intro to java
what is java?
- A programming language
- A Virtual Machine
- A technology that powers devices, computer programs, and internet applications.
java: a brief history
- Released in 1995
- Targeted embedded systems & web
- Original JDK had 8 packages, over 300 in JDK 7
- Designed for portability, garbage collection, simpilicity
- Video History
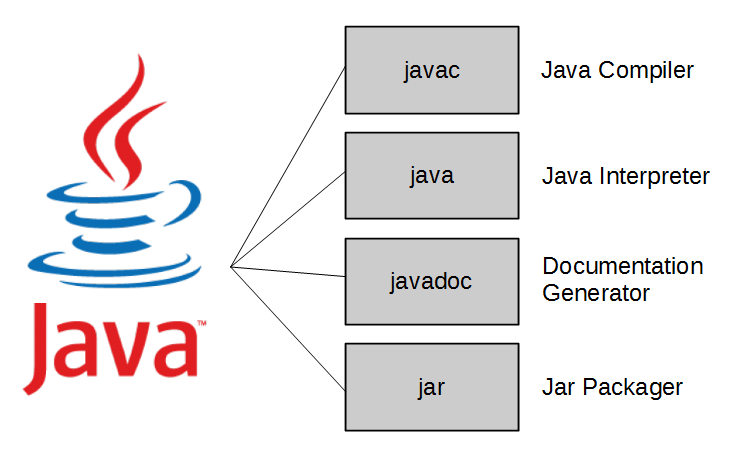
java development kit tools
install java
let's make our first program
Zombie.java:
public class Zombie {
public static void main (String [] args) {
System.out.println("Brains!");
}
}-
Name of class & file must be the same.
- Names are case-sensitive in Java.
- One Public class per file.
- The "public main" method is automatically executed
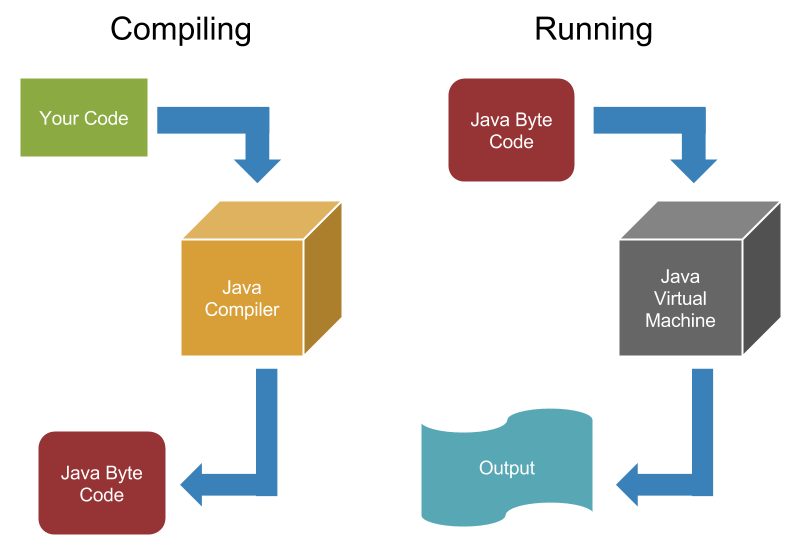
compilation & running
- Open a command line and navigate to the folder where you created Zombie.java.
> javac Zombie.java- This creates Zombie.class, a Java byte code file.
> java Zombie- This runs your Zombie programming
what's happening?
jaring & running a jar
> jar cvf Zombies.jar Zombie.class- This creates a Zombies.jar file
- Jaring is very convenient to distribute & reuse your code
> java -cp Zombies.jar Zombie- This runs the Zombie class in the Zombies jar
key parts of a java program
variables
- Java variables are strongly typed
- Variables are declared using a name
- Variable names start with a letter
- Variable names cannot be reserved keywords
- Variable names are case sensitive
- Java convention is to use camel-cased variable names
- ie. myClass or myVariable
- Variables can represent primitives or references to an actual value (ie. an Object)
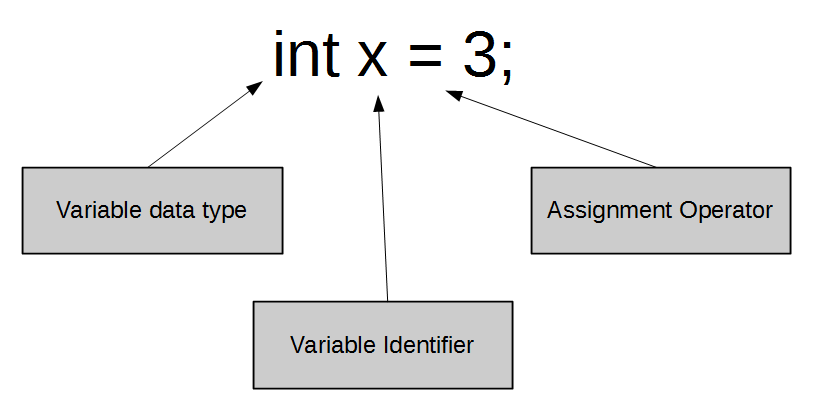
variable declaration
java primitive types
- boolean
- char
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- float
- double
Object declarations
- Same as primitive variable declarations.
- Can use Custom Objects or Library Objects.
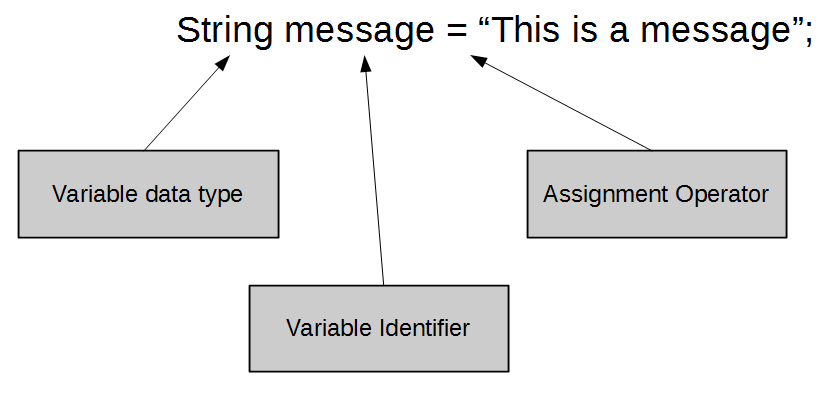
what you can do with variables?
- Assign to them
- Assign from them
- Pass them into methods
- Use them inside of methods
Zombie variable
Zombie.java:
public class Zombie {
public static void main (String [] args) {
String zombieMsg = "Brains!";
System.out.println(zombieMsg);
}
}anatomy of a method
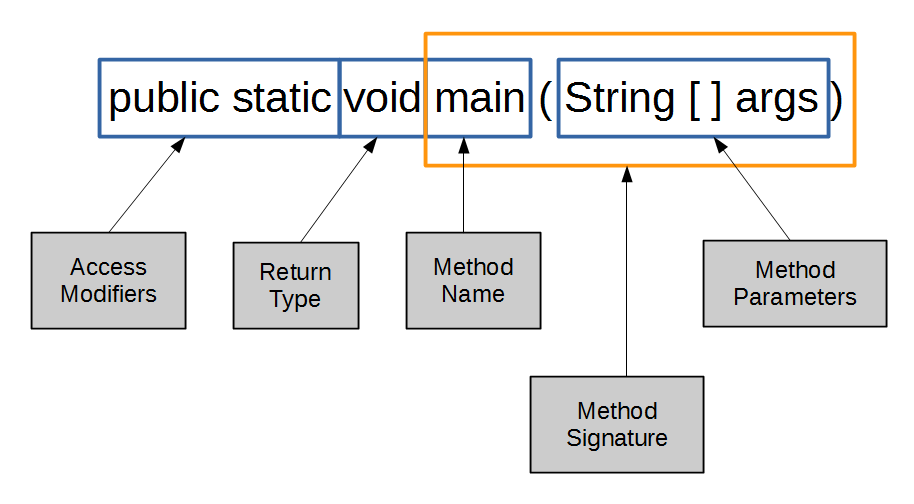
use the main method parameter
Zombie.java:
public class Zombie {
public static void main (String [] args) {
String zombieMsg = args[0];
System.out.println(zombieMsg);
}
}make your zombie sing!
- Compile it
> javac Zombie.java- Run it
> java Zombie "I want brains!"add no argument handler
Zombie.java:
public class Zombie {
public static void main (String [] args) {
if(args.length > 0) {
String zombieMsg = args[0];
System.out.println(zombieMsg);
} else {
System.out.println("Enter a zombie message");
}
}
}JF Lecture 01: Intro to Java
By Ryan Lewis
JF Lecture 01: Intro to Java
- 686



