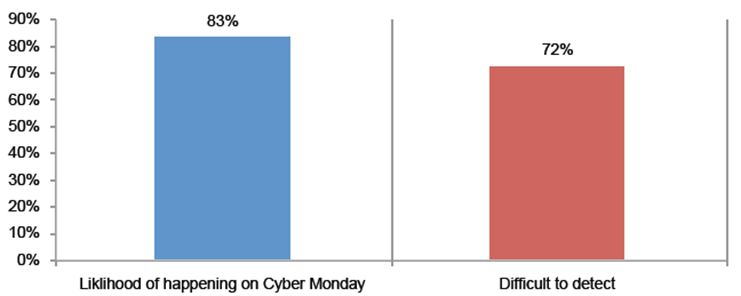
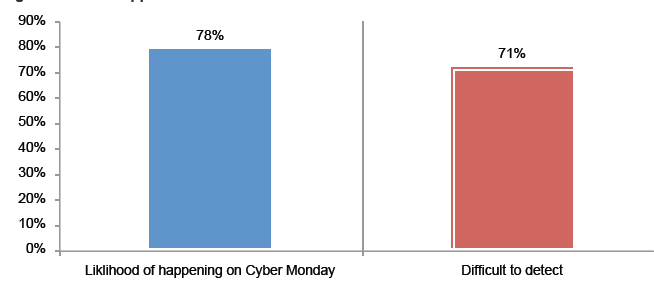
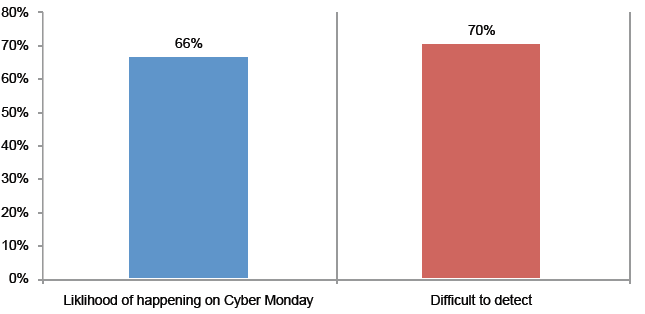
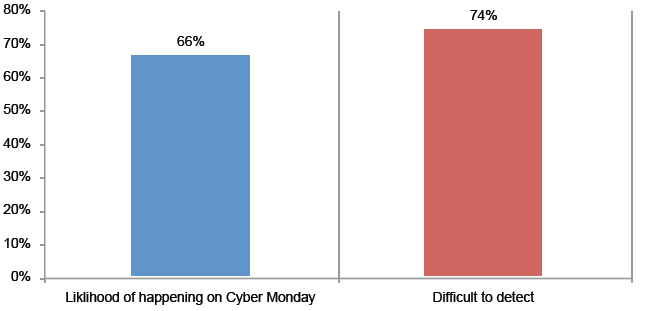
>Isp/Msp:- CDR (Call Details Record)
Cdr will give:- Date, Time, Calling party, Called party, Duration I/O, SMS I/O, SMS Center No, IMEI(International Mobile Station Equipment Identity), IMSI(International Mobile Subscriber Identity ), Call Id.
>Analysis
FCLS- First Call Last Call
Frequency of calling/SMS
Incoming SMS, Service center No translation.
Tower Dump Analysis (Only Used in Dead Cases)
GPRS logs- Sessions, Private Ip, Public IP, Destination Ip, Data usages, Urls.
>Mobile Forensics- Call logs, SMS, Inbox/Sent items, Photos/Videos/Audios.
Tools name:- Oxygen for govt. use only, Purple Radiance for cdr analysis.