Intro to
Akka Streams & HTTP
Lance Arlaus
ny-scala

blog.lancearlaus.com


Going Reactive
quick take
-
Reactive is Real
- four tenets
- expanding options
-
Streams are Effective
- versatile abstraction
Intro to Akka Streams and HTTP
Overview
- Reactive Streams Basics
- concept: push-based streams
- innovation: demand-based flow
- Akka Streams Basics
- capability: reusable flow components
- abstraction: visual flow construction (DSL)
- Akka HTTP Basics
- improvement: fully stream-based
- Sample Service
What is a stream?
natural abstraction for sequenced data
(file, network, events, ...)
- has a beginning
- may be unbounded
- may be non-repeatable
| Example | Bounded | Repeat | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (6, 7, 8, 9) | Fixed integer sequence | Yes | Yes |
| (3, 4, 5, ...) | Infinite integer sequence | No | Yes |
| (9, 3, 1, 6) | Fixed-length random sequence | Yes | No |
| (7, 2, 4, ...) | Infinite random sequence | No | No |
| (GET, ...) | Incoming HTTP requests | ? | ? |
What is the challenge?
mismatched producer and consumer
-
fast producer / slow consumer
- producer blocks (sync only)
- consumer drops
- slow producer / fast consumer
- consumer blocks e.g. iterator.next()
FAST (10/sec)
slooww (2/sec)



Robust Stream Processing
Reactive Streams
handle large data sets or rapid events with bounded resources
- data only flows downstream in response to demand
- all interfaces non-blocking
Akka Streams
reusable, natural expression of stream processing atop Akka
- data transformations
- flow graph components
Reactive Streams Basics
-
Publisher
-
Subscriber
-
Subscription
-
Processor

Publisher
-
how does data flow?
-
key concept: streams are push-based
-
-
data is never directly pulled from a Publisher
- no next() method
-
subscribe to Publisher, receive events (later) via Subscriber
Reactive Streams Basics
public interface Publisher<T> {
void subscribe(Subscriber<? super T> s);
}Subscriber
-
asynchronous data events
- publisher.subscribe(subscriber)
- subscriber.onNext(element), ...
- subscriber.onComplete()
-
events pushed to subscriber
-
what about errors?
-
subscriber.onError(error)
-
Reactive Streams Basics
public interface Subscriber<T> {
void onSubscribe(Subscription s);
void onNext(T t);
void onError(Throwable t);
void onComplete();
}how is this different than traditional event listeners or reactive extensions (Rx.NET, et al)?
Subscription
- deconstruct Iterator.next()
- signal demand (call implies demand)
- deliver data (return value)
- signal error (exception)
- data & error via subscriber.on(Next|Error)
- signal demand
-
- subscribe() implies demand? no
Reactive Streams Basics
Subscription
-
when does data flow?
- key innovation: flow is demand-based
- explicitly signal demand
-
-
subscription.request(count)
-
- no data events flow until demand is signaled
-
-
publisher.subscribe(subscriber)
-
subscriber.onSubscribe(subscription)
-
subscription.request(count)
-
subscriber.onNext(element), ...
-
Reactive Streams Basics
public interface Subscription {
void request(long n);
void cancel();
}Processor
-
both Subscriber and Publisher
- processing stage (e.g. data transformation)
- non-terminal
Reactive Streams Basics
public interface Processor<T, R>
extends Subscriber<T>, Publisher<R> {
}Reactive Streams Basics
Flow Visualization
the flow of demand and data
Summary
- key concept: streams are push-based
- key innovation: flow is demand-based
- Reactive Streams footprint
-
- Publisher
- Subscriber
- Subscription
- Processor
- async/non-blocking
Reactive Streams Basics
public interface Publisher<T> {
void subscribe(Subscriber<? super T> s);
}
public interface Subscriber<T> {
void onSubscribe(Subscription s);
void onNext(T t);
void onError(Throwable t);
void onComplete();
}
public interface Subscription {
void request(long n);
void cancel();
}
public interface Processor<T, R>
extends Subscriber<T>, Publisher<R> {
}
Streams: From Reactive to Akka
Reactive Streams
objective: minimal, well-specified integration API
- multi-vendor integration (part of Java 9?)
- not a user level API (really a SPI)
Akka Streams
objective: develop streaming applications
- component definition (source, sink, flow, etc.)
- transformation library (data, stream)
- graph construction (fan out/in, DSL)
-
- linear, branching, cyclic
- integration / customization
-
- Akka publisher / subscriber
- custom stages
|
|
Level1
(Basic)
|
Level 2
(Intermediate)
|
Level 3
(Advanced)
|
|
Concept
|
Stream
Graph, Shape, Inlet, Outlet
Materialization
|
Buffers
Stream of streams
Attributes
|
Cyclic Graphs
Recovery
|
|
Component
Shape Library
|
Source, Sink, Flow
|
Broadcast, Zip, ZipWith, Unzip, UnzipWith, Merge
|
FlexiRoute, FlexiMerge
BidiFlow
|
|
Transform
|
Data Transformation
|
Custom Transformation
Stream Transformation
Other
|
Custom Materialization
Stream Transformation
Error Handling
|
|
Construct
|
Linear Flows
DSL, Builder
|
Branching Flows
|
Cyclic Flows
Protocol Flows
|
|
Customize
|
N/A
|
|
|
|
Test
|
|
|
|
Akka Streams Topic Map
Today
Basic Building Blocks
- Source
- Sink
- Flow
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
*conceptually
val source = Source(1 to 3)
val sum = Flow[Int].fold(0.0)(_ + _)
val sink = Sink.foreach[Double](println)
// Prints '6.0'
source.via(sum).to(sink).runthe streaming function
Function
Input
Output
Flow
Source
Sink
→
~>
~>
Publisher*
Processor*
Subscriber*
Inlet
→
Outlet
Shape: Inlets & Outlets
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
Shape is to Graph as Signature is to Function
Function :
Graph :
Inputs & Outputs (Signature)
Inlets & Outlets (Shape)

val source: Source[Int] = Source(1 to 3)
val sum: Flow[Int, Double] = Flow[Int].fold(0.0)(_ + _)
val sink: Sink[Double] = Sink.foreach[Double](println)
// What is the shape of the following?
val runnable: RunnableGraph = source.via(sum).to(sink)
runnable.runnote: types intentionally simplified
Running a Graph
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
implicit val system = ActorSystem("akka-streams")
implicit val materializer = ActorMaterializer()
// Create a runnable graph, steps omitted
val runnable: RunnableGraph = source.via(flow).to(sink)
// Run the graph with implicit Materializer
runnable.run()Materializer is to Graph as
ExecutionContext is to Future
- Graph defines blueprint (akin to function def)
- Materializer runs a RunnableGraph (akin to function call)
- materialization allocates runtime resources
- Akka Streams uses Actors
- other (Spark, for example) theoretically possible
Materialized Value
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
// Materialized type is the last type parameter by convention
// Sink that materializes a Future that completes when stream completes
val printer: Sink[Int, Future[Unit]] = Sink.foreach[Int](println)
// Sink that materializes a Future that completes with the first stream element
val head: Sink[Int, Future[Int]] = Sink.head[Int]
// Sources often don't materialize anything
val source: Source[Int, Unit] = Source(1 to 3)
// Source that emits periodically until cancelled via the materialized Cancellable
val ticks: Source[Int, Cancellable] = Source(1.second, 5.seconds, 42)
// Note that the above are merely blueprints
// No materialized values are produced until a graph is materialized
// Materialize a Graph which will run indefinitely or until cancelled
// Any graph can only materialize a single value
// Both printer and ticks materialize values (Future[Unit] and Cancellable)
// runWith() selects the target's materialized value
val cancellable: Cancellable = printer.runWith(ticks)
// Cancel the materialized ticks source
cancellable.cancelGraph materialization result
- runtime resource produced by a Graph during materialization
- related to / used by processing, but not part of the stream itself
Concepts Checkpoint
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
// Create flow materializer
implicit val system = ActorSystem("akka-streams")
implicit val materializer = ActorMaterializer()
// Create graph components
val nums = (1 to 10)
val source: Source[Int, Unit] = Source(nums)
val sum: Flow[Int, Int, Unit] = Flow[Int].fold(0)(_ + _)
val triple: Flow[Int, Int, Unit] = Flow[Int].map(_*3)
val head: Sink[Int, Future[Int]] = Sink.head[Int]
// Assemble and run a couple of graphs
val future1a: Future[Int] = source.via(sum).to(head).run
val future2a: Future[Int] = source.via(triple).via(sum).to(head).run
// Perform some basic tests
whenReady(future1a)(_ shouldBe nums.sum)
whenReady(future2a)(_ shouldBe (nums.sum * 3))
// Equivalent to the above graphs, using shortcuts for brevity
val future1b = Source(nums).runFold(0)(_ + _)
val future2b = Source(nums).via(triple).runFold(0)(_ + _)Transformations
- map, mapAsync
- fold, scan, filter, collect
- take, drop
- take/drop(While|Within)
- grouped, groupedWithin
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
the usual suspects...
// Source[Out, Mat]
def mapAsync[T](parallelism: Int)(f: (Out) ⇒ Future[T]): Source[T, Mat]
def takeWhile(p: (Out) ⇒ Boolean): Source[Out, Mat]
def takeWithin(d: FiniteDuration): Source[Out, Mat]Transformations
- concat, concatMat
- flatten
- prefixAndTail, split(After|When)
- groupBy
- conflate, expand
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
...and a few more
// Source[Out, Mat]
def prefixAndTail[U >: Out](n: Int): Source[(Seq[Out], Source[U, Unit]), Mat]
def splitWhen[U >: Out](p: (Out) ⇒ Boolean): Source[Source[U, Unit], Mat]
def groupBy[K, U >: Out](f: (Out) ⇒ K): Source[(K, Source[U, Unit]), Mat]
def conflate[S](seed: (Out) ⇒ S)(aggregate: (S, Out) ⇒ S): Source[S, Mat]
def expand[S, U](seed: (Out) ⇒ S)(extrapolate: (S) ⇒ (U, S)): Source[U, Mat]Sample Application
Akka Streams & HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
enhanced historical price service
- calculate simple moving average (SMA)
- parse historical price CSV stream
- enhance historical price CSV stream
Part I (Streams)
- expose enhanced price service endpoint
- request historical prices via HTTP
- stream enhanced prices
Part II (HTTP)
Enhanced Price Service
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
sample data
Date, Open, High, Low, Close, Volume, Adj Close
2014-12-31, 25.3, 25.3, 24.19, 24.84, 1438600, 24.84
2014-12-30, 26.28, 26.37, 25.29, 25.36, 766100, 25.36
2014-12-29, 26.64, 26.8, 26.13, 26.42, 619700, 26.42
2014-12-26, 27.25, 27.25, 26.42, 26.71, 360400, 26.71Date, Open, High, Low, Close, Volume, Adj Close, Adj Close SMA(3)
2014-12-31, 25.3, 25.3, 24.19, 24.84, 1438600, 24.84, 25.54
2014-12-30, 26.28, 26.37, 25.29, 25.36, 766100, 25.36, 26.16input
output
- reverse time series (most recent price first)
http://localhost:8080/stock/price/daily/yhoo?calculated=sma(3)
http://real-chart.finance.yahoo.com/table.csv?s=yhoo& ...
Enhanced Price Service
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
- calculate
- enhance
- expose


Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
// Calculate simple moving average (SMA) using scan()
// to maintain a running sum and a sliding window
def sma(N: Int) = Flow[Double]
.scan((0.0, Seq.empty[Double])) {
case ((sum, win), x) =>
win.size match {
case N => (sum + x - win.head, win.tail :+ x)
case _ => (sum + x, win :+ x)
}
}
.drop(N) // Drop initial and incomplete windows
.map { case (sum, _) => sum / N.toDouble }
Source(1 to 5)
.map(n => (n*n).toDouble)
.via(sma(3))
.runForeach(sma => println(f"$sma%1.2f")
// Output:
// 4.67
// 9.67
// 16.67Enhanced Price Stream
simple moving average (SMA)
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
import akka.stream.io.Framing
// A CSV file row, parsed into columns
type Row = Array[String]
// Parse incoming bytes into CSV record stream
// Note: Each ByteString may contain more (or less) than one line
def parse(maximumLineLength: Int = 256): Flow[ByteString, Row, Unit] =
Framing.delimiter(ByteString("\n"), maximumLineLength, allowTruncation = true)
.map(_.utf8String.split("\\s*,\\s*"))
// Select a specific column (including header) by name
def select(name: String): Flow[Row, String, Unit] = Flow[Row]
.prefixAndTail(1).map { case (header, rows) =>
header.head.indexOf(name) match {
case -1 => Source.empty[String] // Named column not found
case index => Source.single(name)
.concatMat(rows.map(_(index)))(Keep.right)
}
}.flatten(FlattenStrategy.concat)
// Convert row into CSV formatted ByteString
val format = Flow[Row].map(row => ByteString(row.mkString("", ",", "\n")))Enhanced Price Stream
CSV handling
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
Enhanced Price Stream
SMA column
// Calculate and format SMA for a column, renaming the column
def smaCol(name: String, n: Int, format: String = "%1.2f") = Flow[String]
.prefixAndTail(1)
.map { case (header, data) =>
Source.single(name).concatMat(
data.map(_.toDouble)
.via(calculate.sma((n)))
.map(_.formatted(format))
)(Keep.right)
}
.flatten(FlattenStrategy.concat)

Adj Close
24.84
25.36
26.42
26.71Adj Close SMA(3)
25.54
26.16
Branching Flows
Akka Streams Level 2 (Intermediate)
a common pattern
- branch stream (fan-out)
- transform each branch
- combine results (fan-in)

Fan-Out Shapes:
Fan-In Shapes:
Broadcast, Unzip, UnzipWith
Zip, ZipWith, Merge, MergePreferred
Graph DSL
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
visual flow construction
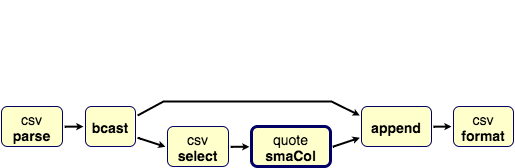
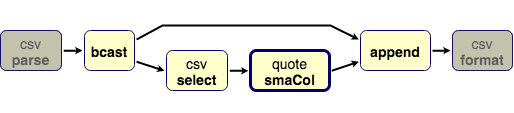
bcast ~> ~> append.in0
bcast ~> select ~> smaCol ~> append.in1
// Calculate and append SMA column
def appendSma(n: Int): Flow[Row, Row, Unit] = Flow(
Broadcast[Row](2),
csv.select("Adj Close"),
smaCol(s"Adj Close SMA($n)", n),
ZipWith((row: Row, col: String) => row :+ col)
)((_, _, _, mat) => mat) {
implicit builder => (bcast, select, smaCol, append) =>
bcast ~> append.in0
bcast ~> select ~> smaCol ~> append.in1
(bcast.in, append.out)
}
appendSma
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)
import akka.stream.io._
val inSource = SynchronousFileSource(new File("input.csv"))
val expSource = SynchronousFileSource(new File("expected.csv"))
val builder = new ByteStringBuilder()
val outSink = Sink.foreach[ByteString](builder ++= _)
val outSource = Source(() => Iterator.single(builder.result()))
val window = 3
val smaName = s"Adj Close SMA($window)"
val future = inSource.via(csv.parse()).via(quote.appendSma(window)).via(csv.format)
.runWith(outSink)
whenReady(future) { unit =>
// Compare SMA column from output and expected
val selectSma = csv.parse().via(csv.select(smaName)).drop(1).map(_.toDouble)
val outFuture = outSource.via(selectSma).runFold(List.empty[Double])(_ :+ _)
val expFuture = expSource.via(selectSma).runFold(List.empty[Double])(_ :+ _)
whenReady(Future.sequence(Seq(outFuture, expFuture))) { case out :: exp :: Nil =>
out should have size exp.size
out.zip(exp).foreach { case (out, exp) =>
out shouldBe exp
}
}
}Enhanced Price Stream
testing
Sample Application
Akka HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
enhanced historical price service
- calculate simple moving average (SMA)
- parse historical price CSV stream
- enhance historical price CSV stream
Part I (Streams)
- expose enhanced price service endpoint
- request historical prices via HTTP
- stream enhanced prices
Part II (HTTP)
Introducing Akka HTTP
stream-based web services
- "Spray 2.0" - address weaknesses and polish features
- key improvement: fully stream-based
- easily handle chunked responses and large entities
- address missing features (WebSockets, anyone?)
- reusable streams transformations
- extensible HTTP model and spec implementation
Akka HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
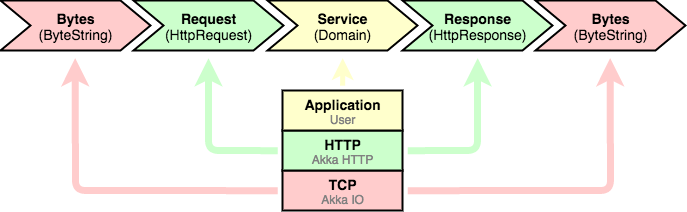
From Akka Streams to HTTP
a natural mapping

in
out
Akka HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
Akka HTTP
fully stream-based
// TCP and HTTP protocols modeled as Flows
// Flow is materialized for each incoming connection
// TCP
Tcp().bindAndHandle(handler: Flow[ByteString, ByteString, _], ...)
// HTTP (server low-level)
// Q: How is HTTP pipelining supported?
Http().bindAndHandle(handler: Flow[HttpRequest, HttpResponse, Any], ...)
// HTTP (client low-level)
Http().outgoingConnection(host: String, port: Int = 80, ...):
Flow[HttpRequest, HttpResponse, Future[OutgoingConnection]]// HTTP entities modeled using ByteString Sources
// Request entity modeled as a source of bytes (Source[ByteString])
val request: HttpRequest
val dataBytes: Source[ByteString, Any] = request.entity.dataBytes
// Use Source[ByteString] to create response entity
val textSource: Source[ByteString, Any]
val chunked = HttpEntity.Chunked.fromData(MediaTypes.`text/plain`, textSource)
val response = HttpResponse(entity = chunked)Akka HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
Enhanced Price Service
Akka HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
mock service endpoint
import akka.http.scaladsl.Http
import akka.http.scaladsl.server.Directives._
import akka.http.scaladsl.model.MediaTypes._
import akka.stream.io.SynchronousFileSource
// Find mock data file (if it exists) for the given symbol
def mockFile(symbol: String): Option[File] =
Option(getClass.getResource(s"/mock/stock/price/$symbol.csv"))
.map(url => new File(url.getFile))
.filter(_.exists)
// http://localhost/stock/price/daily/yhoo
val route: Route =
(get & path("stock"/"price"/"daily" / Segment)) { (symbol) =>
complete {
mockFile(symbol) match {
// Create chunked response from Source[ByteString]
case Some(file) => HttpEntity.Chunked.fromData(`text/csv`, SynchronousFileSource(file))
case None => NotFound
}
}
}
// Run a server with the given route (implicit conversion to Flow[HttpRequest, HttpResponse])
val binding = Http().bindAndHandle(route, "localhost", 8080)Enhanced Price Service
Akka HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
fetching data
import csv.Row
import akka.http.scaladsl.Http
import akka.http.scaladsl.model.HttpEntity
import akka.http.scaladsl.model.MediaTypes._
import akka.http.scaladsl.server.Directives._
trait StockPriceClient {
def history(symbol: String): Future[Either[(StatusCode, String), Source[Row, Any]]]
}
case class YahooStockPriceClient
(implicit system: ActorSystem, executor: ExecutionContextExecutor, materializer: Materializer)
extends StockPricesClient
{
override def history(symbol: String) = {
val uri = buildUri(symbol) // http://real-chart.finance.yahoo.com/table.csv?s=$symbol&...
Http().singleRequest(RequestBuilding.Get(uri)).map { response =>
response.status match {
case OK => Right(response.entity.dataBytes.via(csv.parse())
case NotFound => Left(NotFound -> s"No data found for $symbol")
case status => Left(status -> s"Request to $uri failed with status $status")
}
}
}
}Enhanced Price Service
Akka HTTP Level 1 (Basics)
expose service endpoint
import csv.Row
import akka.http.scaladsl.Http
import akka.http.scaladsl.model.HttpEntity
import akka.http.scaladsl.model.MediaTypes._
import akka.http.scaladsl.server.Directives._
trait StockPriceClient {
def history(symbol: String): Future[Either[(StatusCode, String), Source[Row, Any]]]
}
val client: StockPriceClient
// http://localhost/stock/prices/daily/yhoo/sma(10)
val route: Route =
(get & path("stock"/"prices"/"daily" / Segment / "sma(" ~ IntValue ~ ")")) {
(symbol, window) =>
client.history(symbol).map[ToResponseMarshallable] {
case Right(source) => HttpEntity.Chunked.fromData(`text/csv`,
source.via(quote.appendSma(window)).via(csv.format))
case Left(err @ (NotFound, _)) => err
case Left(_) => ServiceUnavailable -> "Error calling underlying service"
}
}Enhanced Price Service
Akka Streams Level 1 (Basics)



solution review
Full Sample
Intro to Akka Streams & HTTP
https://github.com/lancearlaus/akka-streams-http-intro
- Bitcoin trades OHLCV service
- stackable services
- WebSockets
- custom stage
- custom route segments / parameters
- flow graph packaging
more to explore
⇒ git clone https://github.com/lancearlaus/akka-streams-http-introduction
⇒ sbt run
[info] Running Main
Starting server on localhost:8080...STARTED
Get started with the following URLs:
Stock Price Service:
Yahoo with default SMA : http://localhost:8080/stock/price/daily/yhoo
Yahoo 2 years w/ SMA(200) : http://localhost:8080/stock/price/daily/yhoo?period=2y&calculated=sma(200)
Facebook 1 year raw history : http://localhost:8080/stock/price/daily/fb?period=1y&raw=true
Bitcoin Trades Service:
Hourly OHLCV (Bitstamp USD) : http://localhost:8080/bitcoin/price/hourly/bitstamp/USD
Daily OHLCV (itBit USD) : http://localhost:8080/bitcoin/price/daily/itbit/USD
Recent trades (itBit USD) : http://localhost:8080/bitcoin/trades/itbit/USD
Trades raw response : http://localhost:8080/bitcoin/trades/bitstamp/USD?raw=trueIntro to Akka Streams and HTTP
Summary
- Reactive Streams Basics
- Akka Streams Basics
- Akka HTTP Basics
- Sample Service
Questions?
Copy of Intro to Akka Streams and HTTP
By Gary Gao
Copy of Intro to Akka Streams and HTTP
Got Streams? Streams are an effective way to model many real-world data problems from event processing to the typical service request/response cycle. Learn the basics of Akka Streams & HTTP through a practical introductory training talk, no prior Streams experience required. The talk will cover Akka Streams from the ground up, starting with Reactive Streams concepts, to give participants a solid foundation. Akka Streams & HTTP building blocks and capabilities will be explained and showcased via a stream processing example exposed as an Akka HTTP service.
- 2,097



