JavaScript 101
Web Programming Course
SUT • Fall 2018
TOC
- What is JS?
- History
- How To
- Grammar
- Variables
- Data types
- Value vs Reference
- Functions
- Control Flow
- Operators
- == vs ===
- Scope
- Hoisting
- Strict Mode
What is JS
JavaScript is a scripting language.
- Client-side programming
- Server-side programming
- Updating content dynamically
- Control audio/video
- Handling URL changes
- ...
- Web servers
- Working with databases
- File system
- CLI scripts
- ...
More on MDN
JavaScript
- 1995 Mocha (By Brendan Eich at Netscape)
- 1995 LiveScript
- 1995 JavaScript
- 1996 JScript (Internet Explorer 3)
- 1997 ECMAScript 1.0 (ECMA International) (no closures)
- 1998 ECMAScript 2.0 (ISO version of ES1)
- 1999 ECMAScript 3.0 (closures, do...while, switch, try...catch, ...)
- 2009 ECMAScript 5.0 (Formerly ES3.1, default and strict modes)
- 2011 ECMAScript 5.1
- 2015 ECMAScript 2015
- ...
History

How To
WHAT TOOLS DO YOU NEED?
- A text editor; a program that allows you to edit plain text files. (Notepad++, Sublime Text, VS Code, Brackets, etc.)
- A JavaScript runtime; e.g. a web browser or node. (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Opera.)
How To
More on MDN
- External JavaScript (in
<head>or<body>)
- Internal JavaScript (in
<head>or<body>)
- Inline JavaScript handlers
<script src="script.js"></script><script>
// JavaScript goes here
</script><button onclick="doSomething()">Click me!</button>Grammar
Statement
// declaration statement
var a;
var b = 5;
// assignment statement, also an expression
a = b * 2;
Expression
var a = 5, b;
b = a * 2;
// 2, a, a*2 and b=a*2 are expressions
Grammar
Comments
var foo = 'foo' // Single line comment
/*
Multi-line comment
*/Block Statement
{
statement1;
statement2;
...
statementN;
}Variables
Loosely typed; case-sensitive.
More on MDN
var a = 5;
b = 4; // Throws a ReferenceError in strict mode
var a; // More declarations do NOT change the value
a; //-> 5
// Variable declaration with 'var' keyword
var a = 5;
a = 'changed to string';
a = [1, 2, 3];
a; //-> [1, 2, 3]
Data Types
-
Primitives (are immutable)
stringnumberbooleannullundefinedsymbol (ES2015)
-
Objects
ArrayObjectFunction
// Primitive values
var str = 'my string';
var num = 42;
var bl = true;
// Primitive types wrapper objects
var str2 = new String('my string');
var num2 = new Number(42);
var bl2 = new Boolean(true);
// Objects constructors
var arr = new Array(1, 2, 3);
var obj = new Object();
// literal form of objects
var arr2 = [1, 2, 3];
var obj2 = { key: 'value' };
function add(a, b) { return a+b };More on MDN
Data Types
if (somethingWrong) {
throw new Error("ERR :'(");
}
// Area of a circle
function area(radius) {
return Math.pow(radius, 2) * Math.PI
}
var d = new Date('December 17, 1995');
d.getFullYear(); // 1995
d.getMonth(); // 11
d.getDate(); // 17
var re = new RegExp('[0-9]+');
re.test('Life') // false
re.test('42') // true*More on MDN
Built-in Objects
Data Types
How does this work?
// An object with a method
var myObj = { foo: function() { /* ... */ } }
// Calling the method, just works!
myObj.foo()
/* ===== BUT ===== */
// Primitive string value
var myString = 'my string';
// Calling a method on a primitive value ???
myString.toUpperCase();Online Demo
Data Types
Primitives are passed by value.
Objects are passed by reference.
// Primitive values
var foo = 'foo';
var bar = foo;
bar += 'bar';
// Reference Values
var baz = [1, 2, 3]
var qux = baz;
qux.push(4);Value vs Reference
More on Codeburst
Functions
More on MDN
// Declaration with 'function' keyword
function square(number) {
return number * number;
}
var x = square(4); // x gets the value 16Declaration
// Variable declaration with a function as the value
var square = function(number) {
return number * number;
};
var x = square(4); // x gets the value 16, same result.Expression
Control Flow
More on MDN
if (condition_1) {
statement_1;
} else if (condition_2) {
statement_2;
} else {
statement_last;
}
if...else Statement
Truthy values:
[]{}['']'0'- ...
Control Flow
More on MDN
switch (expr) {
case 'Oranges':
console.log('Oranges are $0.59 a pound.');
break;
case 'Apples':
console.log('Apples are $0.32 a pound.');
break;
case 'Bananas':
console.log('Bananas are $0.48 a pound.');
break;
case 'Mangoes':
case 'Papayas':
console.log('Mangoes and papayas are $2.79 a pound.');
break;
default:
console.log('Sorry, we are out of ' + expr + '.');
}
switch Statement
Control Flow
More on MDN
for (var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
console.log(i);
// more statements
}
for Statement
var i = 0;
for (; i < 9; i++) {
console.log(i);
// more statements
}var i = 0;
for (;;) {
if (i >= 9) break;
console.log(i);
i++;
}Loops
Control Flow
More on MDN
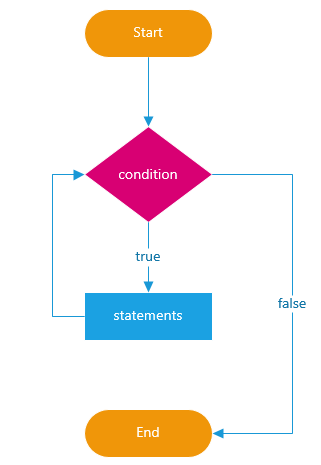
while Statement
Loops
Control Flow
More on MDN
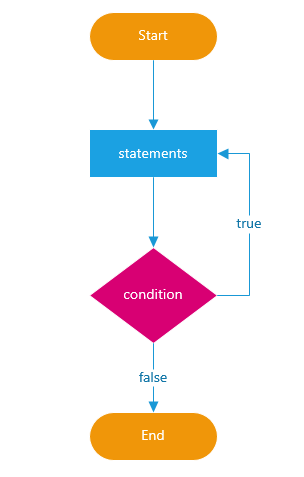
do...while Statement
Loops
Operators
typeof 'foo' // string
1 / 2 // 0.5
prop in obj // true or false
'5' == 5 // true
num & 1 // odd or even
1 && true // true
num > 3 ? 'High' : 'Low'
str += '_suffix'
var a = b = 5, c = b
// a = 5, b = 5, c = 5More on MDN
- Unary Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Equality Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Binary Logical Operators
- Ternary Operator
- Assignment Operators
- Comma Operator
Strict equality (x === y)
var num = 0;
var obj = new String('0');
var str = '0';
num === num; // true
obj === obj; // true
str === str; // true
num === obj; // false
num === str; // false
obj === str; // false
null === undefined; // false
obj === null; // false
obj === undefined; // falseMore on MDN
- Different types? false
- x is undefined or null? true
-
Booleans, strings?
- Same value? true
- Otherwise; false
-
Numbers?
- Same value? true
- NaN? false
- +0, -0? true
- Otherwise; false
-
Objects?
- Same object (reference)? true
- Otherwise; false
== vs ===
Operators
Loose equality ==
More on MDN
var num = 0;
var obj = new String('0');
var str = '0';
num == num; // true
obj == obj; // true
str == str; // true
num == obj; // true
num == str; // true
obj == str; // true
null == undefined; // true
// both false,
// except in rare cases
obj == null;
obj == undefined;- Same types? ...
- undefined or null? true
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
You really don't want to know all the conditions!
== vs ===
Operators
Scope
More on MDN
// The following variables
// are defined in
// the global scope
var num1 = 20,
num2 = 3;
// This function is defined
// in the global scope
function multiply() {
return num1 * num2;
}
multiply(); // Returns 60var name = "John";
// A nested function example
function getScore(num1) {
var num2 = 5;
function add() {
return name + ' scored ' + (num1 + num2);
}
return add();
}
// Returns "John scored 6"
getScore(1);Hoisting
More on MDN
// ReferenceError: foo is not defined
console.log(foo);Accessing undeclared variables:
console.log(foo); //-> undefined
var foo = 'The variable has been hoisted.';Accessing variables before var statement:
Variable Declaration
Why?
Hoisting
More on MDN
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
add(3, 4); //-> 7add(3, 4); //-> ?
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}Function Declaration
Invoking function before function declaration:
"use strict";
- Get rid of some JavaScript silent errors
- Let JavaScript engines perform optimizations
- ...
More on MDN
"use strict";
myFunction();
function myFunction() {
y = 3.14; // Err: y is not declared
}x = 3.14; // This will not cause an error.
myFunction();
function myFunction() {
"use strict";
y = 3.14; // This will cause an error
return this; // this === undefined
}References
JavaScript 101
By Hashem Qolami
JavaScript 101
JavaScript 101 / Web Programming Course @ SUT, Fall 2018
- 1,650



