numbers
& enums
class overview
- Homework Solution
- Number Classes
- Autoboxing & Unboxing
- Enums
- When to use Enums
number classes
- Primitive types don't have methods, other than operators, available to them.
- JDK provides corresponding classes to each primitive type
- int -> Integer
- short -> Short
- long -> Long
- float -> Float
- double -> Double
- byte -> Byte
Number Documentation
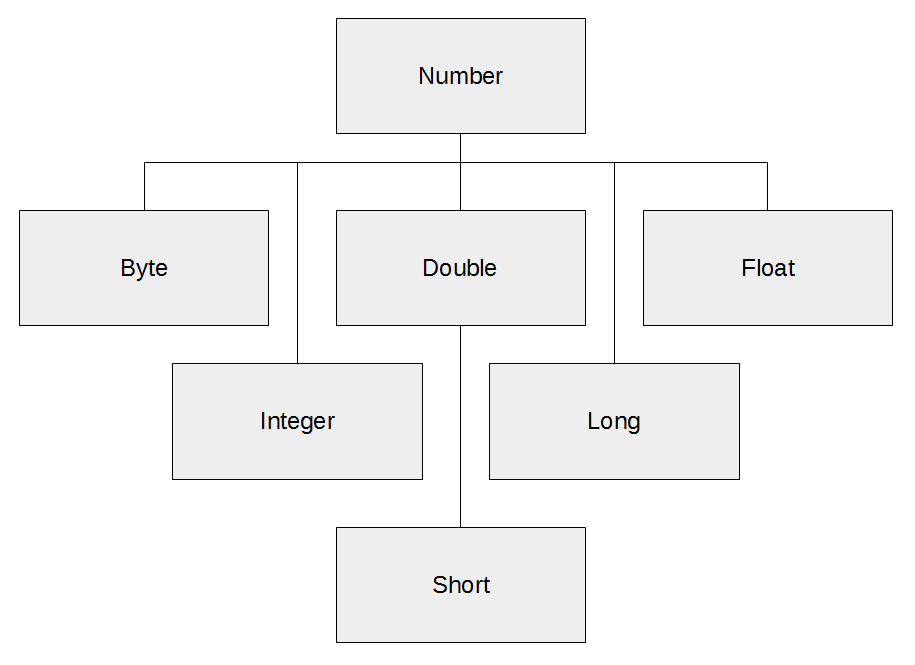
number class hierarchy
auto-boxing & Auto-unboxing
- Auto-boxing is the automagic conversion from a primitive to it's wrapper class.
- Auto-unboxing is the automagic conversion from a wrapper class to it's related primitive.
Integer x = new Integer(5); //Integerint y = 6; //inty = x; //Integer auto-unboxed to intx = 27; //int literal auto-boxed to Integer
enums
-
An enum type is a special data type that enables for a variable to be a set of predefined constants.
- The variable must be set to one of the values that have been predefined for it.
- Enums can also have private constructors (called implicitly when being created) and methods and properties.
- Good examples:
- Cardinal Directions (North, South, East, West)
- Days of the Week (Sun, Mon, Tues, etc.)
enum example
public enum Day {
SUNDAY,
MONDAY,
TUESDAY,
WEDNESDAY,
THURSDAY,
FRIDAY,
SATURDAY
}
Day day1 = Day.MONDAY;
Day day2 = Day.SATURDAY;advance enum example
public enum City {
SEATTLE("Seattle", 47.6097, 122.3331),
SAN_FRANCISCO("San Francisco", 37.7833, 122.4167),
NEW_YORK("New York", 40.7127, 74.0059);
private String cityName;
private double latitude;
private double longitude;
private City(String cityName, double latitude, double longitude) {
this.cityName = cityName;
this.latitude = latitude;
this.longitude = longitude;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.cityName;
}
}when to use enums
- Set group of values that don’t change (think of a drop-down box on a web site)
- Constants that will be used throughout your program
- Good for switches and logic expressions
JF Lecture 08: Numbers & Enums
By Ryan Lewis
JF Lecture 08: Numbers & Enums
- 751



