Large deviations of the giant in spatial random graphs
Joost Jorritsma
joint with Júlia Komjáthy, Dieter Mitsche



Junior Probability Seminar University of Oxford, November '24


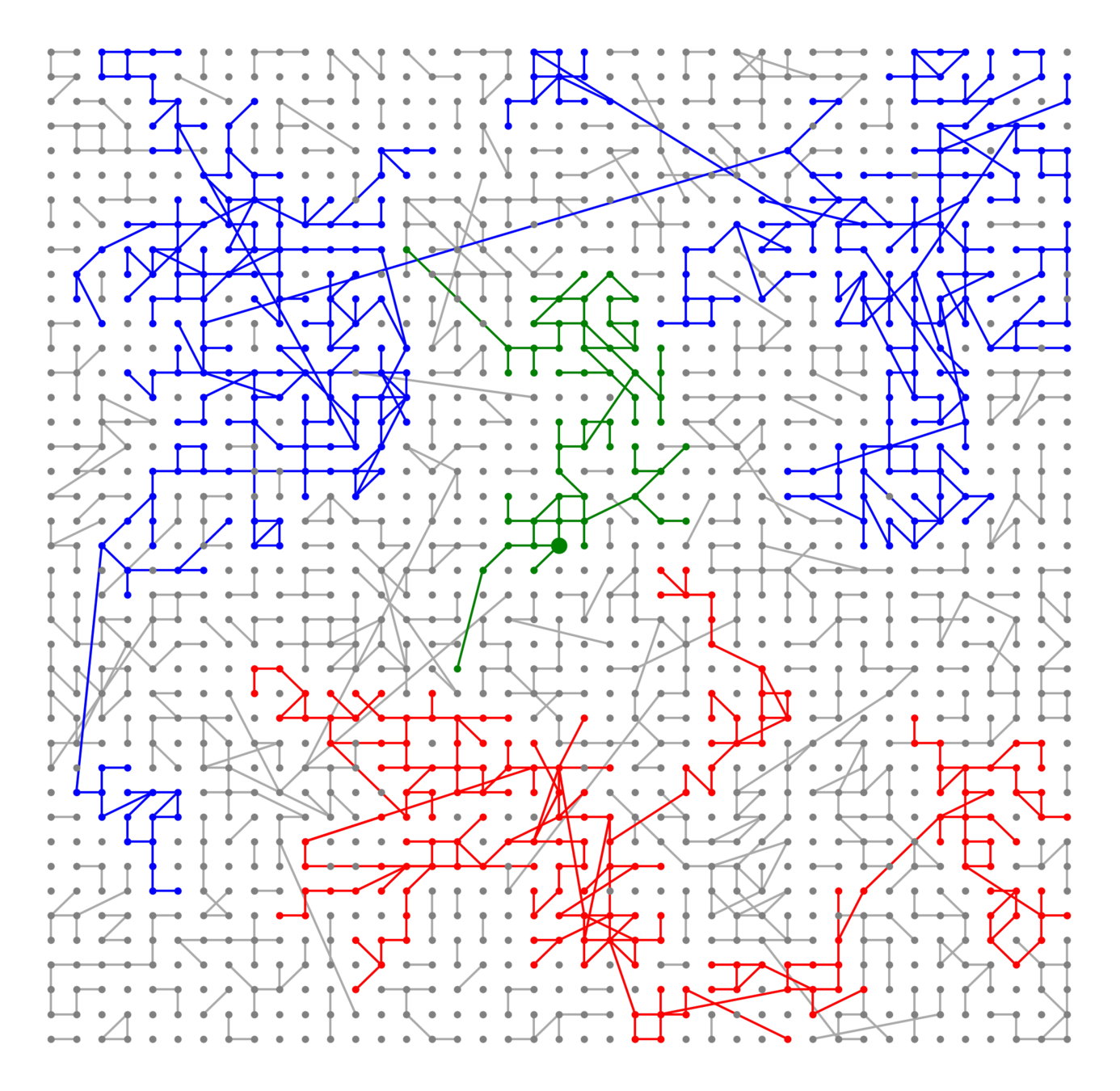

Hyperbolic random graph
Scale-free percolation
Long-range percolation
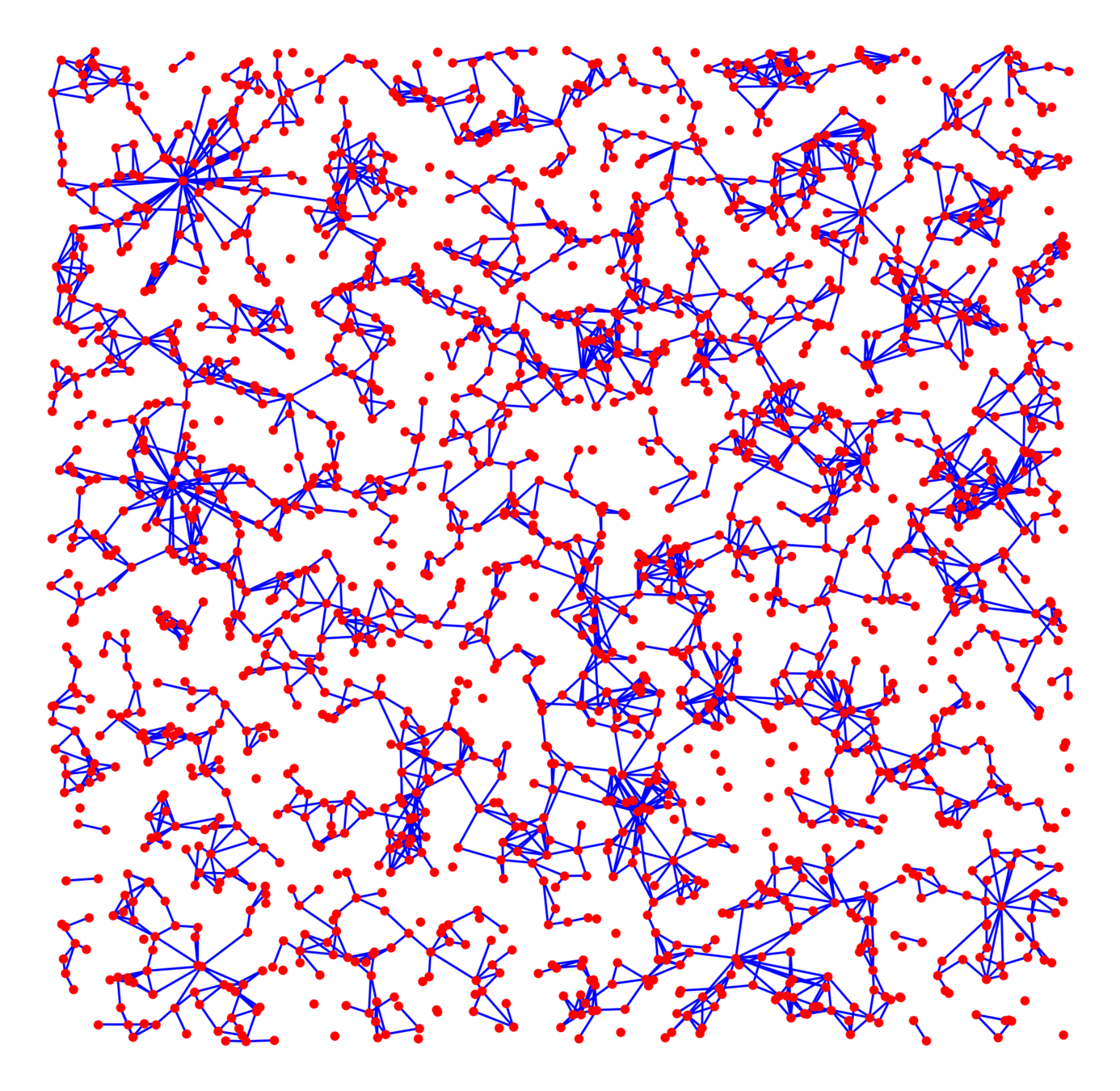
Scale-free Gilbert RG
Random geom. graph
Nearest-neighbor percolation

Kernel-based spatial random graphs
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
-
Spatial locations, either
- Lattice \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)
- Poisson point process (unit intensity)
- Power-law i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\):
\(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
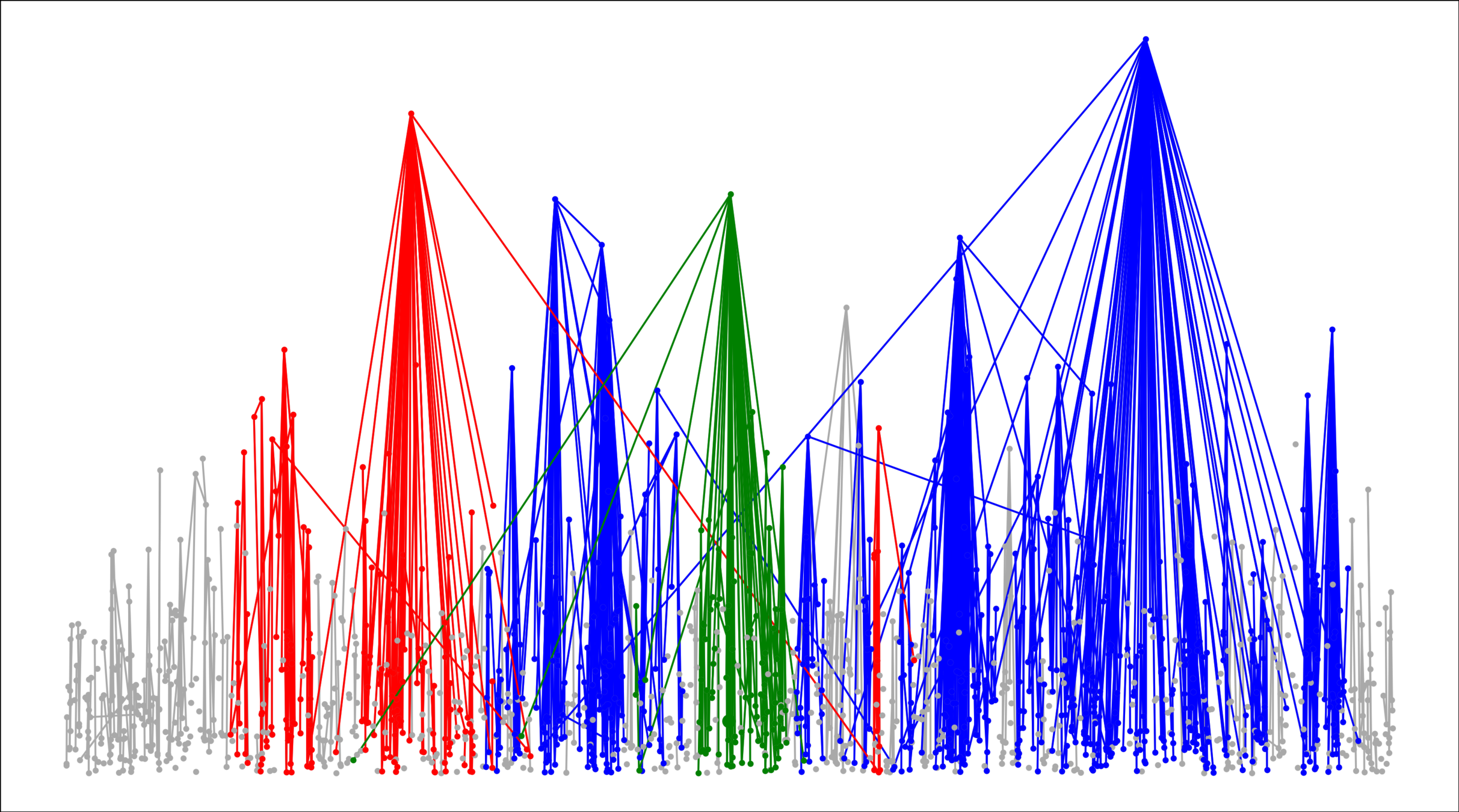
Kernel-based spatial random graphs
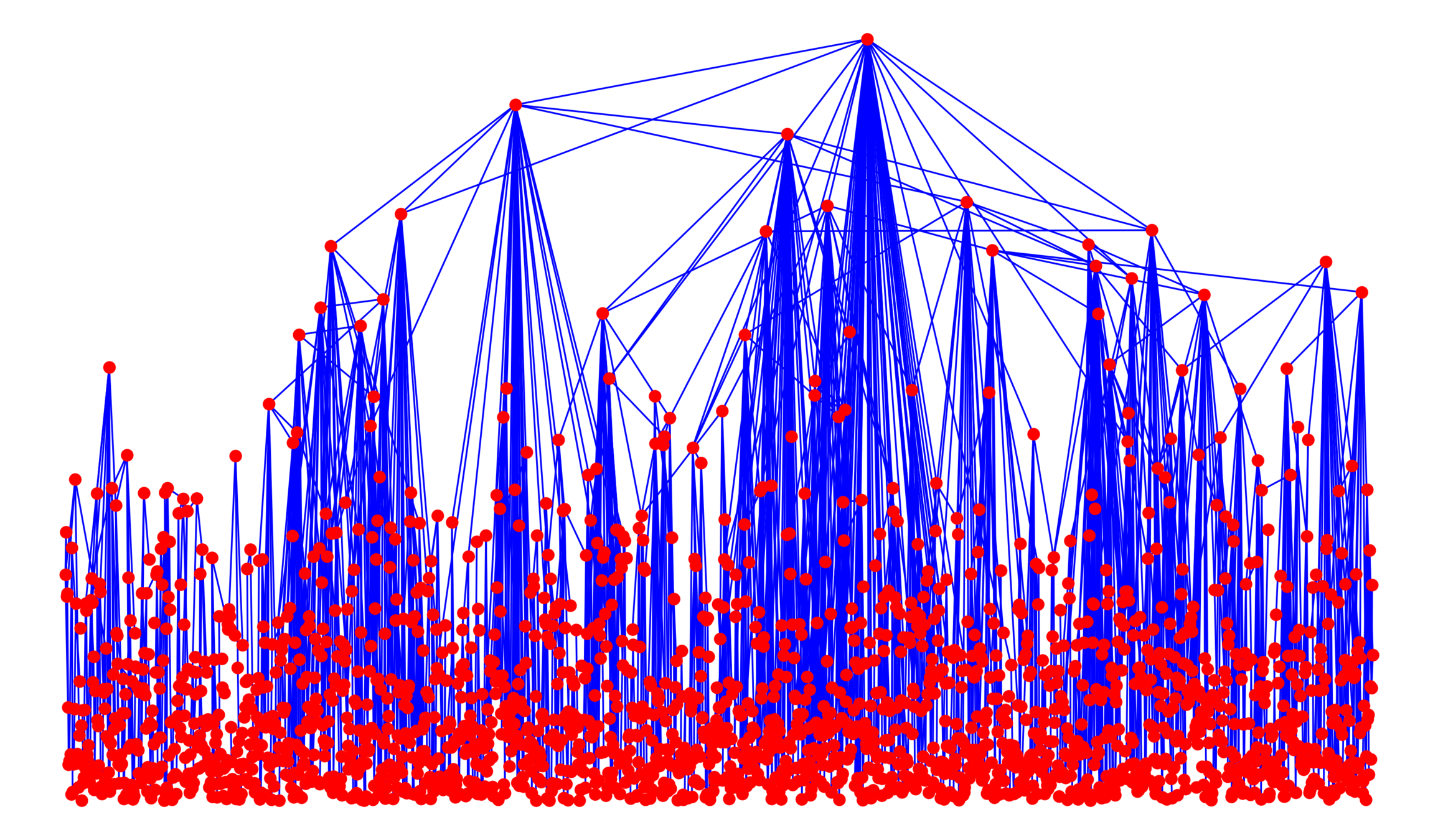
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Symmetric kernel \(\kappa(w_u, w_v)\),
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha\in(1,\infty]\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
Connection probability
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1$$
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
-
Spatial locations, either
- Lattice \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)
- Poisson point process (unit intensity)
- Power-law i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\):
\(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{\bigg(\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\phantom{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}}\phantom{\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1}$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{\bigg(\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\phantom{\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1}$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\phantom{\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha\phantom{\wedge 1}$$
Kernel-based spatial random graphs
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Symmetric kernel \(\kappa(w_1, w_2)\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha\in(1,\infty]\),

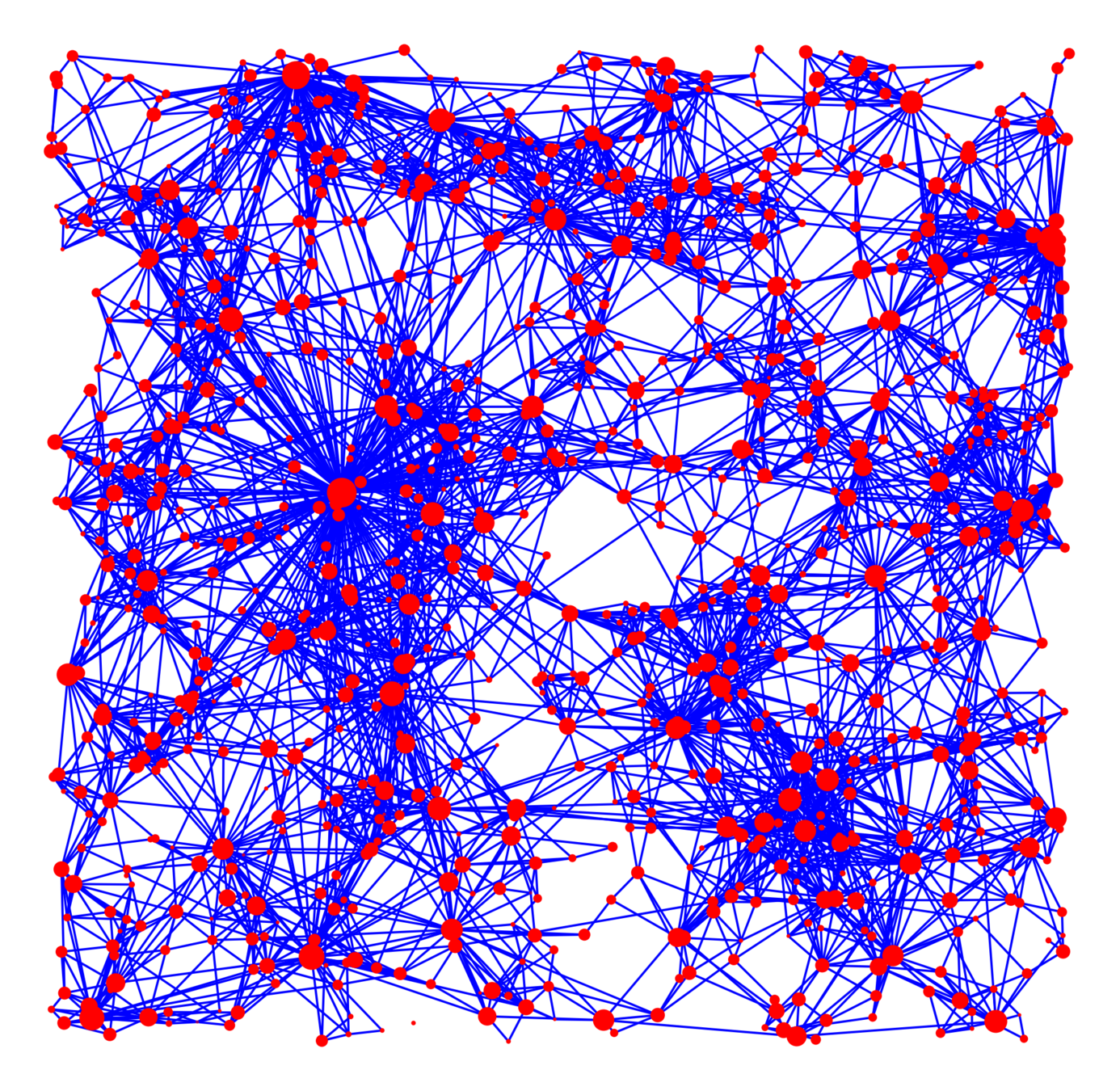
Connection probability
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1$$
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
-
Spatial locations, either
- Lattice \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)
- Poisson point process (unit intensity)
- Power-law i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\):
\(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
Geom. Inhom. RG

Hyperbolic RG

Geom. RG

Long-range perc.
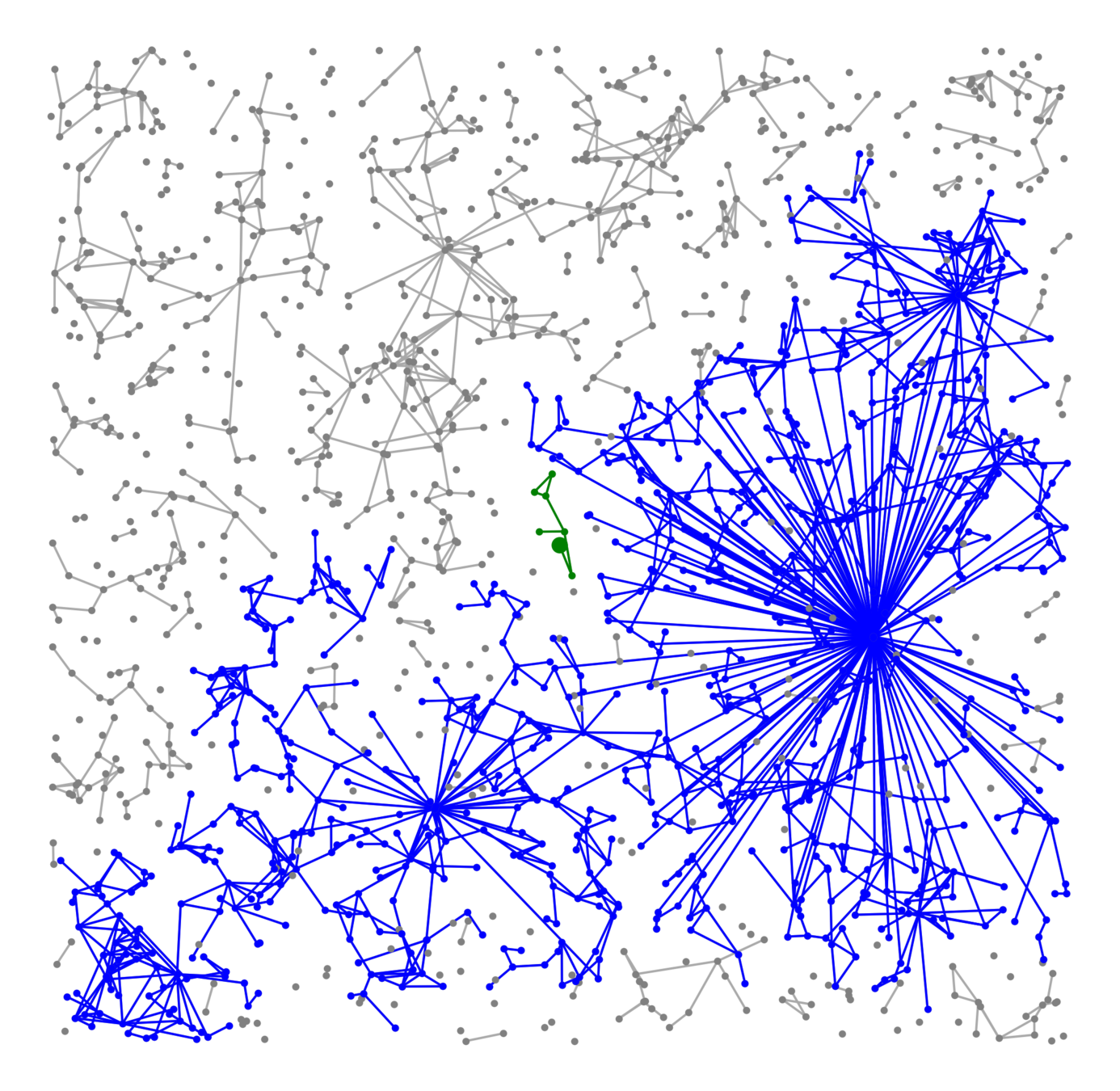
Scale-free Gilbert RG
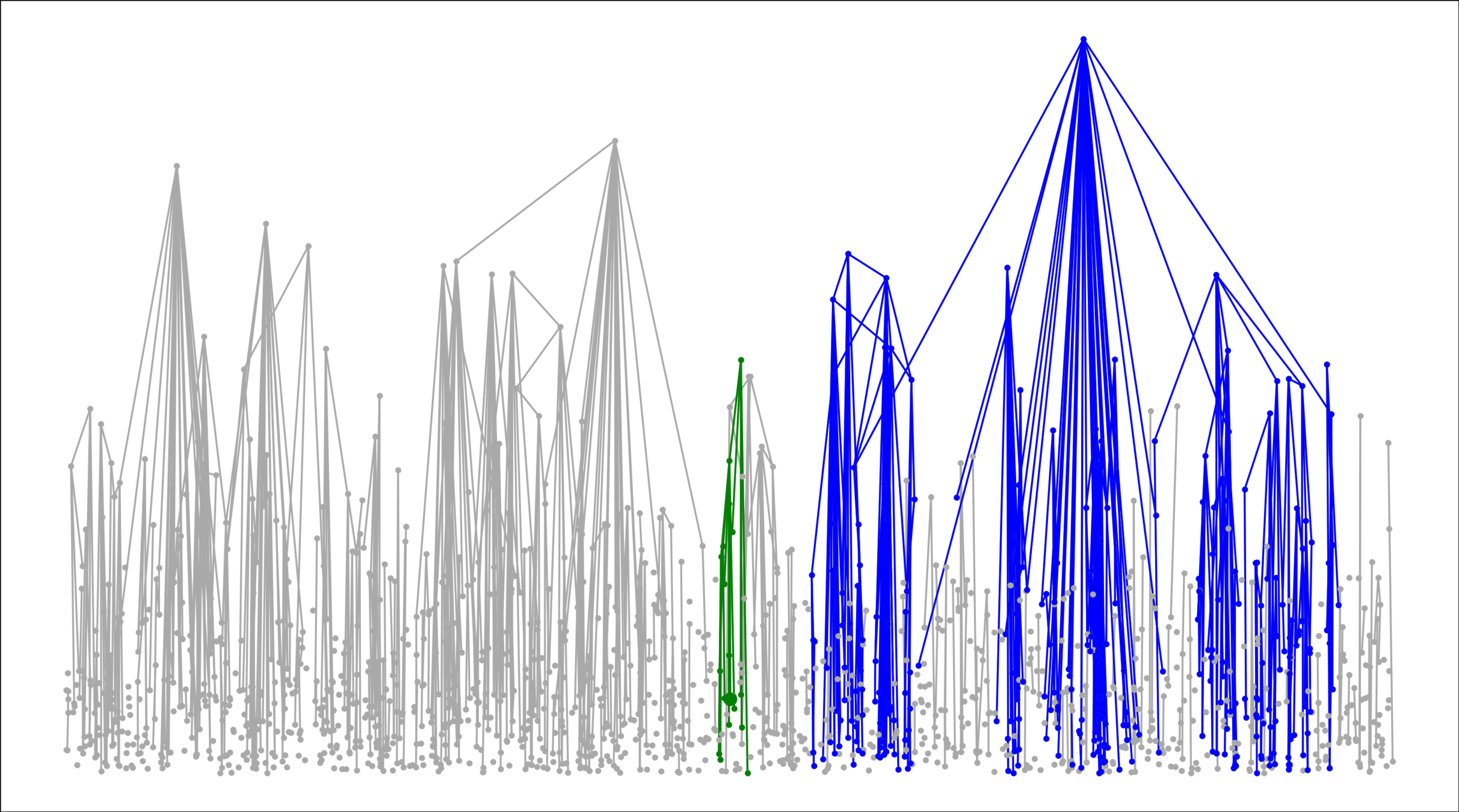
Age-dependent RCM
Theorem. When \(\tau<2\) or \(\alpha<1\):
- Infinite degrees
- Bounded diameter
[Deijfen, v.d. Hofstad, Hooghiemstra '13], [Gracar, Grauer, Lüchtrath, Mörters '18]
[Heydenreich, Hulshof, J. '17], [Hirsch '17], [v.d. Hofstad, v.d. Hoorn, Maitra '22],
[J., Komjáthy, Mitsche, '23], [Lüchtrath '22]
Theorem. When \(\tau>2\) and \(\alpha>1\):
$$\mathbb{P}(\mathrm{deg}(0)\ge k)\sim k^{-(\tau-1)}.$$
\(\tau\) small: many hubs
\(\alpha\) small: many long edges
The interpolating kernel
Connection probability
$${\color{grey}\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\bigg(\beta}\frac{\kappa(w_u, w_v)}{\color{grey}\|x_u-x_v\|^d}{\color{grey}\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1}$$
A parameterized kernel: \(\sigma\ge 0\)
$$\kappa_{\sigma}(w_u, w_v):=\max\{w_u, w_v\}\min\{w_u, w_v\}^\sigma$$
- \(\tau: \mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}.\)
- \(\sigma\): assortativity
- \(\sigma\): interpolation

SFP/GIRG

Hyperbolic RG
Age-dep. RCM
Scale-free Gilbert
Long-range percolation
Random geom. graph
Nearest-neighbor percolation
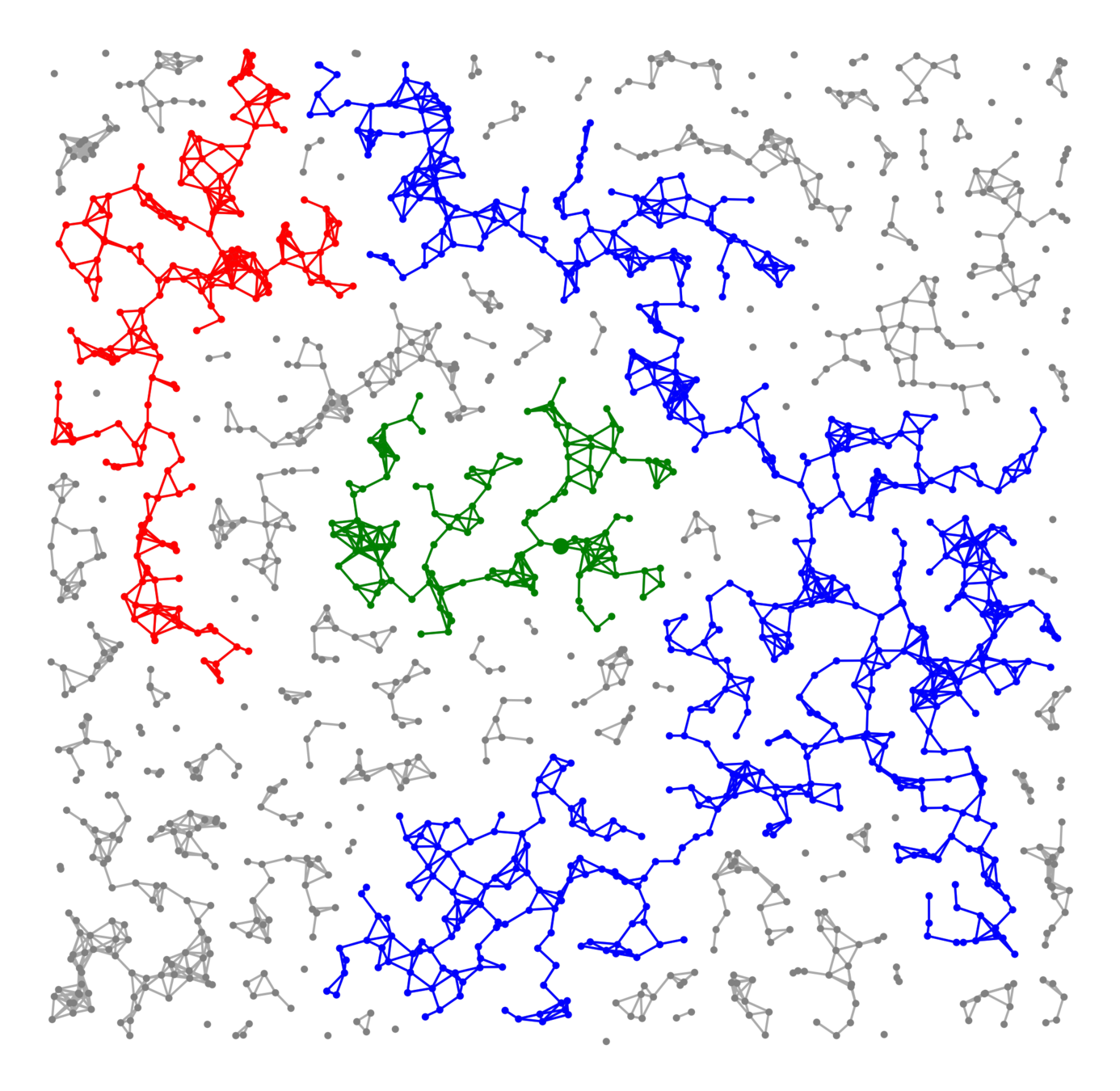
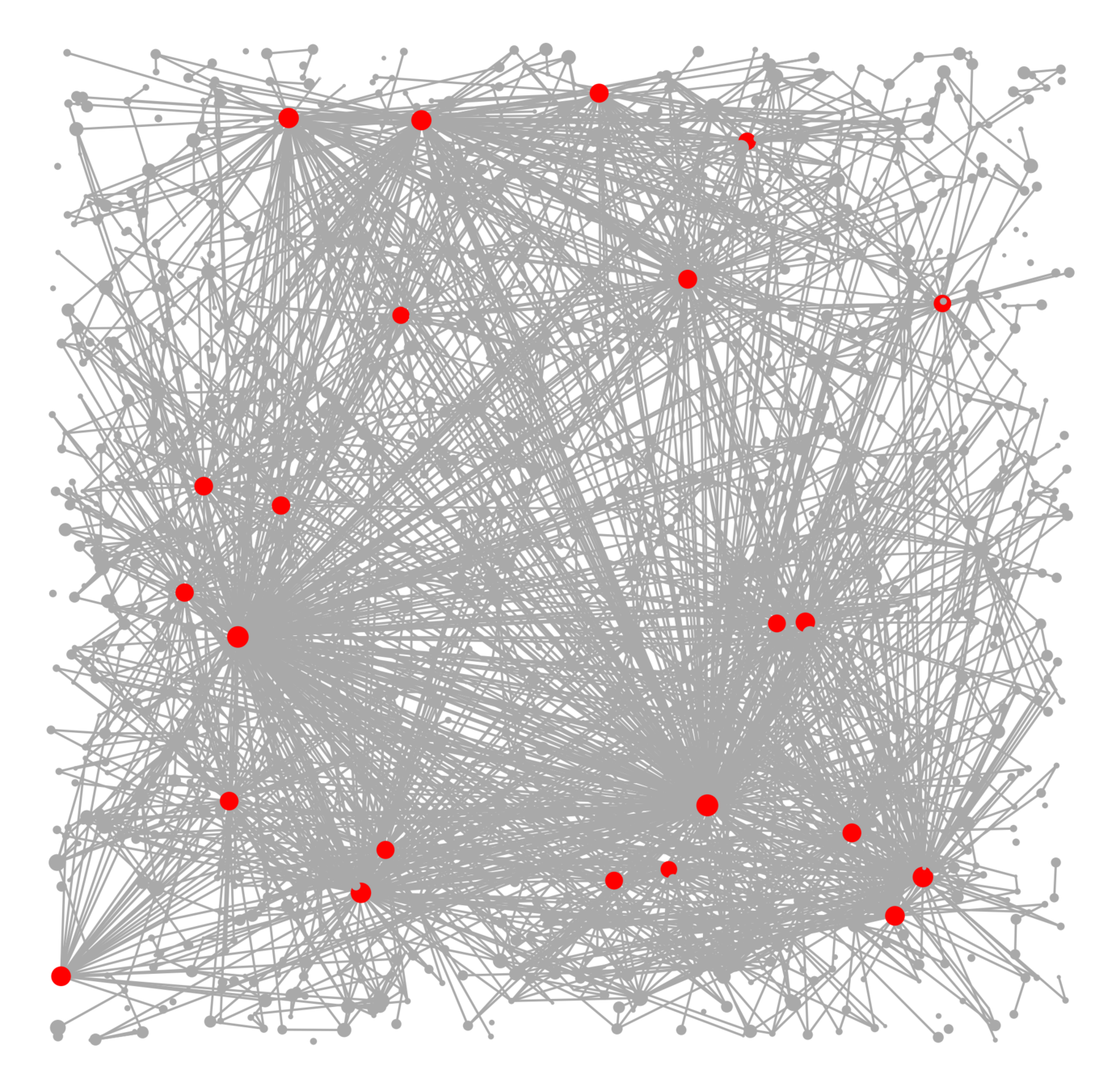
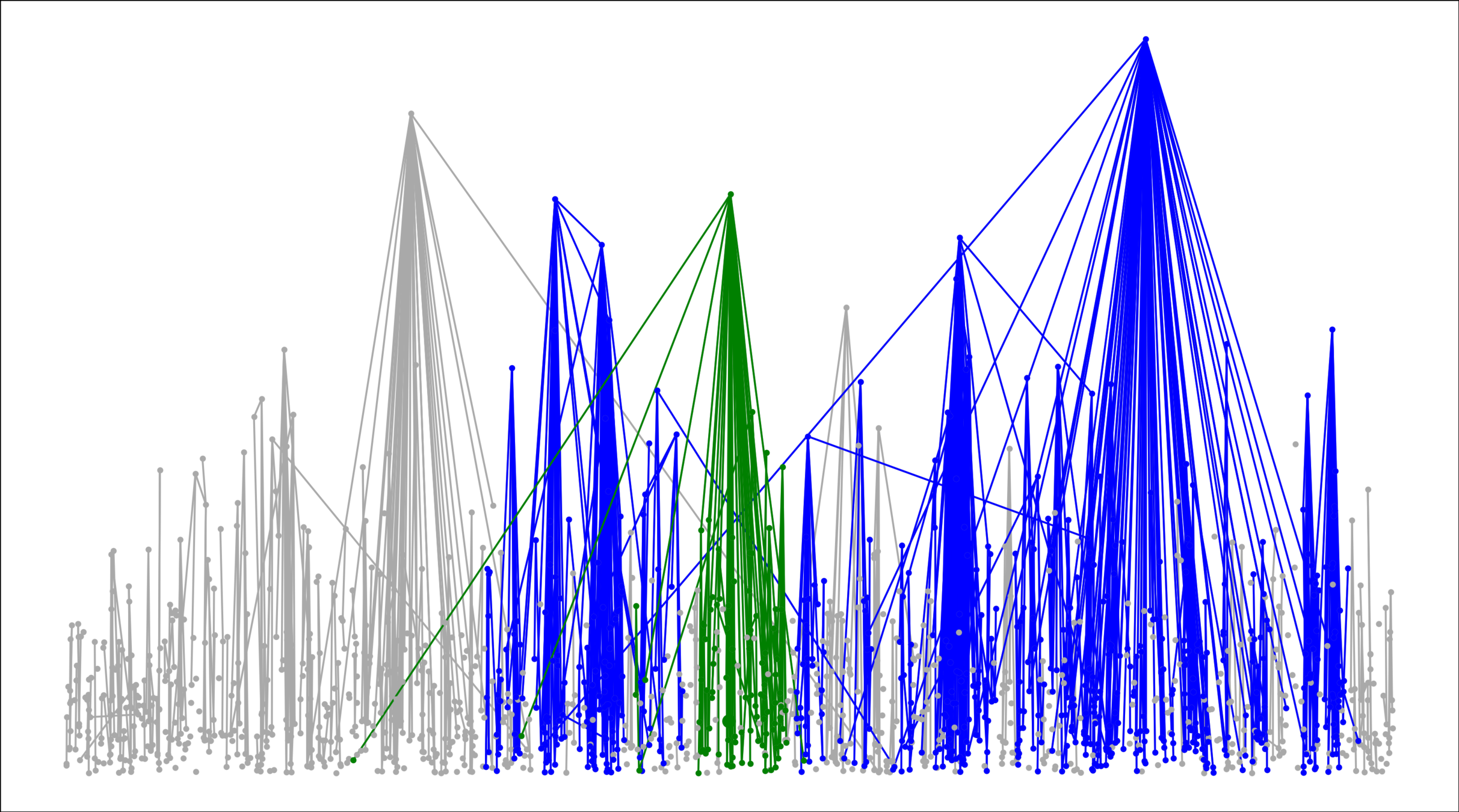
Components in supercritical graphs
-
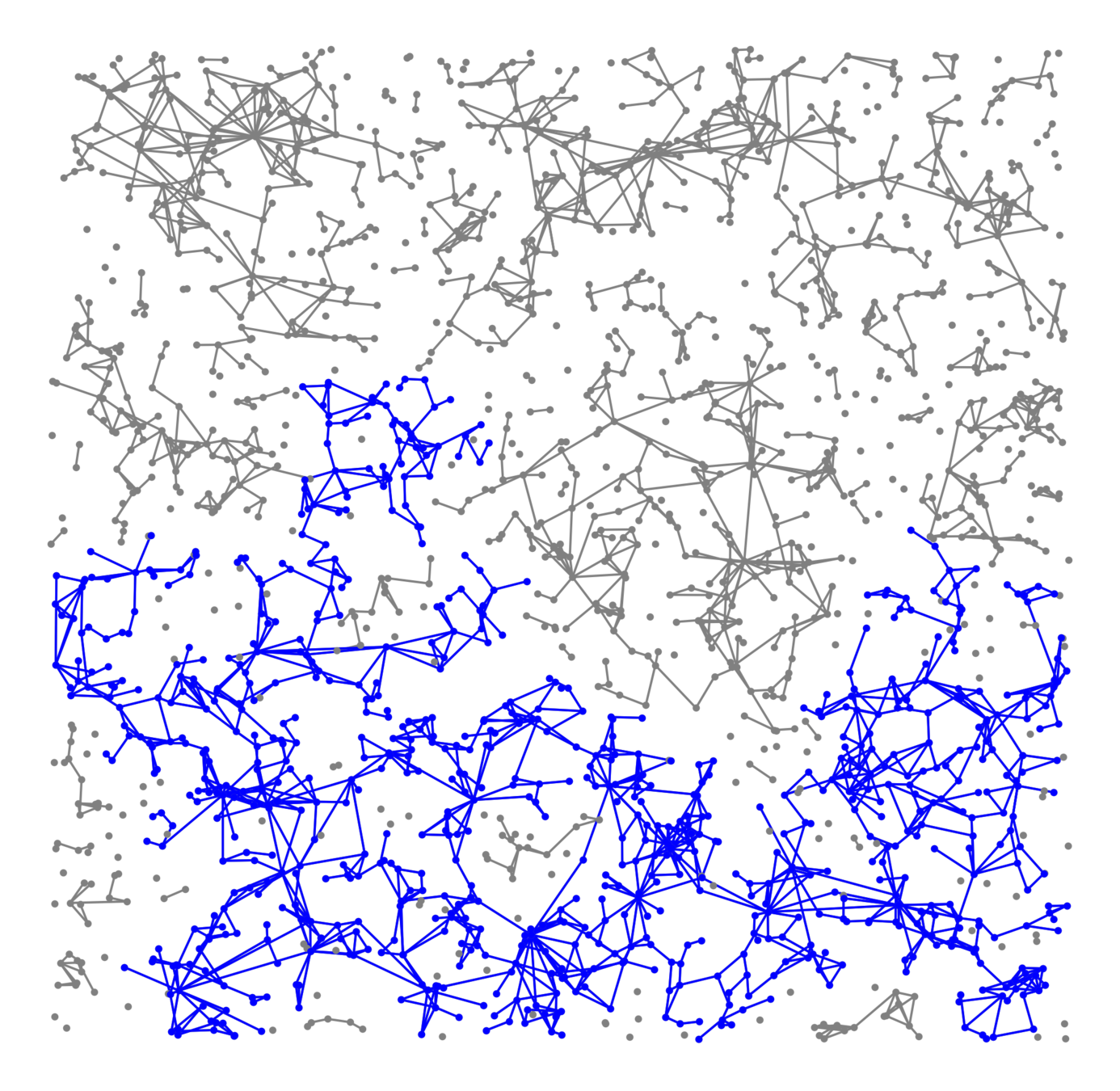
Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Questions




Components in supercritical graphs
-
Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Questions






Previous results
[Alexander & Chayes & Chayes '90], [Grimmett & Marstrand, '90], [Kesten & Zhang '90], ..., [Deuschel, Pisztora, '96], [Biskup '04], [Penrose '05], [Sly & Crawford'12], [Kiwi & Mitsche '17], [Lichev, Lodewijks, Mitsche, Schapira '22], [Bläsius, Friedrich, Ruff, Zeiff, '23]




Lower tail large deviations of the giant*:
One decay exponent governing cluster sizes
*log(log)-corrections at phase transition
Small components*:
If \(\mathbb{E}[\# \text{edges of length } \Omega(n^{1/d})]\to\infty\)
If \(\zeta>(d-1)/d\)
Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Lower bounds: cluster-size decay
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.





Aim: Find \(\gamma\) s.t.
Lower bounds: cluster-size decay
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.




Aim: Find \(\gamma\) s.t.
Lower bounds: large deviations






(FKG)





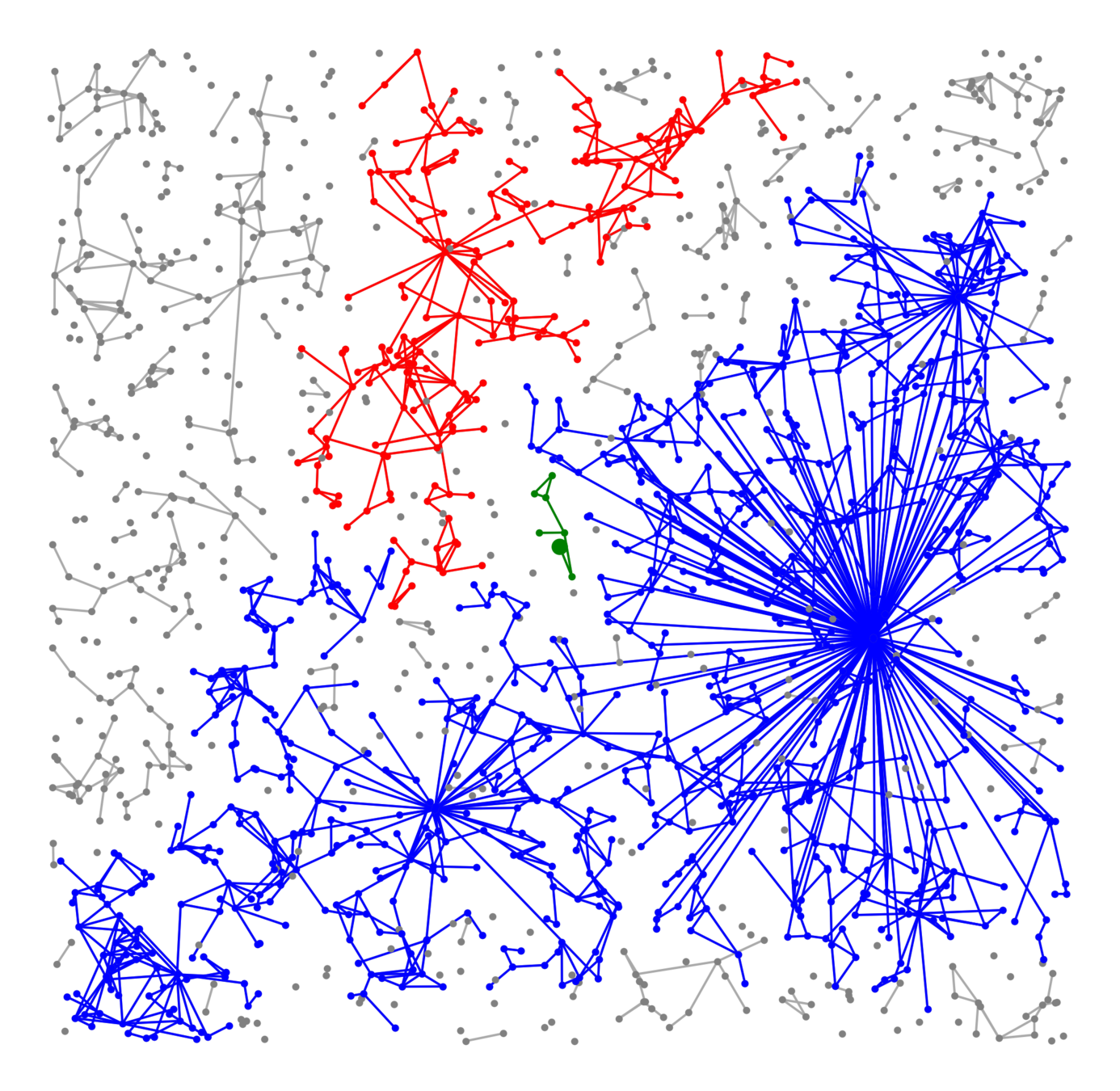
Lower bounds: \(|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|\)
\(\delta\) small
Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Upper bounds
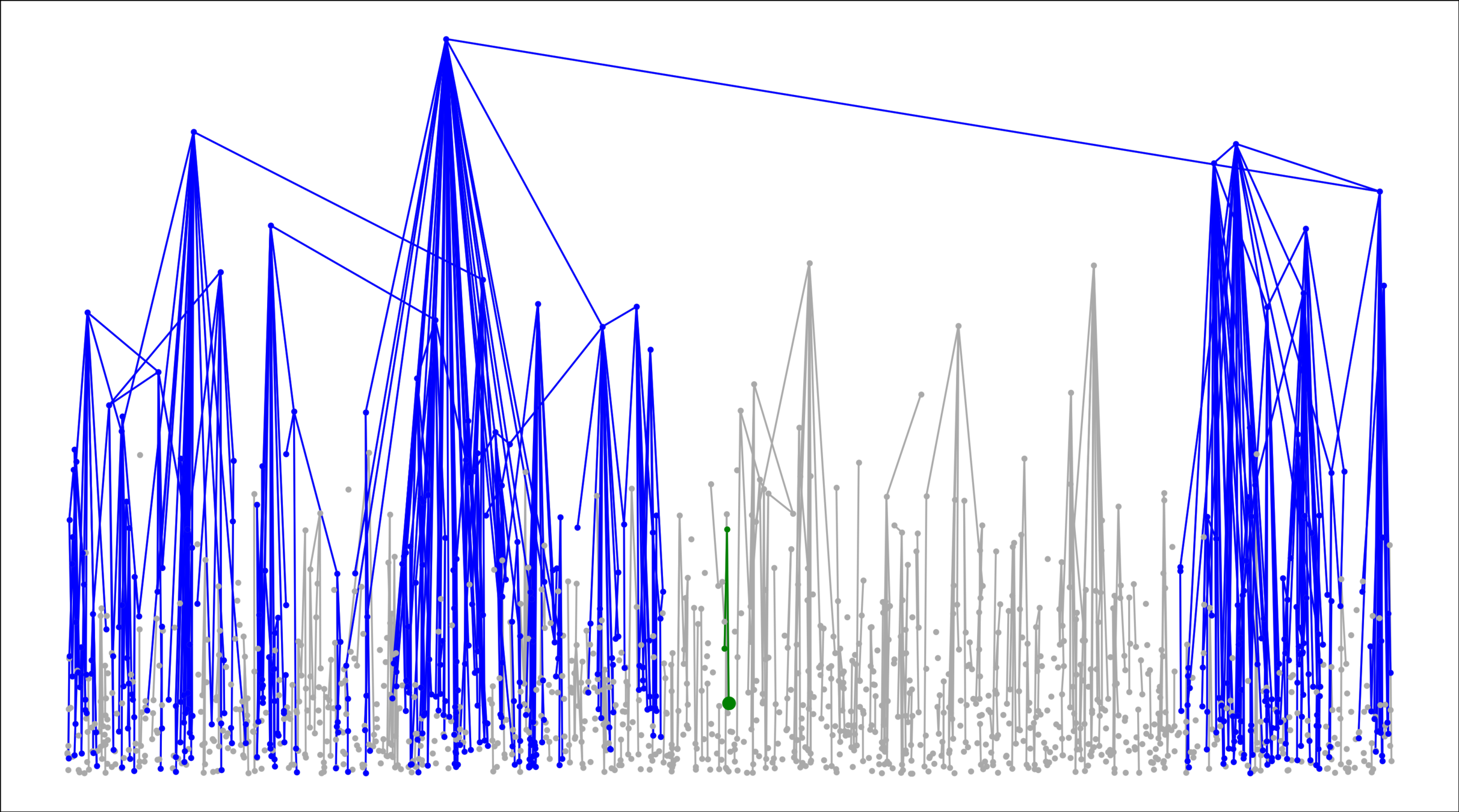
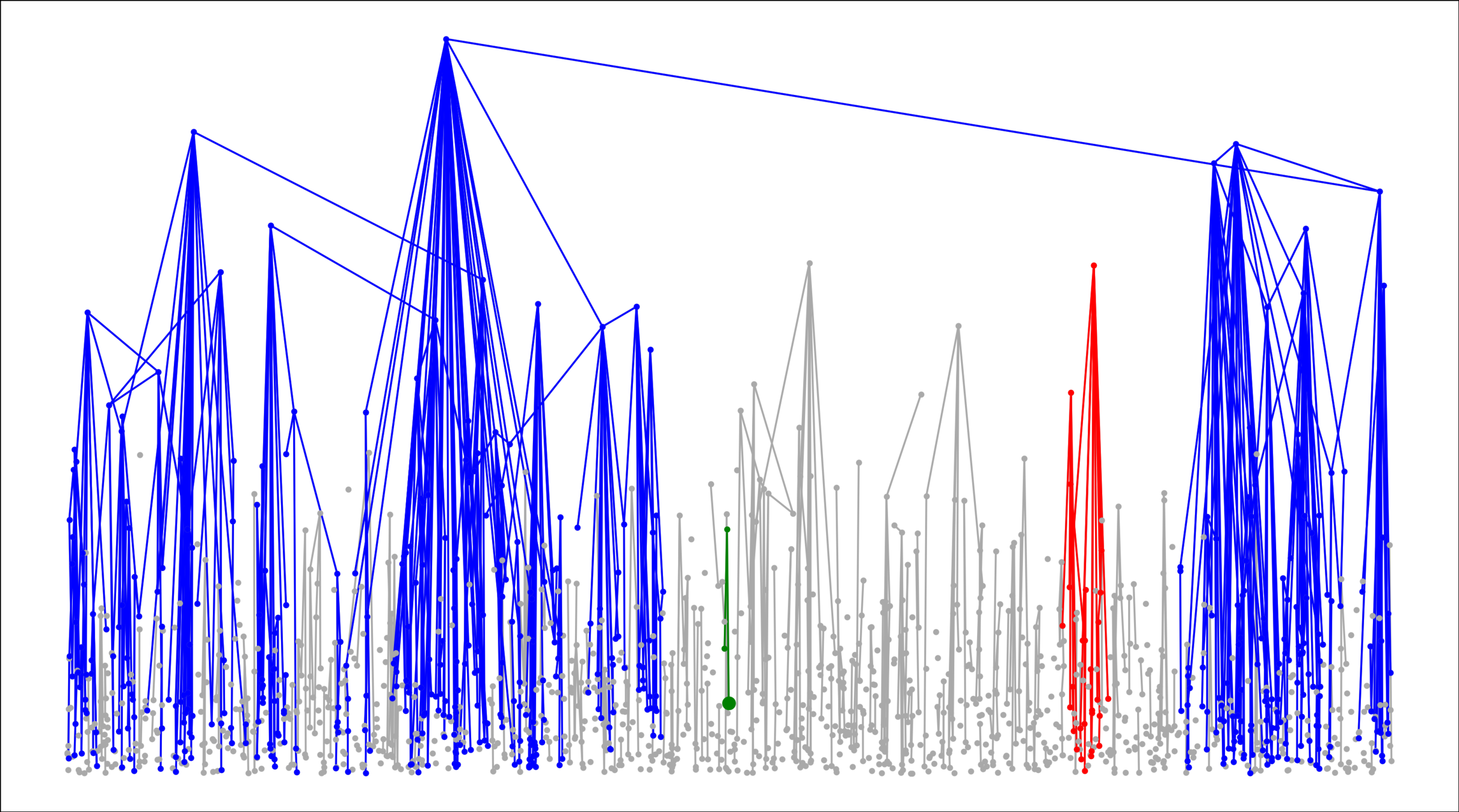
Challenge: Delocalized components
# possibilities for \(|{\color{red}2^{\mathrm{nd}}\text{-largest}}|\ge k\)

Upper bound: \(|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|\)

What about other values \(\zeta_\ast\)?

\(\kappa_\mathrm{prod}=w_u w_v\)
\(\kappa_\mathrm{max}=w_u\vee w_v\)
Description of weight distribution in large components
Prevent "small-to-large" merging
(Second-)largest component in supercritical spatial random graphs
- Cluster-size decay
- Second-largest component
Open problems:
-
Largest component:
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Large deviations
Answered questions (\(d=1\))
- Phase transition boundaries.
- Partial results \(d\ge 2\)
- Extension from PPP to grid
- Central limit theorem





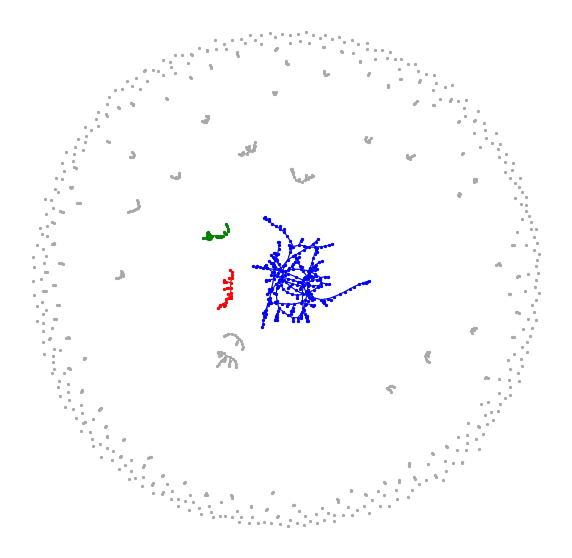
- \(\zeta\in\big[(d-1)/d, 1\big)\)
Thank you!

Supercritical Erdős–Rényi random graph \(G(n, \lambda/n)\)
[Erdős, Rényi '59; O'Connell '98; Andreis, König, Langhammer, Patterson'23]
Exponential growth of neighbourhood
The largest component

Supercritical bond percolation on \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)

[Alexander, Chayes, Chayes '90; Cerf '00; Gandolfi '88; Grimmett & Marstrand '90, Kesten & Zhang '90, Pisztora '96]
Surface-tension driven behavior
The largest component

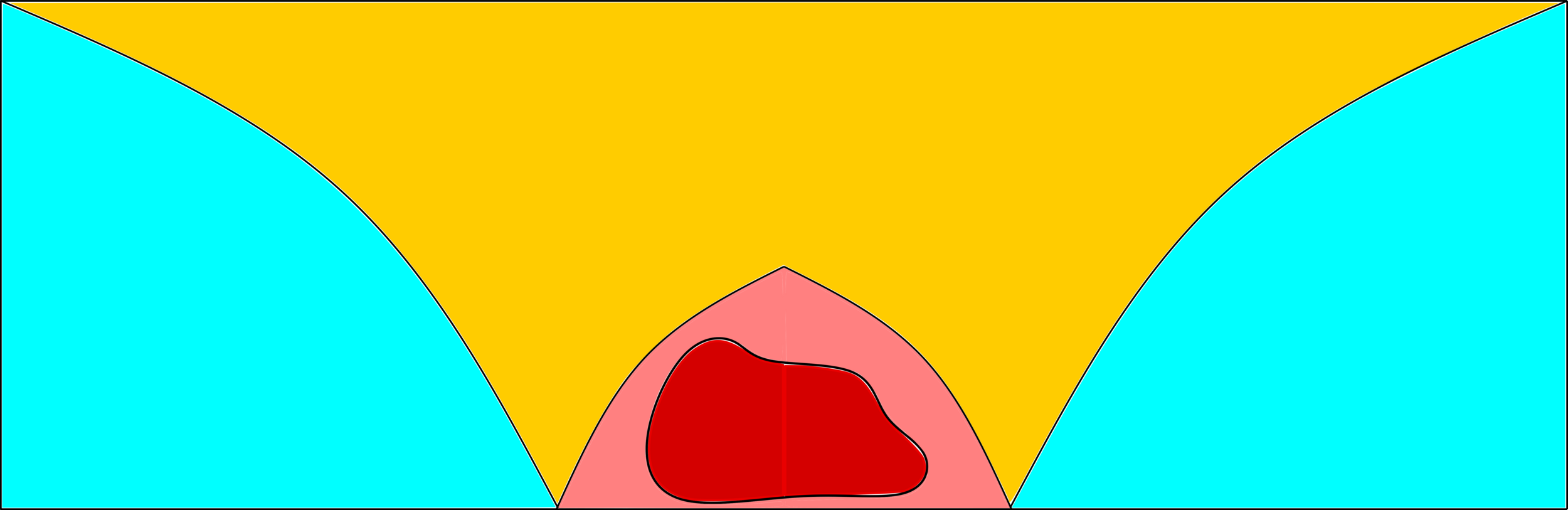
Remarks.
- \(\zeta_\ast<0\): subcritical*
-
\(d\ge 2\):
- \((d-1)/d\)
- partial results: upper bounds
- Product kernel: 2nd term

No known results
- \(|{\color{blue}\text{largest}}|/n\)
- \({\color{red}2^{\mathrm{nd}}\text{-largest}}\)
Example 1:
Scale-free Gilbert RG in \(d=1\)
Power-law degrees: \(\tau>2\)

\(d\ge 2\)
* [Gracar, Lüchtrath, Mönch '22]
Theorem. (J., Komjáthy, Mitsche '23+)
Set
If \(\zeta_\ast>0\), then LLN for \(|{\color{blue}\text{largest}}|\), and
Long-range parameter: \(\alpha>1\)
\(\kappa_\mathrm{max}=w_u\vee w_v\)
\(\kappa_\mathrm{prod}=w_uw_v\)
Example 2:
Geom. Inhomog. RG in \(d=1\)
Upper bounds
Challenge: Delocalized components
# possibilities for \(|{\color{red}2^{\mathrm{nd}}\text{-largest}}|\ge k\)

Components in supercritical graphs
-
Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Questions






Components in supercritical graphs
-
Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Questions






Previous results
[Alexander & Chayes & Chayes '90], [Grimmett & Marstrand, '90], [Kesten & Zhang '90], ..., [Deuschel, Pisztora, '96], [Biskup '04], [Penrose '05], [Sly & Crawford'12], [Kiwi & Mitsche '17], [Lichev, Lodewijks, Mitsche, Schapira '22], [Bläsius, Friedrich, Ruff, Zeiff, '23]



Conjecture: \(\exists \zeta\in \big[\tfrac{d-1}{d},1\big)\):


Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Upper bounds

What about other value \(\zeta_\ast\)?

Description of weight distribution in large components
Prevent "small-to-large" merging
Components in supercritical graphs
- Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Answered questions (\(d=1\))




(Second-)largest component in supercritical spatial random graphs
- Cluster-size decay
- Second-largest component
Open problems:
-
Largest component:
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Large deviations
Answered questions (\(d=1\))
- Phase transition boundaries.
- Partial results \(d\ge 2\)
- Extension from PPP to grid
- Central limit theorem






- \(\zeta\in\big[(d-1)/d, 1\big)\)
Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Small
Large
Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Remarks.
- \(\zeta_\ast<0\): subcritical*
-
\(d\ge 2\):
- \((d-1)/d\)
- partial results: upper bounds
- Product kernel: 2nd term
Power-law degrees: \(\tau>2\)
\(d\ge 2\)
* [Gracar, Lüchtrath, Mönch '22]
Theorem. (J., Komjáthy, Mitsche '23+)
Set
If \(\zeta_\ast>0\), then LLN for \(|{\color{blue}\text{largest}}|\), and
Long-range parameter: \(\alpha>1\)

Example 2:
Geom. Inhomog. RG in \(d=1\)





Hyperbolic random graph
Scale-free percolation
Long-range percolation
Scale-free Gilbert RG
Random geom. graph
Nearest-neighbor percolation

Copy of Largest component in spatial random graphs
By joostjor
Copy of Largest component in spatial random graphs
- 271



