Parallel
Computing
Outline
-
What is parallel programming
-
Parallel computer
-
Flynn's classic taxonomy
-
Heterogeneous computing
-
-
Parallel programming model
-
Shared memory model
-
Distributed memory model
-
Hybrid model
-
Outline
-
What is parallel programming
-
Parallel computer
-
Flynn's classic taxonomy
-
Heterogeneous computing
-
-
Parallel programming model
-
Shared memory model
-
Distributed memory model
-
Hybrid model
-
-
What is parallel programming
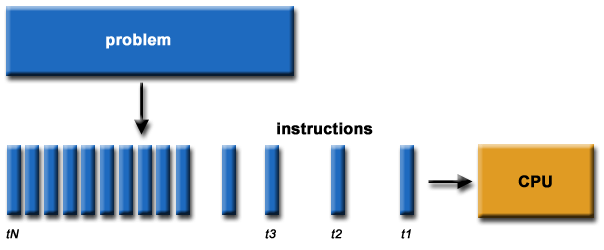
Sequential Program
-
The single program is computed by one processor
-
Deal the instruction one after another
-
Only one instructin may execute at any moment
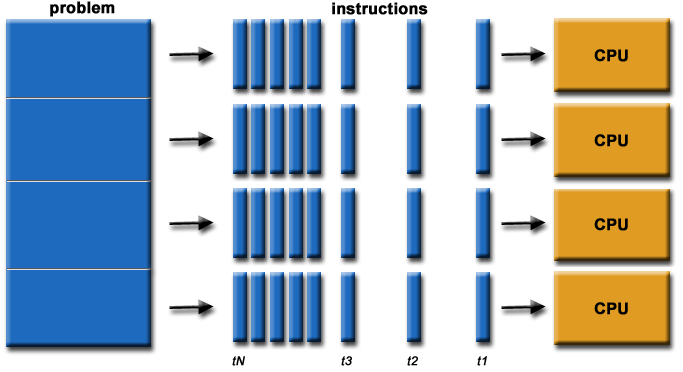
Parallel Program
-
Break a program into several parts
-
Instructions from each part execute simultanously
Why parallel programming
-
Advantages
Higher performance: save larger problem
Better resource utilization: taking advantage of multi-core processors
-
Disadvantages
Harder to program
Harder to debug
Not all problem can be parallelized efficiency ( dependency )
Parallel programs & application
-
Scientific applications
-
Computer animations
-
Computer games
-
Image processing
-
Data mining
Outline
-
What is parallel programming
-
Parallel computer
-
Flynn's classic taxonomy
-
Heterogeneous computing
-
-
Parallel programming model
-
Shared memory model
-
Distributed memory model
-
Hybrid model
-
-
Parallel computer
-
Flynn's classic taxonomy
-
Heterogeneous computing
-
Paralle computer classification
-
Flynn's Classical Taxonomy
-
Processing unit, instruction, data
-
SISD
-
MISD
-
SIMD
-
MIMD
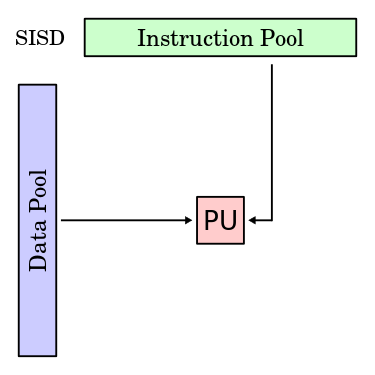
SISD
-
Single Instruction, Single Data (SISD)
-
A serial (non-parallel) computer
-
Executes a single instruction stream, to operate on data stored in a single memory
-
Example: old mainframes,
single-core processor
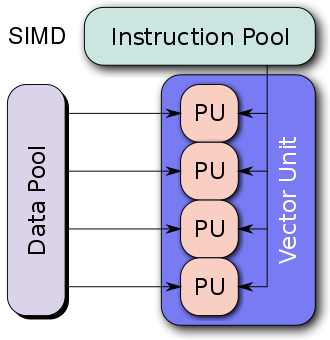
SIMD
-
Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD)
-
Multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points concurrency
-
Example: GPU
vector pipelines computer
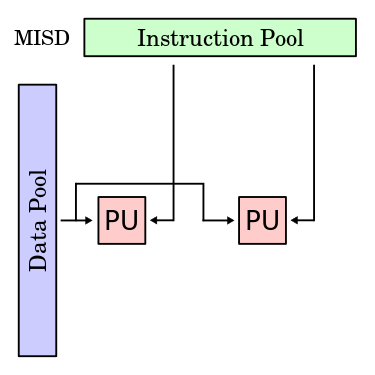
MISD
-
Multiple Instruction, Single Data (SIMD)
-
Many functional units perform different operations on the same data
-
Fault-tolerant computers execute
the same instructions to detect
and mask errors -
Example:
space shuttle
MIMD
-
Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data (MIMD)
-
At any time, different processors may be executing different instructions on different data
-
Example:
Most modern computers,
multi-core PCs
supercomputer
cluster
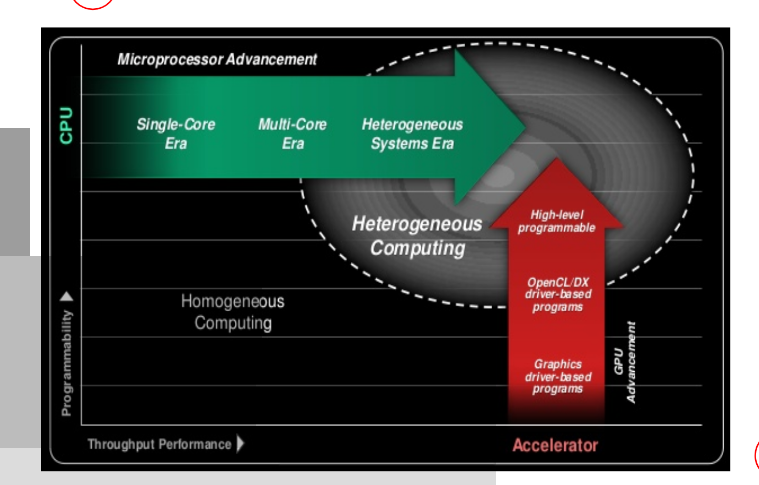
Heterogenous Computing
-
Heterogeneous computing is an integrated system that consists of different types of (programmable) computing units
-
DSP (digital signal processor) -
FPGA (field-programmable gate array) -
ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit) -
GPU (graphics processing unit) -
Co-processor (Intel Xeon Phi)
-
CPU v.s GPU
-
CPU is latency oriented design, can do lots of sophisticated control
-
GPU is throughput oriented design, long latency but heavily pipeline for high throughput
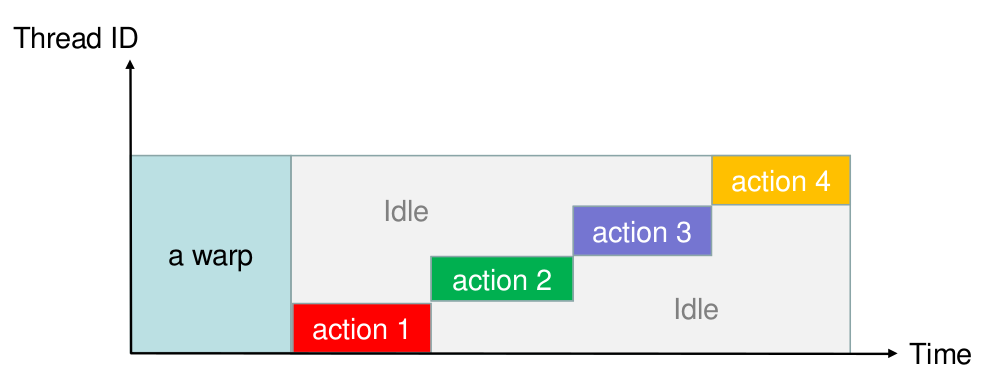
Latency v.s Thoughtput
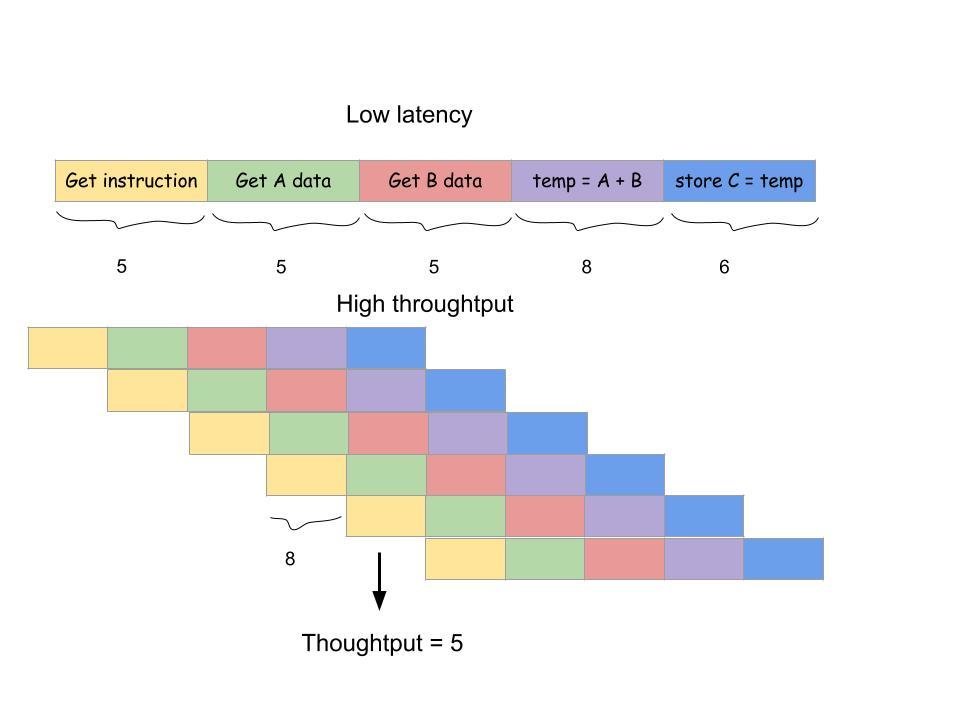
Performance
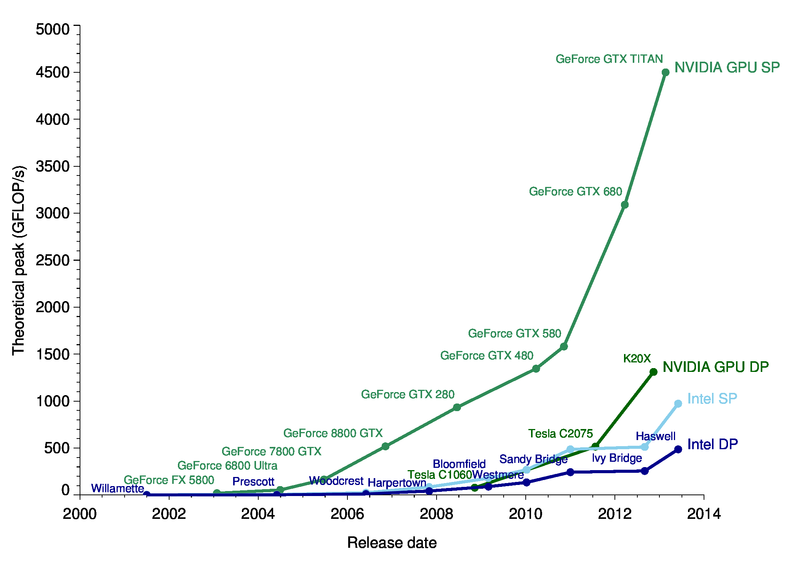
Trend
Outline
-
What is parallel programming
-
Parallel computer
-
Flynn's classic taxonomy
-
Heterogeneous computing
-
-
Parallel programming model
-
Shared memory model
-
Distributed memory model
-
Hybrid model
-
-
Parallel programming model
Shared memory model
Distributed memory model
Hybrid model
Shared Memory Model
-
Memory can be simultaneously access by multiple process with an intent to provide communication among them or avoid redundant data copies
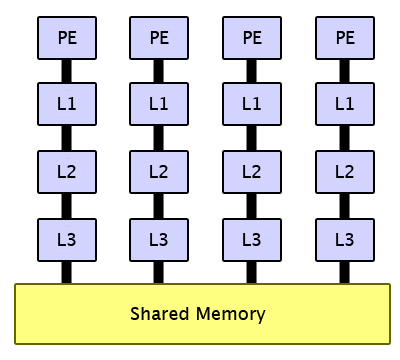
Shared Memory/Thread Model
-
A single process can have multiple, concurrent execution paths
-
Threads have local data, but also, shares resources
-
Threads commucnication through global memory
-
Thread can come and go, but the main program remains
-
to provide the necessary shared resources until the application has complete
-
Shared Memory/Thread Model
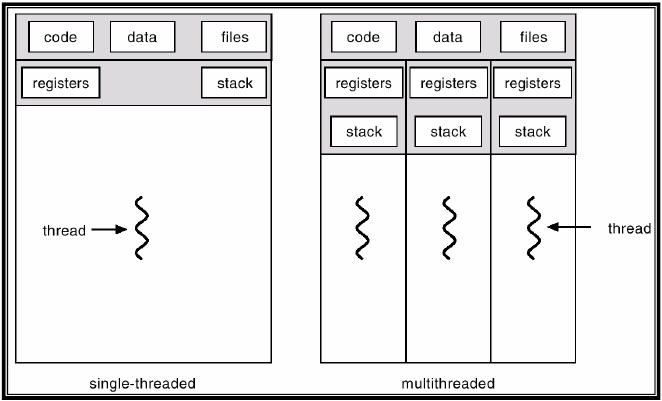
Shared Memory/Thread Model
-
Implementation methodology
-
A library of subroutines called from parallel source code
e.g: POSIX Thread (Pthread)
-
-
A set of compiler directives embedded in either serial or parallel source code
-
e.g: OpenMP
-
Shared Memory/Thread Model
-
Important issues
-
Race Condition: A situation where the computing output depending on the sequence order of process executions
-
Deadlock: Two or more competing action are waiting for the other to finish
-
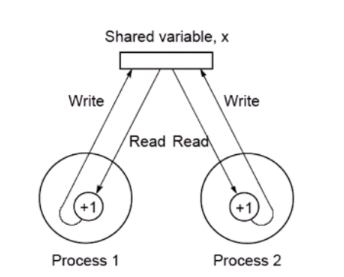
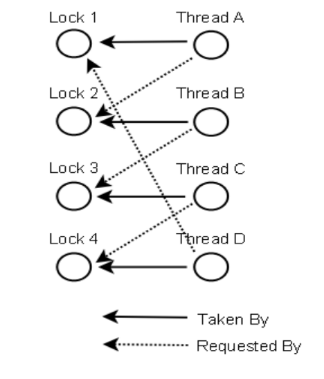
Distributed Memory/MPI Model
-
A set of tasks that use their own local memory during computaion
-
Tasks exchange data through communications by sending and receive messages
-
Memory copy
-
-
Implementation: MPI
-
An API specification that allows computers to communicate by means send, receive, broadcast ... etc
-
Distributed Memory/MPI Model
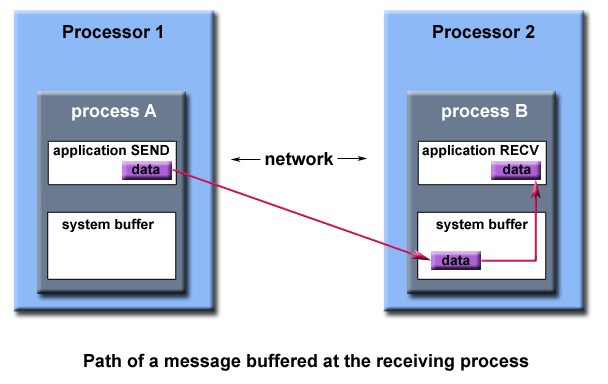
Distributed Memory/MPI Model
-
Important issues
-
Synchronization
programmer should make sure the correctness of timing dependency between processes -
Communication time
Network speed is much slower than CPU speed
Network latency causes a constant delay time
-
Hybrid Parallel computing Model
-
Combine both shared & distributed memory
-
MPI + pthread/OpenMP -
Implement parallelism with MPI libraries among nodes -
Implement parallelism with pthread/OpenMP libraries within each node
-
Q & A
Parallel
By zlsh80826
Parallel
- 880



