Bidirectional BCI Control of a Mini-Robot
- transformation of signals from one region of brain to another
- lamprey's brain to robot- translate optical sensors to electrical stimuli with varying light intensity
- post rhombencephalic reticular nuclei (PRRN) -generates commands to robot's wheels
- faster firing rates - robot wheels turn faster, eventually turn in the opposite direction
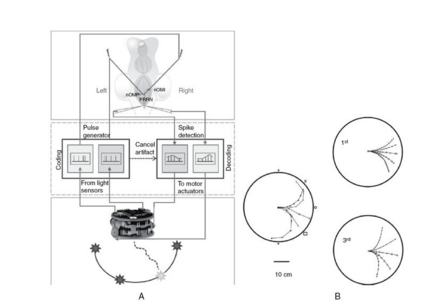
so there are two directions this can go in, but can arbitrary movement be generated using neural plasticity?
Cortical Control of Muscles via Functional Electrical Stimulation
- restore movement for paralysis from spinal cord injury
- neural signals from motor cortex to stimulate spinal cord/muscle- reanimate limbs
- operant condition monkeys to move a cursor, monkey continues to move cursor with neural activity without actual hand movement
- can't operate for a long period of time because it results in muscle fatigue
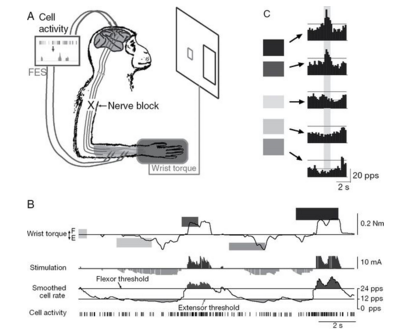
A is the set up of the experiment
B is the firing rate of neurons
C shows the five target levels of the firing rates
Establishing New Connections between Brain Regions
- establish an artificial connection to induce neural plasticity and functional reorganization.
- recall principle of plasticity
- Neurochip implant into M1- instructed simulator circuit to deliver constant-current pulses
- artificial connections mimicked the real connections
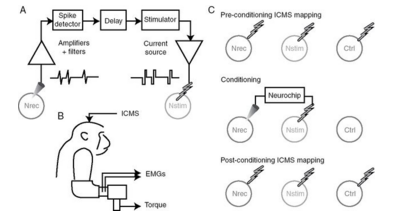
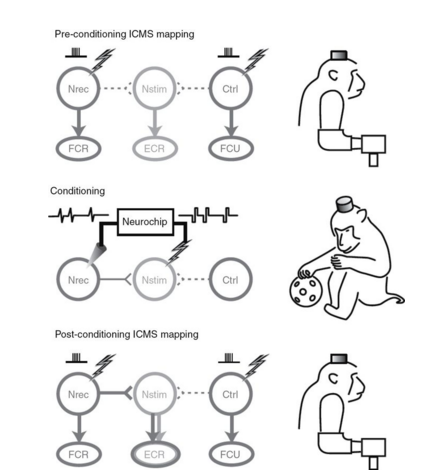
Nstim didn't cause the muscle to move, but it did after the conditioning and stimulation.
BCI Ch 11
By tsunwong625
BCI Ch 11
- 573



