

Quantum Computing





Hacking into Nature's Computer
About Presenter James Weaver
Java Champion, JavaOne Rockstar, plays well with others, etc :-)


Author of several Java/JavaFX/RaspPi books

Developer Advocate & International Speaker for Pivotal
Mission: "Transform how the world builds software"







Mission: "Transform how the world builds software"


About Presenter Dr. Johan Vos
Developer / Physicist / Writer / Speaker - Gluon



About Gluon


Gluon CloudLink

Concepts we'll address today
Introduction to quantum computing
Representing qubits
Axioms of quantum mechanics
- Superposition principle
- Measurement
- Unitary evolution
Quantum computing algorithms
Quantum entanglement
More algorithms
Supplementary resources
Intro to Quantum Computing
History repeating itself


massive hardware, limited bits, software infancy
Quantum computers make direct use of quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data.
Some QC proofs of concept
mini-universe in your garage
Don't try this at home, kids!


Why use a quantum computer?
Feasible on classical computers
Feasible on quantum computers
Solutions to problems
some problems may be solved exponentially faster
Transistors can't get much smaller
the quantum tunneling struggle is real

Breaking RSA crypto

someday maybe, using Shor's algorithm
“If you start factoring 10-digit numbers then it’s going to start getting scary”
Dr. Peter Shor, 2013
Related paper published 25 Jan 1997 by Dr. Shor:
Note: Shor's algorithm was formulated in 1994
Quickly searching unsorted data

using Grover's algorithm
"Programming a quantum computer is particularly interesting since there are multiple things happening in the same hardware simultaneously. One needs to think like both a theoretical physicist and a computer scientist."
Dr. Lov Grover, 2002
Related paper published 17 Jul 1997 by Dr. Grover:
Simulating nature

complex chemical reactions, for example
“Nature isn't classical, dammit, and if you want to make a simulation of nature, you'd better make it quantum mechanical, and by golly it's a wonderful problem, because it doesn't look so easy.”
Dr. Richard Feynman, 1981


Leveraging quantum computing for chemistry

Quantum communication and cryptography


Concepts we'll address today
Introduction to quantum computing
Representing qubits
Axioms of quantum mechanics
- Superposition principle
- Measurement
- Unitary evolution
Quantum computing algorithms
Quantum entanglement
More algorithms
Supplementary resources
Classical bits vs. qubits
two discrete states vs. infinite superpositions

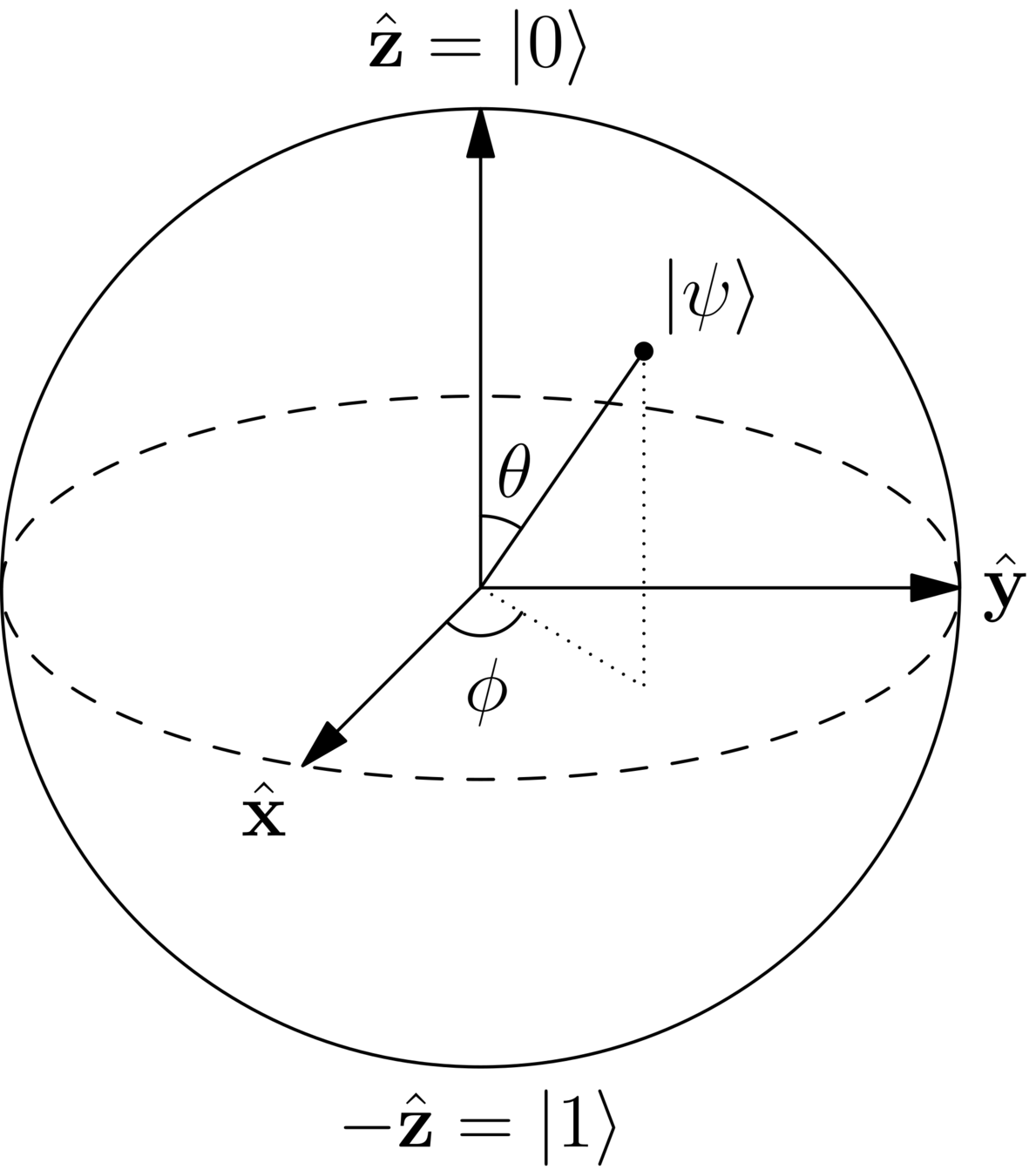
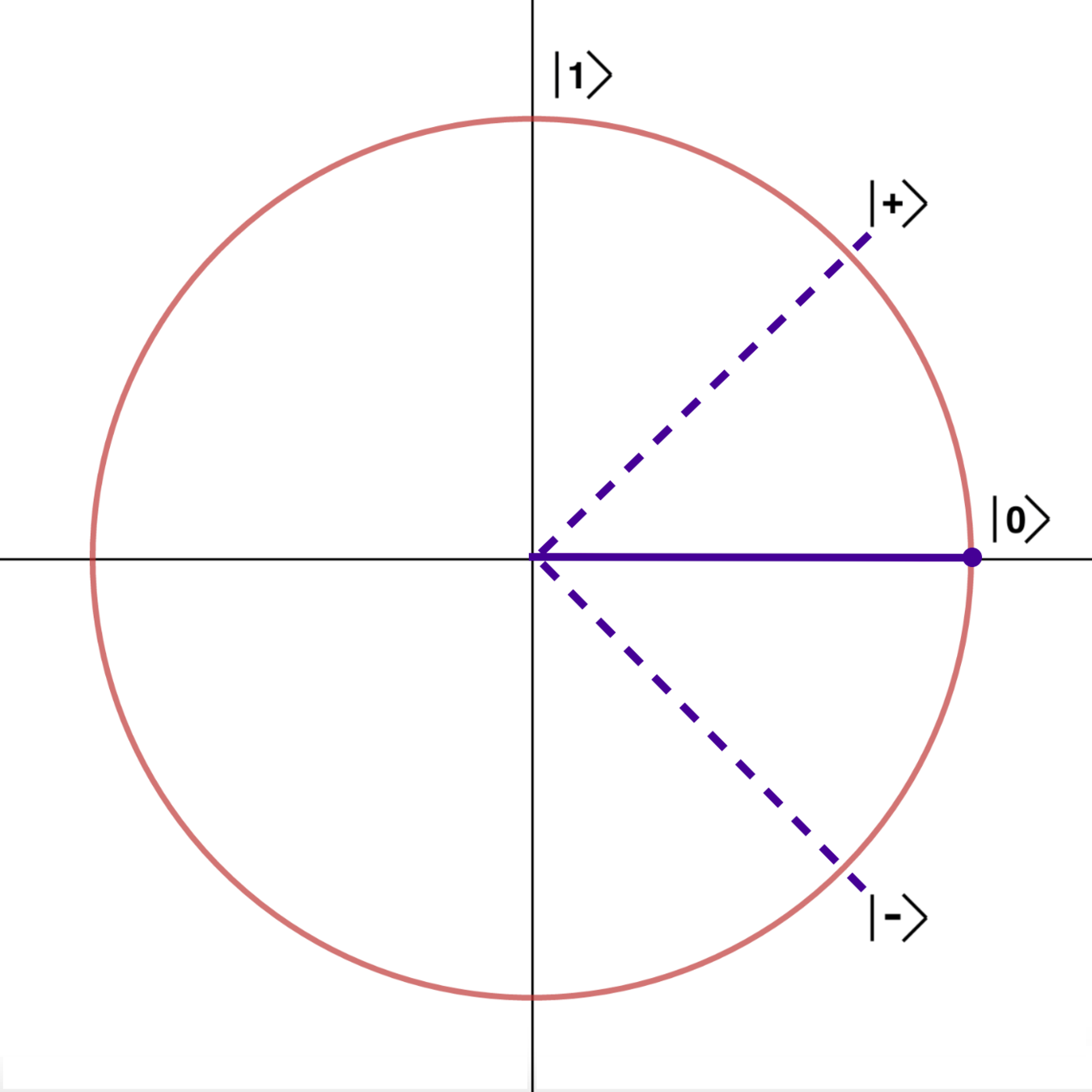
Qubit geometry

Representing qubits


ket notation, vectors, and geometrically
Hardware representation of qubits
| Physical support | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Photon | Polarization | Horizontal | Vertical |
| Electrons | Spin | Up | Down |
| Superconductor | Charge | Uncharged | Charged |
Superconducting qubits on a chip

Concepts we'll address today
Introduction to quantum computing
Representing qubits
Axioms of quantum mechanics
- Superposition principle
- Measurement
- Unitary evolution
Quantum computing algorithms
Quantum entanglement
More algorithms
Supplementary resources
Diagonally polarized photon
collapsing to a measurement basis state
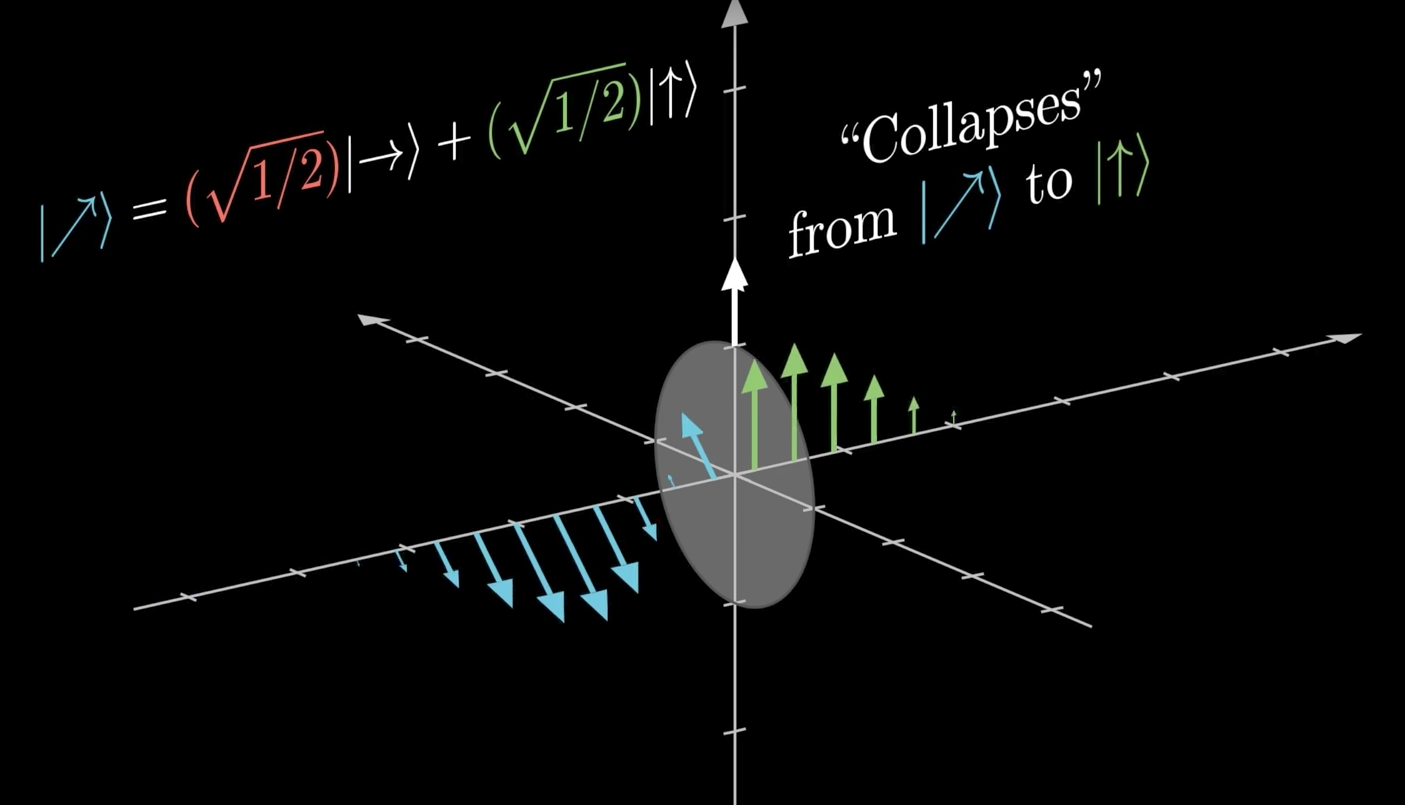
Measuring in the computational basis

Visualizing quantum measurement
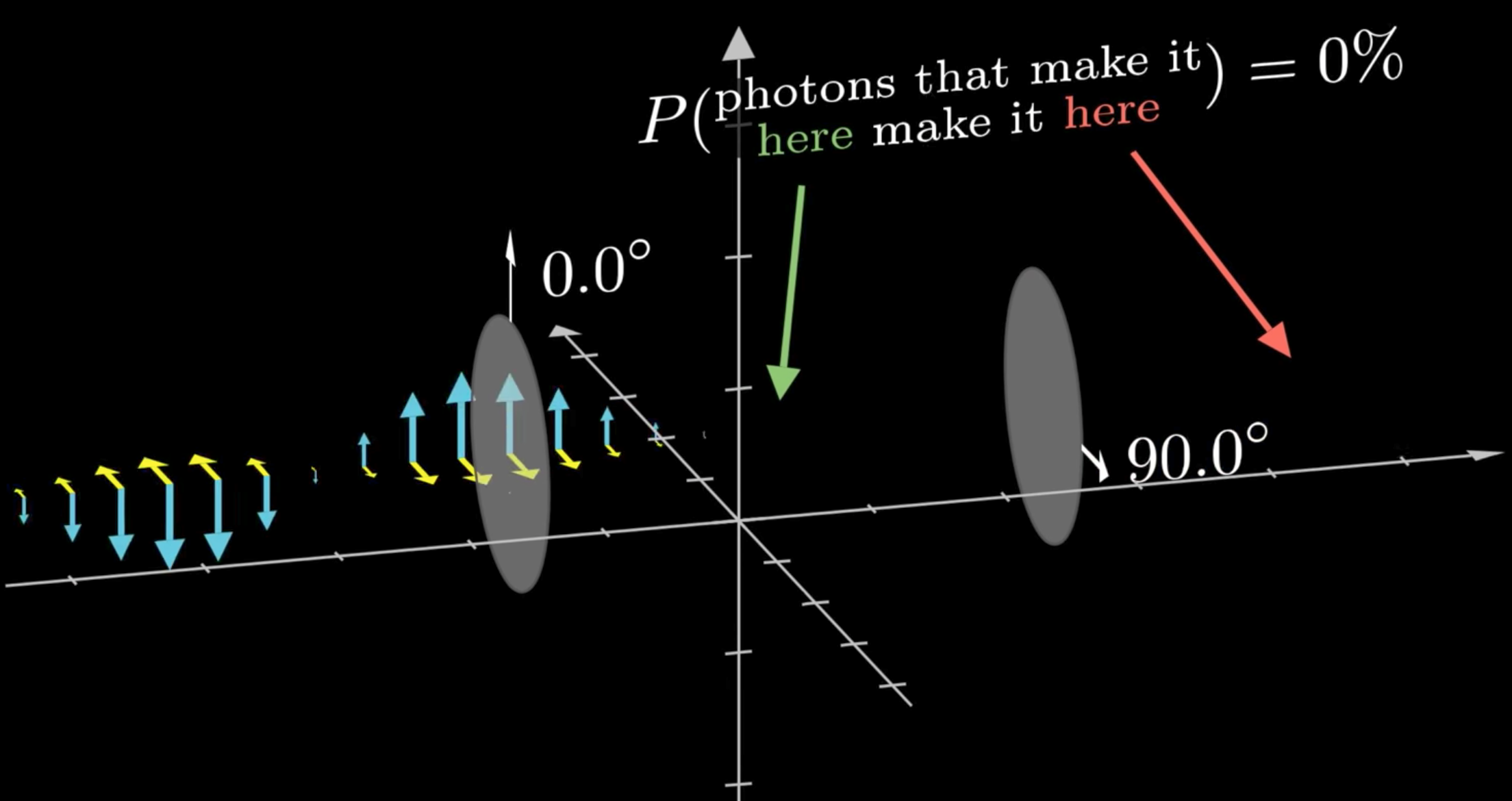
Polarized lenses blocking light

Vertically polarized photon
won't pass through horizontally polarized filter
Superposition collapse
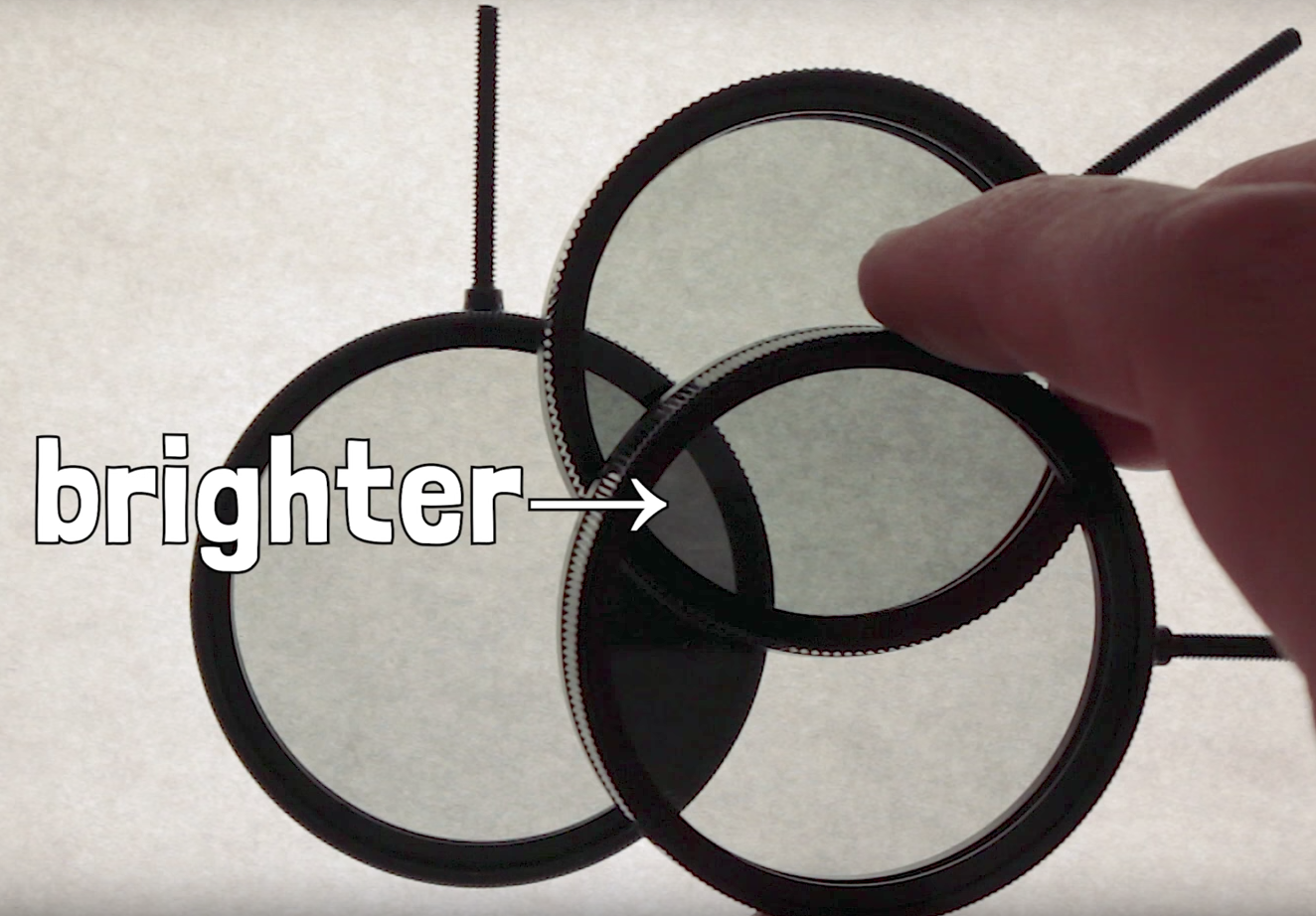
Why does adding a lens let more light through?
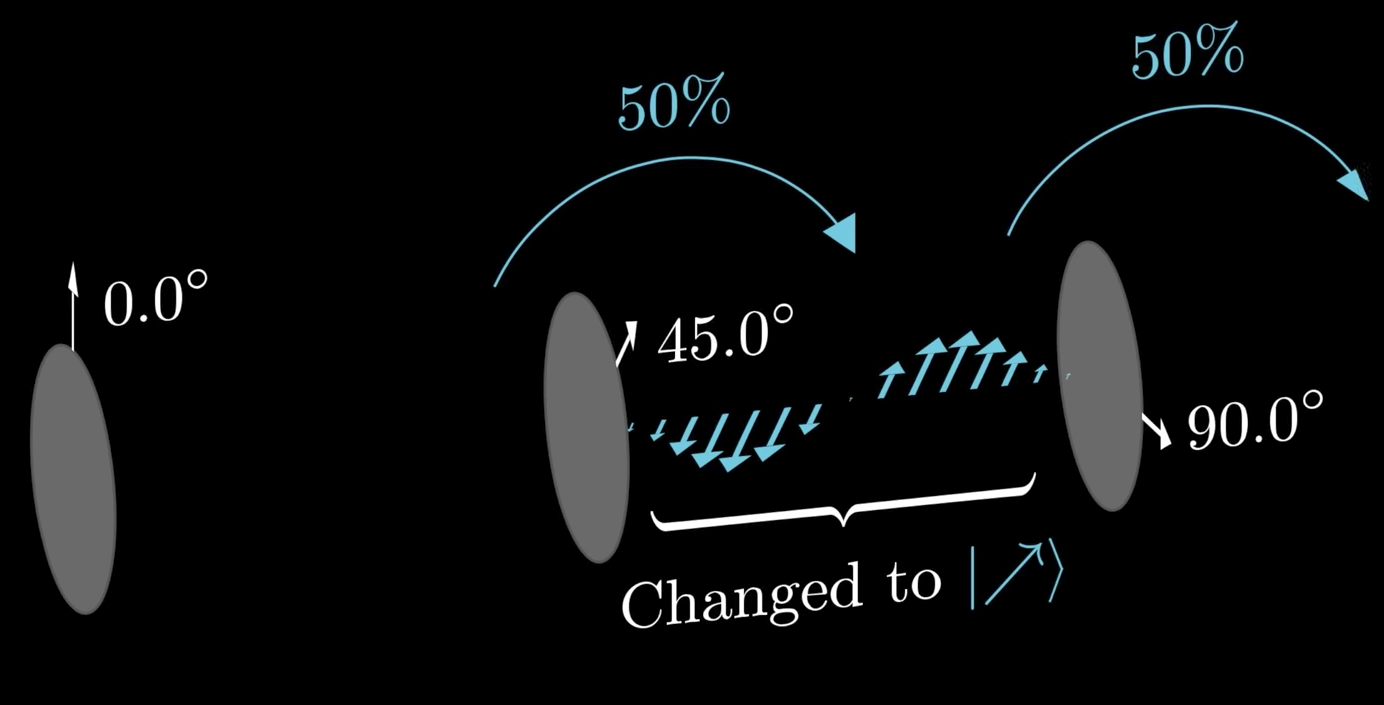
Measuring in an alternative basis
Orchestrating superpositions

Measuring in various basis states
Double-slit experiment
constructive and destructive interference

Text
Classic logic gates
a quick review for comparison to quantum gates

Some quantum gates

matrix operations model quantum mechanical behavior
More quantum gates
just going though a phase
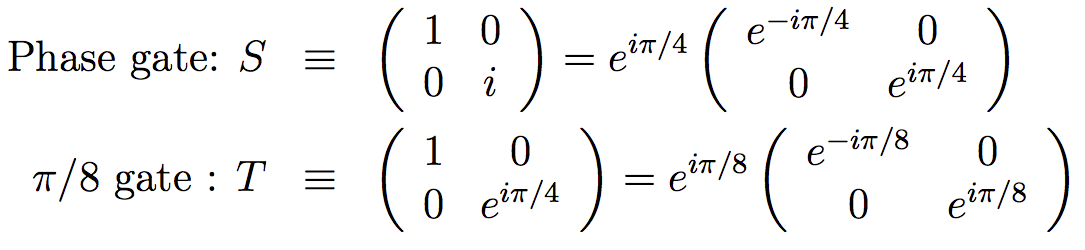
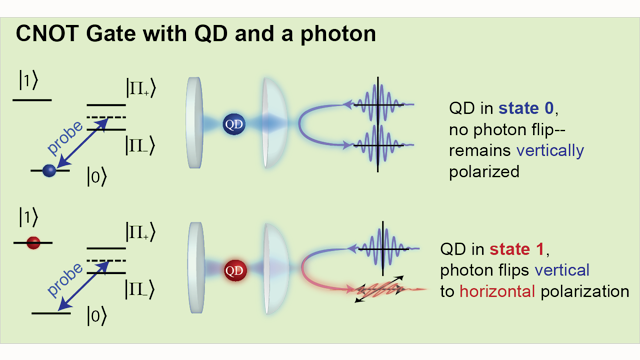
Quantum gate hardware
example using photons
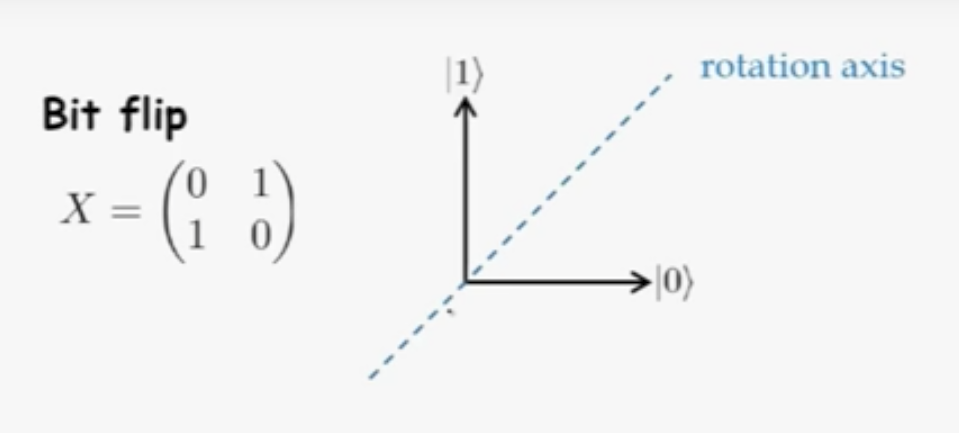
NOT / Pauli-X / Bit flip gate
from video: Single qubit gates - Umesh Vazirani
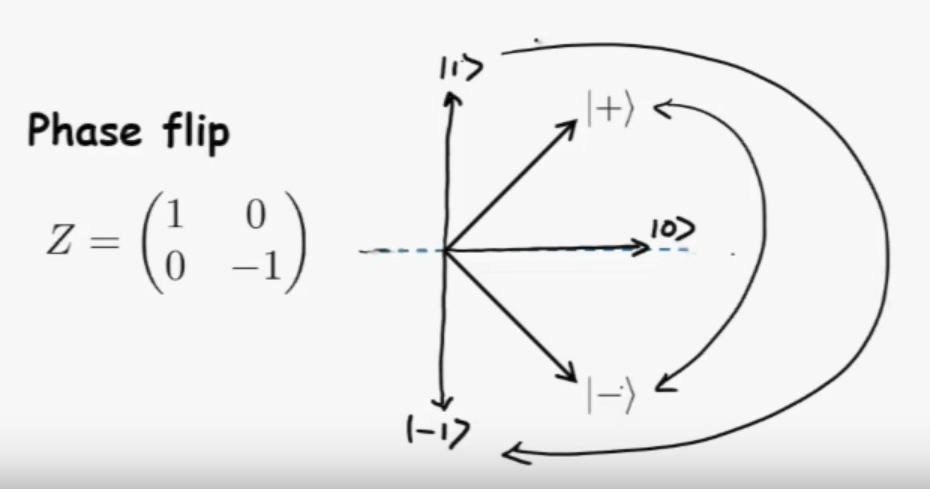
Pauli-Z / Phase flip gate
from video: Single qubit gates - Umesh Vazirani
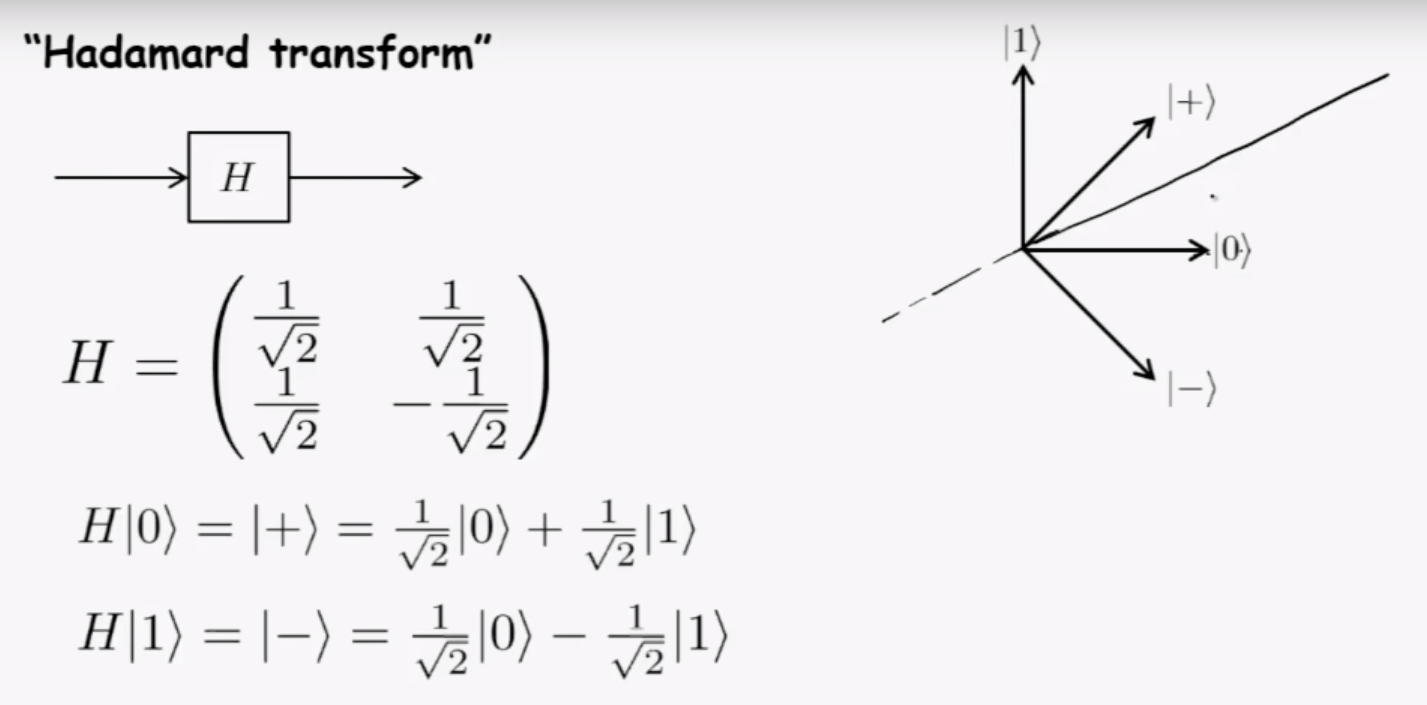
Hadamard gate
from video: Single qubit gates - Umesh Vazirani
CNOT gate
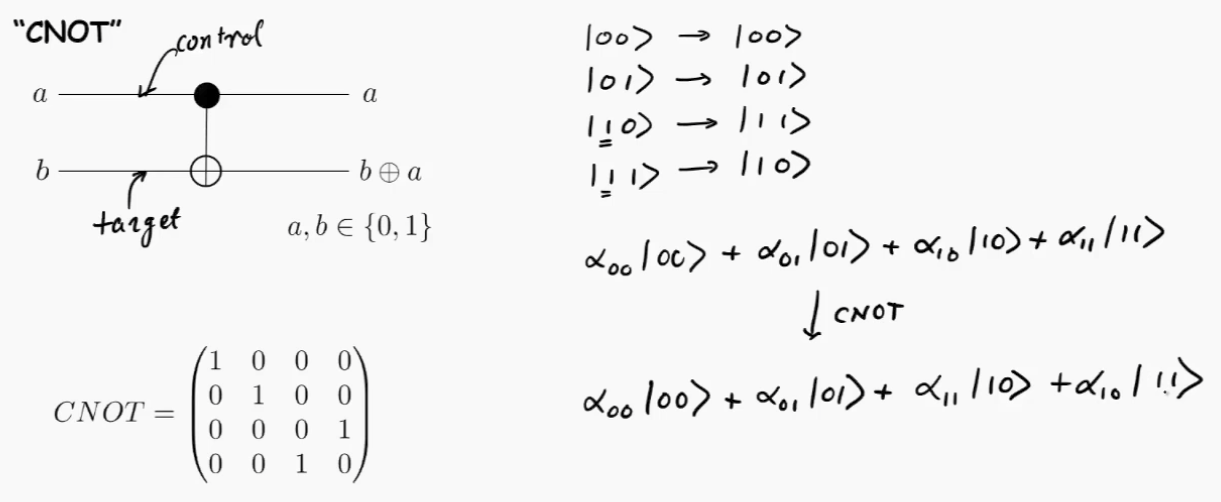
Strange?
Java-based quantum simulator

Exploring the quantum simulator
e.g. visualize states of multiple qubits: |00>


Exploring the quantum simulator
e.g. visualize states of multiple qubits: |01>


Simple quantum circuit
collapses to 8 random states with equal probability

Quantum superpositions

and observability
Measuring qubits
collapses to a basis state, discarding superposition

Measuring quantum state
a Java analogy

from an IndicThreads slide deck
Measuring quantum state
Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy analogy

Deep Thought after 7.5 million years of calculation
Concepts we'll address today
Introduction to quantum computing
Representing qubits
Axioms of quantum mechanics
- Superposition principle
- Measurement
- Unitary evolution
Quantum computing algorithms
Quantum entanglement
More algorithms
Supplementary resources
Deutsch's algorithm (1985)
Literally the Hello World of quantum algorithms

Deutsch's algorithm
Determine if function is constant or balanced
| Input a | Constant f(a) | Constant f(a) | Balanced f(a) | Balanced f(a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |

Deutsch's algorithm
How many queries of the oracle to solve?
Classical:
This oracle requires 2 queries classically
Quantum:
We create a superposition of inputs to the oracle for constructive/destructive interference.
Querying the oracle classically

example: f (0) = 0 and f (1) = 1 balanced
Quantum parallelism
what is it, really?

Double-slit experiment
constructive and destructive interference

Text
Choreographing interference
to increase the chance of getting the right answer
Text

Excerpts from “THE TALK” by Scott Aaronson and Zach Weinersmith

Querying the oracle quantumly
example: f (0) = 0 and f (1) = 1 balanced

Lecture 3: One Qubit, Two Qubit by Dave Bacon, University of Washington (Deutsch slightly modified)

Deutsch (slightly modified)
Why constant vs. balance require only one query
| Inp | Con |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 |
| Inp | Con |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| Inp | Bal |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| Inp | Bal |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |




Deutsch's algorithm
with oracle having constant function
Leverages phase-kickback from the bottom wire to choreograph constructive and destructive interference
Expected result is 100% probability of measuring


Deutsch's algorithm
with oracle having balanced function
Expected result is 0% probability of measuring

Leverages phase-kickback from the bottom wire to choreograph constructive and destructive interference

Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
exponentially faster than classical

Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm, 1992
Determine if function is constant or balanced
| Input | Constant | Constant | Balanced | Balanced |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 000 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 001 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 010 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 011 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 100 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 101 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 110 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 111 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Results when querying our example oracle
Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
How many invocations of the oracle to solve?
Classical:
Our oracle (black box) requires 5 invocations classically
Quantum:
We create a superposition of inputs to the oracle, and use the phase-kickback trick, for constructive/destructive interference. See:
see also: Wikipedia Deutsch-Jozsa Decoherence section
(Exponentially faster!)
Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
with oracle having constant function

Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
example oracle with constant function

Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
with oracle having balanced function

Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm
example oracle with balanced function

Deutsch-Jozsa implemented in Quil


Deutsch-Jozsa implemented in Quil


Concepts we'll address today
Introduction to quantum computing
Representing qubits
Axioms of quantum mechanics
- Superposition principle
- Measurement
- Unitary evolution
Quantum computing algorithms
Quantum entanglement
More algorithms
Supplementary resources
Quantum entanglement
Alice and Bob's long running relationship

Quantum entanglement

basic circuit
Quantum teleportation

and the no cloning theorem
Superdense coding

example circuit
Bell inequality test
(CHSH game)

Concepts we'll address today
Introduction to quantum computing
Representing qubits
Axioms of quantum mechanics
- Superposition principle
- Measurement
- Unitary evolution
Quantum computing algorithms
Quantum entanglement
More algorithms
Supplementary resources
Bernstein-Vazirani algorithm
basic circuit

Simon's algorithm
the quantum portion

Shor's algorithm

Period finding
using Quantum Fourier Transform

Grover's search
finding a needle in a haystack

Concepts we'll address today
Introduction to quantum computing
Representing qubits
Axioms of quantum mechanics
- Superposition principle
- Measurement
- Unitary evolution
Quantum computing algorithms
Quantum entanglement
More algorithms
Supplementary resources
Complex numbers

aren't complicated
Complex numbers encode
amplitude and phase
Roots of unity
are useful for Shor

Matrices
think two-dimensional arrays

Vector spaces
a home for vectors and scalars



Quantum Computing





Quantum Computing Exposed: Deep Dive
By javafxpert
Quantum Computing Exposed: Deep Dive
Helping developers get started with quantum computing
- 6,470



