Four questions
Jeremias Sulam
On learned proximals and conformal risk control



Inverse Problems
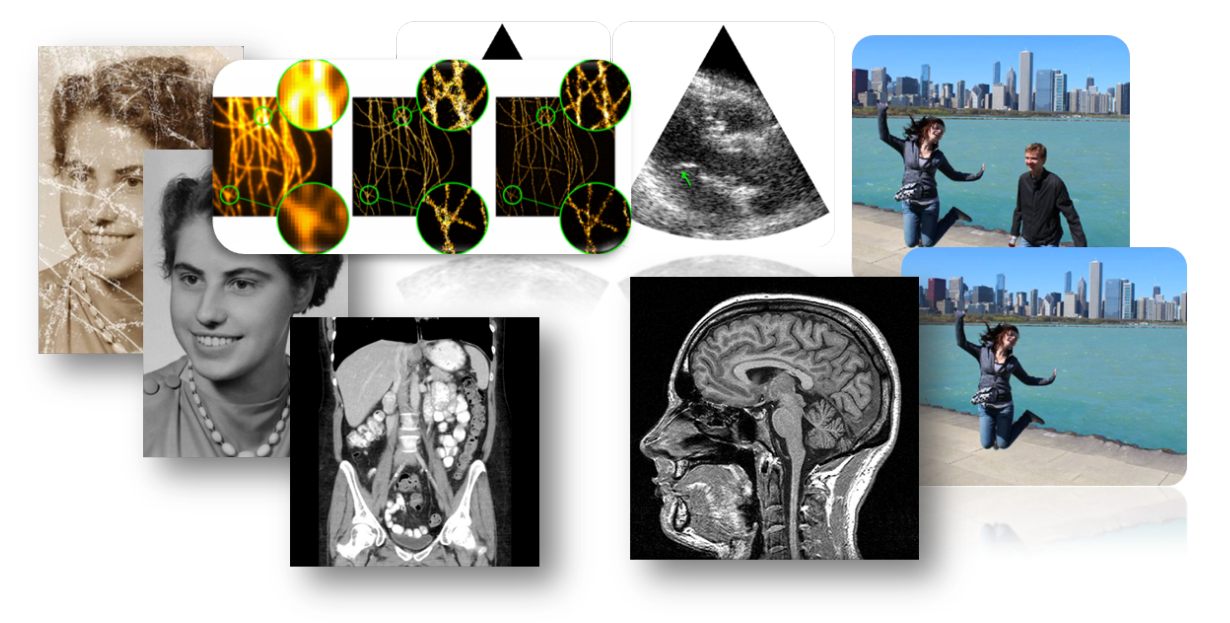
measurements
reconstruction
Inverse Problems

measurements
reconstruction
Mathematical tractability vs Complexity
in a box
simpler models
more assumptions
any model
no assumptions
Denoiser
Linear models
Linear networks
Shallow
ReLU Networks
PnP
Just ask GPT
Learned Proximals
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models


Proximal Gradient Descent: \( x^{t+1} = \text{prox}_R \left(x^t - \eta A^T(Ax^t-y)\right) \)
... a denoiser
\({\color{red}f_\theta}\)
[Venkatakrishnan et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2017b; Meinhardt et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2021; Gilton, Ongie, Willett, 2019; Kamilov et al., 2023b; Terris et al., 2023; S Hurault et al. 2021, Ongie et al, 2020; ...]
Learned Proximals
: revisiting PnP
Question 1)
When will \(f_\theta(x)\) compute a \(\text{prox}_R(x)\), and for what \(R(x)\)?
Question 2)
How do we find \(f(x) = \text{prox}_R(x)\) for the "correct"
\(R(x) \propto -\log p_x(x)\)?
Proximal Gradient Descent: \( x^{t+1} = \text{prox}_R \left(x^t - \eta A^T(Ax^t-y)\right) \)
... a denoiser
\({\color{red}f_\theta}\)

[Venkatakrishnan et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2017b; Meinhardt et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2021; Gilton, Ongie, Willett, 2019; Kamilov et al., 2023b; Terris et al., 2023; S Hurault et al. 2021, Ongie et al, 2020; ...]
Learned Proximals
: revisiting PnP
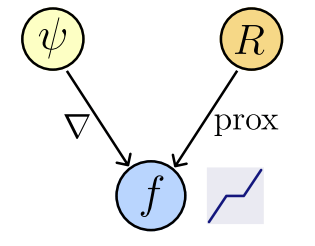
Theorem [Fang, Buchanan, S.]
Question 1)
When will \(f_\theta(x)\) compute a \(\text{prox}_R(x)\), and for what \(R(x)\)?
Let \(f_\theta : \mathbb R^n\to\mathbb R^n\) be a network : \(f_\theta (x) = \nabla_\theta \psi (x)\),
where \(\psi_\theta : \mathbb R^n \to \mathbb R,\) convex and differentiable (ICNN).
Then,
1. \(\exists ~R_\theta : \mathbb R^n \to \mathbb R\) not necessarily convex : \(f_\theta(x) \in \text{prox}_{R_\theta}(x),\)
(1. Follows from [Gribonval & Nikolova, 2020, Corollary 1])
2. We can compute \(R_{\theta}(x)\) by solving a convex problem
Learned Proximals
: revisiting PnP
Question 2)
How do we find \(f(x) = \text{prox}_R(x)\) for the "correct" \(R(x) \propto -\log p_x(x)\)?
Learned Proximals
: revisiting PnP
Theorem [Fang, Buchanan, S.] (informal)
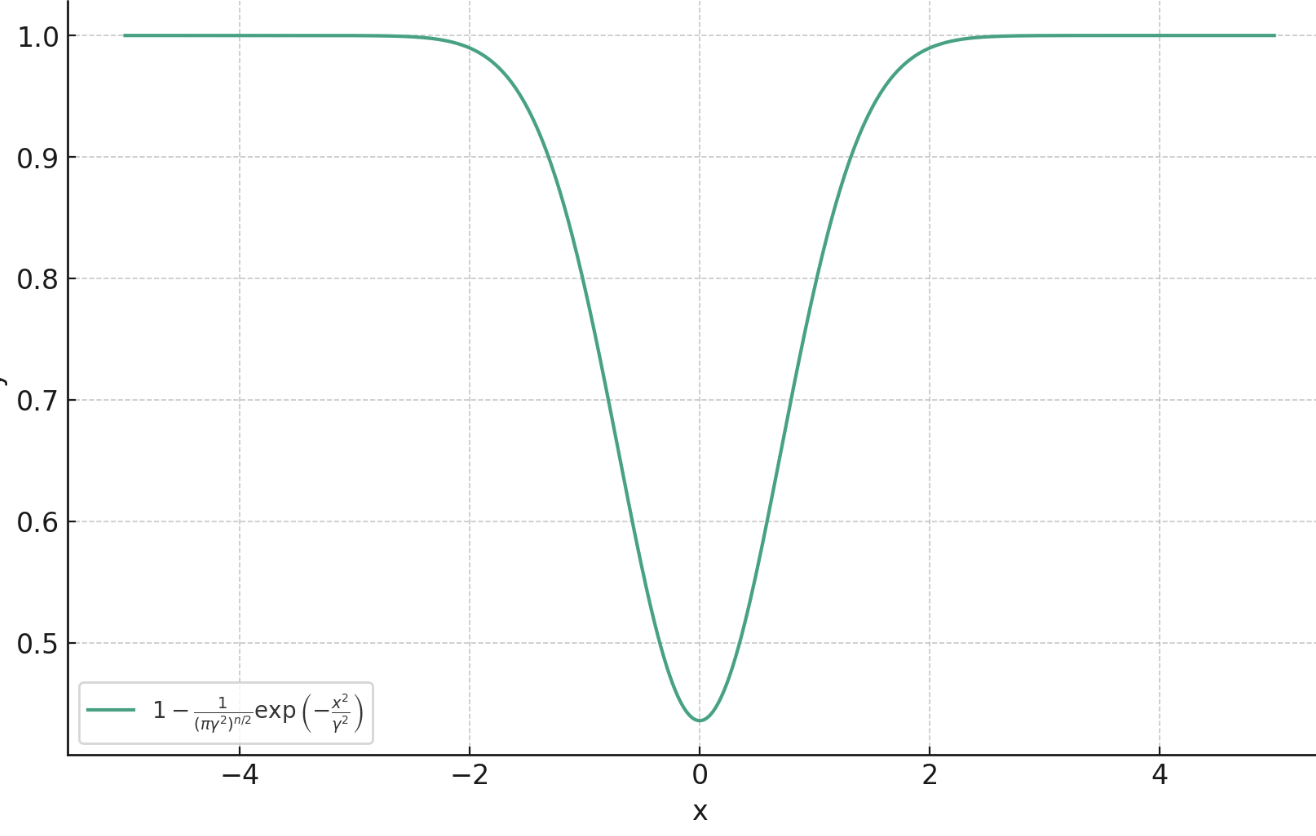
Proximal Matching Loss:\(\gamma\)
Learned Proximal Networks
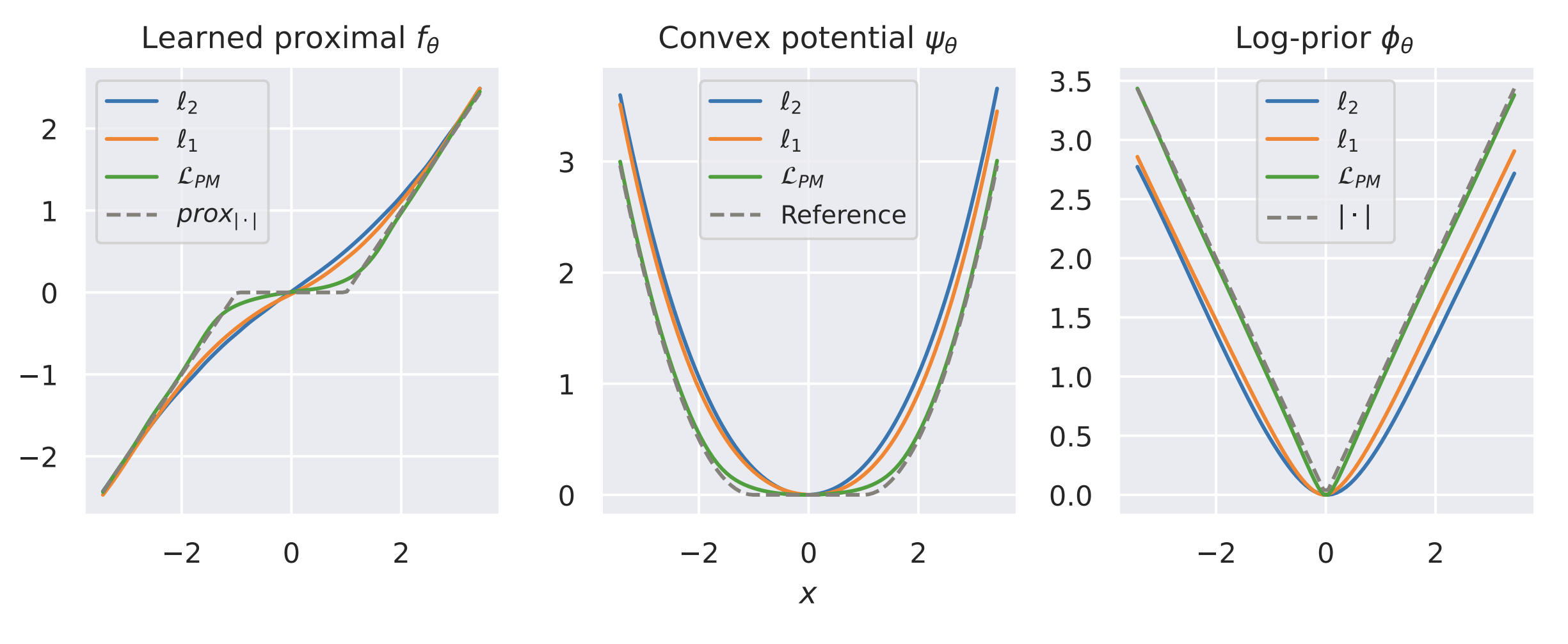


Example 1: recovering a prior
Fang, Buchanan & S. What's in a Prior? Learned Proximal Networks for Inverse Problems, ICLR 2024.

Learned Proximal Networks
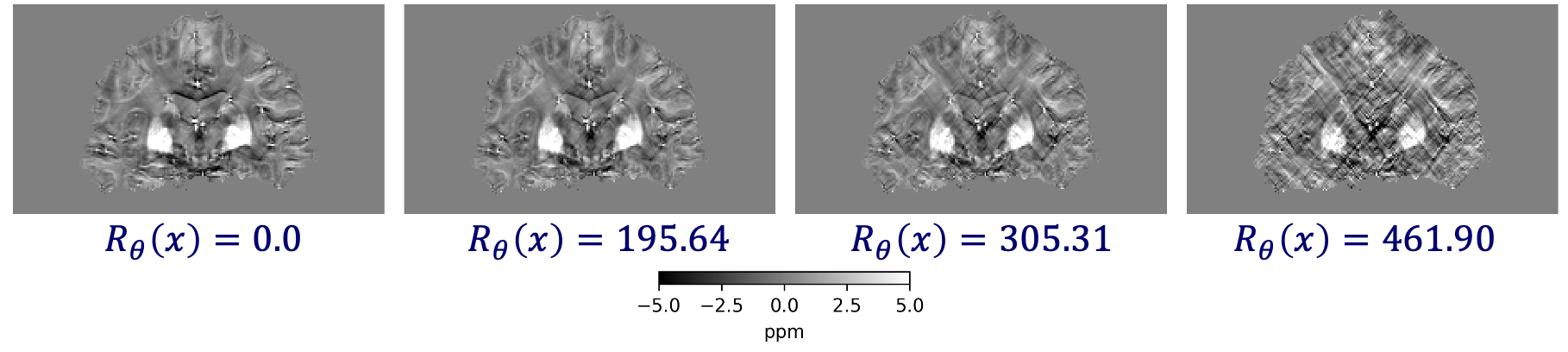
\(R_\theta(x) = 0.0\)
\(R_\theta(x) = 127.37\)
\(R_\theta(x) = 274.13\)
\(R_\theta(x) = 290.45\)
Convergence guarantees
Mathematical tractability vs Complexity

in a box
simpler models
more assumptions
any model
no assumptions
Denoiser
Linear models
Linear networks
Shallow
ReLU Networks
PnP
Just ask GPT
Learned Proximals
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models



in a box
Denoiser
diffusion
Measurements
\[y = Ax + \epsilon,~\epsilon \sim \mathcal{N}(0, \sigma^2\mathbb{I})\]
\[\hat{x} = F(y) \sim \mathcal{P}_y\]
Hopefully \(\mathcal{P}_y \approx p(x \mid y)\), but not needed!







Reconstruction
Question 3)
How much uncertainty is there in the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y?\)
Question 4)
How far will the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y\) be from the true \(x\)?
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
Lemma
Given \(m\) samples from \(\mathcal P_y\), let
\[\mathcal{I}(y)_j = \left[ Q_{y_j}\left(\frac{\lfloor(m+1)\alpha/2\rfloor}{m}\right), Q_{y_j}\left(\frac{\lceil(m+1)(1-\alpha/2)\rceil}{m}\right)\right]\]
Then \(\mathcal I(y)\) provides entriwise coverage for a new sample \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y\), i.e.
\[\mathbb{P}\left[\hat{x}_j \in \mathcal{I}(y)_j\right] \geq 1 - \alpha\]
\(0\)
\(1\)
low: \( l(y) \)
\(\mathcal{I}(y)\)
up: \( u(y) \)
Question 3)
How much uncertainty is there in the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y?\)
(distribution free)
cf [Feldman, Bates, Romano, 2023]

\(y\)
lower
upper
intervals
\(|\mathcal I(y)_j|\)
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
\(0\)
\(1\)
ground-truth is
contained
\(\mathcal{I}(y_j)\)
\(x_j\)
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
Question 4)
How far will the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y\) be from the true \(x\)?
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
[Angelopoulos et al, 2022]
[Angelopoulos et al, 2022]
Risk Controlling Prediction Set
For risk level \(\epsilon\), failure probability \(\delta\), \(\mathcal{I}(y_j) \) is a RCPS if
\[\mathbb{P}\left[\mathbb{E}\left[\text{fraction of pixels not in intervals}\right] \leq \epsilon\right] \geq 1 - \delta\]
[Angelopoulos et al, 2022]
Question 4)
How far will the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y\) be from the true \(x\)?
\(0\)
\(1\)
ground-truth is
contained
\(\mathcal{I}(y_j)\)
\(x_j\)
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
[Angelopoulos et al, 2022]
ground-truth is
contained
\(0\)
\(1\)
\(\mathcal{I}(y_j)\)
\(\lambda\)
\(x_j\)
Procedure:
\[\hat{\lambda} = \inf\{\lambda \in \mathbb{R}:~ \hat{\text{risk}}_{(\mathcal S_{cal})} \leq \epsilon,~\forall \lambda' \geq \lambda \}\]
[Angelopoulos et al, 2022]
single \(\lambda\) for all \(\mathcal I(y_j)\)!
Risk Controlling Prediction Set
For risk level \(\epsilon\), failure probability \(\delta\), \(\mathcal{I}(y_j) \) is a RCPS if
\[\mathbb{P}\left[\mathbb{E}\left[\text{fraction of pixels not in intervals}\right] \leq \epsilon\right] \geq 1 - \delta\]
[Angelopoulos et al, 2022]
Question 4)
How far will the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y\) be from the true \(x\)?
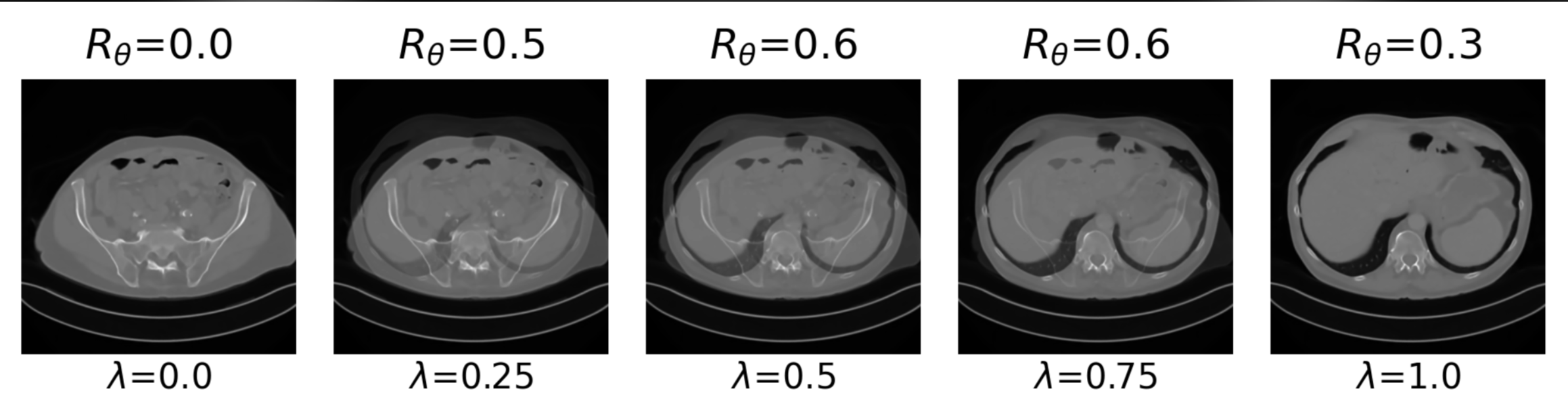
\(\mathcal{I}_{\bm{\lambda}}(y)_j = [l_\text{low,j} - \lambda, l_\text{up,j} + \lambda]\)
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
\(K\)-RCPS: High-dimensional Risk Control
\[\tilde{{\lambda}}_K = \underset{\lambda \in \mathbb R^K}{\arg\min}~\sum_{k \in [K]}\lambda_k~\quad \text{s.t. }\quad \mathcal I_{\lambda_j}(y) : \text{RCPS}\]
scalar \(\lambda \in \mathbb{R}\)
vector \(\bm{\lambda} \in \mathbb{R}^d\)
\(\mathcal{I}_{\lambda}(y)_j = [\text{low}_j - \lambda, \text{up}_j + \lambda]\)
\(\mathcal{I}_{\bm{\lambda}}(y)_j = [\text{low}_j - \lambda_j, \text{up}_j + \lambda_j]\)
\(\rightarrow\)
\(\rightarrow\)
Procedure:
1. Find anchor point
\[\tilde{\bm{\lambda}}_K = \underset{\bm{\lambda}}{\arg\min}~\sum_{k \in [K]}\lambda_k~\quad\text{s.t.}~~~\hat{\text{risk}}^+(\bm{\lambda})_{(S_{opt})} \leq \epsilon\]
2. Choose
\[\hat{\beta} = \inf\{\beta \in \mathbb{R}:~\hat{\text{risk}}_{S_{cal}}^+(\tilde{\bm{\lambda}}_K + \beta'\bf{1}) \leq \epsilon,~\forall~ \beta' \geq \beta\}\]
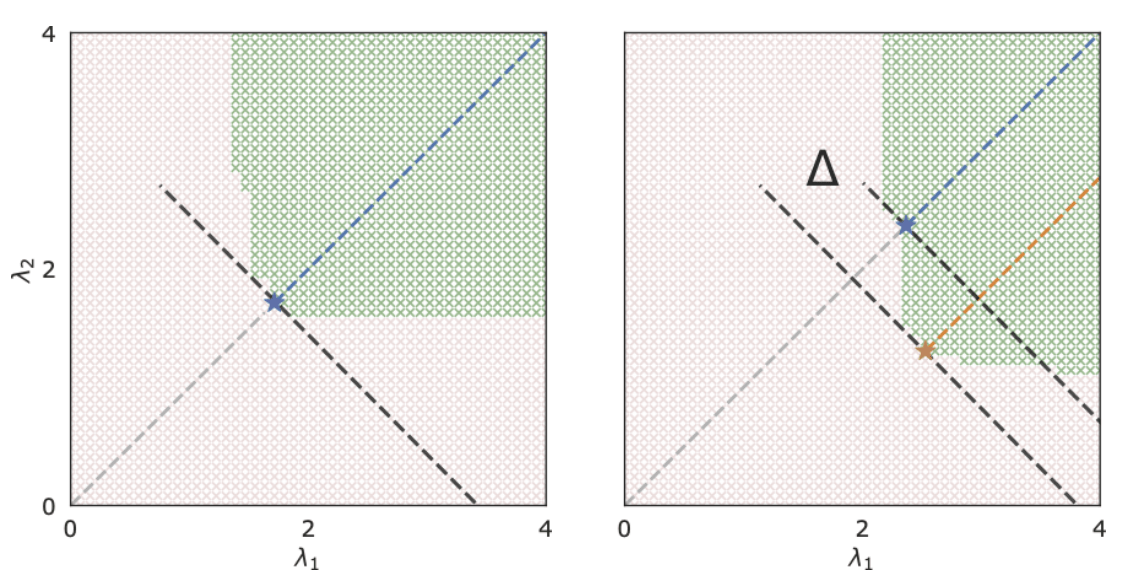
\(\tilde{\bm{\lambda}}_K\)
Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
\(K\)-RCPS: High-dimensional Risk Control
\[\tilde{{\lambda}}_K = \underset{\lambda \in \mathbb R^K}{\arg\min}~\sum_{k \in [K]}\lambda_k~\quad \text{s.t. }\quad \mathcal I_{\lambda_j}(y) : \text{RCPS}\]
scalar \(\lambda \in \mathbb{R}\)
vector \(\bm{\lambda} \in \mathbb{R}^d\)
\(\rightarrow\)
\(\rightarrow\)
Procedure:
1. Find anchor point
\[\tilde{\bm{\lambda}}_K = \underset{\bm{\lambda}}{\arg\min}~\sum_{k \in [K]}\lambda_k~\quad\text{s.t.}~~~\hat{\text{risk}}^+(\bm{\lambda})_{(S_{opt})} \leq \epsilon\]
2. Choose
\[\hat{\beta} = \inf\{\beta \in \mathbb{R}:~\hat{\text{risk}}_{S_{cal}}^+(\tilde{\bm{\lambda}}_K + \beta'\bf{1}) \leq \epsilon,~\forall~ \beta' \geq \beta\}\]

\(\hat{R}^{\gamma}(\bm{\lambda}_{S_{opt}})\leq \epsilon\)
Guarantee: \(\mathcal{I}_{\bm{\lambda}_K,\hat{\beta}}(y)_j \) are \((\epsilon,\delta)\)-RCPS
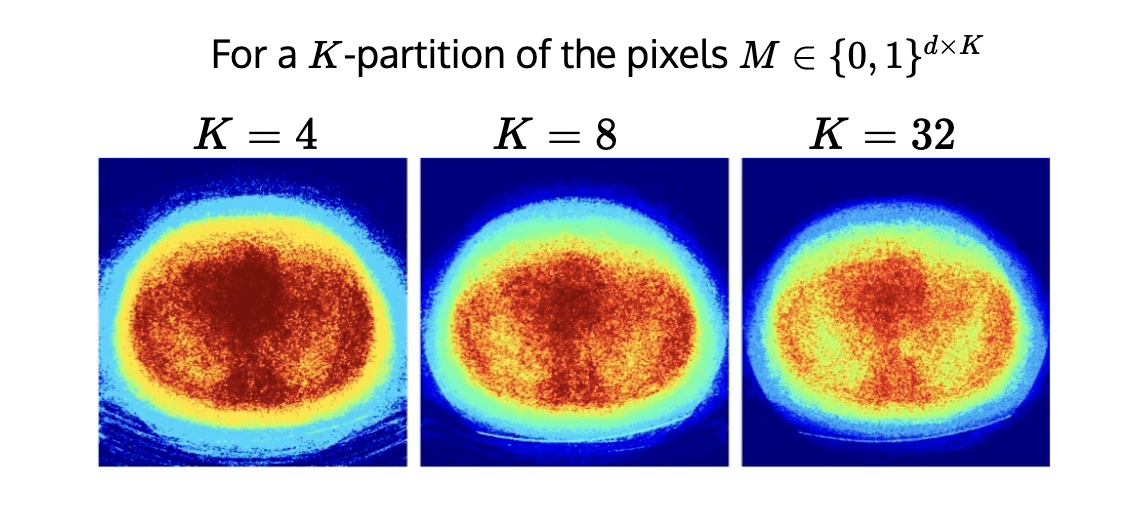
\(\tilde{\bm{\lambda}}_K\)
\(\mathcal{I}_{\lambda}(y)_j = [\text{low}_j - \lambda, \text{up}_j + \lambda]\)
\(\mathcal{I}_{\bm{\lambda}}(y)_j = [\text{low}_j - \lambda_j, \text{up}_j + \lambda_j]\)

\(\hat{\lambda}_K\)
conformalized uncertainty maps
\(K=4\)
\(K=8\)

\[\mathbb{P}\left[\mathbb{E}\left[\text{fraction of pixels not in intervals}\right] \leq \epsilon\right] \geq 1 - \delta\]
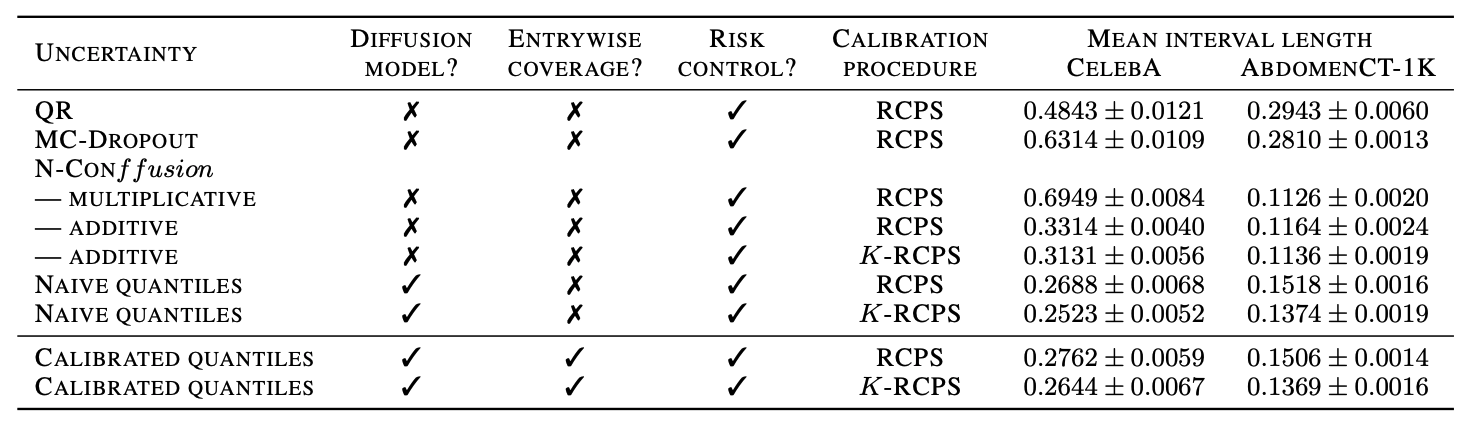

Conformal guarantees for diffusion models
c.f. [Kiyani et al, 2024]
Teneggi, Tivnan, Stayman, S. How to trust your diffusion model: A convex optimization approach to conformal risk control. ICML 2023
Question 1)
When will \(f_\theta(x)\) compute a \(\text{prox}_R(x)\), and for what \(R(x)\)?
Gradients of ICNN, and computable \(R(x)\)
Question 2)
How do we find \(f(x) = \text{prox}_R(x)\) for the "correct"
\(R(x) \propto -\log p_x(x)\)?
Use proximal matching loss
Calibrated quantiles
Question 3)
How much uncertainty is there in the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y?\)
Use K-RCPS to conformalize
Question 4)
How far will the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y\) be from the true \(x\)?
Question 1)
When will \(f_\theta(x)\) compute a \(\text{prox}_R(x)\), and for what \(R(x)\)?
Gradients of ICNN, and computable \(R(x)\)
Question 2)
How do we find \(f(x) = \text{prox}_R(x)\) for the "correct"
\(R(x) \propto -\log p_x(x)\)?
Use proximal matching loss
Calibrated quantiles
Question 3)
How much uncertainty is there in the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y?\)
Use K-RCPS to conformalize
Question 4)
How far will the samples \(\hat x \sim \mathcal P_y\) be from the true \(x\)?







...that's it!





Zhenghan Fang
JHU
Jacopo Teneggi
JHU
Sam Buchanan
TTIC

Learned Proximal Networks
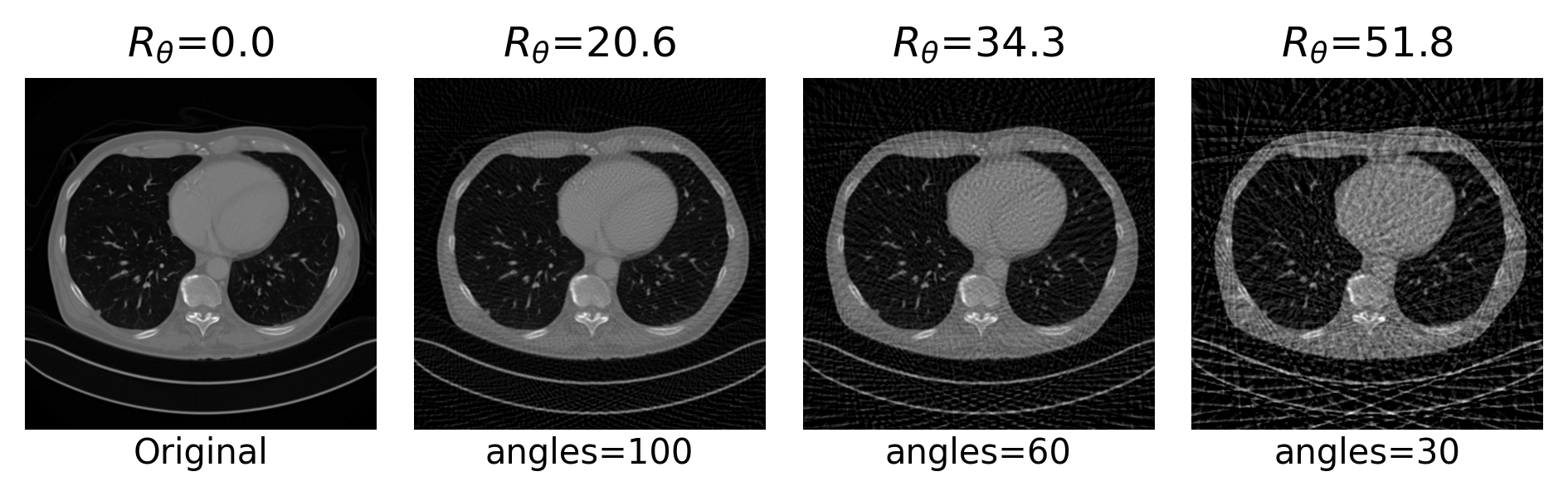
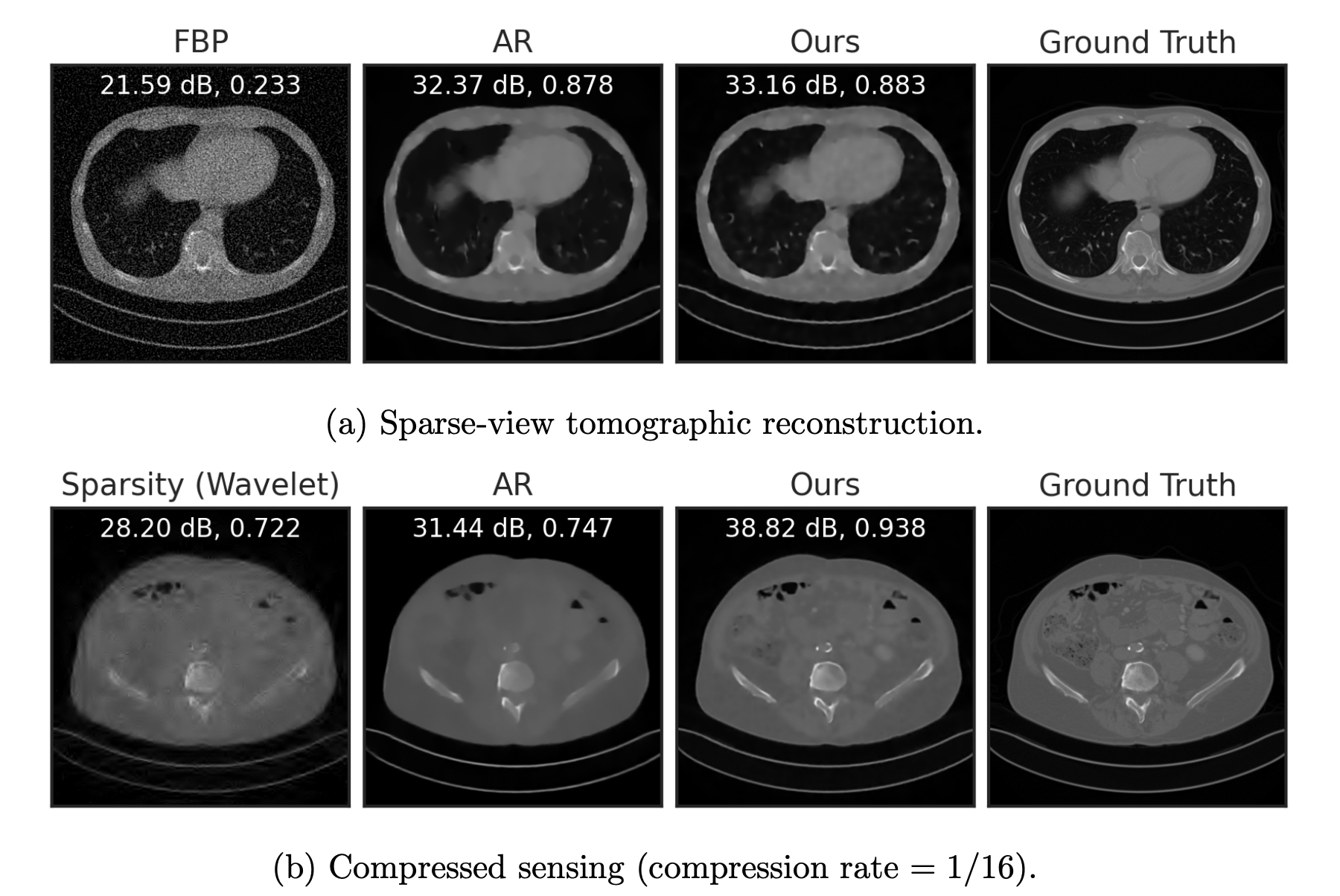
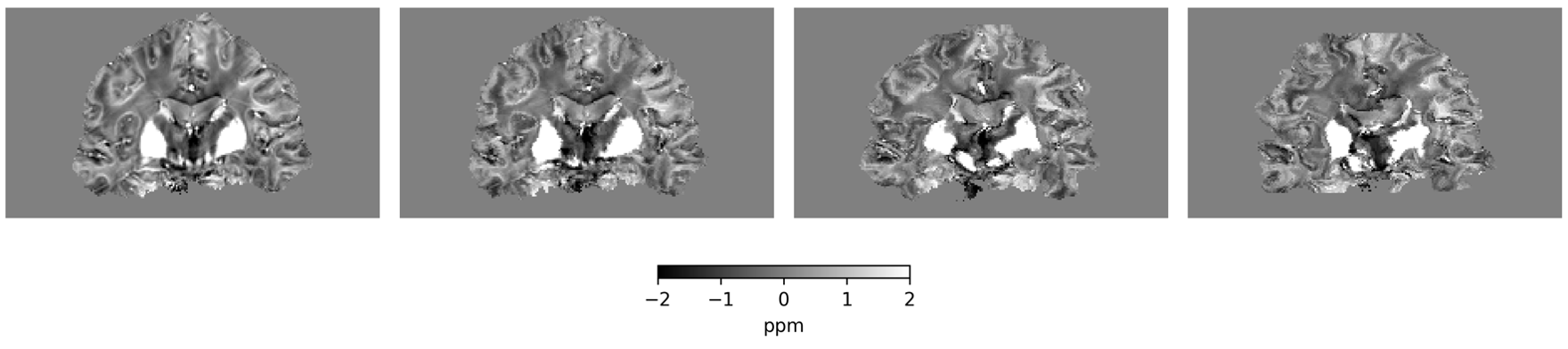
Example 2: a prior for CT
Learned Proximal Networks

Example 2: a prior for CT
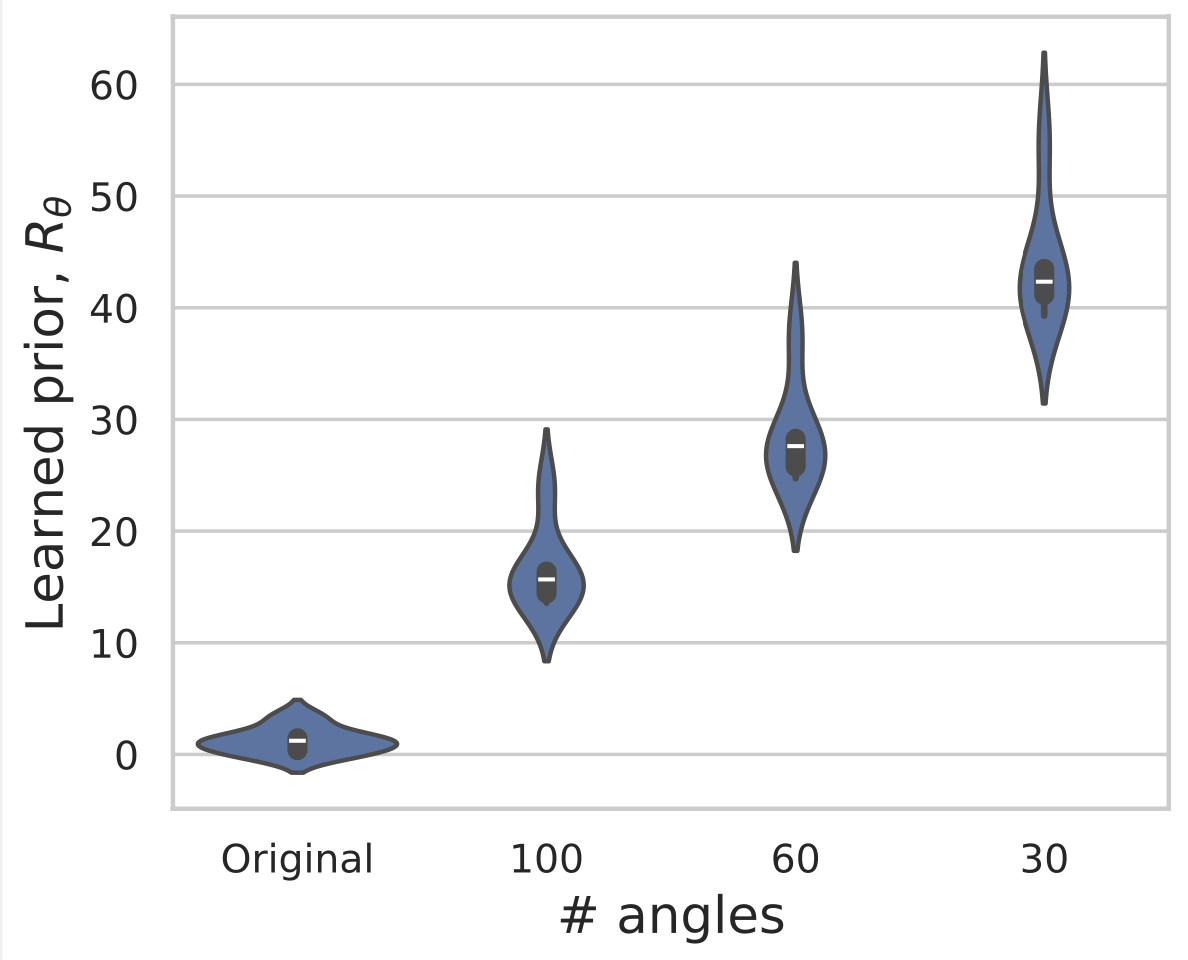
Learned Proximal Networks

Example 2: a prior for CT


Learned Proximal Networks
Example 2: a prior for CT
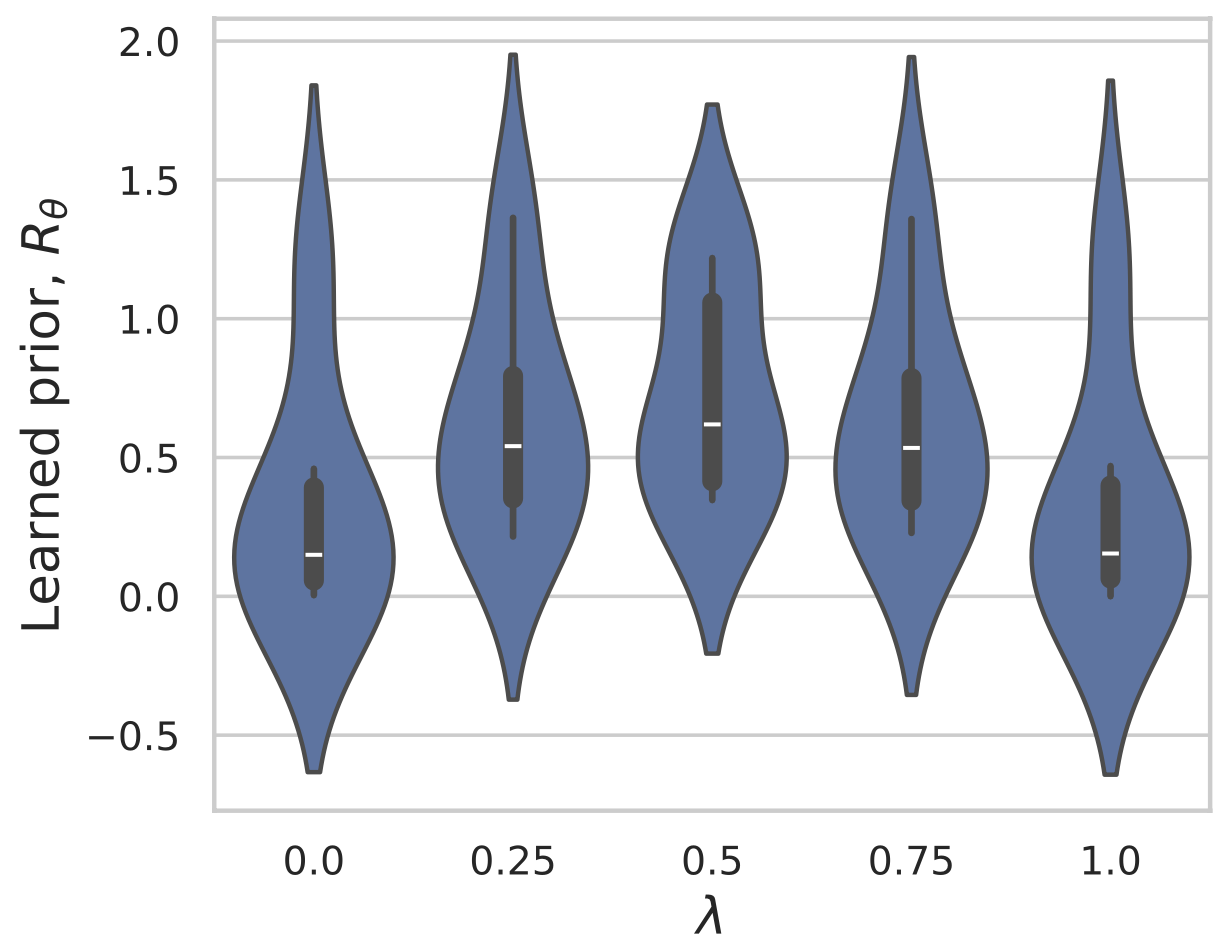




Learned Proximal Networks
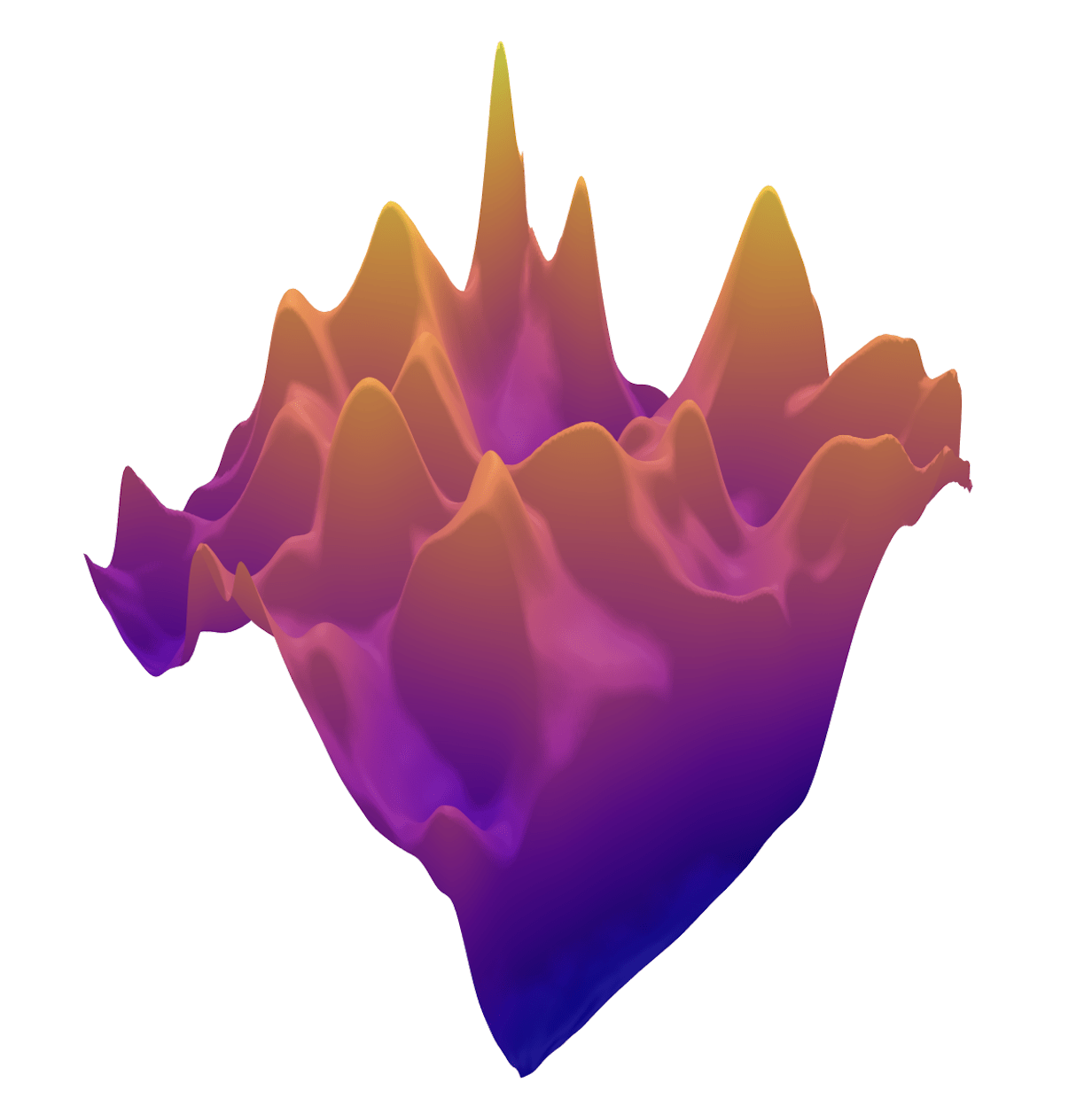
\(R(\tilde{x})\)
Example 2: priors for images
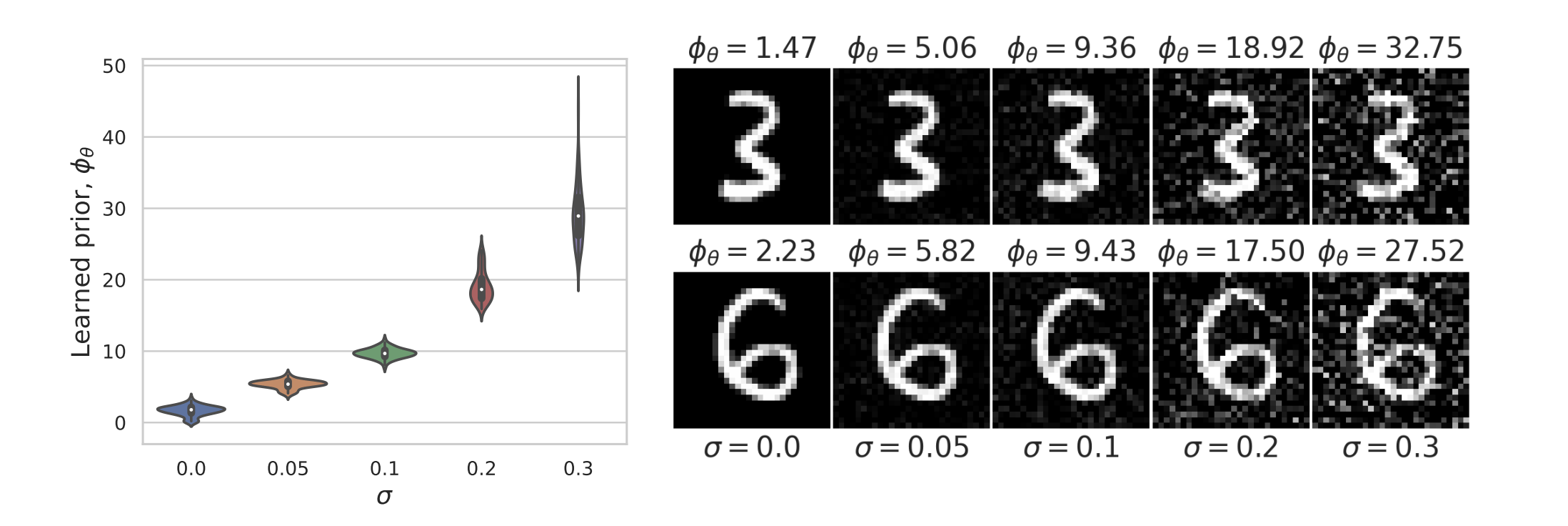












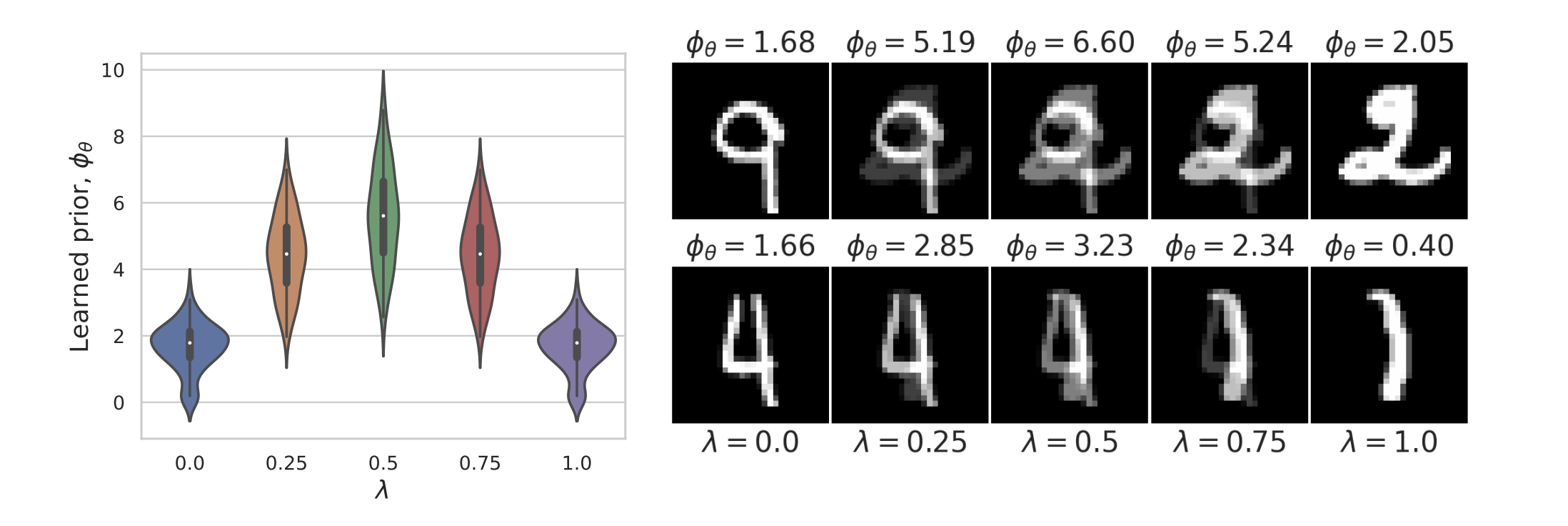













Learned Proximal Networks
Example 2: priors for images
Learned Proximal Networks
via
Convergence Guarantees
Theorem (PGD with Learned Proximal Networks)
Let \(f_\theta = \text{prox}_{\hat{R}} {\color{grey}\text{ with } \alpha>0}, \text{ and } 0<\eta<1/\sigma_{\max}(A) \) with smooth activations
(Analogous results hold for ADMM)
Learned Proximal Networks
Convergence guarantees for PnP
Black box guarantees for modern methods in inverse problems
By Jeremias Sulam
Black box guarantees for modern methods in inverse problems
- 425



