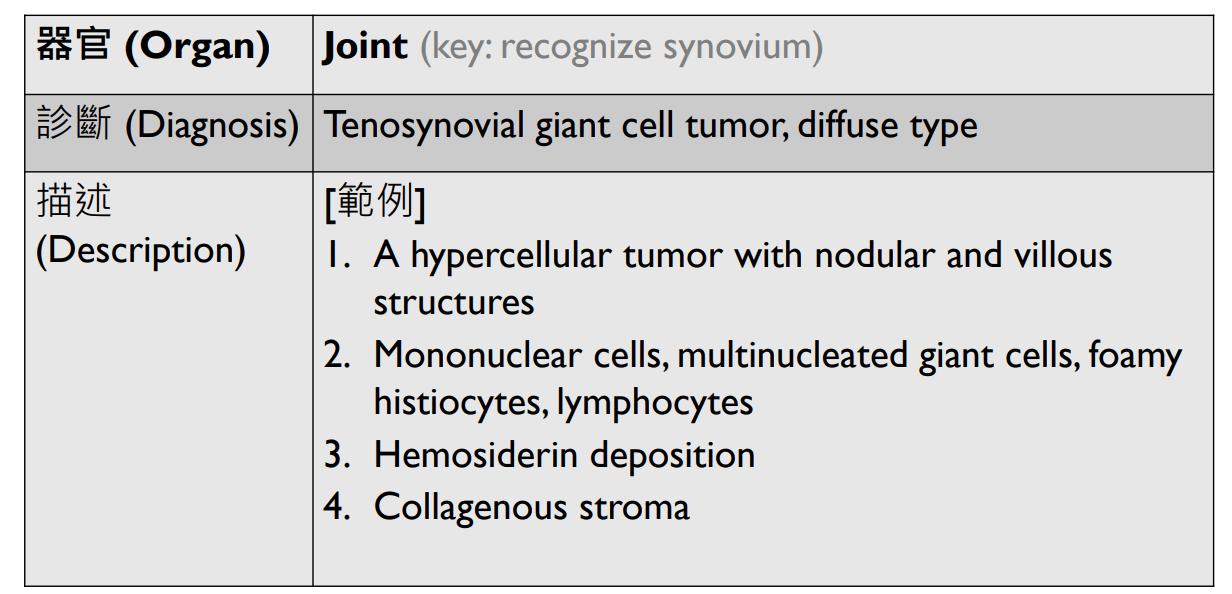
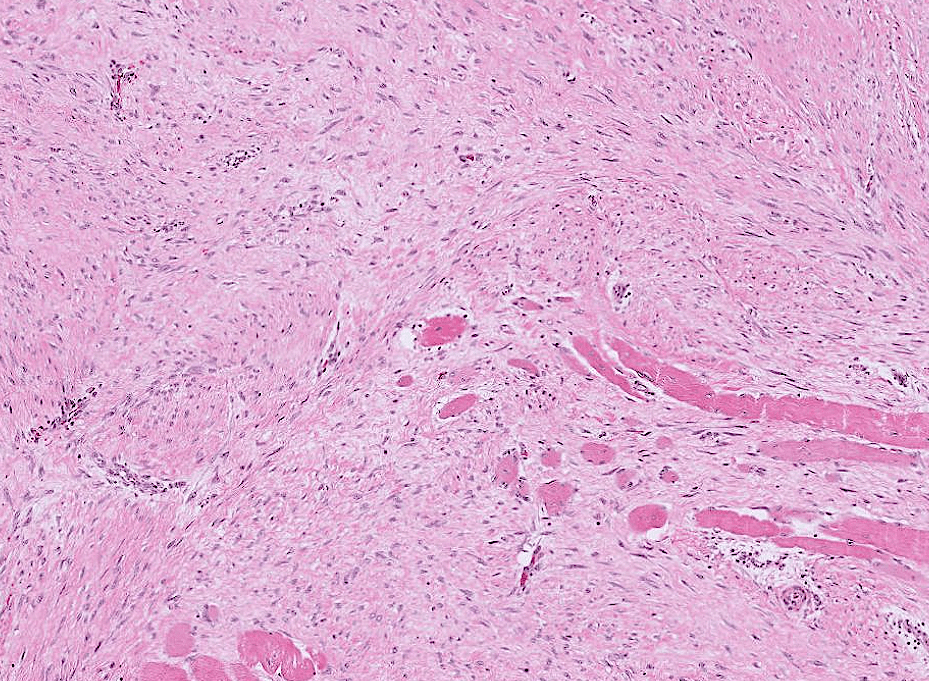
Organ: Kidney
Diagnosis: Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Discription:
1. Interstitial fibrosis/inflammation, tubular atrophy
2. some glomeurili show segmental sclerosis and adhesion to Bowman's capsule
3. arteriosclerosis
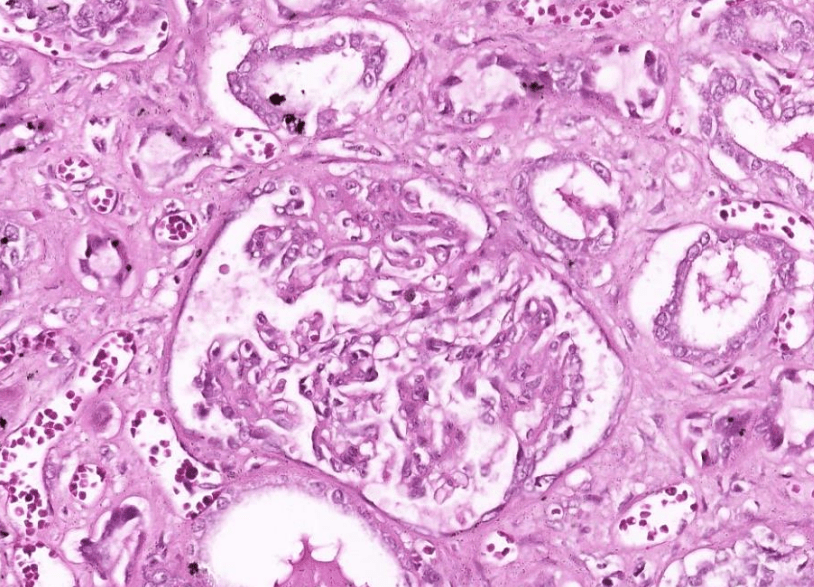
Organ: Kidney
Diagnosis: Diabetic Nephropathy
Discription:
1. interstitial fibrosis/inflammation, tubular atrophy
2. Diffuse mesangial sclerosis
3. Nodular glomerulosclerosis
4. hyaline arteriolosclerosis
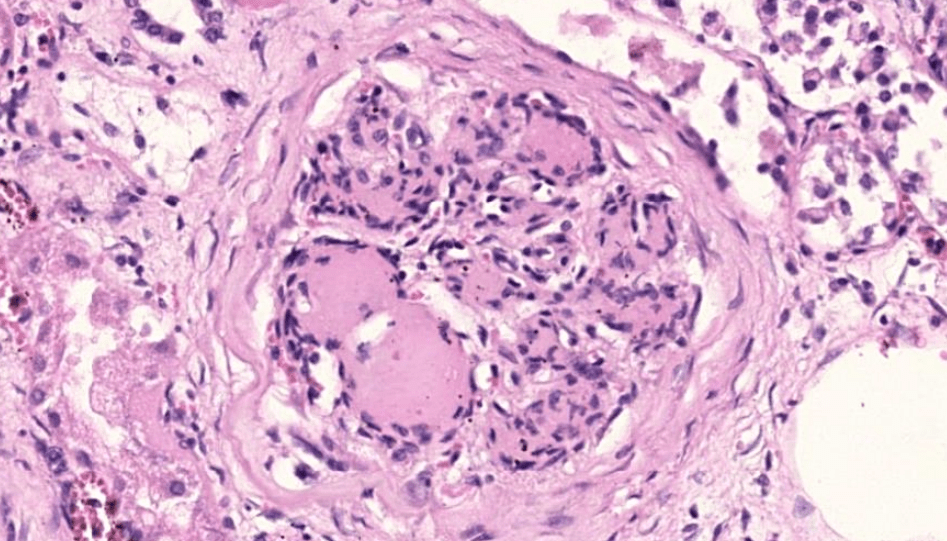
Organ: Kidney
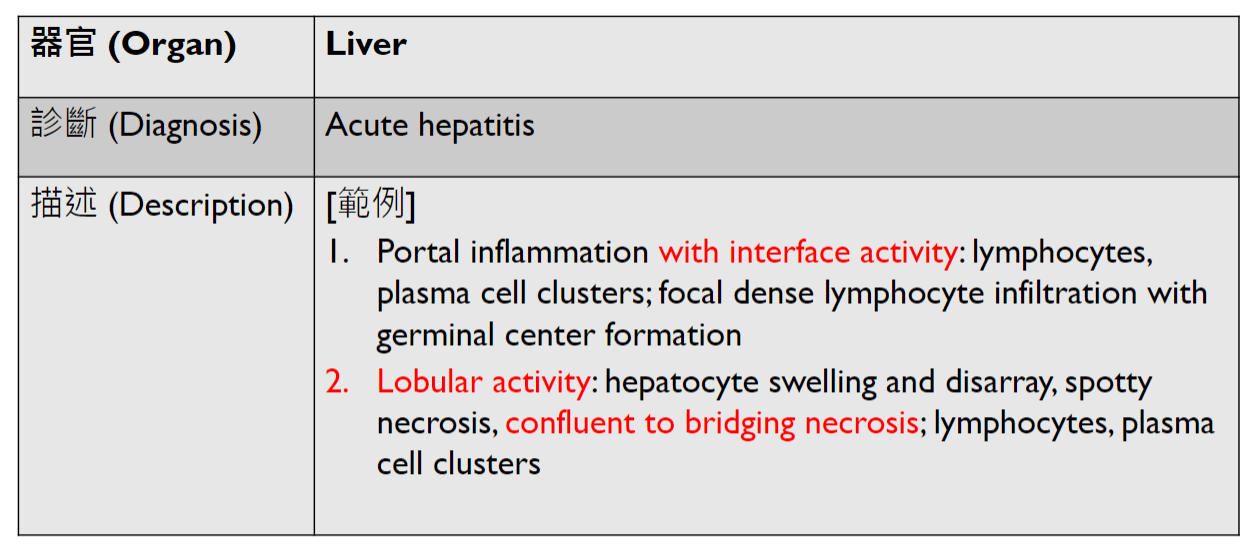
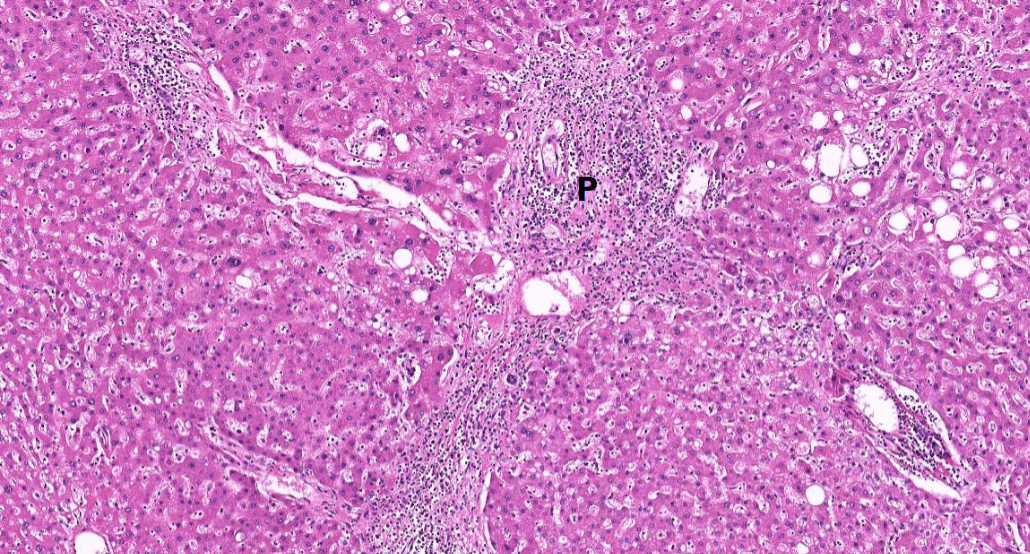
Diagnosis: Class 4 lupus nephritis with crescents
Discription:
1. Hypercellular glomeruli with capillary wall thickening (wire loop)
2. crescent-shaped extracapillary proliferation
(3. interstitial fibrosis/inflammation, tubular atrophy)
Pathology-Micro 5
(碎塊可能是CNS)
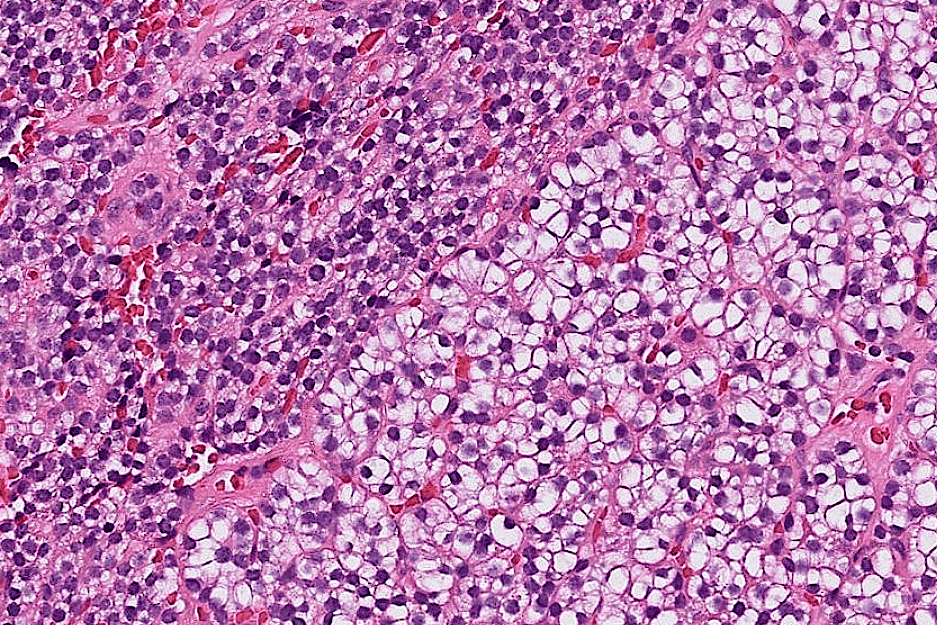
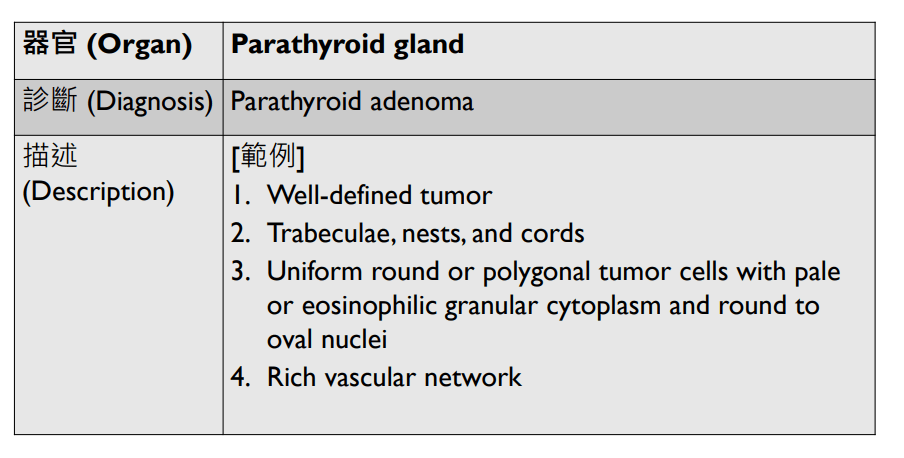
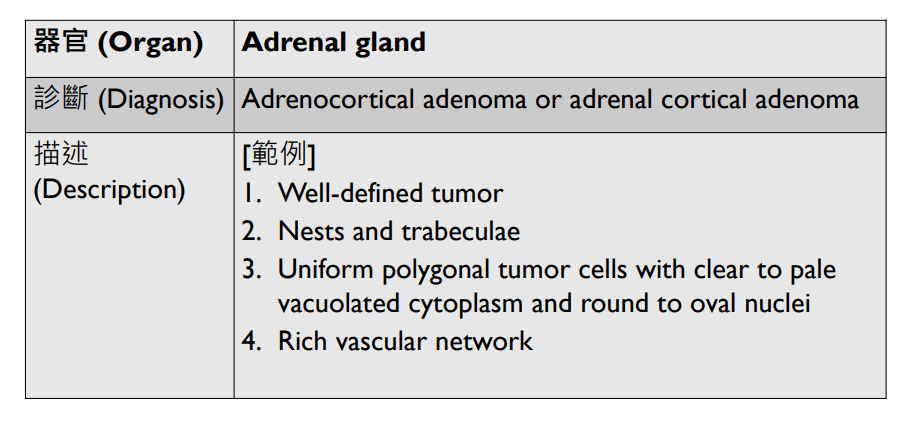
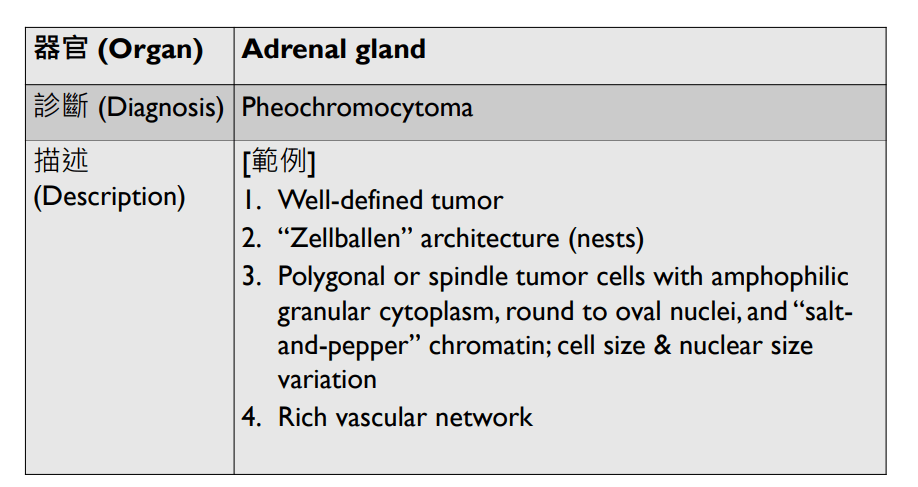
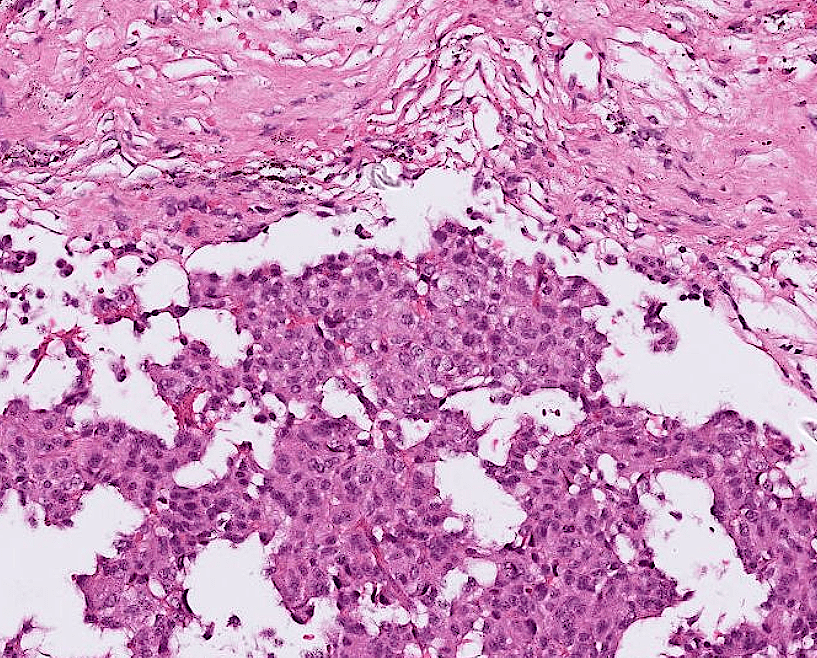
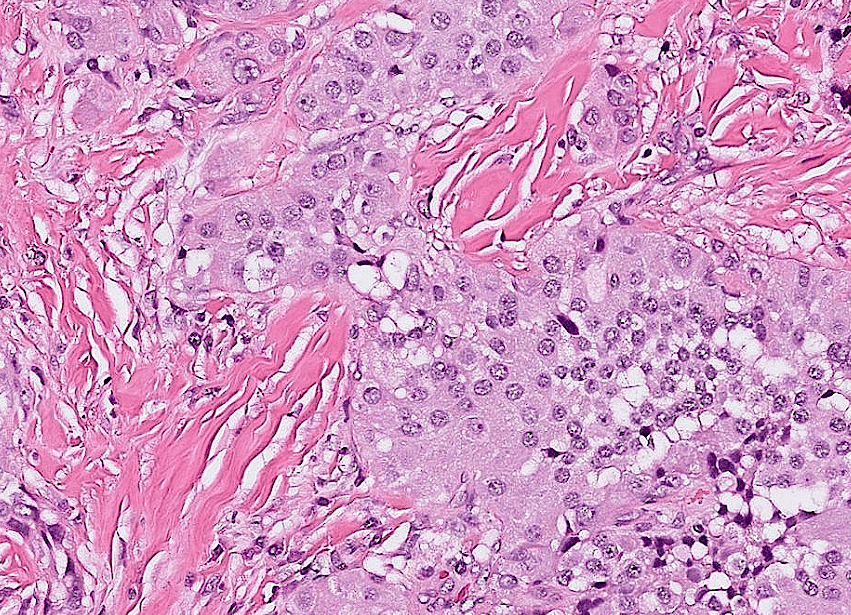
Organ: Pituitary Gland
Diagnosis: adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma
Descriptions:
- Heterogenous tissue fragments, pale and darker regions
- Epithelial cells with peripheral palisading and central stellate reticulum
- Wet keratin with ghost cells
- Interstitial myxoid stroma
,pseudoinclusions
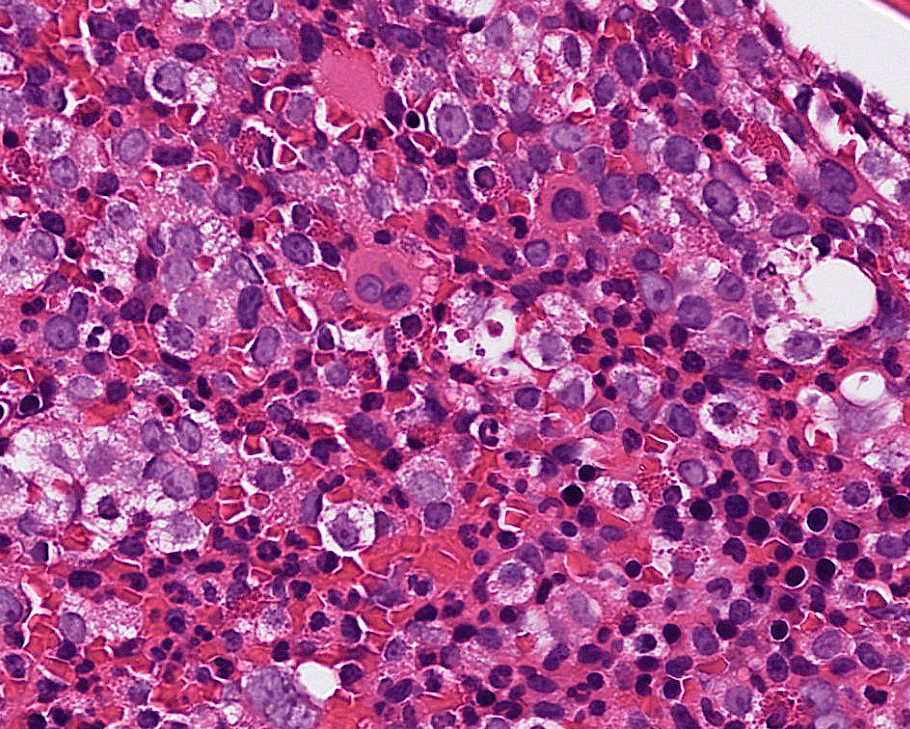
5. Amyloid deposition
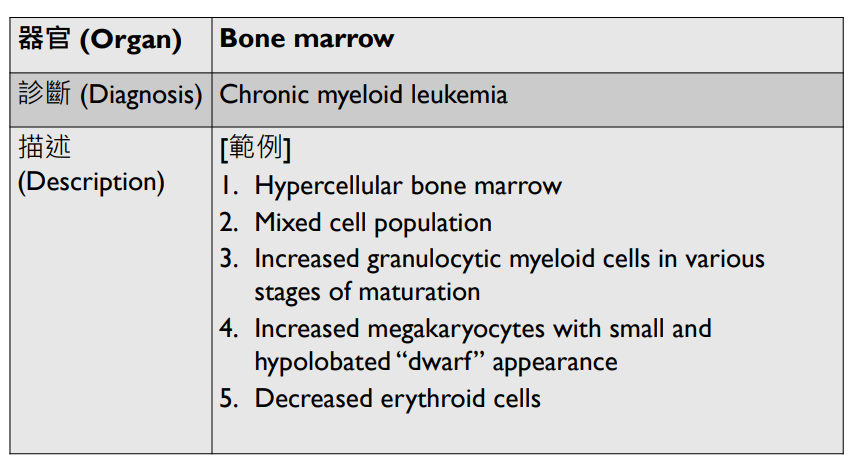
Increased dwarf megakaryocytes
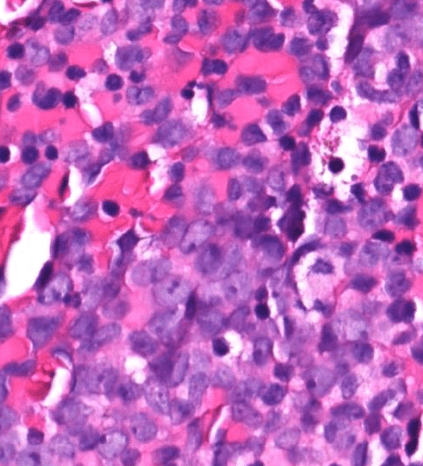
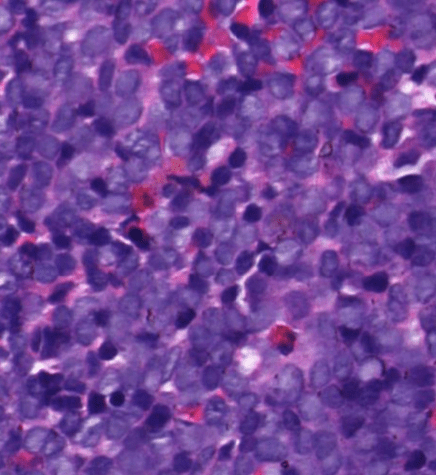
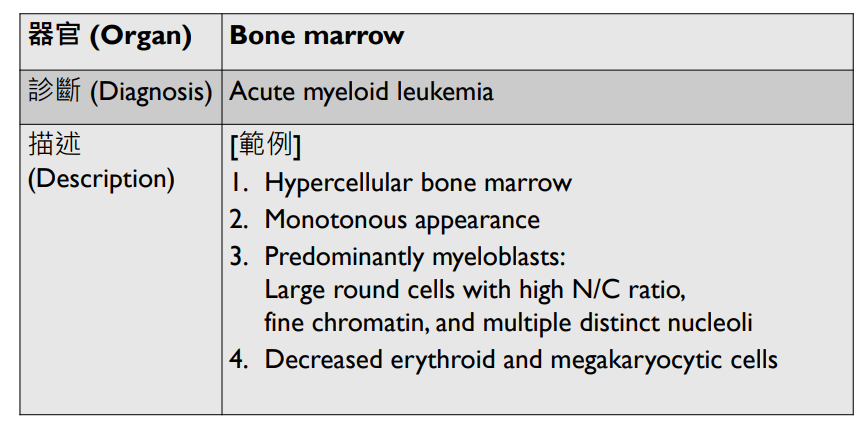
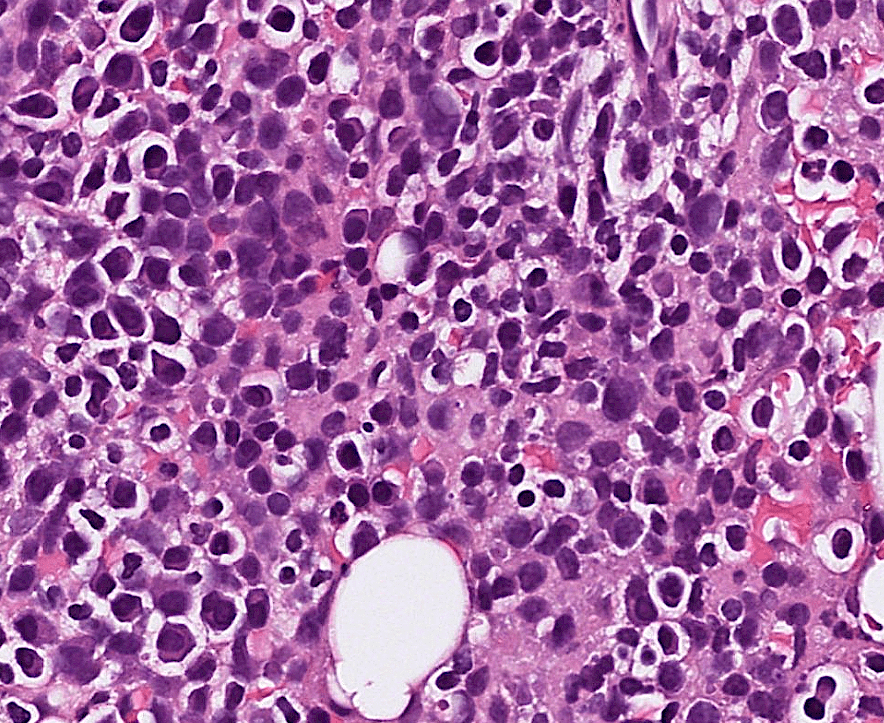
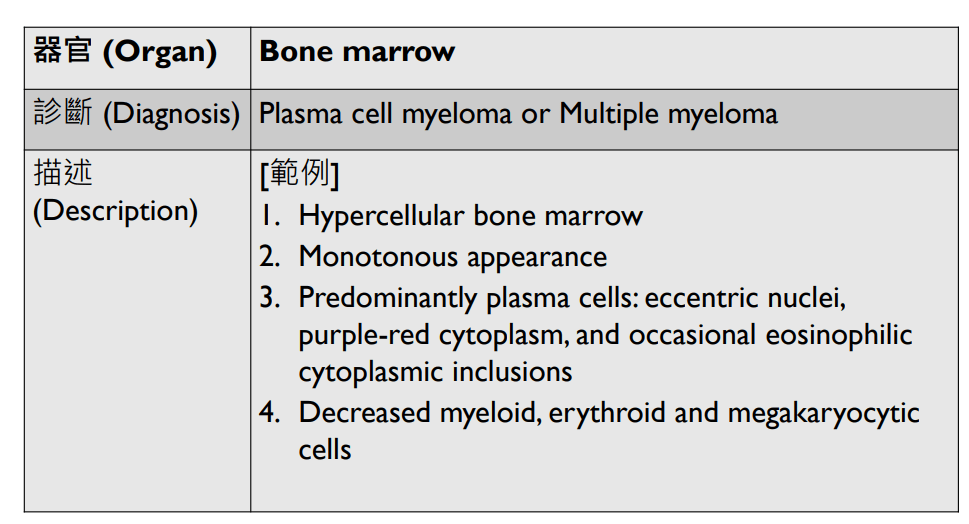

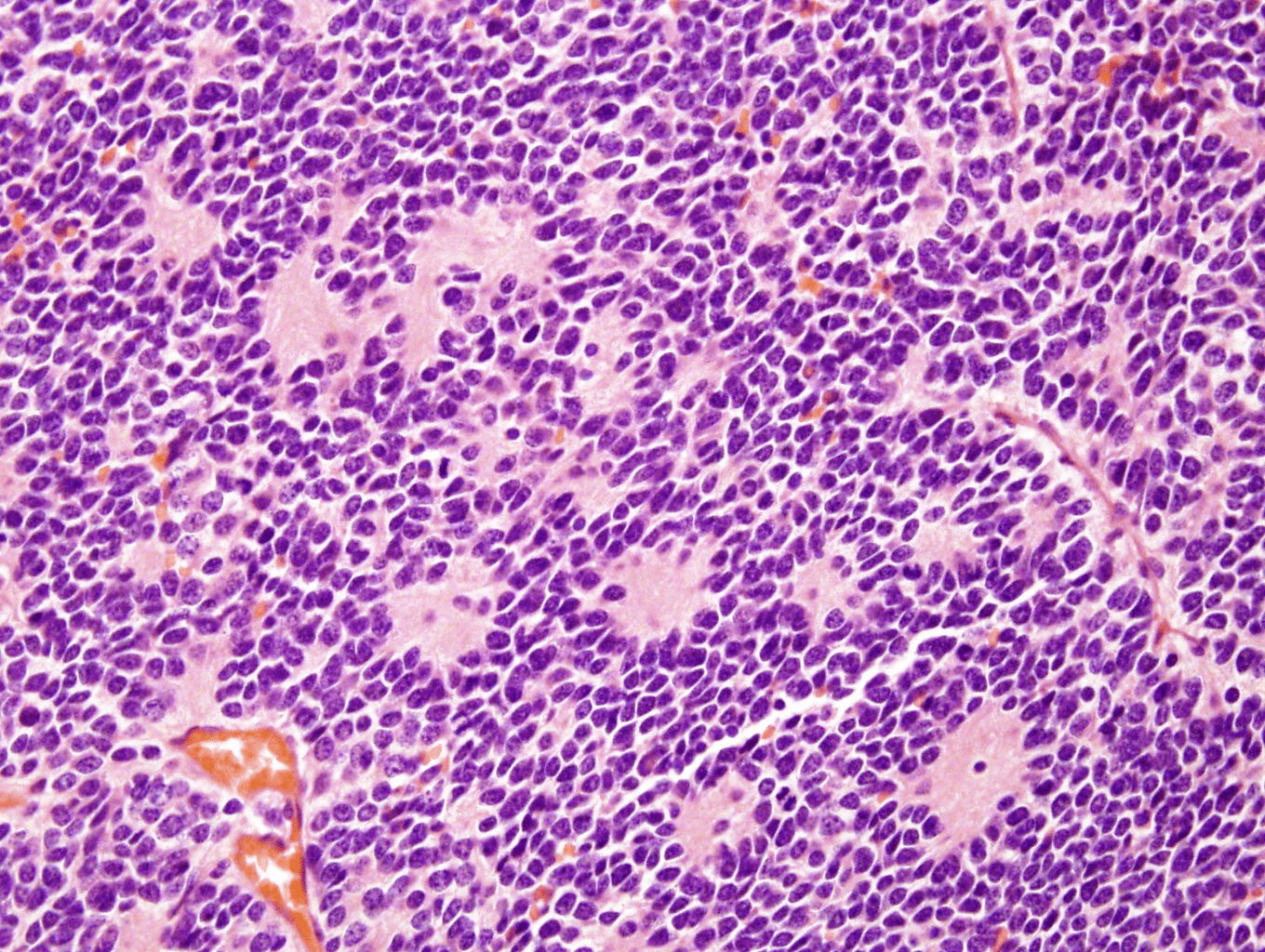
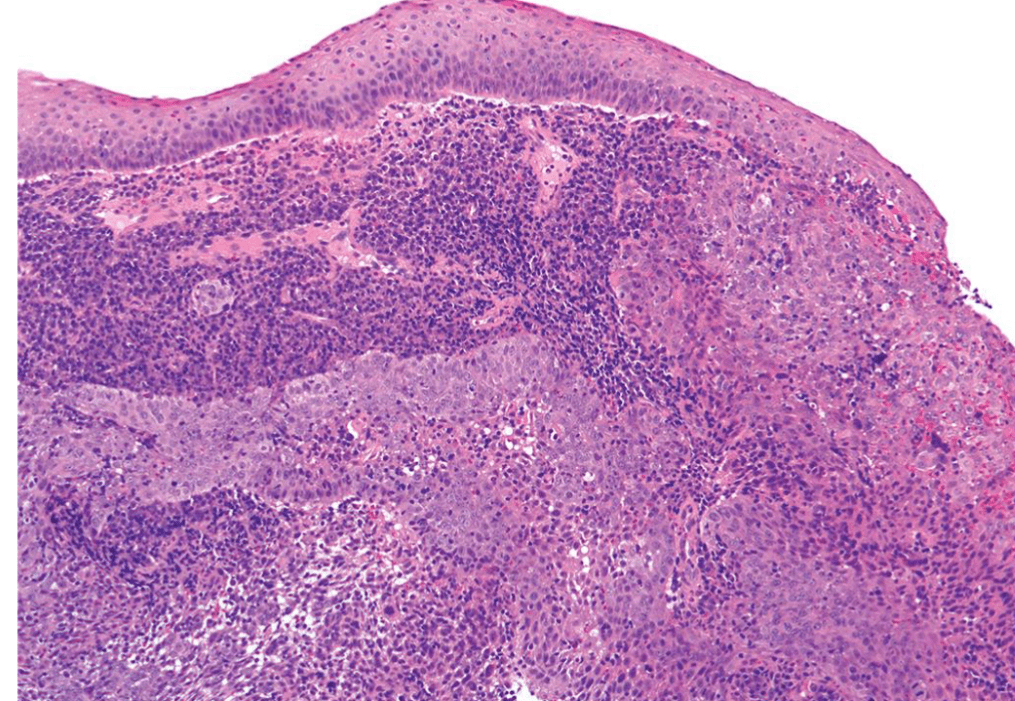
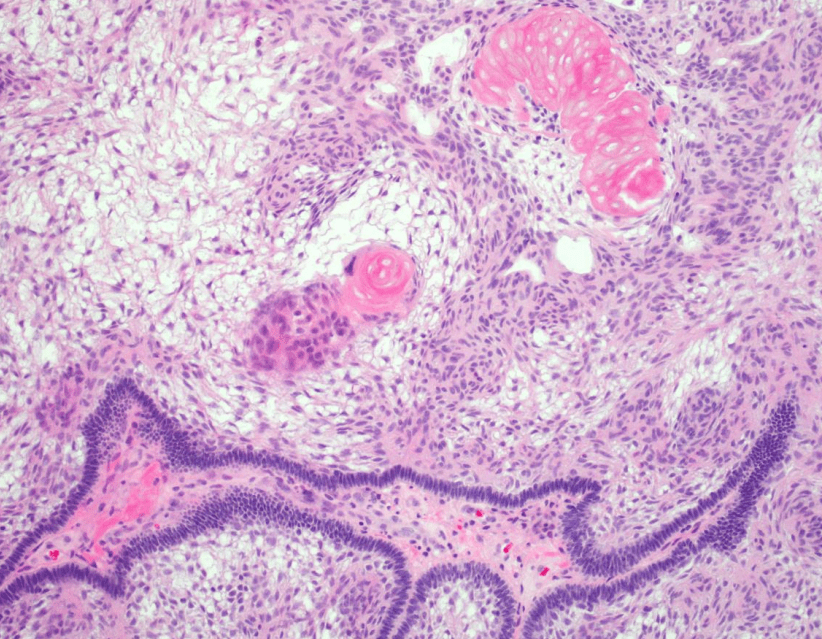
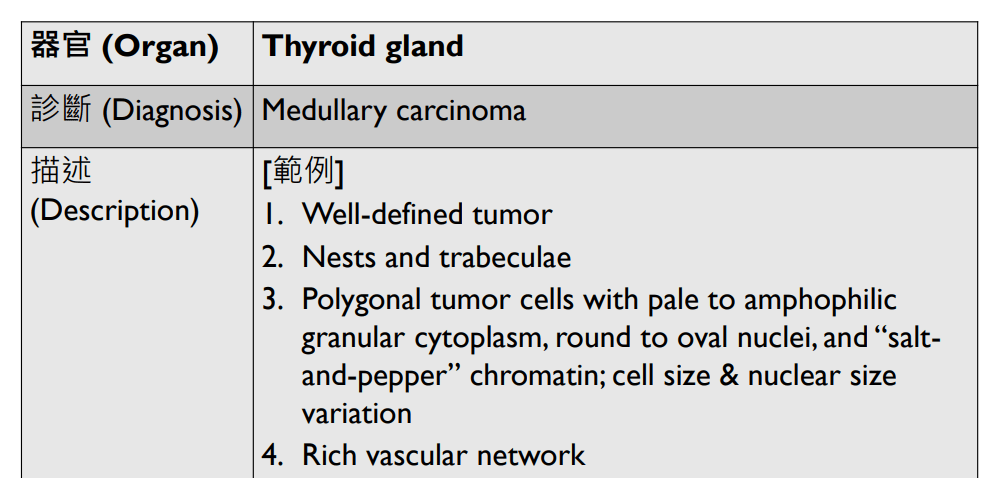
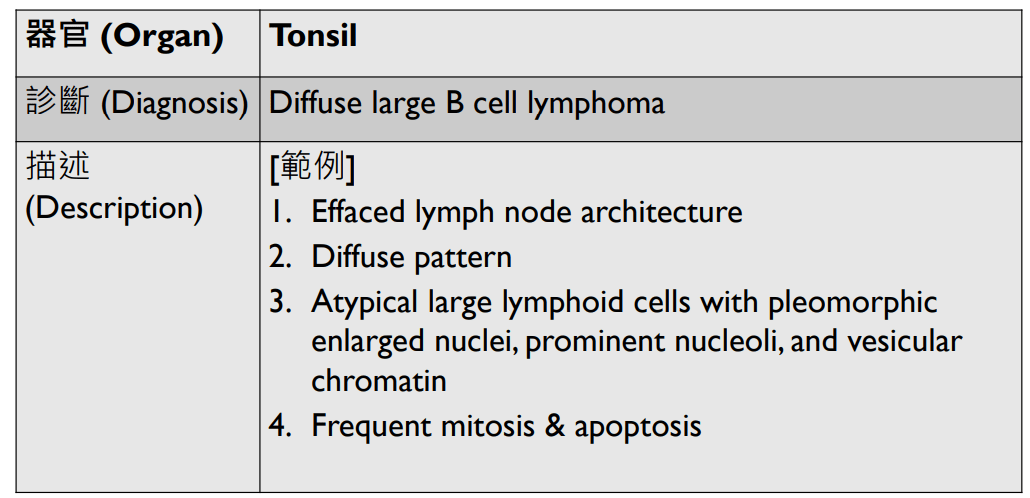
Organ: Lymph node
Diagnosis: Lymphoid hyperplasia
Descriptions:
- Increased number and size of follicles
- Follicles have distinct mantle zones and polarized germinal center
- Normal cell composition and tingible-body macrophages in the follicles
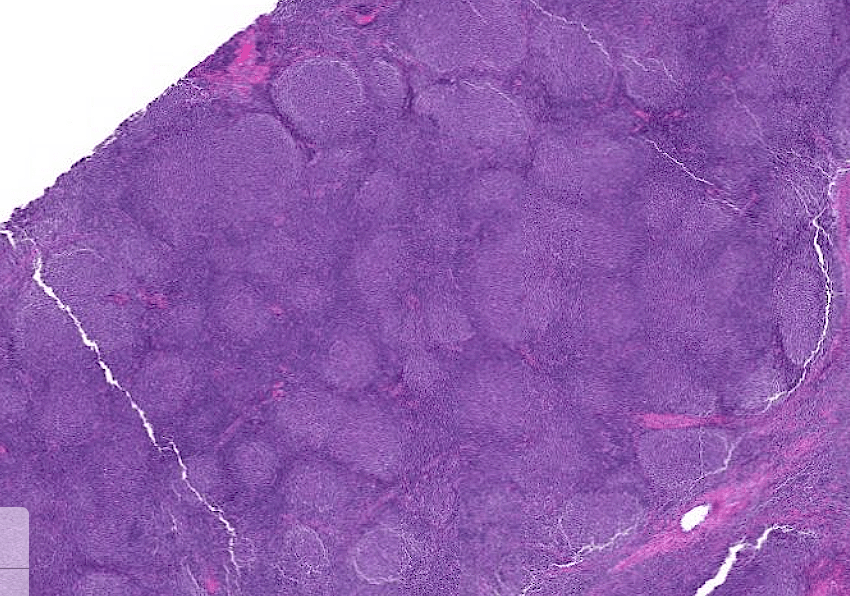
Lymph node

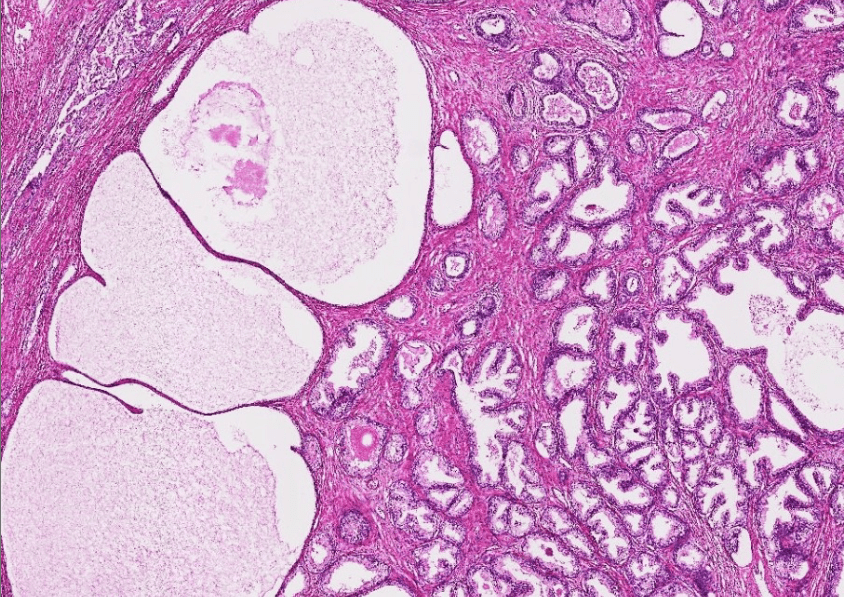
2/26 小組討論
問題一:良性攝護腺增生引起的下泌尿道症狀(low urinary tract symptom, LUTS)有哪些?有哪些藥物可治療,治療機轉為何?
LUTS (Low Urinary Tract Symptoms)
| Obstructive symptoms | Irritative symptoms |
|---|---|
| urinary hesitancy | urinary frequency |
| straining | urgency |
| weak stream | urge incontinence |
| terminal dribbling | small voided volumes |
| prolonged voiding | |
| incomplete emptying |
Scher HI, Eastham JA. Benign and Malignant Diseases of the Prostate. In: Loscalzo J, Fauci A, Kasper D, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson J. eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 21e. McGraw-Hill Education; 2022. Accessed February 26, 2025. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=3095§ionid=263547112
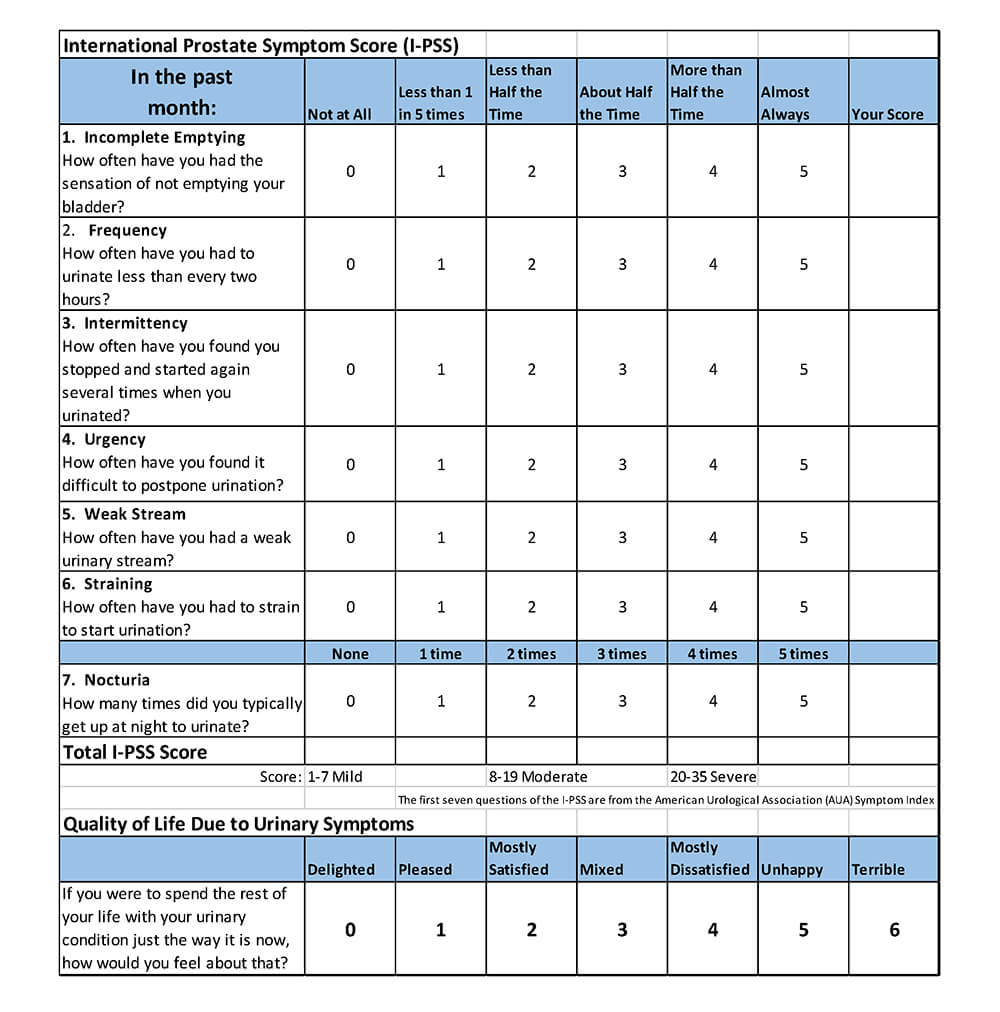
IPSS
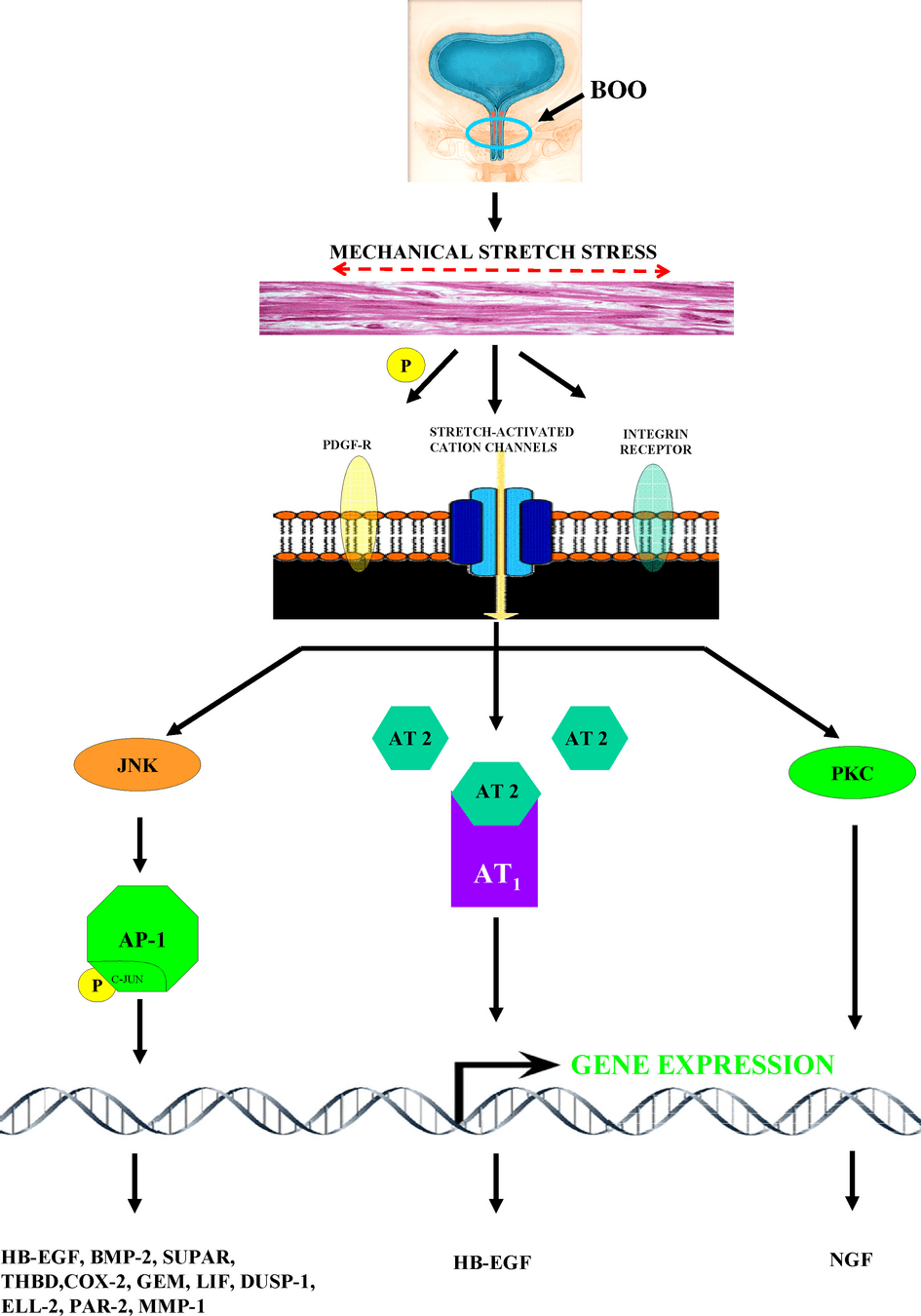
Mirone V, Imbimbo C, Longo N, Fusco F. The detrusor muscle: an innocent victim of bladder outlet obstruction. Eur Urol. 2007 Jan;51(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2006.07.050. Epub 2006 Aug 14. PMID: 16979287.
Detrusor muscle of bladder
問題一:良性攝護腺增生引起的下泌尿道症狀(low urinary tract symptom, LUTS)有哪些?有哪些藥物可治療,治療機轉為何?
Medical Treatment of BPH
- Goal: Relief symptoms
- Drugs
- \(\alpha1\)-adrenergic receptor antagonist
- Terazosin, Doxazosin, Alfuzosin, Tamsulosin, Silodosin
- \(5\alpha\)-reductase inhibitor (5ARI)
- Finasteride, Dutasteride
-
phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor
- Tadalafil
-
anticholinergics (controversial)
- Tolterodine, Oxybutynin
- \(\alpha1\)-adrenergic receptor antagonist
Mechanisms of Action
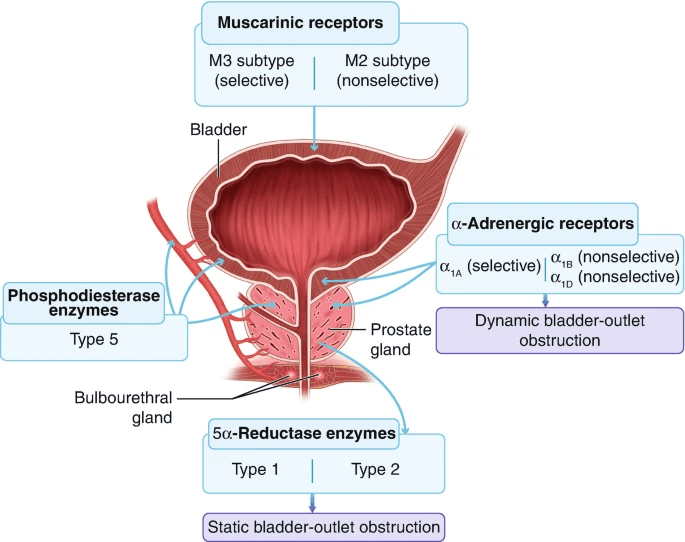
Testosterone
DHT
(only for irritative symptoms)
Showalter, V.C., Raynor, M.C. (2020). Medical Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. In: Isaacson, A., Bagla, S., Raynor, M., Yu, H. (eds) Prostatic Artery Embolization. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23471-3_3
??
PDE5 inhibitor?
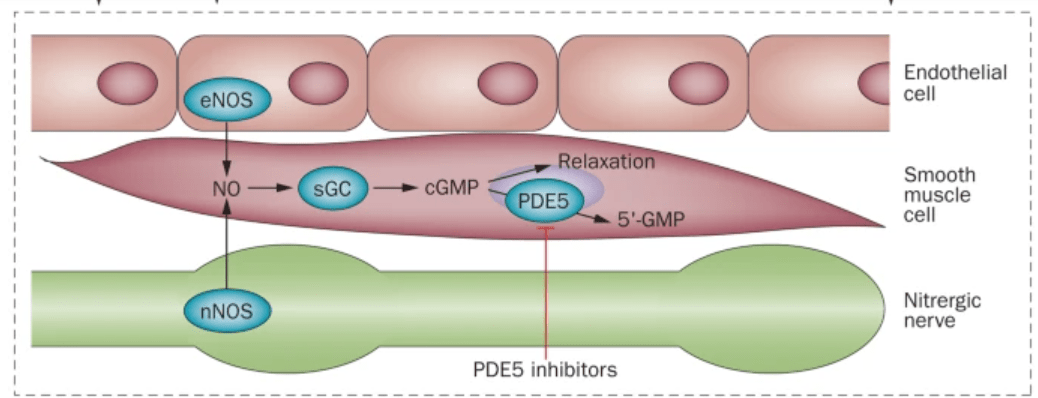
Cellek, S., Cameron, N., Cotter, M. et al. Microvascular dysfunction and efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors in BPH–LUTS. Nat Rev Urol 11, 231–241 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2014.53
PDE5 inhibitor?
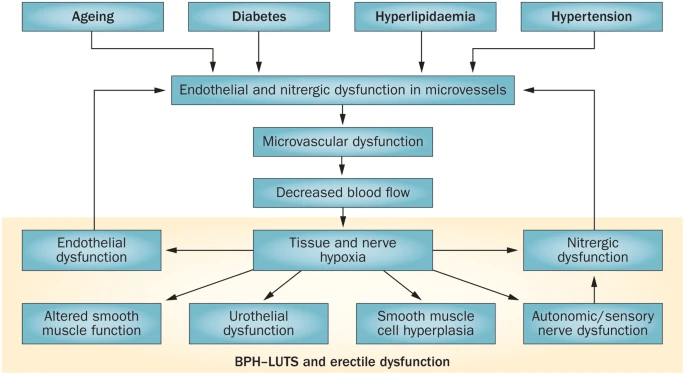
Cellek, S., Cameron, N., Cotter, M. et al. Microvascular dysfunction and efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors in BPH–LUTS. Nat Rev Urol 11, 231–241 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2014.53
Q(A)/Discussion
Kidney Exchange:
Theory and Practice
https://www.kidneyfund.org/node/1437
Chronic Kidney Disease: Epidemiology
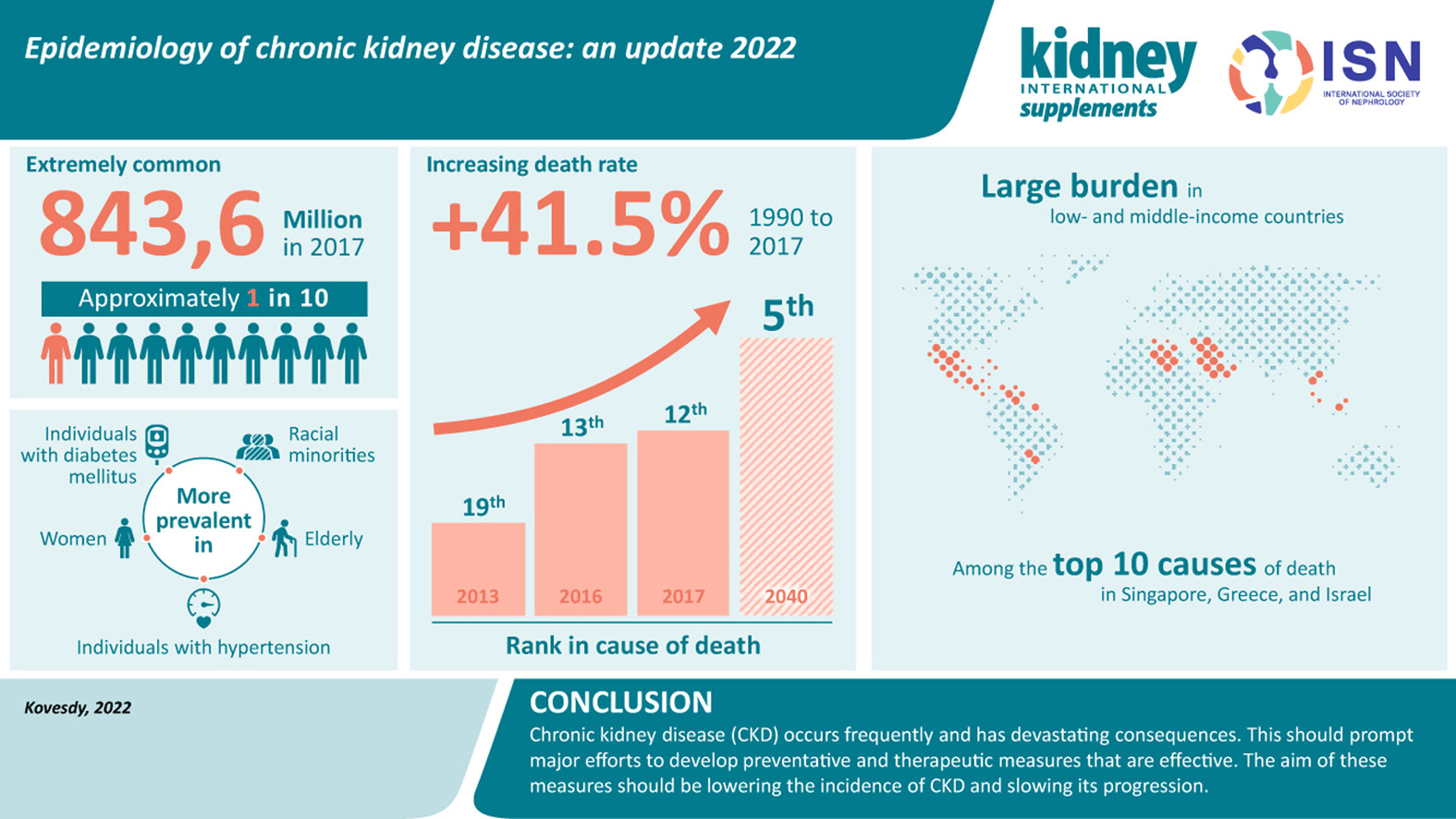
Chronic Kidney Failure: Epidemiology
- More than 808,000 people in the United States are living with kidney failure
- Medicare-related spending for kidney failure totaled $52.3 billion in 2021
Chronic Kidney Failure: How to Treat?
Two options!
- Dialysis
- Kidney Transplant
Better quality of life, and lower mortality!
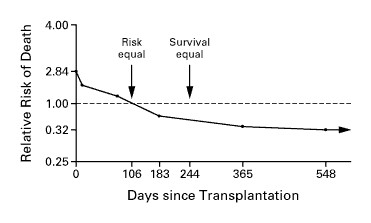
But also harder to get a real kidney!
Where are the kidneys from?
- Deceased donors
- Only a tiny fraction of deaths allow kidneys to be recovered for transplantation.
- Living donors
- Who would like to give you his/her kidney?
Living Donors
- Non-Directed Donation
- A person can choose to donate a kidney to an unknown recipient.
- HARD: It's illegal to pay a living donor to donate a kidney, so there's little incentive.
- Directed Donation
- In the U.S., the donor can be the recipient's relative or friend.
- HARD: Incompatibility.
Compatibility
ABO Compatibility
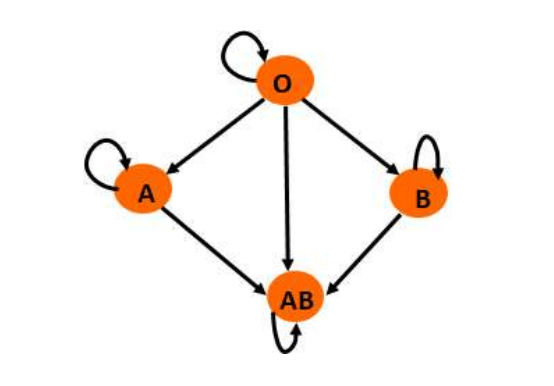
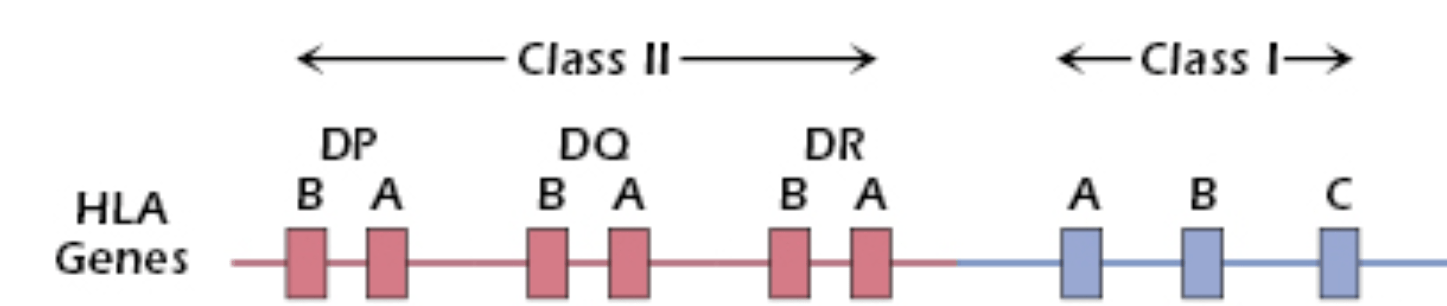
Tissue Type Compatibility
Kidney Exchange!
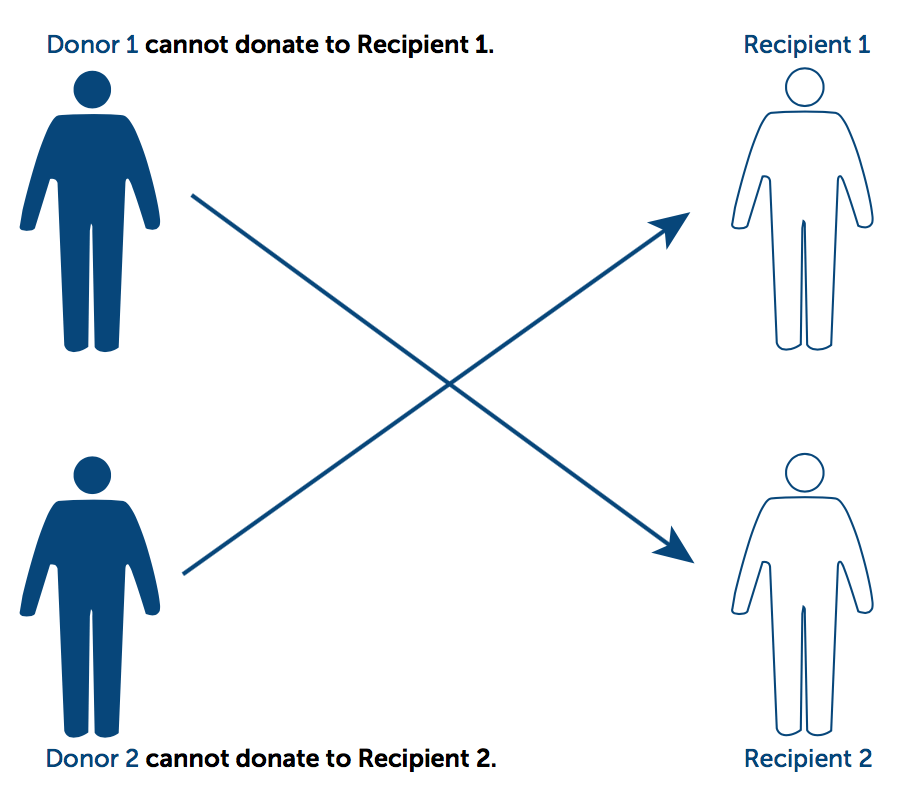
Kidney Exchange!

Donor
Recipient
How to Exchange?
Mechanism Design: What do we want?
- Efficacy?
- We might want to maximize the number of recipients that get a kidney.
- Fairness?
- We don't want people to gain by being dishonest.
- For example, if the mechanism always match the recipients with fewer available donors first, ...
Idea 1: Top Trading Cycle Algorithm
- Step 1: Every remaining recipient points to the remaining donor which provides the most compatible kidney.
- Step2: There is at least 1 cycle, and we exchange the kidneys according to the cycle(s).
- Step3: Delete the recipients and donors involved in the previous step, and go to step 1.
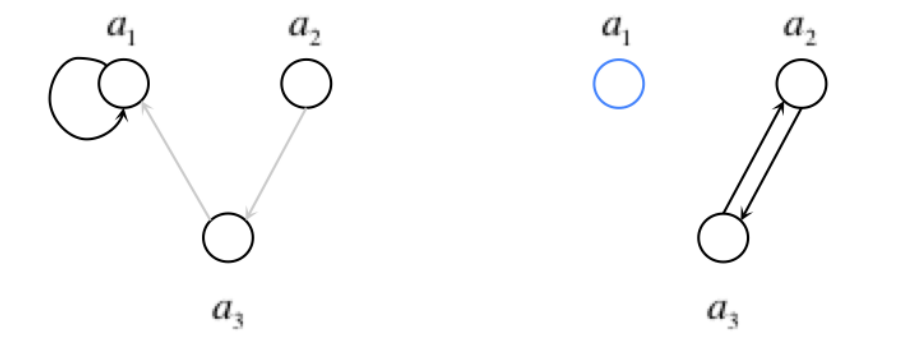

Idea 1: Top Trading Cycle Algorithm
Pros:
- The recipients gain nothing by misreporting.
- It provides the only allocation such that no other allocation makes every recipient gets a kidney that is "not worse".
Cons:
- It doesn't deal with deceased donors/non-directed donations.
- This can be solve: see Alvin E. Roth, Tayfun Sönmez, M. Utku Ünver. Kidney Exchange
- In kidney exchange, there is no need to find the "most compatible" kidney.
- It may produce long cycles.
Why are long cycles bad?
- Too many surguries that need to happen simultaneously.
- A donor might disappear if they don't!
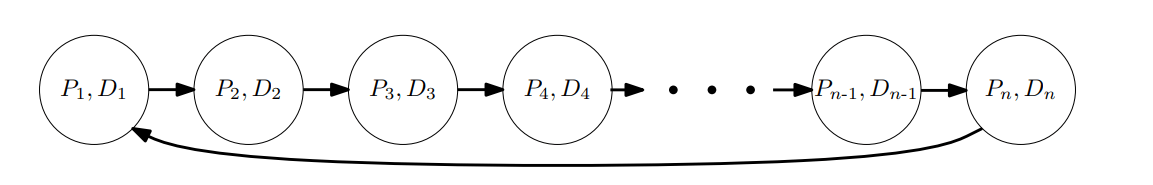
Idea 2: Matching
- Step 1: Every recipient reports the set of donors that can provide a compatible kidney.
- Step 2: Find a "maximum matching".
Idea 2: Matching
Pros:
- If step 2 is implemented carefully, the recipients gain nothing by misreporting.
- The exchange is simple since we only allow cycles of length 2.
- Under the previous assumption, we still try to maximize the number of people getting a kidney.
Cons:
- It doesn't deal with deceased donors/non-directed donations.
- Long chains starting from a deceased donor could be great.
- Maybe cycles of length 3 or 4 is also acceptable?
Idea 3: Just Optimize
\(\max \sum_C \ell_C z_C\)
s.t. \(\sum_{C \in C(v)} z_C \leq 1, \forall v \in V\)
\(z_C \in \{0,1\}\)
\(\ell_C\): the length of the cycle \(C\)
\(V\): the set of all recipient-donor pairs
\(C(v)\) : the set of cycles containing \(v\)
Idea 3: Just Optimize
Pros:
- The number of recipients that gets a kidney is maximized.
- It can be easily modified to restrict the length of the cycles and chains.
Cons:
- There seems to be no fairness gaurantee.
- The problem is hard to solve for a computer. It might take a lot of time to compute the solution if there are too many people involved.
Enough Theory!
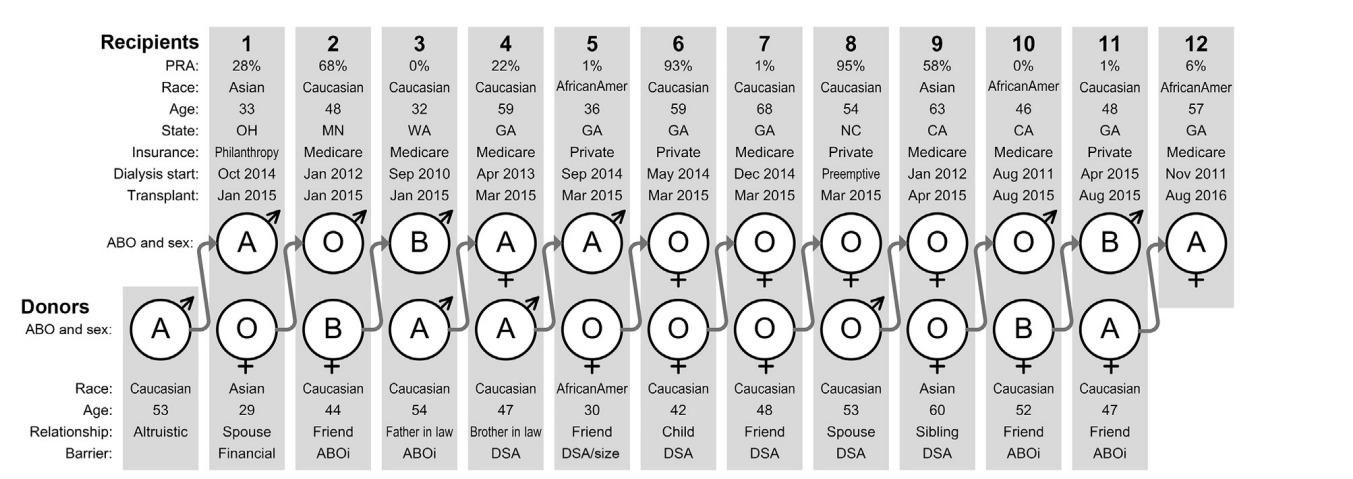
Kidney Exchange in the US
- Since 1988, there has been 188,677 living donor kidney transplants in the US , and 13,383 (7.1%) of them are paired donations.
- In 2024, there were 6418 living donor kidney transplants in the US, and 1443 (22.5%) of them are paired donations.
The next step: Global Kidney Exchange?
First Global Kidney Exchange in 2015

https://news.utoledo.edu/index.php/05_27_2015/ut-health-transplant-surgeon-creates-concept-to-solve-u-s-kidney-shortage
A win-win situation?
Taiwan?
-
人體器官移植條例第八條第五項(2015年新增):
- 腎臟之待移植者未能於第一項第四款規定範圍內,覓得合適之捐贈者時,得於二組以上待移植者之配偶及該款所定血親之親等範圍內,進行組間之器官互相配對、交換及捐贈,並施行移植手術,不受該款規定之限制。
- 衛服部2019年發布 活體腎臟交換捐贈移植手術管理辦法

Want to know more?
- A talk by Alvin Roth: Kidney Exchange: Algorithms and Incentives
- A book by Alvin Roth about market design: Who gets what and why
- Lecture notes on algorithmic game theory by Tim Roughgarden
- Controversies in kidney exchange:
References
[1] Csaba P. Kovesdy, Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022, Kidney International Supplements, Volume 12, Issue 1, 2022, Pages 7-11, ISSN 2157-1716, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kisu.2021.11.003
[2] https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/kidney-disease
[3] Robert A Wolfe, Valarie B Ashby, Edgar L Milford, Akinlolu O Ojo, Robert E Ettenger, Lawrence YC Agodoa, Philip J Held, and Friedrich K Port. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. New England Journal of Medicine, 341(23):1725–1730, 1999.
[4] https://oncohemakey.com/how-t-cells-recognize-antigen-the-role-of-the-major-histocompatibility-complex/
[5] https://kidneydonor.org.nz/donor/guides/becoming-live-kidney-donor/kidney-exchange-programme
[6] http://kidneyregistry.com/news/60-lives-30-kidneys-all-linked/
[7] MICHAEL WALLACE. HOUSING ALLOCATION: EXISTING TENANTS AND MULTIPLE-OCCUPANCY.
[8] Danielle N. Bozek, Ty B. Dunn, Christian S. Kuhr, Christopher L. Marsh, Jeffrey Rogers, Susan E. Rees, Laura Basagoitia, Robert J. Brunner, Alvin E. Roth, Obi Ekwenna, David E. Fumo, Kimberly D. Krawiec, Jonathan E. Kopke, Puneet Sindhwani, Jorge Ortiz, Miguel Tan, Siegfredo R. Paloyo, Jeffrey D. Punch, Michael A. Rees, Complete Chain of the First Global Kidney Exchange Transplant and 3-yr Follow-up,European Urology Focus, Volume 4, Issue 2, 2018, Pages 190-197, ISSN 2405-4569, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2018.07.021.
3/20 小組討論
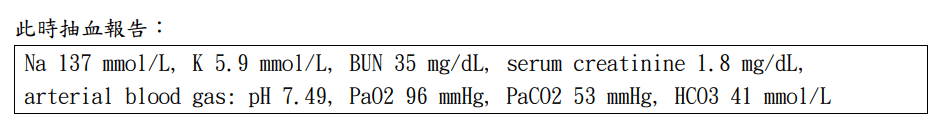
討論問題 3:請判讀此時的抽血報告之異常。請藉由複習各種利尿劑的作用機轉,思考可能造成這種異常的藥物為何(不限定利尿劑)?依據病人此時的病況,藥物應如何調整或者加上其他藥物矯正?
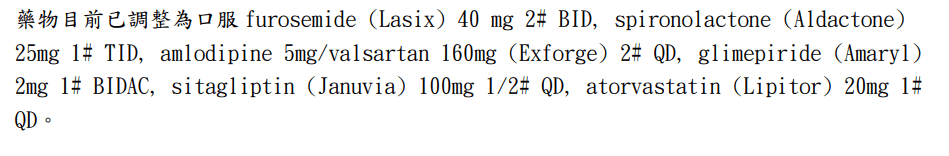

Normal Ranges:
- Na: 136-145 mmol/L
- K: 3.5-5.1 mmol/L
- BUN: 7-25 mg/dL
- creatinine: 0.6-1.3 mg/dL
- pH: 7.35-7.45
- PaCO2: 35-45 mmHg
- PaO2: 80-100 mmHg
- Bicarbonate: 22-26 mmol/L
eGFR= 38.59 ml/min/1.73m2
(simplified MDRD)
Abnormalities:
- Hyperkalemia
- Azotemia
- 病患有CKD:"BUN 33 mg/dL, creatinine 1.8 mg/dL,與病人過去一年來 baseline creatinine 變化區間類似"
- Metabolic Alkalosis
- well-compensated
討論問題 3:請判讀此時的抽血報告之異常。請藉由複習各種利尿劑的作用機轉,思考可能造成這種異常的藥物為何(不限定利尿劑)?依據病人此時的病況,藥物應如何調整或者加上其他藥物矯正?
Diuretics: MoA
https://basicmedicalkey.com/drug-therapy-of-hypertension-edema-and-disorders-of-sodium-and-water-balance/
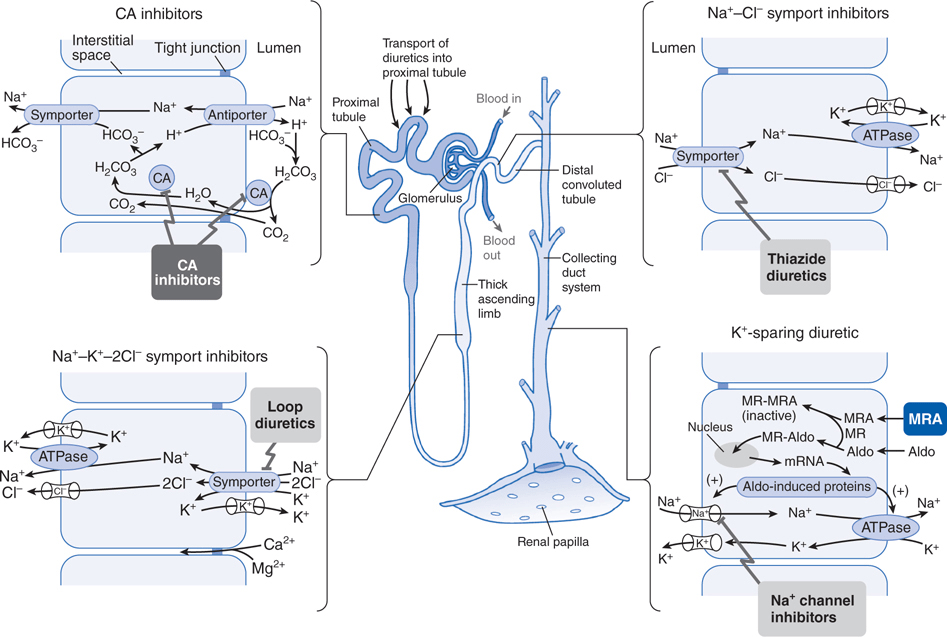
- Osmotic Diuretics
- Increase tubular fluid osmolality
- ADH antagonists
- inhibit insertion of aquaporin on collecting ducts
furosemide
spironolactone


from Dr. 賴俊夫
Other Drugs
| Drug | Indication | MoA | Side effects on pH / electrocyte homeostasis / renal function |
|---|---|---|---|
| amlodipine | HTN/CAD | calcium channel blocker | edema (1-10%) |
| valsartan | HTN/HF/diabetic kidney disease | Angiotensin II receptor blocker | BUN/creatinine raised(1-10% in HF patients) Hyperkalemia (esp. when used with spironolactone) |
| glimepiride | Type 2 DM | insulin secretagogue | hyponatremia(rare) |
| sitagliptin | Type 2 DM | preventing breakdown of GLP-1 and GIP (thus increase insulin and suppress glucagon release) | |
| atorvastatin | hypercholesterolemia | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor |
reference: micromedex
Conclusion:
Hyperkalemia: Spironolactone + Valsartan
Metabolic Alkalosis: ?? (Maybe partially by furosemide)
討論問題 3:請判讀此時的抽血報告之異常。請藉由複習各種利尿劑的作用機轉,思考可能造成這種異常的藥物為何(不限定利尿劑)?依據病人此時的病況,藥物應如何調整或者加上其他藥物矯正?
Hyperkalemia Emergency?
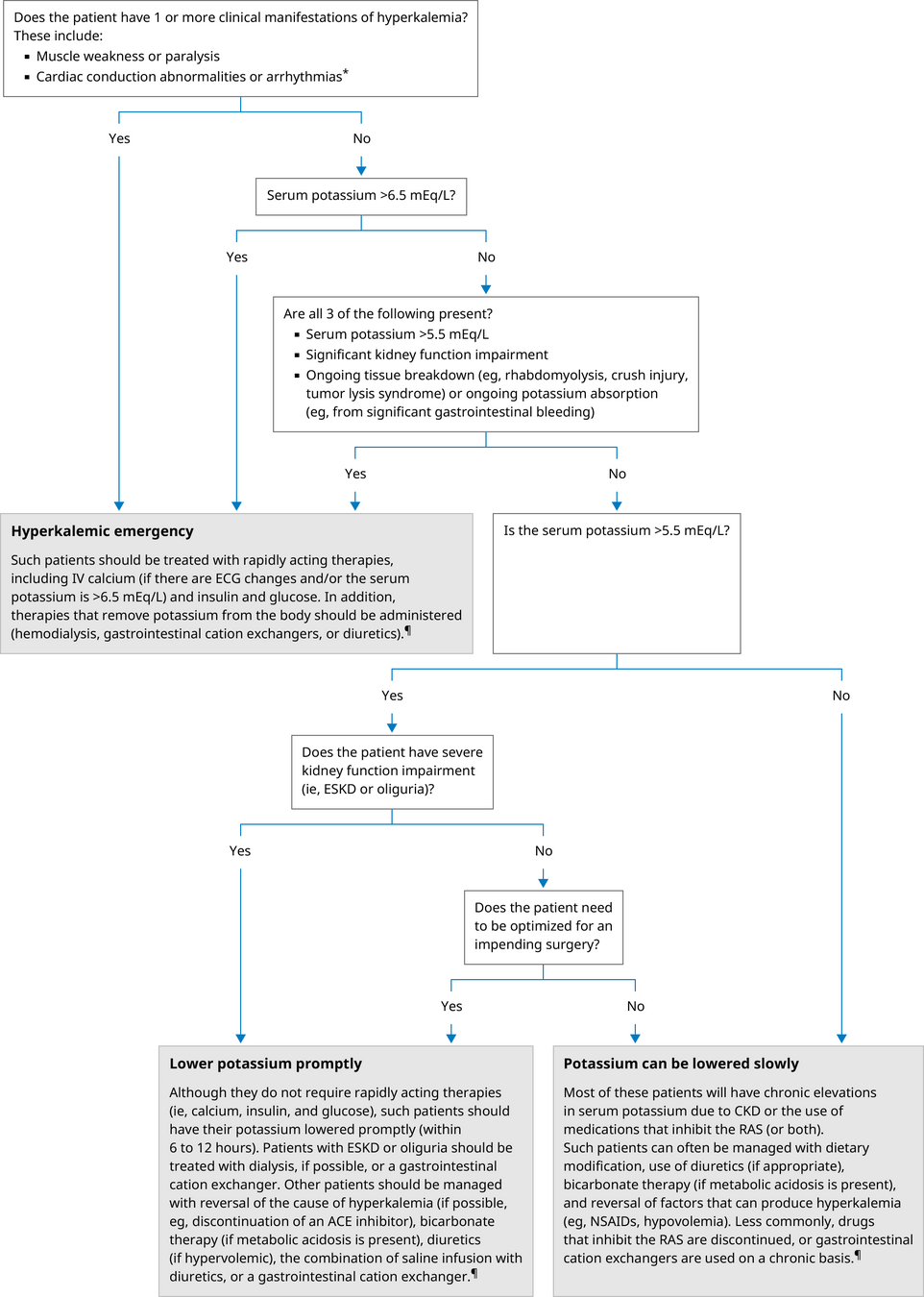

https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-hyperkalemia-in-adults#H2
Recommendation of RAASi Use

Giuseppe M C Rosano, Juan Tamargo, Keld P Kjeldsen, Mitja Lainscak, Stefan Agewall, Stefan D Anker, Claudio Ceconi, Andrew J S Coats, Heinz Drexel, Gerasimos Filippatos, Juan Carlos Kaski, Lars Lund, Alexander Niessner, Piotr Ponikowski, Gianluigi Savarese, Thomas A Schmidt, Petar Seferovic, Sven Wassmann, Thomas Walther, Basil S Lewis, Expert consensus document on the management of hyperkalaemia in patients with cardiovascular disease treated with renin angiotensin aldosterone system inhibitors: coordinated by the Working Group on Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy of the European Society of Cardiology, European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy, Volume 4, Issue 3, July 2018, Pages 180–188, https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjcvp/pvy015
Symptoms/LVEF improved, maybe we can remove spironolactone?
(furosemide alone may lower potassium level)
Patiromer
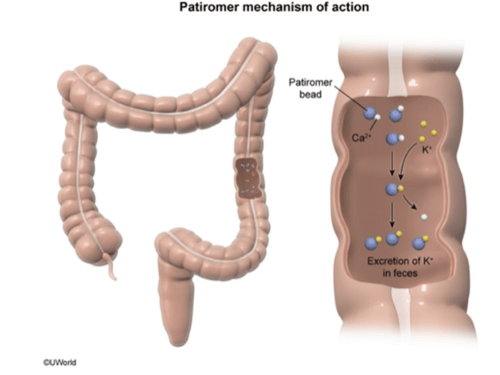
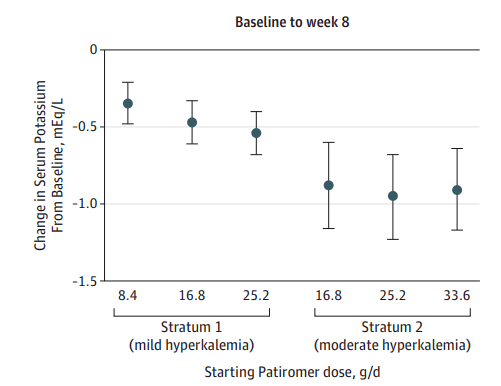
patients with CKD using ACEi/ARB and often spironolactone
https://quizlet.com/577891973/kidney-physiology-flash-cards/
Q(A)/Discussion
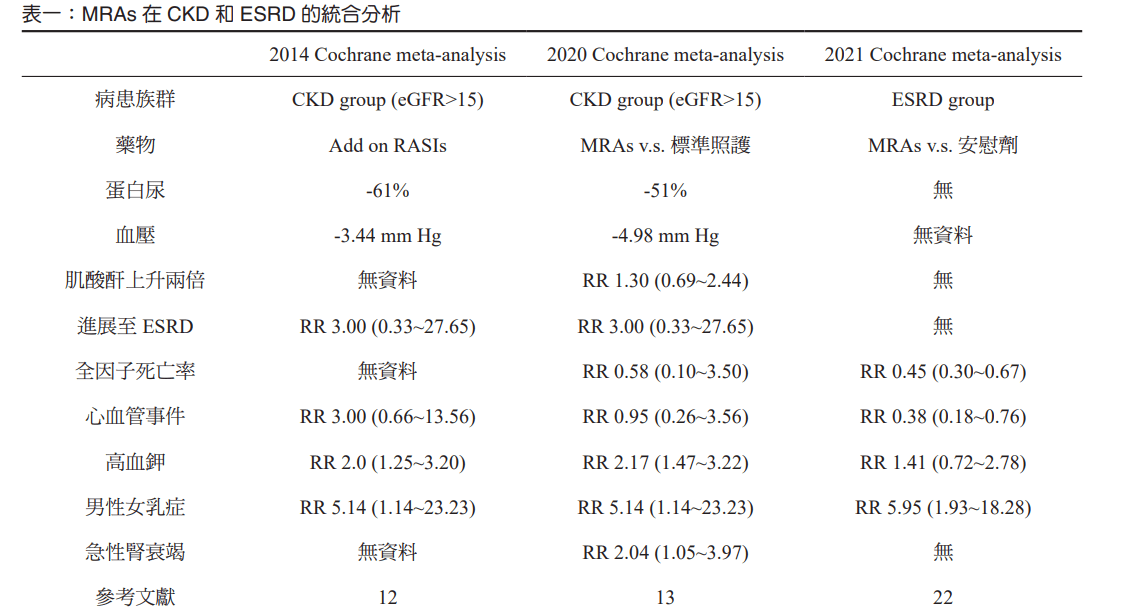
討論問題 6:ACEi, ARB, DRI, MRA 這些與 RAS 相關的藥物作用機轉分別為何?哪種或哪些是被證實有腎臟保護作用的?合併使用比較好嗎?
RAAS Inhibitor
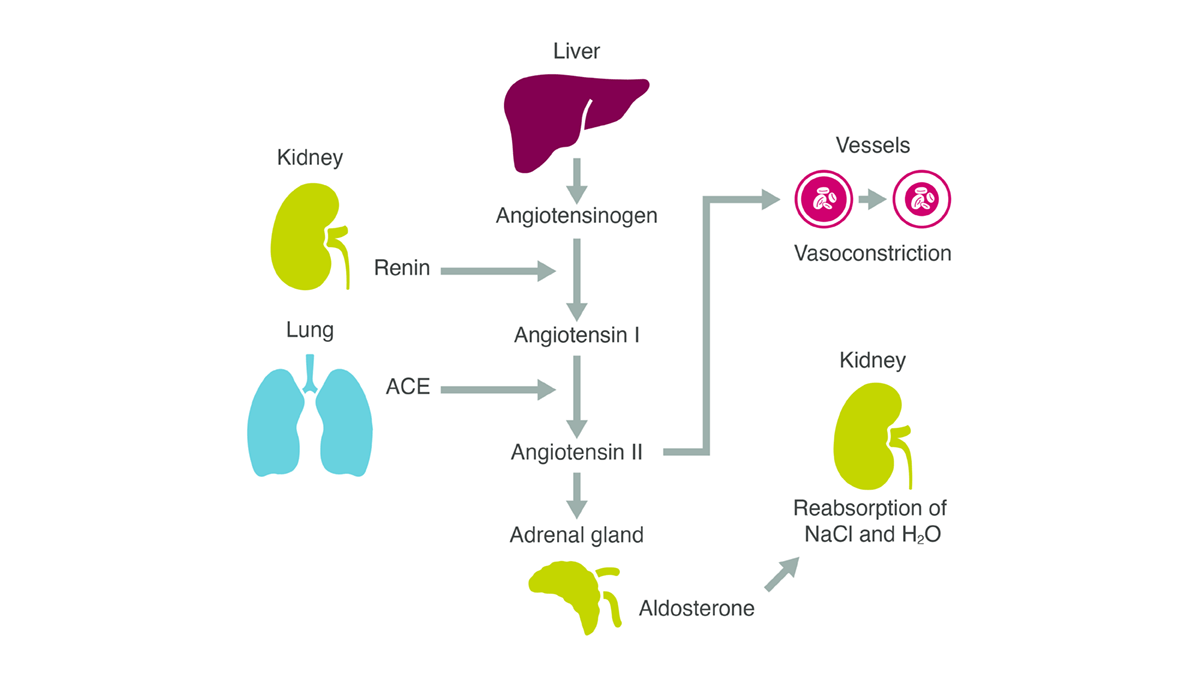
https://www.astrazeneca.com/what-science-can-do/topics/disease-understanding/unpacking-raas-pathway-role-aldosterone.html
DRI
ACEi
MRA
ARB
討論問題 6:ACEi, ARB, DRI, MRA 這些與 RAS 相關的藥物作用機轉分別為何?哪種或哪些是被證實有腎臟保護作用的?合併使用比較好嗎?
Kidney Protection
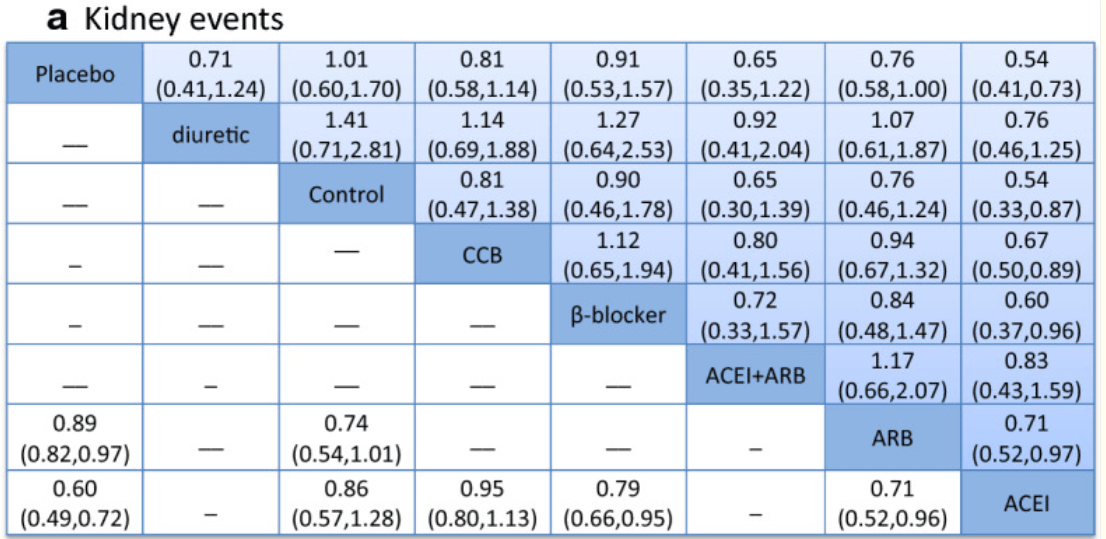
(for Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3–5)
Zhang Y, He D, Zhang W, Xing Y, Guo Y, Wang F, Jia J, Yan T, Liu Y, Lin S. ACE Inhibitor Benefit to Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes for Patients with Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3-5: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Clinical Trials. Drugs. 2020 Jun;80(8):797-811. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01290-3. PMID: 32333236; PMCID: PMC7242277.
Direct Renin Inhibitors (DRI)?
- The AVOID Trial
- Aliskiren may have renoprotective effects that are independent of its blood-pressure-lowering effect in patients with hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and nephropathy who are receiving the recommended renoprotective treatment.
- The ALTITUDE Trial
- The trial was stopped prematurely after the second interim efficacy analysis
- The addition of aliskiren to standard therapy with renin–angiotensin system blockade in patients with type 2 diabetes who are at high risk for cardiovascular and renal events is not supported by these data and may even be harmful.
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (MRA)?

Q(A)/Discussion
4/10 小組討論
問題一、請試圖整理這些病人的症狀,並列出您認為這位蔡小姐有什麼可能的鑑別診斷?請列出最有可能的五種,並嘗試思考應該再多詢問什麼病史、以及執行什麼理學檢查?以及她初次就診要安排什麼必要的檢查。
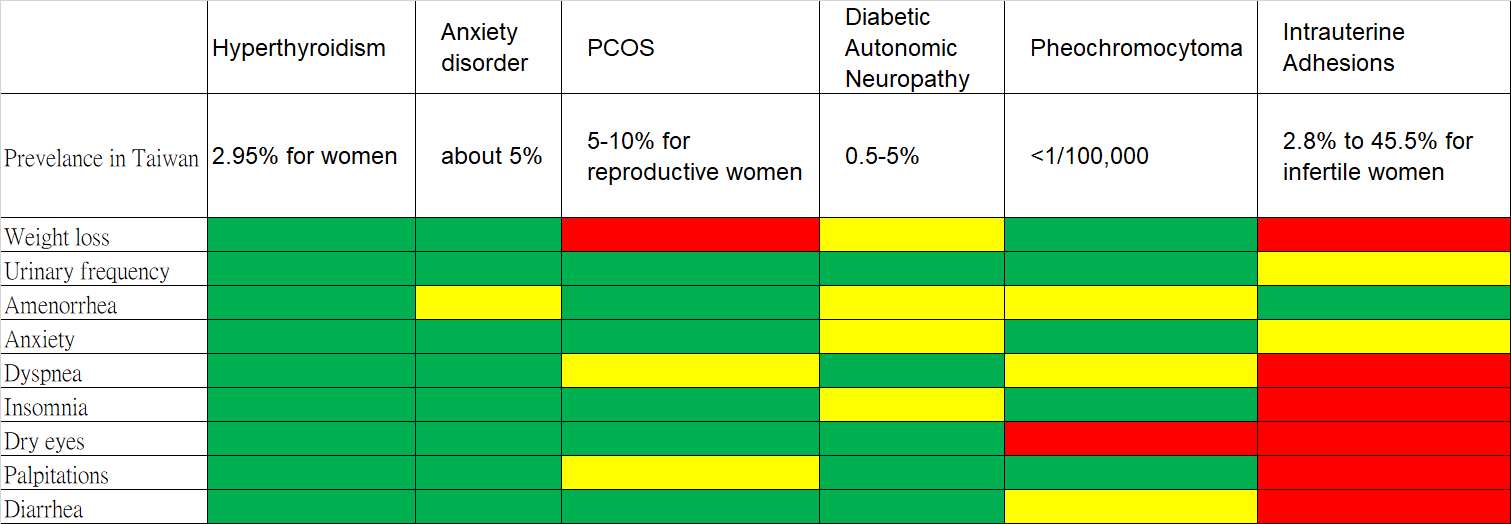
Symptoms
- Unintended weight loss (51kg to 47 kg in 2 months)
- Urinary frequency
- Amenorrhea for more than 6 months
- Anxiety
- Tachypnea/Exertional Dyspnea
- Insomnia
- Dry eyes
- Palpitation
- Diarrhea
Symptoms
- Unintended weight loss (51kg to 47 kg in 2 months)
- Urinary frequency
- Amenorrhea for more than 6 months
- Anxiety
- Tachypnea/Exertional Dyspnea
- Insomnia
- Dry eyes
- Palpitation
- Diarrhea
Sympathetic Overactivity?
}
Differential Diagnoses
Sympathetic Overactivity
- Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
- Anxiety disorder
- Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis)
- Pheochromocytoma
- Drugs (adrenergic/anticholinergic)
- CNS injury
Secondary Amenorrhea
- (r/o) Pregnancy
-
Intrauterine adhesions
- Asherman syndrome
- Tuberculous endometritis
-
Disorders of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Thyroid disease
- Primary ovarian insufficiency
- hypogonadotripic hypogonadism
- PCOS
Top 5?
References in the next page
Wakil A, Atkin S. Secondary amenorrhoea due to pheochromocytoma: a case report. Cases J. 2008 Jul 11;1(1):30. doi: 10.1186/1757-1626-1-30. PMID: 18620585; PMCID: PMC2481240.
Sackel SG, Manson JE, Harawi SJ, Burakoff R. Watery diarrhea syndrome due to an adrenal pheochromocytoma secreting vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Dec;30(12):1201-7. doi: 10.1007/BF01314057. PMID: 3905308.
Kölükçü E, Gülücü S, Erdemir F. Association between lower urinary tract symptoms and polycystic ovary syndrome. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2023 May 15;69(5):e20221561. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20221561. PMID: 37194796; PMCID: PMC10185050.
Dybciak P, Humeniuk E, Raczkiewicz D, Krakowiak J, Wdowiak A, Bojar I. Anxiety and Depression in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 16;58(7):942. doi: 10.3390/medicina58070942. PMID: 35888661; PMCID: PMC9319705.
Underdal MO, Salvesen Ø, Henriksen AH, Andersen M, Vanky E. Impaired Respiratory Function in Women With PCOS Compared With Matched Controls From a Population-Based Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jan 1;105(1):dgz053. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgz053. PMID: 31613965.
Asfuroğlu Y, Kan Ö, Asfuroğlu M, Baser E. Association Between Dry Eye and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Subclinical Inflammation May Be Part of the Process. Eye Contact Lens. 2021 Jan 1;47(1):27-31. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000716. PMID: 32496281.
Saei Ghare Naz M, Ghasemi V, Amirshekari S, Ramezani Tehrani F. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Is There a Common Pathway? Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024 Mar;7(2):e00477. doi: 10.1002/edm2.477. PMID: 38494583; PMCID: PMC10944984.
Fava, G. A., Trombini, G., Grandi, S., Bernardi, M., Evangelisti, L. P., Santarsiero, G., & Orlandi, C. (1984). Depression and anxiety associated with secondary amenorrhea. Psychosomatics: Journal of Consultation and Liaison Psychiatry, 25(12), 905–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(84)72922-7
He Q, Chen Z, Xie C, Liu L, Wei R. The Association Between Dry Eye Disease With Depression, Anxiety and Sleep Disturbance During COVID-19. Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jan 5;12:802302. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.802302. PMID: 35069294; PMCID: PMC8766963.
Uptodate: Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
Shim U, Oh JY, Lee HJ, Hong YS, Sung YA. Long menstrual cycle is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in korean women. Diabetes Metab J. 2011 Aug;35(4):384-9. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.384. Epub 2011 Aug 31. PMID: 21977458; PMCID: PMC3178699.
Tummanapalli SS, Wang LL, Dhanapalaratnam R, Poynten A, Papas EB, Krishnan AV, Markoulli M. Moderate-severe peripheral neuropathy in diabetes associated with an increased risk of dry eye disease. Optom Vis Sci. 2024 Sep 1;101(9):563-570. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000002178. Epub 2024 Sep 16. PMID: 39269688.
梁怡鈴(2013)。台灣甲狀腺機能亢進症之流行病學研究。﹝碩士論文。國立成功大學﹞臺灣博碩士論文知識加值系統。 https://hdl.handle.net/11296/d86r6p。
廣泛性焦慮症-精神醫學部-三軍總醫院https://wwwv.tsgh.ndmctsgh.edu.tw/unit/10058/17028
糖尿病神經病變之診斷與治療-臺大醫院https://www.ntuh.gov.tw/neur/Fpage.action?fid=4275
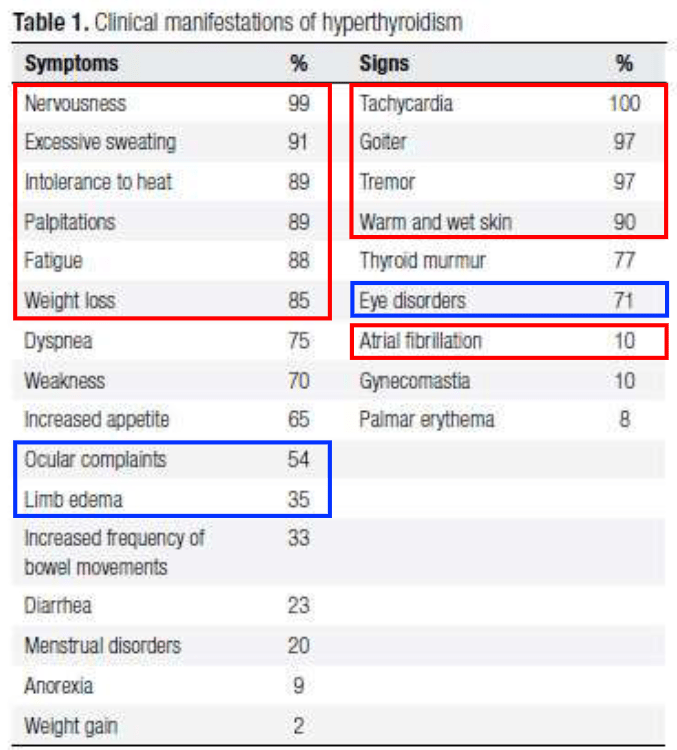
問題一、請試圖整理這些病人的症狀,並列出您認為這位蔡小姐有什麼可能的鑑別診斷?請列出最有可能的五種,並嘗試思考應該再多詢問什麼病史、以及執行什麼理學檢查?以及她初次就診要安排什麼必要的檢查。
Hyperthyroidism: History/PE
Dr. 吳婉禎's 投影片
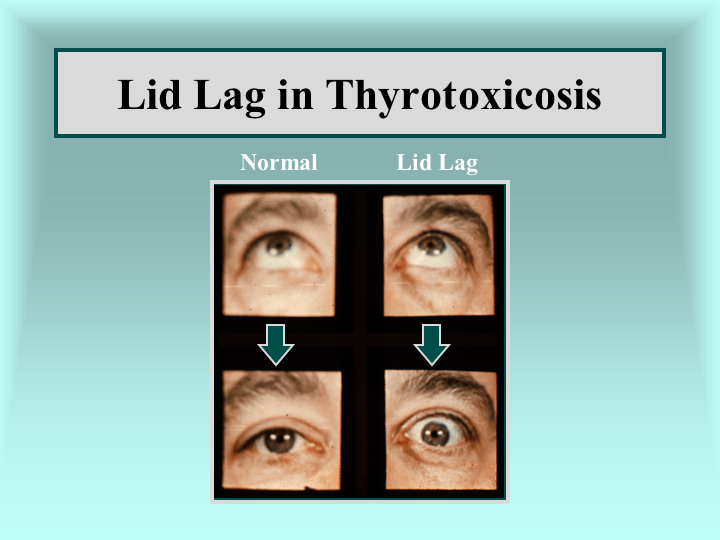
https://www.lumen.luc.edu/lumen/meded/medicine/endonew/hyperthy/slide41.htm
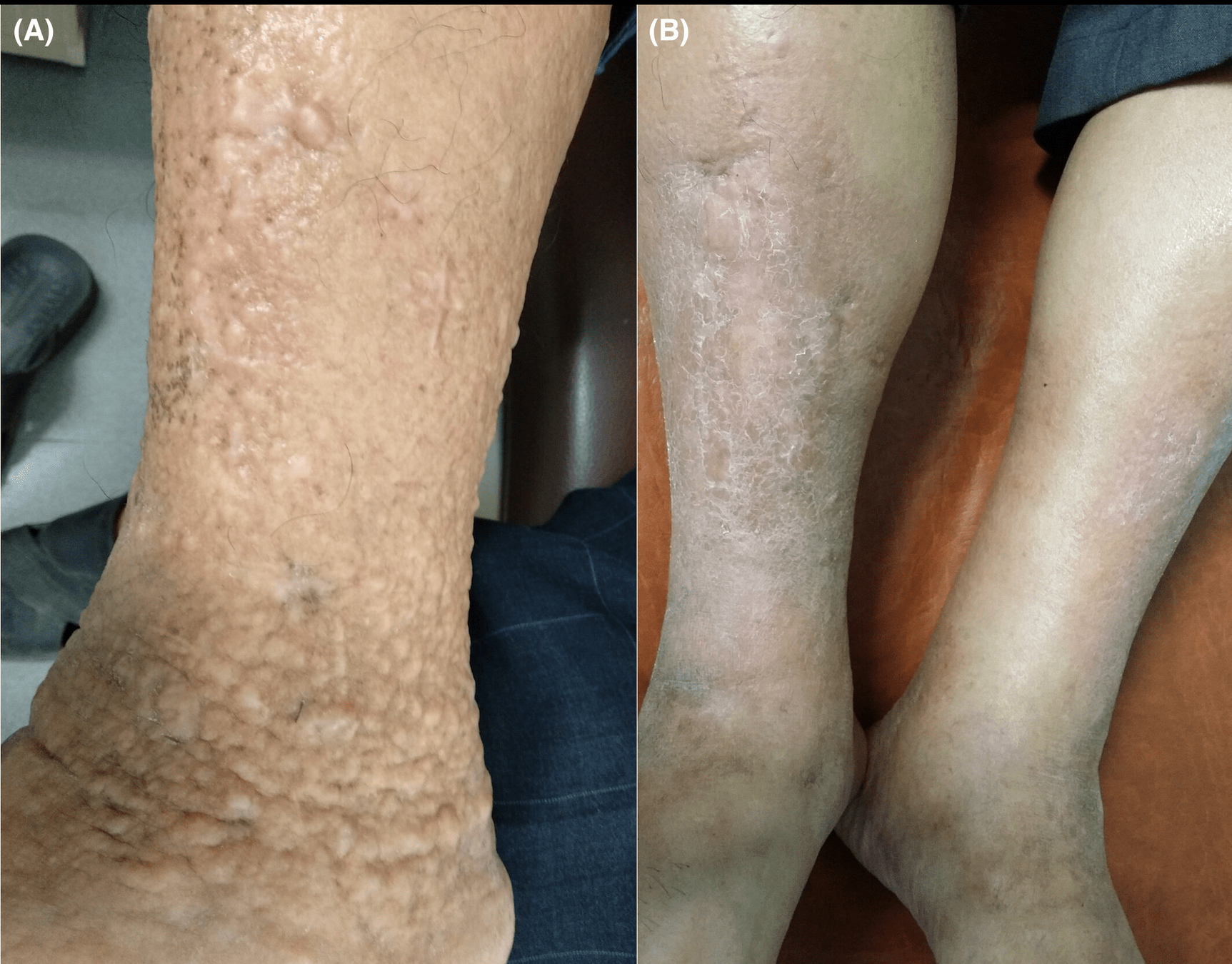
Grave's disease: pretibial myxedema
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ccr3.8478
Anxiety Disorder: History/PE
For, suspected physical cause of anxiety, should do general PE and lab tests.
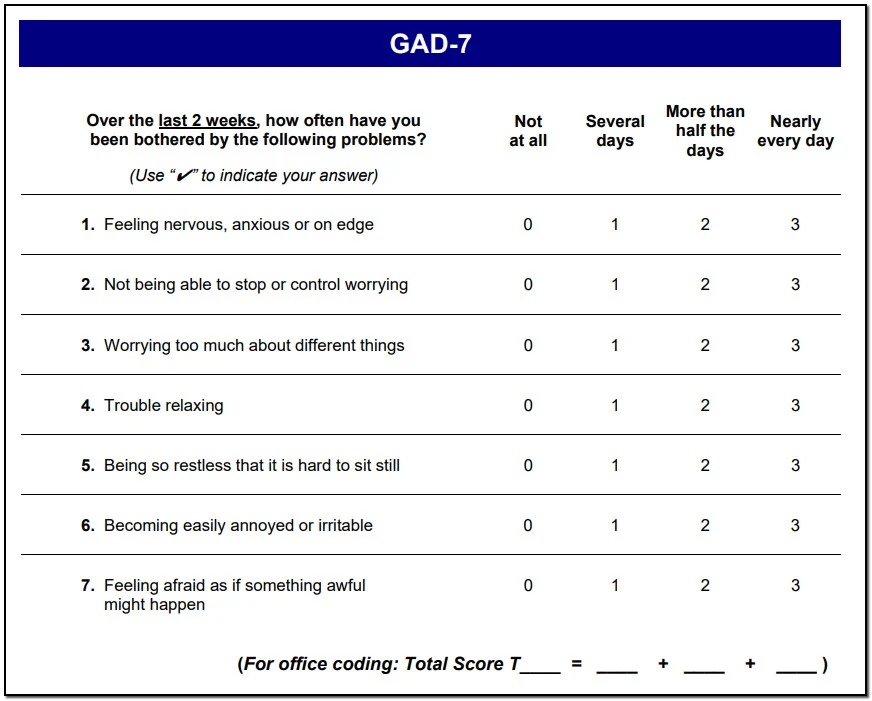
https://betteroutcomesnow.com/blog/gad-7-scoring/
Uptodate: Generalized anxiety disorder in adults: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, course, assessment, and diagnosis
PCOS: History/PE
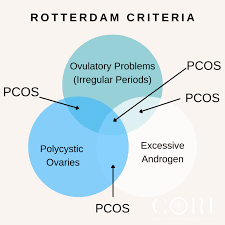
https://www.corephilippines.com/polycystic-ovarian-syndrome-and-the-rotterdam-criteria/
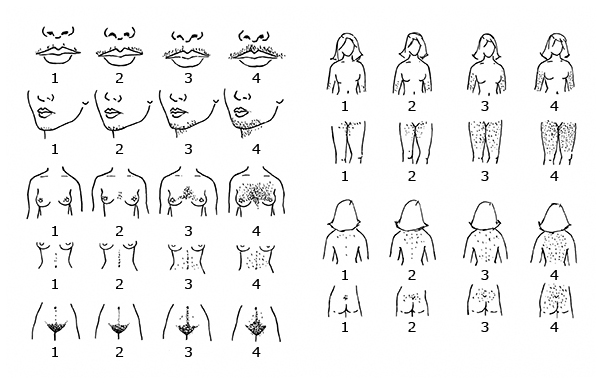
Ferriman-Gallwey hirsutism scoring system
Uptodate:Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome in adults
Abnormal in the US: >= 8 points
Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy: History/PE
- Confirm DM first
- History
- orthostatic dizziness
- palpitation
- bloating
- dry skin
- PE
- Heart rate
- Heart rate variability
- Orthostatic hypotension
Uptodate:Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
Pheochromocytoma: History/PE
Uptodate:Clinical presentation and diagnosis of pheochromocytoma
- History
- Classic Triad: headache, sweating, and tachycardia
- young/resistant hypertension
- familial syndrome: MEN2/NF1/VHL
- PE
- Blood pressure
- Orthostatic hypotension
Other Tests
- Hyperthyroidism: TSH, free T4, T3
- PCOS: Androgen, Transvaginal ultrasound
- Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy: Fasting glucose, HbA1c
- Pheochromocytoma: plasma/urine fractionated metanephrines and catecholamines (CT/MRI if abnormal)
Q(A)/Discussion
問題二、基於目前的急診檢查結果,請試圖排除或納入某些診斷,您現在剩下哪一些可能的鑑別診斷?有哪些檢查您認為還需要做?病人目前在您手上,您認為他需要什麼立即的治療嗎?
Signs
- Tachypnea (respiratory rate: 30)
- Tachycardia (pulse: 125)
- Temperature : 37.3
- SpO2: 94%
- Bilateral leg pitting edema (1+)
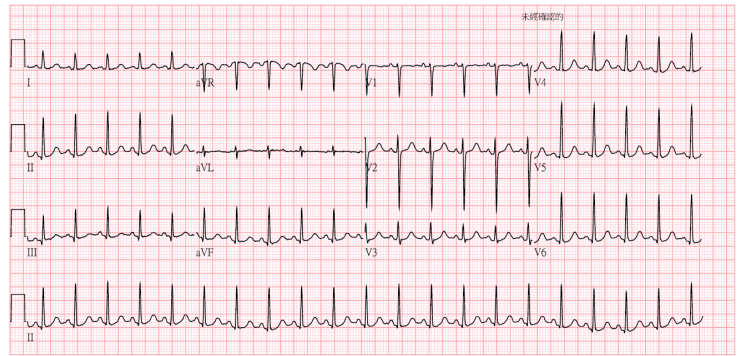
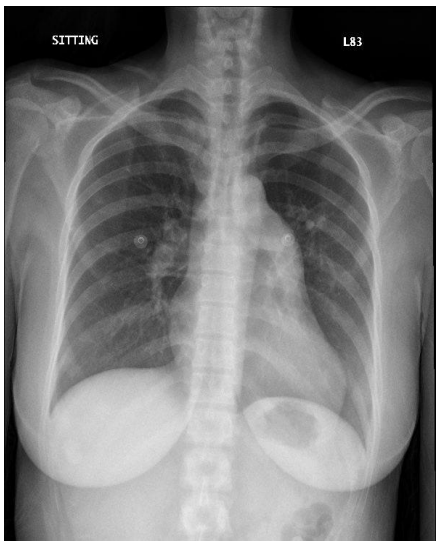
cardiomegaly(-), lung infiltrates(-)
Lab Test Results - 1
- Polycythemia
- Microcytosis
- Thrombocytopenia
-
Neutrophilic Leukocytosis
- ANC: 16000 (>7700)
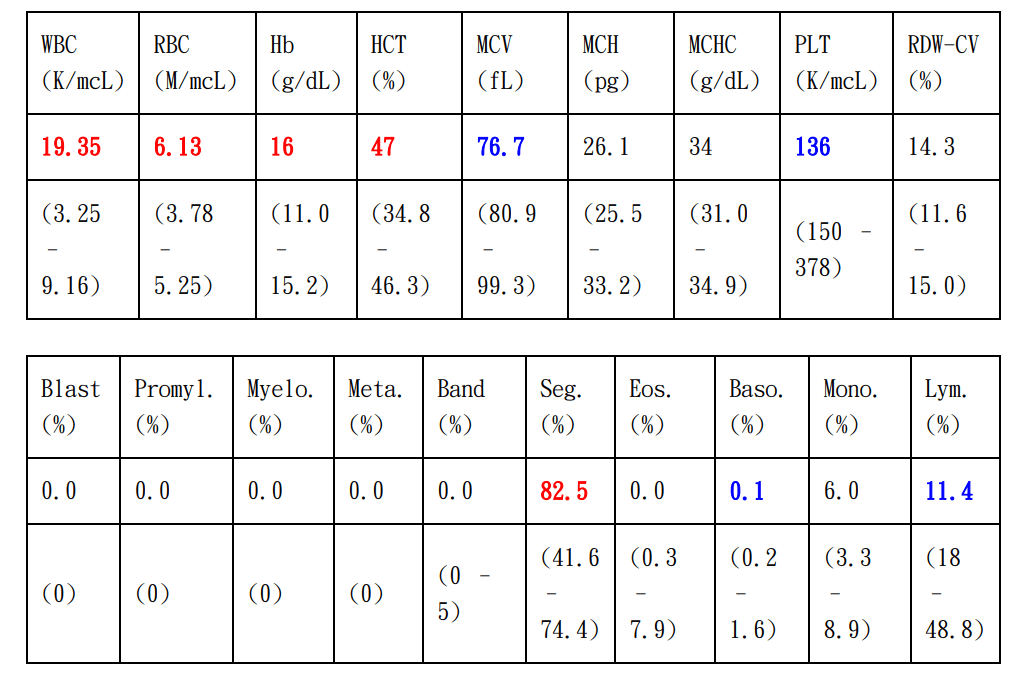
Lab Test Results - 2
- Elevated ALT
- Hyperglycemia?
- Elevated CRP
- Respiratory Alkalosis
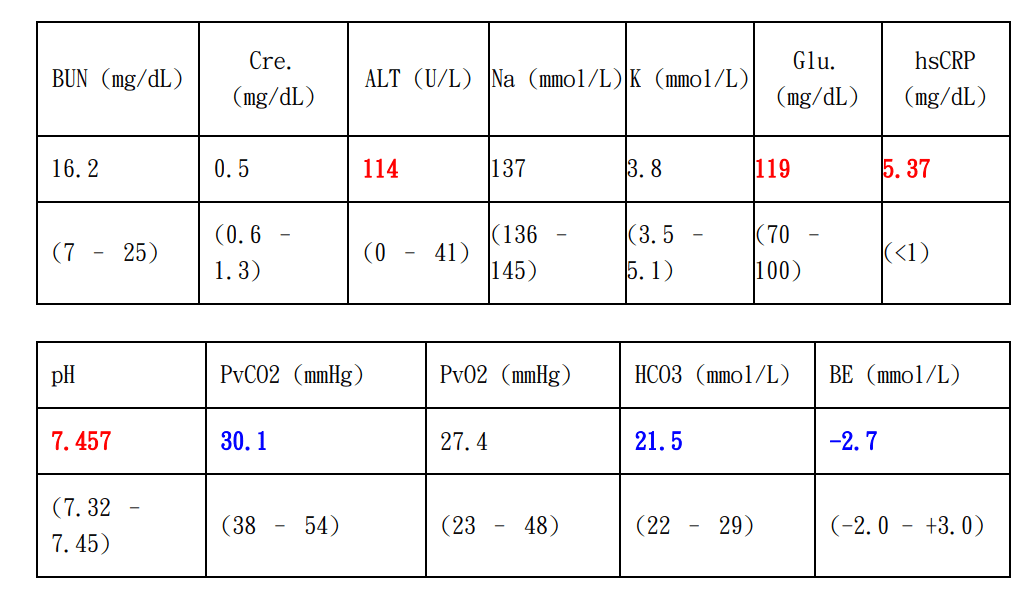
Differential Diagnosis?
Covington JD, Tam CS, Pasarica M, Redman LM. Higher circulating leukocytes in women with PCOS is reversed by aerobic exercise. Biochimie. 2016 May;124:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.10.028. Epub 2014 Nov 12. PMID: 25446648; PMCID: PMC4429000.
Michael, Sarah E. MD1; Darbinian, Jeanne A. MPH2; Ramalingam, Nirmala D. MPP1; Wu, Stephanie J. MD1; Khil, Jaclyn MD1; Lo, Joan C. MD2; Greenspan, Louise C. MD3. S1156 PCOS Is an Independent Predictor of Elevated ALT in Adolescent Girls With Obesity. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 115():p S578-S579, October 2020. | DOI: 10.14309/01.ajg.0000706672.34009.10
Uptodate: Approach to the patient with neutrophilia
Baruah MP, Bhattacharya B. Significant role of serum CRP in differentiating inflammatory from non-inflammatory causes of thyrotoxicosis. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Nov;16(6):976-81. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.103002. PMID: 23226645; PMCID: PMC3510970.
N. Boulman, Y. Levy, R. Leiba, S. Shachar, R. Linn, O. Zinder, Z. Blumenfeld, Increased C-Reactive Protein Levels in the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Marker of Cardiovascular Disease, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Volume 89, Issue 5, 1 May 2004, Pages 2160–2165, https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-031096
Leukocytosis: Normal variation? Infections? Cigarette smoking? Medications?
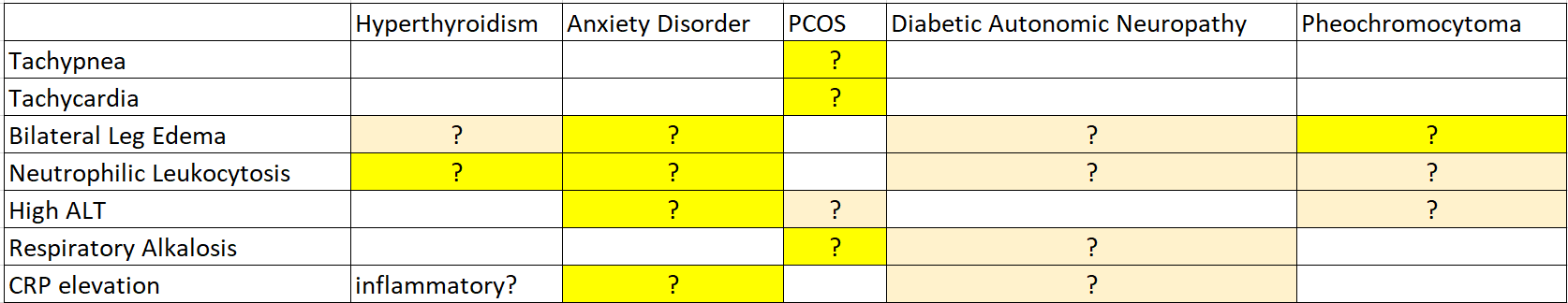
問題二、基於目前的急診檢查結果,請試圖排除或納入某些診斷,您現在剩下哪一些可能的鑑別診斷?有哪些檢查您認為還需要做?病人目前在您手上,您認為他需要什麼立即的治療嗎?
Other Tests?
- Blood Pressure
- Hyperthyroidism: TSH, free T4, T3
- Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy: HbA1c
- Pheochromocytoma: plasma/urine fractionated metanephrines and catecholamines (CT/MRI if abnormal)
問題二、基於目前的急診檢查結果,請試圖排除或納入某些診斷,您現在剩下哪一些可能的鑑別診斷?有哪些檢查您認為還需要做?病人目前在您手上,您認為他需要什麼立即的治療嗎?
Immediate Intervention?
- Neutrophilic leukocytosis?
- no hypotension, high fever, hypothermia, abdominal rebound tenderness
-
Tachycardia
- Should treat underlying cause.
-
Respiratory Alkalosis
- Rarely life-threatening, should correct underlying disorder.
-
Tachypnea
- Should treat
- 給氧氣?
Uptodate:Approach to the patient with neutrophilia, Sinus tachycardia: Evaluation and management,
Q(A)/Discussion
5/1 小組討論
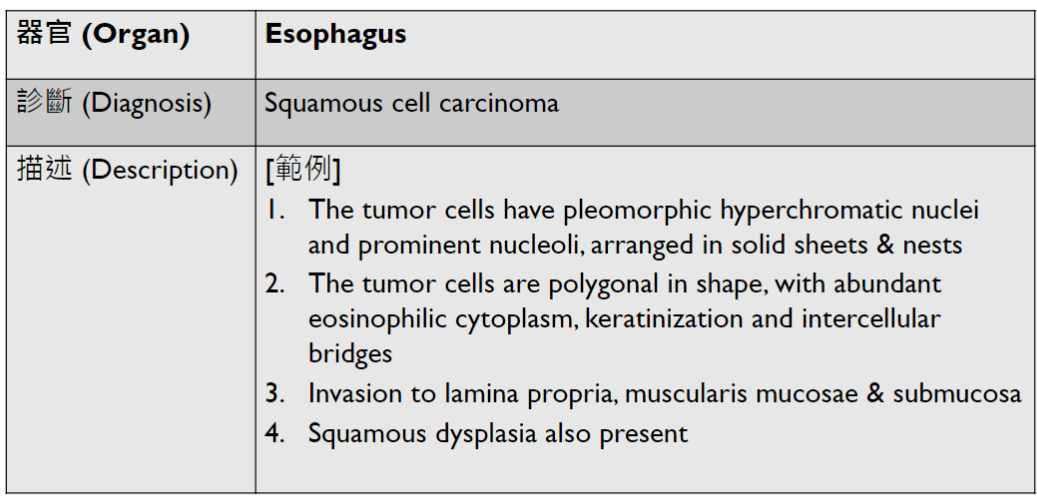
問題一:食道癌常見的組織學型態與對應的危險因子有哪些?
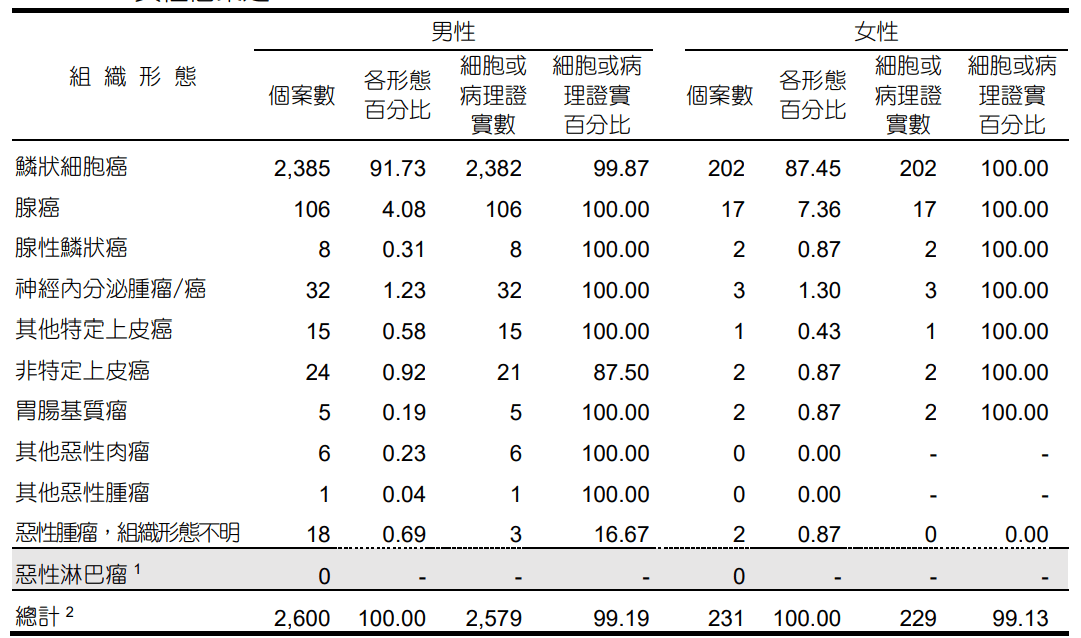
民國111年癌症登記報告
Squamous Cell Caricinoma
Adenocarcinoma
Carcinoma, NOS
Adenosquamous Carcinoma
NET/NEC
1
2
3
鱗狀上皮癌(Squamous Cell Carcinoma, SCC)
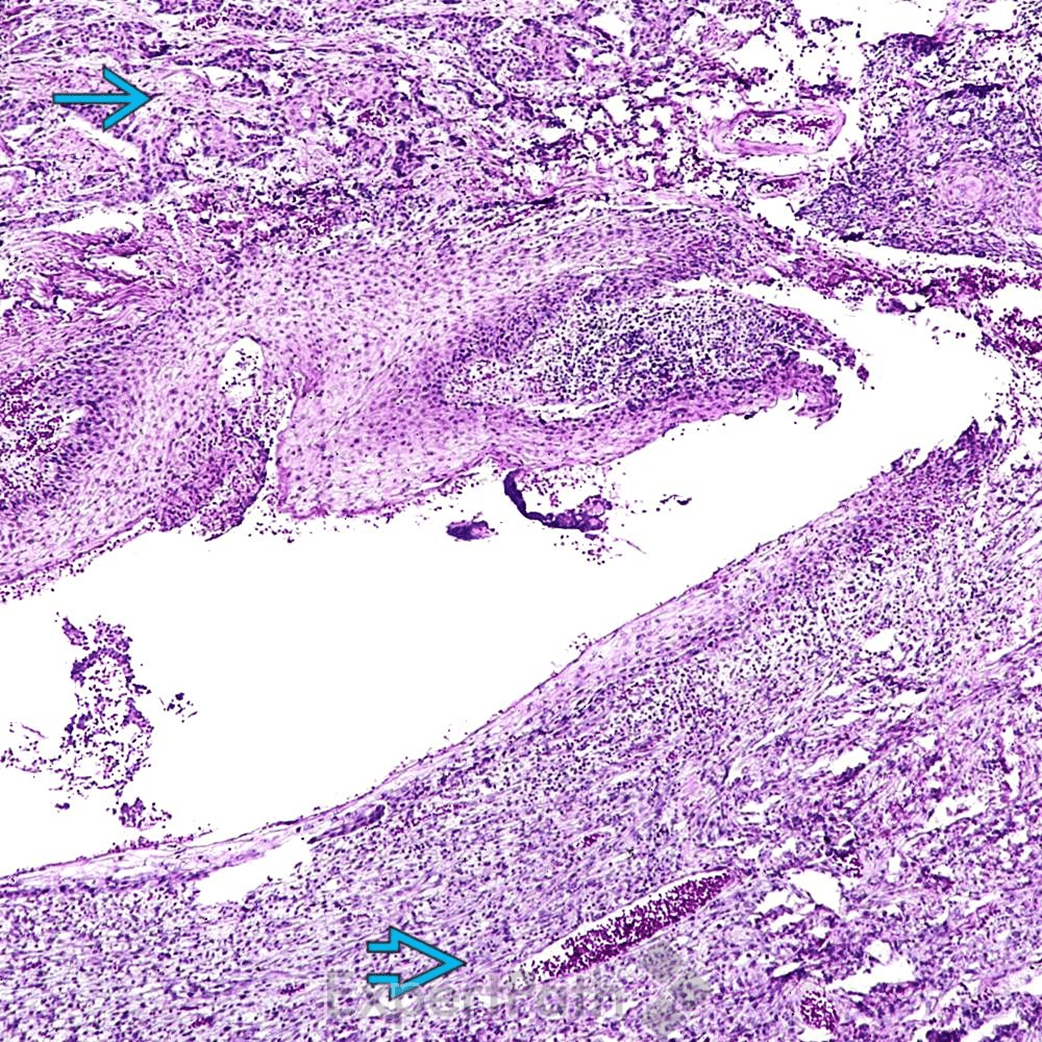
pictures from ExpertPath
Well-differentiated SCC
basaloid SCC
sarcomatoid SCC
Risk Factors for Esophageal SCC
- Smoking, Alcohol, Hot tea
- Demographic factors
- Incidence higher in East Asia, East Africa, Southern Africa
- Age
- Rare before 30, median: 65
- HPV
- Sex?
-
In high-incidence regions, the disease has no sex specificity. By contrast, SCC is more common in males in low-incidence regions.
-
腺癌(Adenocarcinoma)
pictures from Pathology Outlines
Tubular Pattern
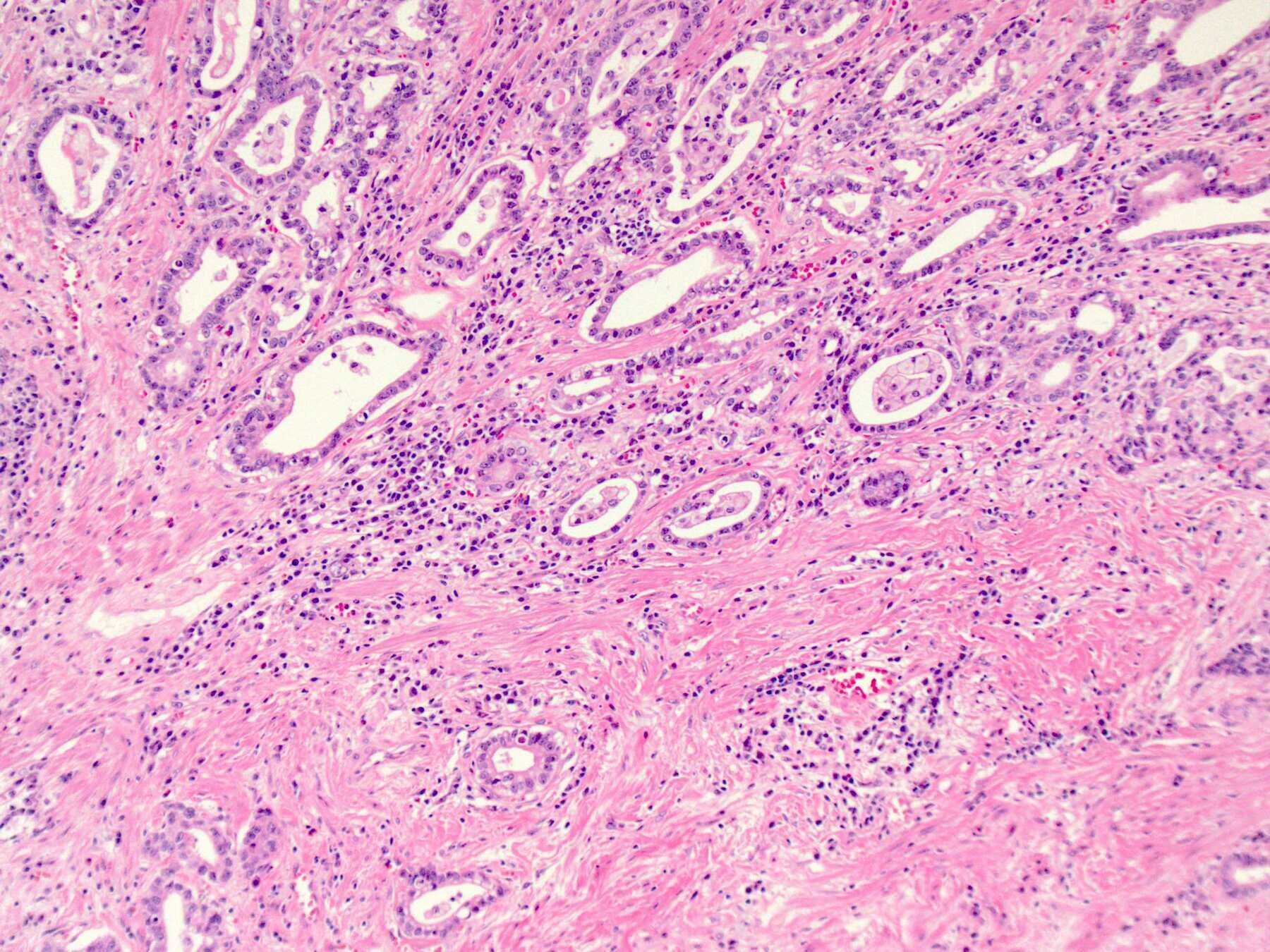
Signet Ring Cell Pattern
Risk Factors for Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
- 胃食道逆流(GERD)/Barrett's Esophagus
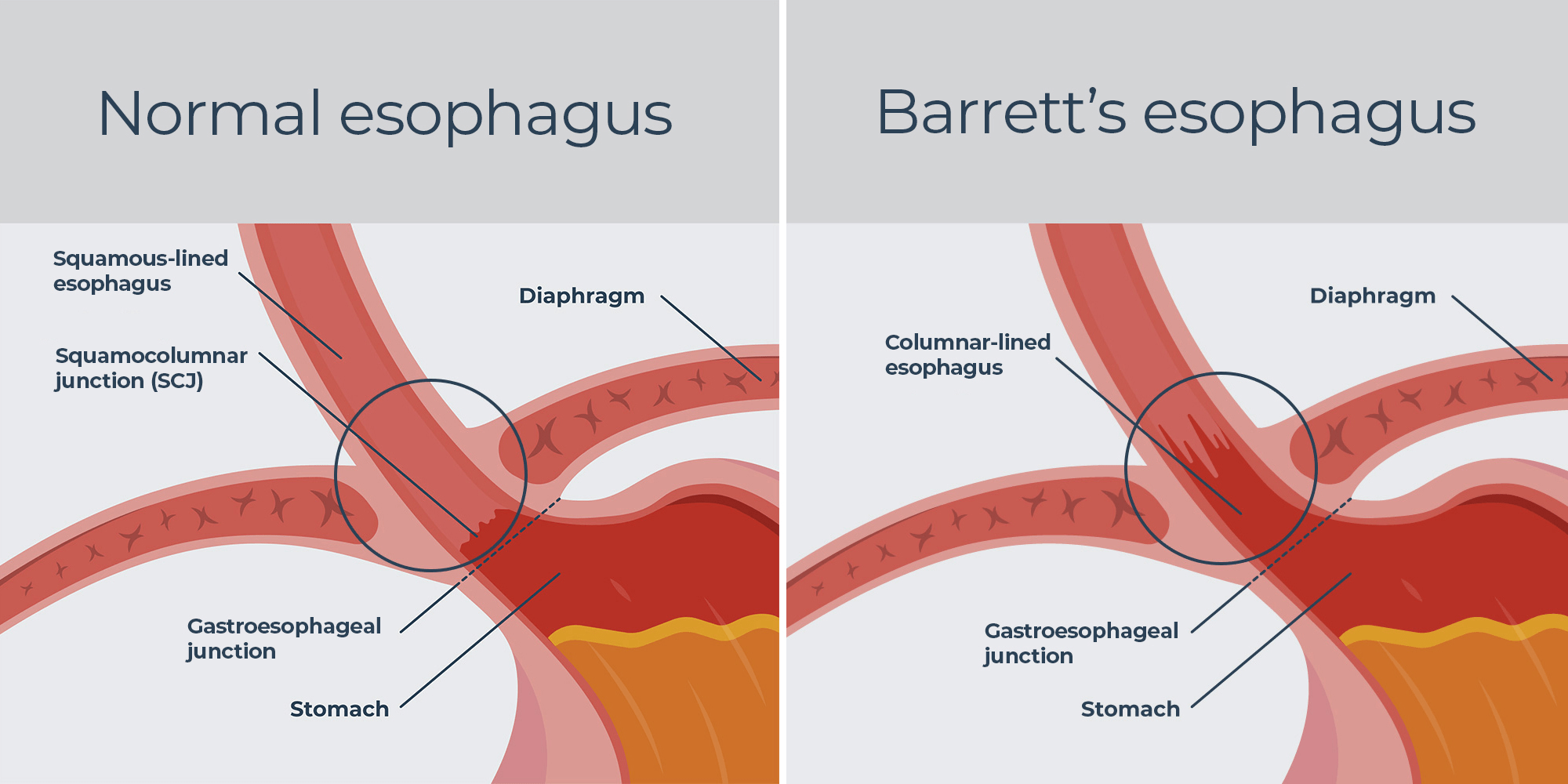
https://castlebiosciences.com/patient-information/gastroenterology/barretts-esophagus/overview
Risk Factors for Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
- Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome
- May be independent of GERD
- Smoking
- Not as strong as SCC
- Diet low in fruits and vegetables
- Male
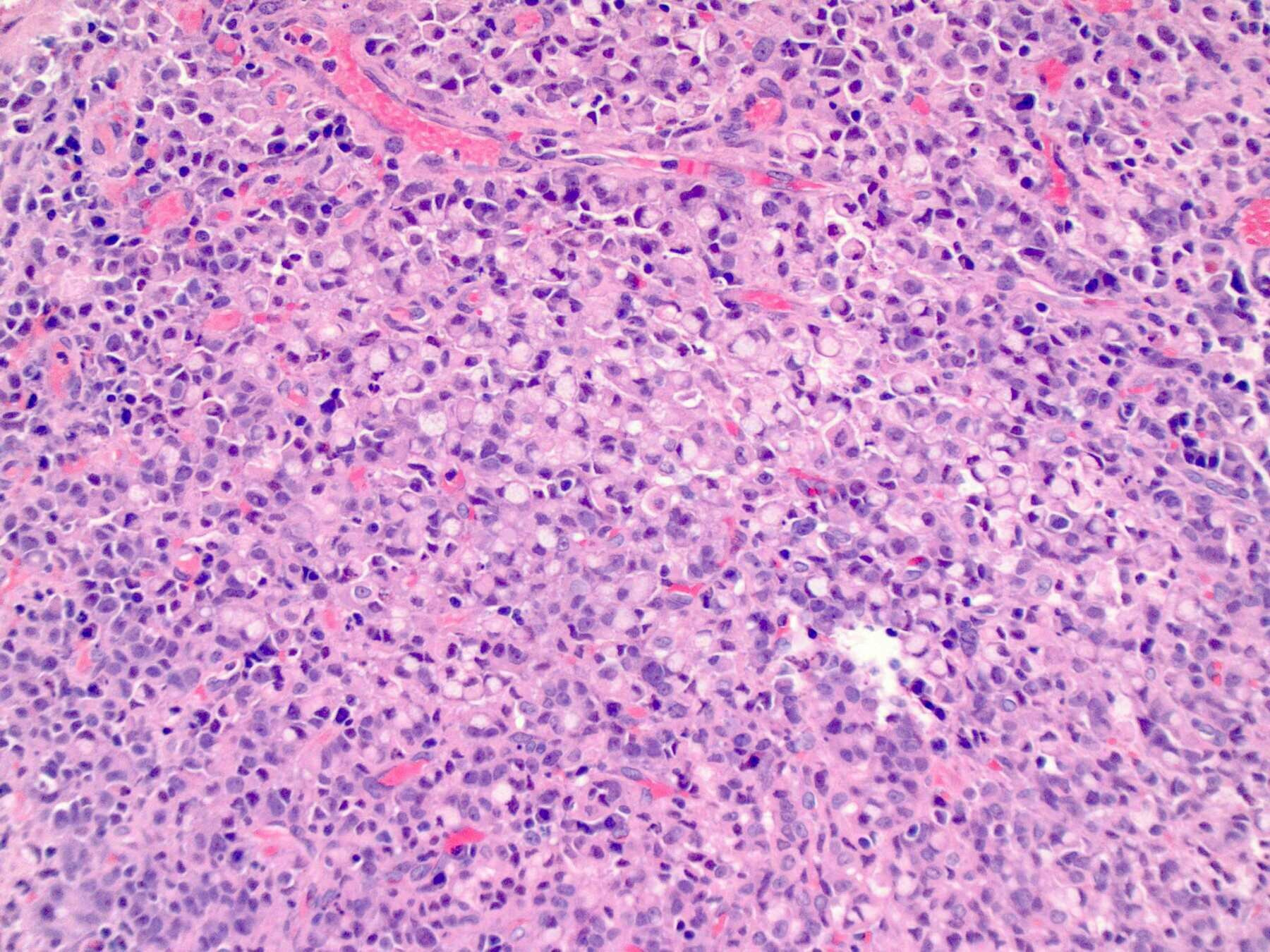
神經內分泌腫瘤/癌 (NET/NEC)
https://ar.iiarjournals.org/content/33/2/595
Small Cell Carcinoma
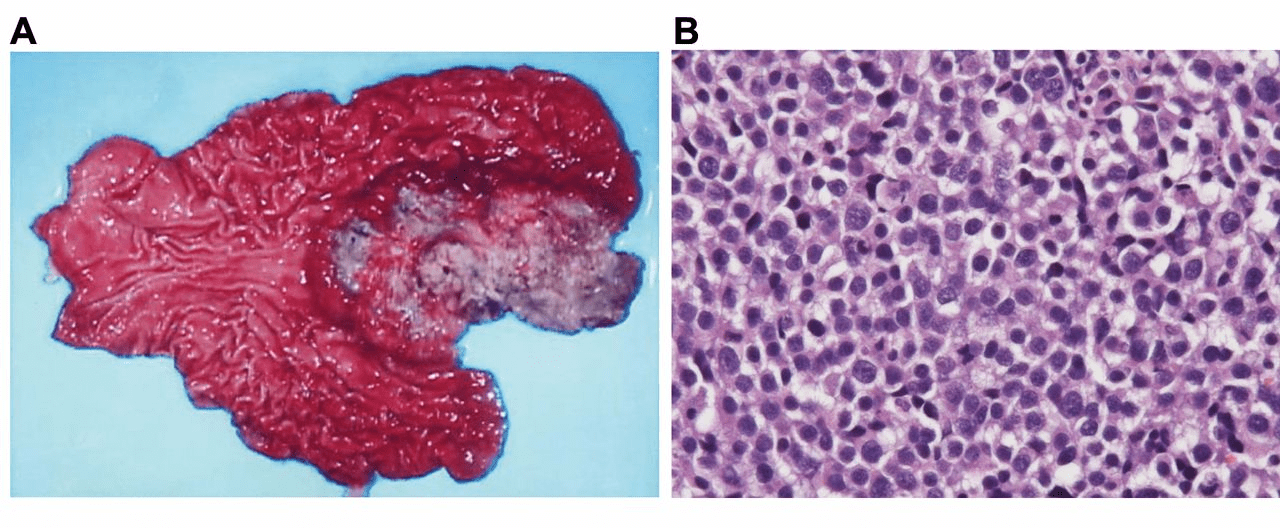
Risk factors?
Q(A)/Discussion
問題三:概述免疫檢查點抑制劑(immune checkpoint inhibitor,programmed cell death-1 [PD1]及 programmed death-ligand-1 [PD-L1])在癌症的發展?
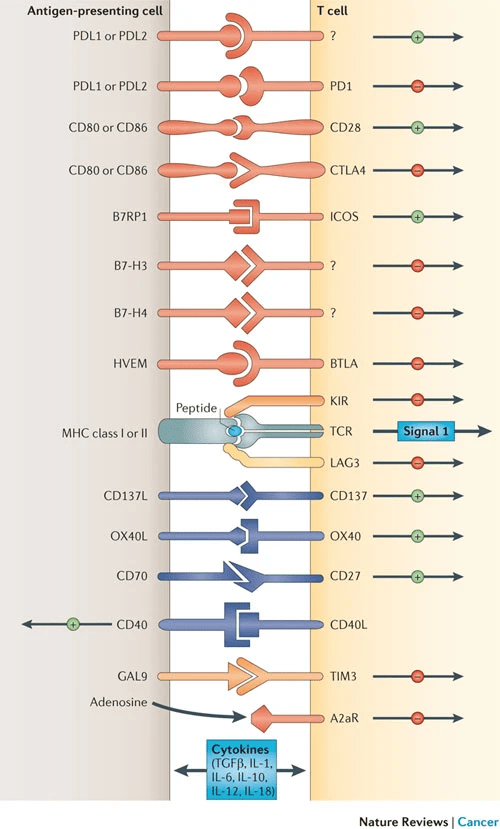
免疫檢查點 (Immune Checkpoints)

2018 諾貝爾生醫獎
The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2012;12:252- 264.
ipilimumab: Approved in 2010 for melanoma
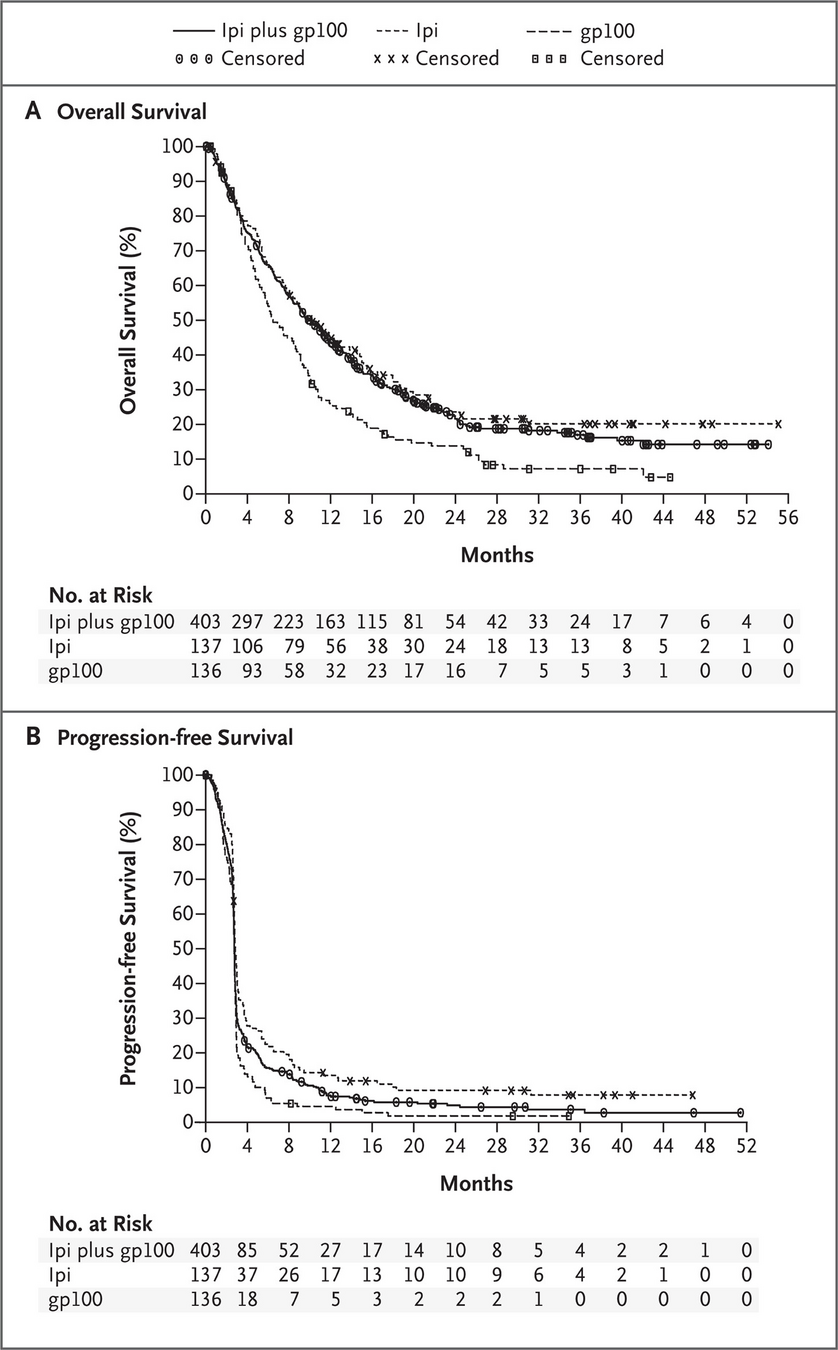
Hodi FS, O'day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC et al: Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 2010, 363(8): 711-723.
anti-CTLA4 antibody
https://www.kcuk.org.uk/ipilimumab-yervoy/
PD-L1 on Tumor Cells?
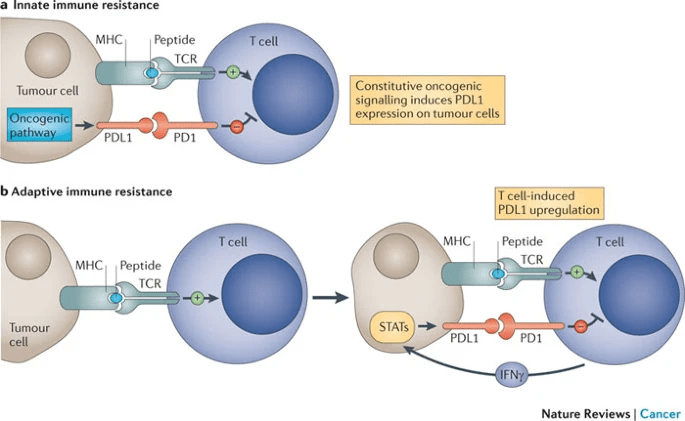
The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2012;12:252- 264.
Makuku, Rangarirai, Khalili, Neda, Razi, Sepideh, Keshavarz-Fathi, Mahsa, Rezaei, Nima, Current and Future Perspectives of PD-1/PDL-1 Blockade in Cancer Immunotherapy, Journal of Immunology Research, 2021, 6661406, 15 pages, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6661406
FDA-approved indications for PD-1 Inhibitors
- Pembrolizumab
Melanoma Breast cancer Non-small-cell lung cancer Small-cell lung cancer Head and neck squamous cell cancer Hodgkin lymphoma Gastric/gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma Cervical cancer Endometrial carcinoma Primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma Hepatocellular carcinoma Merkel cell carcinoma Renal cell cancer Urothelial cancer
-
Nivolumab
Melanoma Non-small-cell lung cancer Small-cell lung cancer Renal cell cancer Hodgkin lymphoma Head and neck squamous cell cancer Urothelial cancer Colorectal cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)
- Cemiplimab
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Makuku, Rangarirai, Khalili, Neda, Razi, Sepideh, Keshavarz-Fathi, Mahsa, Rezaei, Nima, Current and Future Perspectives of PD-1/PDL-1 Blockade in Cancer Immunotherapy, Journal of Immunology Research, 2021, 6661406, 15 pages, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6661406
FDA-approved indications for PD-L1 Inhibitors
-
Atezolizumab
Urothelial carcinoma Non-small-cell lung cancer Small-cell lung cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Breast cancer
-
Durvalumab
Urothelial carcinoma Non-small-cell lung cancer Small-cell lung cancer
-
Avelumab
Merkel cell carcinoma Urothelial carcinoma Renal cell cancer
Makuku, Rangarirai, Khalili, Neda, Razi, Sepideh, Keshavarz-Fathi, Mahsa, Rezaei, Nima, Current and Future Perspectives of PD-1/PDL-1 Blockade in Cancer Immunotherapy, Journal of Immunology Research, 2021, 6661406, 15 pages, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6661406
Biomarkers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- PD-L1 expression
- Tumor mutational burden
- Microsatellite instability-high
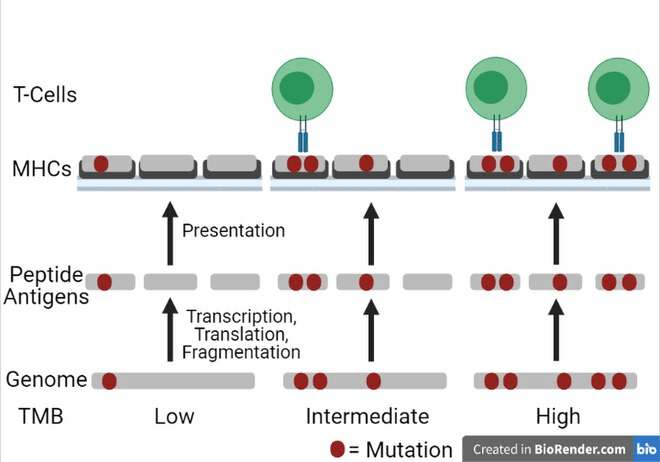
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tumor_mutational_burden
The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2012;12:252- 264.
Future Prospects: Combinations?
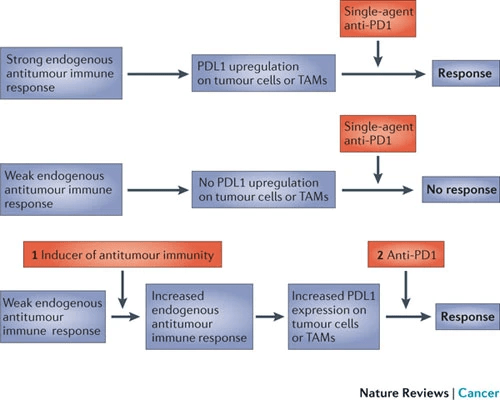
- vaccines
- target therapy
- chemotherapy
- ...
Q(A)/Discussion
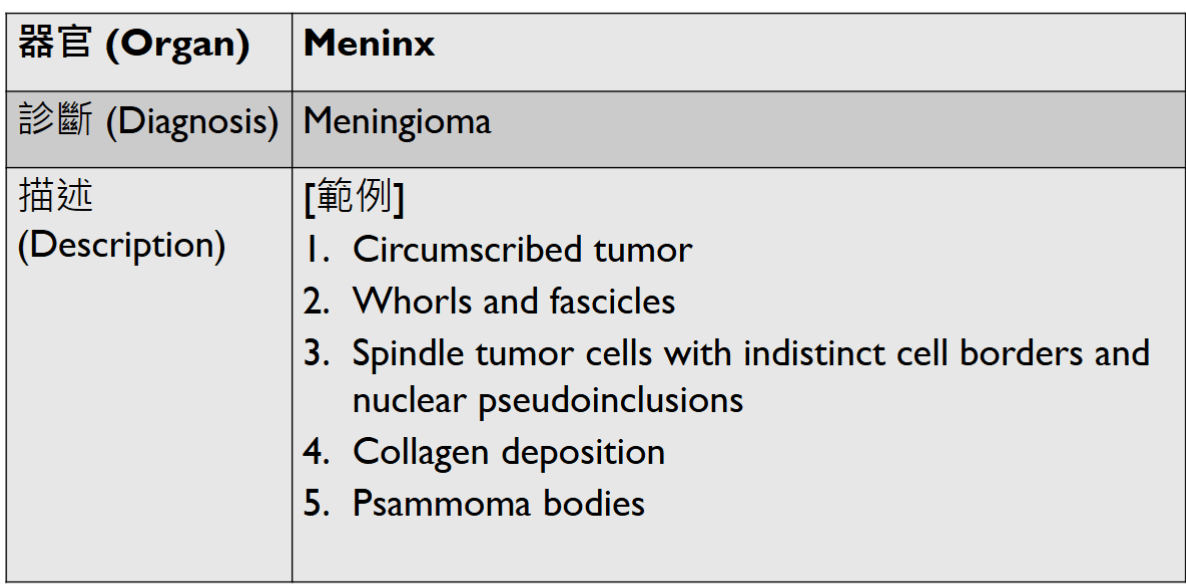
Last Micro
organ CNS寫brain, soft tissue寫soft tissue
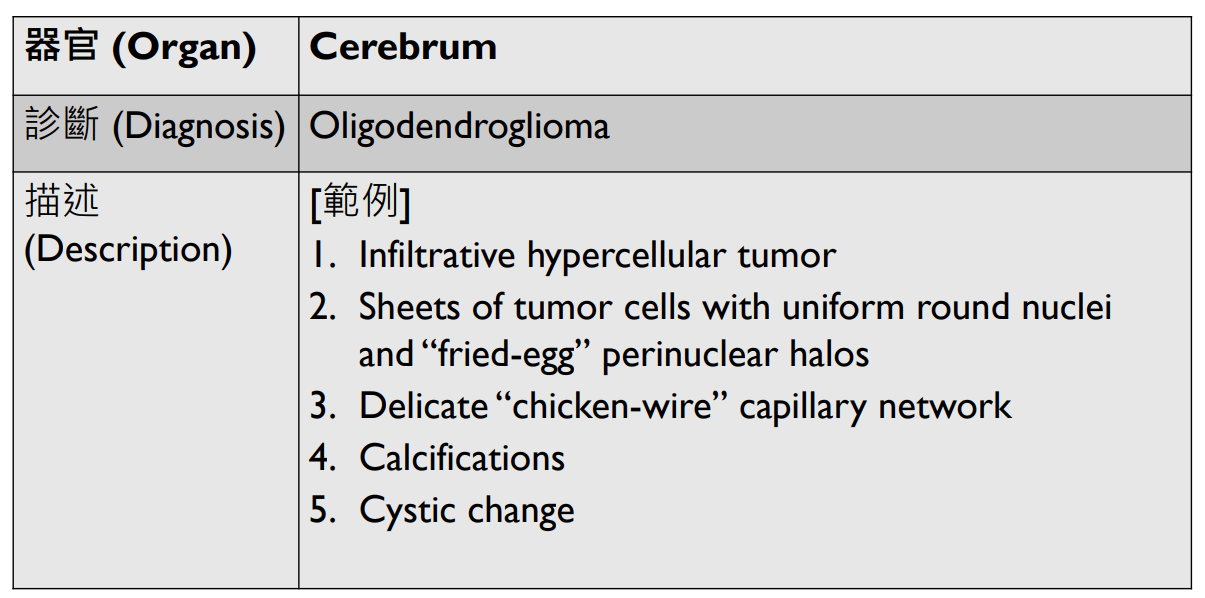
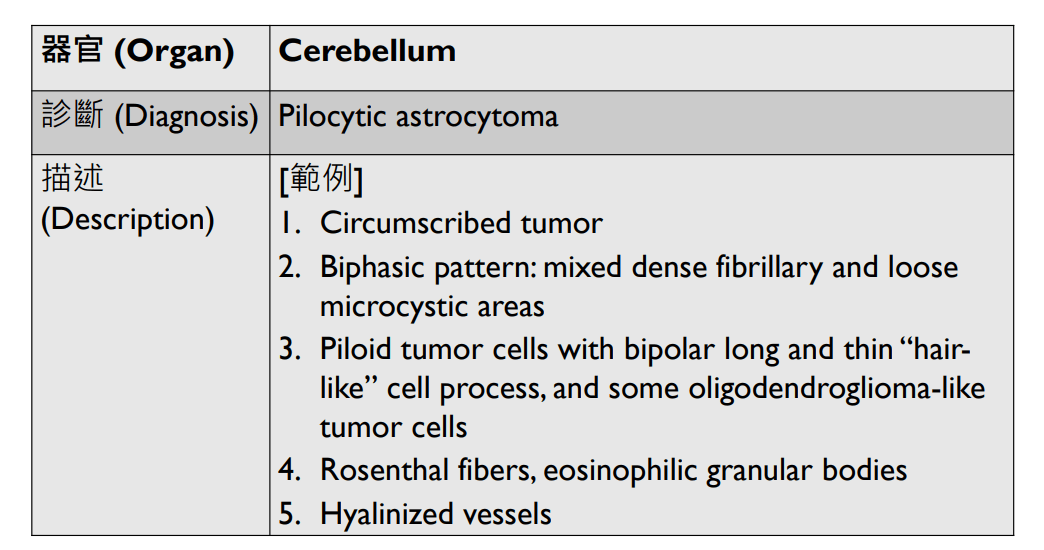
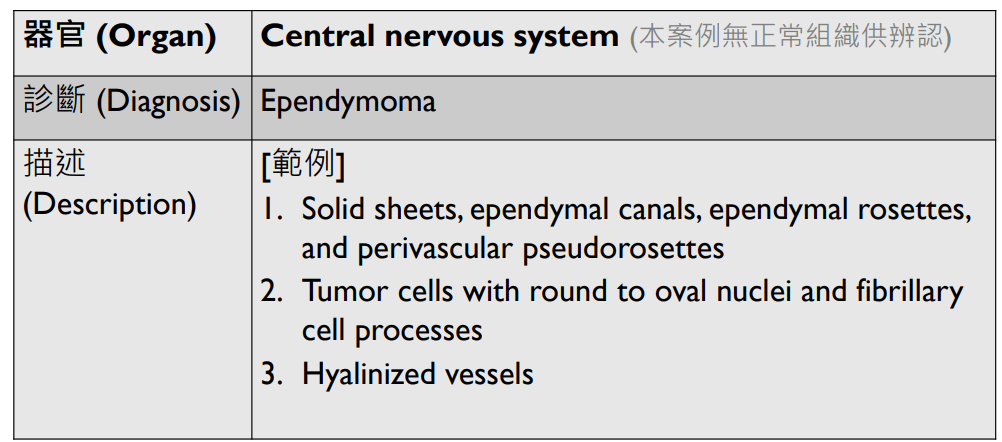
(circumscribed)
(well-defined)
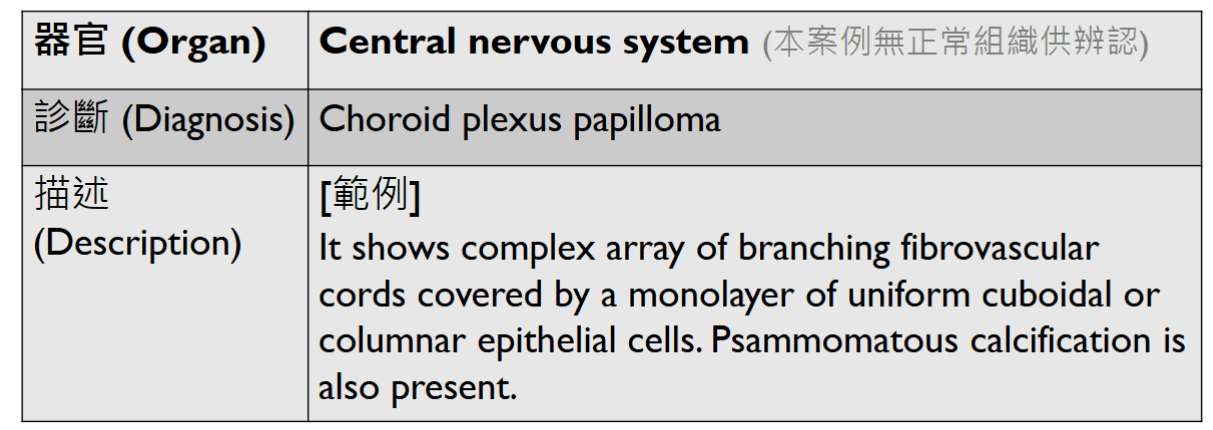
- A complex branching papillary structure covered by a single layer of uniform cuboid to columnar epithelial cells
- psammomatous calcification
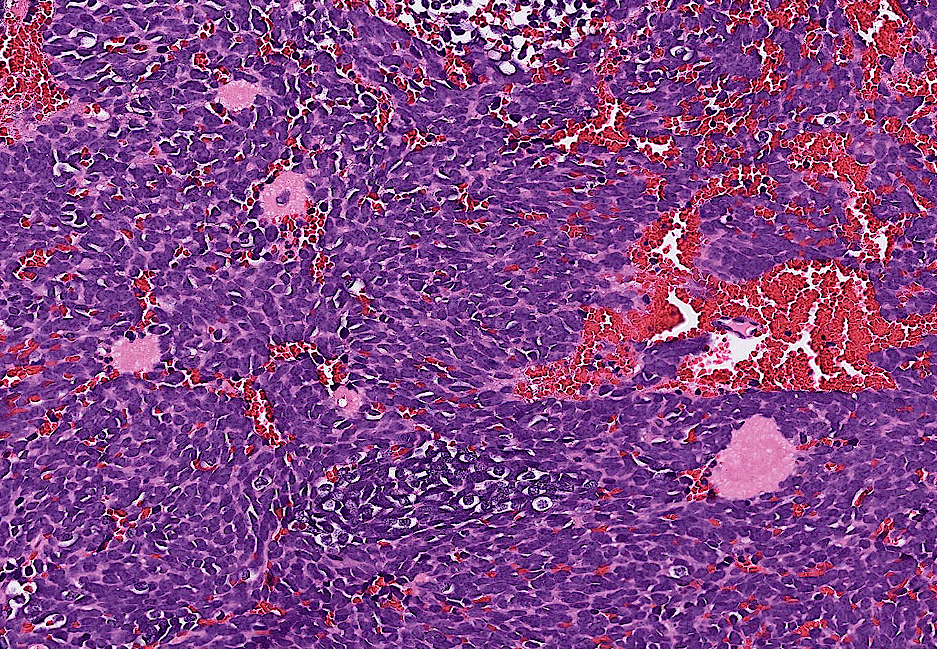
(well-defined)
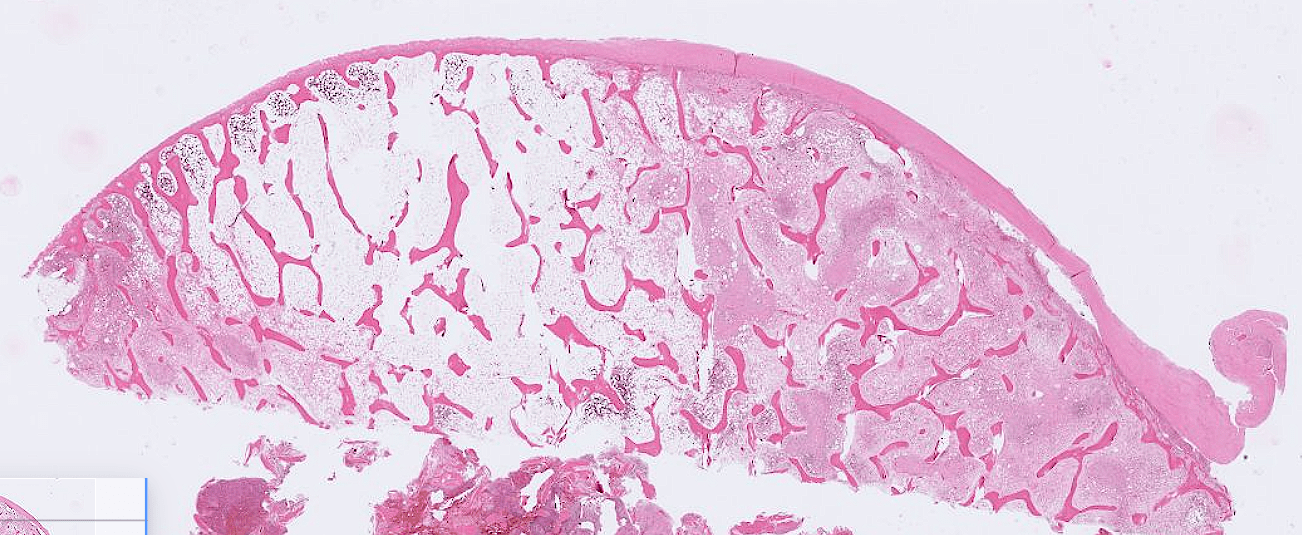
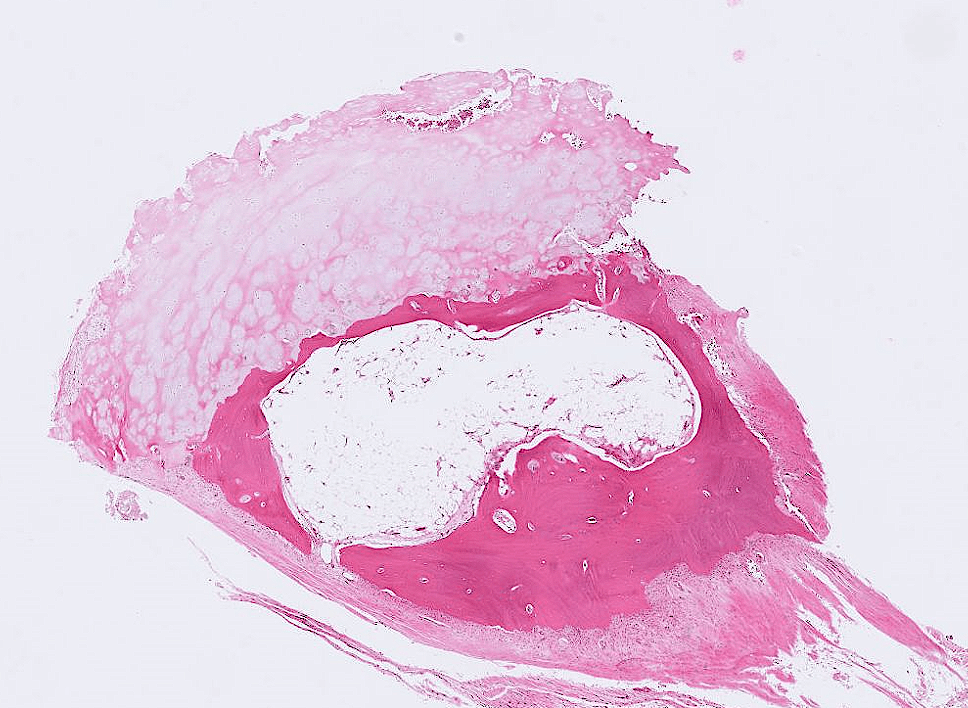
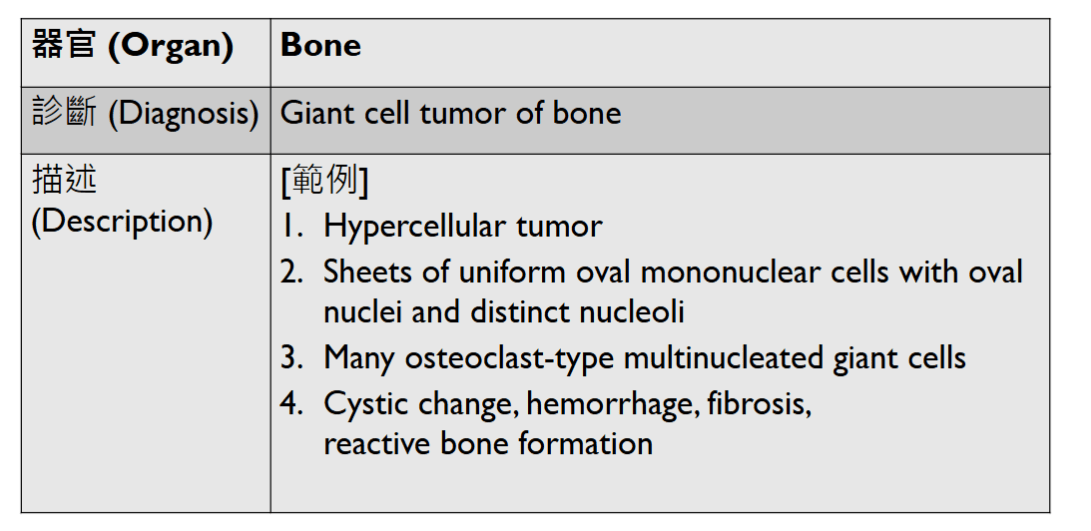
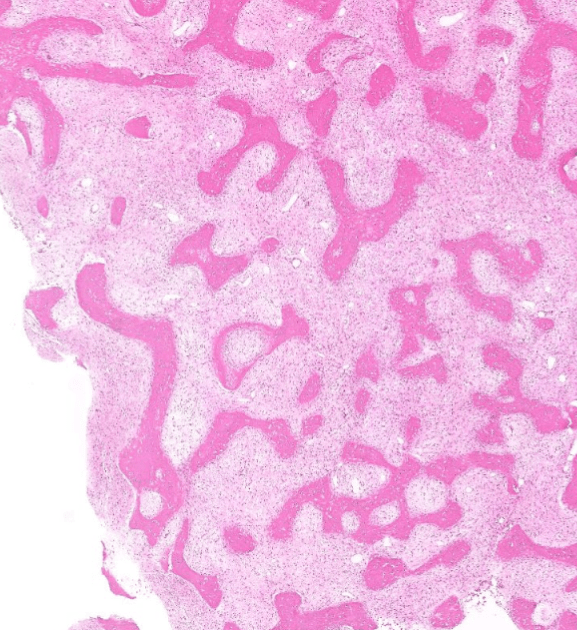
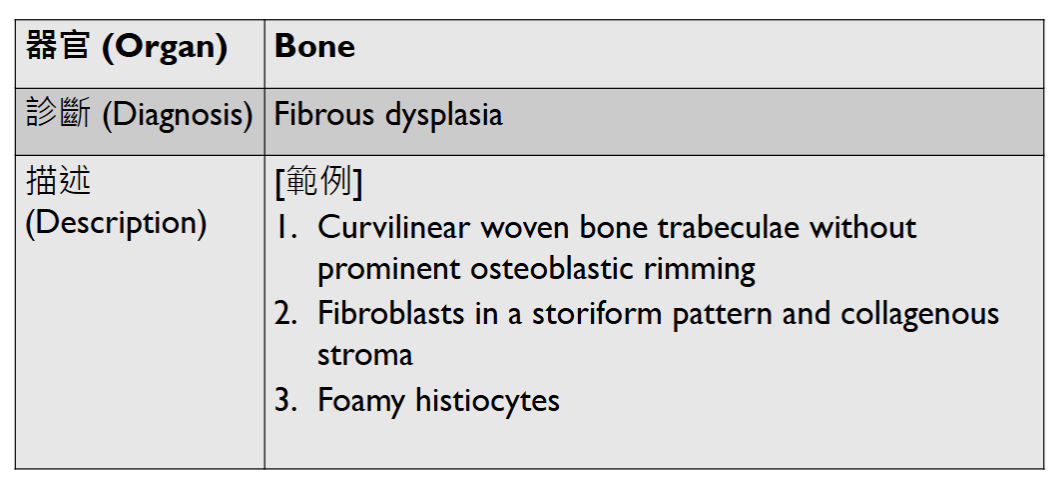
- Organ: Bone (joint)
- Diagnosis: Osteoarthritis
- Description
- Cartilage degeneration:
- chondrocyte clustering
- surface fibrillation, fissures, cartilage thinning
- Tidemark duplication
- Subchondral bone change: sclerosis, subchondral cyst
- synovial hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltrate, fibrosis
- Cartilage degeneration:
(chondrocytes arranged in columns at base)
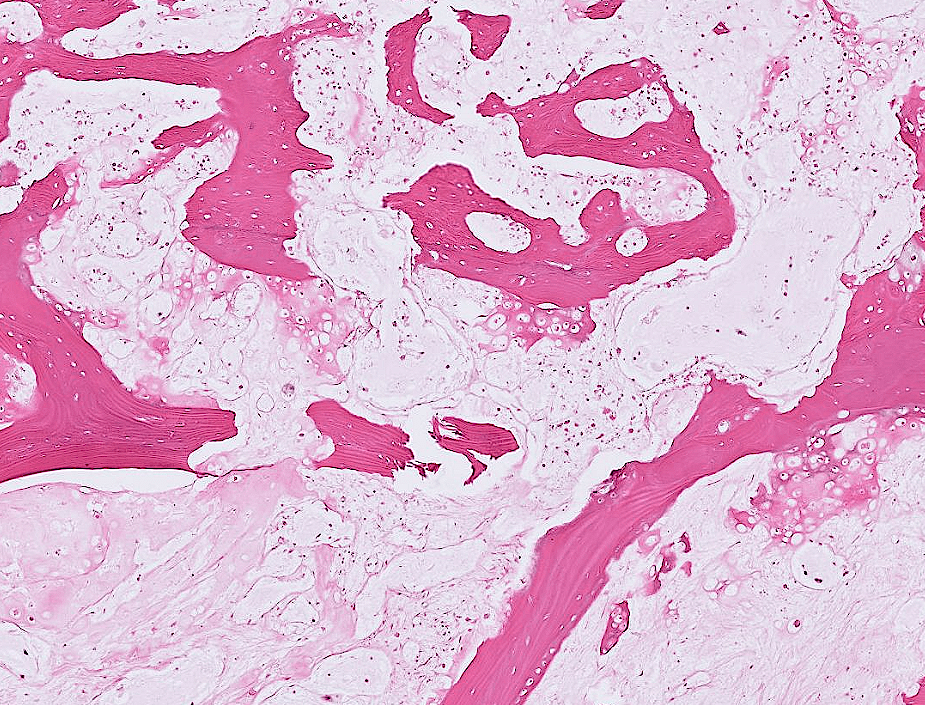

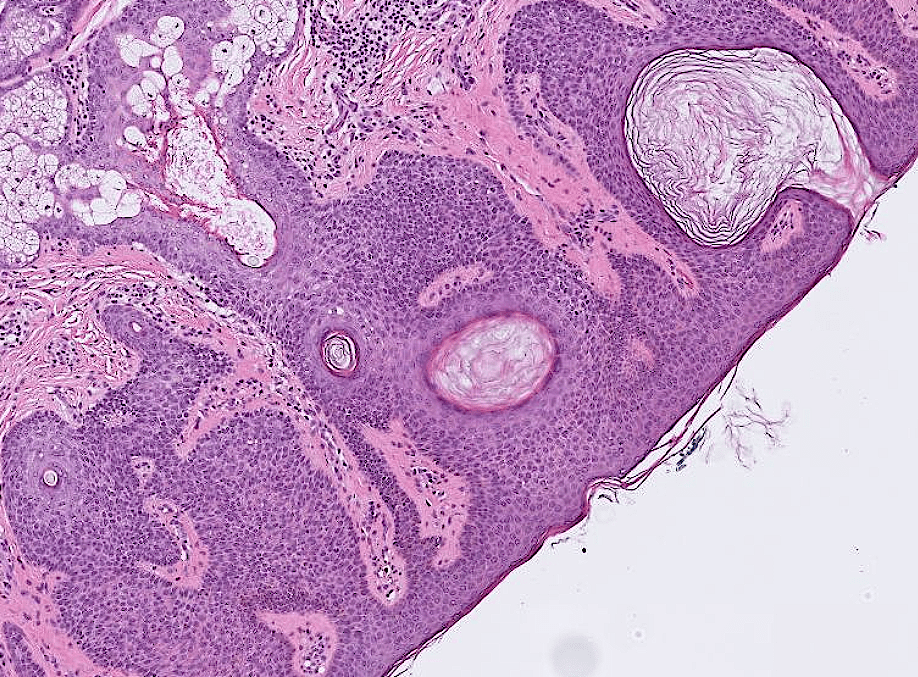

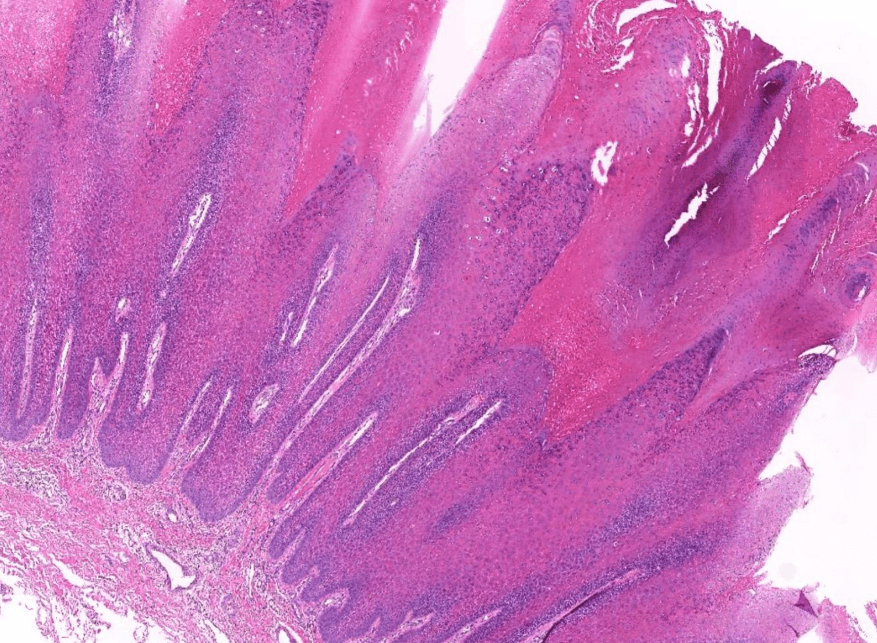
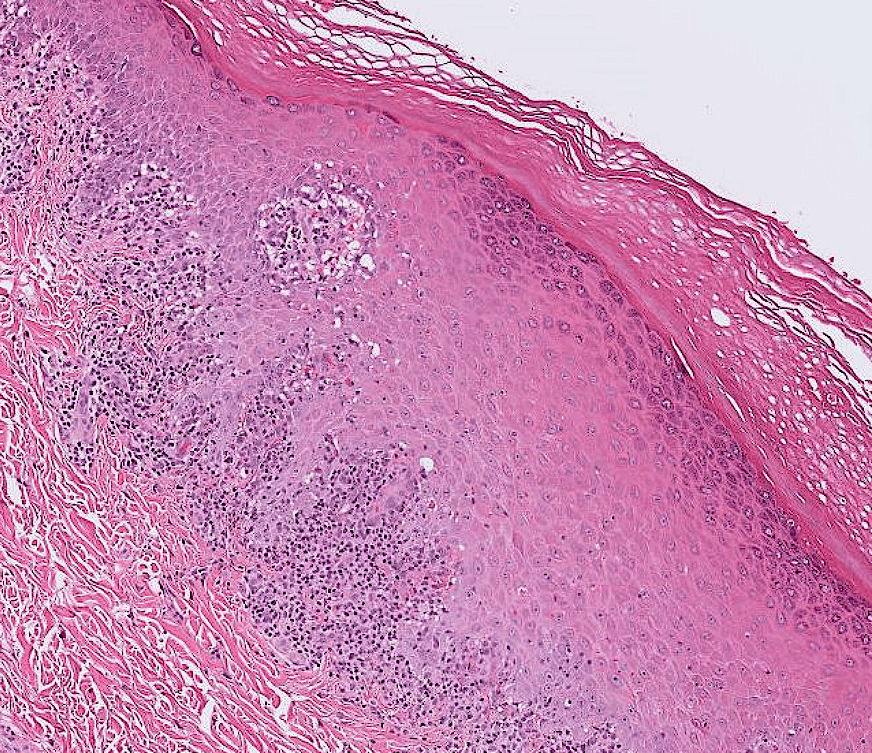

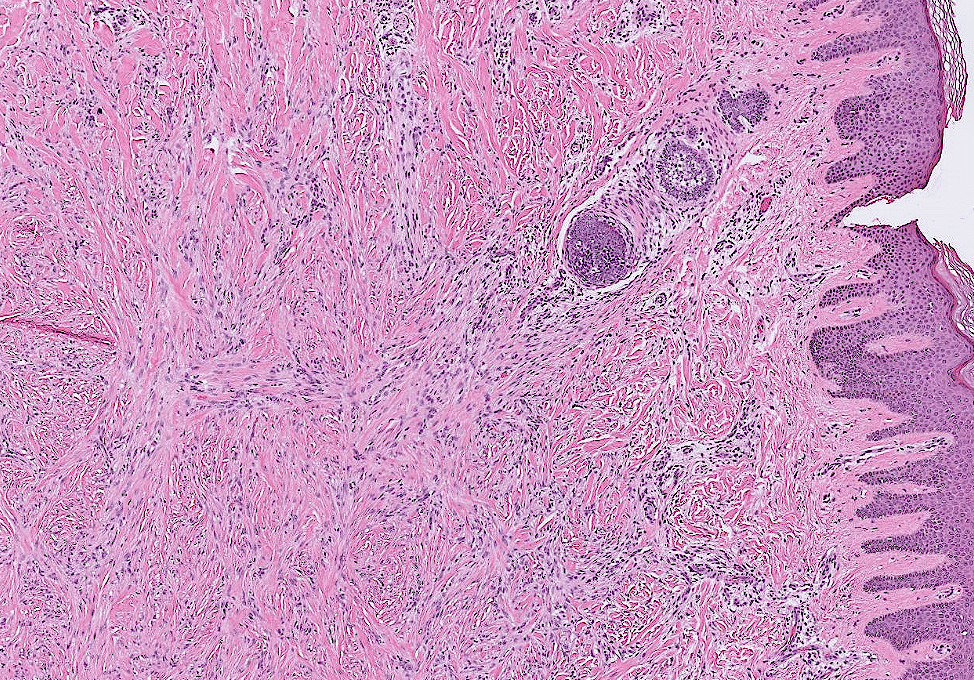
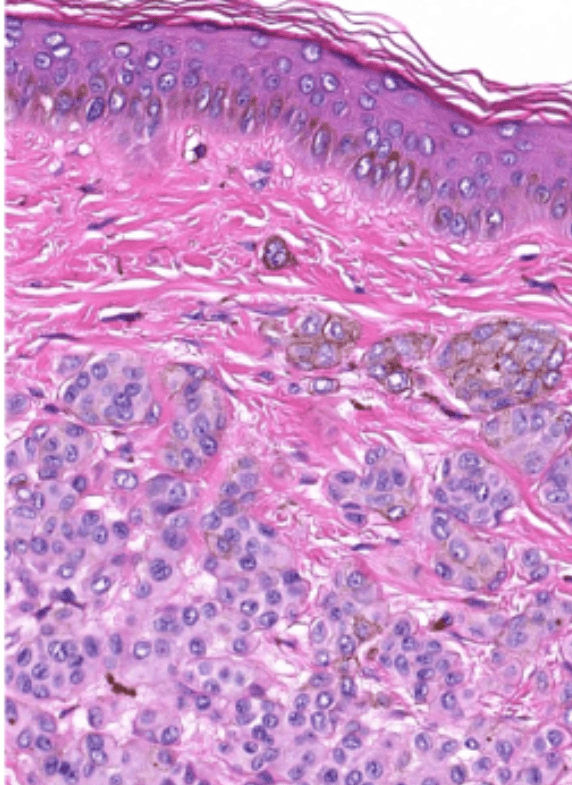
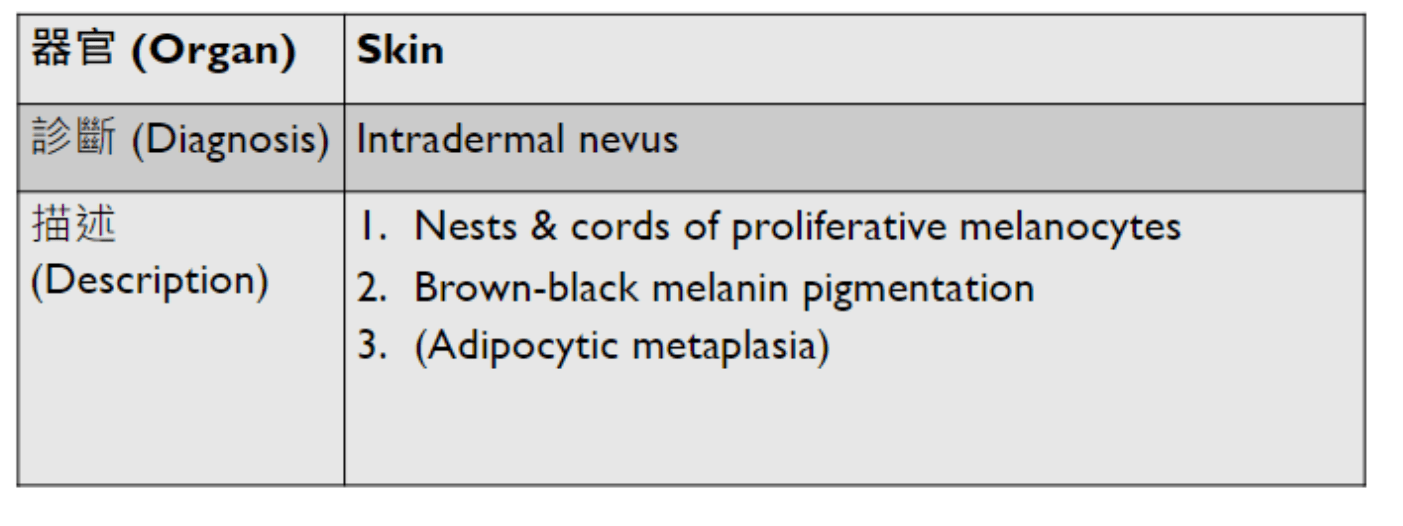
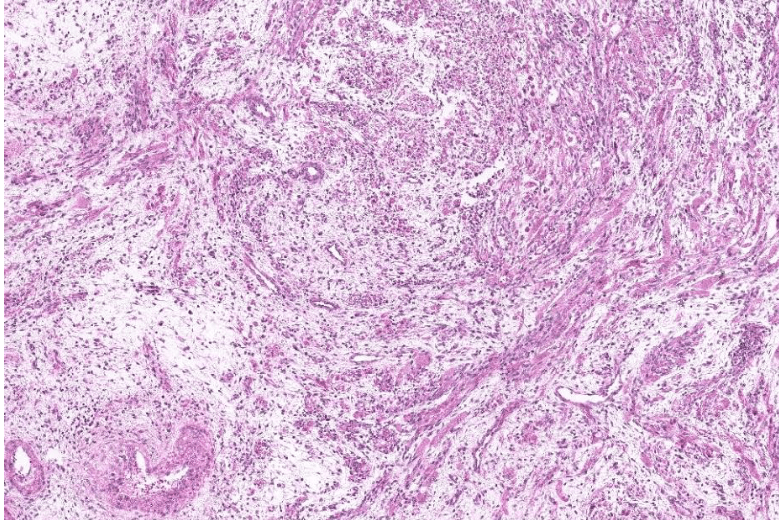
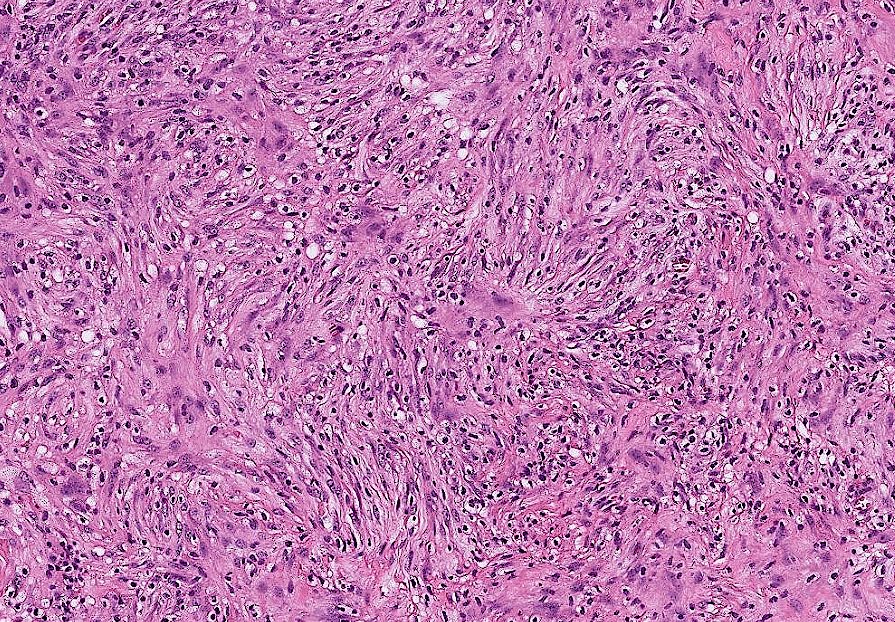
- Organ: Skin
- Diagnosis: Dermatofibroma
- Description
- A poorly circumscribed dermal tumor with peripheral collagen trapping
- Areas of hypercellularity or hypocellularity
- Fascicles or whorls of spincle cells or histiocytic cells
- May have epidermal hyperplasia or basal hyperpigmentation


(or in diffuse sheets)
(or monophasic)
overlapping
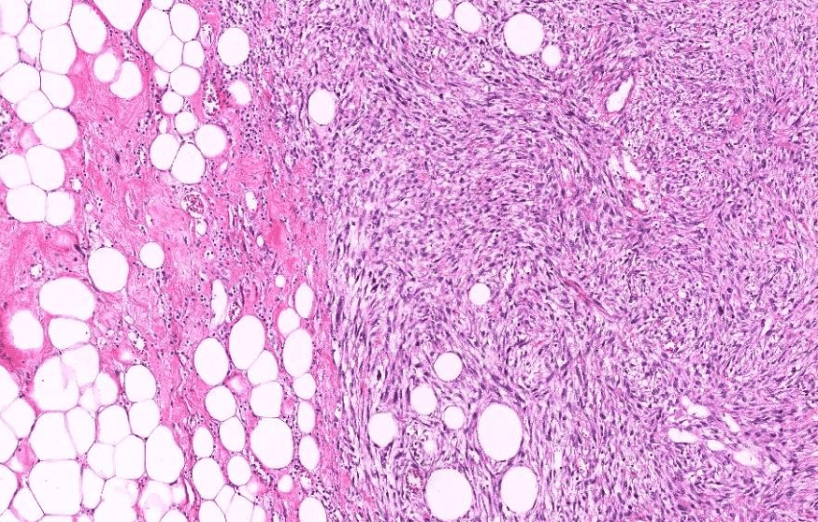
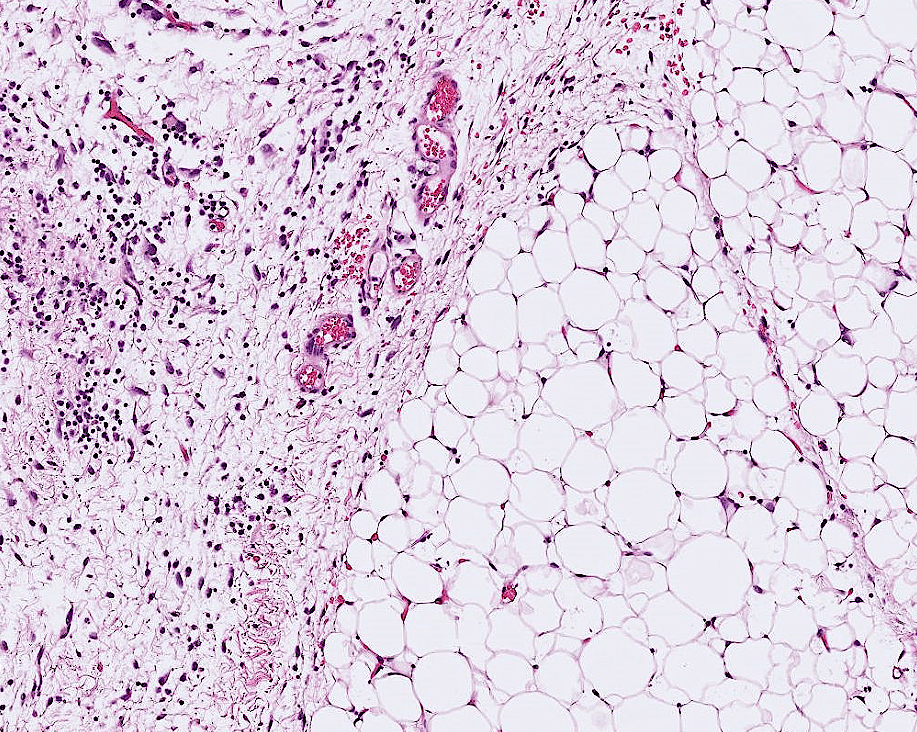

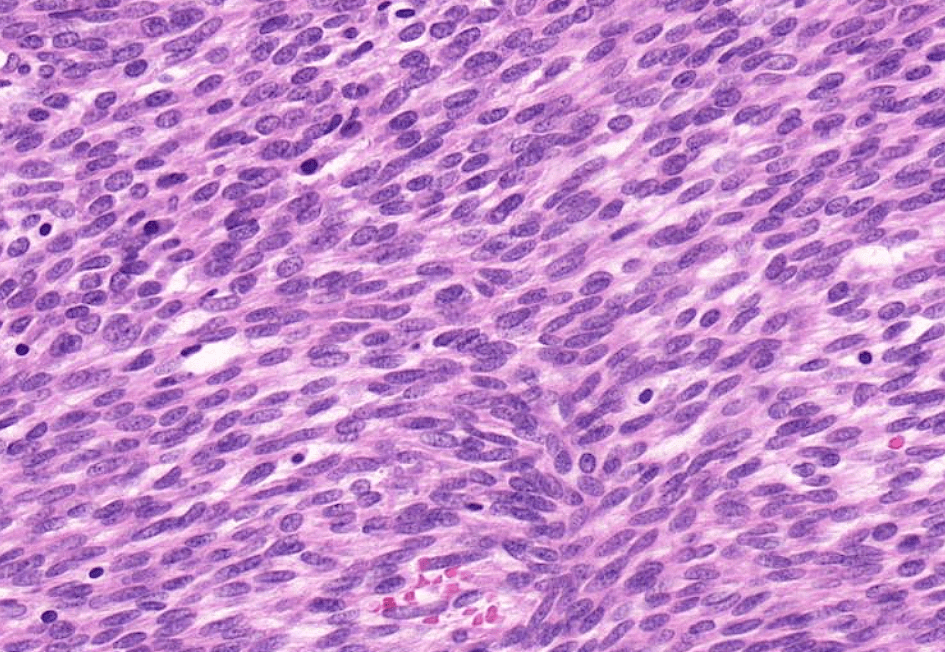
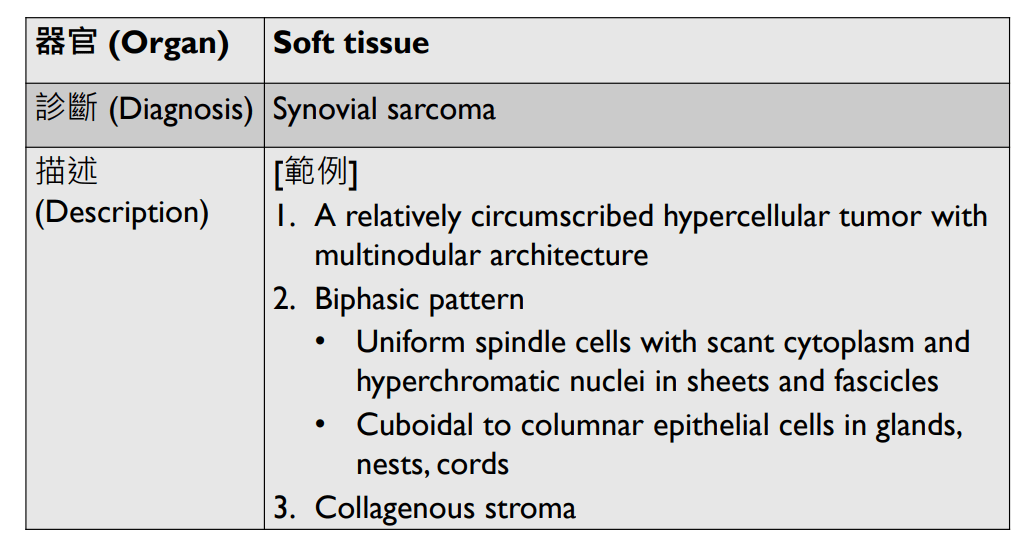
- Organ: soft tissue
- Diagnosis: myxoid liposarcoma
- Description
- A lobulated tumor with increased peripheral cellularity
- patternless array of of uniform small ovoid to spindle cells
- myxoid stroma with a delicate arborizing capillary network
- small lipoblasts are seen focally
Last Micro Review


(melanin pigment)
(circumscribed/infiltrative)


(pagetoid spread)
(hyperchromatic也可)




4. maturation with descent
5/15 小組討論

"醫療疏失"?

醫療法 82條


刑法
"醫療疏失"?
1. 過失:應注意,能注意,而不注意
- 違反醫療上必要之注意義務、逾越合理臨床專業裁量
- 應以該醫療領域當時當地之醫療常規、醫療水準、醫療設施、工作條件及緊急迫切等客觀情況為斷。
reference: 最高法院 97 年度台上字第 2346 號刑事判決、刑法第14條、謝碧珠,吳欣席:淺談醫療刑事事件疏失與過失之法律構成要件問題
3. 過失與損害之間有相當因果關係
2. 造成損害
1. or 1.+2.+3.?
醫療鑑定
- 由法院/檢察官委託衛服部醫審會醫事鑑定小組進行
- 含醫事、法學專家,學者,社會人士等
- 或交由醫學中心等機構
- 常提供以下之意見
- 醫事人員做了哪些處置?
- 醫療常規之作法為何?
- 因果關係:作為/不作為是否導致負面結果?
謝碧珠,吳欣席:淺談醫療刑事事件疏失與過失之法律構成要件問題
Example: 103年醫事鑑定及調處案例彙編集 案例四
- (民國96年12月31日) 食慾不振及體重減輕
- 至診所找A醫師健康檢查
- 發現B肝帶原,GOT= 90 (12-37)
- 肝腎腹部超音波檢查,發現腎結石
-
(97年2月21日) 經症狀治療後未改善
- 至第二家診所找B醫師就診
- 因病人有上腹疼痛及胃酸逆流,加上之前作超音波肝無異常,懷疑胃潰瘍、幽門桿菌感染
- 進行治療18天後未改善,且腹脹、腳腫
- 再找B醫師就診
- 第二次腹部超音波
- 發現肝硬化及腹水,轉介至區域醫院
- 隔天住院
- 作第三次超音波、CT
- 發現15-16 cm 肝腫瘤
- 之後經多種治療腫瘤仍持續擴大,病人於97/6/14死亡
病人家屬認為A醫師及B醫師有醫療疏失,故提出告訴。
Example:問題爭點及鑑定意見


Example:問題爭點及鑑定意見



Example:問題爭點及鑑定意見


結果?

我們的案例
- 醫事人員做了哪些處置?
- 照X光、建議吃止痛藥、復健
- 醫療常規之作法為何?
- 下背痛合併左大腿痠痛;且X光發現L4,L5 椎間盤退化、有骨刺
- 是否應懷疑癌症而進行相關檢查?
- 相當因果關係?
- 若當時進行相關檢查,是否能避免損害發生?
謝碧珠,吳欣席:淺談醫療刑事事件疏失與過失之法律構成要件問題
是/非醫療過失之原因
Hung GY, Horng JL, Chen PC, Lin LY, Chen JY, Chuang PH, Chao TC, Yen CC. Incidence of soft tissue sarcoma in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based study (2007-2013). Cancer Epidemiol. 2019 Jun;60:185-192. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 May 2. PMID: 31055220.
| 是醫療過失! | 不是醫療過失! | |
|---|---|---|
| 未盡注意義務? | 1. 左大腿之疼痛在下背痛改善後仍持續,應考慮是其他原因造成 | 1. soft tissue sarcoma發生率低(5.62/100,000人/year in Taiwan) 2. disc degeneration合併骨刺為low back pain常見、合理之原因,也可能導致thigh pain 3. 這一年中雖病人左大腿的痠痛仍然斷斷續續會發作,但亦未因此回診 4. 考慮病人之過去病史、家族史、臨床表現,病人癌症風險不高(? |
| 損害? | 1. 病人這一年中左大腿的痠痛仍然斷斷續續會發作,也會因此擔心 2. 開刀對病人來說也是一種負擔 |
1. 這一年中病人並無重大不適 2. 目前開刀後只剩輕微的傷口不適,後續追蹤腫瘤也沒有復發的跡象 3. 病人也無明顯之財產或其他權益受到損害 |
| 相當因果關係? | 1. 診斷正確,即可早點開刀,避免左大腿痠痛之症狀 2. 延遲開刀可能導致切除範圍增加 |
1. 病人腫瘤為low grade,晚一年開刀對病情無太大影響 |
大家的想法?
如何跟病人解釋?
- 我可以理解你不開心以及想責怪我們的心情。
- 但當時根據症狀以及X光,椎間盤退化合併骨刺生成造成下背痛及大腿痠痛是最合理的解釋。
- 因此我們先開了止痛藥以及復健;後續因為你也沒有回診,我們也不知道大腿痠痛的情形沒有改善。
- 不過幸好你之後很警覺,現在有正確診斷,手術看起來也很成功,真是太好了。
Q(A)/Discussion

如何跟病人解釋?
- 我可以理解你不開心以及想責怪我們的心情。
- 當初在評估要不要進行化療時真的是一個兩難的狀況。因為目前對於這種可以切除的軟組織腫瘤,化療到底有多少幫助還不太確定;而且還要面對化療的各種副作用。(詳見第四題)
- 相信我們當時與您討論的時候也有說明化療的好處與風險;雖然轉移的風險不高,但還是被我們遇到了,真的很遺憾。
- 不過這次腫瘤轉移只有一處,還可以開刀切除,算是不幸中的萬幸。希望你再相信我們一下,跟我們一起完成接下來的治療,好嗎?
Q(A)/Discussion
5/29 小組討論

- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LIza4BiEoOk
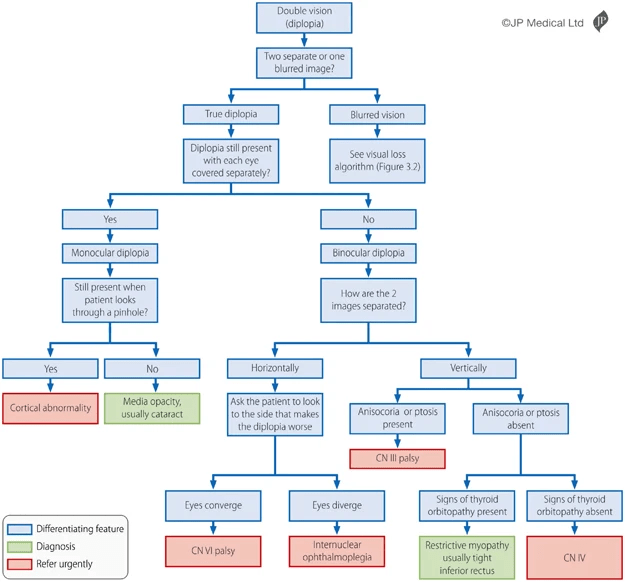
Edinburgh diplopia diagnostic algorithm
refractive abnormalities
Butler, L., Yap, T. & Wright, M. The accuracy of the Edinburgh diplopia diagnostic algorithm. Eye 30, 812–816 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.44
Monocular Diplopia
- Refractive abnormalities
- astigmatism, keratoconus, tear-film abnormalities, cataract, ...
- tilted intraocular lens
-
Cerebral diplopia
- rare, bilateral occipital or temporal lobe lesions

Pinhole Test
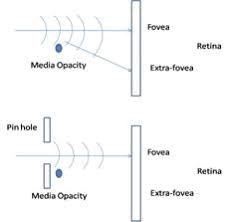
https://entokey.com/diplopia-2/
https://www.e-mfp.org/issues/2010v5n3/monocular_diplopia.html
Binocular Diplopia: Etiologies
UpToDate: Overview of diplopia
- Cranial nerve palsy
- 3rd, 4th, 6th
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia
- Myasthenia gravis
- Thyroid ophthalmopathy
- Other causes
- Guillain-Barré syndrome, Botulism, Skull base lesions, Giant cell arteritis, ...
Cranial Nerve Palsy
- 3rd cranial nerve
- vertical/horizontal diplopia
- ptosis, dilated pupil
- 4th cranial nerve
- vertical diplopia
- tilted head
- 6th cranial nerve
- horizontal diplopia
- More than one?
- Consider MRI
UpToDate: Overview of diplopia
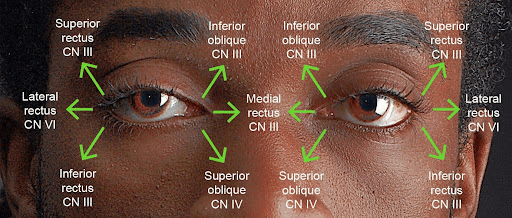
Eye Movement

Ptosis, Dilated Pupil
https://pressbooks.library.torontomu.ca/assessmentnursingmain/chapter/extraocular-eye-movement/
https://eyewiki.org/Congenital_Third_Nerve_Palsy
Internuclear Ophthalmoparesis
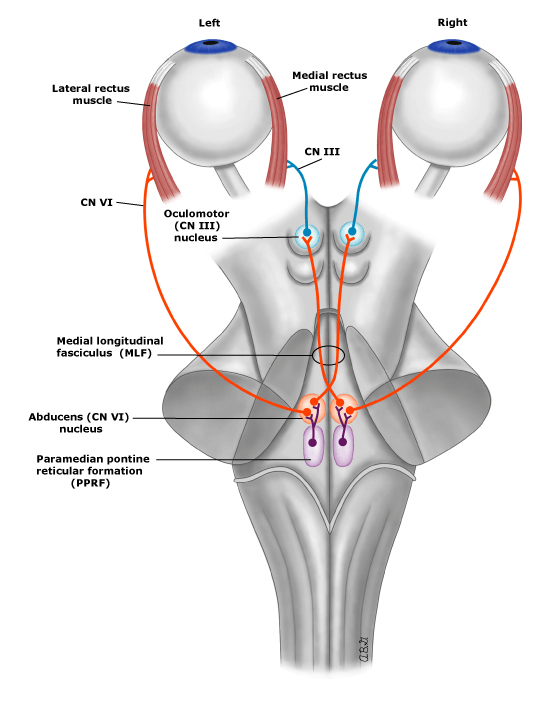
- Lesion of Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF)
- caused my multiple sclerosis, stroke, ...
-
Signs
- Adduction Weakness
- Abduction Nystagmus
- Normal Convergence
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ext-ijq-nr4
UpToDate: Internuclear ophthalmoparesis
Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
- Autoantibody against nAChR (usually)
- Fluctuating, fatigable weakness
-
Signs
-
Ptosis
- enhanced by sustained upgaze
-
Peek-a-boo sign
- or eye opened by examiner against forced eyelid closure
-
Ptosis
UpToDate: Ocular myasthenia gravis
Thyroid Ophthalmopathy
- Asscociated with Grave's disease
- Restricted extraocular eye movement
-
Signs
- Proptosis
- Conjunctival inflammation
- Periorbital edema
- Hyperthyroidism
UpToDate: Clinical features and diagnosis of thyroid eye disease

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graves%27_ophthalmopathy

refractive abnormalities
Butler, L., Yap, T. & Wright, M. The accuracy of the Edinburgh diplopia diagnostic algorithm. Eye 30, 812–816 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.44
myasthenia gravis: peek-a-boo sign / proptosis enhanceed by sustained upgaze
Q(A)/Discsussions


要怎麼處理?
- 傾聽
- 表達同理
- 解釋清楚
- 轉診
Slide from Dr.廖士程
解釋清楚?
- Monocular/Binocular Diplopia
- Incidence

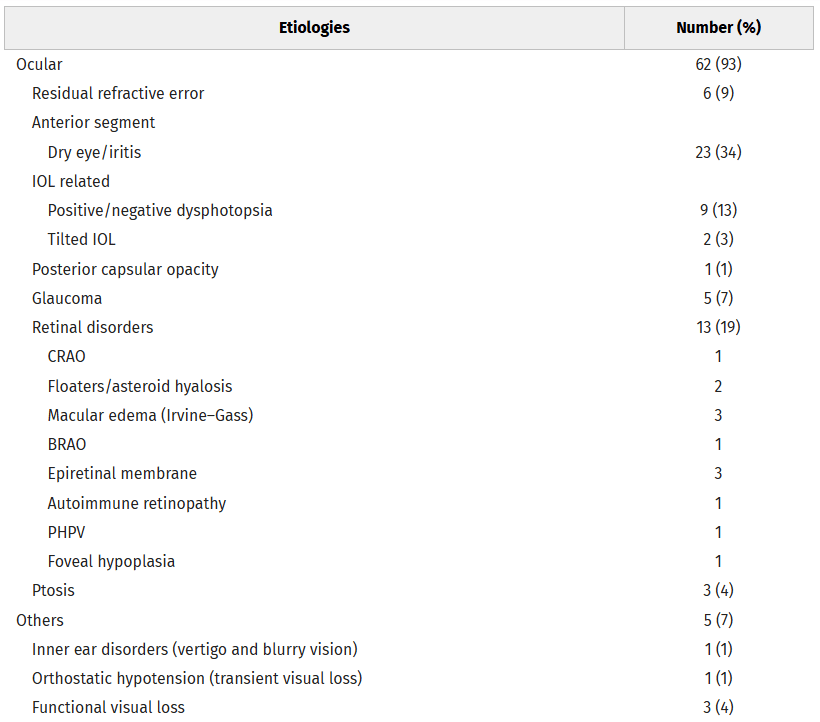
Lin, Shuai-Chun MD; Giang, Angie BS; Liu, Grant T. MD; Avery, Robert A. DO; Shindler, Kenneth S. MD; Hamedani, Ali G. MD, MHS; Ross, Ahmara G. MD, PhD; Tamhankar, Madhura A. MD. Frequency and Etiologies of Visual Disturbance After Cataract Surgery Identified in Neuro-Ophthalmology Clinics. Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology 43(3):p 359-363, September 2023. | DOI: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001792
n = 173
Q(A)/Discsussions
Skin Lesions

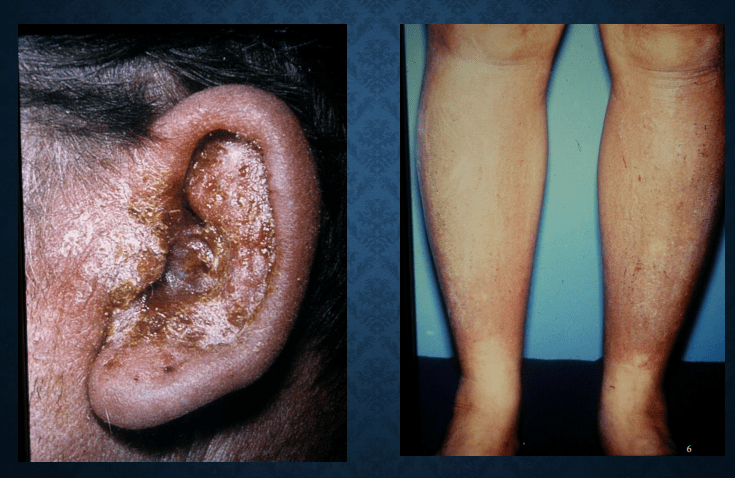
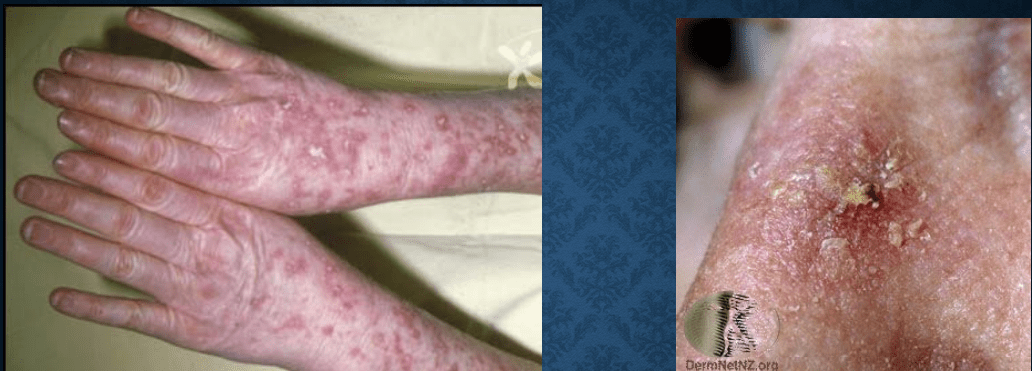
Eczema
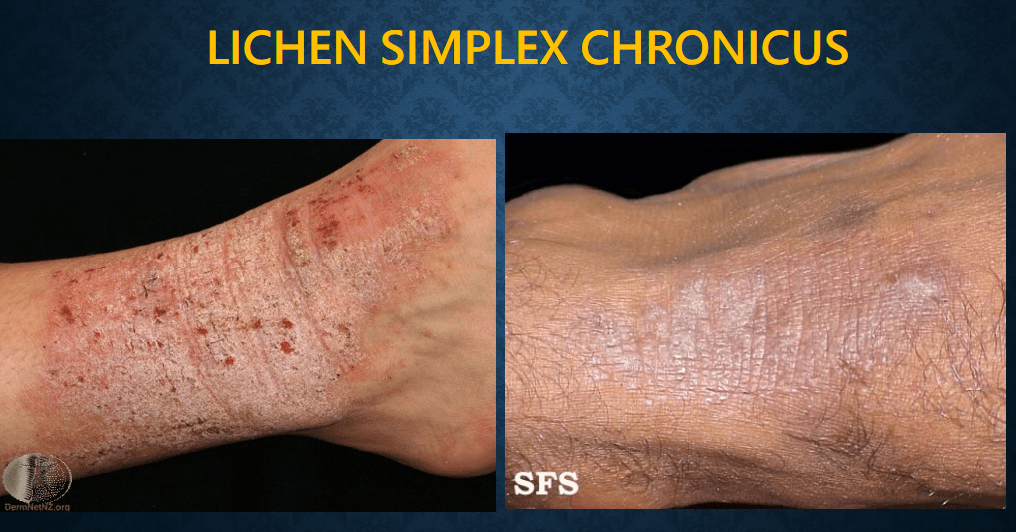
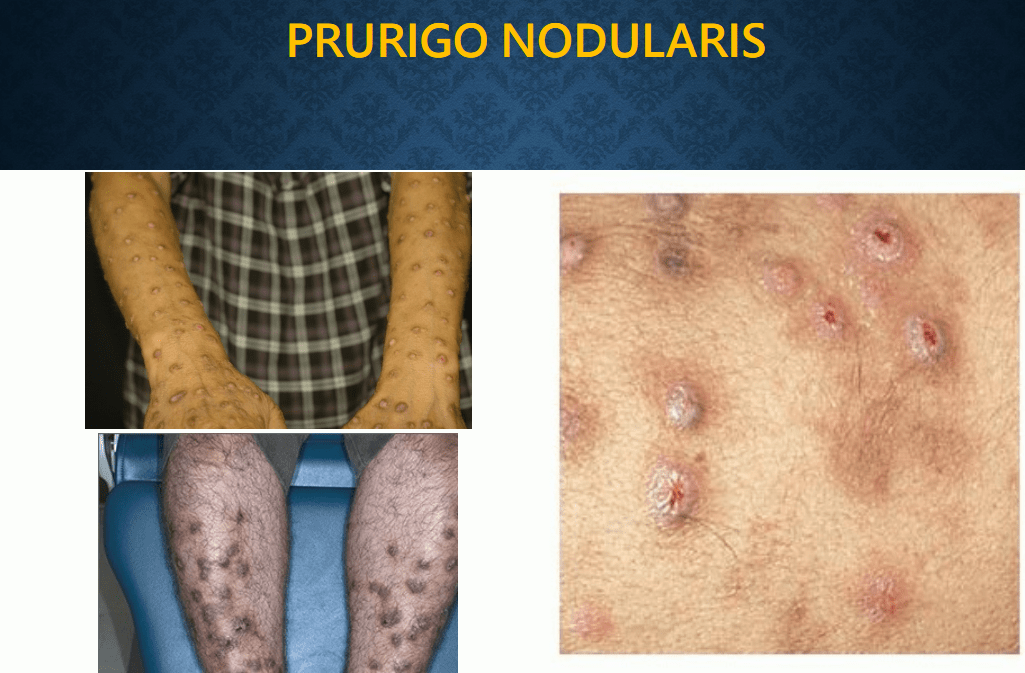
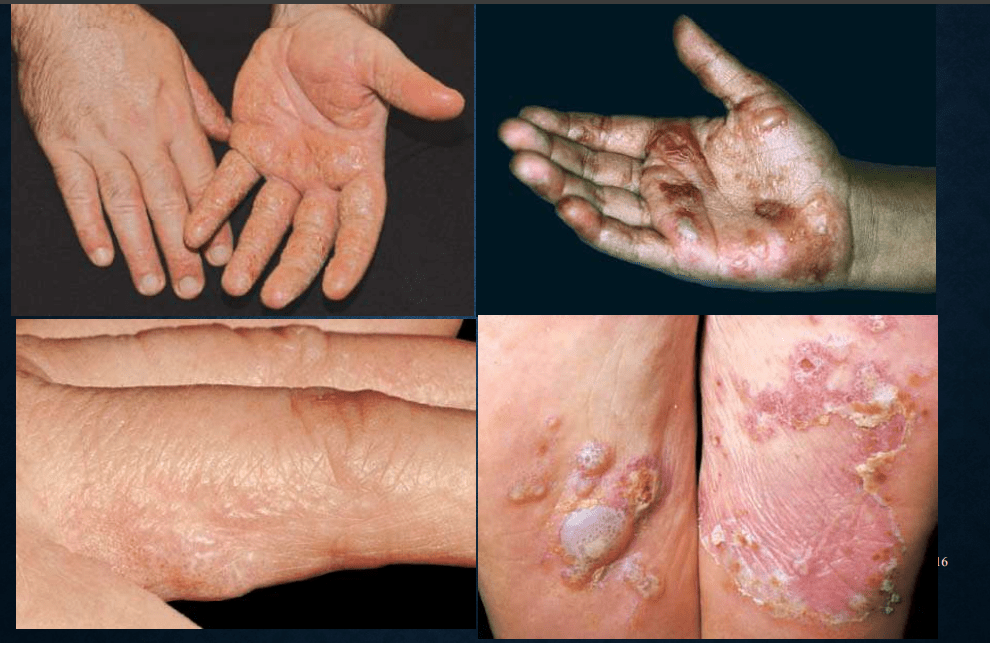
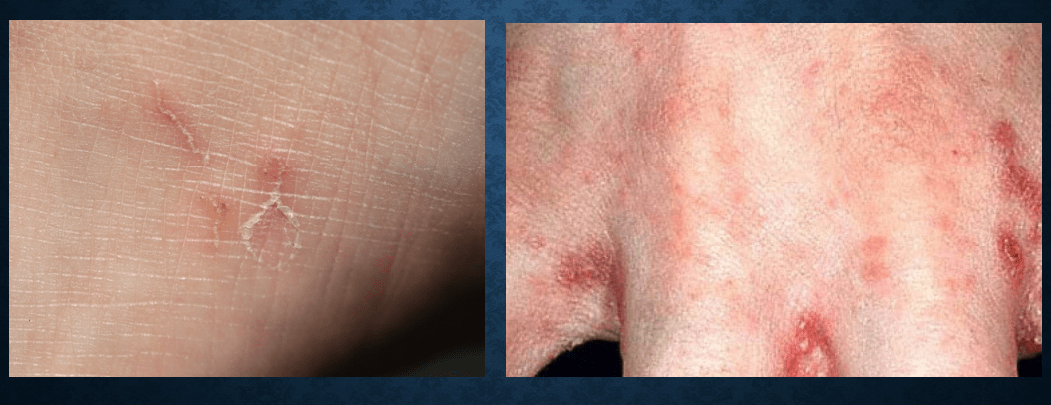
pompholyx
Scabies
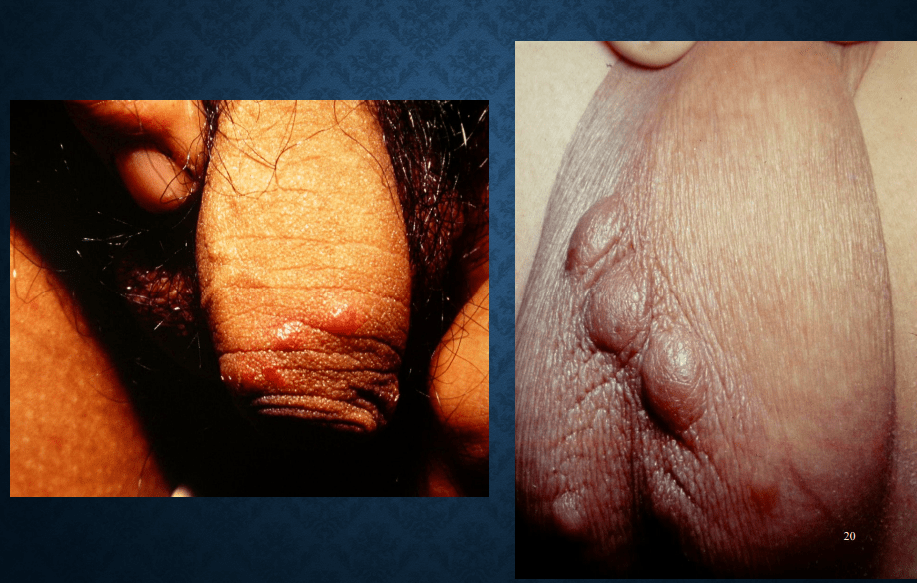
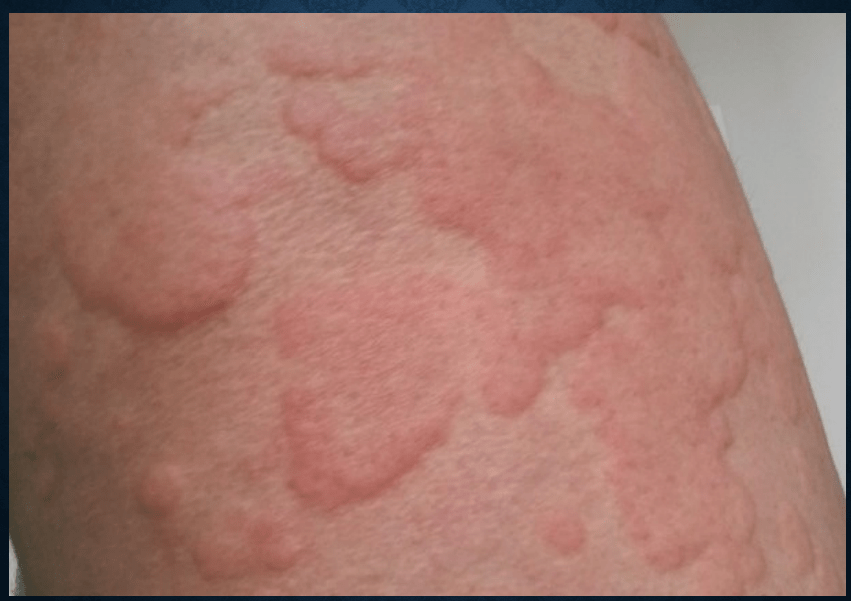
urticaria
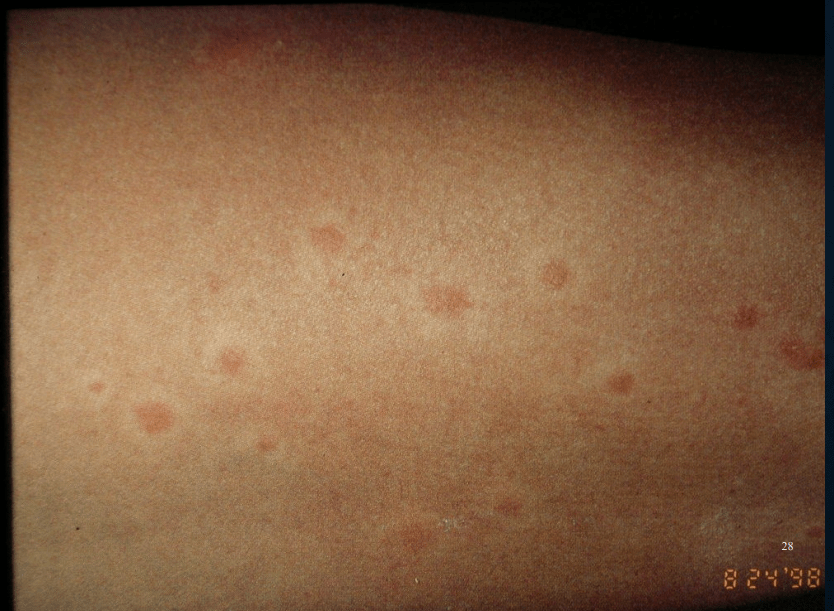
Lichen Urticatus
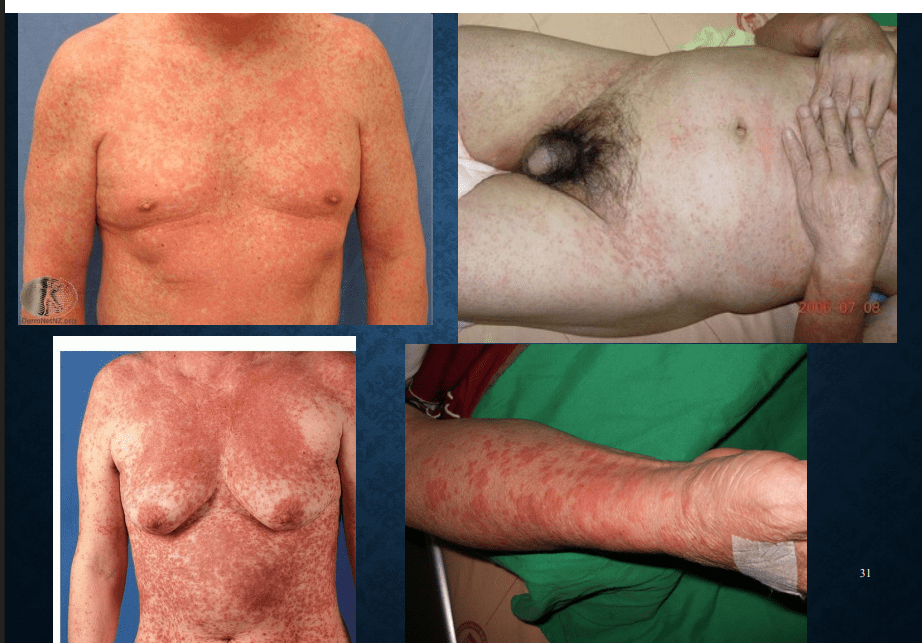
Toxic erythema

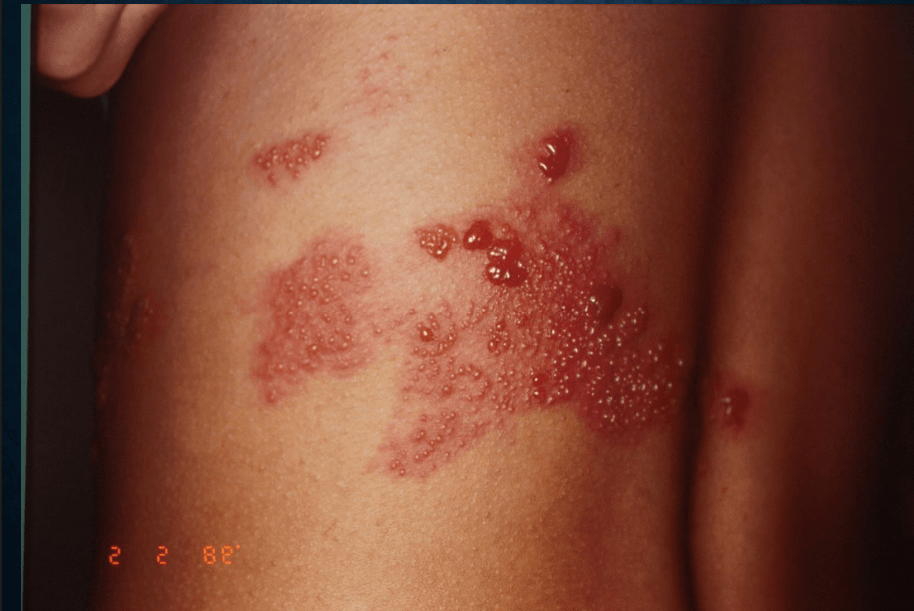
Herpes zoster: Hutchinson's sign
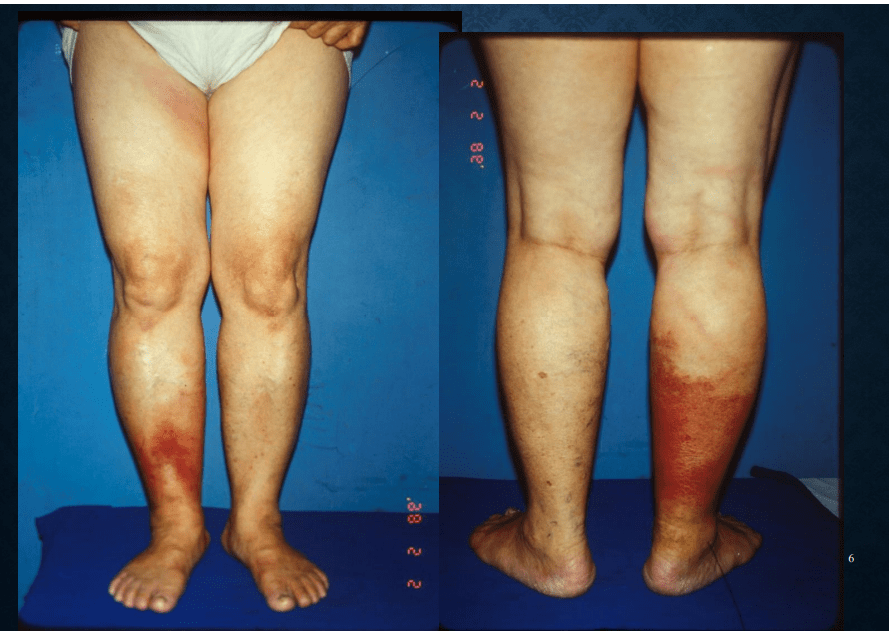
cellulitis
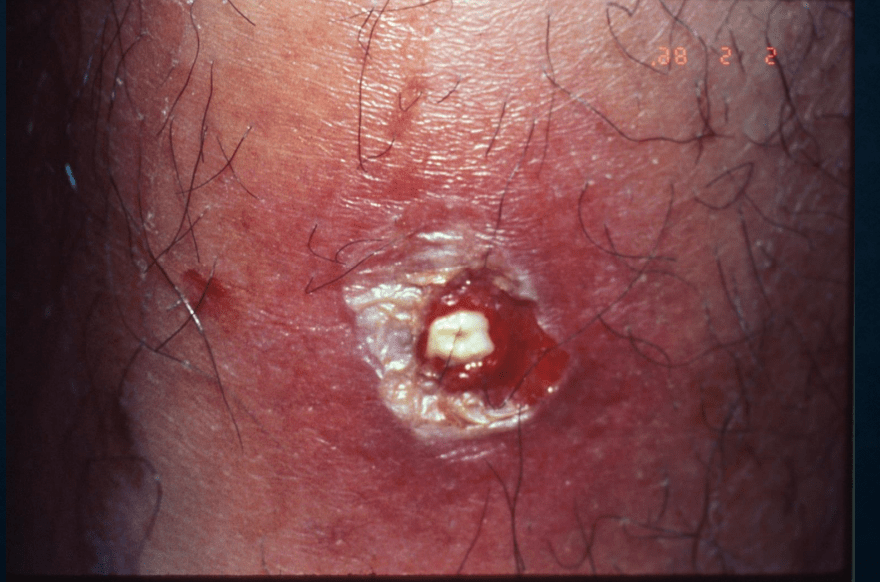
furunculosis
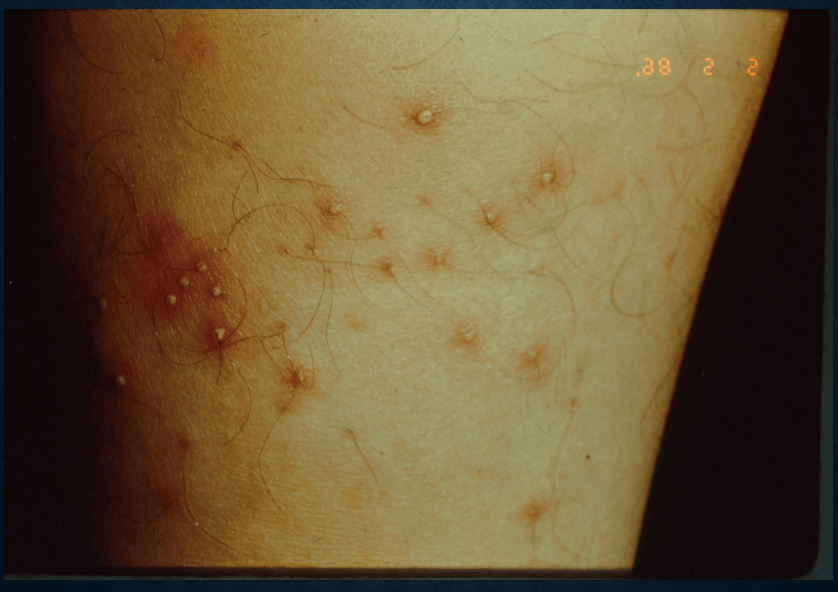
folliculitis
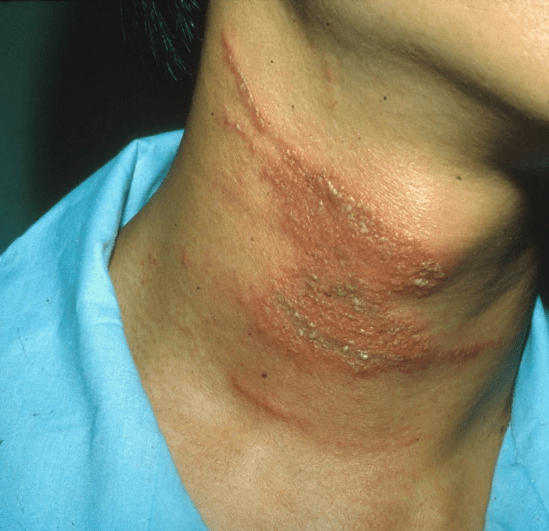
paederus dermatitis
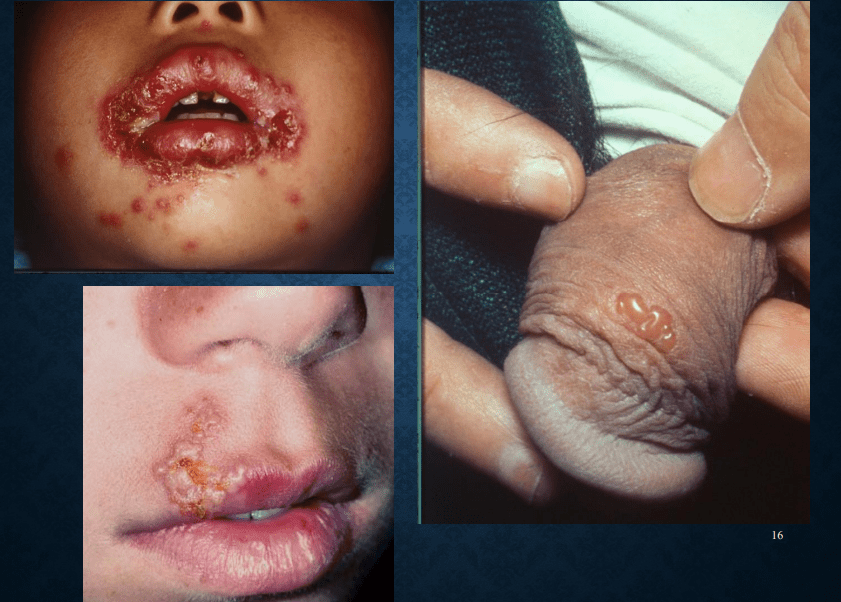
Herpes simplex
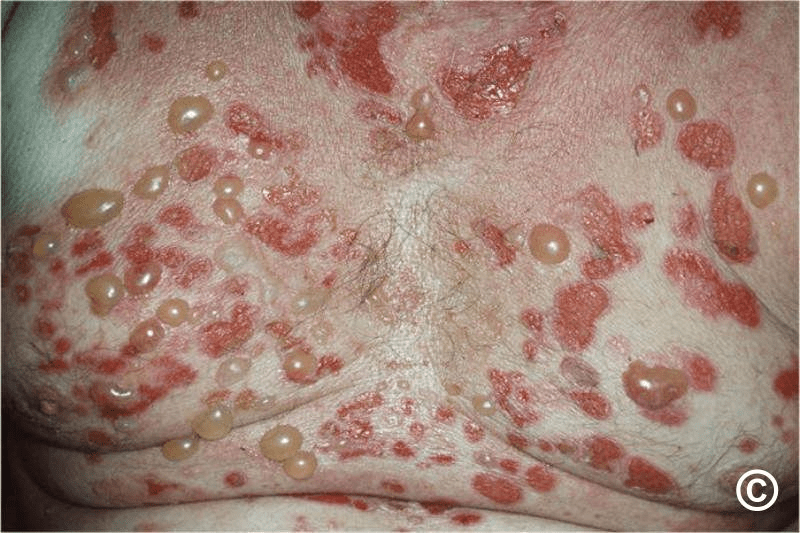
bullous pemphigoid: Nikolsky's sign
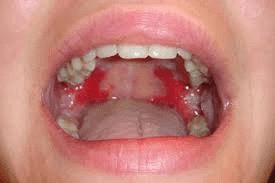
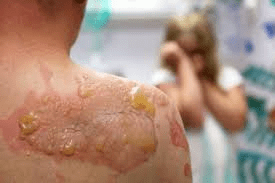
pemphigus vulgaris

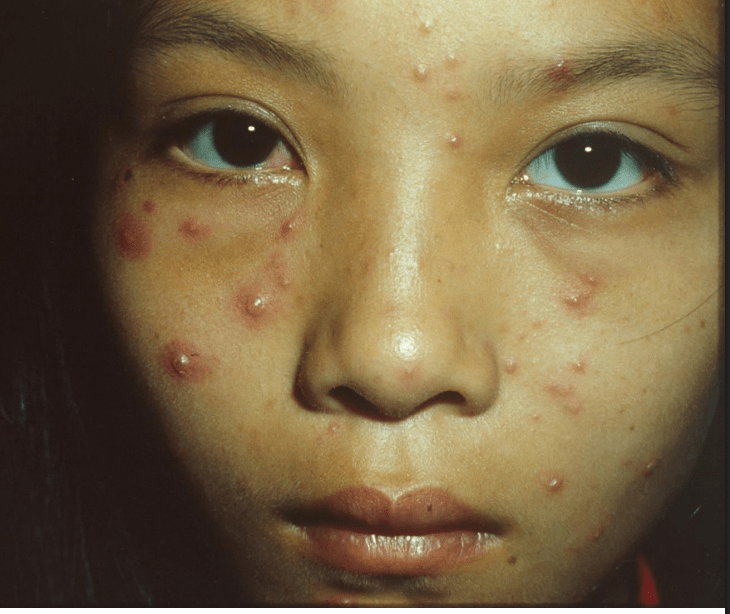
varicella
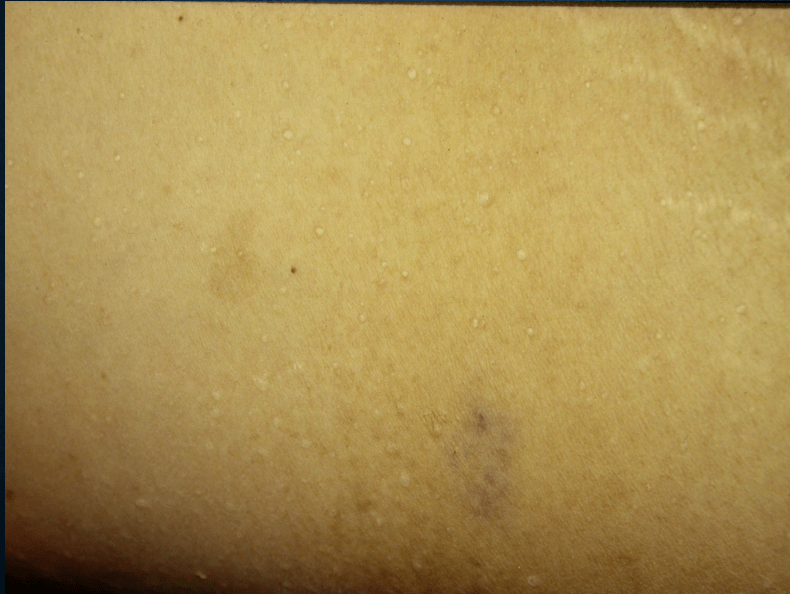
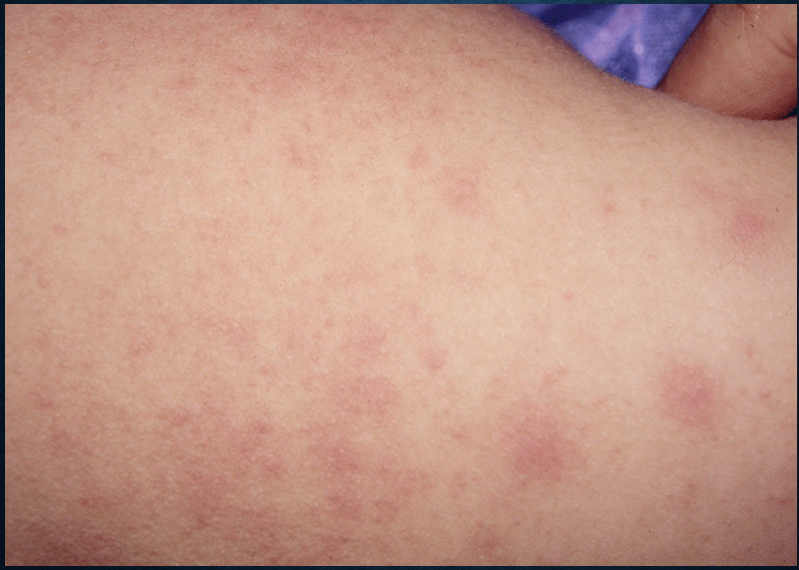
miliaria
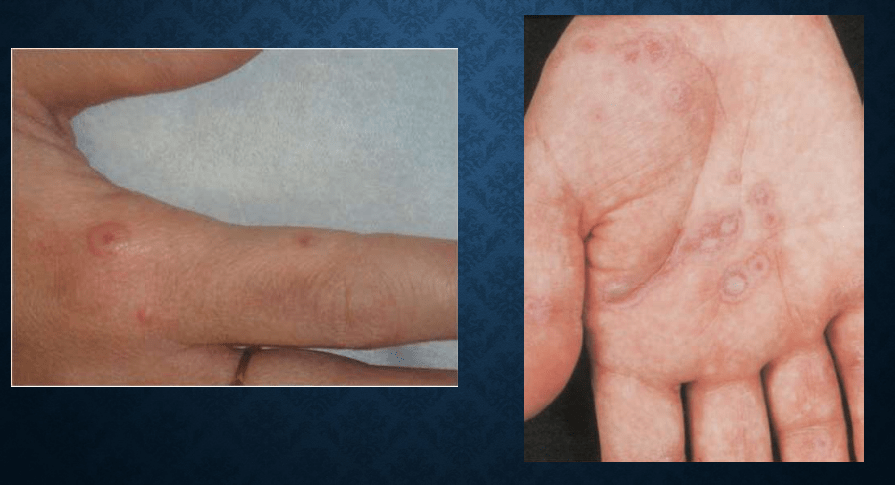
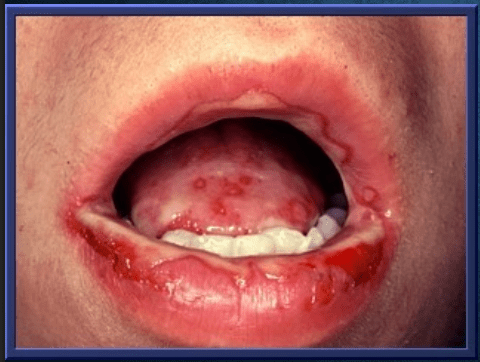
Erythema multiforme
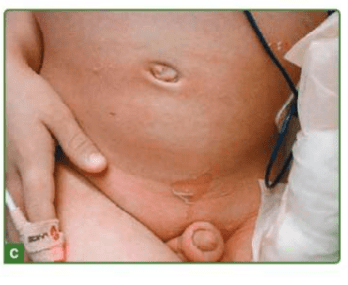
staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
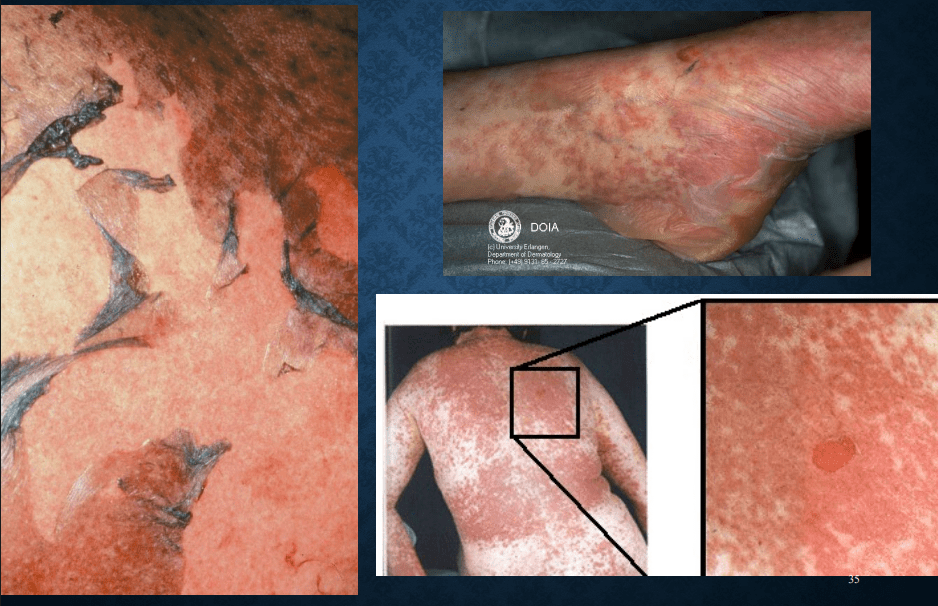
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
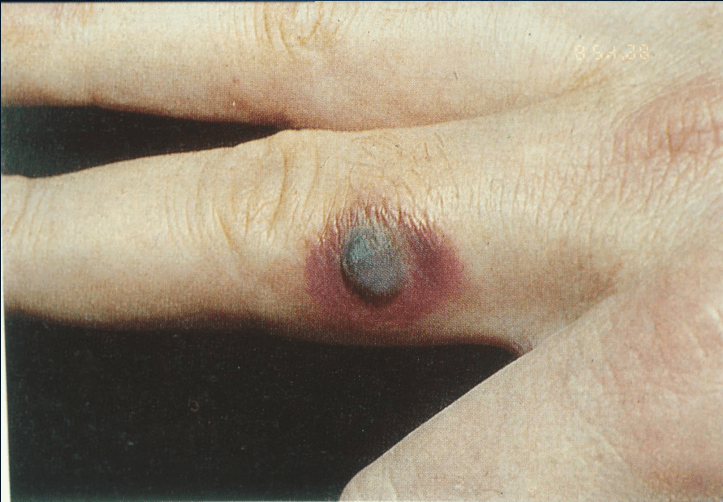
Fixed drug eruption
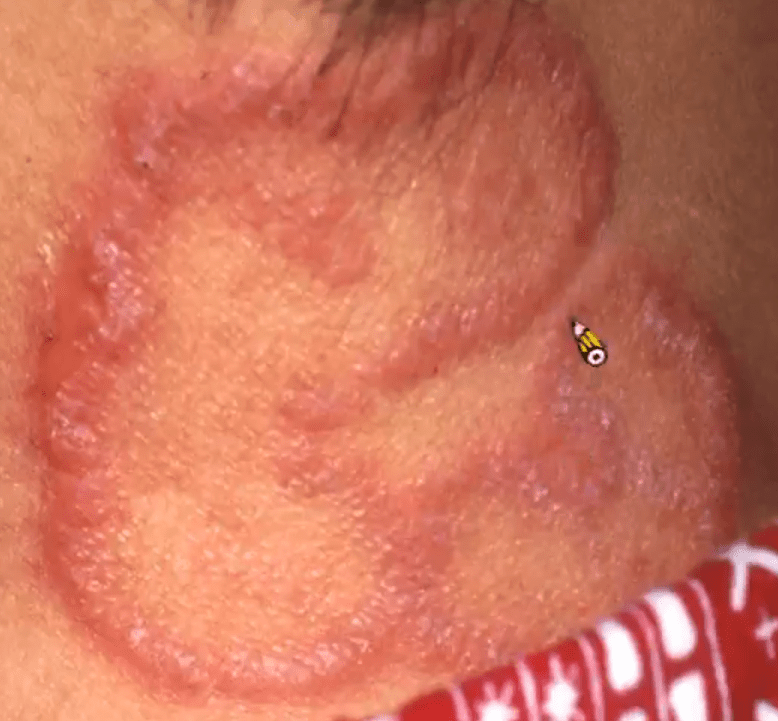
Tinea corporis
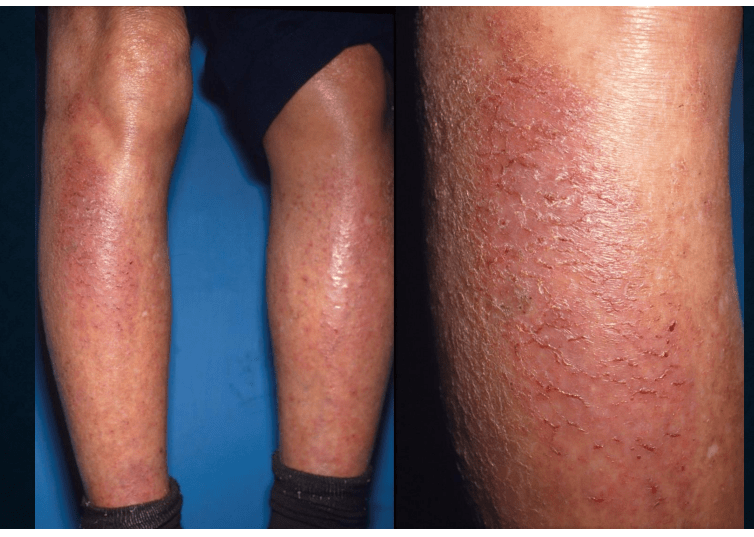
asteatotic dermatitis
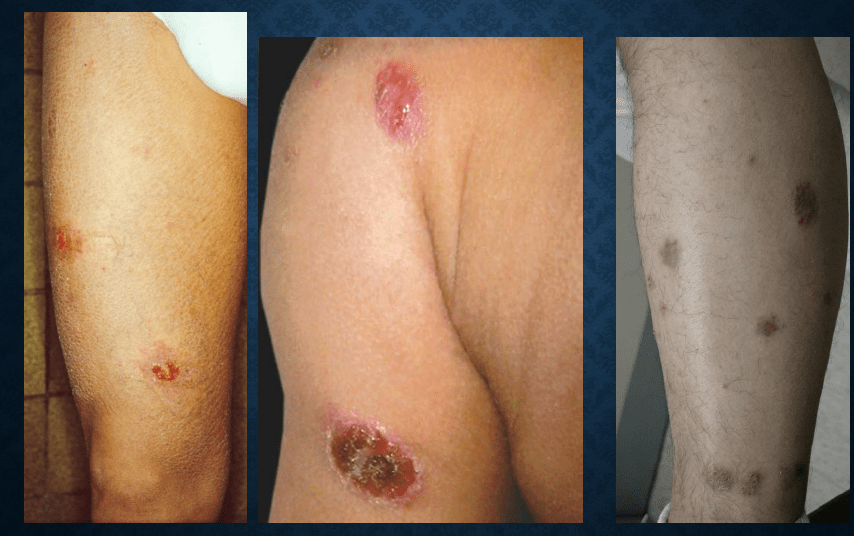
nummular eczema
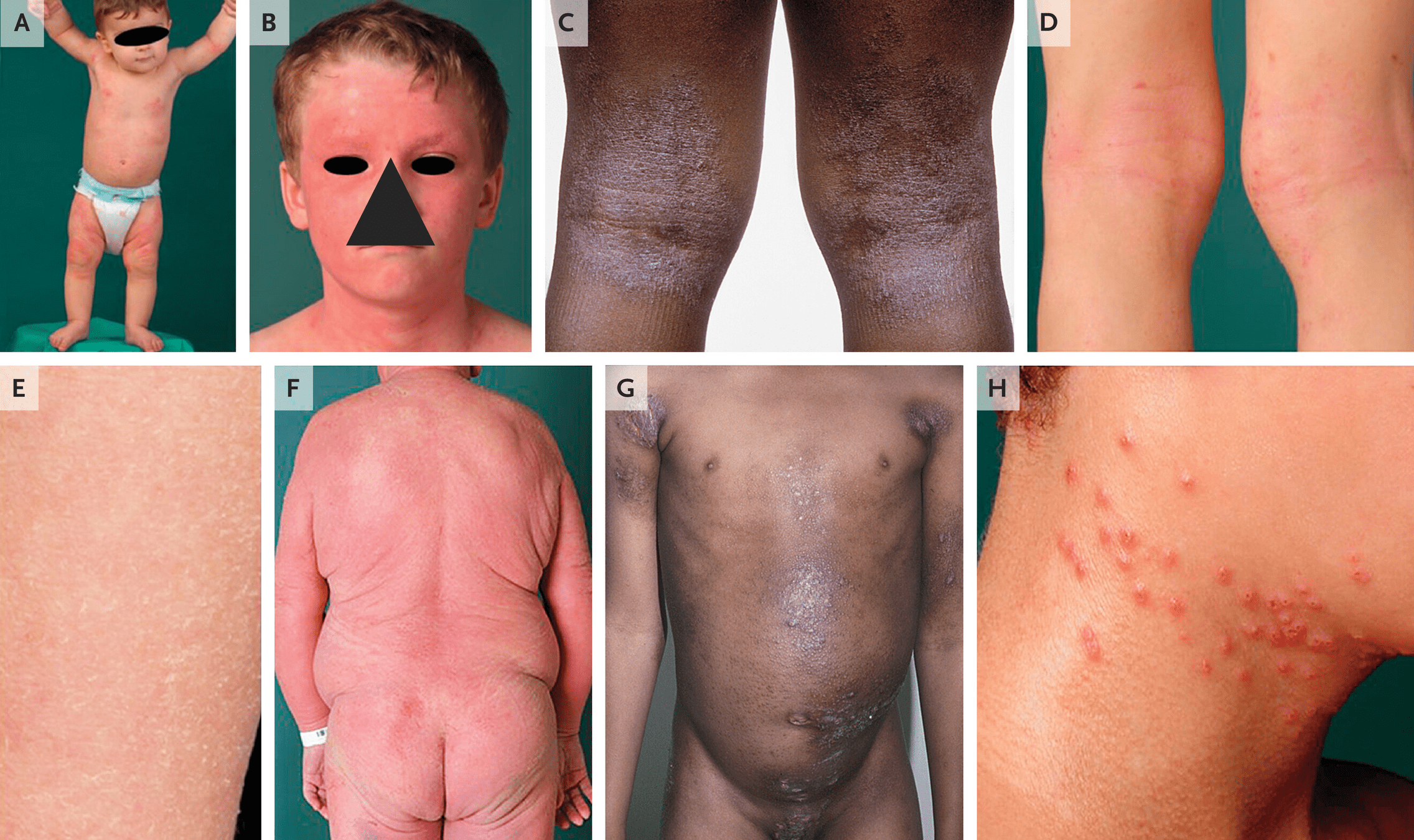
atopic dermatitis
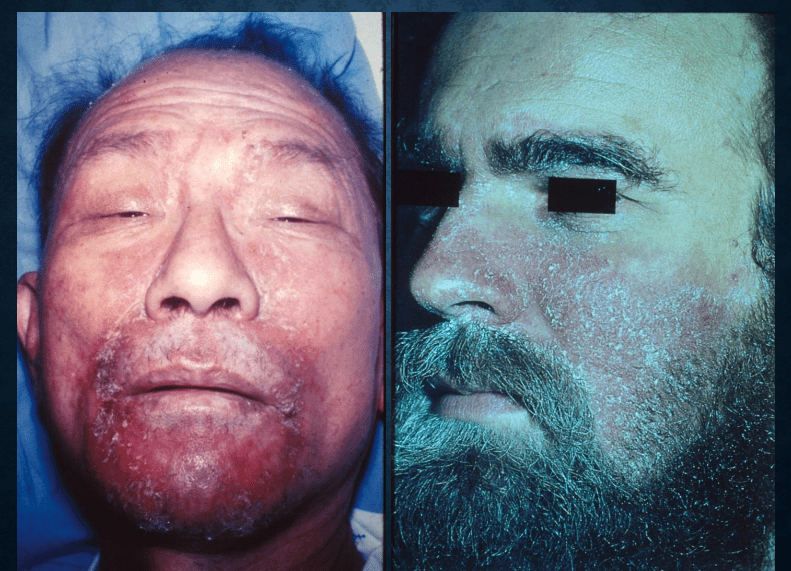

Seborrheic dermatitis
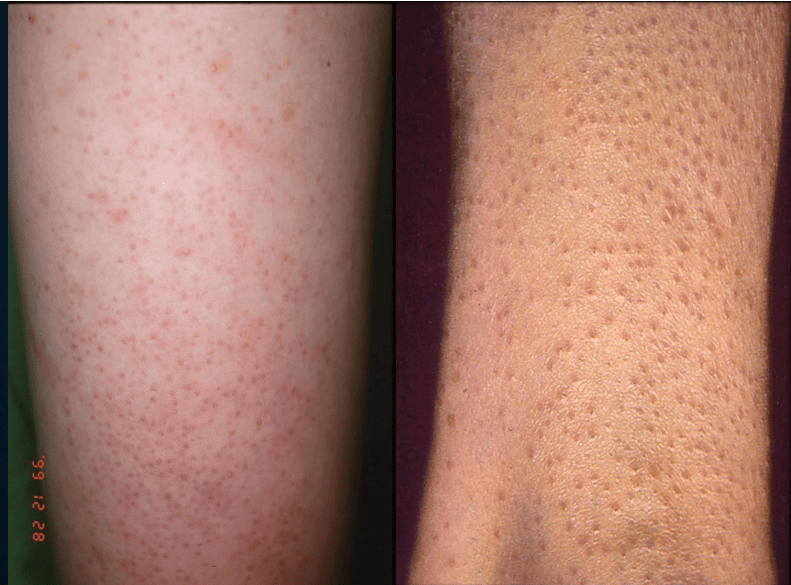
keratosis pilaris

tinea versicolor

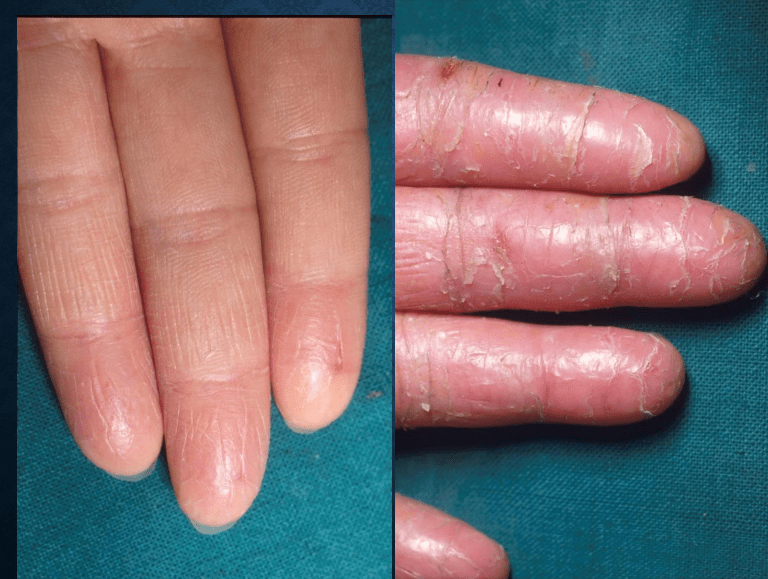
KTPP
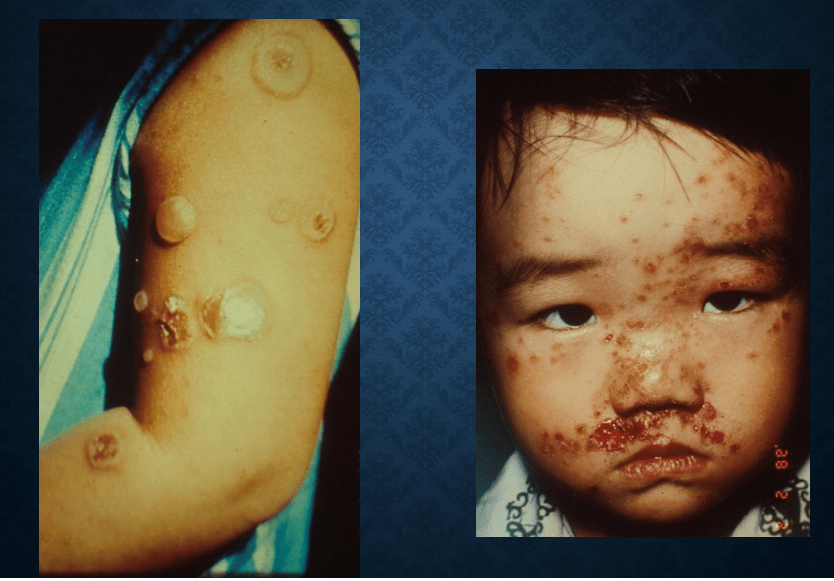
impetigo bullosa/contagiosa
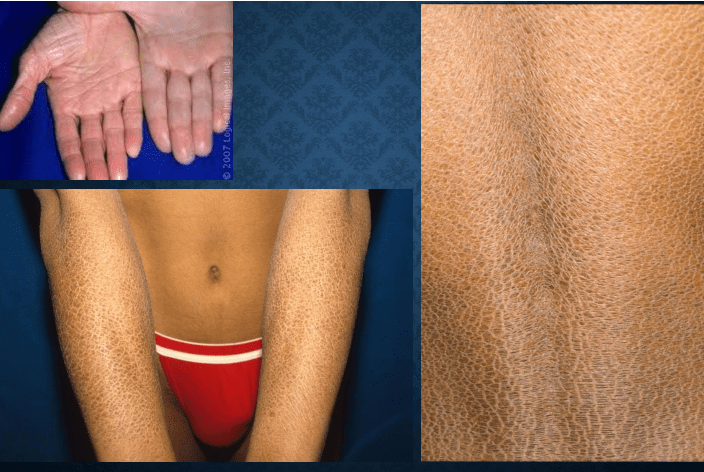
icthyosis vulgaris
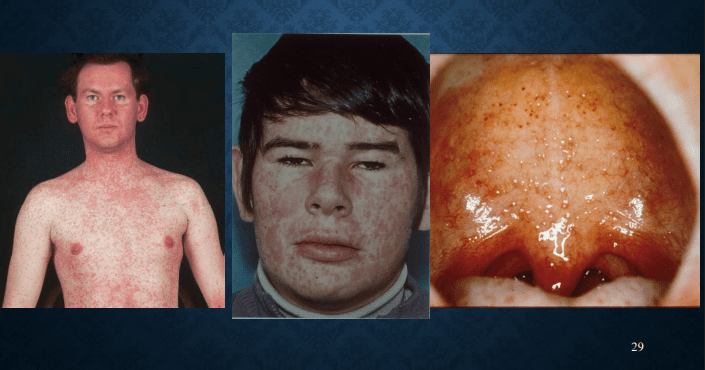
measles: Koplik's spot, 3C (cough, coryza, conjunctivitis)
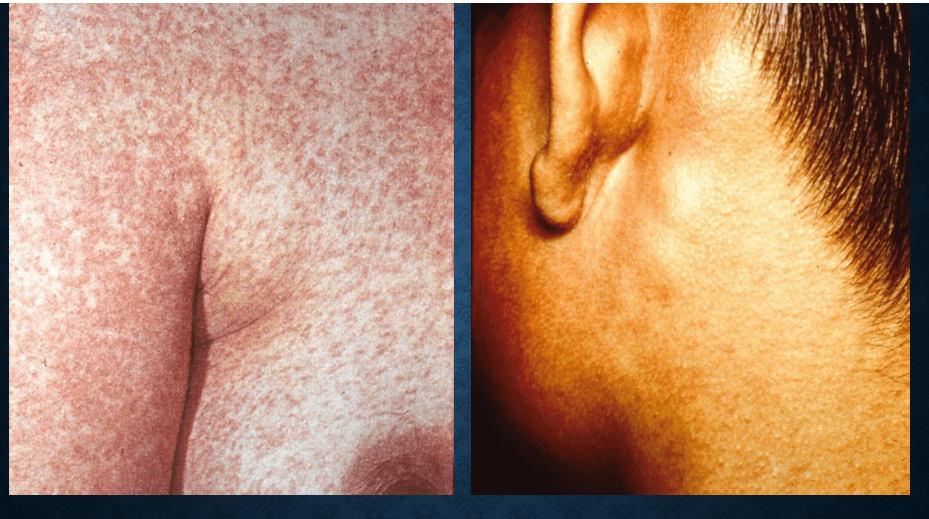
Rubella: Forcheiner's sign
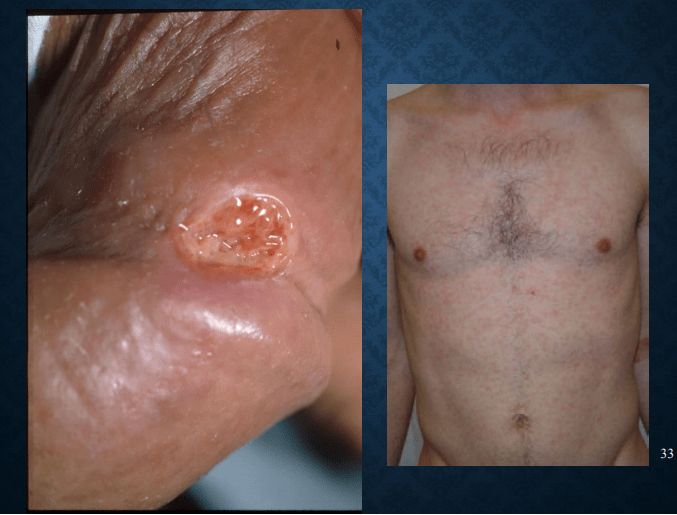
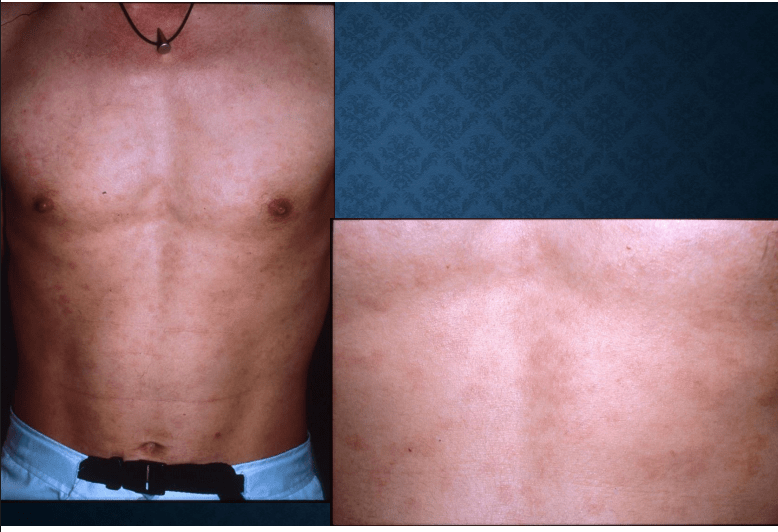
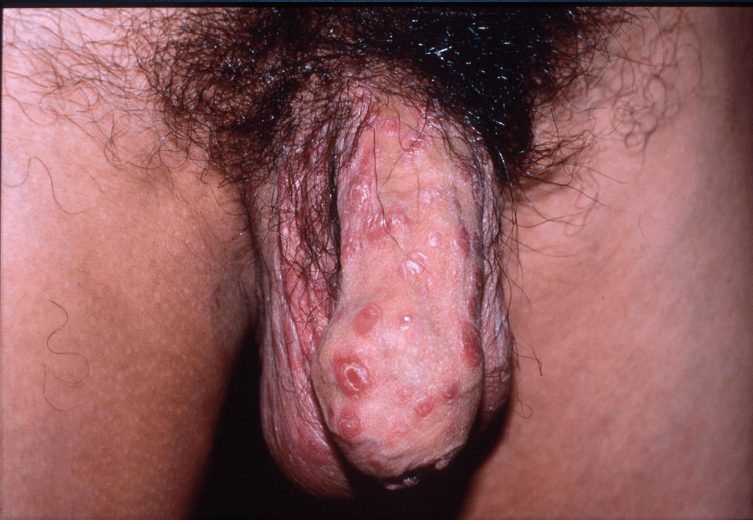
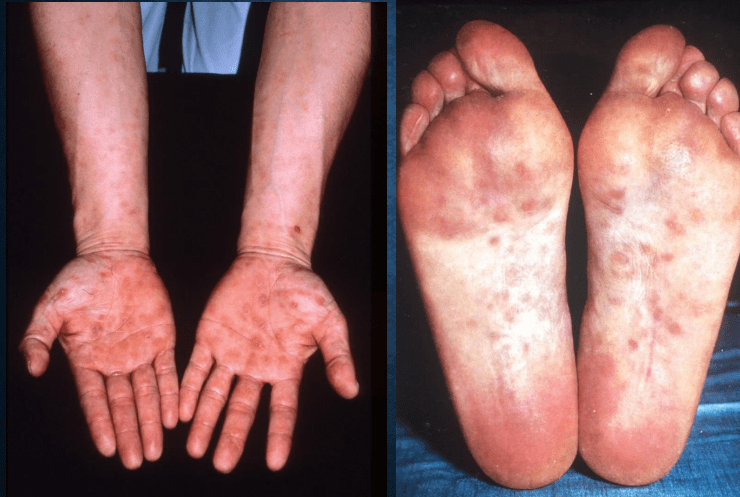
syphilis
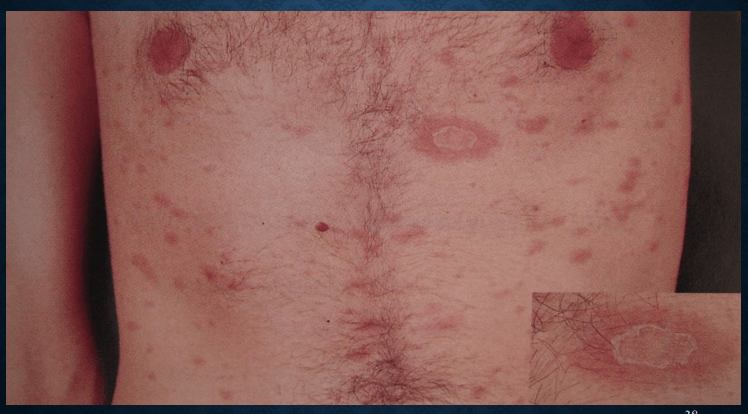
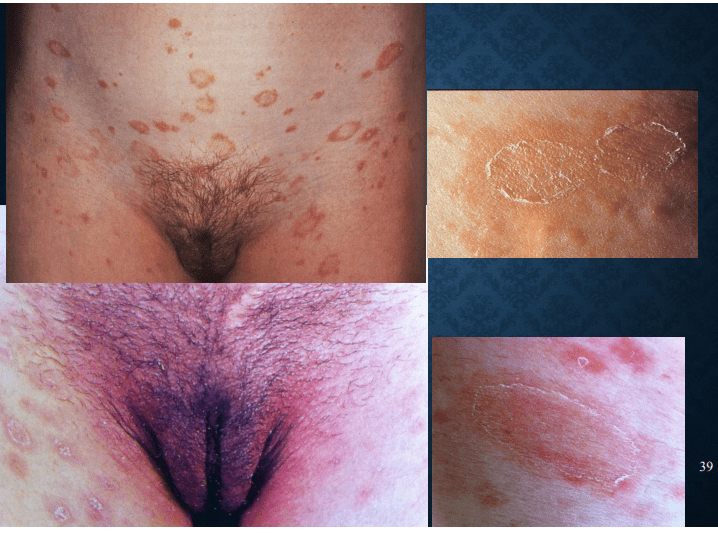
pityriasis rosea

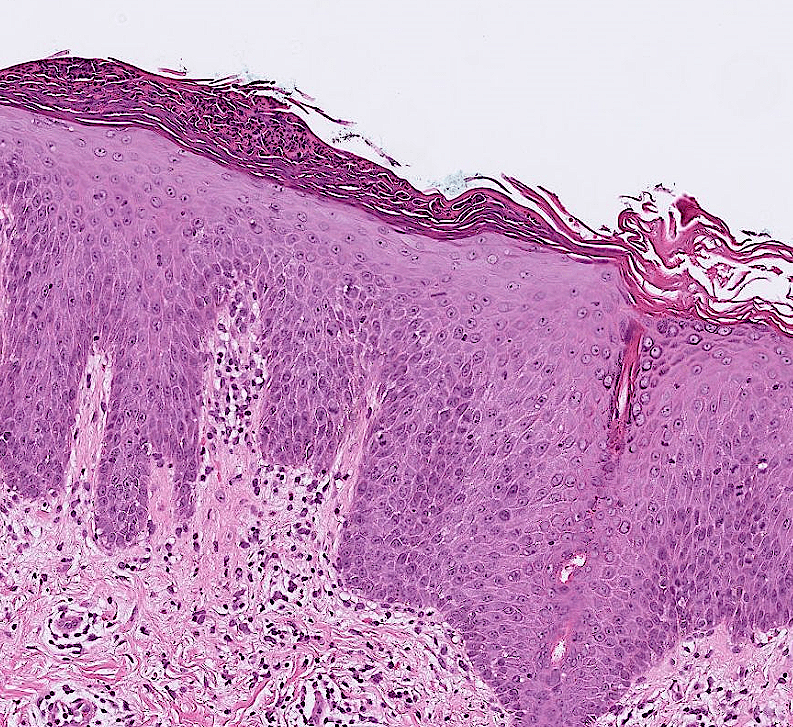
psoriasis vulgaris: auspitz sign
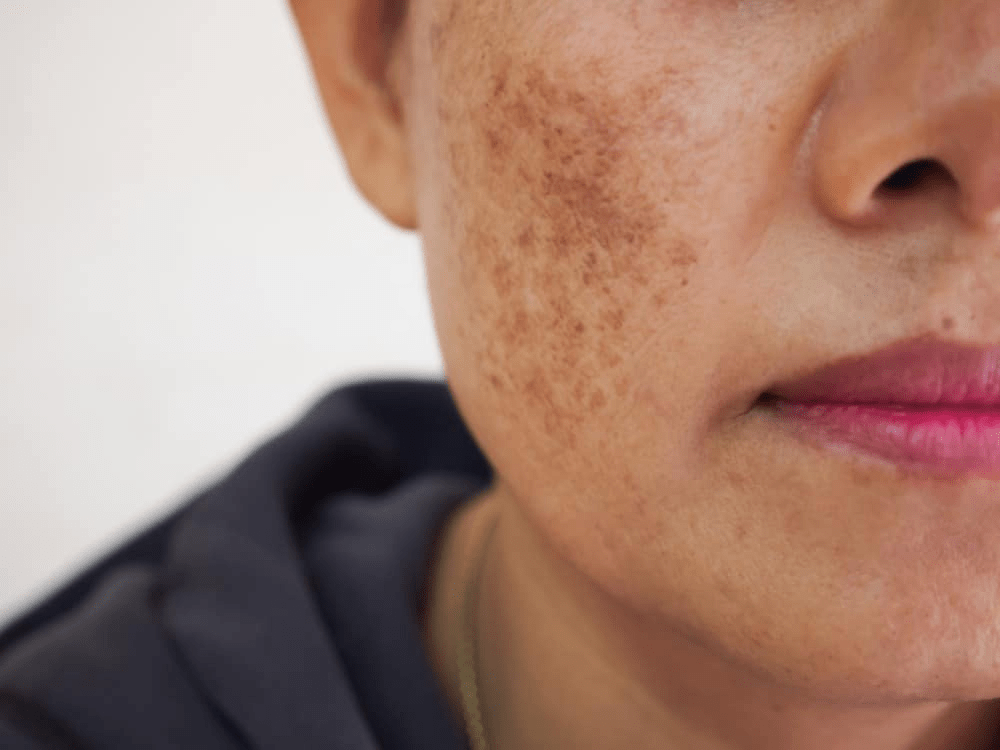
melasma
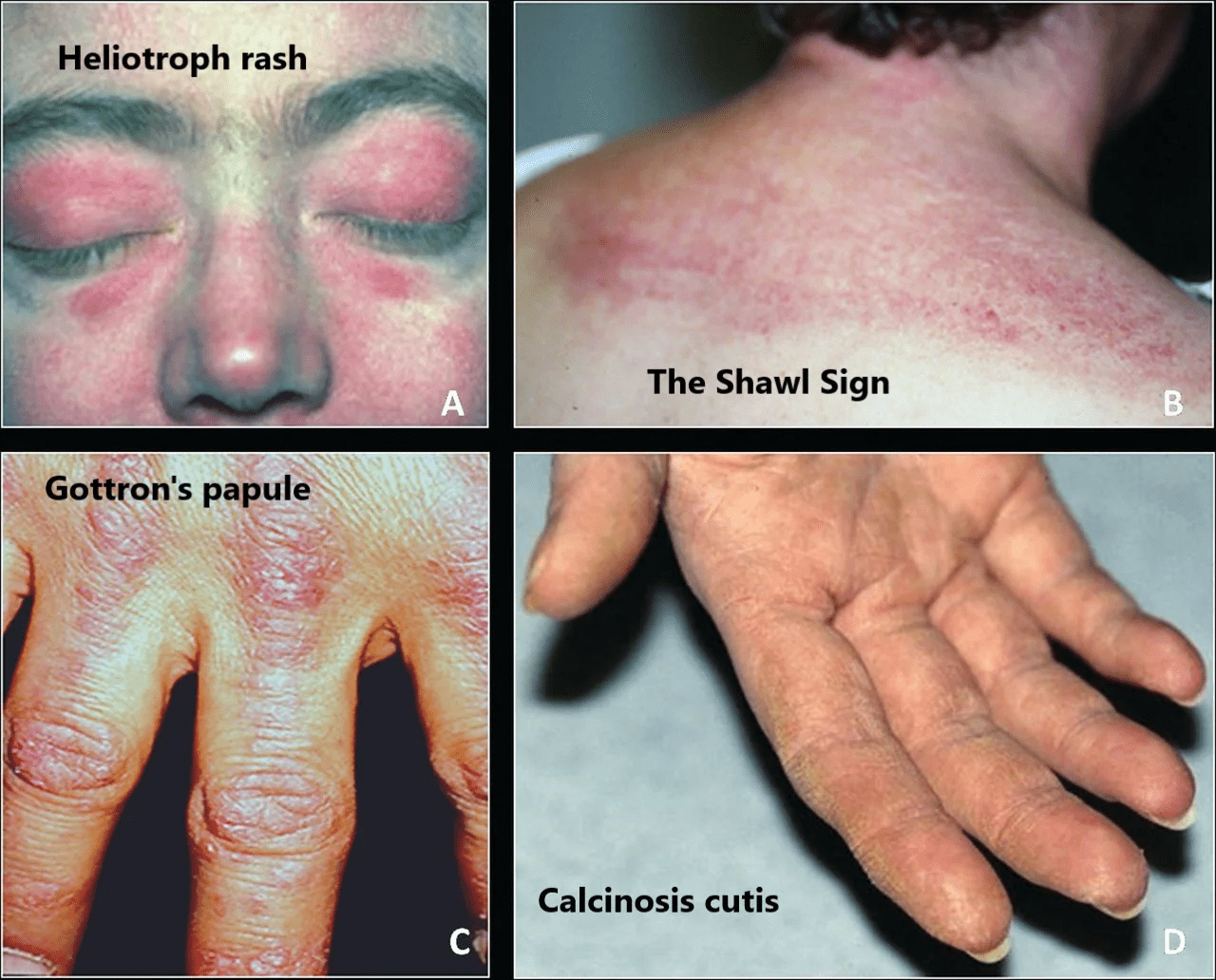
dermatomyositis: v-sign (胸前)
e
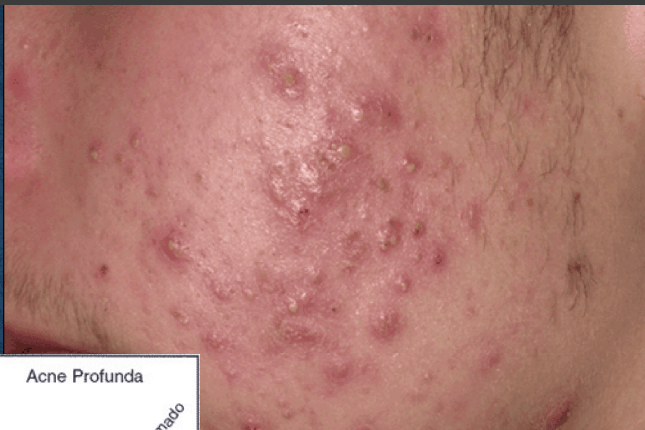
acne
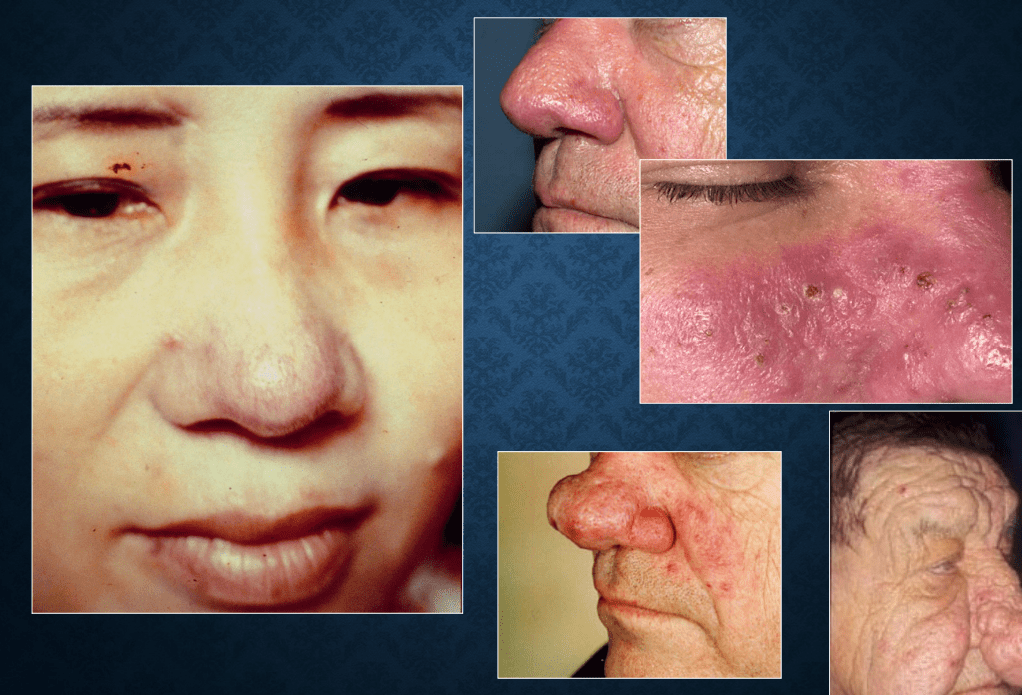
rosacea
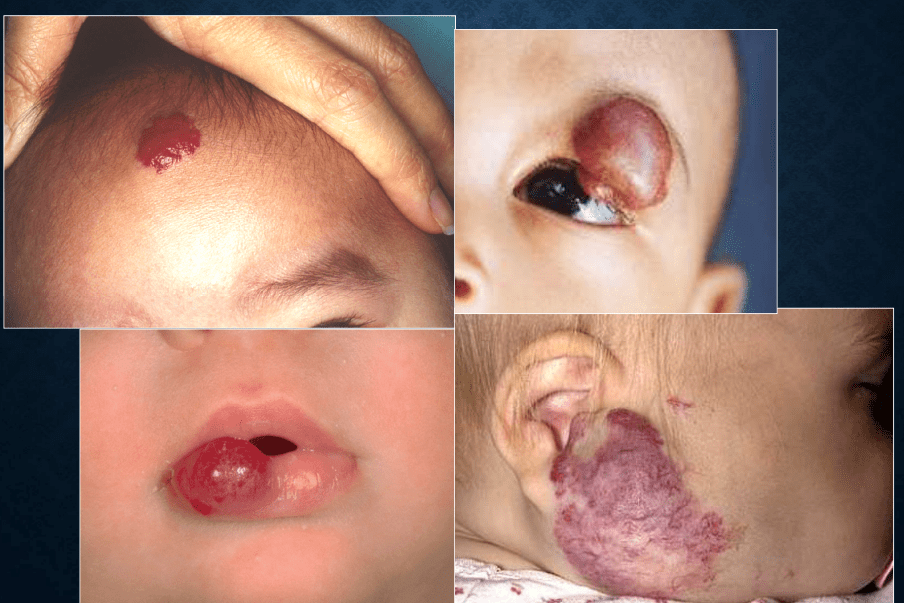
infantile hemangioma
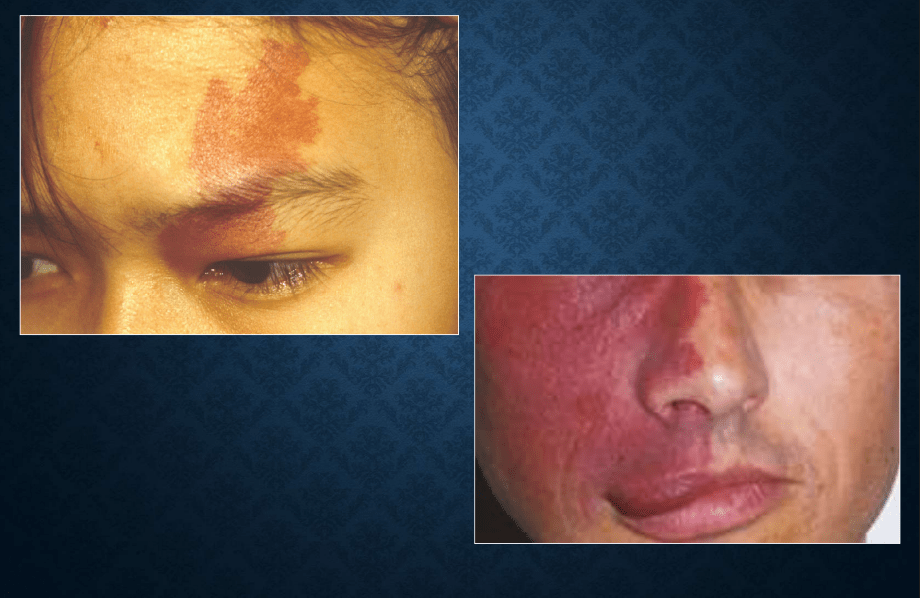
port-wine stain
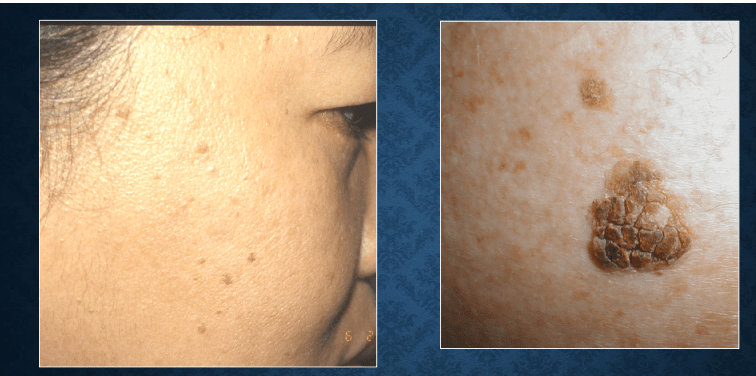
seborrheic keratosis: Leser-Trélat sign
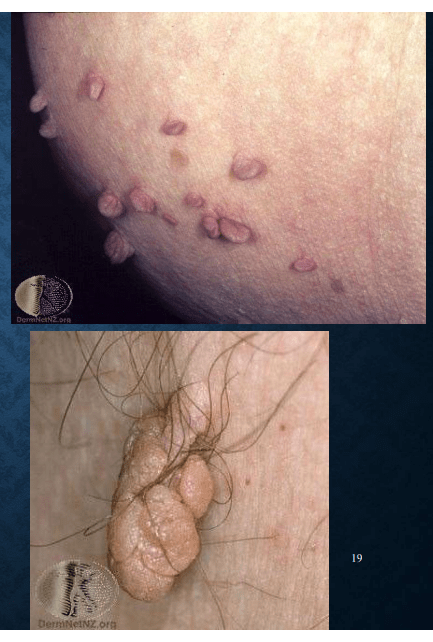
skin tag
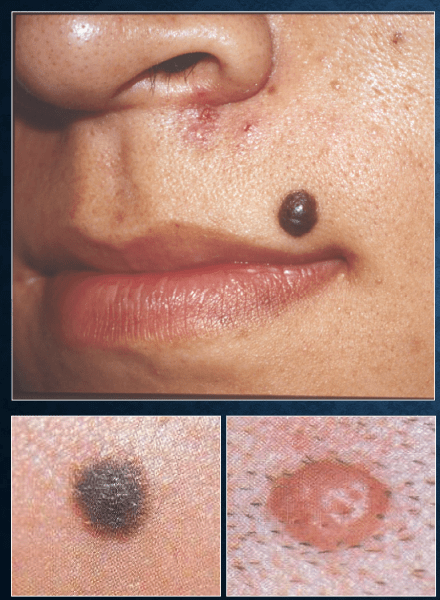
nevocellular nevus
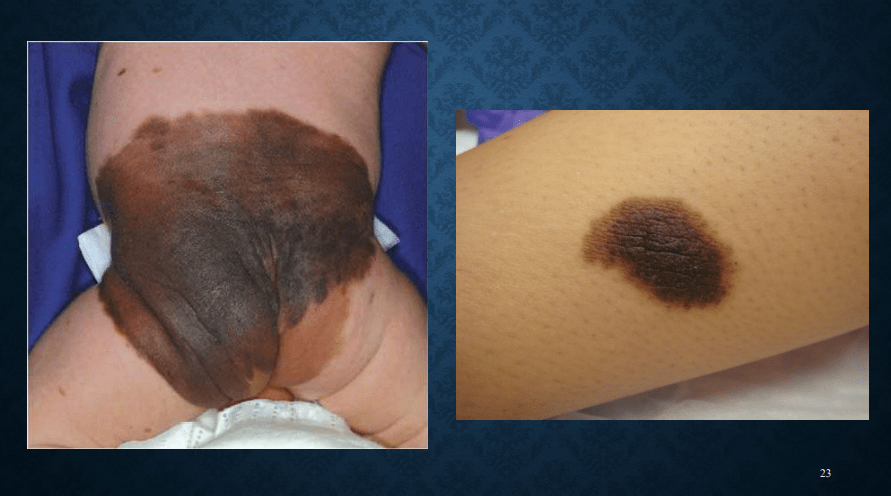
congenital nevomelanocytic nevus
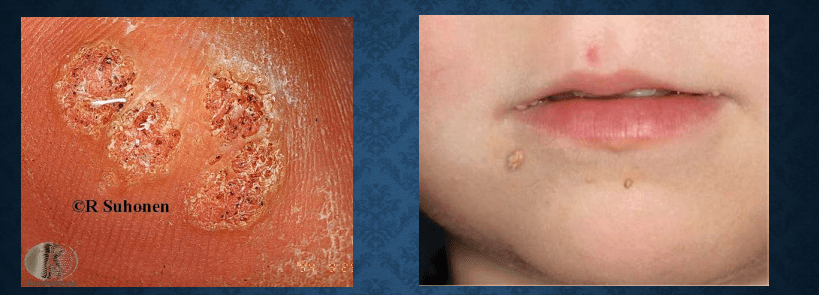
verruca vulgaris
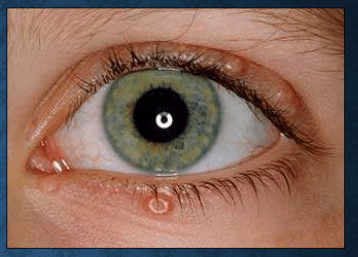
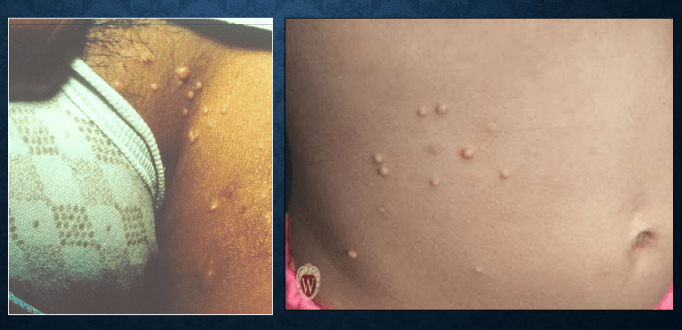
molluscum contagiosum
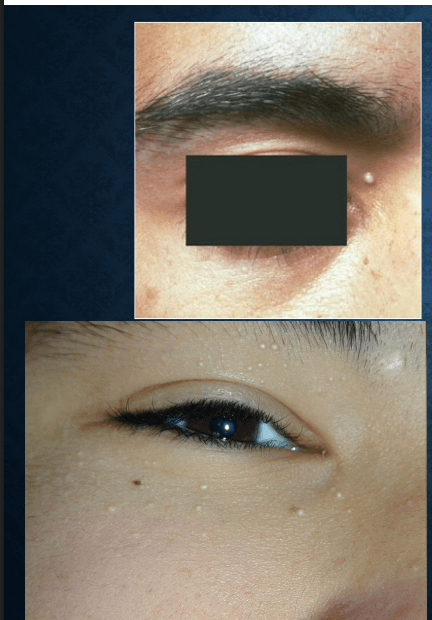
milia
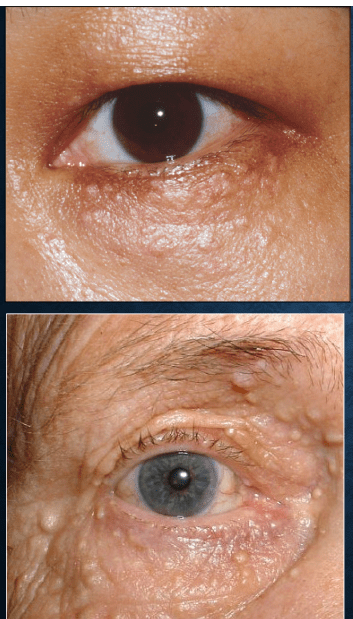
syringoma
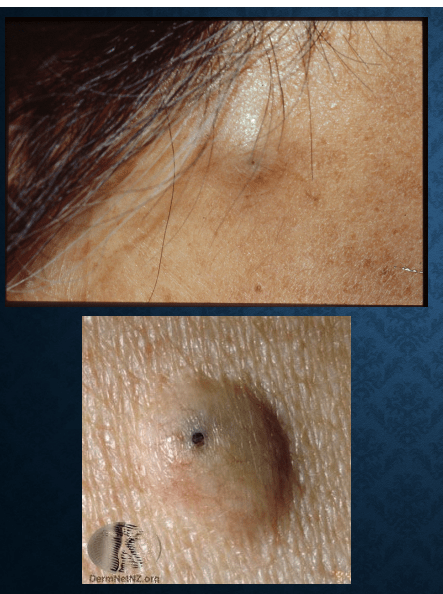
epidermal cyst
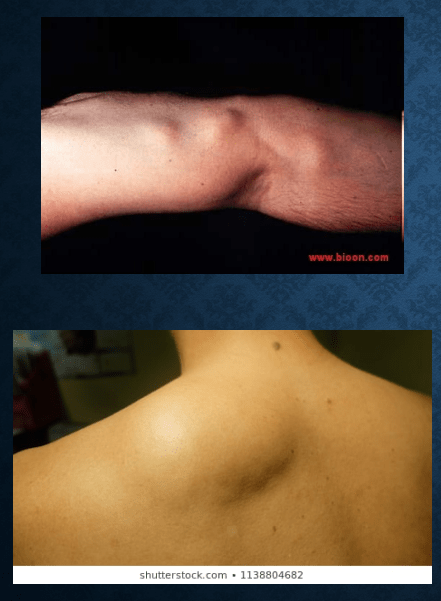
lipoma
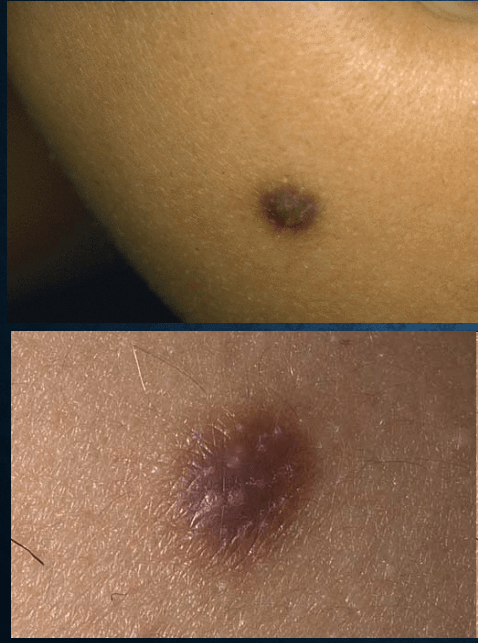
dermatofibroma
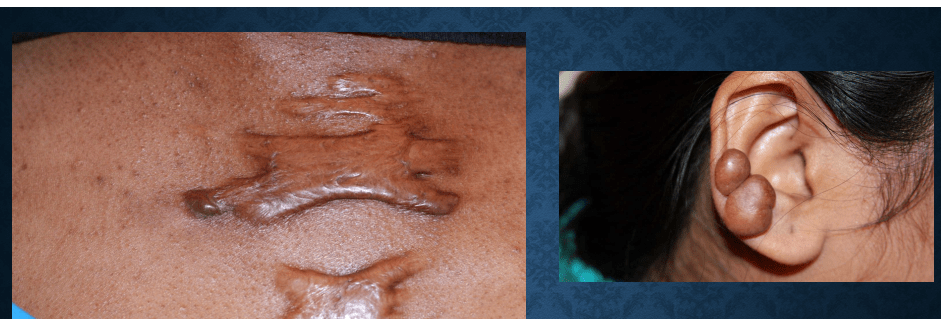
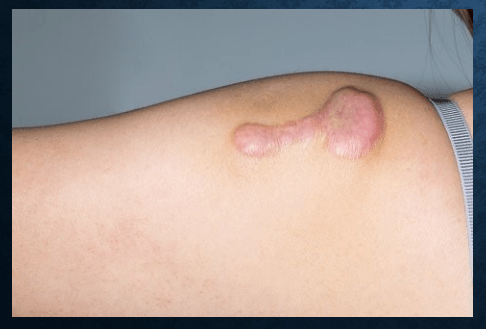
keloid
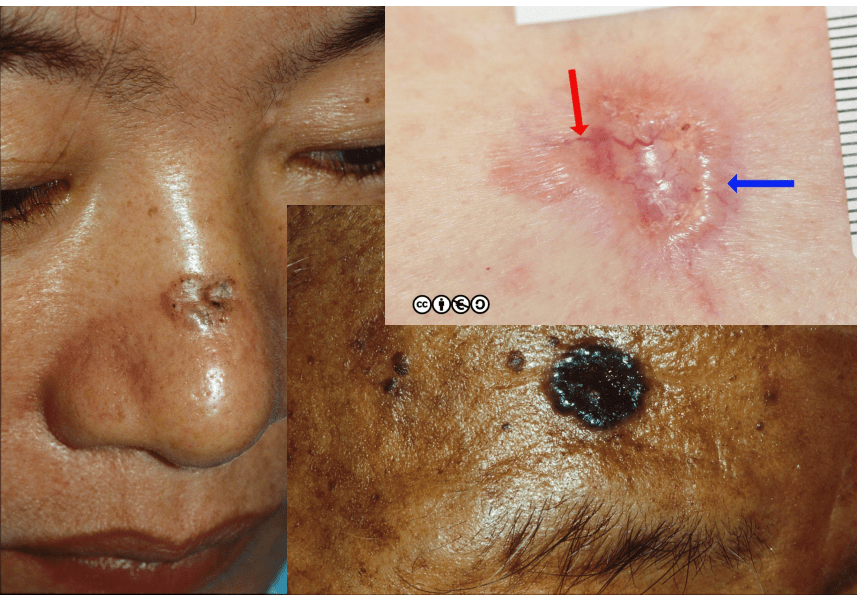
basal cell carcinoma
actinic keratosis
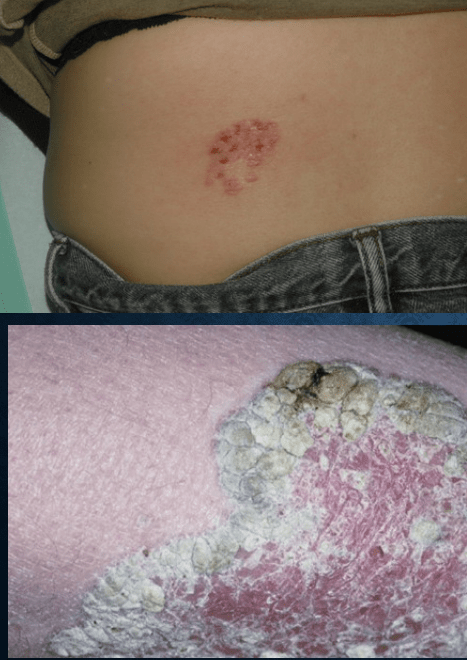
Bowen's disease
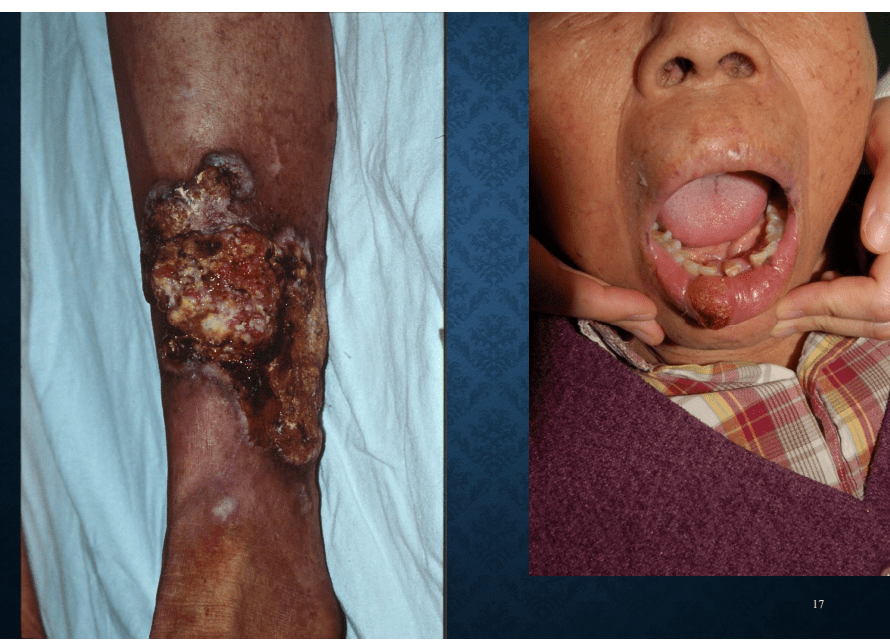
squamous cell carcinoma
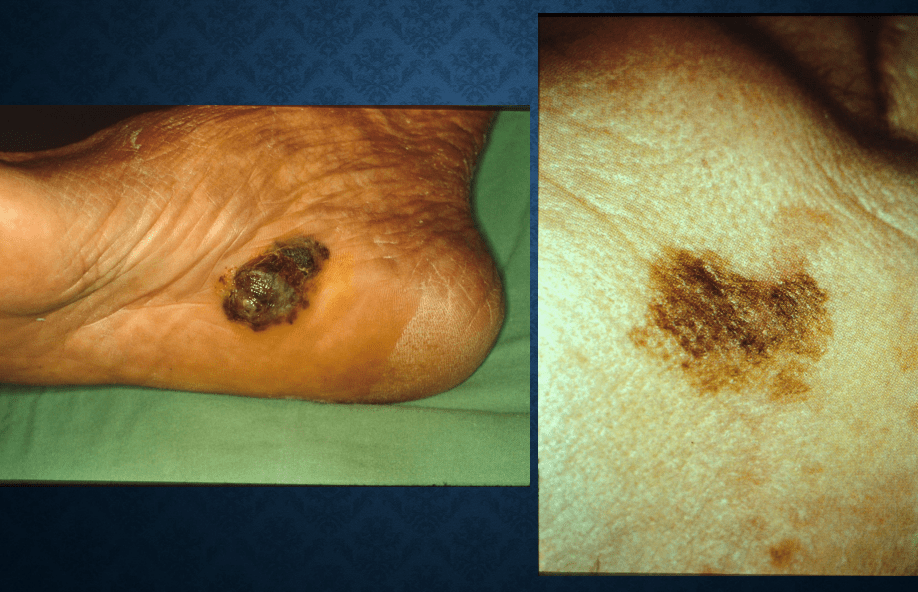
malignant melanoma
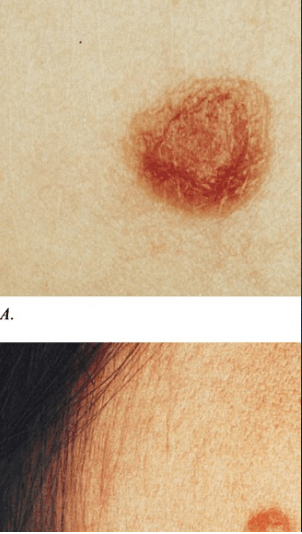
spitz nevus
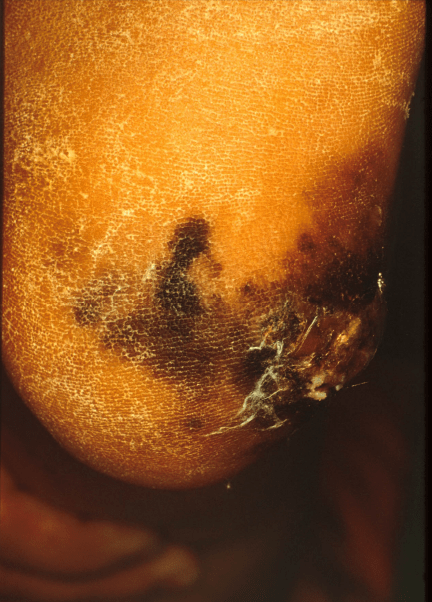
acral lentiginous melanoma
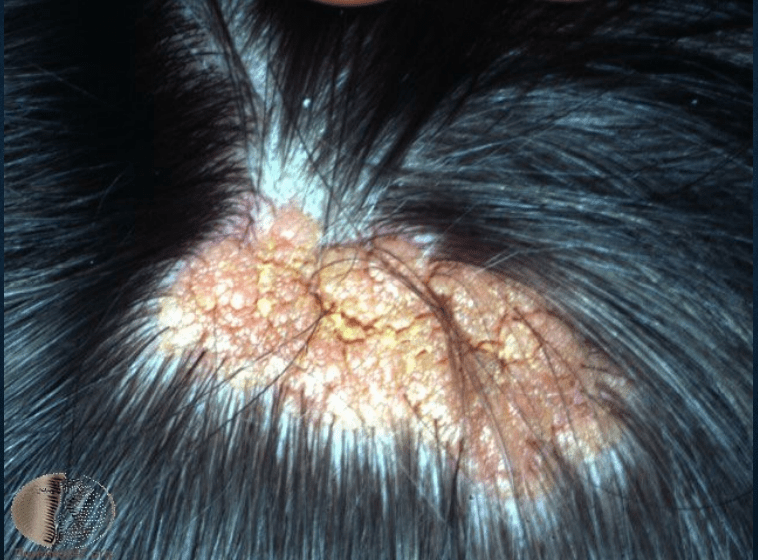
nevus sebaceus
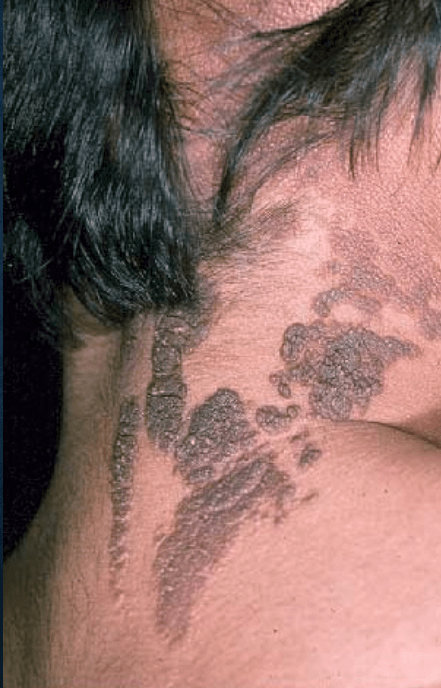
epidermal nevus
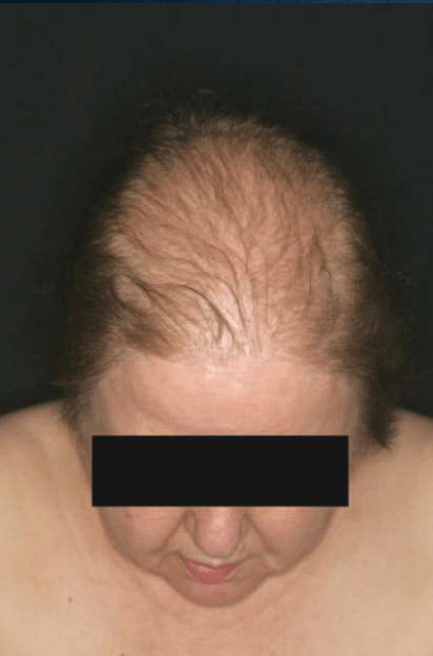
androgenetic alopecia
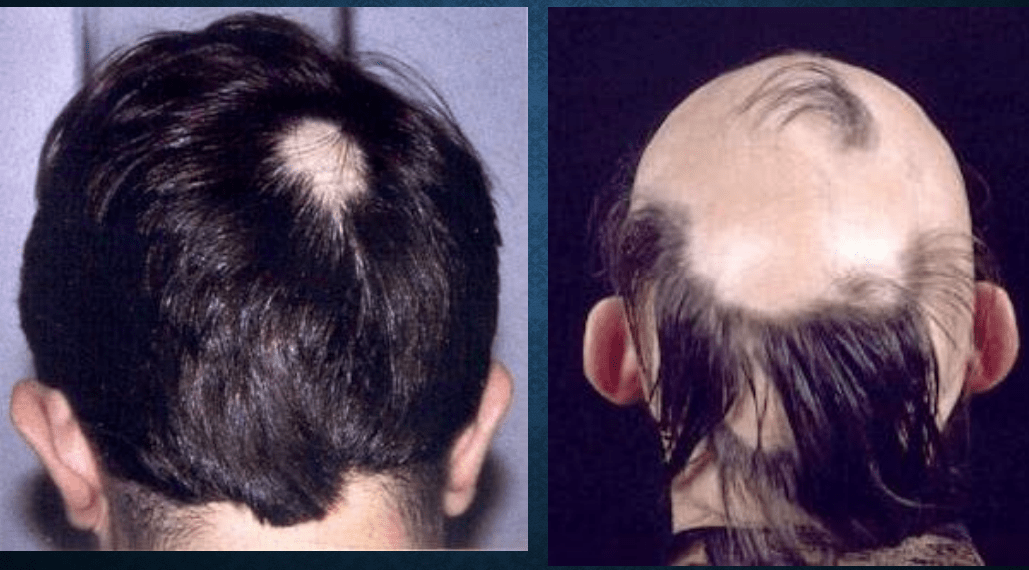
alopecia areata
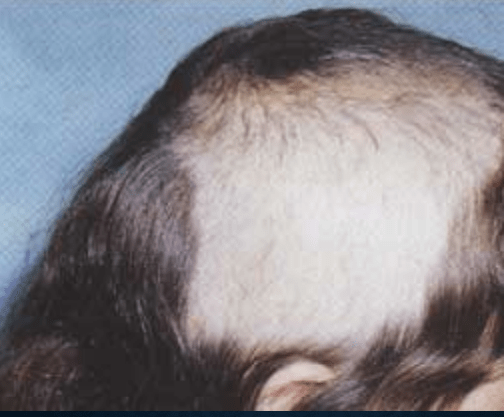
trichotillomania
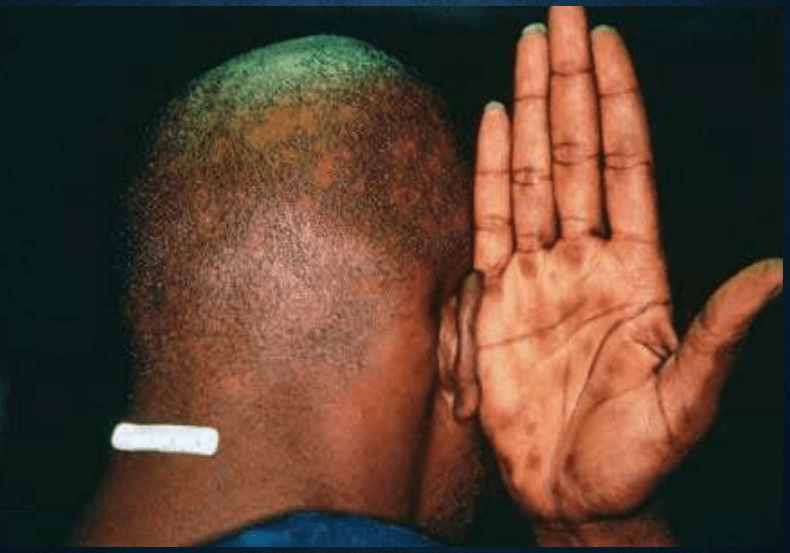
alopecia syphilitica
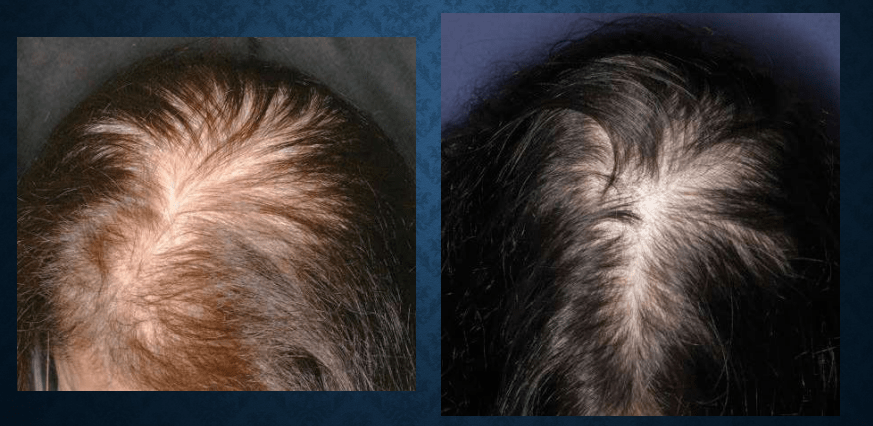
telogen effluvium
deck
By Zi-Hong Xiao
deck
- 386



