collections
& Maps
class overview
- Homework Review
- Collection
- List
- Set
- Map
- Homework Overview
collection & map
-
Collection represent a collection of objects.
- Lists are ordered collection of objects.
- Sets are un-ordered collection of unique objects.
- Map contains associations between a key object and value object.
relationship diagram
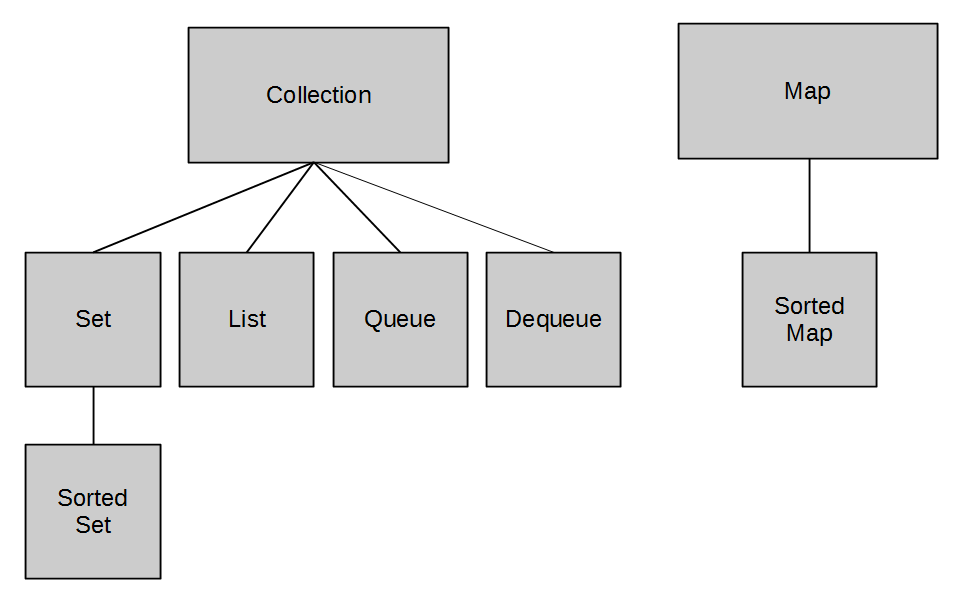
collection interface
- Typical methods on collections are:
- get size of collection
- add, remove, get an object
- Collections can be navigated using iterators
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
void remove(); //optional
}*Maps cannot be navigated with iterators
**Collection is the interface. Collections is a static class.
list interface
- Most commonly used implementations:
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Stack
- Vector
- Unlike arrays, List capacities are dynamic.
- Lists contain only Objects, not primitives.
- Any primitives added will be autoboxed.
foreach loops & Lists
public static void main (String[] args) {
List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
names.add("John");
names.add("Jane");
names.add("Dan");
names.add("Suzie");
for(String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}common list functions
- List elements can be removed using the remove() method
names.remove("John");- List elements can be added using the add() method
names.add("John");- Count of List elements can be determined using size().
int size = names.size();finding objects in collections
- An element can be found in a collection by using:
- contains(Object o) : returns true/false
- indexOf(Object o) : returns the index or -1 if not found
boolean found = names.contains("John");
int index = names.indexOf("John");* Both methods use the equals() method by default to find an Object. Overriding the equals() method can change the way an Object is found.
collections methods
- sort(List<E> list) - sorts a List collection
List<String> names = ArrayList<String>();
...
Collections.sort(names);- copy(List<E> dest, List<E> src) - copies values from one list to another.
List<String> filledList = ArrayList<String>();
List<String> emptyList = ArrayList<String>();
...
Collections.sort(emptyList, filledList);set interface
- Sets are iterable, un-ordered Collections
- Sets do not allow duplicates
public static void main (String [] args) {
Set<String> names = new HashSet<String>();
names.add("John");
names.add("Jane");
System.out.println(names);
}* TreeSet is an ordered implementation of Set
map interface
- Non-iterable Collection that contains key-value pairs.
- Keys cannot have duplicates.
- Common implementations:
- HashMap
- TreeMap
public static void main(String [] args) {
Map<String, String> myMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
myMap.put("John", "Seattle");
myMap.put("Dan", "Nashville");
}JF Lecture 09: Collections & Maps
By Ryan Lewis
JF Lecture 09: Collections & Maps
- 624



