
CVIP 2.0

- Neural Networks (NNs) are feature extractors
- Feature Extraction using NNs recap
- AutoEncoders
- Transpose Convolutions
- AutoEncoders PyTorch Coding Example
- Inference in AutoEncoders
- Variational AutoEncoders
- Notation in Variational AutoEncoders (VAEs)
- ELBO in VAEs
- VAES PyTorch Coding Example
\( \text{Agenda of this Lecture:}\)

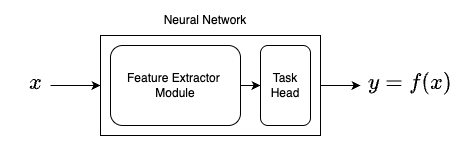
Neural Networks have two components:
- Feature Extractor Module
- Task specific head
You can experiment with simple neural networks at Tensorflow Playground
Usually extracted features are of
lower dimension than data (x)

but, what does it mean when two images are closer to each other?
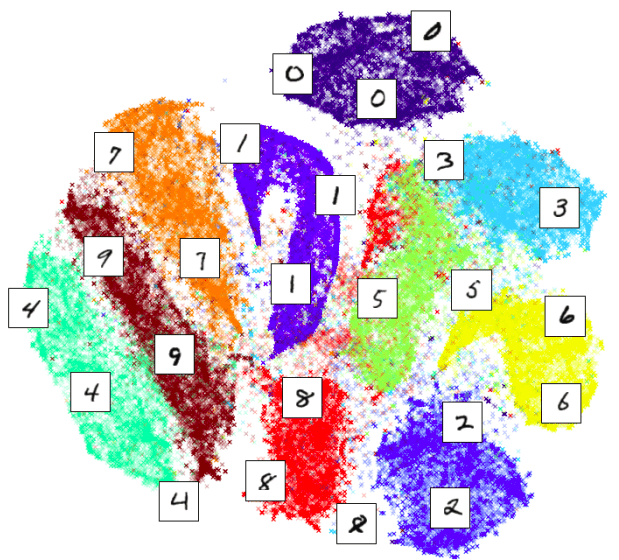
Closer in Low-Dimensional Feature Space



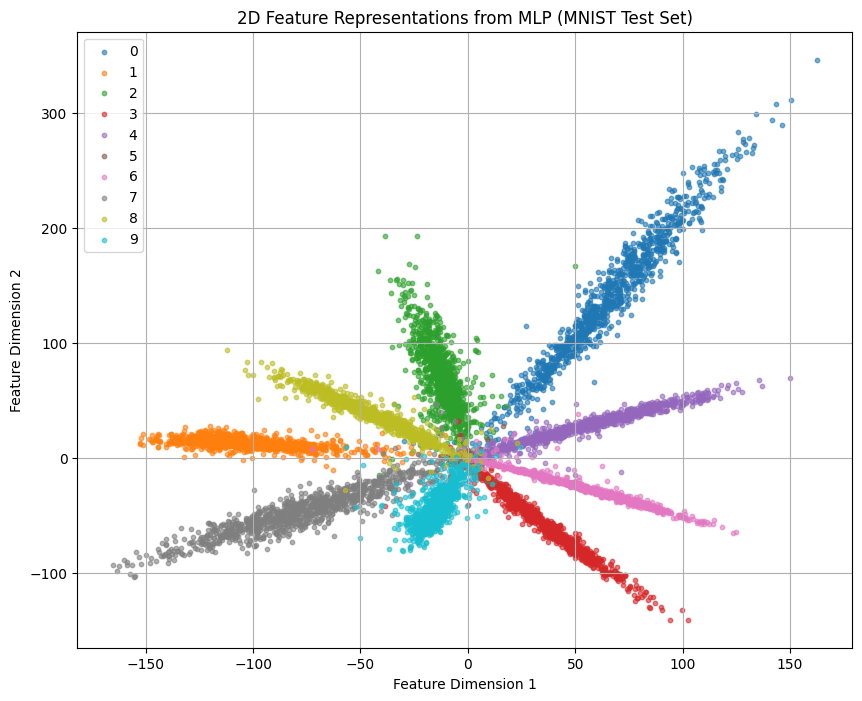



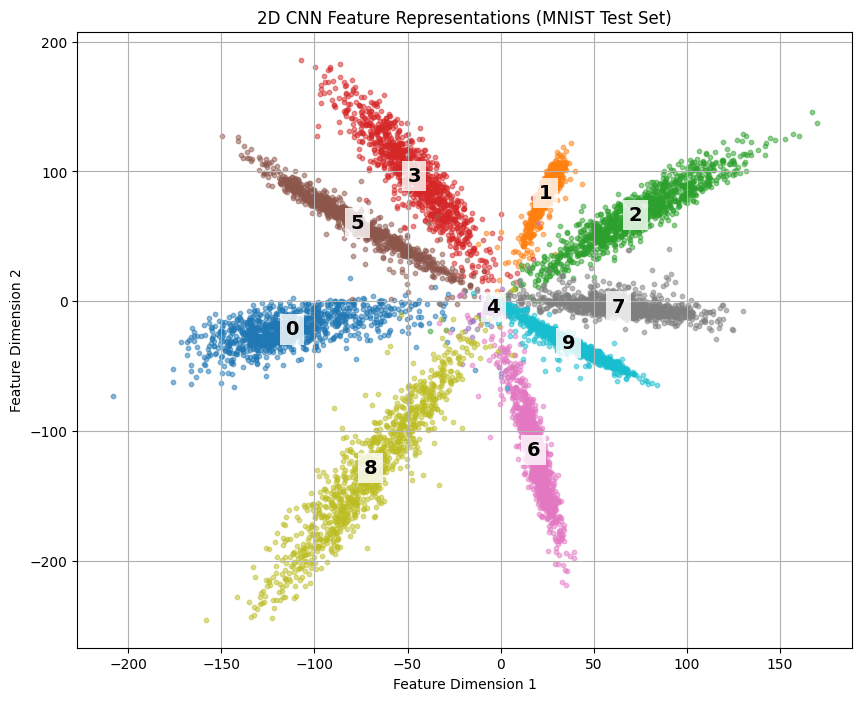

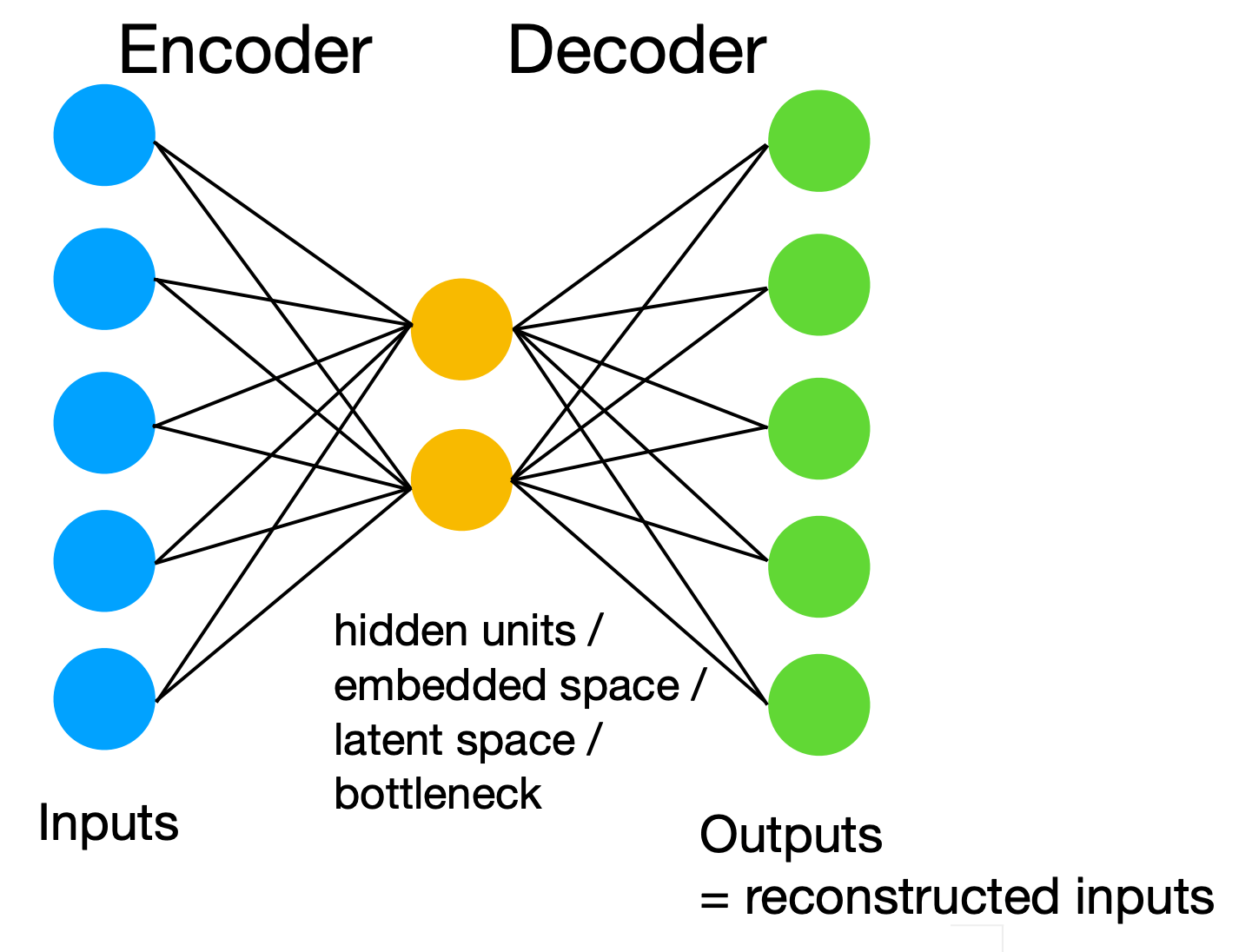
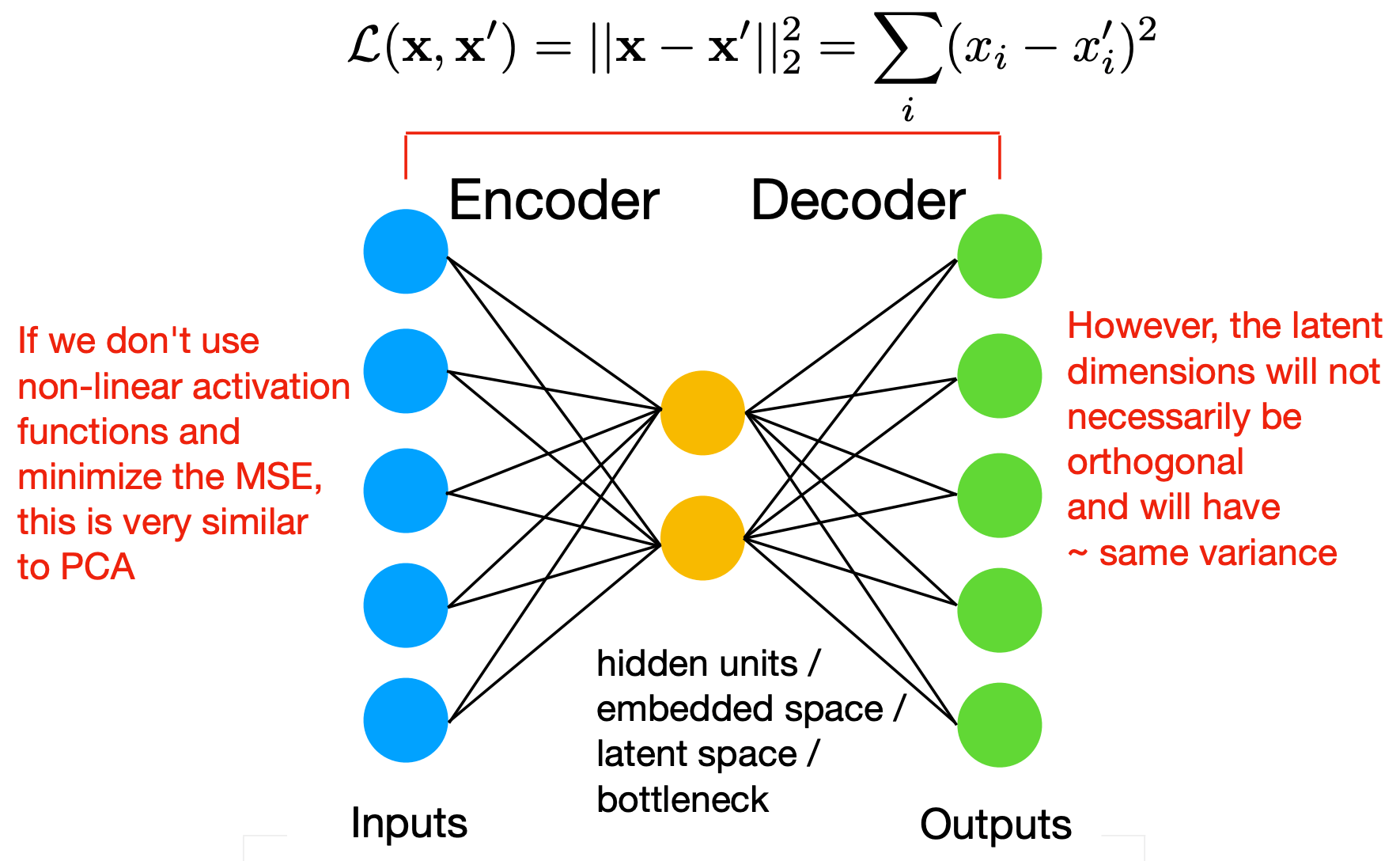
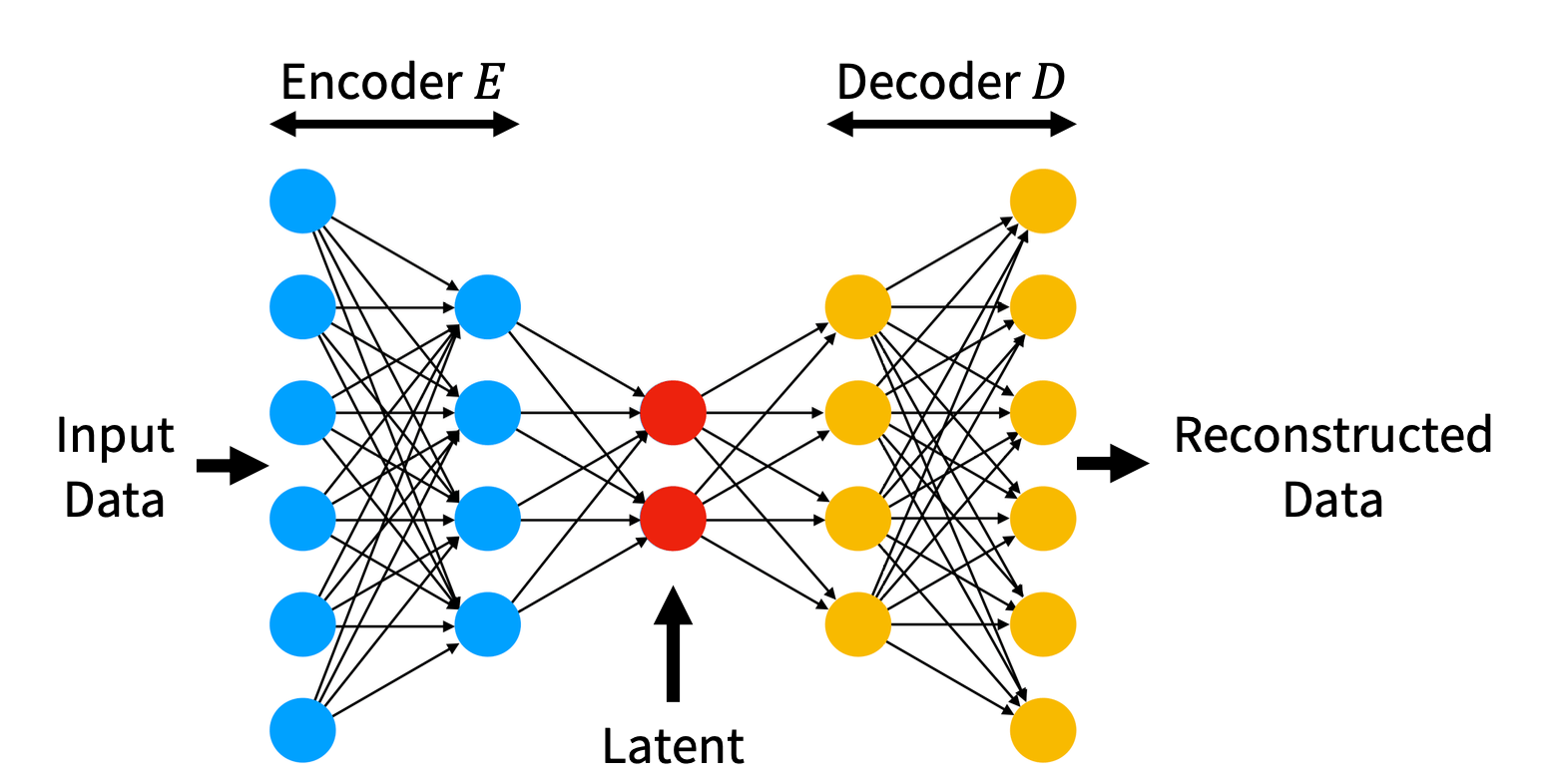
Simple MLP AutoEncoder

Simple MLP AutoEncoder

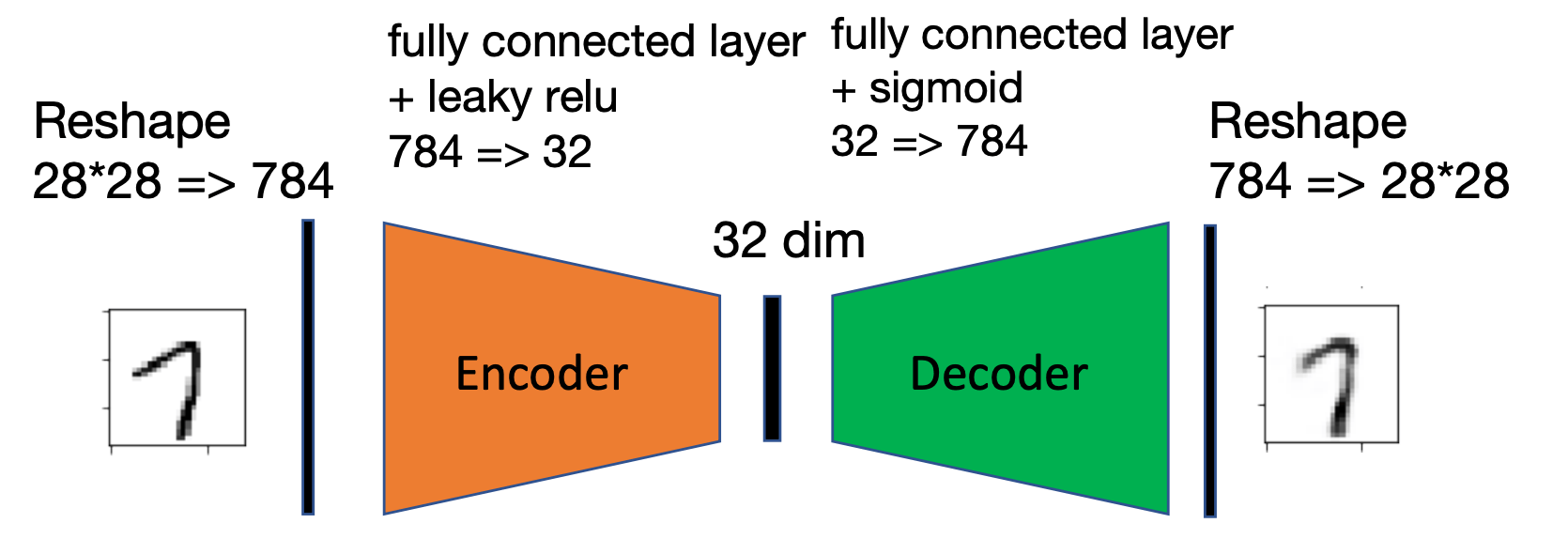

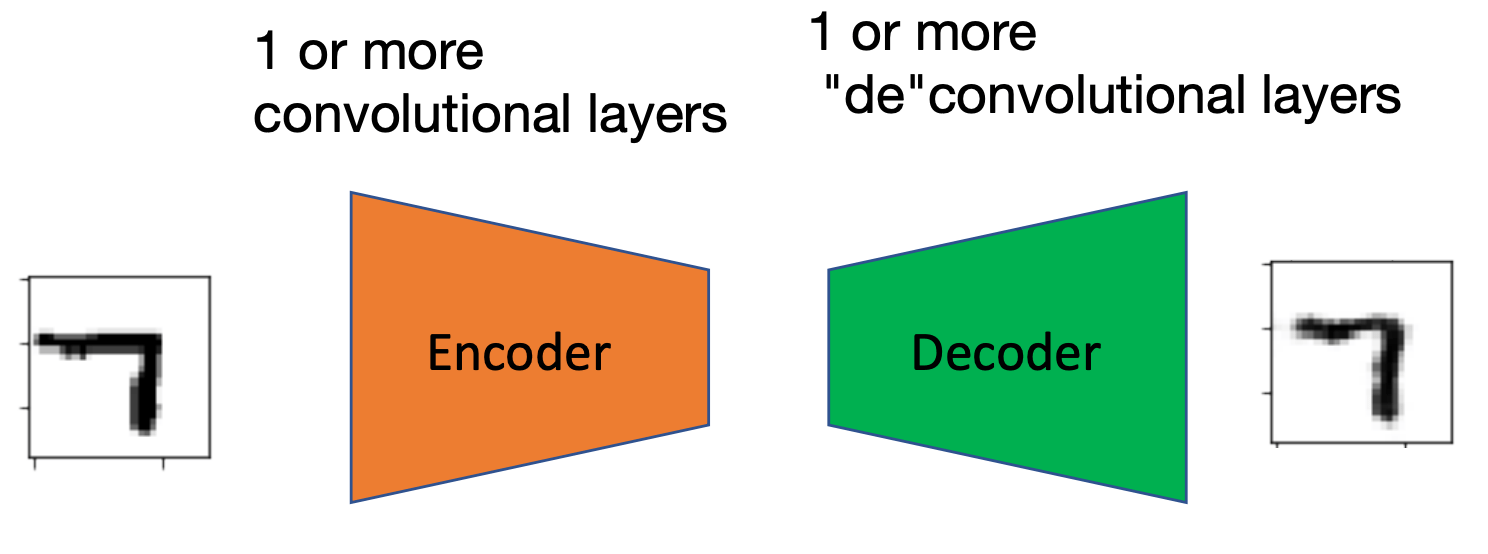
Convolutional AutoEncoder

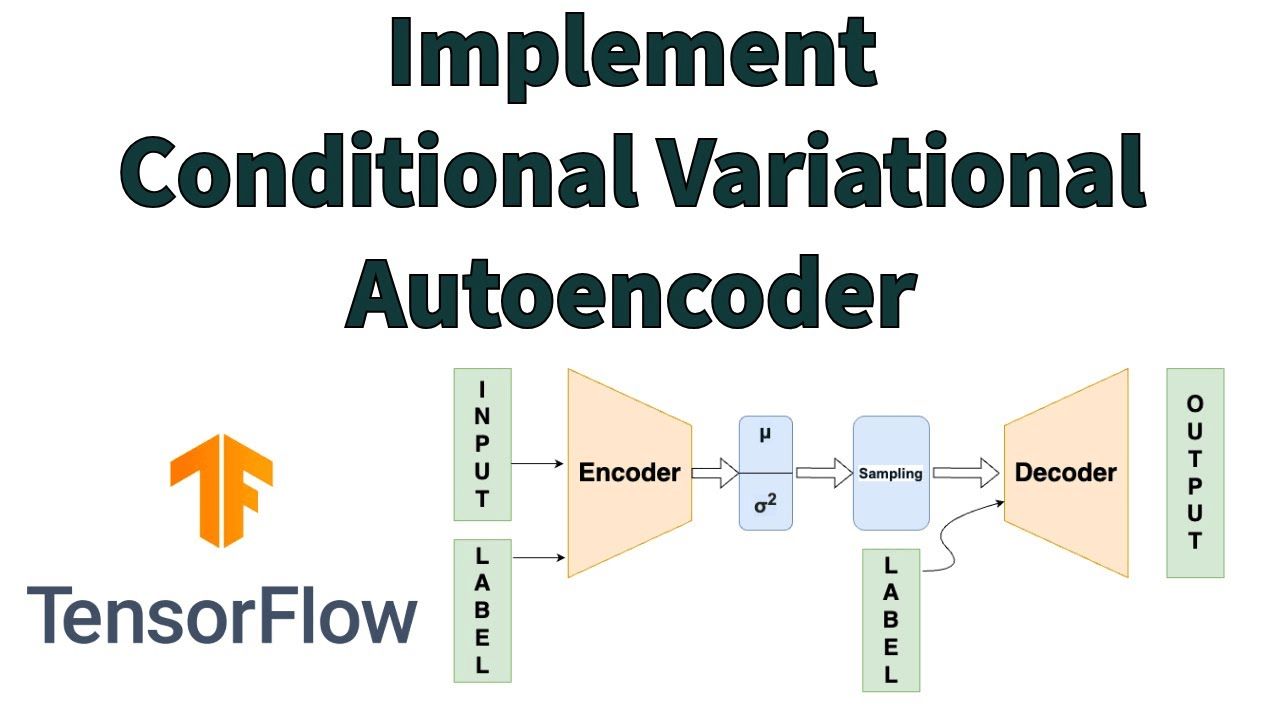
Posterior
Generative Model


Posterior
Generative Model



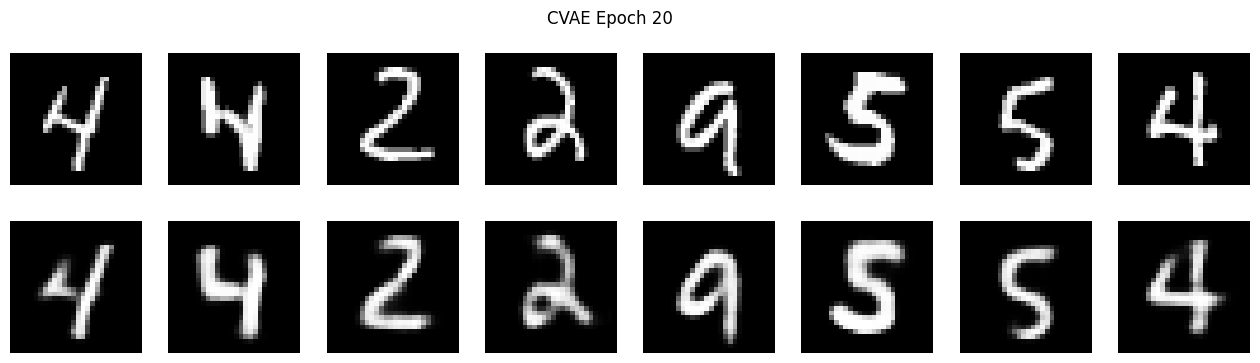


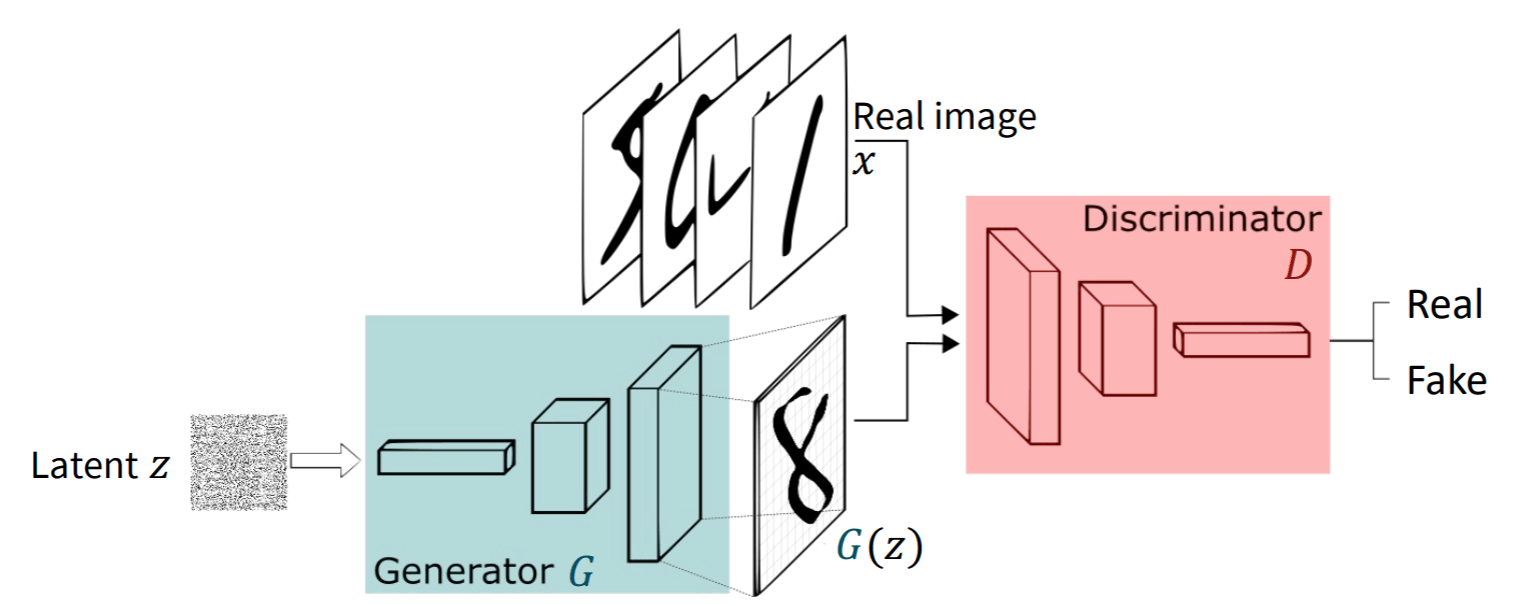


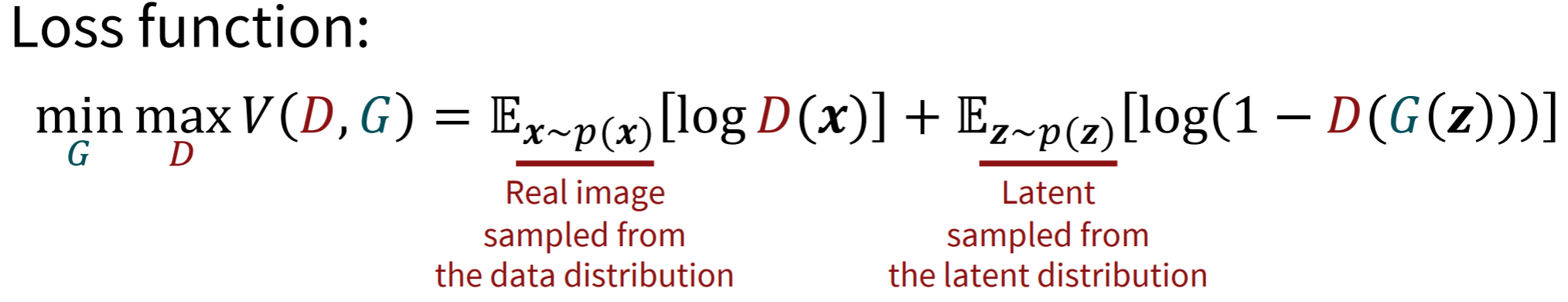

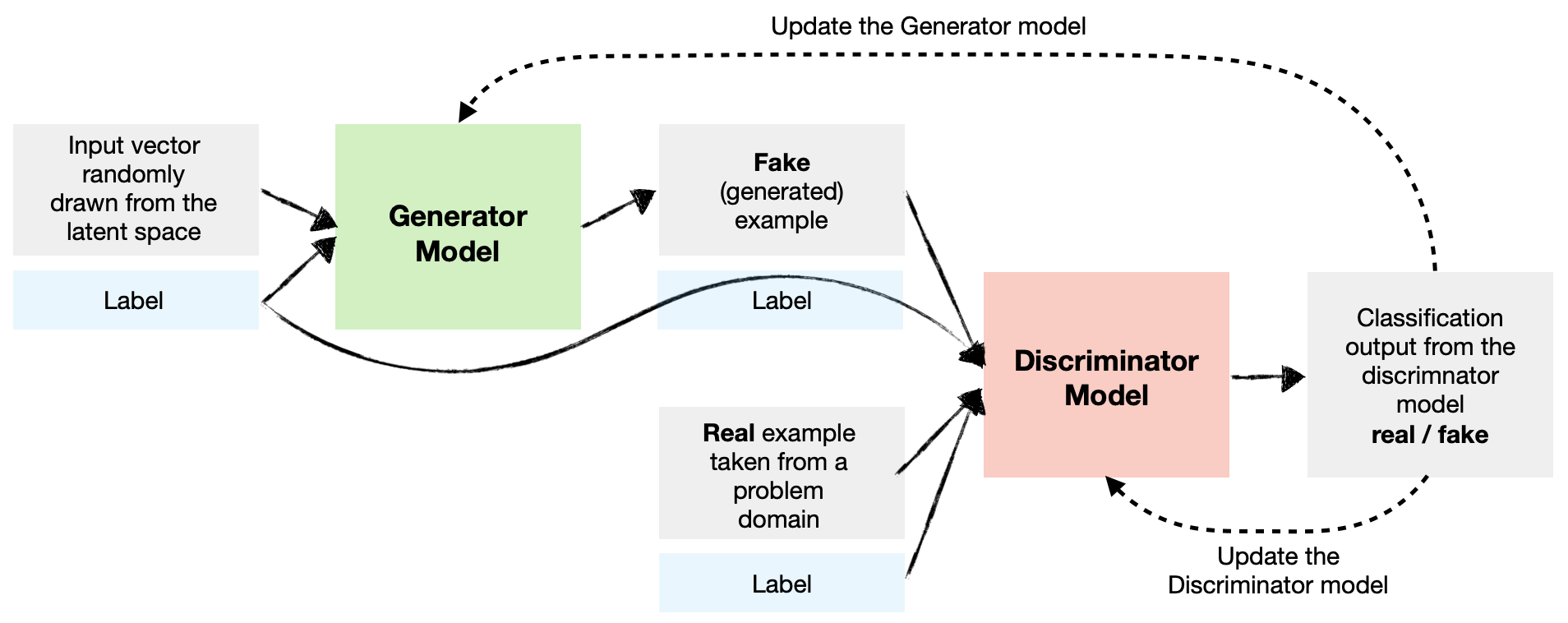
Training dynamics
1. Draw a batch of real images \( x_i \) with labels \( y_i \).
2. Sample noise \( z_i \) and random labels \( y_i \).
3. Update Discriminator on real \( (x_i,y_i) \) vs. fake \( (G(z_i,y_i),y_i) \).
4. Update Generator to fool \( D\bigl(G(z_i,y_i),y_i\bigr) \) into thinking those fakes are real.


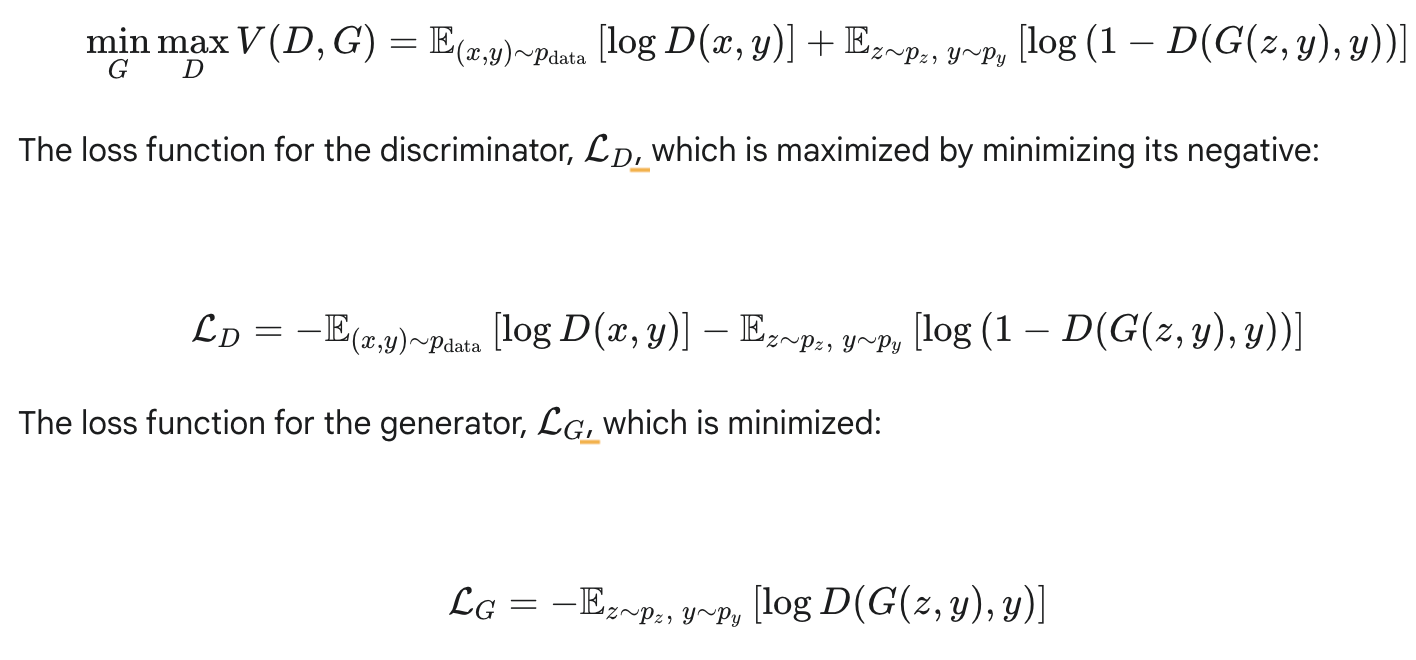
Lectures 13,14 : AutoEncoders, VAEs, CVAEs, GANs, CGANs
By Naresh Kumar Devulapally
Lectures 13,14 : AutoEncoders, VAEs, CVAEs, GANs, CGANs
- 281



