Supervised Open Information Extraction
Gabriel Stanovsky, Julian Michael, Luke Zettlemoyer, and Ido Dagan
Presented By:
Dharitri Rathod
Lamia Alshahrani
Yuh Haur Chen
What is
Open Information Extraction?
It is a system to extract tuples of natural language expression that represents the basic propsitions asserted by a sentence
Open Information Extraction (OIE)
Usages
- Textual entailment
- Question answering
- Knowledge based populations
Background
(Banko,2007)
Idea of Open IE
(Fader,2011)
Reverb
(Michael,2018)
(Stanovsky,2016)
OpenIE4
OIE2016
QAMR
BIO tagging
Supervised OpenIE
(He et,2015)
QA-SRL
Custom BIO Tagging
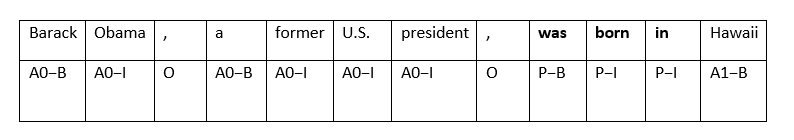
Each tuple is encoded with respect to a single predicate, where argument labels indicate their position in the tuple.
“Barack Obama, a former US President, was born in Hawaii”
Tuples:
(Barack Obama; was born in; Hawaii)
(a former US President; was born in; Hawaii)
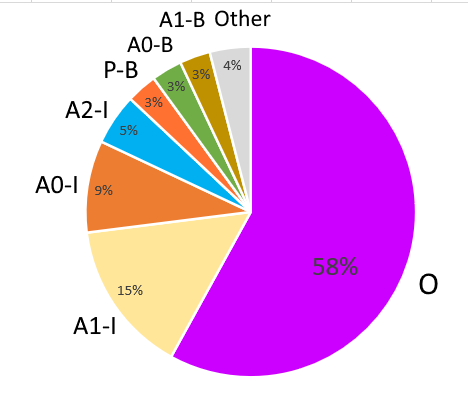
Word label distribution:
Predicate
Argument1
Argument0
Argument0
QA-SRL QAMR
- Who did What to whom, when, and where?
"Mercury filling, particularly prevalent in the USA, was banned in the EU, partly because it causes antibiotic resistance. "
QA-SRL:
| Predicate | question | answer |
|---|---|---|
| banned(v) | what was banned? | Mercury filling |
| where was something banned? | in the EU |
| prevalent (adj) |
what was particularly prevalent in the USA? |
|---|

QA-MR:
| particularly prevalent |
what was particularly prevalent in the USA? | Mercury filling |
|---|

OPENIE4 RNNOIE
- Introduce new content words
- Have more than one wh-word
- Do not start with who, what, when, or where
- Ask what did X do? (delegating the predicate to answer )
Avoid questions which:
RNNOIE(QAMR):
(mercury filling; was banned; in the EU)
(mercury filling; particularly prevalent; in the USA)
RNN OIE
a supervised Open IE Model
"working love learning we on deep"
"we love working on deep learning" :)
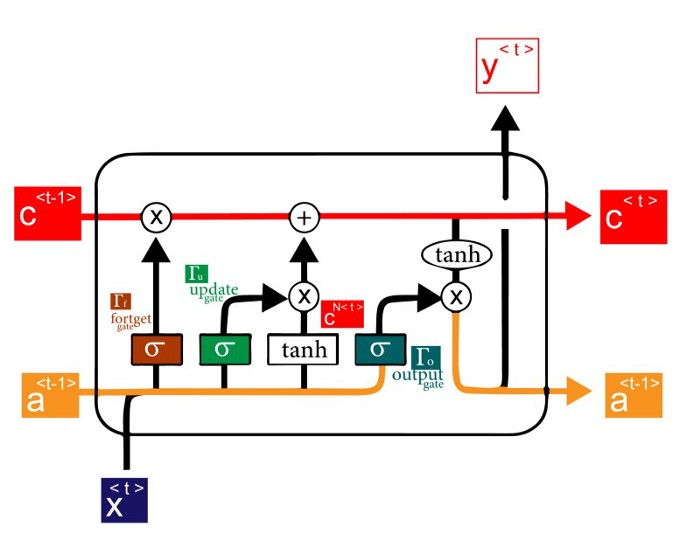
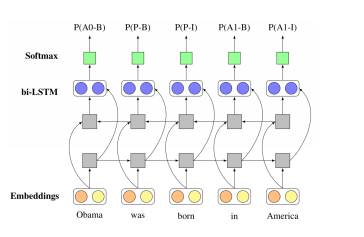
LSTM
BI-LSTM
Obama was
in America
Extraction confidence: by multiplying probabilities of B and I labels in E, which is useful for tuning their PR tradeoff

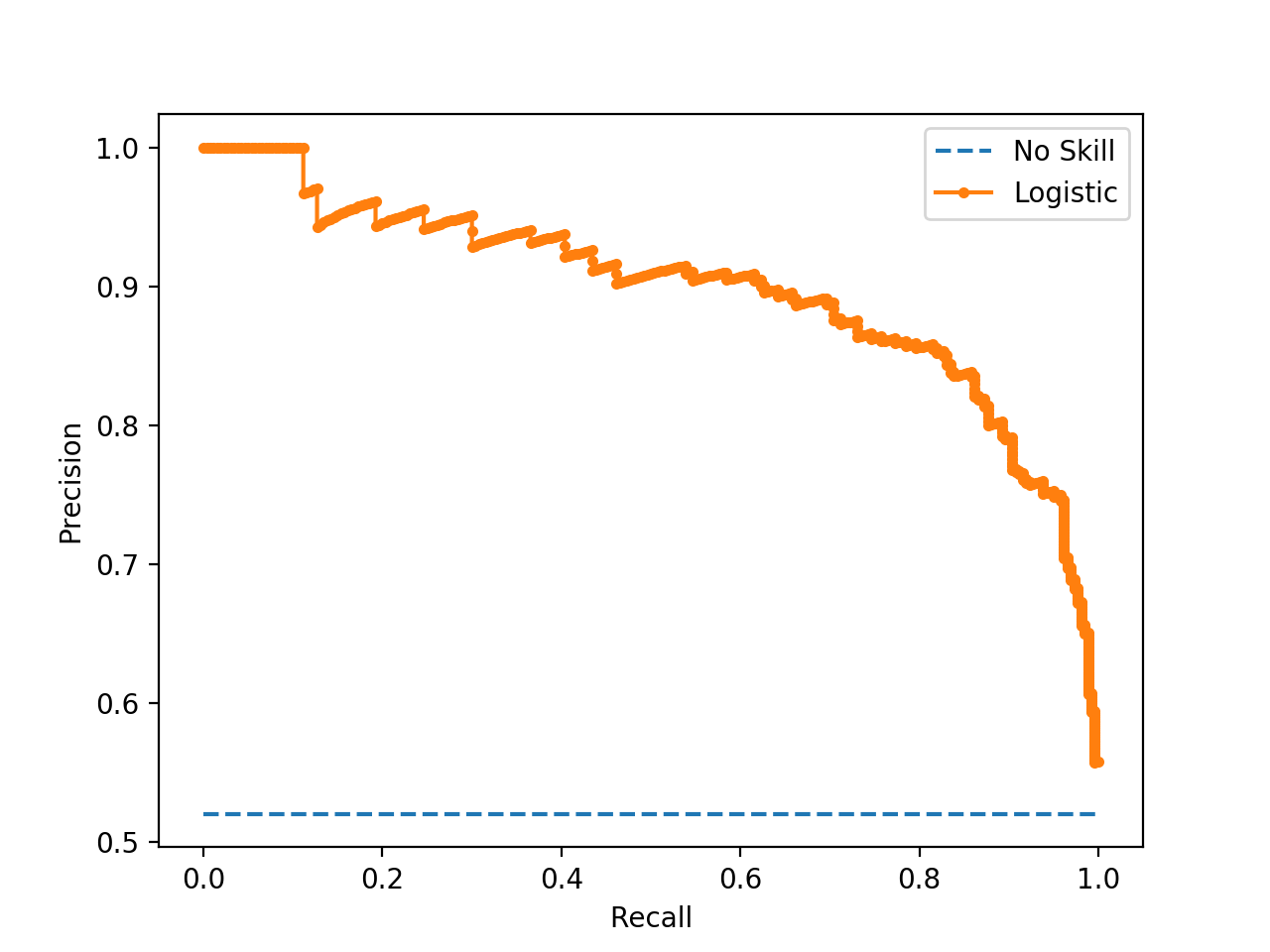
Evaluation
Metrics
-
Precision-recall (PR) curve
-
Compute the area under the PR curve(AUC)
-
F-measure
Precision =
True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)
Recall =
True Positives / (True Positives + False Negatives)
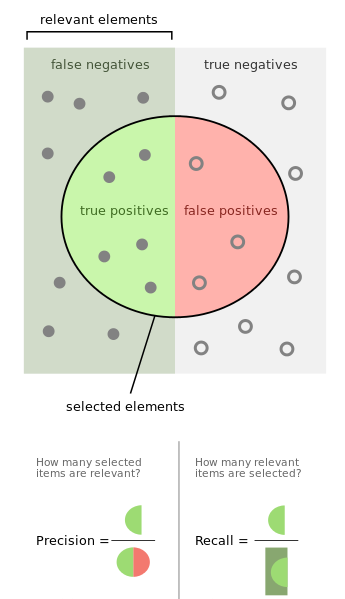
F1 = 2* precision* recall/ precision + recall
Metrics
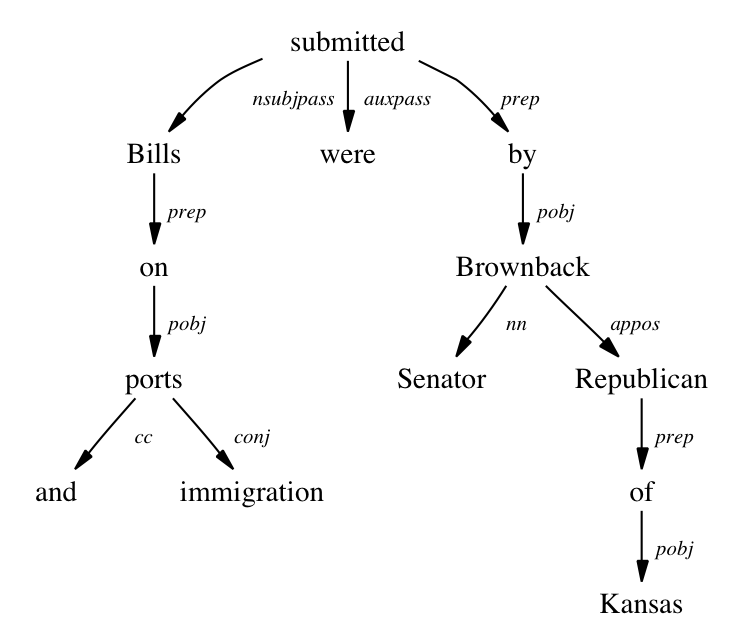
The sheriff standing against the wall spoke in a very soft voice
Matching function
The Sheriff;
spoke; &
in a soft voice
The sheriff standing against the wall;
spoke;
in a very soft voice
| OIE2016 | WEB, NYT, PENN |
|---|---|
| Penn Treebank gold syntactic trees | predicted trees |

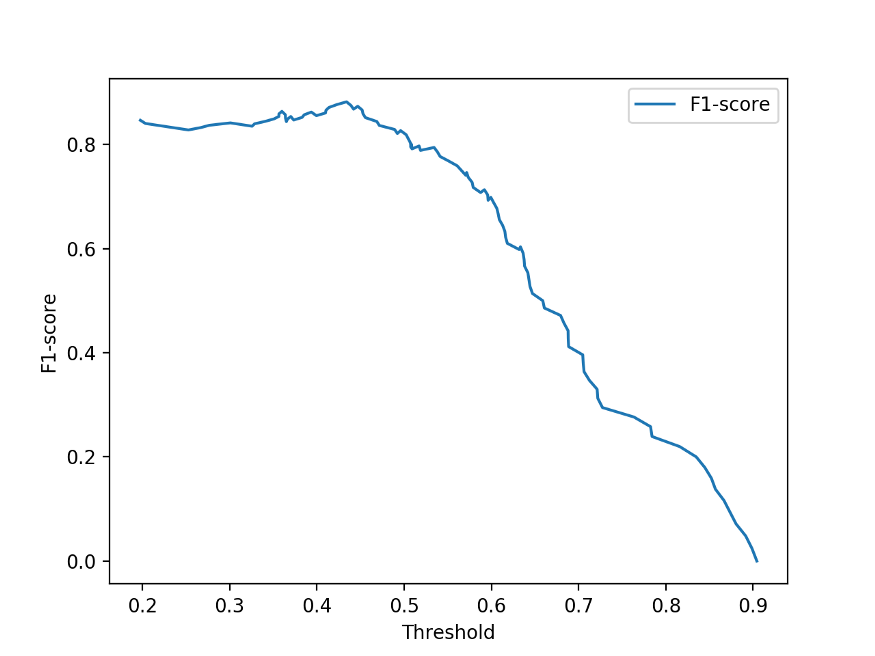
Evaluation result-1
Rank 1 1 1 1 1 3 2 1
Test set: Only | Include
verb predicates | nominalizations
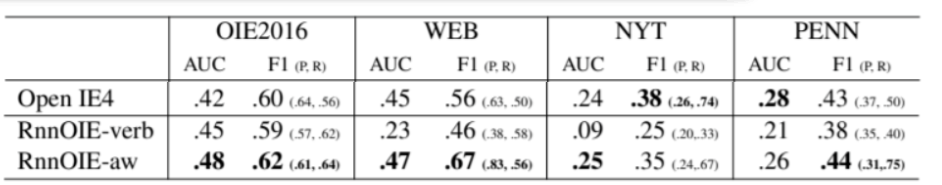
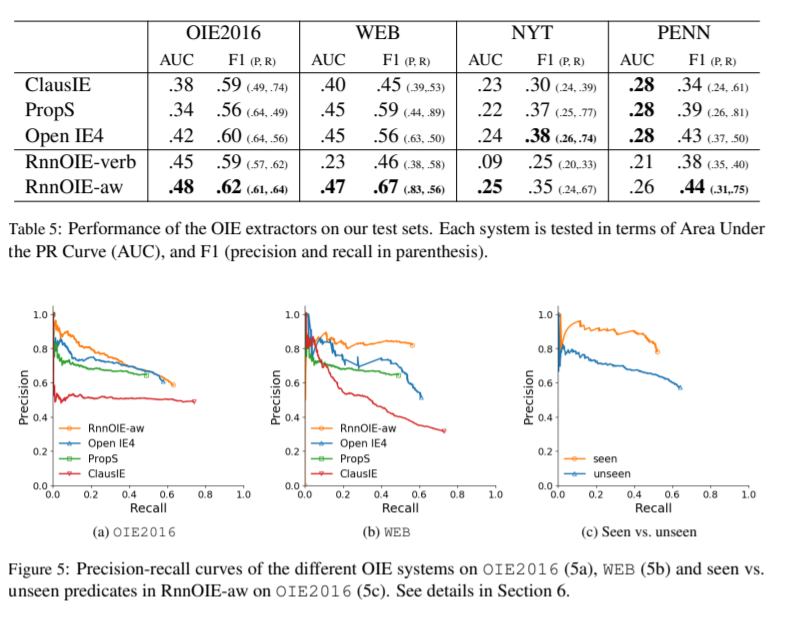
Evaluation result-2
"Furthermore, on all of the test sets,
extending the training set significantly improves our model’s performance"
Performance Analysis - Runtime analysis
| ClausIE | PropS | Open IE4 | RnnOIE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xeon 2.3GHz CPU | 4.07 | 4.59 | 15.38 | 13.51 |
| Efficiency % | 26.5% | 29.8% | 100% | 87.8% |
Data set: 3200 sentences from OIE2016
Using GPU : RnnOIE get 11.047 times faster (149.25 sentences/sec)
(sentences/sec)
Performance Analysis - Error analysis
a random sample of 100 recall errors:
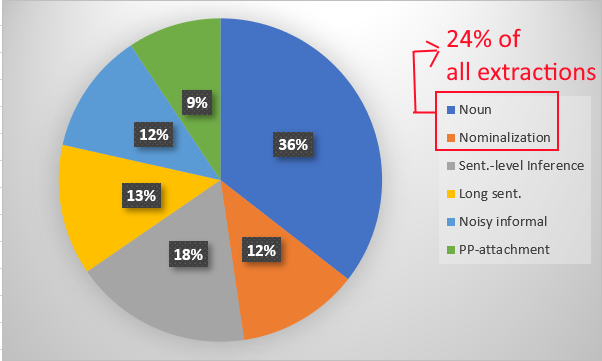
> 40 words
(Avg. :29.4 words/sentence )
Pros and Cons
What's unique and impressive?
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Supervised system | Lack of comparison group to compare CPU and GPU runtime performance |
| Provide confidence scores for tuning their PR tradeoff | It is dependent on the probabilities of B and I labeling |
| Their system did perform well compare to others (PR Curve, AUC) |
QAMR: what filling was made of? mercury RNNOIE: ???? (due to the restriction) |
Summary
Open IE

Bi-LSTM
Sequence tagging problem
formulating
BIO encoding
confidence score
extend
OIE2016
QAMR
train
QA-SRL
Open IE

Bi-LSTM
Sequence tagging problem
formulating
BIO encoding
confidence score
extend
OIE2016
QAMR
train
QA-SRL
Extend RNNOIE Using all QAMR
References
- Luheng He, Mike Lewis, and Luke Zettlemoyer, 2015, Question-answer driven semantic role labeling: Using natural language to annotate natural language. In the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP).
- Julian Michael, Gabriel Stanovsky, Luheng He, Ido Dagan, and Luke Zettlemoyer. 2018. Crowdsourcing question-answer meaning representations. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Jie Zhou and Wei Xu. 2015. End-to-end learning of semantic role labeling using recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing of the Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing, ACL 2015, July 26-31, 2015, Beijing, China, Volume 1: Long Papers, pages 1127–1137.
- Rudolf Schneider, Tom Oberhauser, Tobias Klatt, Felix A. Gers, and Alexander Loser. 2017. Analyzing errors of open information extraction systems. CoRR abs/1707.07499.
- Michele Banko, Michael J. Cafarella, Stephen Soderland, Matthew Broadhead, and Oren Etzioni. 2007. Open information extraction from the web. In IJCAI 2007, Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hyderabad, India, January 6-12, 2007, pages 2670–2676.
- https://medium.com/@raghavaggarwal0089/bi-lstm-bc3d68da8bd0
- Anthony Fader, Stephen Soderland, and Oren Etzioni. 2011. Identifying relations for open information extraction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 1535–1545.
- https://gabrielstanovsky.github.io/assets/papers/naacl18long/poster.pdf
Supervised Open Information Extraction - paper review-Team 10
By jackiechen08
Supervised Open Information Extraction - paper review-Team 10
- 398