
CVIP 2.0

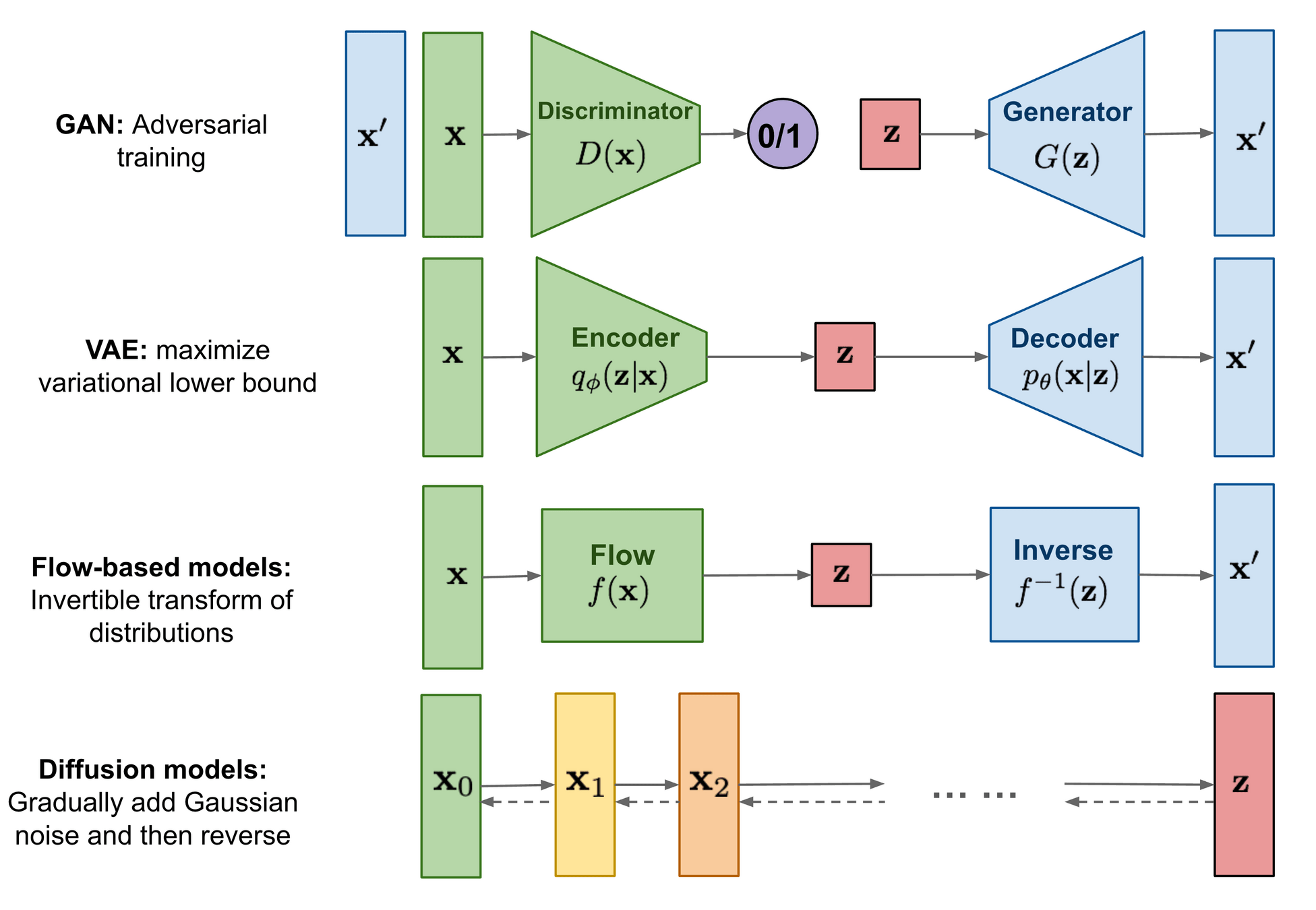
- Recap of the Generative AI model architectures.
- The bigger picture in all generative models.
- The bottleneck in Variational AutoEncoders.
- Diffusion Models (Recent Models).
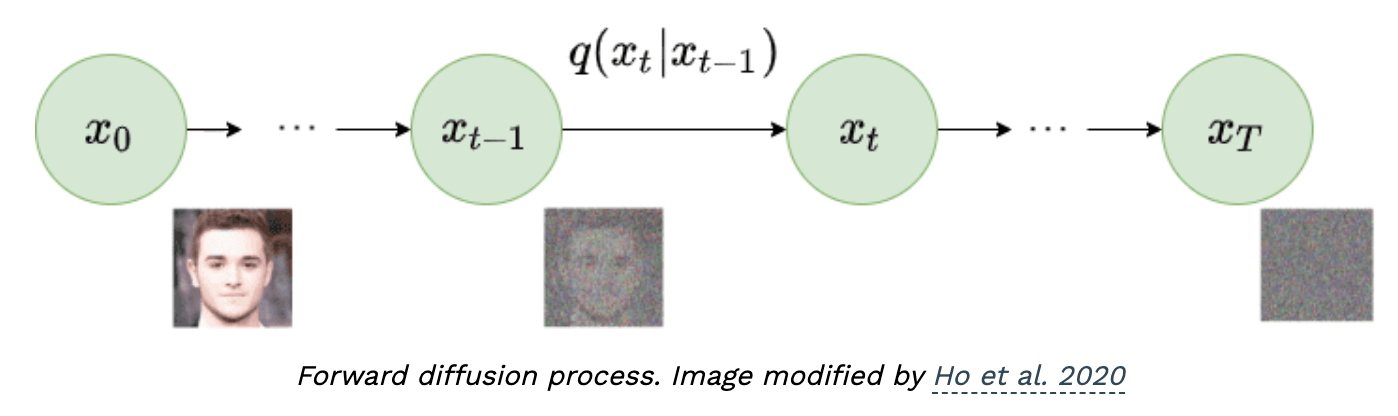
- Forward Diffusion Process
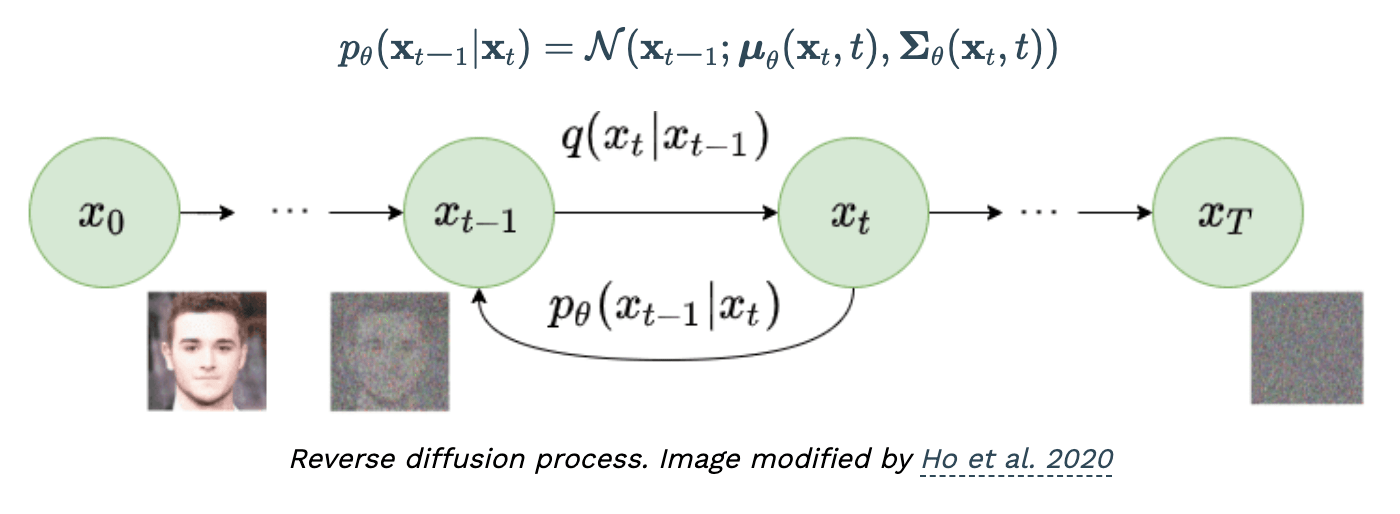
- Reverse Diffusion Process
- Training Architecture
- Coding Example
\( \text{Agenda of this Lecture:}\)

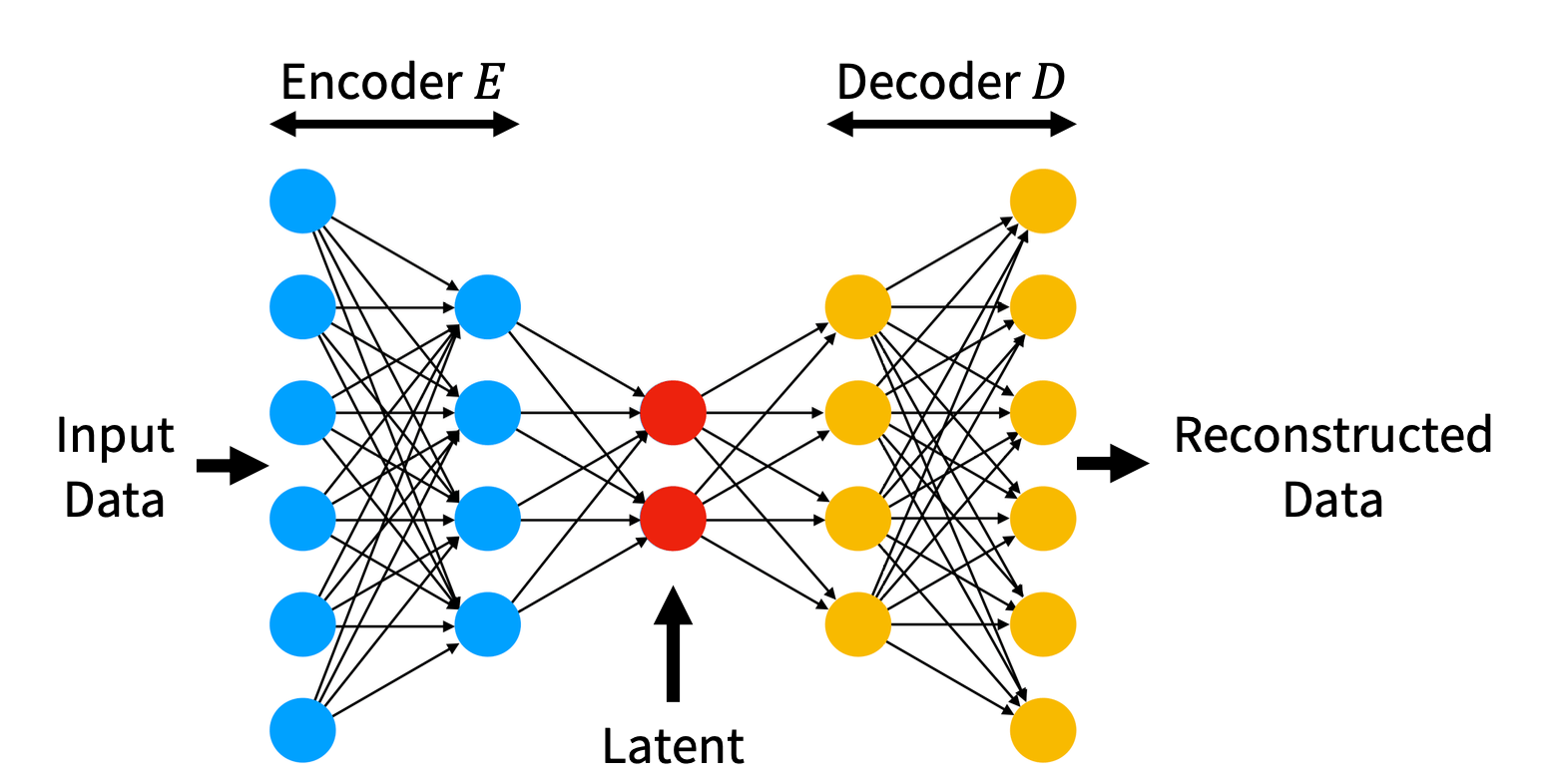
Posterior
Generative Model


Posterior
Generative Model
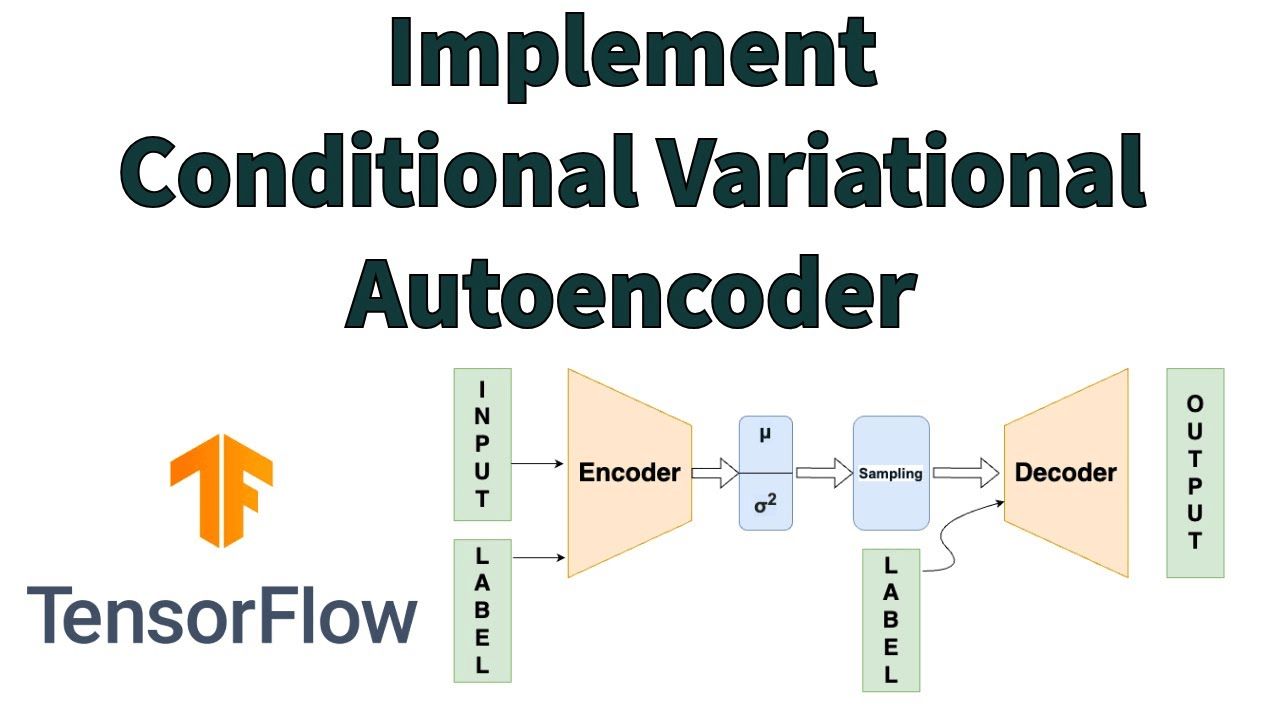


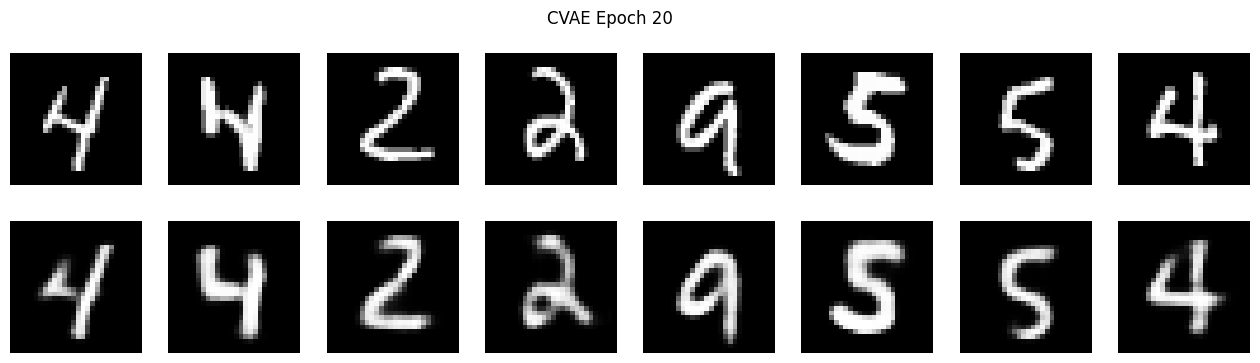


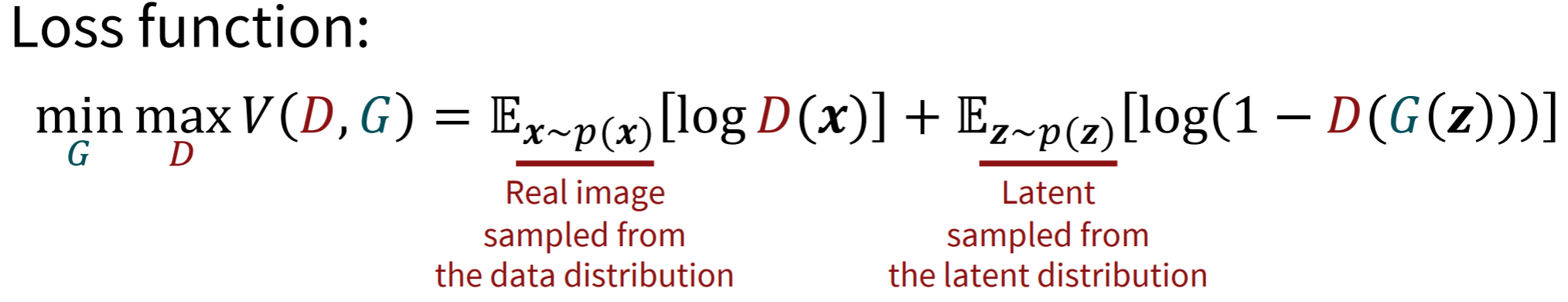


Data reconstruction using VAEs

- Forward Process
- Reverse Process
Diffusion Models







CVIP 2.0

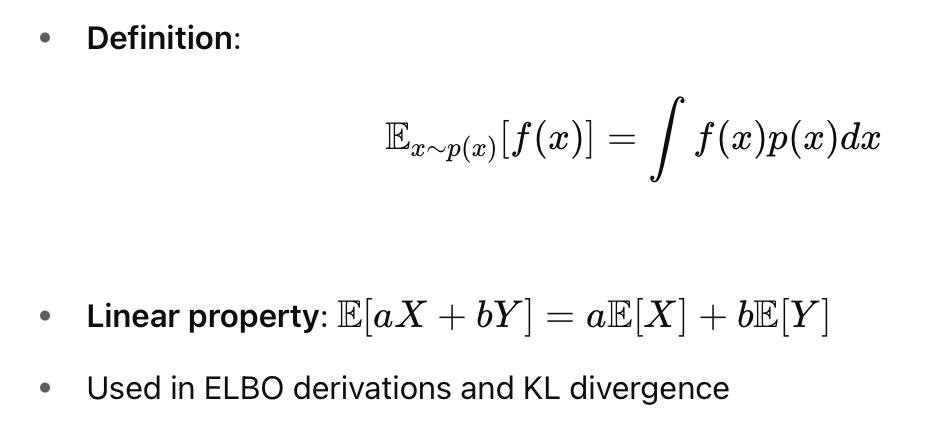
Expectation

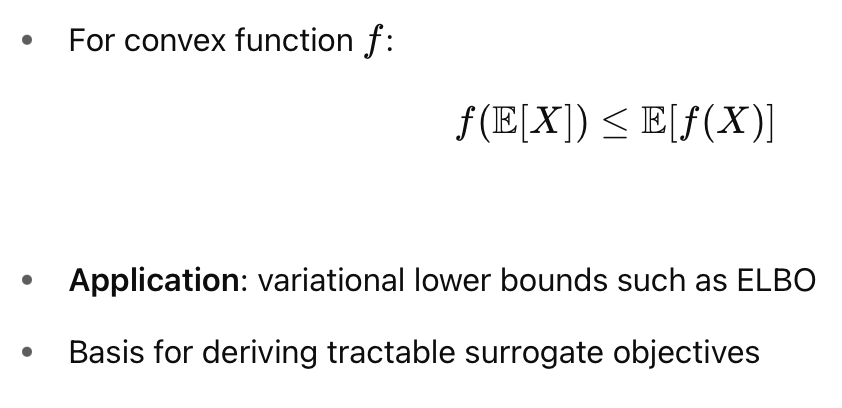
Jensen's Inequality

KL Divergence
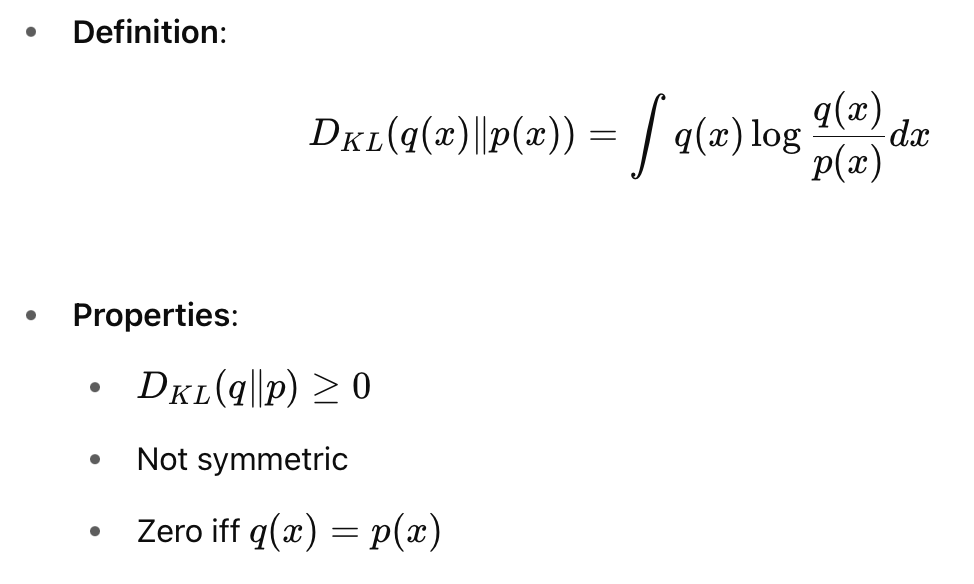

VAE Loss


Notation
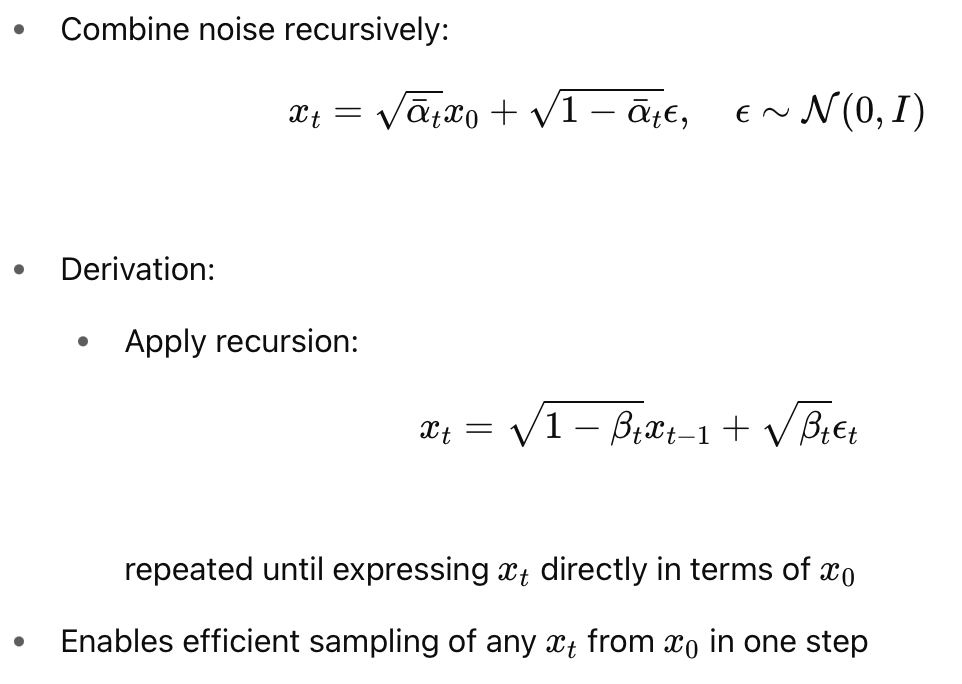
- \( x_0 \) : Original data sample (image, audio, etc.)
- \( x_t \): Noised version of \( x_0 \) at timestep \( t \)
- \( x_T \): Final noise, ideally standard Gaussian
- \( \beta_t \): Variance schedule, determines noise magnitude at step \( t \)
- \( \alpha_t = 1 - \beta_t,\quad \bar{\alpha}_t = \prod_{s=1}^t \alpha_s \)
- Noise is added as:




What does \( \beta_t \) do?


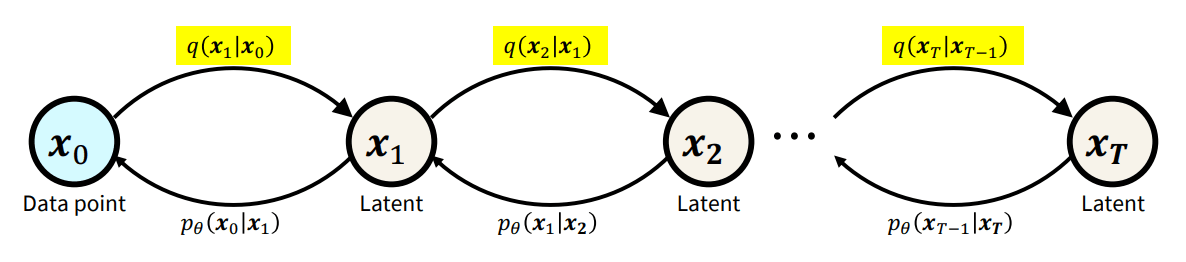
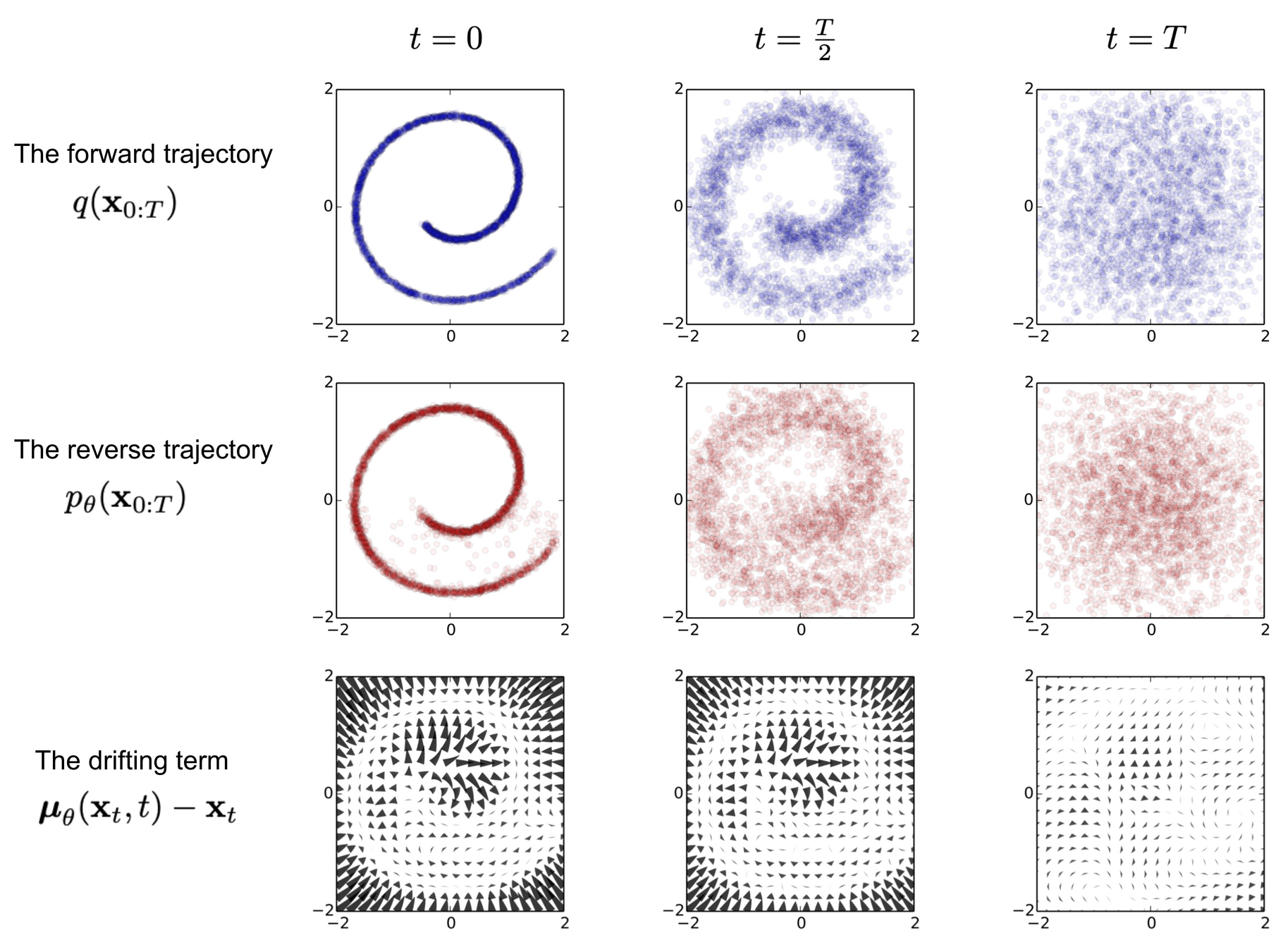
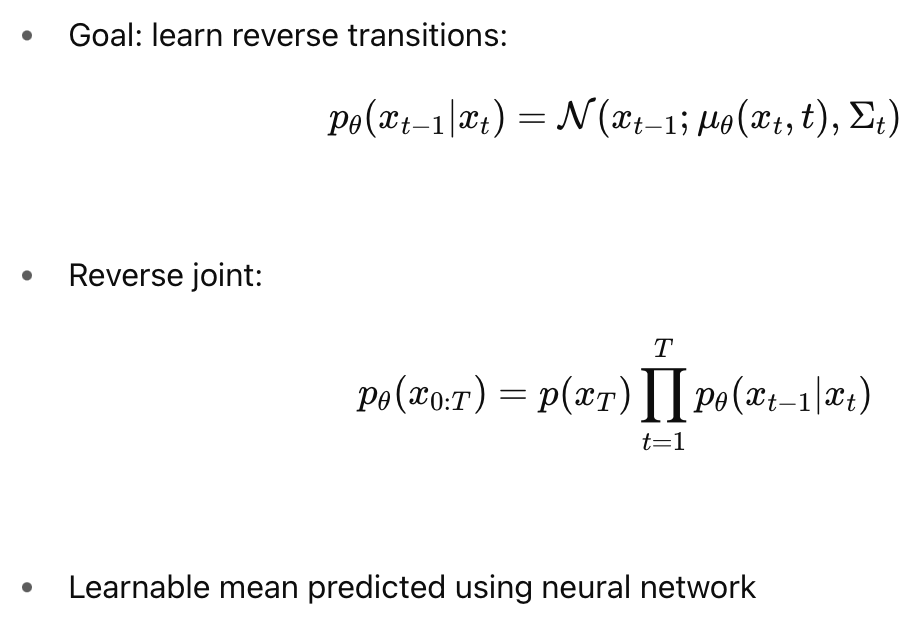
Forward and Reverse Processes


Forward Process
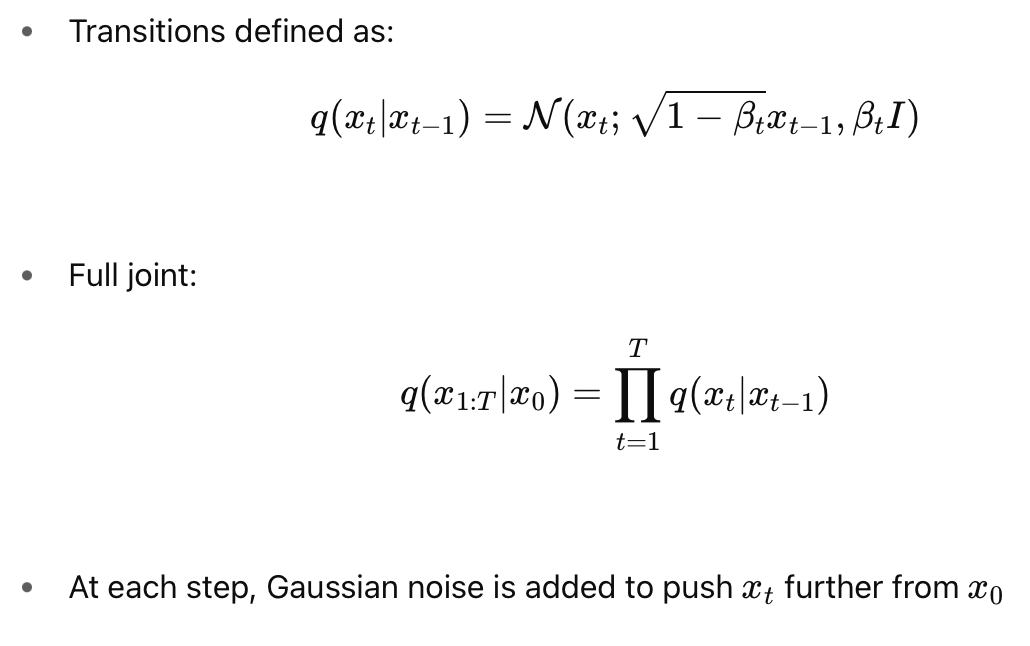

Forward Process

Reverse Process

Diffusion Loss
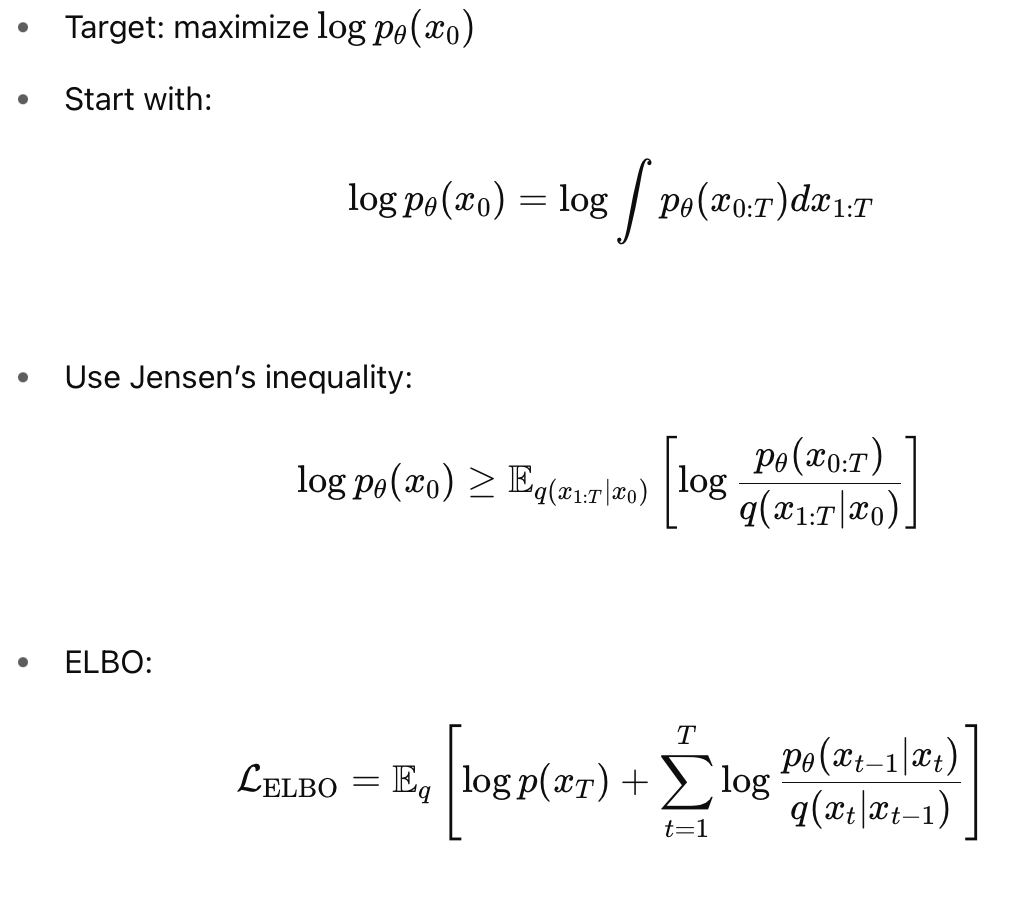

Diffusion Loss
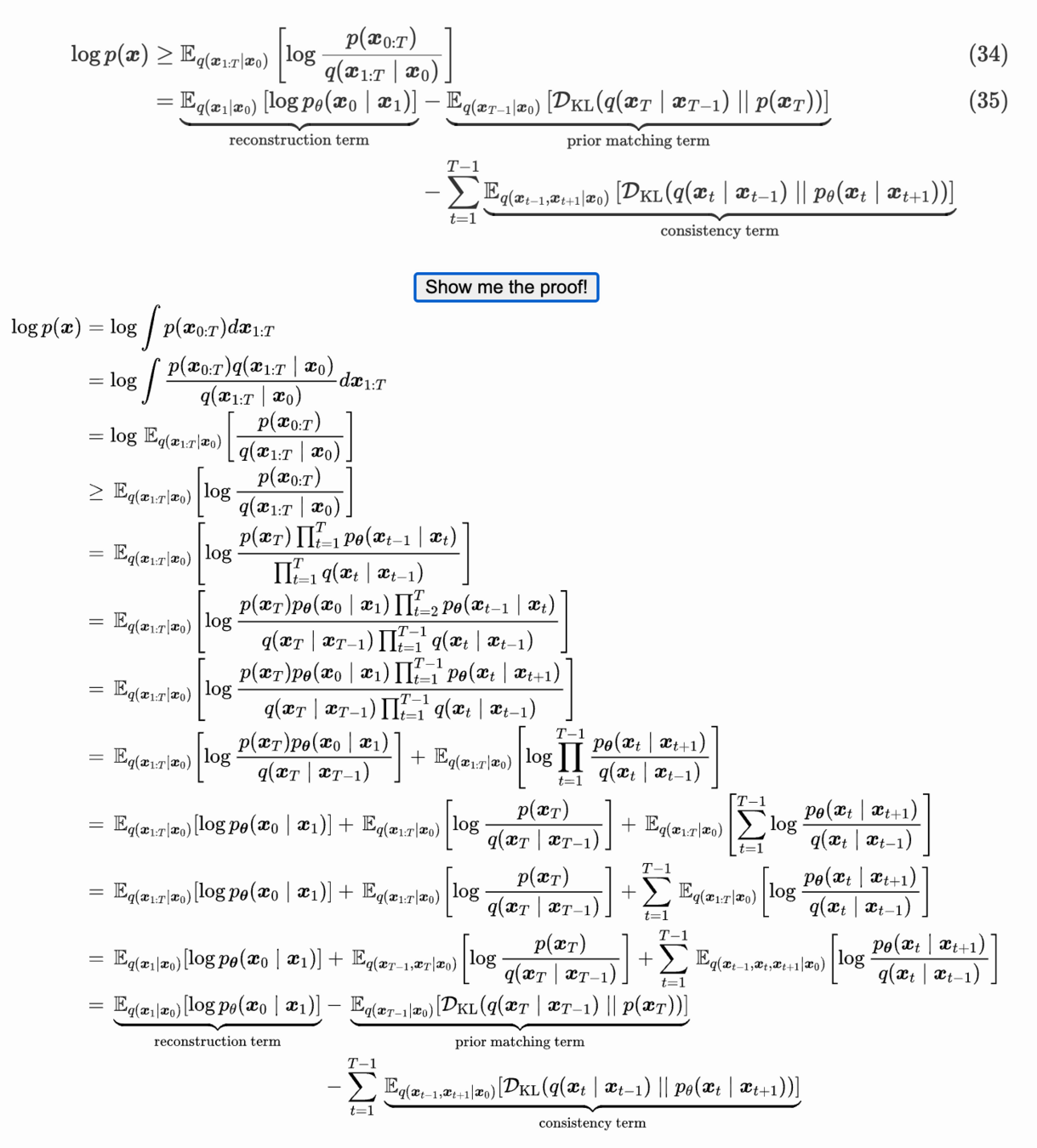
Calvin Luo's
Diffusion Tutorial

Diffusion Loss
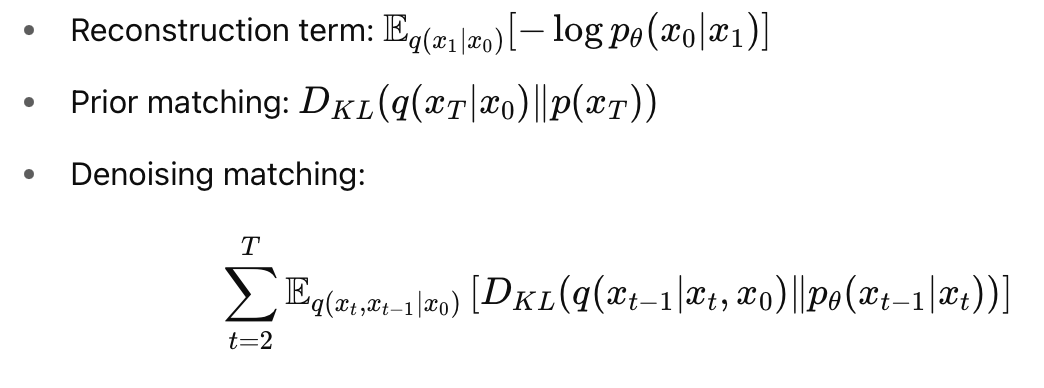

Diffusion Loss
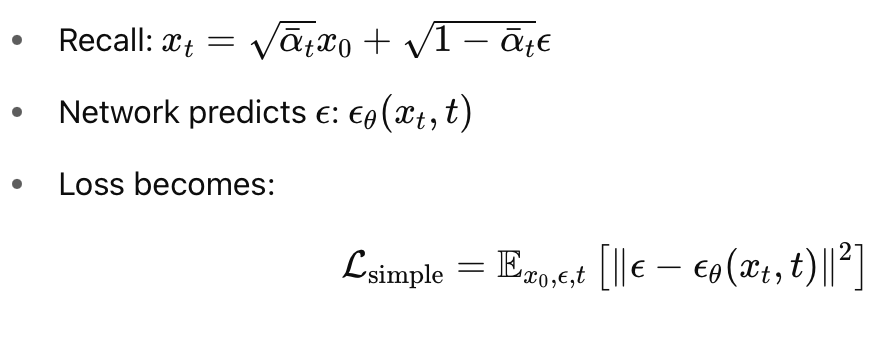

Reverse Process Update
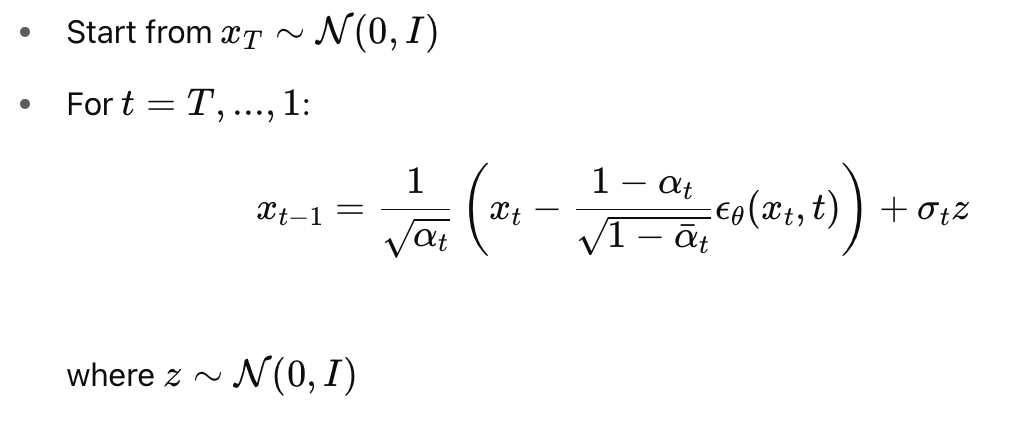

Summary


References


CVIP 2.0

- Recap of the VAE Architecture
- Recap of the Pixel Level Diffusion Model
- Conditional Diffusion Model
- Classifier Guidance v/s Classifier Free Guidance
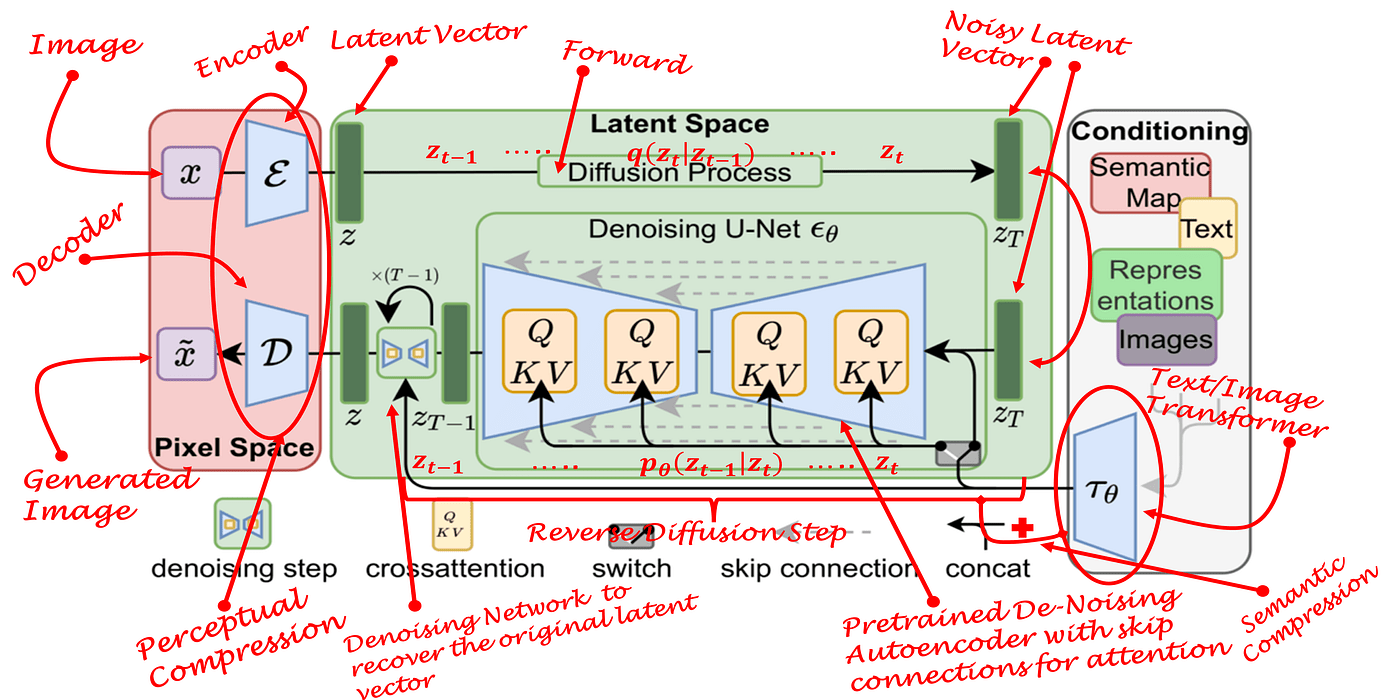
- Why Latent Diffusion Models?
- Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) explained
- Cross Attention in LDMs.
- Diffusion Models for various Computer Vision tasks.
- Tips to complete capstone project milestone 2.
- Information about Guest Talk on July 31 2025.
\( \text{Agenda of this Lecture:}\)



Gaussian Variable
Gaussian Variable
\( \mathcal{L}_{\text{VAE}} = \text{Reconstruction} + \text{Prior Matching} \)
\( \mathcal{L}_{\text{Diff}} = \text{Reconstruction} + \text{Prior Matching} + \text{Noise Matching} \)



Gaussian Variable
Gaussian Variable
\( \mathcal{L}_{\text{VAE}} = \text{Reconstruction} + \text{Prior Matching} \)
\( \mathcal{L}_{\text{Diffusion-Training}} = \text{Noise Matching} \)







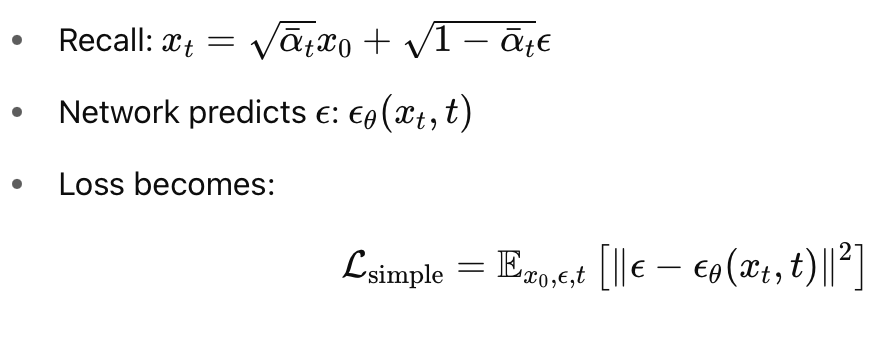
Unconditional Image Generation

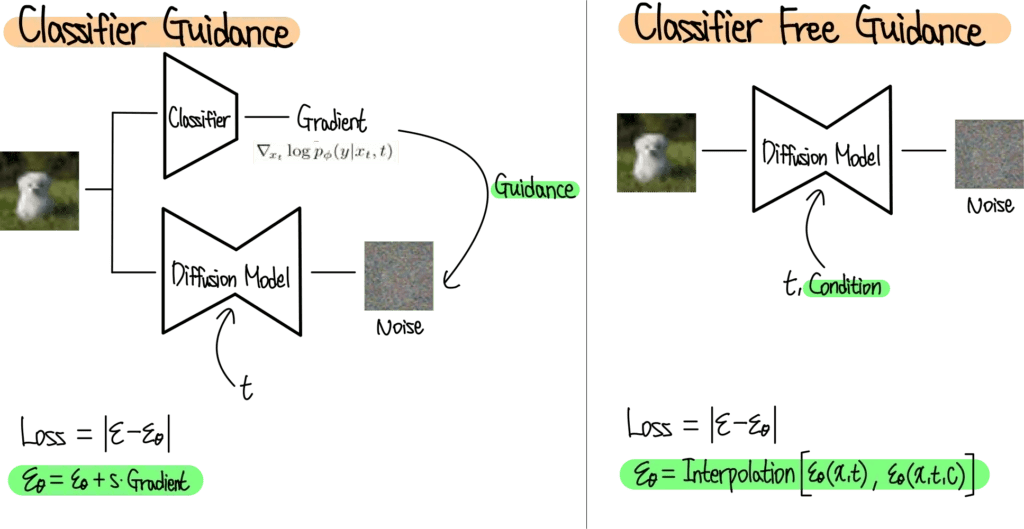
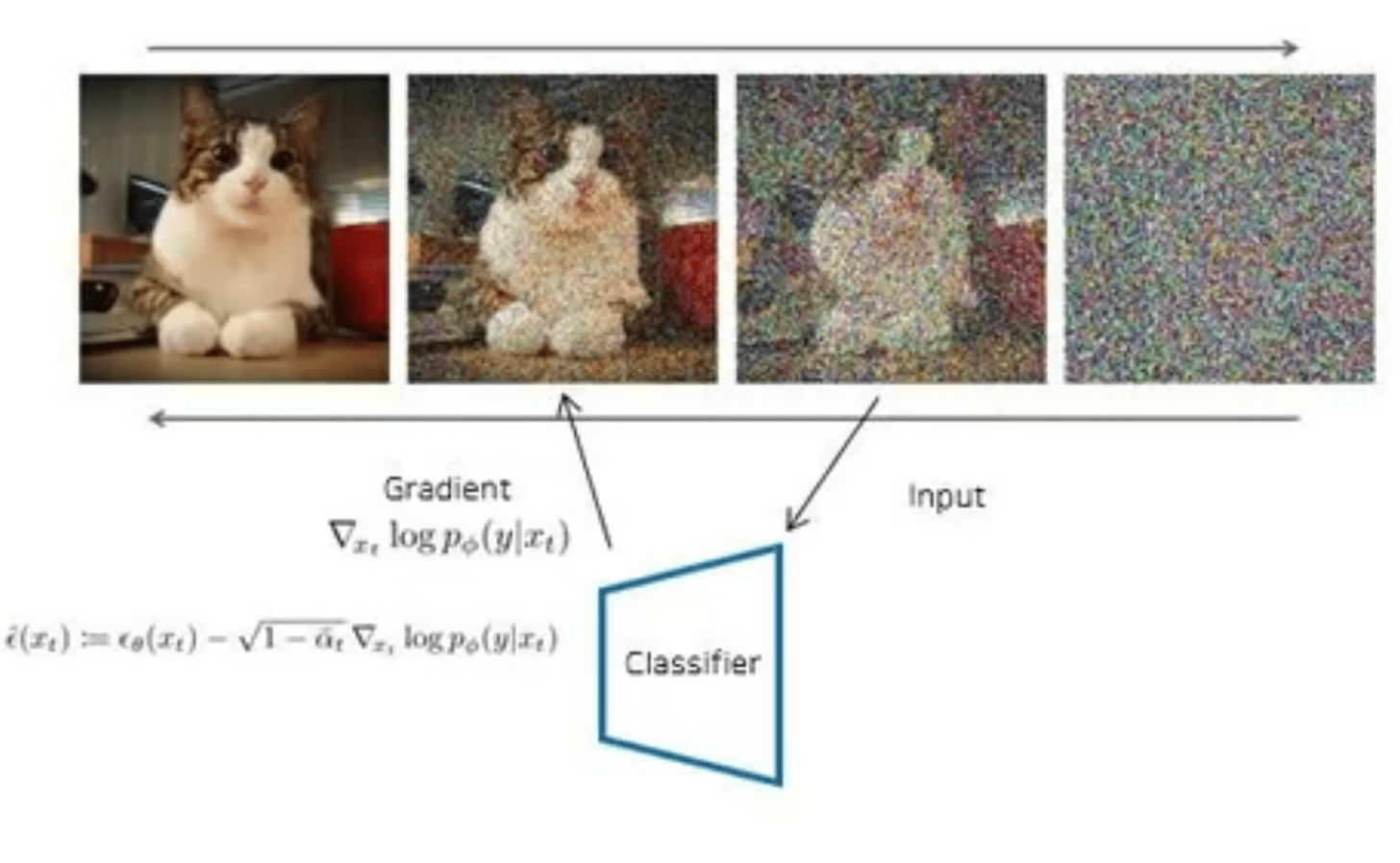
Classifier Guidance

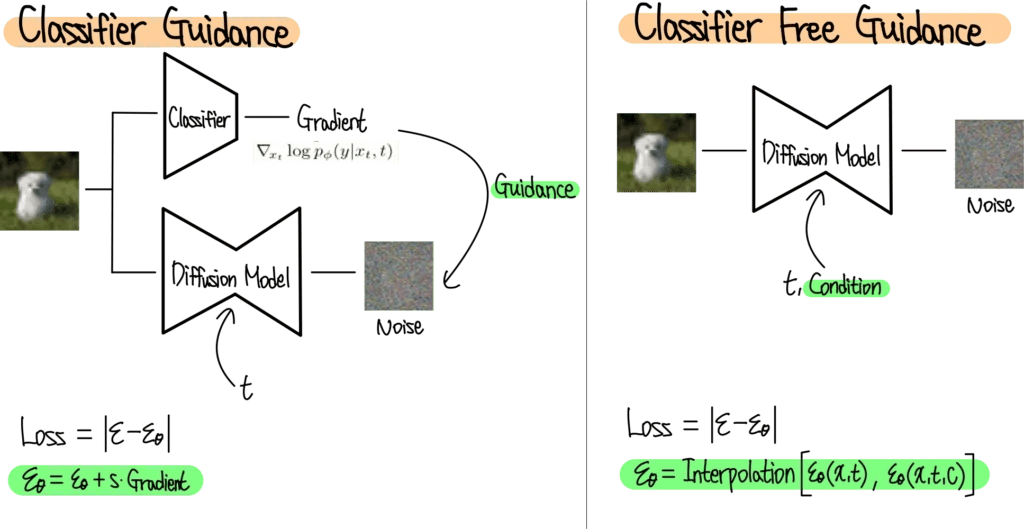
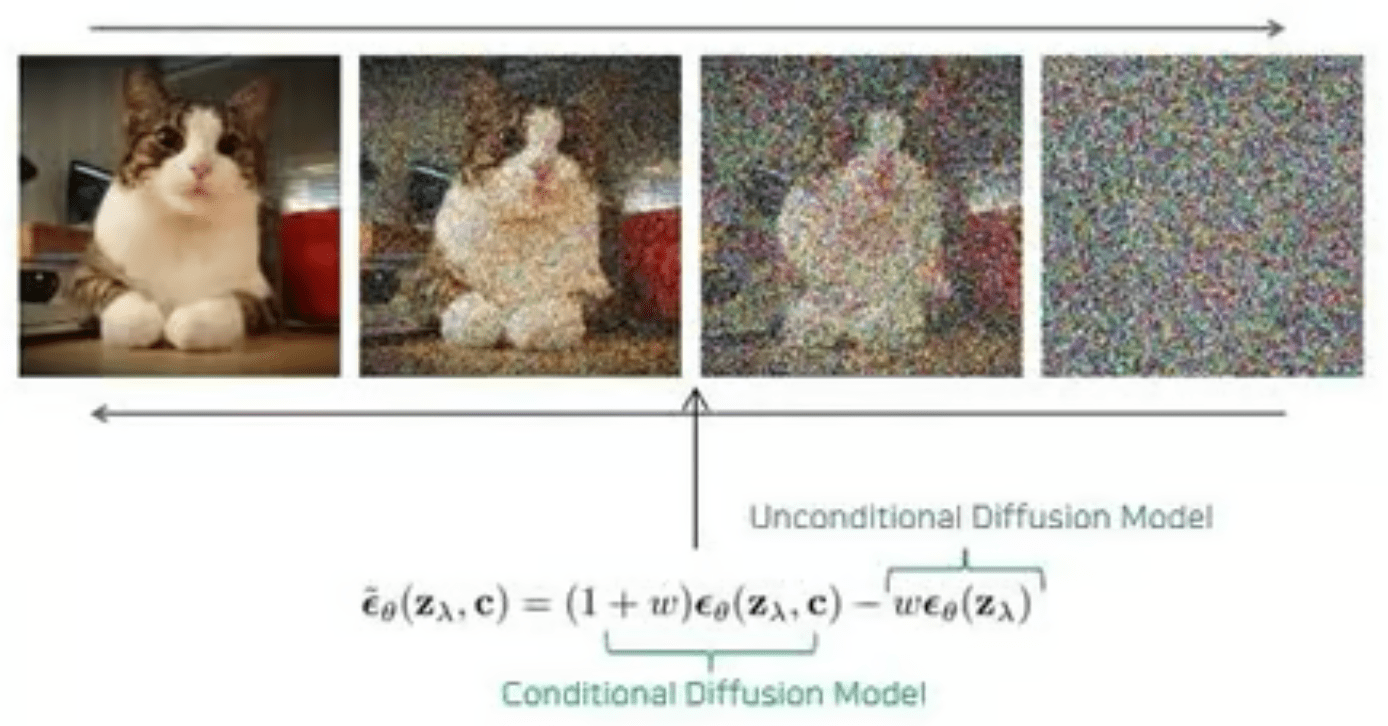

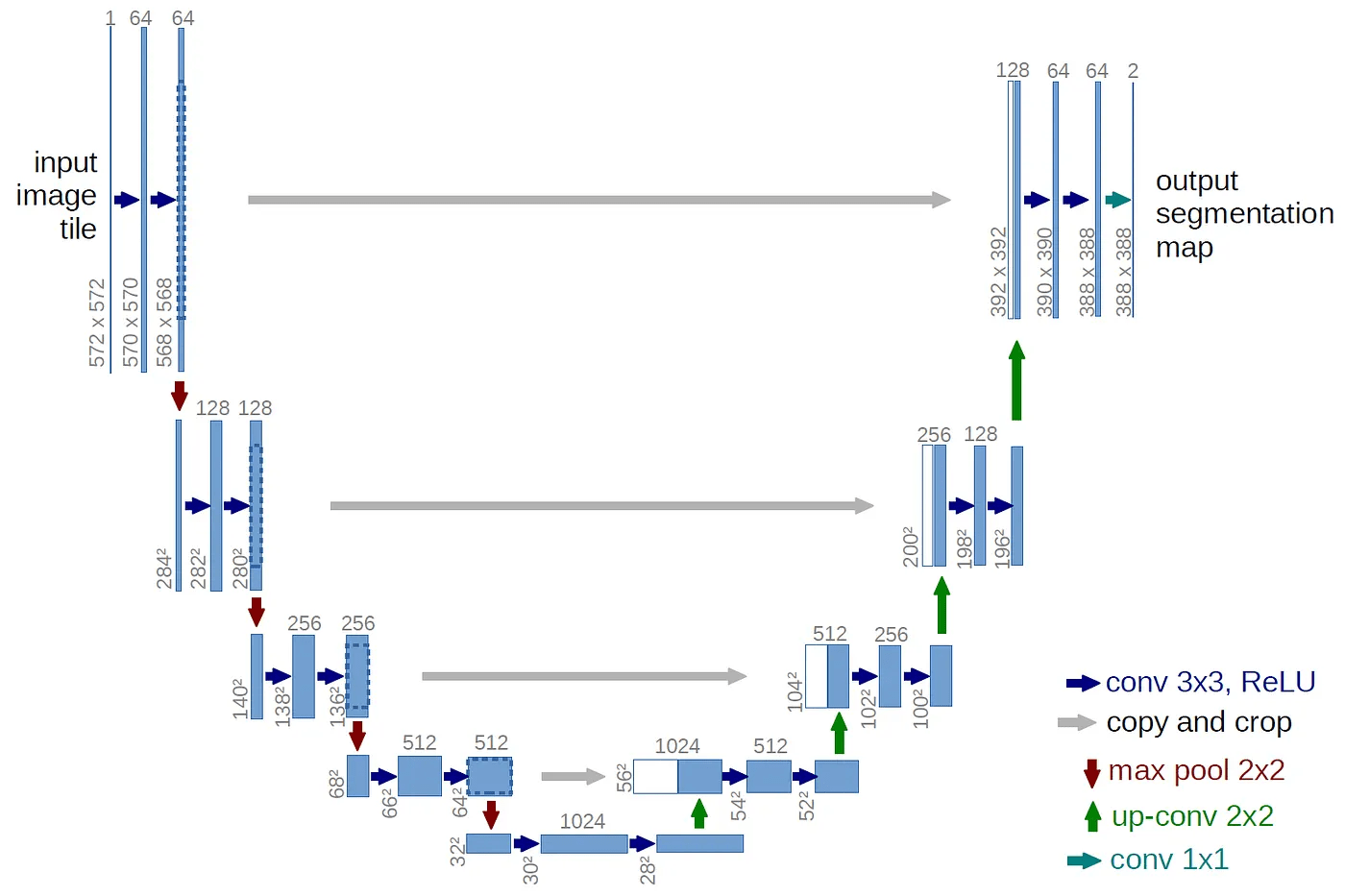
UNet

UNet

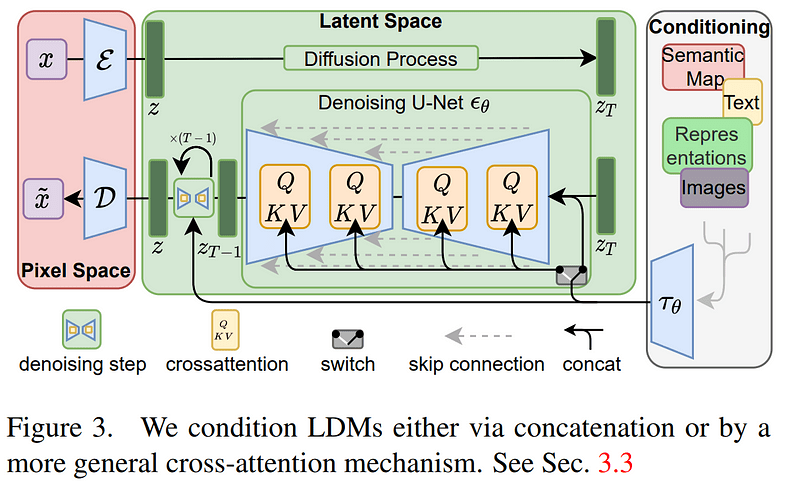


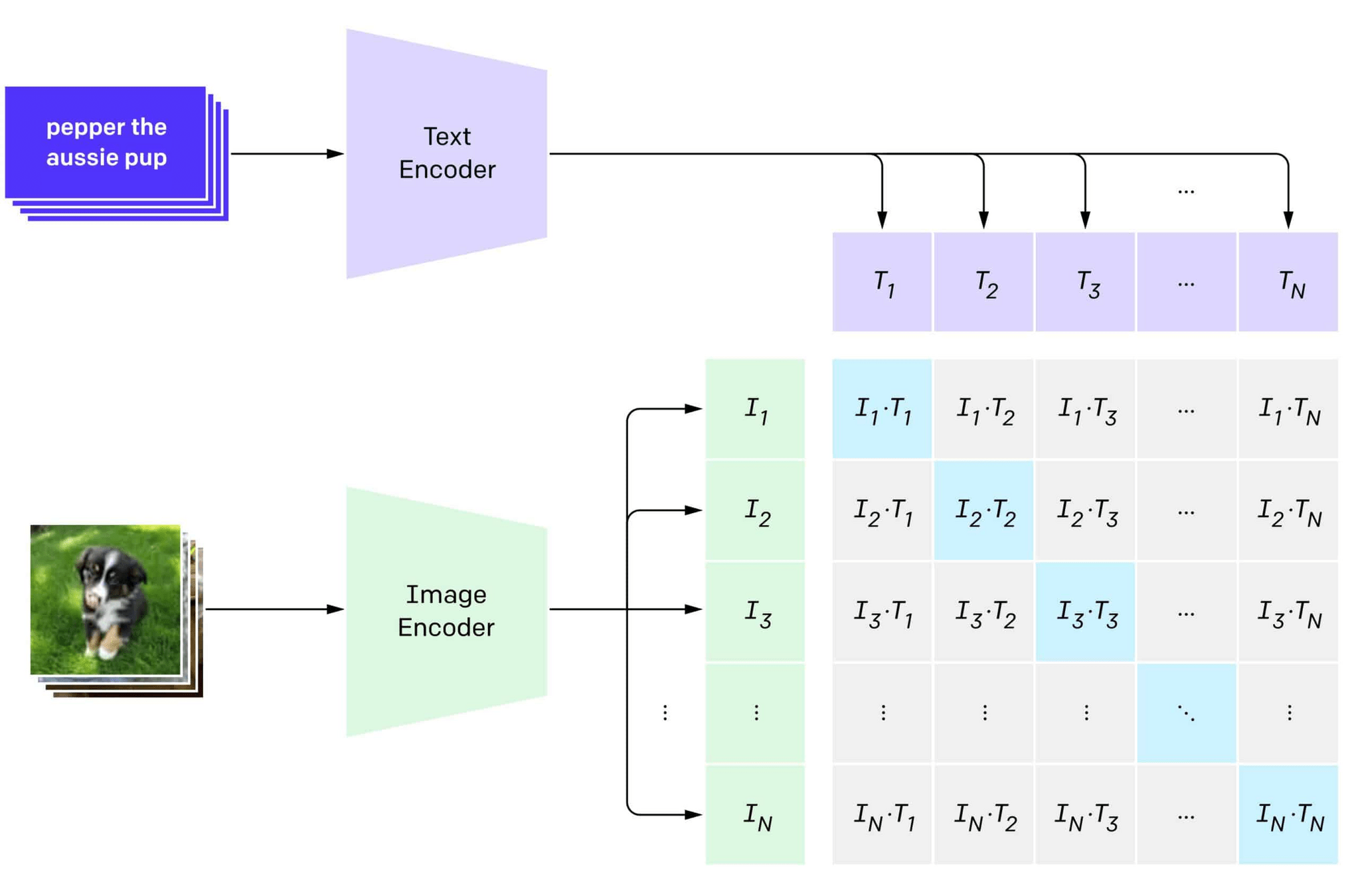




Cross Attention Maps

Cross Attention Maps for Editing
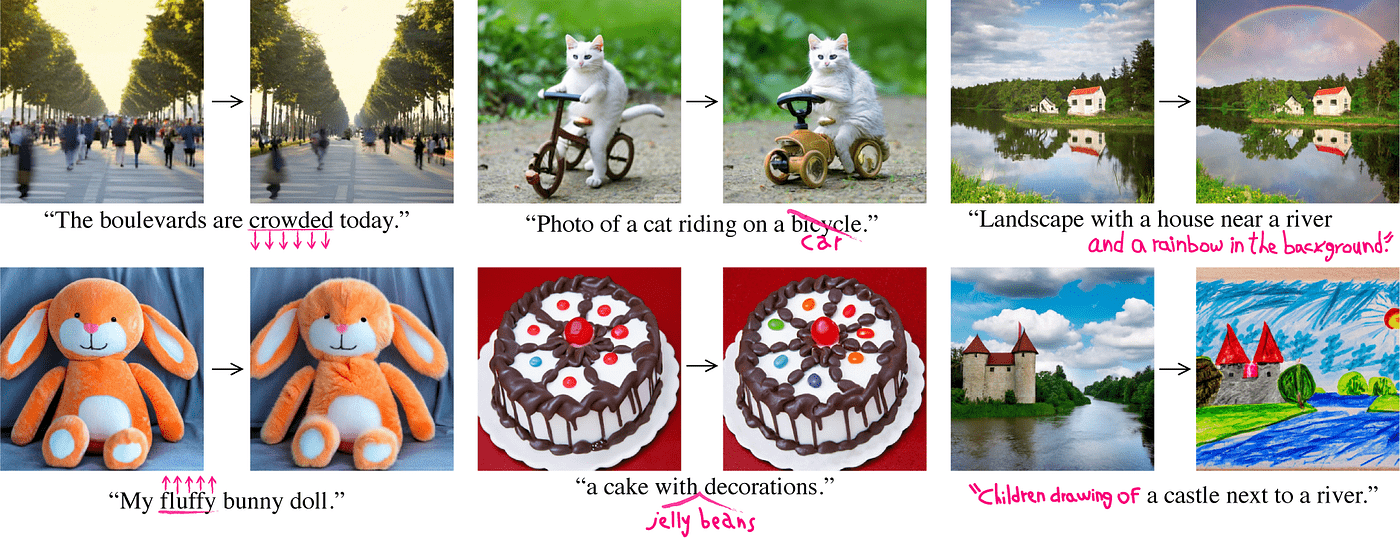
Lectures 15,16,17: Diffusion Models
By Naresh Kumar Devulapally
Lectures 15,16,17: Diffusion Models
- 331



