資安期末 Project
RAPPOR
Randomized Aggregatable Privacy-Preserving
Ordinal Response
RAPPOR
- Signal
- Permanent randomized response
-
Instantaneous randomized response
-
Report
RAPPOR
- Signal
使用h個hash function
將要傳送的value v
hash onto Bloom filter B
RAPPOR
- Permanent randomized response
將Bloom filter B 上的每個bit
做以下轉換,得到Fake Bloom filter B'
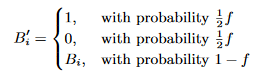
RAPPOR
- Instantaneous randomized response
Allocate a bit array S of size k and initialize to 0
並依照以下機率設定S的每個bit為1
(p,q為預先設定的機率)
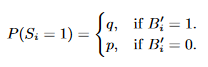
RAPPOR
- Report
將S作為報告送到server
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter( frequent values )
Identification
-
Frequency Oracles
- Generalized Randomized Response (GRR)
- Optimized Local Hashing (OLH)
- Prefix Extending Method (PEM)
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Frequency Oracles
一個滿足LDP的協定
使用兩種演算法:
π: 使用者用來noisy report的方法
Γ: 研究者用來取得想要資訊的方法
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Generalized Randomized Response (GRR)
Frequency Oracles的一種協定
適用於small d較佳
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Generalized Randomized Response (GRR)
假設有 n users 且所有user回答的value v ∈ D,
D的domain size |D| = d
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Generalized Randomized Response (GRR)
π(v)=v 的機率為p
π(v)=v'的機率為p' (且v != v')
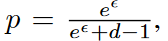
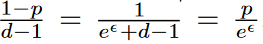
p'=
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Generalized Randomized Response (GRR)
Γ(v)=
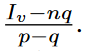
使用者報告v的數量
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Generalized Randomized Response (GRR)
但當d很大時,π(v)=v的機率p會很小
造成統計的準確度極速下降
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Optimized Local Hashing (OLH)
the best accuracy while maintaining a low communication cost
適用於處理large d較佳
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Optimized Local Hashing (OLH)
π(v)=( H, π'(H(v)) )
π'為GRR的π
H: hash function, 將D to {1...d'}
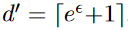
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Optimized Local Hashing (OLH)
Γ(v)=
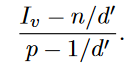
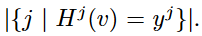
第j個使用者用的hash function
第j個使用者的報告
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Frequency Oracles
- Generalized Randomized Response (GRR)
- Optimized Local Hashing (OLH)
- Prefix Extending Method (PEM)
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Prefix Extending Method (PEM):
用來解決d太大造成 frequency oracle的計算不可行
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Prefix Extending Method (PEM):
參數: 兩正整數
使用者會被分配到g個groups中的1個group
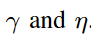
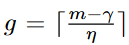
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Prefix Extending Method (PEM)
使用者回傳的report形式:
第i group回傳
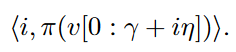
Locally Differentially Private Heavy Hitter
Identification
- Prefix Extending Method (PEM)
運作流程:
第1群統計frequent prefixes -> 第2群統計frequent prefixes ->...
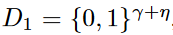
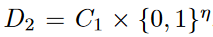
RAPPOR code分析
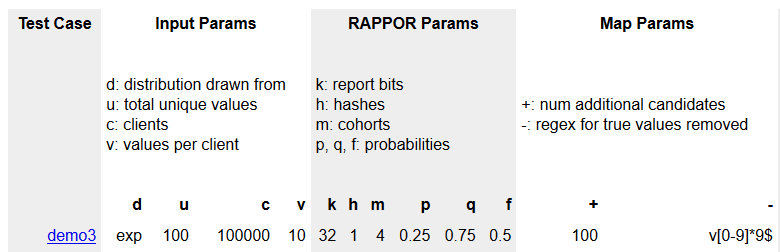
參數設定
regtest_spec.py
...
DEMO = (
# (case_name distr num_unique_values num_clients values_per_client)
# (num_bits num_hashes num_cohorts)
# (p q f) (num_additional regexp_to_remove)
('demo1 unif 100 100000 10', '32 1 64', '0.25 0.75 0.5', '100 v[0-9]*9$'),
('demo2 gauss 100 100000 10', '32 1 64', '0.25 0.75 0.5', '100 v[0-9]*9$'),
('demo3 exp 100 100000 10', '32 1 4', '0.25 0.75 0.5', '100 v[0-9]*9$'),
('demo4 zipf1 100 100000 10', '32 1 64', '0.25 0.75 0.5', '100 v[0-9]*9$'),
('demo5 zipf1.5 100 100000 10', '32 1 64', '0.25 0.75 0.5', '100 v[0-9]*9$'),
)
...demo.sh
quick-python() {
./regtest.sh run-seq '^demo3' python
}
quick-cpp() {
# For now we build it first. Don't want to build it in parallel.
./build.sh cpp-client
./regtest.sh run-seq '^demo3' cpp
}
quick() {
quick-python
quick-cpp
}
if test $# -eq 0 ; then
quick
else
"$@"
firegtest.sh
...
# Run tests sequentially. NOTE: called by demo.sh.
run-seq() {
local spec_regex=${1:-'^r-'} # grep -E format on the spec
shift
time _run-tests $REGTEST_SPEC $spec_regex F $@
}
_run-tests() {
local spec_gen=$1
local spec_regex="$2" # grep -E format on the spec, can be empty
local parallel=$3
local impl=${4:-"cpp"}
local instances=${5:-1}
local regtest_dir=$REGTEST_BASE_DIR/$impl
rm -r -f --verbose $regtest_dir
mkdir --verbose -p $regtest_dir
local func
local processors
if test $parallel = F; then
func=_run-one-instance # output to the console
processors=1
else
func=_run-one-instance-logged
# Let the user override with MAX_PROC, in case they don't have enough
# memory.
processors=${MAX_PROC:-$(default-processes)}
log "Running $processors parallel processes"
fi
local cases_list=$regtest_dir/test-cases.txt
# Need -- for regexes that start with -
$spec_gen | grep -E -- "$spec_regex" > $cases_list
# Generate parameters for all test cases.
cat $cases_list \
| xargs -l -P $processors -- $0 _setup-one-case $impl \
|| test-error
log "Done generating parameters for all test cases"
local instances_list=$regtest_dir/test-instances.txt
_setup-test-instances $instances $impl < $cases_list > $instances_list
cat $instances_list \
| xargs -l -P $processors -- $0 $func || test-error
log "Done running all test instances"
make-summary $regtest_dir $impl
}
...regtest.sh
...
_run-one-instance() {
...
case $impl in
python)
banner "Running RAPPOR Python client"
# Writes encoded "out" file, true histogram, true inputs to
# $instance_dir.
time tests/rappor_sim.py \
--num-bits $num_bits \
--num-hashes $num_hashes \
--num-cohorts $num_cohorts \
-p $p \
-q $q \
-f $f \
< $true_values \
> "$instance_dir/case_reports.csv"
;;
cpp)
banner "Running RAPPOR C++ client (see rappor_sim.log for errors)"
time client/cpp/_tmp/rappor_sim \
$num_bits \
$num_hashes \
$num_cohorts \
$p \
$q \
$f \
< $true_values \
> "$instance_dir/case_reports.csv" \
2>"$instance_dir/rappor_sim.log"
;;
*)
log "Invalid impl $impl (should be one of python|cpp)"
exit 1
;;
esac
...rappor_sim.py
import csv
import collections
import optparse
import os
import random
import sys
import time
import rappor # client library
try:
import fastrand
except ImportError:
print >>sys.stderr, (
"Native fastrand module not imported; see README for speedups")
fastrand = None
...rappor.py
包含RAPPOR所需要的功能
regtest.sh
...
_run-one-instance() {
...
banner "Summing RAPPOR IRR bits to get 'counts'"
bin/sum_bits.py \
$case_dir/case_params.csv \
< $instance_dir/case_reports.csv \
> $instance_dir/case_counts.csv
...
}
...Read the RAPPOR'd values on stdin, and sum the bits to produce a Counting Bloom
filter by cohort. This can then be analyzed by R.
regtest.sh
...
_run-one-instance() {
...
TIMEFORMAT='Running compare_dist.R took %R seconds'
time {
# Input prefix, output dir
tests/compare_dist.R -t "Test case: $test_case (instance $test_instance)" \
"$case_dir/case" "$instance_dir/case" $out_dir
}
}
...實際分析各value的頻率
RAPPOR 實際運作結果
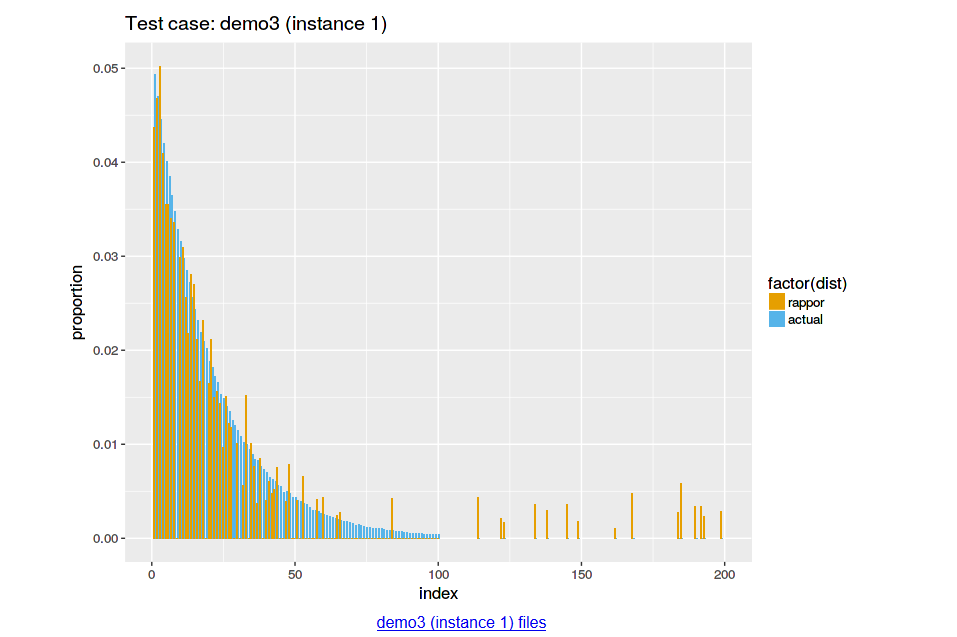
實作PEM成果
看程式碼~
修改:
1. 在hash value時, 將參數cohort固定為1
原因: 避免每個cohort hash的結果不同
2. 在hash_candidates.py中get_bloom_bits, 把將參數cohort固定為1
原因同上
資安期末 project + 構想(參考)
By jackiechen08
資安期末 project + 構想(參考)
- 593



