Buffer overflow
What is the stack?
- First In Last Out (FILO) data structure
- Two main operations: push & pop
- Commonly used on architectural level for memory allocation and access
- Holds bools, ints, chars, arrays, and etc.
- Doesn't hold structs, classes, and etc
Which are the stack types?
Element #0
Element #1
Element #2
Stack Direction
Element #2
Element #3
Element #0
Element #1
Element #2
Element #3
Stack Direction
Descending
Ascending
Low memory addresses
Low memory addresses
What is a buffer?
- Space located in memory
- Temporarily stores data while the data is in the process of moving from one place to another
Element #2
Buffer
Stack security
- Stack canaries
- Data Execution Prevention (DEP)
- Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR)
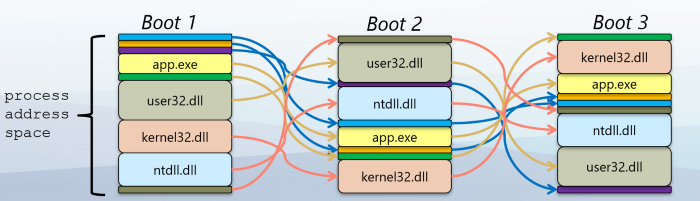
Exploits
Buffer overflow with variable value override
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char buffer[500];
int deadbeef = 0xdeadbeef;
scanf("%600s",&input);
return 0;
}Return address
Base pointer
input[500]
0xdeadbeef
The user inputs more than 500 characters
Exploits
Buffer overflow with EIP override and shellcode execution
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char buffer[500];
int deadbeef = 0xdeadbeef;
scanf("%600s",&input);
return 0;
}Return address
Base pointer
input[500]
0xdeadbeef
The user inputs more than 500 characters with shellcode.
Shellcode
Exploits
NOP slides
Return address
Base pointer
input[500]
0xdeadbeef
Shellcode
NOP Slide
Intel x86 instruction - 0x90
ARM A64 instruction - 0xD503201F
Intel 8051 instruction - 0x00
Let's do some exercises
Binary: tinyurl.com/y4uhekk7
Buffer overflow
By Ivan Zlatanov
Buffer overflow
- 110



