classes
part 2
class overview
- Homework Solution
- Inheritance
- Super
- Packages
- Import
- Polymorphism
- Overloading Methods
inheritance
- "is-a" relationship
- A sub-class (child) inherits properties and behaviors from a super-class (parent)
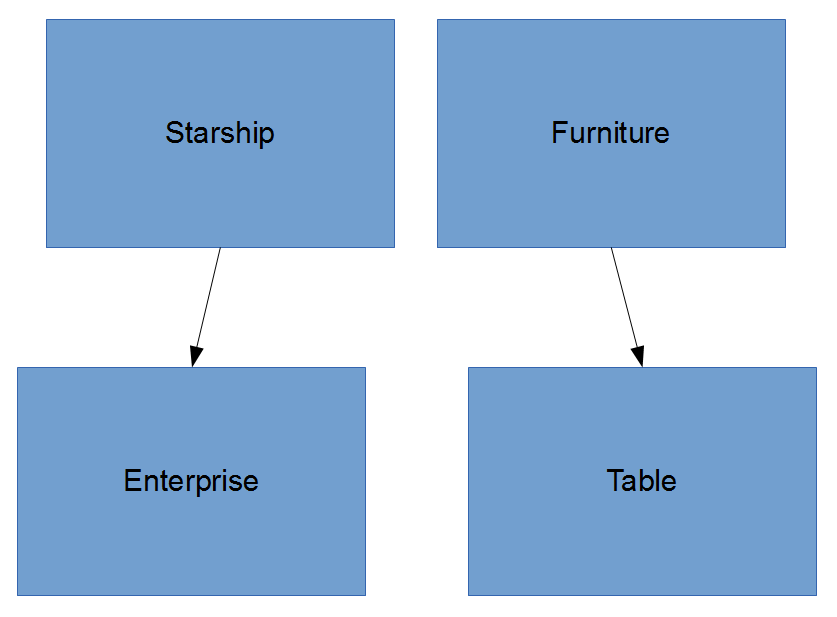
inheritance
- Properties & Methods that are common to child Classes should go in the parent Class
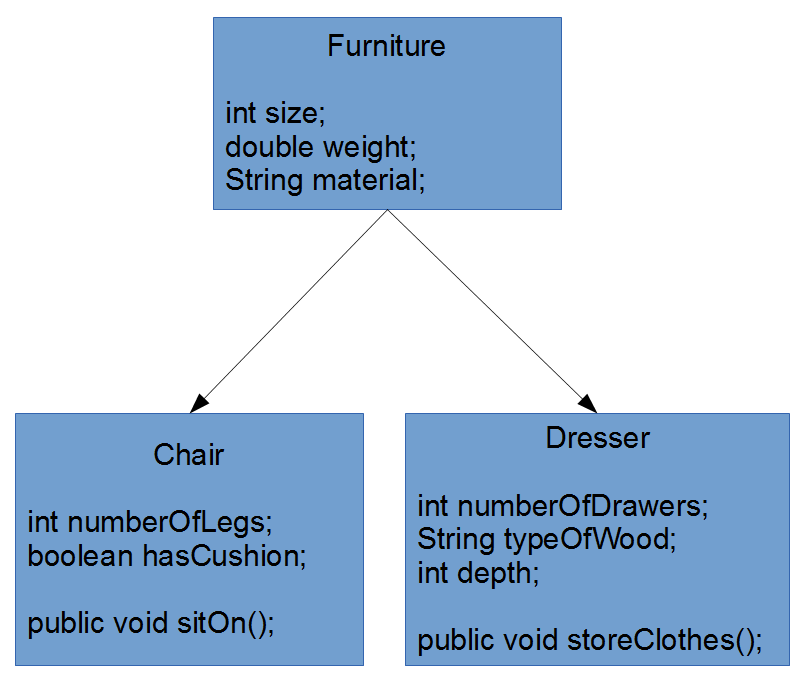
inheritance syntax
public class Starship {
private int warpSpeed;
private int distanceTraveled;
private int numberOfCrewMembers;
public boolean travelTo(int xCoord, int yCoord, int zCoord);
}
public class Enterprise extends Starship {
private int episodesAppearedIn;
public void fireTorpedos(Starship target);
public void teleport(String crewMember);
}
Enterprise enterprise = new Enterprise();
enterprise.travelTo(0, 13, 26);object inheritance
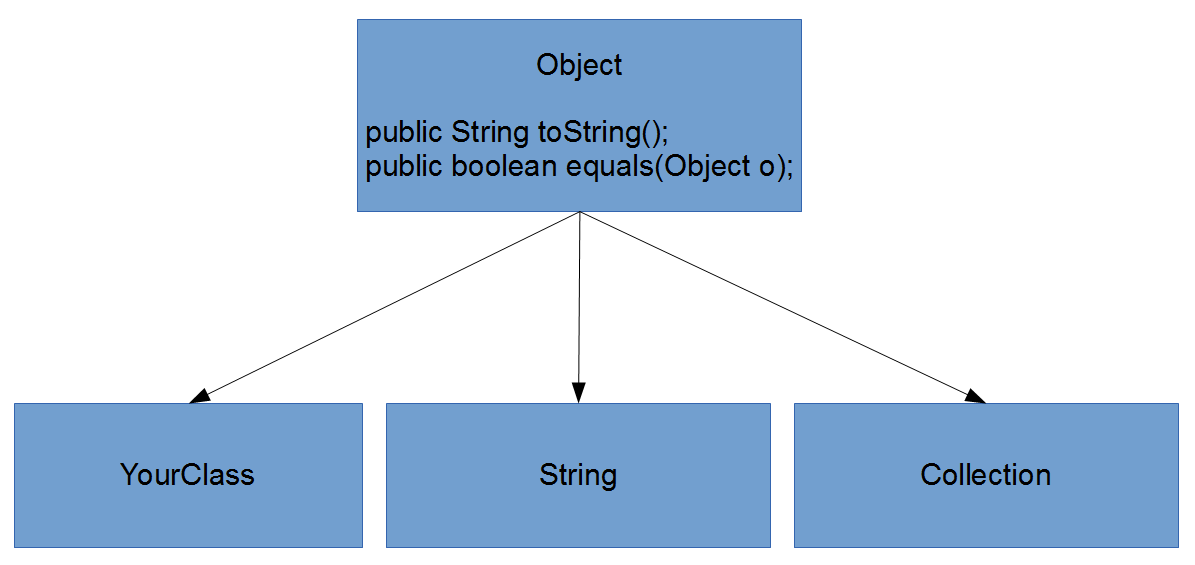
- Every Class inherits from another Class
- Every Class has Object as a super-class
- Object provides methods like toString() & equals()
- Object is inherited by default, even if not explicit
super
- The "super" keyword references a Class's parent Class.
- Used to call a parent Class's constructor, access a parent Class's properties, or call a parent Class's methods.
- Calling the super constructor must be the first line of a Constructor.
public class Enterprise extends Starship {
//Enterprise constructor
public Enterprise(int crewlimit) {
super(crewlimit);
}
public String printDetails() {
super.printStarship();
}
}packages
- Used to organize and uniquely name Classes
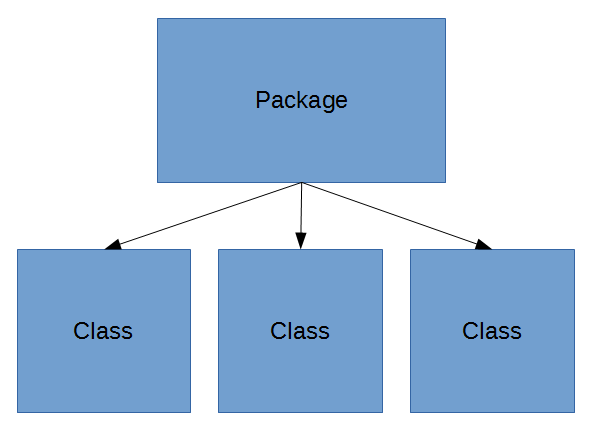
adding a class to a package
- The directory structure where a .java file exists, decides it's Package.
- Eclipse will automatically move files for you once you've added the package declaration to the top of a Java file.
package com.foundations.furniture;
public class Chair {}import
- To use Classes from a different Package, import them at the top of your .java file.
- You can import an individual Class or a Package as a whole.
import Java.lang.Math;
import Java.io;polymorphism
public abstract class Animal { public abstract String speak(); } public class Dog extends Animal { public String speak() { return "ruff"; } } public class Cat extends Animal { public String speak() { return "meow"; } } Animal dog = new Dog(); Animal cat = new Cat();dog.speak(); cat.speak();
overloading methods
- Method overloading occurs when a method is declared with the same identifier as an existing method, but has a different set of arguments.
- Methods cannot have the same identifier and the same arguments.
- Different return types alone will not overload a method.
public static void aMethod(int x) {}
public static void aMethod(String word) {}
public static void aMethod(int num1, int num2) {}JF Lecture 06: Classes Part 2
By Ryan Lewis
JF Lecture 06: Classes Part 2
- 630



