
A Full Day of Vue.js

03. Components & Single-File Components
Everything we've discussed thus far has been within the context of a single Vue Instance.
new Vue({
el: '#app',
});<body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {},
created() {},
computed: {},
methods: {},
...
});What if our application was really large?
Can we create modules that can group markup and logic separately?
Components
Vue Components
Vue Components are self-contained modules that can group markup (HTML), logic (JS), and even styles (CSS) within them
Simplest, most straightforward way to create a component:
Vue.component('name-of-component', {});
options
Vue Components
Vue Components are Vue Instances!
Contain instance data/events/methods except for root-specific functionality (e.g. el)
Vue Components
Vue Components
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
data() {
return {}
}
});
Data must be a function for Components!
Vue Components
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
template: ``,
});
Vue Components
Vue.component('hello-world', {
template: '<div>Hello World</div>',
});
Vue Components
Vue.component('hello-world', {
template: `
<div>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<p>This is the Hello World component</p>
</div>
`,
});
Vue Components
Must have a single root element
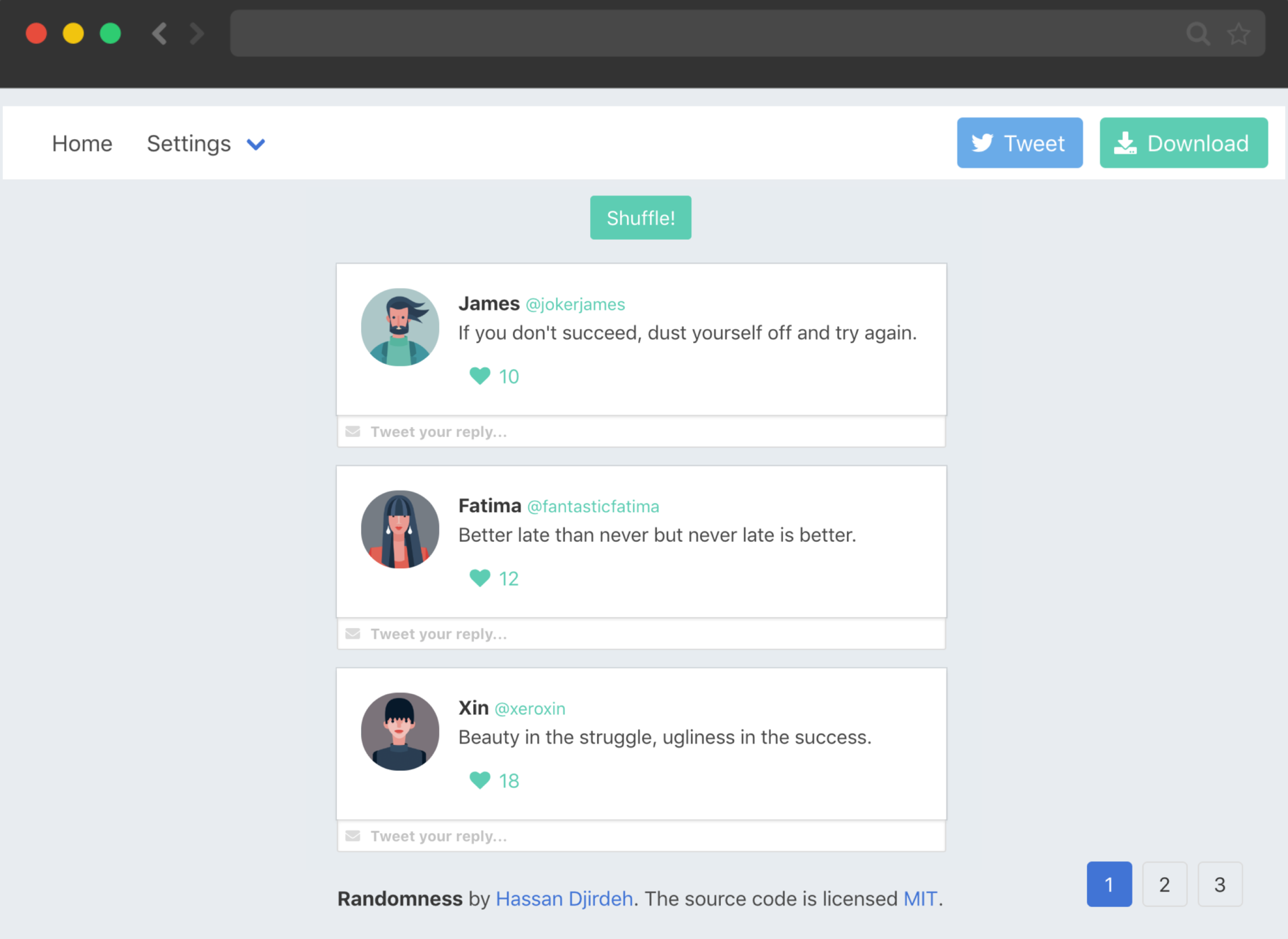
Vue.component('tweet-component', {
template: `
<div class="tweet" v-for="tweet in tweets" :key="tweet.id">
<div class="box">
<article class="media">
<div class="media-left">
<figure class="image is-64x64">
<img :src="tweet.img">
</figure>
</div>
<div class="media-content">
<div class="content">
<p>
<strong>{{tweet.name}}</strong>
<small>{{tweet.handle}}</small>
<br>
{{tweet.tweet}}
</p>
</div>
<div class="level-left">
<a class="level-item">
<span class="icon is-small">
<i class="fas fa-heart"></i>
</span>
<span class="likes">{{tweet.likes}}</span>
</a>
</div>
</div>
</article>
</div>
<div class="control has-icons-left has-icons-right">
<input class="input is-small" placeholder="Tweet your reply..." />
<span class="icon is-small is-left">
<i class="fas fa-envelope"></i>
</span>
</div>
</div>`
});Vue Components
Vue.component('tweet-component', {
template: `
<div class="tweet" v-for="tweet in tweets" :key="tweet.id">
// ...
</div>
`,
});
tweets is unrecognizable here
tweet-component shouldn't render a list of tweets
Vue Components
Vue Instance
tweet-component
tweets
props
Vue Components
Props allow us to pass data from parent instance/component down to child components.
Vue Components
2 things to do to declare props
1. Declare the value of the prop attribute where the child component is being rendered.
<component greeting="Hello!"></component>
2. Have the child component declare the props it receives in a props option.
Vue.component('component', {
props: ['greeting'],
});
Vue Components - Props
2 things to do to declare props
1. Bind the value of the prop attribute where the child component is being rendered.
<tweet-component v-for="tweet in tweets"
:key="tweet.id"
:tweet="tweet">
</tweet-component>
2. Have the child component declare the props it receives in a props option.
Vue.component('tweet-component', {
props: ['tweet'],
});
Vue Components - Props
Vue.component('tweet-component', { props: { tweet: { type: Object, required: true
}
},
});
We can also specify prop validation requirements in the props option.
Vue Components - Props
Vue.component() creates the component globally.
Vue Components - Props
Vue.component('tweet-component', {
// ...
});
As long as we construct the component before instance creation - the component is registered globally
Vue Components - Props
We could instead define components as plain objects.
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
template: ``,
});
const nameOfComponentObject = {
template: ``,
};
Vue Components - Component Registration
For us to use the component created object, we'll have to register it in a components property in the parent.
new Vue({
// ...,
components: {
'name-of-component': nameOfComponentObject
}
});
Component Object
Name of Component in template
<name-of-component></name-of-component/>
Vue Components - Component Registration
const tweetComponent = {
template: `...`,
props: ['tweet']
};
new Vue({
// ...,
components: {
'tweet-component': tweetComponent
}
});Vue Components - Component Registration
Components can be nested multiple levels deep.
Vue Instance
Component #1
Component #2
Component #3
props
props
props
Important Note: Props (data) can only be passed downwards!
Vue Components - Component Registration
Vue Components - Component Registration

Vue Components - Component Registration
const tweetContent = {
template: `..`,
props: ['tweet']
}
const tweetComponent = {
template: `...`,
props: ['tweet'],
components: {
'tweet-content': tweetContent
}
};
new Vue({
// ...,
components: {
'tweet-component': tweetComponent
}
});tweet
tweet
Ways to define a Vue Component
1. Global Vue Components
2. Component Objects
Vue.component('name-of-component', {
// options
});
const nameOfComponentObject = {
// options
};
3. Single File Components!
Template options are in strings (or back-ticks). No syntax highlighting.
No isolated CSS styling.
Disadvantages of 1. and 2.
Vue Components - Component Registration
Single File Components allow us to define HTML/CSS and JS of a component all within a single .vue file
Vue Components - Single File Components
Single File Components contain three parts
-
<template> which contains the component’s markup in plain HTML
Vue Components - Single File Components
-
<script> which consists of all the JS logic within the component
-
<style> which contains all the component styles
<template>
<div class="hello-world">
<h2>{{ getGreeting }}</h2>
<p>This is the Hello World component.</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () {
return {
reversedGreeting: '!dlrow olleH'
}
},
computed: {
getGreeting() {
return this.reversedGreeting.split("").reverse().join("");
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.hello-world {
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
Vue Components - Single File Components
HelloWorld.vue
What are all these other files?
package.json | index.html | main.js | etc.
Vue Components - Single File Components
Single File Components are only made possible with build tools like Webpack.
These tools work alongside built Vue packages (e.g. vue-loader library) to compile .vue components to plain JavaScript modules that can be understood in browsers.
Vue Components - Single File Components
*Webpack is a module bundler.
This is where we level up from:
Simple Standalone Vue Applications
Webpack bundled Vue Applications
Vue Components - Single File Components
But...how do we set up a Webpack bundled Vue application?
🤔
Vue Components - Single File Components
Setting up a Webpack based project often involves understanding how to set up:
-
Webpack Configuration
-
Babel Configuration
-
Styles Preprocessing (if we use SASS/LESS)
-
ESLint (if we'd like a linter)
-
Vue Single-File Compilation
....
😓
Vue Components - Vue Cli
The vue-cli (i.e the Vue command line interface) is a tool built by the Vue.js team to help facilitate the rapid building and developing of Vue applications.
Vue Components - Vue Cli
Using the vue-cli
Assuming you have npm (or yarn) and Node already installed
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create name_of_project
1. Install the vue-cli globally
2. Create a new Vue project
3. Follow the prompts and create!
Vue Components - Vue Cli
Let's see this in action!
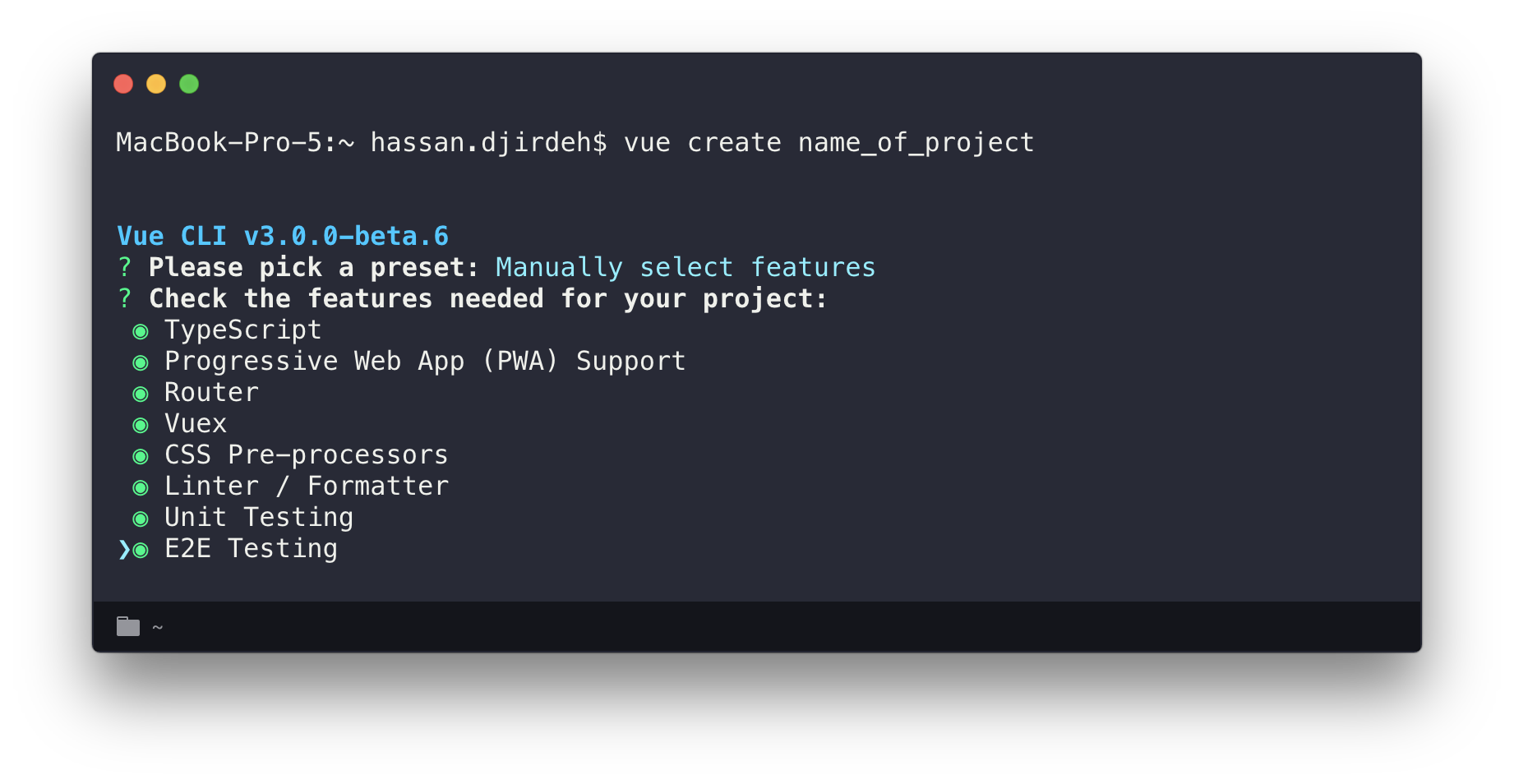
Vue Components - Vue Cli
Vue Components - Vue Cli
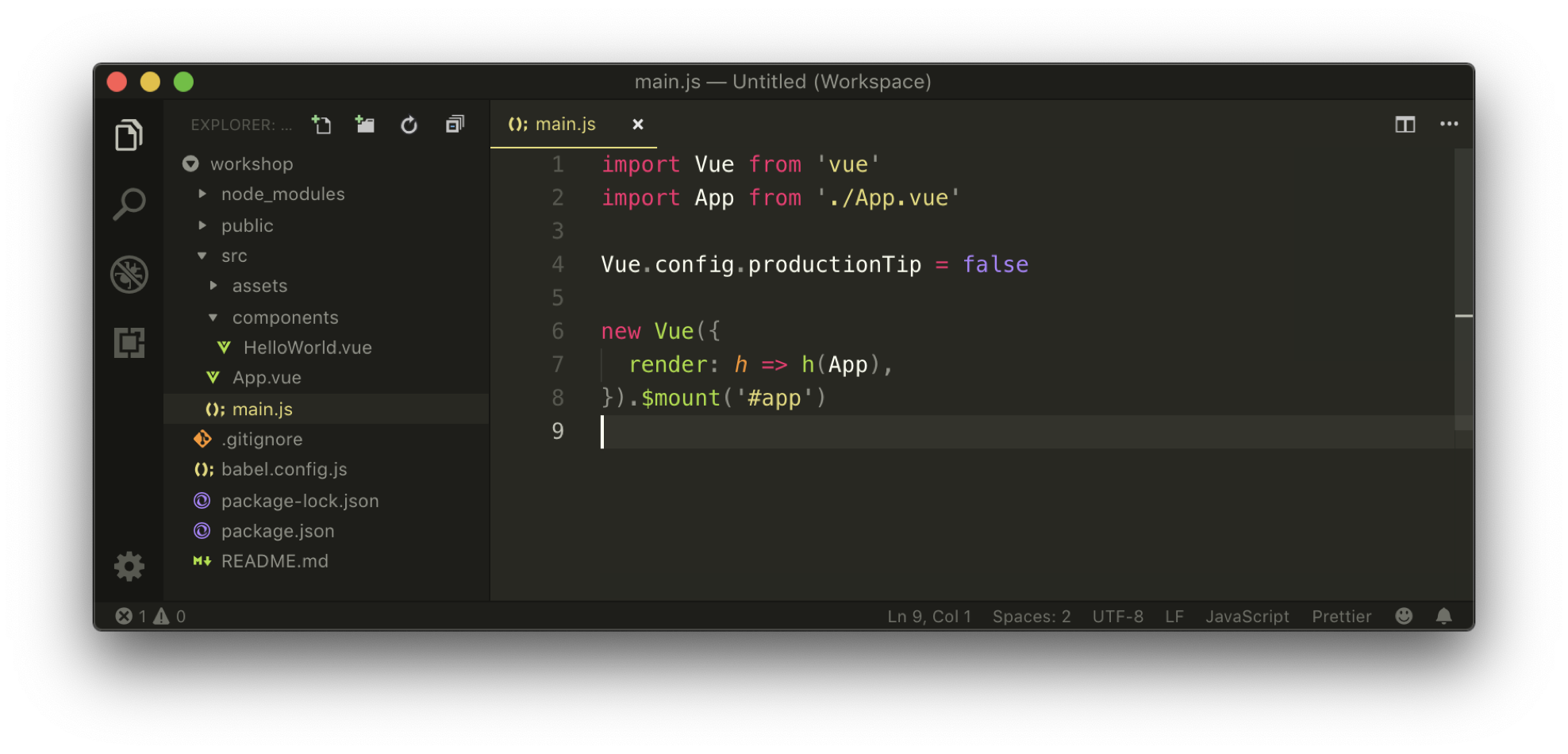
Quick walkthrough of a vue-cli scaffolded project:
-
babel.config.js: Configuration of Babel presets and plugins to transpile ES6 JS
-
node-modules/: All the different libraries that have been installed.
-
package.json: Listing of all installed libraries.
Listing of script commands to serve, build, and lint an app.
Can contain certain Webpack configuration if intended.
-
public/: Contains the root markup page (index.html)
-
src/: Contains all Vue code
. . .
Vue Components - Vue Cli
Vue Components - Vue Cli
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
Vue Components - Vue Cli
.$mount('#app')
is somewhat equivalent to
el: '#app'
Main difference being we can call mount after the instance has been instantiated.
Vue Components - Vue Cli
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
render (createElement) {
return createElement(App);
}
render (h) {
return h(App);
}
render: h => h(App)
Helpful Article (Sarah Drasner): what-does-the-h-stand-for-in-vues-render-method/
Helpful Comment (Bobby Juncosa): What is render: h => h (App)
Vue Components - Vue Cli
new Vue({
el: '#app',
template: '<App />'
components: { App }
});
We can also stick with this - with which we're more familiar with!
Single File Components - Separation of concerns, but more fine-grained
Templates
Scripts
Styles
SFC
SFC
SFC
Vue Components - Chapter Summary!
-
Vue Components are self-contained modules that can group markup, logic, and even styles.
Global Components:
Component Variables:
Single File Components
Vue.component('name-of-component', {});
const nameOfComponentObject = {};
-
Single File Components allow us to define HTML/CSS and JS of a component within a single .vue file
<template> section - HTML
<script> section - JS
<style> section - CSS
-
Props (data) can only be passed downwards in a single direction (parent - child - etc.).
-
vue-cli can help facilitate the rapid building and developing of Vue applications.
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create name_of_project
Vue Components - Chapter Exercise 💪!
With Single-File Components and in a module based Vue application.
Vue Components - Chapter Exercise 💪!
SubmissionComponent
SubmissionContent
SubmissionComponent
SubmissionContent
Vue Components - Chapter Exercise 💪!
Complete example from last exercise - Codepen
Starting Point - CodeSandbox
Solution 👀 - CodeSandbox
A Full Day of Vue.js Workshop - 03 Components and Single-file Components
By djirdehh
A Full Day of Vue.js Workshop - 03 Components and Single-file Components
- 387
