What a real Startup Deployment Process looks like
"From local code to production"
Tri Tran @ NFQ Asia
May 2018
about me
Tri D. Tran
Senior Technical Architect
tri.tran@nfq.asia
@moprit
NFQ Asia | 8Bit Rockstars
Member of .NFQ Group


I'm happy if you call me 'Mụp'
we WILL discuss about
-
Software deployment process:
A pipeline process
-
Advantages and challenges
-
Tools
- Conclusion & Open Discussion
we WON'T talk about
-
Open-source process
-
Enterprise process
-
DOTA 2, LoL, Counter Strike...
- Drink or party
How did they do in Stone Age?

Source: StoneAgeComics
They did
- SysAdmin will handle manually
- FTP / SFTP / Shell
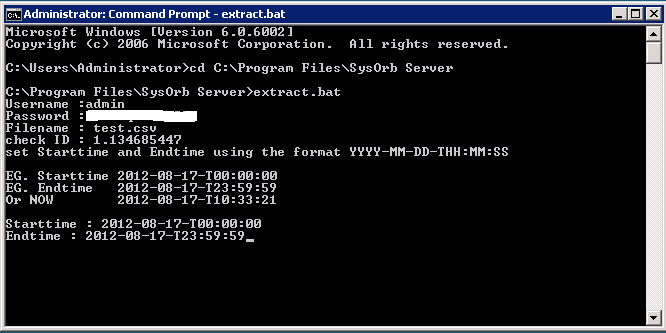
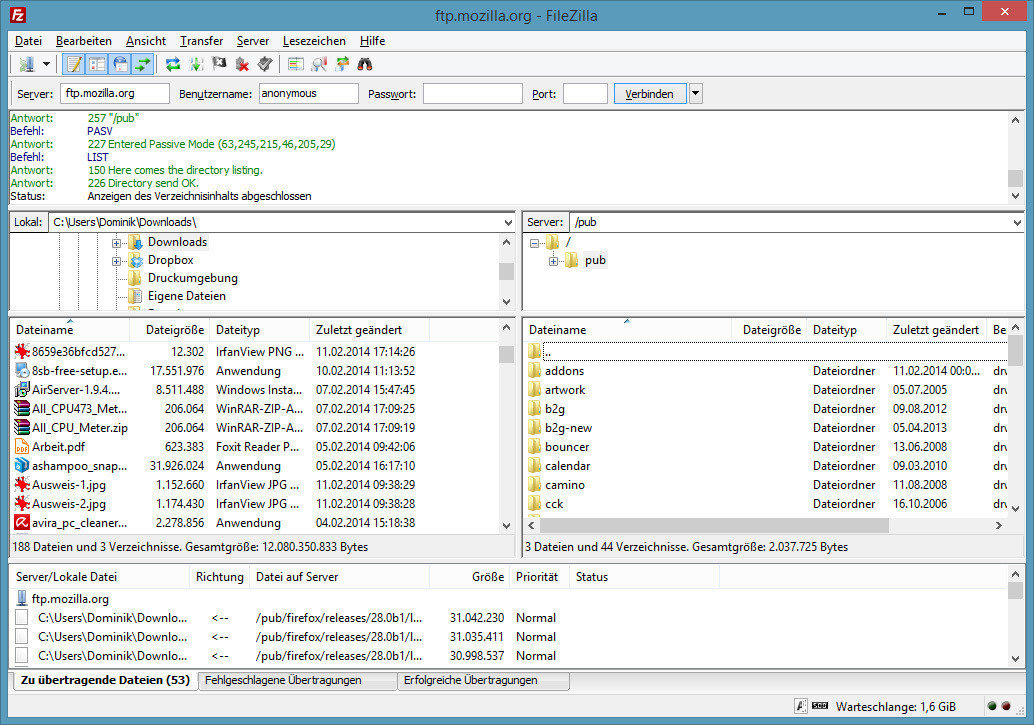
Source: SysOrb
Source: SysOrb
Pros
- Easy to apply
- Don't require many experience, technology
Cons
- Human mistakes
- Difficult to track the changes
- Risk management

Source: StoneAgeComics
Nowadays

Source: SysOrb
Just Kidding
Continuous
Delivery
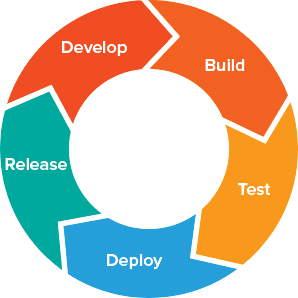
What does a Startup need?
- Releasing new features frequently
- Automated testing - Bug zero
- Automated deployment
What is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous Delivery is the ability to get changes of all types—including new features, configuration changes, bug fixes and experiments—into production, or into the hands of users, safely and quickly in a sustainable way.
https://continuousdelivery.com
The Tools of Continuous Delivery?
- Version Control
- Continuous Integration (CI)
- Automated Deployment
- Logging & Monitoring
The Tools of Continuous Delivery?
-
To keep a record of every version of every feature, add-on or other change to the code base.
-
All tests, scripts, documentation and configuration files
- Subversion, GIT, Mercurial, etc.
Version Control
The Tools of Continuous Delivery?
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of frequently checking code in with the main code base, triggering automated tests
Continuous Integration
- Checks the version control system for changes to the application
- Builds the application and runs automated tests on each build.
- Provides reports on whether each build passed or failed the tests.
-
Jenkins, Bamboo, CircleCI, Travis, etc.
The Tools of Continuous Delivery?
Automated Deployment
-
Ensure code can be deployed to production at any time, any environment automatically:
-
Development
-
UAT / Testing
-
Staging
-
Production
-
-
AWS CodeDeploy & Pipeline, Ansible, Puppet, etc.
The Tools of Continuous Delivery?
Logging / Monitoring
-
Bug Tracing
-
Collect and analyze data
-
Monitor all devices / services
- Availability, performance monitoring, and/or health status
- Alert / Reporting about what has happened/is happening
- Logstash, Nagios, New Relic, LogEntries, Tideways, etc.
And more...
-
Code Review
-
Testing Environments
-
Git Workflow
-
Test-Driven Design
Continuous Delivery Is …
-
Incremental: You can implement continuous delivery practices just a step at a time and still get great benefits.
-
Automated: By making successful processes repeatable, you can make changes more quickly and safely, with less likelihood of error.
-
Fast: By making frequent releases of smaller changes, you can isolate and fix problems more quickly, or roll back to a previous working state more easily.
-- Martin Fowler
You're Doing Continuous Delivery When ...
-
You can perform push-button deployments of any version of the software to any environment on demand.
-
You're leveraging automation, making frequent releases, testing at every stage of the process, and using a pull-based architecture that permits only successful releases to move to the next stage.
-
You work together as a single team, with everyone — developer, QA engineer and sysadmin — responsible for delivering quality code.
-- Martin Fowler
Thanks
Tri D. Tran
tri.tran@nfq.asia
@moprit
we are HIRING

Source: Kieu Lam @ NFQ Asia
Simply send us an email with your enclosed updated CV to:
career@nfq.asia
Floor 11 Vincom Center
72 Le Thanh Ton, Ben Nghe Ward,
District 1, Ho Chi Minh City
Vietnam
Deployment Process
By Tri Tran
Deployment Process
- 871



