- Calculer une intégrale
Calcul intégral
\displaystyle\int_{a}^{b} f(x) \mathrm{d} x =F(b)-F(a)
La plupart du temps pour calculer l'intégrale d'une fonction \(f\) sur un intervalle, il faut connaître une primitive \(F\)
1er cas : La primitive est donnée
f(x)=\left (x^2-11\right ) \mathrm{e}^{-0,2x}
F(x)=\left (-5x^2 -50x -195\right ) \mathrm{e}^{-0,2x}
I=\displaystyle\int_{10}^{20} f(x) \mathrm{d} x =F(20)-F(10)
F(20)=(-5\times 20^2-50\times 20 - 195)\mathrm{e}^{-0,2\times20}= - 3195\mathrm{e}^{-4}
F(10)=(-5\times 10^2-50\times 10 - 195)\mathrm{e}^{-0,2\times10}= - 1195\mathrm{e}^{-2}
I=-3195\mathrm{e}^{-4} + 1195\mathrm{e}^{-2}\approx 103,21
2ème cas : La primitive est à déterminer
f(x) = 2x -1 + \text{e}^{0,05x}
x=x^1
\text{Si }f(x) = x^n\text{ alors }F(x) = \frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1}
\frac{x^2}{2}
\textcolor{orange}{2}x
\textcolor{orange}{2}\frac{x^2}{2}=x^2
F(x) = x^2\dots
f(x) = 2x -1 + \text{e}^{0,05x}
\text{Si }f(x) = k\text{ alors }F(x) = kx
-1
-1x=-x
F(x) = x^2-x\dots
f(x) = 2x -1 + \text{e}^{0,05x}
\text{Si }f = u'\mathrm{e}^u\text{ alors }F =\mathrm{e}^u
\text{e}^{0,05x}
\mathrm{e}^u
Il manque \(u'\) !
u(x) = 0,05x\text{ donc }u'(x) =0,05
Il manque \(u'\) !
on fait apparaître \(u'\) !

\frac{1}{0,05}\times0,05\text{e}^{0,05x}
f(x) = 2x -1 + \text{e}^{0,05x}
\text{Si }f = u'\mathrm{e}^u\text{ alors }F =\mathrm{e}^u
\textcolor{orange}{\frac{1}{0,05}\times}0,05\text{e}^{0,05x}
\textcolor{orange}{\frac{1}{0,05}\times}\text{e}^{0,05x}=20\text{e}^{0,05x}
F(x) = x^2-x+20\text{e}^{0,05x}
I=\displaystyle\int_{0}^{100} f(x) \mathrm{d} x =F(100)-F(0)
=\left ( 9900 + 20\mathrm{e}^{5}\right ) - 20
F(x) = x^2-x+20\text{e}^{0,05x}
=9880 + 20\mathrm{e}^{5}
\approx 12848
- Calculer la valeur moyenne d'une fonction
\mu=\frac{1}{b-a}\displaystyle\int_{a}^{b} f(x) \mathrm{d} x =\frac{1}{b-a}(F(b)-F(a))
On reprend l'exemple précédent : la valeur moyenne de la fonction \(f\) sur l'intervalle [0 ; 100] est :
\mu=\frac{1}{100-0}\displaystyle\int_{0}^{100} f(x) \mathrm{d} x =\frac{1}{100}(9880 + 20\mathrm{e}^{5})\approx 128,48
- Encadrer une intégrale avec deux aires...
\text{Encadrer l’intégrale}\displaystyle\int_{2}^{4} f(x) \mathrm{d} x \text{ par deux entiers consécutifs}
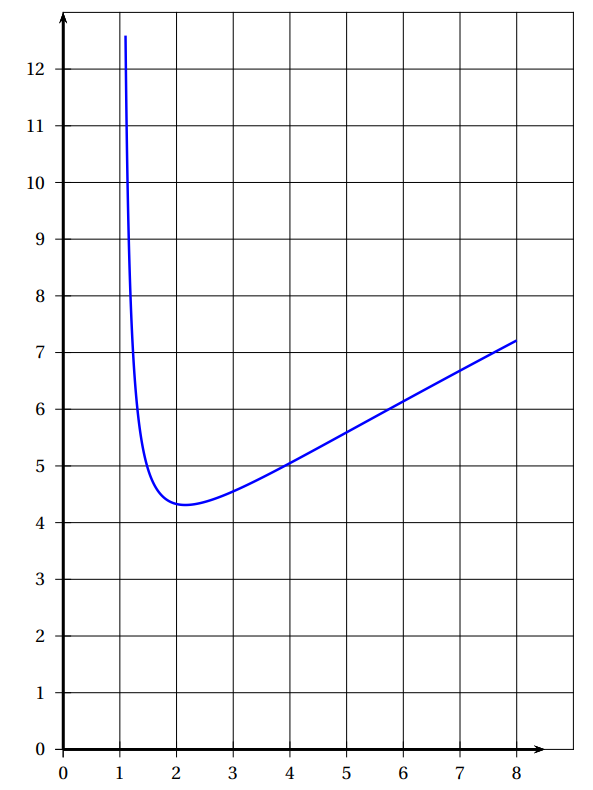
- Encadrer une intégrale avec deux aires...
9\leqslant\displaystyle\int_{2}^{4} f(x) \mathrm{d} x \leqslant10
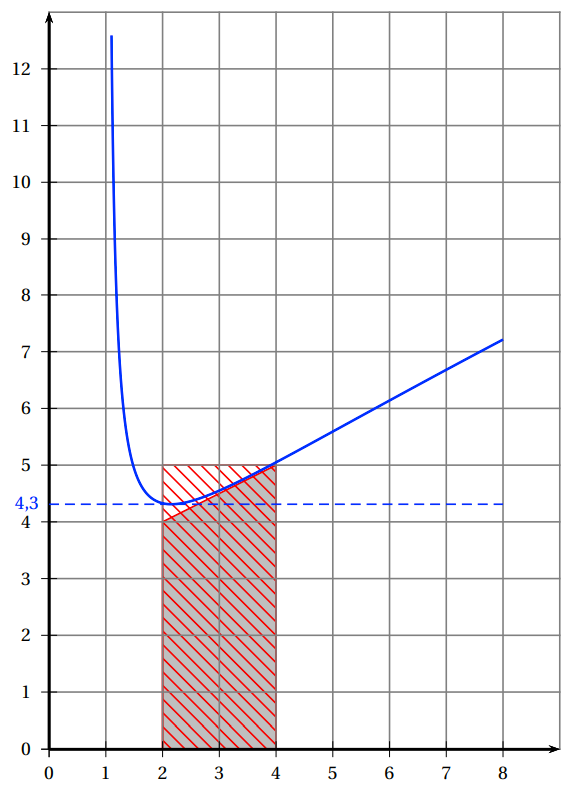
- Signe d'une intégrale
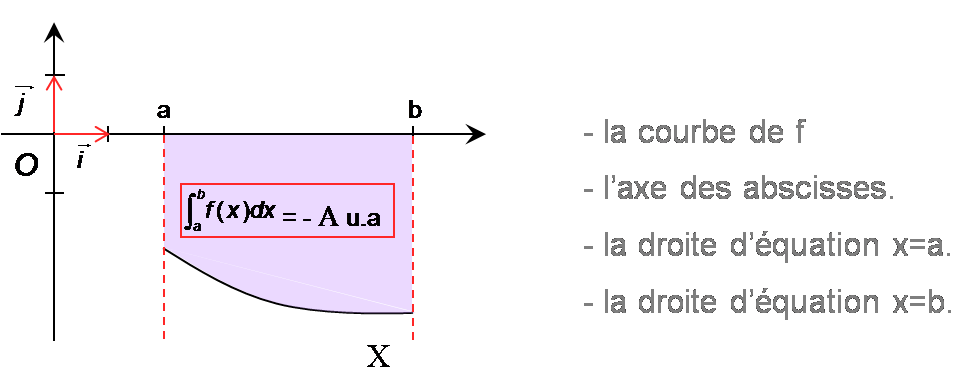
Si une fonction est négative sur un intervalle, son intégrale sur cet intervalle est négative.
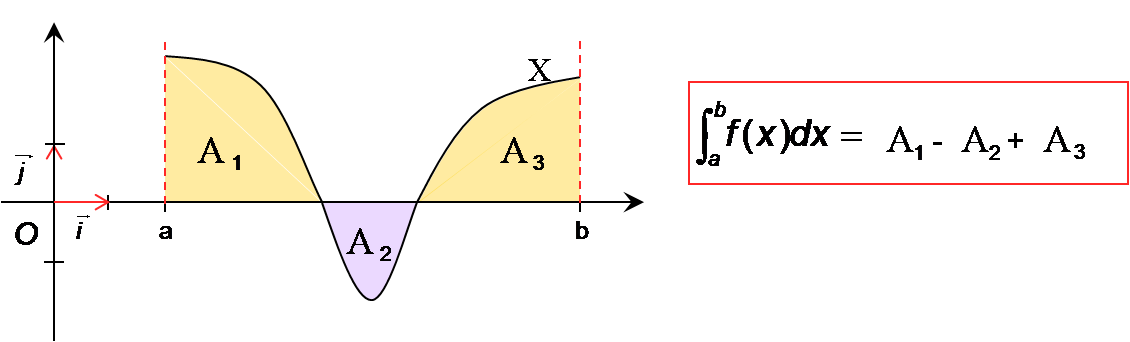
Si une fonction change de signe sur un intervalle...
...
Term ES : Calcul intégral
By Jean-Marc Kraëber
Term ES : Calcul intégral
Lycée Saint-Exupery
- 1,159



