Fuzzy Dark Matter on Galactic Scales
Bodo Schwabe
(University of Göttingen)
credit: J.Veltmaat
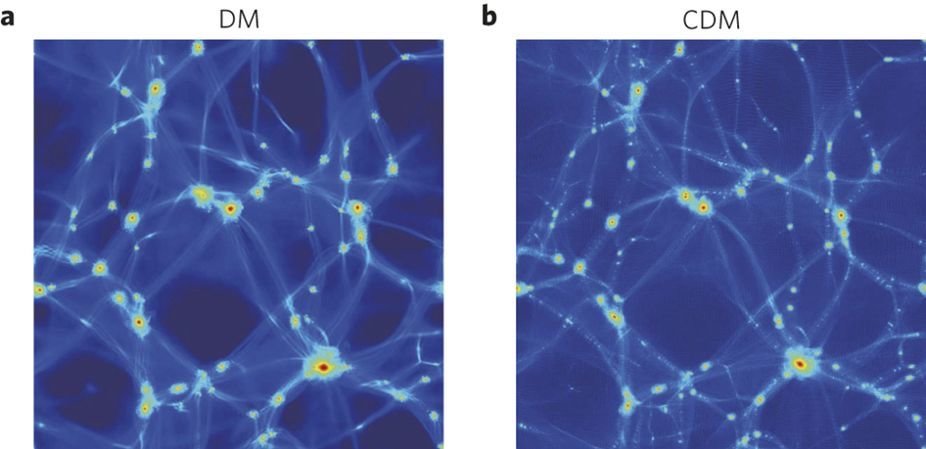
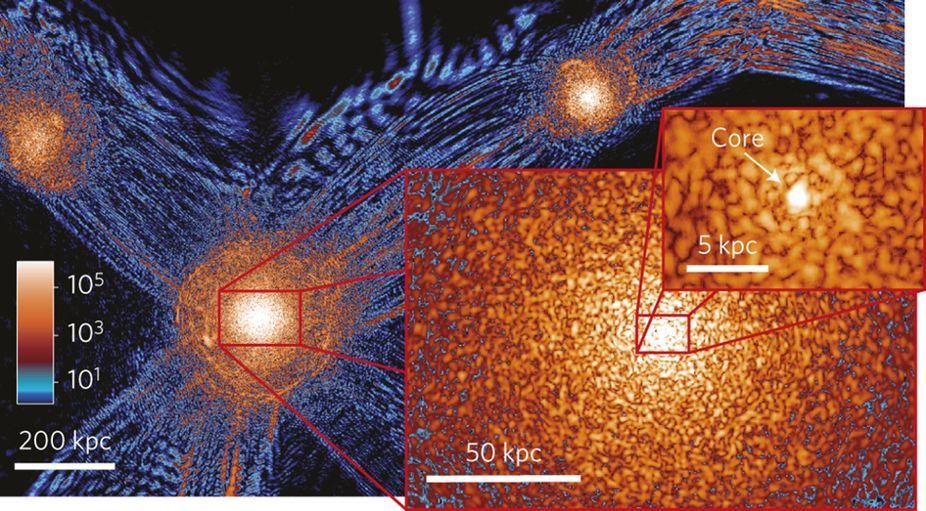
FDM Structure Formation
H.-Y. Schive, T. Chiueh, and T. Broadhurst, Nature Physics, 2014
FDM Solitonic core dynamics
- Formation
- Merger history
- Tidal disruption
- Equilibration in halo
FDM halo dynamics
- CDM velocity dispersion vs. FDM granular structure
B. Eggemeier, J.C. Niemeyer, Phys. Rev. D, September 2019
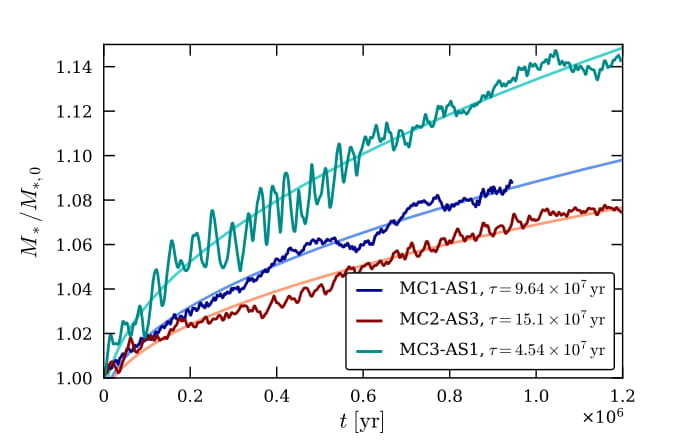
D.G. Levkov, A.G. Panin, I.I. Tkachev, Phys. Rev. Lett., October 2018
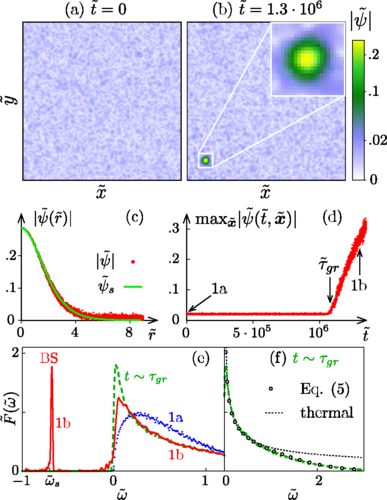
Formation and Mass Growth of Axion Stars in Axion Miniclusters
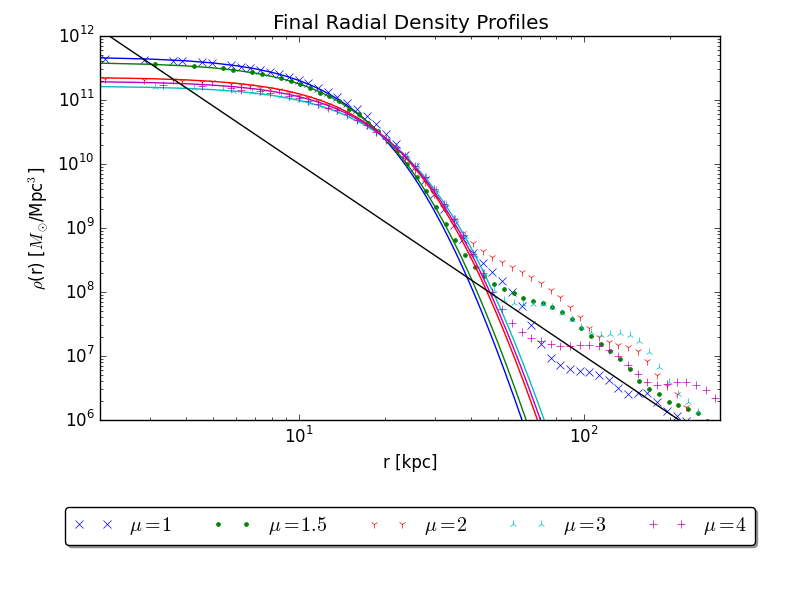
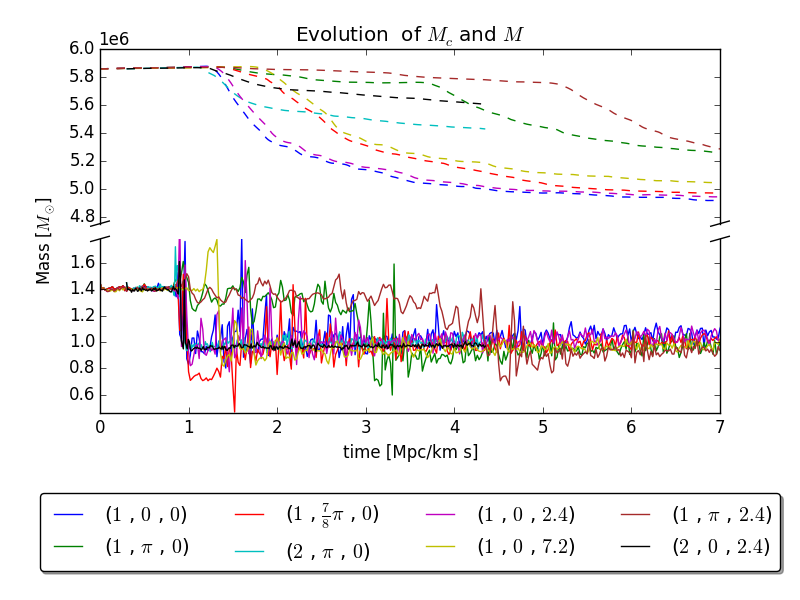
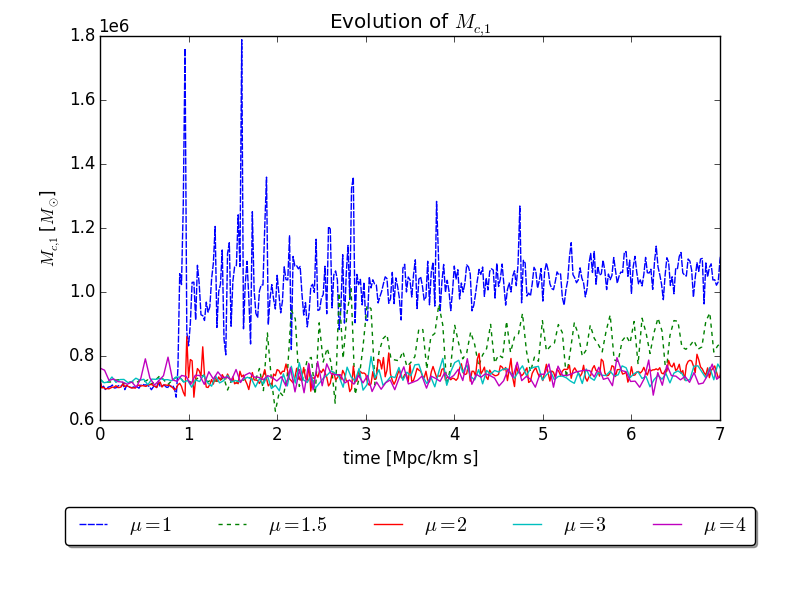
Solitonic Core Mergers
BS, J. C. Niemeyer, and J. F. Engels, Physical Review D, August 2016.
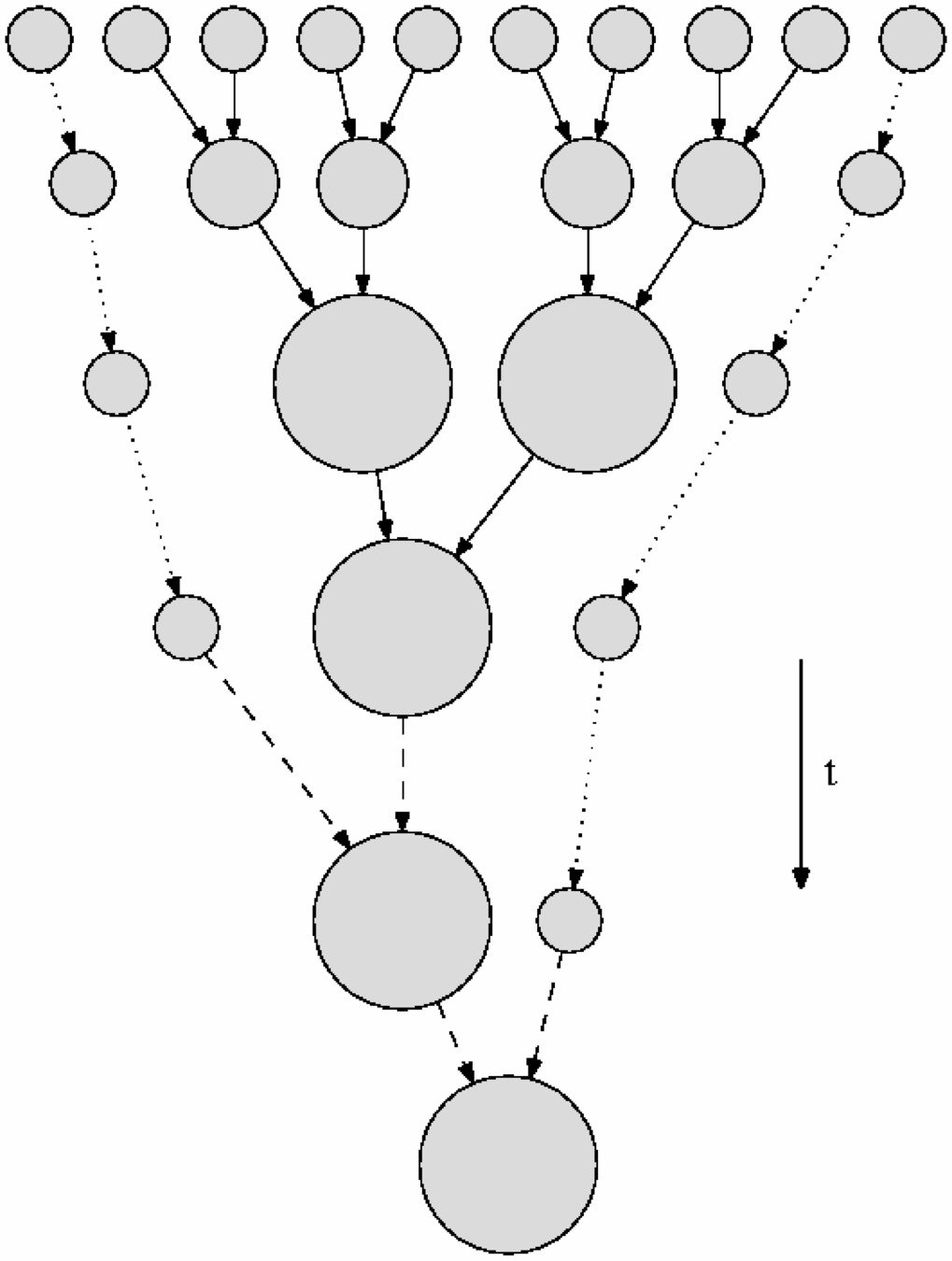
Recipe for Core Evolution
- Bound core mergers result in new solitonic core
- Cores merge rapidly once they overlap
- Merger history is a series of binary mergers
- Only major mergers with mass ratio yield increased core mass
- Minor mergers and smooth accretion leave heavier core unchanged
- Numerically find
- Recover the scaling relation found in cosmological simulations
BS, J. C. Niemeyer, and J. F. Engels, Physical Review D, August 2016.
X. Du, C. Behrens, J. C. Niemeyer, and BS, Physical Review D, February 2017.
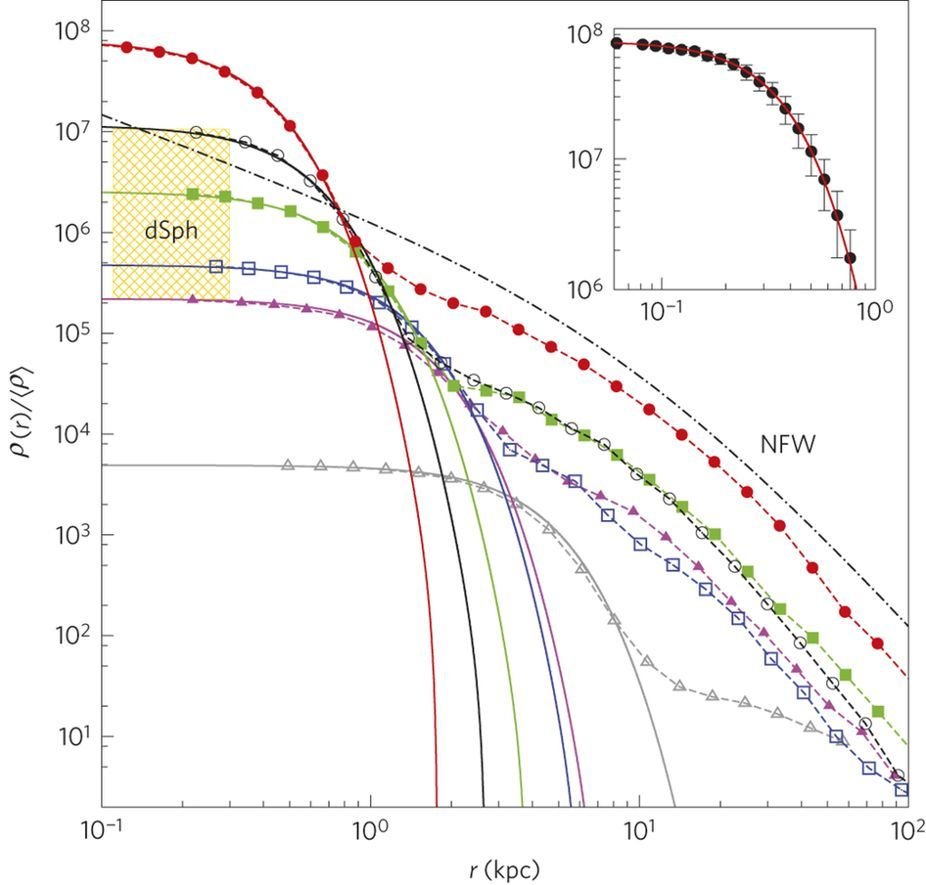
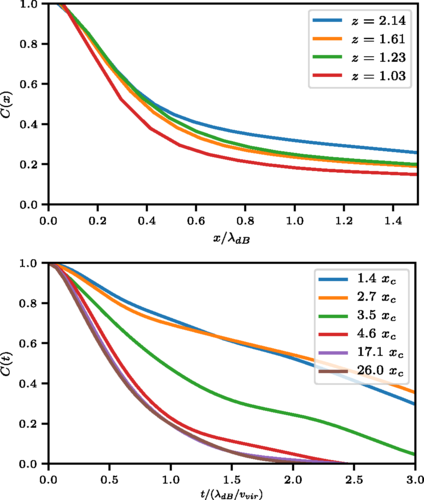
Tidal Disruption of Subhalo Cores
X. Du, BS, J. C. Niemeyer, and D. Bürger, Physical Review D, March 2018.
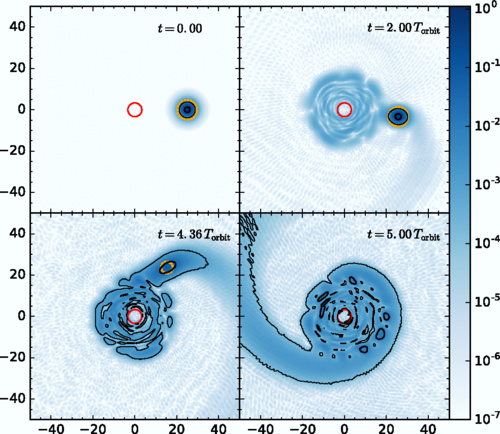
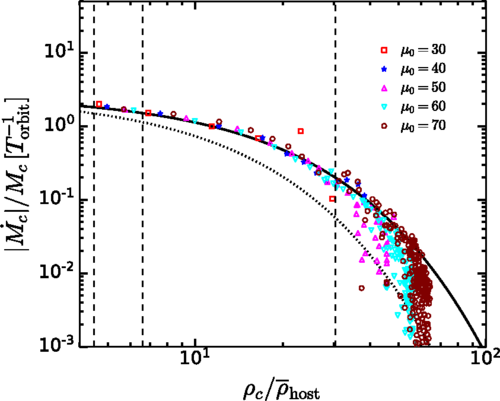
- Lightest satellites close to the Galactic center will only survive for more than one orbital time if the particle is as heavy as .
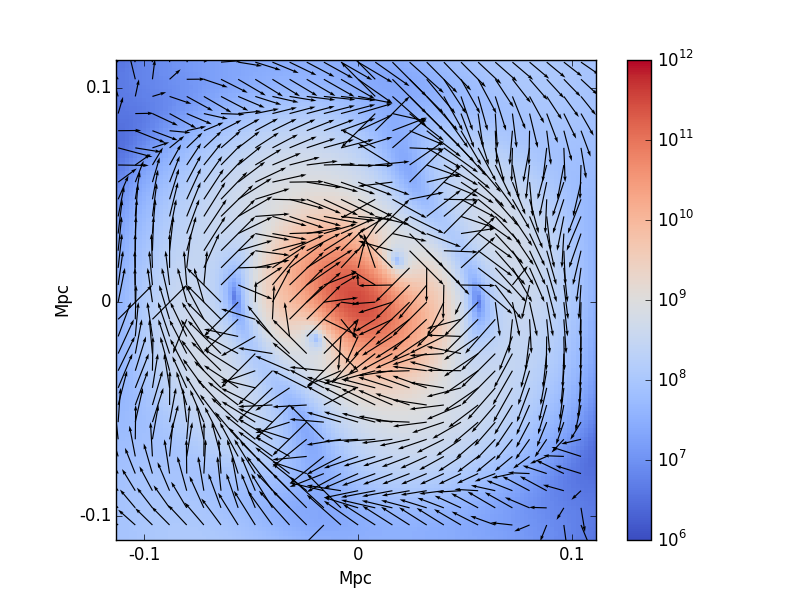
Tidal core deformation
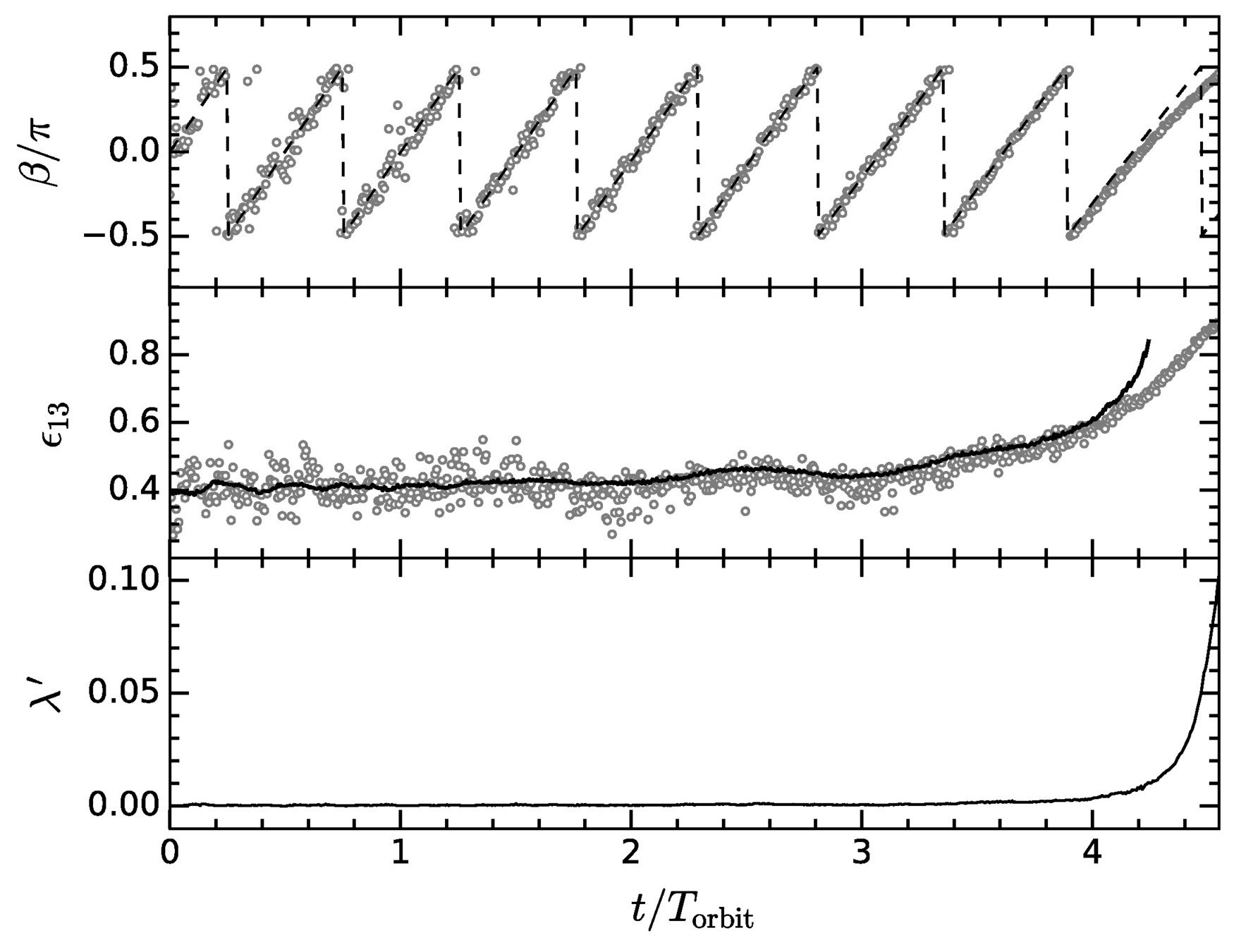
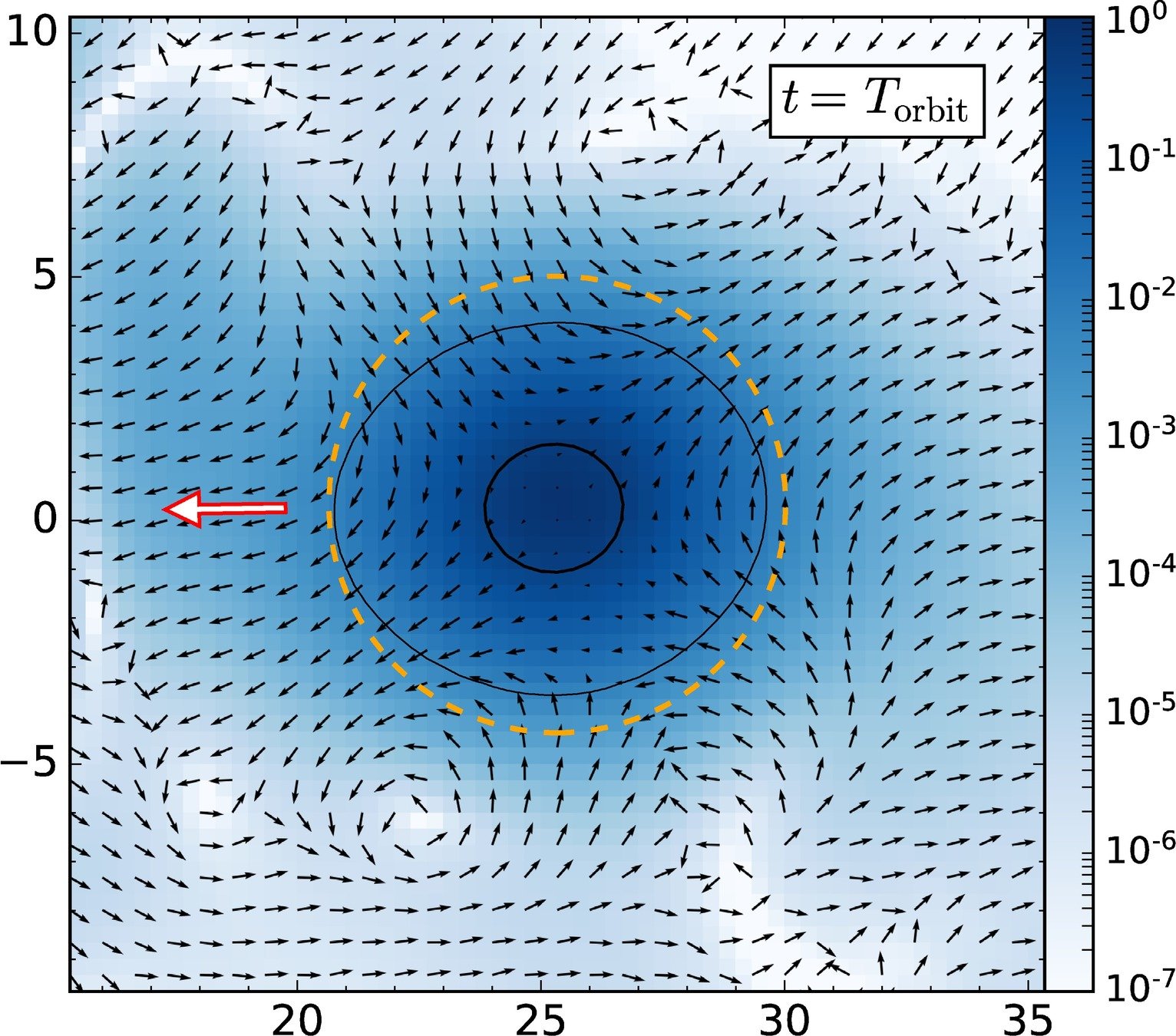
X. Du, BS, J. C. Niemeyer, and D. Bürger, Physical Review D, March 2018.
Tidally locked ellipsoid with decreasing mass and central density
(-> smaller tidal radius) and increasing core radius and eccentricity
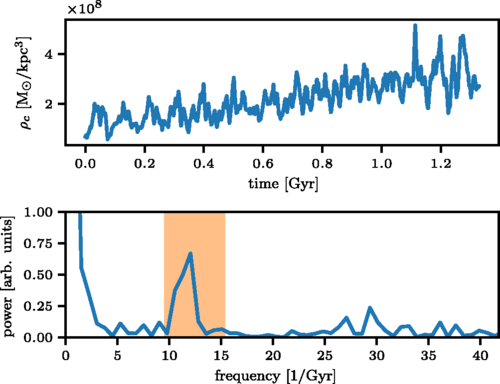
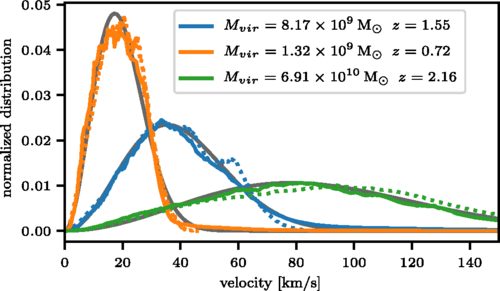
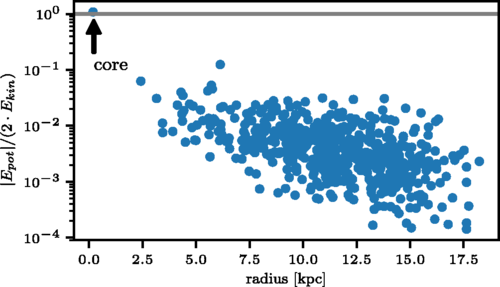
J. Veltmaat, J. C. Niemeyer, and BS, Physical Review D, August 2018.
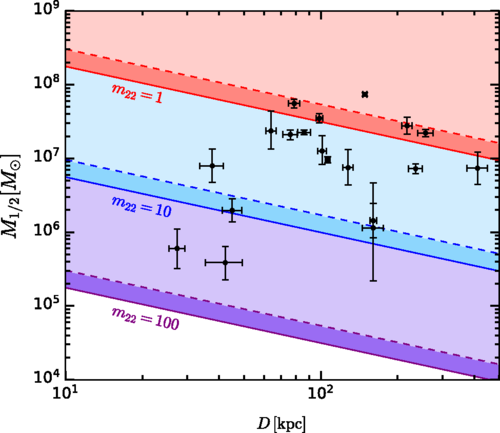
Structure of FDM halos
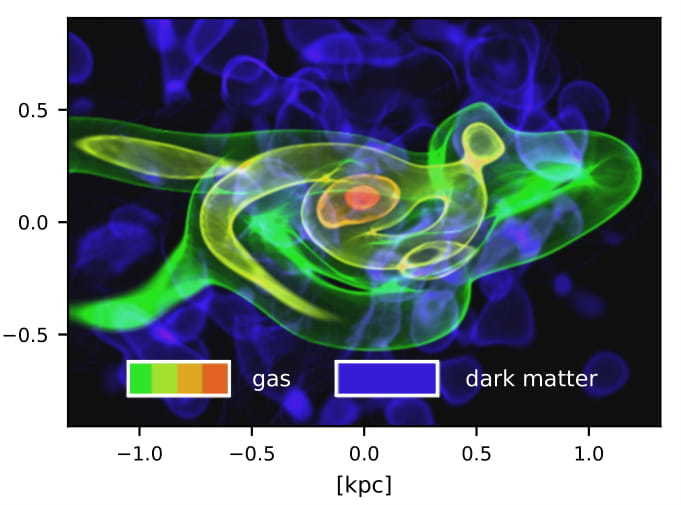
FDM dwarf galaxy with baryons
J. Veltmaat, J. C. Niemeyer, and BS, arXiv:1911.09614, November 2019.
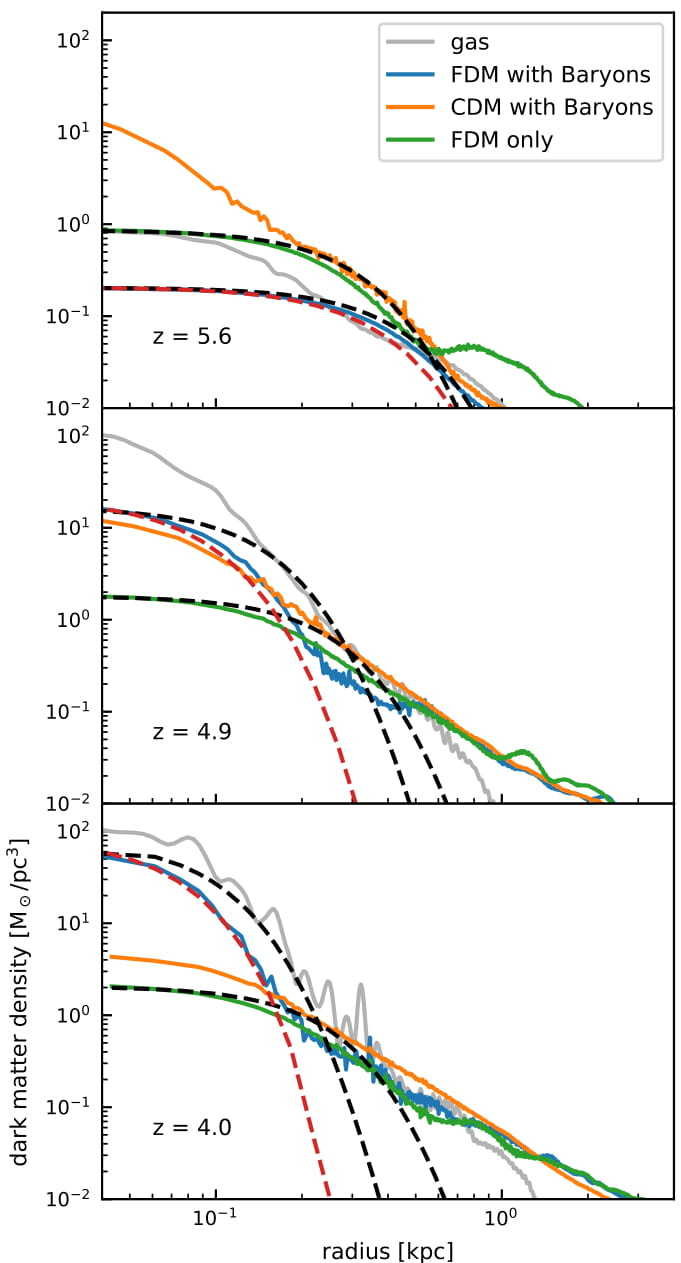
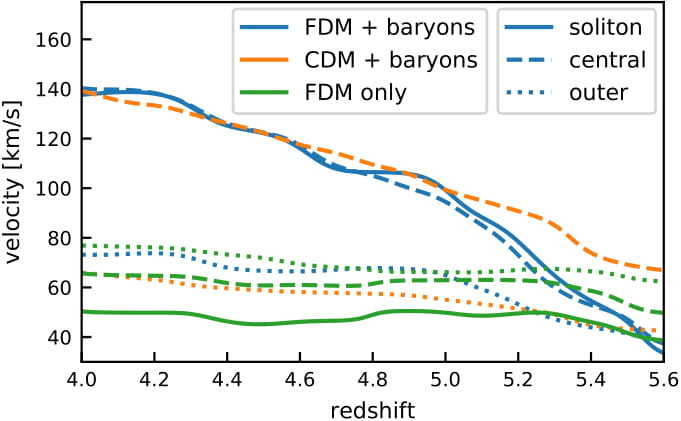
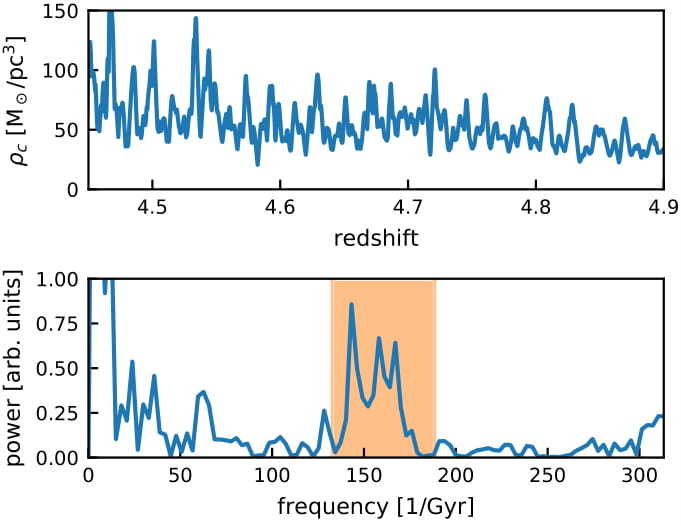
Conclusions
- FDM structure formation similar to CDM on super deBroglie scales (except cut-off in initial power spectrum as for WDM)
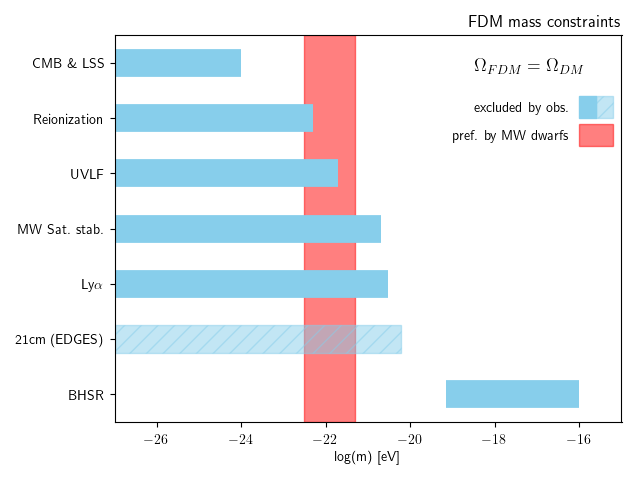
- Weakly non-linear probes like Lyman-alpha exclude
-
Distinguishing features of FDM: Strong stochastic density fluctuations in halos on deBroglie length and time scales and formation of stable, oscillating soliton cores in center of halos
- Heavier FDM mass can be best constrained on non-linear, galactic scales (soliton osc., soliton mergers, gravitational heating/cooling, tidal disruption,...)
- Local FDM density important for experiments but not well constraint yet
-- Need further dedicated FDM simulations on galactic scales --
deck
By bschwabe
deck
- 224



