Mysql
What is a database
-
store data : so it can be persisted
-
structure data : so it is easier to manipulate
-
process data : to derive data value from it
DAtabases
-
a standard interface for accessing data
-
multiple user with simultaneous ability to modify data.
-
changes to the data without risk of losing data
-
tools for data backup, restore and recovery
-
security
RDBMS
-
relational database management system (RDBMS)
-
based on the relational model
Relational Data Model means:
-
tables
-
rows
-
colums
-
data type
ER diagram
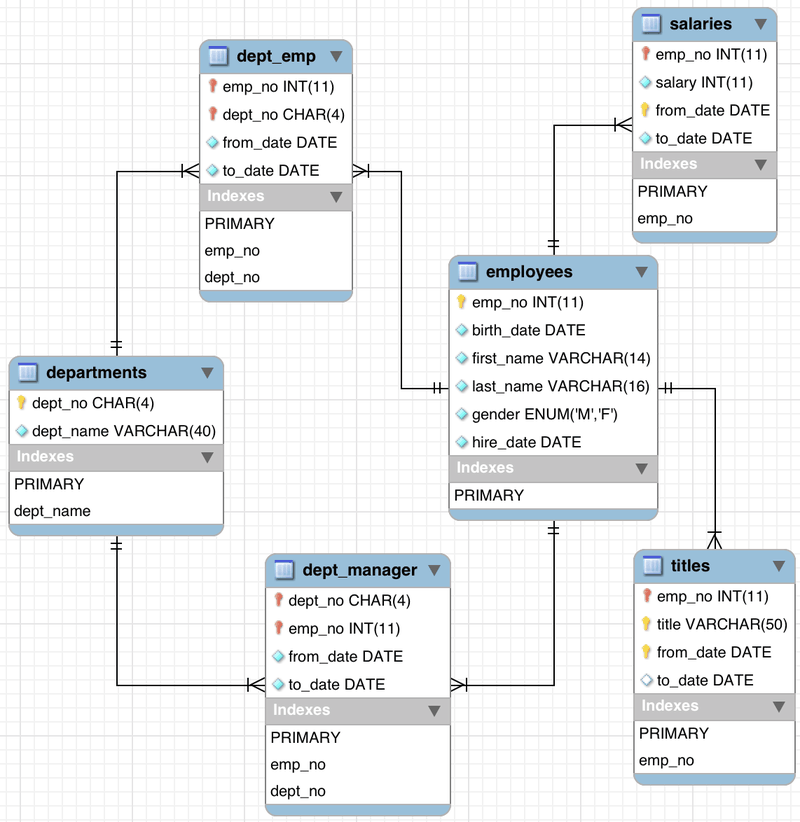
dataBase Design
Primary keys
- uniquely specifies an record within a table
- composed from one or more data attributes of that data entity.
Foreign keys
- a field in a relational table that matches the primary key column of another table
Index
-
way of providing quicker access to data.
Database normalization
FN1
-
there are no repeating or duplicate keys
-
each records is unique
-
each cell contains only a value
FN2
- all non-keys fields depend on all components of the primary key
FN3
-
no non-key field depends upon another
SQL
Structured Query Language
DDL: defines properties of data objects
create, alter, drop DML: used to retrieve, add, edit and delete data
select, insert, update, delete DCL : controls acces to databases objects
grant, revoke Transaction control: groups dml statements into trasactions
commit, rollbackDatabase transaction
- unit of work performed within a database management system against a database
- by defition is ACID: atomic, consistent, isolated and durable
BEGIN WORK//do work here//commit or rollback at the end of the workCOMMITROLLBACK
Create tables
CREATE TABLE employee (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
firstName VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
lastName VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
hiredDate DATE,
salary INT,
PRIMARY KEY ( id )
); -
NOT NULL is being used because we do not want this field to be NULL.
-
AUTO_INCREMENT tells to MySQL to go ahead and add the next available number to the id field.
-
PRIMARY KEY is used to define a column as primary key. You can use multiple columns separated by comma to define a primary key.
Select statement
select <%EXPRESSIONS%> from <%TABLE REFERENCES%>
select * from employee;
select * from employee where salary > 1000;
select * from employee order by salary desc;-
Where: only some rows are returned
-
Group by: allows you to consolidate the query
-
Order by: allows you to sort the query
Aggregate functions
- Count
select count(*) from employee;-
Sum
select sum(salary) from employee;
select sum(salary) from employee group by departamentId;Insert statement
insert into employee(id, firstName, lastName) values ( 1, "Posa", "Bogdan");Update statement
update employee set salary = 1000;
update employee set salary = 1000 where id = 1; Delete statement
delete from employee;
delete from employee where id = 1; Transactions
begin work;
delete from employee;
select * from employee;
rollback; JOINs
-
inner join
select * from employee e
join departament d on d.id = e.departamentId-
left join
select * from employee e left join departament d on d.id = e.departamentId;-
right join
select * from employee e
right join departament d on d.id = e.departamentId;Mysql
By Bogdan Posa
Mysql
- 1,383



