exception
handling
exceptions
-
Exceptions are Objects thrown when a problem occurs with your program
-
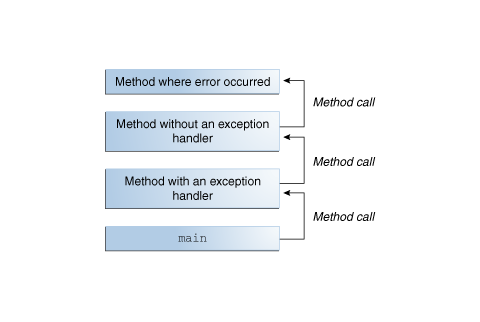
An Exception trace shows where the exception happened
exception hierarchy
- Exceptions can be caught by any of the methods in the call stack.
- If nothing catches the Exception, the program terminates
throwing an exception
public class ExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
handleArgs(args);
}
public static void handleArgs(String[] args) {
if(args.length == 0)
throw new RuntimeException("Must pass an argument to the
function.");
if(args[0].length() <= 1)
throw new RuntimeException("Argument must be at least 2
characters.");
}
}
catching an exception
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
handleArgs(args);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}checked vs unchecked
-
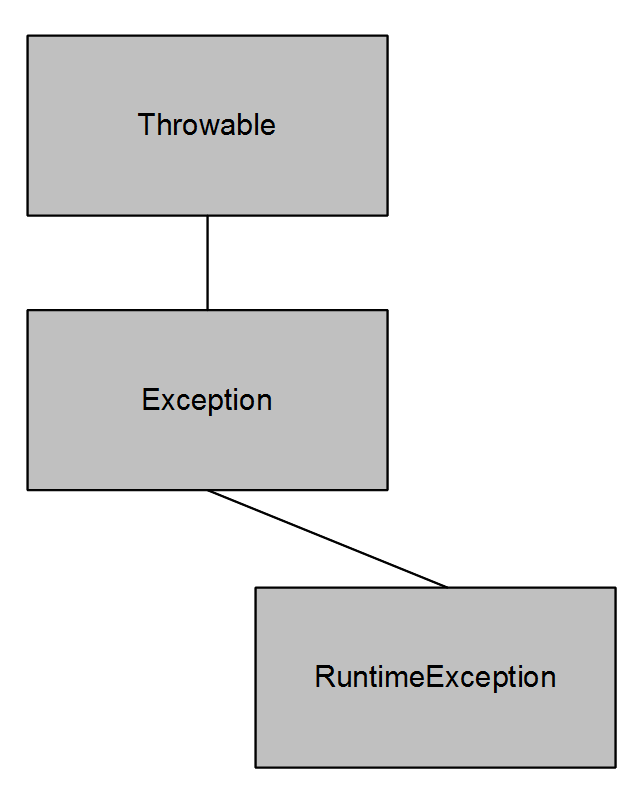
Exception (checked)
- An expected condition that the program will handle
- Derived from java.lang.Exception
- Must be declared up the call-stack, until it is handled
- IOException is a checked exception
- RuntimeException (unchecked)
- Not an expected situation
- Derived from java.lang.RuntimeException
- Does not need to be declared on the methods in the call stack.
- NumberFormatException is a RuntimeException
finally
public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {
try {
handleArgs(args);
} finally {
System.out.println("We handled args");
}
}finally example
public static void fileRead (File file) throws Exception {
Reader in = null;
try {
in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
System.out.println(in.read());
} finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
}
}foundations class overview
- JDK Tools
- Data Types
- Operators
- Variables & Methods
- Strings
- Arrays
- Conditional Statements (if...else)
- Control Flow (break, continue, return)
- Classes -> Objects
- Inheritance
- Aggregation
- Constructors
class overview cont.
- Encapsulation
- Access Modifiers
- Packages
- Polymorphism
- Abstract Classes
- Interfaces
- OO Design
- Number Classes
- Enums
- Generic Classes
- UML
- Javadocs
class overview cont.
-
Collections
- Maps
- Files
- Streams
- Readers/Writers
- Exceptions
JF Lecture 10: Exception Handling
By Ryan Lewis
JF Lecture 10: Exception Handling
- 570



